Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
CH 25 of Guyton
Caricato da
Bea SamonteCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CH 25 of Guyton
Caricato da
Bea SamonteCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lectured on: August 29, 2013 Lectured by: Dra.
Felices Emerita Pascual - Perez RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Topic: THE BODY FLUIDS COMPARTMENTS : ECF & ICF Maintenance of a relatively constant volume and a stable composition of the body fluids is essential for homeostasis Water Balance to maintain a steady state, water intake must equal water excretion. Average INTAKE per day 2300 mL
2100 mL from ingested food and beverages 200 mL from metabolism Average OUTPUT per day 2300 mL 100 mL feces (4%) 100 mL sweat (8%) 700 mL insensible losses via skin and lungs (25%) 1400 mL urine (60%) BALANCE CONCEPTS Balance is necessary, in the long-term, to maintain life. Fluid Loss = Fluid Intake Electrolyte Loss = Electrolyte Intake Fluid Intake: regulated by thirst mechanism, habits Electrolyte intake: governed by dietary habits Fluid Output: regulated mainly by kidneys Electrolyte output: regulated mainly by kidneys BODY FLUIDS COMPARTMENTS TOTAL BODY WATER IN RELATION TO BODY WEIGHT: EFFECTS OF GENDER, BODY BUILD AND AGE
Transcellular fluid compartment a specialized type of ECF 1-2 liter Synovial fuid Peritoneal fluid Pericardial fluid CSF (cerebrospinal fluid)
BODY FLUID COMPARTMENTS ECF 20% of body weight = 14 L (++) Na+, Cl- and Bicarbonate ions Has small amount of Potassium, Calcium, Magnesium phosphate and organic acids Proteins: Plasma > ISF ICF 40% of total body weight = 28 L Only small amount of Na+ and Clions and almost no Calcium Large amount of K+ and PO4- ions. Moderate quantities of Mg++ and Sulfate ions Proteins -4x greater than ECF
FLUID BALANCE (ml/day) 70 kg Adult
ABCJJKKMP- Batch 2017
Page 1
REGULATION OF FLUID EXCHANGE AND OSMOTIC EQUILIBRIUM b/w ICF & ECF The distribution of fluids between ECF and ICF is determined mainly by the osmotic effect of smaller solutes. Sp. NaCl and other electrolyte acting across the cell membrane Involves semi-permeable cell membrane Permeability: Water >>> NaCl Thus water moves very rapidly across the membrane so that the ICF remains isotonic with the ECF. CONTROL OF BODY FLUID DISTRIBUTION Distribution across cell membranes determined by osmotic forces (mainly from electrolytes) Distribution across capillaries determined by hydrostatic and colloid osmotic forces. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF OSMOSIS AND OSMOTIC PRESSURE BLOOD VOLUME Both ECF & ICF Average blood volume = 5 L (7 % of body weight) 60% plasma, 40% RBC Hematocrit Fraction of the blood composed of RBC Men 0.40 Females 0.36 Anemia low levels Polycythemia excessive production COMPUTATION OF BODY WATER (for a 70 kg man) Total Body Water (TBW) = 60% or 0.6 x Body weight (BW) B. 42L ECF =20% or 0.2 x BW 13L Plasma 1/3 of ECF 3.5L MEASUREMENT OF BLOOD VOLUME Total Volume = Plasma volume 1-Hematocrit An average 70 kg man: Total blood volume = 3.5 L / 1-0.40 = 5.8 L Blood volume = 7% of body weight Hct in male = .40 Osmole - refers to the number of osmotically active particles in a solution. 1 osmole is equal to 1 molecule of solute 1 mole of Glucose L = 1 osmole L 1 mole of NaCl L = 2 osmoles L 1 mole of Na2SO4 L = Osmoles L 1 milliosmole = 1 1000 osmole ICF =40% or 0.4 x BW 28L Pure water Osmosis Net diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from a region of high water concentration that has a lower water concentration. - The higher the solute concentration the lower the water concentration. Rate of osmosis Rate of diffusion of water WHAT IS THE DIRECTION OF OSMOSIS? A.
ISF of ECF 10.5L
C.
* * *
With solute
* * *
ABCJJKKMP- Batch 2017
Page 2
OSMOLARITY AND OSMOLALITY Osmolality Osmolal concentration of solution OSmoles per kg of water (osm/kg H2O) Osmolarity Osmoles per literof solution (osm/L) OSMOLARITY Fluid Osmolarity: ECF: Na and Cl ions ICF: 50% due to K+ Corrected osmolarity is 282 mosm/L RELATION BETWEEN OSMOTIC PRESSURE AND OSMOLARITY Osmotic pressure of a solution is directly proportional to the concentration of osmotically active substances regardless of the size of the solute/
OSMOLARITY OF A 0.9% NaCl SOLUTION
OSMOLARITY Plasma mosm/L 301.8* 282 mosm/L 5443 ISF 300.8 281 mosm/L 5423 ICF 300.8 281 mosm/L 5423
Which has a higher osmotic pressure? Albumin, Glucose, NaCl OSMOTIC PRESSURE : VAN HOFFS LAW
Total mosm/L Corrected** Total osm. Pressure at 37C
*Slightly higher in plasma due to osmotic effects of plasma proteins **Correction factor (osmotic coefficient) for NaCl is 0.93 EFFECTS OF DIFFERENT CONCENTRATION OF IMPERMEANT SOLUTES IN ECF ON CELL VOLUME
PRINCIPLES OF OSMOTIC EQUILIBRIUM
Tonicity of solution, refers to whether solution will cause a change in a cell volume; depends on concentration of impermeant solute . Isosmotic solution has same osmolarity as body fluids CALCULATION OF THE OSMOLARITY AND OSMOTIC PRESSURE OF A SOLUTION What is the osmotic pressure of a -.9% NaCl solution? Is this isotonic, hypotonic or hypertonic? Hyperosmotic higher osmolarity than body fluids Hyposmotic lower osmolarity than body fluids Osmolarity of solution refers to solution with higher or lower osmolarity compared with Normal ECF without regard for whether it can permeate the cell membrane.
ABCJJKKMP- Batch 2017
Page 3
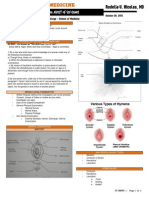
REVIEW: WHATS THE EFFECT OF SOLUTIONS OF CARYING TONICITY ON RBC?
WHAT ARE THE CHANGES IN THE FF VARIABLES AFTER GIVING 2.0 L OF WATER I.V.? ECF Volume? Increase ECF Osmolarity? Decrease ICF Volume? Increase ICF Osmolarity? Decrease
280 mOsm/L QUESTIONS:
200 mOsm/L
360 mOsm/L
What is the osmolarity of a 5% glucose solution? (MW is 180 g/mol) Is the solution hyperosmotic, hypo-osmotic or isosmotic? What is a hypo-osmotic solution? OSMOLARITY OF A 5% GLUCOSE SOLUTION
REMEMBER!!! Water moves rapidly across cell membranes, thus osmolarities between ECF & ICF remain almost equal. Cell membrane are almost impermeable to many solutes therefore the number of osmoles in ECF or ICF generally are constant unless solutes. WHAT ARE THE CHANGES IN THE FF VARIABLES AFTER GIVING 2L OF 3% NaCl I.V.? ECF Volume? Increase > 2.0 L ECF Osmolarity? Increase ICF Volume? Decrease ICF Osmolarity? Increase
ABCJJKKMP- Batch 2017
Page 4
SUMMARY
ABNORMALITIES OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION ABN Hyponatremic Dehydration Cause Diarrhea, vomiting, adrenal insuff; overuse of diuretics, Addisons Excess ADH, bronchogenic tumor Lack ADH, Diabetes insipidus, excessive sweating Cushingsm primary aldosteronism Plasma Na+ Conc ECF Vol ICF Vol
Hyponatremic overhydration Hypernatremic dehydration
Hypernatremic overhydration
HYPO/HYPER OSMOTIC REFERS TO PLASMA Na+ CONCENTRATION EDEMA Presence of excess fluid in the body tissues.
INTRACELLULAR EDEMA Depression of tissue metabolic systems (e.g. hypothyroidism) Inadequate tissue nutrition (e.g. ischemia) Inflammation of tissues (increased cell membrane permeability)
EXTRACELLULAR EDEMA ABNORMALITIES OF ECF FLUID Na+ CONCENTRATION Causes of increased interstitial fluid volume Increased Capillary Filtration Failure of lymphatics to return interstitial fluid to circulation
3 Factors that can increase capillary filtration 1. Increased capillary hydrostatic pressure (Pc) 2. Decreased plasma colloid osmotic pressure 3. Increased capillary filtration coefficient (permeability) (Kf) DETERMINANTS OF CAPILLARY FILTRATION ECF solute is 90% due to NaCl, hence an indicator of plasma osmolarity. CONSEQUENCES OF HYPONATREMIA AND HYPERNATREMIA Water moves in and out of cells cells swell or shrink This has profound effects on the brain. Neurologic function is altered Rapid shrinking can tear vessels and cause hemorrhage Rapid swelling can cause herniation because the skull is rigid, the brain cannot increase its volume by more than 10% without being forced down the neck (herniation).
ABCJJKKMP- Batch 2017
Page 5
CAUSES OF INCREASED CAPILLARY FILTRATION
NORMAL FILTRATION FILT = Kf x Net Filt Pressure = 6.6 x ( 17.3 - (-3) - 28 +8) = 6.6 x ( + 0.3) = 1.89 ml/min FILT = 2722 ml/day Where does all of this fluid (and protein in it) go? FUNCTION OF LYMPHATICS LOW TISSUE COMPLIANCE AND NEGATIVE INTERSTITIAL FLUID HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE
NEGATIVE PRESSURE SUCKS. (If negative IFPr, IF volume does NOT change much if +3 fluid start to accumulate), because tissue became highly compliant,
Lymphatic Failure = Edema
INCREASED LYMPH FLOW
CAUSES OF ECF EDEMA Lymphatic blockage Infection Cancer Surgery Congenital absence of lymphatics SAFETY FACTORS AGAINST EDEMA Low compliance of interstitium when = 3 mmHg interstitial fluid pressure is negative Increased lymph flow = 7 mmHg Washdown of interstitial protein = 7 mmHg at high lymph flow rates TOTAL SAFETY FACTORY = 17 mmHg
Lymph Flow
EFFECT OF INTERSTITIAL FLUID PRESSURE ON LYMPH FLOW
Increases lymph flow 10-50x
ABCJJKKMP- Batch 2017
Page 6
PITTING VS NON PITTING EDEMA Thumbprint - When the thumb press against the tissue area, it pushes the fluid away from the area. When tissue cell swells instead of interstitium, fluid do not move away from the area. WASHDOWN OF INTERSTITIAL PROTEINS
CONDITIONS CAUSING EDEMA 1. High capillary hydrostatic pressure Excess fluid retention by kidneys acute or chronic kidney failure glomerulonephritis mineralocorticoid excess Decreased arteriolar resistance vasodilator drugs autonomic insufficiency Increased venous pressure congestive heart failure high output heart failure (e.g. anemia) -venous obstruction venous valve failure cirrhosis 2. Decreased plasma proteins (low oncotic pressure) Loss of proteins burns, wounds nephrosis gastroenteropathy Failure to produce proteins - malnutrition (kwashiorkor) - cirrhosis - analbuminemia 3. Increased capillary permeability Immune reactions (histamine) Toxins Burns Prolonged ischemia Vitamin deficiency (e.g. vitamin C) Pre-eclampsia and eclampsia in Pregnancy 4. Blockage of lymphatics Cancer Surgery Infections (e.g. filaria nematodes) FLUIDS IN THE POTENTIAL SPACES OF THE BODY Pleural, peritoneal, pericardial, synovial cavities Fluid is exchanged between the capillaries and the potential spaces Lymphatic vessels drain protein from the potential spaces Effusion Edema fluid in the potential spaces Abdominal cavity ascites Normal Interstitial hydrostatic pressure of Pleural cavity (-) 7 to (-) 8 mmHg Pericardial cavity (-) 5 to (-) 6 mmHg Joint spaces (-3) to (-) 5 mmHg
ABCJJKKMP- Batch 2017
Page 7
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Heart Muscle: The Heart As A Pump and FunctionDocumento4 pagineHeart Muscle: The Heart As A Pump and Functionmcwnotes100% (1)
- Cardiac Action PotentialDocumento9 pagineCardiac Action PotentialswennecaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 33, 36 - GuytonDocumento8 pagineChapter 33, 36 - GuytonRoderick Palattao100% (2)
- Pharmacokinetics & Pharmacodynamics ExplainedDocumento2 paginePharmacokinetics & Pharmacodynamics Explainedgeldevera100% (1)
- EveryDay AyurvedaDocumento11 pagineEveryDay AyurvedacvmraviNessuna valutazione finora
- Guyton Respiration OverviewDocumento6 pagineGuyton Respiration Overviewbahahahah100% (1)
- A Case-Based Guide To Clinical Endocrinology (October 23, 2015) - (1493920588) - (Springer)Documento434 pagineA Case-Based Guide To Clinical Endocrinology (October 23, 2015) - (1493920588) - (Springer)AbdulraHman KhalEd100% (2)
- Abdominal Aortic AneurysmDocumento20 pagineAbdominal Aortic AneurysmPortia Rose RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.14 Chapter 3 Water and Electrolytes Balance and ImblanceDocumento140 pagine3.14 Chapter 3 Water and Electrolytes Balance and ImblanceShourav SarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Arteries & Circulation (Guyton, Chapter 14-16)Documento21 pagineArteries & Circulation (Guyton, Chapter 14-16)Dianne IgnacioNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid & Parathyroid GlandsDocumento21 pagineThyroid & Parathyroid GlandsAzizan HannyNessuna valutazione finora
- Nerve PhysiologyDocumento31 pagineNerve Physiologynirilib100% (4)
- 2.membrane Physiology, Nerve and MuscleDocumento6 pagine2.membrane Physiology, Nerve and MuscleCLEMENT100% (1)
- Correlation Between Strabismus and AmblyophiaDocumento17 pagineCorrelation Between Strabismus and AmblyophiaAyu W. AnggreniNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap. 18 GuytonDocumento4 pagineChap. 18 GuytonMarian Joyce Princess Yuque100% (2)
- MOH Pocket Manual in Obstetrics and GynaecologyDocumento194 pagineMOH Pocket Manual in Obstetrics and GynaecologyBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- PHYSIOLOGY OF RED BLOOD CELLSDocumento7 paginePHYSIOLOGY OF RED BLOOD CELLSRoderick PalattaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal McqsDocumento13 pagineRenal McqsShahabuddin Shaikh100% (1)
- Chapter 27 GuytonDocumento6 pagineChapter 27 GuytonGabriella ChafrinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physiology 100q.with TopicsDocumento11 paginePhysiology 100q.with TopicsdocaliNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ Question BankDocumento102 pagineMCQ Question BankdrmadaanpiyushNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 21 Muscle Blood FlowDocumento17 pagineChapter 21 Muscle Blood Flowelmedina omeragicNessuna valutazione finora
- The Special Senses: Vision, Hearing, Taste, and SmellDocumento31 pagineThe Special Senses: Vision, Hearing, Taste, and SmellDemuel Dee L. BertoNessuna valutazione finora
- St. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: PhysiologyDocumento4 pagineSt. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: PhysiologyMavic VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.3b Medico-Legal Aspect of Sex CrimesDocumento2 pagine1.3b Medico-Legal Aspect of Sex CrimesJaybee SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- Legal Med Identification & Death AspectsDocumento4 pagineLegal Med Identification & Death AspectsBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.about Some GIT Hormones (True or False)Documento71 pagine1.about Some GIT Hormones (True or False)JOSEPH NDERITU100% (2)
- Basics On NeurophysiologyDocumento12 pagineBasics On NeurophysiologyRausche Anne Blaser Sausa100% (1)
- Chapter 20Documento6 pagineChapter 20g_komolafeNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 21 - Coronary CirculationDocumento5 pagineCHAPTER 21 - Coronary Circulationg_komolafeNessuna valutazione finora
- 47 MCQs On GI and Nutrition PhysiologyDocumento14 pagine47 MCQs On GI and Nutrition Physiologyrazsubedi100% (1)
- Guyton Chapter 36Documento6 pagineGuyton Chapter 36g_komolafe100% (1)
- Physiology Summary Chapter 21Documento5 paginePhysiology Summary Chapter 21gail018Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ten Days in A Mad-House by Nellie BlyDocumento122 pagineTen Days in A Mad-House by Nellie BlyCharmaineTanti100% (1)
- Ee Mock Test 2 Jan 2017 Qa 2Documento92 pagineEe Mock Test 2 Jan 2017 Qa 2EmadSamirNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdomen ExaminationDocumento37 pagineAbdomen ExaminationJaaydevNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 16Documento9 pagineChapter 16g_komolafeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 26 Guyton and HallDocumento5 pagineChapter 26 Guyton and HallSanna Asila AkramNessuna valutazione finora
- MB 1 Past QuestionsDocumento90 pagineMB 1 Past QuestionsmoRty ex0% (1)
- 5 - Cardiac Output - Ass. Prof. Dalia Abd El-Salam - 2020Documento6 pagine5 - Cardiac Output - Ass. Prof. Dalia Abd El-Salam - 2020Hossam BaniisNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 13Documento6 pagineChapter 13Teehee Jones100% (1)
- Chapter 34 Guyton and HallDocumento5 pagineChapter 34 Guyton and Hallg_komolafeNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochem Final Exam MCQs PDFDocumento173 pagineBiochem Final Exam MCQs PDFzeeshan jaskaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Physiology Summary Chapter 20Documento9 paginePhysiology Summary Chapter 20gail01850% (2)
- Nerve and Muscle PhysiologyDocumento82 pagineNerve and Muscle PhysiologychandsriNessuna valutazione finora
- PhysiologicDocumento50 paginePhysiologicRochelle Joyce AradoNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnostic Test - Pedia With Answer 50 Items Without RatioDocumento4 pagineDiagnostic Test - Pedia With Answer 50 Items Without RatioDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiration 6 PDFDocumento27 pagineRespiration 6 PDFSardar jiNessuna valutazione finora
- Development of the Digestive System from Foregut to HindgutDocumento90 pagineDevelopment of the Digestive System from Foregut to Hindgutyusrah mukhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- Catatan Koas THT 1Documento5 pagineCatatan Koas THT 1MEDS easyNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Body FluidsDocumento9 pagine1 Body FluidsSenthereng MoaisiNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Cell PhysiologyDocumento39 pagineIntroduction To Cell Physiologywaqas_xsNessuna valutazione finora
- SGD 4 - Skeletal Muscle PhysiologyDocumento3 pagineSGD 4 - Skeletal Muscle PhysiologyKriska Noelle0% (1)
- Osmolarity vs OsmolalityDocumento13 pagineOsmolarity vs OsmolalityBurhan HameedNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 33 Guyton and HallDocumento4 pagineChapter 33 Guyton and Hallg_komolafeNessuna valutazione finora
- Nerve Muscle PhysiologyDocumento79 pagineNerve Muscle Physiologyroychanchal562100% (2)
- Chapter 17Documento6 pagineChapter 17g_komolafe100% (1)
- Physiology QuestionsDocumento14 paginePhysiology QuestionsLamis Alhaj KaddamNessuna valutazione finora
- Guyton Hall PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 5 PDFDocumento9 pagineGuyton Hall PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 5 PDFOsman NazirNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 62: General Principles of GI Function-Motility, Nervous Control, and Blood CirculationDocumento36 pagineChapter 62: General Principles of GI Function-Motility, Nervous Control, and Blood Circulationjackie funtanillaNessuna valutazione finora
- REV Micro HSB RemedsDocumento16 pagineREV Micro HSB RemedsPatricia HariramaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz On Lipid Metabolism - BIOCHEMISTRYDocumento12 pagineQuiz On Lipid Metabolism - BIOCHEMISTRYAlliah Turingan100% (1)
- MTHISTO100 Lesson 2 Excretory SystemDocumento9 pagineMTHISTO100 Lesson 2 Excretory SystemJaeri HuangNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems 1st Set - PDF S2 PDFDocumento8 pagineProblems 1st Set - PDF S2 PDFZinca IoanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 70-GuytonDocumento9 pagineChapter 70-Guytonswoljaswol1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biochem 2.1 Introduction To MetabolismDocumento5 pagineBiochem 2.1 Introduction To Metabolismlovelots1234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lange Endocrine Physiology Self-Assessment QuestionsDocumento19 pagineLange Endocrine Physiology Self-Assessment QuestionsDimsy Flora KpaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Physiology Part 2 Dr. OlivarDocumento5 pagineBlood Physiology Part 2 Dr. OlivarJorelyn FriasNessuna valutazione finora
- Circulation Qs Pool Along With Answer Keys by DR Sadia For 1st Yr MbbsDocumento25 pagineCirculation Qs Pool Along With Answer Keys by DR Sadia For 1st Yr MbbsMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- Body FluidsDocumento59 pagineBody FluidsAmmar SmadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic of Fluid Therapy ImaDocumento69 pagineBasic of Fluid Therapy Imal Made ArtawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bleeding Disorders & Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocumento5 pagineBleeding Disorders & Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinpharm SGD Organophosphayte PoisoningDocumento2 pagineClinpharm SGD Organophosphayte PoisoningBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: N. GonorrhoeaeDocumento2 paginePelvic Inflammatory Disease: N. GonorrhoeaeBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinpharm SGD Bronchial AsthmaDocumento9 pagineClinpharm SGD Bronchial AsthmaBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1e Sudden Cardiac ArrestDocumento4 pagine1.1e Sudden Cardiac ArrestBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Bone Marrow Failure Diseases & TreatmentsDocumento2 pagineBone Marrow Failure Diseases & TreatmentsBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1k Coronary Artery DiseaseDocumento6 pagine1.1k Coronary Artery DiseaseBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1b AutopsyDocumento3 pagine1.1b AutopsyBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.3G Forensic Path PDFDocumento17 pagine1.3G Forensic Path PDFBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Pharmacology SGD 3 - HypertensionDocumento2 pagineClinical Pharmacology SGD 3 - HypertensionBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Collection of Biological Sample For Dna-Oct 9Documento84 pagineCollection of Biological Sample For Dna-Oct 9Bea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1d EvidenceDocumento2 pagine1.1d EvidenceBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd Year Clinical Nephrology Preceptorial-1Documento1 pagina3rd Year Clinical Nephrology Preceptorial-1Bea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Group DiscussionDocumento3 pagineSmall Group DiscussionBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.4A Intro To HemaDocumento4 pagine1.4A Intro To HemaBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- History PEDocumento6 pagineHistory PEBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1c Rdu ProcessDocumento3 pagine1.1c Rdu ProcessBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1a Prescription WritingDocumento4 pagine1.1a Prescription WritingBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1b Clinical PharmacologyDocumento1 pagina1.1b Clinical PharmacologyBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.6e CopdDocumento6 pagine1.6e CopdBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.2a PhlebotomyDocumento7 pagine1.2a PhlebotomyBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Semen AnalysisDocumento8 pagineSemen AnalysisBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- CPC-Patho Version 6Documento20 pagineCPC-Patho Version 6Bea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Thyroid CA Case Pres EditDocumento42 pagineThyroid CA Case Pres EditBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1A Total Quality Management in Health Care: Hospital ErrorsDocumento3 pagine1.1A Total Quality Management in Health Care: Hospital ErrorsBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Dilatation Clock Time Hour of Labor: Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PartographDocumento1 paginaDilatation Clock Time Hour of Labor: Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PartographBea SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- SJAMS 43B 750 754 Thesis Tibial PlateauDocumento5 pagineSJAMS 43B 750 754 Thesis Tibial PlateauNisheshJainNessuna valutazione finora
- HTC Intake Form - September 4 - Final - Doc 7.9.13Documento10 pagineHTC Intake Form - September 4 - Final - Doc 7.9.13Kealeboga Duece ThoboloNessuna valutazione finora
- Teen Pregnancy Rates in BoliviaDocumento2 pagineTeen Pregnancy Rates in BoliviaVanessa Sandoval Aguilera100% (1)
- ASPEN Pocket Cards - Guidelines For The Provision and Assessment of Nutrition Support Therapy in The Pediatric Critically Ill Patient-1Documento12 pagineASPEN Pocket Cards - Guidelines For The Provision and Assessment of Nutrition Support Therapy in The Pediatric Critically Ill Patient-1Ceren KamalıNessuna valutazione finora
- Telemedicine - Who, What, When, Where and How!Documento65 pagineTelemedicine - Who, What, When, Where and How!Ebtisam HamedNessuna valutazione finora
- The Welfare of Cattle Kept For Beef ProductionDocumento150 pagineThe Welfare of Cattle Kept For Beef ProductionIsabel CarrilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemicals Zetag MSDS Powder Zetag 4139 - 1010Documento6 pagineChemicals Zetag MSDS Powder Zetag 4139 - 1010PromagEnviro.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychology All Case Studies PDFDocumento54 paginePsychology All Case Studies PDFArmeen AmirNessuna valutazione finora
- Forever ARGI+® Stick Packet Product InformationDocumento1 paginaForever ARGI+® Stick Packet Product InformationArif Zaman SiddiqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Combat Lifesaver Guide to One-Person Bag Valve Mask VentilationDocumento1 paginaCombat Lifesaver Guide to One-Person Bag Valve Mask VentilationSae TumNessuna valutazione finora
- Spinal Cord Reflexes Protect the BodyDocumento2 pagineSpinal Cord Reflexes Protect the BodyriyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Masters in Medical Science - MMSCDocumento12 pagineMasters in Medical Science - MMSCtexilaamericanNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 25 Respiration Study GuideDocumento2 pagineCH 25 Respiration Study Guide99646qbkdwNessuna valutazione finora
- SURAT KETERANGAN DOKTERDocumento1 paginaSURAT KETERANGAN DOKTERalha egaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cure - Family Health MatterzDocumento14 pagineCure - Family Health MatterzGeorge AniborNessuna valutazione finora
- Epidemiology of AsthmaDocumento8 pagineEpidemiology of AsthmaMaria Alejandra Siachoque JaraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Medication Order Unit 11Documento10 pagineThe Medication Order Unit 11novie100% (2)
- Hepatites A, B, CDocumento22 pagineHepatites A, B, CsanthiagoschneiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Continuous Passive Motion (CPM) : Theory and Principles of Clinical ApplicationDocumento10 pagineContinuous Passive Motion (CPM) : Theory and Principles of Clinical ApplicationlaurentiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample ResumeDocumento3 pagineSample Resumeapi-380209683% (6)
- 10 Furunculosis (Aeromonas Salmonicida)Documento86 pagine10 Furunculosis (Aeromonas Salmonicida)Jose AntonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal Manajemen Pelayanan Kesehatan: Artikel PenelitianDocumento8 pagineJurnal Manajemen Pelayanan Kesehatan: Artikel PenelitianDiah AdhyaksantiNessuna valutazione finora