Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
12 Reproiduction in Plants
Caricato da
Jaskirat SinghCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
12 Reproiduction in Plants
Caricato da
Jaskirat SinghCopyright:
Formati disponibili
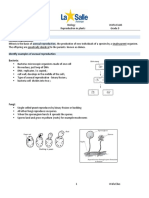
TEST NO.2 TOPIC: REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS MM:3O 1.
Name the part of an angiosperm flower in which development of male & female gametophyte takes place.[1] 2. Why apple is called a false fruit. Which part of plant forms the fruit? [1] 3. Name the part of plant producing seed & fruit after fertilization. [1] 4. What is apomixis? What is its importance? [2] 5. Draw a well labeled diagram of longitudinal section of pistil showing pollen germination?[2] 6. List the advantages of pollination to angiospermic plants? [2] 7. Incompatibility is the natural barrier in fusion of gamete. Justify this statement.[3] 8. How dose pollination takes place in salivia. List any four adaptations required for such type of pollination.[3] 9. i) Why is zygotes dominant for sometime in fertilized ovule.[5] ii) What is polyembryony? Give an example. iii) In fruits, what is formed from following parts :a) Ovary wall b) Outer integument c) Inner integument d)zygote e) primary endosperm f) Ovary g) Nucellus 10. Difference between(2,3) a) Parthenogenesis and parthenocarpy b) Perisperm and Pericarp 11.a)What is Pollen kitt? Write its various functions.(2) b)How do the embryos of dicots different from that of monocots?(3)
[ANSWERS] Ans1. Development of male gametophyte takes place in microspore in pollen grains & development of female gametophyte occurs in megaspore in ovule. Ans2. Apple is called a false fruit because it develops from ovary along with accessory floral plants e.g. Thalamus Ans3. After fertilization, ovule develops into seed & ovary develops into fruit. Ans4. The development of reproductive propagules without meiosis & syngamy is called apomixis. It is also called asexual reproduction. It is a method of reproduction which produces new individuals with the help of vegetative part of plant body.
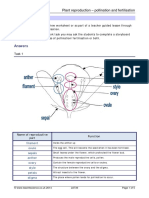
Ans5.
Ans6. i) Pollination leads to fertilization & production of seeds & fruits which are necessary for continuity of life. ii) It is important for new varieties of plants. iii) It is important for production of hybrid seeds. iv) It helps in genetic recombination in plants. Ans7. Pollen grains of a plant species cannot germinate on stigma of other unrelated species because both the species are incompatible & process is called pollen pistil incompatibility. In many angiospermic plants, it is seen that pollen grains germinate on stigma of unrelated species but male gametes produced in pollen tube cannot fertilize egg. This is called gametic incompatibility Self incompatibility can be achieved by any of the following ways :i) Pollen Stigma interaction: - In this phenomenon, pollen grains fails to germinate on Stigma because of incompatibility. ii) Pollen tube style interaction: - In this phenomena, pollen grains become able to germinate on stigma & pollen tube penetrate stigmatic surface but due to incompatibility growth of pollen tube within stigma & style is inhibited. iii) Pollen ovule interaction: - pollen tube successfully pierces & grows within style & its growth is inhibited at micropyle of ovule. Ans8. In salivia, entomophily or pollination lay insects occurs. The flowers of salivia are bilipped. Its upper lip consists of two petals & lower lip consists of three petals. The lower lip functions as sitting pad for insects. In normal conditions, the connective remains upright. When insect enters the tube of corolla towards nectar sitting on lower lip, it pushes sterile anther lobe which automatically brings about fertile anther to touch the back of insects gets the blow of fertile lobe. Pollen grains are dusted on back feather & legs of insects. ADAPTAIONS EOR ENTOMOPHILY :i) Flowers are brightly coloured.
ii) Flowers possess nectar glands. iii) pollen grains are usually sticky & spiny iv) flowers are large sized & stout Ans 9 (i) Zygote remain dominant for sometime in a fertilized ovule because embryo develops after formation of endosperm therefore zygote wants for formation of endosperm which supplies food material for developing embryo (ii) The presence of more than one embryo in a seed is called polyembryony eg. Sometimes more than one embryo is formed within an embryo sac either by cleavage or splitting of egg, synergid, antipodal or endosperm. (iii) In fruits, the following is formed from given parts:a) Ovary wall - Per carp b) Outer integument -Testa c) Inner integument -Tegmen d) zygote- embryo e) primary endosperm -endosperm f) Ovary- fruit g) Nucellus- perisperm. Ans 10. Parthenogenesis Parthenocarpy 1.It is the phenomenon in which the 1.It is the phenomenon of formation of fruits unfertilized female gamete/ovum develops without fertilization into a seed/individual 2. It may result in haploid individual. 2. Usually seeds are not produced and hence e.g., drones of honey bee. no new individual. e.g. Pineapple, banana. b) Perisperm Pericarp 1. It is unused nucellus. 1. It is the covering of fruit that develops from ovary wall. 2. It is a part of seed. 2. It is part of fruit. 3. It is usually dry. 3. It is dry or fleshy. 4. It is nonfunctional for seed. 4. It is protective covering and also helps in dispersal and nutrition. Ans 11. a) In insect pollinated flowers, pollen grains are covered by an oily and sticky layer, the pollen kitt, which provide sticky property, colour and specific odour to the pollen grains and thus helps in insect pollination. The materials for the formation of pollen kitt are chiefly contributed by tapetal cells. Functions: i) Helps in insect attraction and pollination. ii) Helps in adhering with the body of insects and helps in dispersal of pollen grains. iii) Prevent the pollen grains by UV radiation effect. iv) Indirectly takes part in sporophytic incompatibility.
b) Dicot embryo 1. There are two cotyledons attached to an embryonal axis. 2. Plumule occur distally 3. Cotyledon occur laterally. 4. Cleoptile absent 5.coleorhiza is absent. 6.Scutellum absent. 7. Suspensor large Monocot embryo 1. Only one cotyledon attached to the embryonal axis. 2.Here ,it is lateral. 3. A single cotyledon occupies terminal position. 4. The envelope of plumule is called cleoptile. 5. coleorhizae is a protective sheath of radical. 6. A single cotyledon called scutellum is present. 7. Comparatively small.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Cactus FamilyDocumento777 pagineThe Cactus Familycellorock100% (13)
- Angiosperm Life Cycle-Flowers, Fruits and SeedsDocumento7 pagineAngiosperm Life Cycle-Flowers, Fruits and SeedsEunnie ChongNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Work 6Documento3 pagineLab Work 6Bella LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Revised Flora of The White Mountains, California and NevadaDocumento227 pagineRevised Flora of The White Mountains, California and NevadaDWTaylor100% (4)
- Elias 2Documento37 pagineElias 2Mohammed Elias AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Biology Imp ch2 2Documento9 pagine12 Biology Imp ch2 2priyanjalaproNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Passing Package For Ii PucDocumento38 pagineBiology Passing Package For Ii PucRishi Kesh100% (1)
- Marks Wise Questions CH-1Documento27 pagineMarks Wise Questions CH-1lakshshah5116Nessuna valutazione finora
- GSB Textback ch.1. Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants DR - Phemie FernandesDocumento8 pagineGSB Textback ch.1. Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants DR - Phemie Fernandespranavjain558Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Questions With AnswersDocumento6 pagineSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Questions With AnswersPrajwal dNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento8 pagineBiology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsYasir SalahNessuna valutazione finora
- Vedantu Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantDocumento28 pagineVedantu Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantNakul SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 36 - ch2 - Reproduction in PlantsDocumento21 pagine36 - ch2 - Reproduction in PlantsAnonymous Azxx3Kp9100% (1)
- 12-BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK (With Value Based Questions) - 1Documento33 pagine12-BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK (With Value Based Questions) - 1venkatesh kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12-Reproduction in PlantsDocumento4 pagineChapter 12-Reproduction in PlantsrajeshkumarkashyapNessuna valutazione finora
- XX 3 LOl An 45 G OG7 Eo Dam FDocumento9 pagineXX 3 LOl An 45 G OG7 Eo Dam FGauri PopalghatNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Test Paper 02 Ch-2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento4 pagineCBSE Test Paper 02 Ch-2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsShahid ansariNessuna valutazione finora
- QnA (Reproduction)Documento30 pagineQnA (Reproduction)Vishal PrajapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 12 Reproduction in PlantsDocumento5 pagineChapter - 12 Reproduction in Plantsanju singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Xamidea Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento31 pagineXamidea Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsShireen SuhailNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants FlowerDocumento7 pagineChapter-2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants FlowerbpmbhamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Notes PDF 1 Beq2woDocumento373 pagineBiology Notes PDF 1 Beq2woarmanmalik5216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Important QuestionsDocumento23 pagineChapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Important QuestionsDivyanshu BothraNessuna valutazione finora
- Seed Plants Lab: Learning ObjectivesDocumento11 pagineSeed Plants Lab: Learning Objectivesapi-232487761Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bot01 Lec4Documento11 pagineBot01 Lec4Jan Leo QuinioNessuna valutazione finora
- ANTHOPHYTEDocumento3 pagineANTHOPHYTEIrish Nicole BigtasNessuna valutazione finora
- IndexDocumento10 pagineIndexRheman RaphaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants PyqDocumento24 pagineSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants PyqSoumya Ranjan NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproduction Chapter-1 Reproduction in OrganismsDocumento10 pagineReproduction Chapter-1 Reproduction in OrganismsSharafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maharashtra Board Class 12 Solutions For Biology Chapter 1 Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants - Download Free PDFDocumento10 pagineMaharashtra Board Class 12 Solutions For Biology Chapter 1 Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants - Download Free PDFRudranil ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento9 pagineUntitledAarnav Kumar [AMISA ]Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reproduction in Plants: Module - 3Documento35 pagineReproduction in Plants: Module - 3Nelle DelanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 2 PucDocumento23 pagineBiology 2 PucTULASI BAINessuna valutazione finora
- Reproduction in Plants Final ExamDocumento5 pagineReproduction in Plants Final Examsatyaprakash11991Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento8 pagineSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsKrittika DasNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT6Documento14 pagineUNIT6James OrtegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology HolidayDocumento3 pagineBiology Holidayshikeb aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Class Vii G.SC Asm - Unit-4 (2021-22)Documento22 pagineClass Vii G.SC Asm - Unit-4 (2021-22)Arsh KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Notes For Grade Week 9-10 For Grade 12Documento25 pagineBiology Notes For Grade Week 9-10 For Grade 12Adeola YusufNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology PDFDocumento34 pagineBiology PDFBIBEK KUNDUNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 2 - TEXTUAL EXERCISE - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento6 pagineCHAPTER 2 - TEXTUAL EXERCISE - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSyed Mohdammad AliNessuna valutazione finora
- KSEEB Solutions: 2nd PUC Biology Question Bank Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento23 pagineKSEEB Solutions: 2nd PUC Biology Question Bank Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsjäšħwâñtħ rNessuna valutazione finora
- The Sexual Reproductive System of Flowering PlantsDocumento5 pagineThe Sexual Reproductive System of Flowering PlantsHafiy Yusoff100% (1)
- c-2 & 3 Q.B.Documento9 paginec-2 & 3 Q.B.Amiyo SarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- ScienceDocumento8 pagineScienceBryl MedrozoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pollen: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocumento19 paginePollen: Jump To Navigationjump To Searchjessito2100% (2)
- Topic 10 Reproduction in Plants Revised Roysci Notes 2021Documento14 pagineTopic 10 Reproduction in Plants Revised Roysci Notes 2021shealtielchigariso06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento25 pagineSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsGagan DesaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproduction in Plants 1Documento8 pagineReproduction in Plants 1subhroNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Worksheets - XIIDocumento188 pagineBiology Worksheets - XIIlatishabasilNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Xii Unit Test 1Documento2 pagineBiology Xii Unit Test 1Viraj TaywadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 WorksheetDocumento6 pagineChapter 8 WorksheetNaisha JaiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 12 Subject: Biology Chapter-2: FlowerDocumento30 pagineClass 12 Subject: Biology Chapter-2: FlowerSufiyanNessuna valutazione finora
- How Do Organisms Reproduce - Notes-Class 10Documento11 pagineHow Do Organisms Reproduce - Notes-Class 10Varshini PeraNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 3 2 1 3Documento15 pagine1 3 2 1 3Himanshu GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook Plant Reproduction of Small Chilli Pepper Flowers IZZUDDIN ISHAK (D20191088261)Documento14 pagineHandbook Plant Reproduction of Small Chilli Pepper Flowers IZZUDDIN ISHAK (D20191088261)Izzuddin IshakNessuna valutazione finora
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento9 pagineSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSri DharshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants 2020Documento22 pagineReproduction in Flowering Plants 2020Kestina MillerNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Reproduction #106. Types of ReproductionDocumento18 pagine12 Reproduction #106. Types of ReproductionJorifNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 2 Rep. in Flowering Plants 2023 - 24 WSDocumento3 pagineCH 2 Rep. in Flowering Plants 2023 - 24 WSArchfab73Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reproduction in PlantsDocumento17 pagineReproduction in Plantswafa eliasNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFDocumento51 pagine12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFUmair Khan Marwat100% (1)
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3Da EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gardeners' Guide To Botany: Gardener's Guide Series, #4Da EverandGardeners' Guide To Botany: Gardener's Guide Series, #4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Synonyms Part - 3: (Directed By: Rahul Rituraj)Documento15 pagineSynonyms Part - 3: (Directed By: Rahul Rituraj)Jaskirat SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Antonyms Part - 5: (Directed By: Rahul Rituraj)Documento17 pagineAntonyms Part - 5: (Directed By: Rahul Rituraj)Jaskirat SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- # Stadium Capacity Game(s) City State Home Team: The Following Is A List Of, Ordered by CapacityDocumento24 pagine# Stadium Capacity Game(s) City State Home Team: The Following Is A List Of, Ordered by CapacityJaskirat SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Niti AyogDocumento1 paginaNiti AyogJaskirat SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Details of International Food Festivals For Exam 2015Documento1 paginaDetails of International Food Festivals For Exam 2015Jaskirat SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Short Notes On CBS..!!Documento1 paginaShort Notes On CBS..!!Jaskirat SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Banking Awareness: Bretton Woods Twins: International Monetary FundDocumento3 pagineBanking Awareness: Bretton Woods Twins: International Monetary FundJaskirat SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- New Cabinet MinistersDocumento4 pagineNew Cabinet MinistersJaskirat SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 16 NovDocumento14 pagine16 NovJaskirat SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Funds and Investment: What Is InsuranceDocumento5 pagineFunds and Investment: What Is InsuranceJaskirat SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Important Taglinesof Insurance BanksDocumento3 pagineImportant Taglinesof Insurance BanksJaskirat SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Quick Notes For SBI Associates 2014Documento7 pagineMarketing Quick Notes For SBI Associates 2014Jaskirat SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Affairs Mega Capsule 2014 15Documento241 pagineCurrent Affairs Mega Capsule 2014 15Jaskirat SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 1700 Toefl WordsDocumento262 pagine1700 Toefl WordsHanh PhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Test 4 (Unit - 3 & 4) : Smart-Gen Learning Centre 780, SST Nagar Patiala M: 7589469383, 8146529787Documento4 pagineRevision Test 4 (Unit - 3 & 4) : Smart-Gen Learning Centre 780, SST Nagar Patiala M: 7589469383, 8146529787Jaskirat SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Cwecl Iv Roll Display PDFDocumento454 pagineCwecl Iv Roll Display PDFShiva SankarNessuna valutazione finora
- August General Awareness PDFDocumento36 pagineAugust General Awareness PDFRajkumarRathodNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Structures and Physiology NotesDocumento97 paginePlant Structures and Physiology Notesapi-292966101Nessuna valutazione finora
- Revision 2. Rearrange The Words To Make Correct SentencesDocumento1 paginaRevision 2. Rearrange The Words To Make Correct SentencesallyaziqNessuna valutazione finora
- Second Lecture Exam ReviewerDocumento7 pagineSecond Lecture Exam ReviewerKen RubioNessuna valutazione finora
- Cordate Leaf: © B. Domangue 2014 Leaf Piece OrigamiDocumento3 pagineCordate Leaf: © B. Domangue 2014 Leaf Piece Origamikatrins18Nessuna valutazione finora
- Field Id Common Grasses - ADADocumento35 pagineField Id Common Grasses - ADAAllan EPNessuna valutazione finora
- AESTIVASIDocumento12 pagineAESTIVASIannisa kNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio PROJECT 2024 (AKASH) (Correct)Documento14 pagineBio PROJECT 2024 (AKASH) (Correct)Sk Samir UddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Latihan Soal Bahasa InggrisDocumento4 pagineLatihan Soal Bahasa InggrisAYU IMTYAS RUSDIANSYAHNessuna valutazione finora
- 18958-Article Text-39255-1-10-20230501Documento7 pagine18958-Article Text-39255-1-10-20230501dimas aryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Seed Plant Unit OutlineDocumento27 pagineSeed Plant Unit Outlineapi-246014137Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vol. XIDocumento333 pagineVol. XICamila AlcantaraNessuna valutazione finora
- DronapushpiDocumento6 pagineDronapushpiGAURAVNessuna valutazione finora
- Adaptation of Plants From Different Habitats For PhotosynthesisDocumento6 pagineAdaptation of Plants From Different Habitats For Photosynthesisridwan100% (7)
- Adaptive and Protective SystemsDocumento40 pagineAdaptive and Protective Systemsrutwick100% (8)
- Plant FamiliesDocumento2 paginePlant FamiliesZahid Mehmood100% (1)
- GPB 243 Objective Questions 1Documento4 pagineGPB 243 Objective Questions 1SelvalumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio320 Lab 4Documento6 pagineBio320 Lab 4Mirza KarmilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Parts of The Flower and Seed IIIDocumento8 pagineParts of The Flower and Seed IIISydney UyNessuna valutazione finora
- Nota Biologi UniDocumento28 pagineNota Biologi UniMuhammad FadhilNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues Class 9 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 6 (PDF)Documento2 pagineTissues Class 9 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 6 (PDF)Dharya Pratap Singh RajpootNessuna valutazione finora
- HaldinaDocumento2 pagineHaldinaAngel AngelNessuna valutazione finora
- EpigynyDocumento5 pagineEpigynyNirmala BhatNessuna valutazione finora
- 1561550108FLOWERDocumento55 pagine1561550108FLOWERArjun SajeevNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers: Plant Reproduction - Pollination and Fertilisation Teaching NotesDocumento5 pagineAnswers: Plant Reproduction - Pollination and Fertilisation Teaching NotesKhoo Ying WeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Rahayu 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1918 052042Documento6 pagineRahayu 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1918 052042Muhammad AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- G3 - LSR - 2Y - 3.01 Plants and Trees GrowingDocumento14 pagineG3 - LSR - 2Y - 3.01 Plants and Trees GrowingPhạm SửuNessuna valutazione finora