Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Ch10 Bond
Caricato da
Uday Prakash SahuDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Ch10 Bond
Caricato da
Uday Prakash SahuCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Prime Classes
FURTHER CONCEPTS OF CHEMICAL BONDING
1. In order to form a set of sp2 hybrid orbitals, how many pure atomic orbitals of each type must be mixed? (a) one s and two p (b) two s and two p (c) two s and one p (d) one s and three p In order to form a set of sp3 hybrid orbitals, how many pure atomic orbitals of each type must be mixed? (a) one s and two p (b) two s and two p (c) two s and one p (d) one s and three p Which of the following elements is most likely to display dsp3 hybridization? (a) oxygen (b) nitrogen (c) phosphorus (d) carbon Which of the following elements is most likely to display d2sp3 hybridization? (a) fluorine (b) sulfur (c) nitrogen (d) carbon What is the maximum number of hybrid orbitals that can be formed by oxygen? (a) three (b) four (c) five (d) six What is the maximum number of hybrid orbitals that can be formed by boron? (a) three (b) four (c) five (d) six Atomic orbitals will combine most effectively to form molecular orbitals when the atomic orbitals have similar . (a) number of electrons (b) energies (c) hybridization (d) bond order What is the effect of electrons in antibonding orbitals upon the bond order? (a) Each antibonding electron increases the bond order by one. (b) Each antibonding electron increases the bond order by one-half. (c) Each antibonding electron decreases the bond order by one. (d) Each antibonding electron decreases the bond order by one-half. What is the effect of electrons in bonding orbitals upon the bond order? (a) Each bonding electron increases the bond order by one. (b) Each bonding electron increases the bond order by one-half (c) Each bonding electron decreases the bond order by one. (d) Each bonding electron decreases the bond order by one-half.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Prime Classes
UPS 1
10.
What is the maximum number of hybrid orbitals that a phosphorus atom may form? (a) three (b) four (c) six (d) eight What type of hybrid orbital set is used by the nitrogen atom in the molecule NH3? (a) (c) sp sp3 (b) (d) sp2 d2sp3
11.
12.
What type of hybrid orbital set is used by the sulfur atom in the compound H2S? (a) (c) sp sp3 (b) (d) sp2 d2sp3
13.
What type of hybrid orbital set is used by the beryllium atom in the compound BeF2? (a) (c) sp sp3 (b) (d) sp2 d2sp3
14.
What type of hybrid orbital set is used by the boron atom in the compound BF3? (a) (c) sp sp3 (b) (d) sp2 d2sp3
15.
What type of hybrid orbital set is used by the xenon atom in the compound XeF4? (a) (c) sp sp3 (b) (d) sp2 d2sp3
16.
What type of hybrid orbital set is used by the sulfur atom in the compound SF6? (a) (c) sp sp3 (b) (d) sp2 d2sp3
17.
What type of hybrid orbital set is used by the boron atom in the BCl4- ion? (a) (c) sp sp3 (b) (d) sp2 d2sp3
18. What type of hybrid orbital set is used by the nitrogen atom in the NH4+ ion? (a) (c) 19. sp sp3 (b) (d) sp2 d2sp3
What type of hybrid orbital set is used by the aluminum atom in the AlF63- ion? (a) sp (c) sp3 (b) (d) sp2 d2sp3
Prime Classes
UPS 2
20.
Which of the following statements regarding pi bonding is incorrect ? (a) Pi ( ) bonds do not occur unless the bonded atoms are already being joined by a sigma () bond. (b) In order for a pi ( ) bond to form, there must be an unhybridized p atomic orbital on the atom where the hybridization will occur. (c) The number of pi ( ) bonds formed will equal the number of atomic orbitals on the hybridized atom. (d) All three of the above statements are correct. What hybrid orbital set is used by the underlined carbon atom in the allene molecule?
21.
H HC
(a) (c) 22. sp sp3
H C CH
(b) (d) sp2 d2sp3
What hybrid orbital set is used by the underlined carbon atom in the following molecule?
H HC
(a) (c) 23. sp sp3
H C CH
(b) (d) sp2 d2sp3
What hybrid orbital set is used by the oxygen atom in the following molecule?
H HCOCH H H
(a) (c) sp sp3 (b) (d)
sp2 d2sp3
Prime Classes
UPS 3
24.
Methylbenzoate, called oil of Niobe, is used in perfumes.
carbon 1 H C H
(i)
H C
oxygen 1 carbon 3 H C C OCH H C H carbon 2 O
C H
What hybrid orbital set is used by carbon atom 1 in benzoic acid? (a) sp (b) sp2 (c) sp3 (d) d2sp3 What hybrid orbital set is used by carbon atom 2 in the above molecule? (a) sp (b) sp2 3 (c) sp (d) d2sp3 What hybrid orbital set is used by carbon atom 3 in the above molecule? (a) sp (b) sp2 (c) sp3 (d) d2sp3 What hybrid orbital set is used by oxygen atom 1 in the above molecule? (a) sp (b) sp2 3 (c) sp (d) d2sp3
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
25.
What hybrid orbital set is used by the indicated carbon atom in the following molecule?
H HCOCH H H
(b) (d)
(a) (c)
sp sp3
sp2 d2sp3
26. What hybrid orbital set is used by the sulfur atom in the following molecule?
O S
Cl
(a) (c) 27. sp sp3
Cl
(b) (d)
sp2 d2sp3
What hybrid orbital set is used by the nitrogen atom in the following molecule?
H3 CN
(a) (c)
sp sp3
(b) (d)
sp2 d2sp3
Prime Classes
UPS 4
28.
What type of orbital set is used by the nitrogen atom in nitric acid?
N O
H
(b) (d) sp2 d2sp3
(a) (c)
sp sp3
MOLECULAR ORBITALS The molecular orbital diagram below can be used in answering questions 29-43.
Energy
2 p *2p 2 p 2p *2s 2s *1s 1s
29.
A molecular orbital that decreases the electron probability between the nuclei is said to be (a) antibonding (b) nonbonding (c) bonding (d) hybridized Which of the following statements regarding molecule orbital theory is not correct? (a) The number of molecular orbitals formed is equal to the number of atomic orbitals contributed by the atoms involved. (b) Electrons are assigned to orbitals of successively higher energy. (c) The Pauli Principle is obeyed. (d) A bonding molecular orbital is higher in energy than the parent atomic orbital from which it was formed.
30.
Prime Classes
UPS 5
31.
In a diatomic molecule, when two atomic orbitals of the same type combine to form molecular orbitals, which of the following statements best describes the energy of the resulting pair of molecular orbitals? (a) Both molecular orbitals will be higher in energy than the component atomic orbitals. (b) Both molecular orbitals will be lower in energy than the component atomic orbitals. (c) One molecular orbital will be higher in energy and one will be lower in energy than the component atomic orbitals. (d) Both molecular orbitals will be identical in energy to the component atomic orbitals. According to the molecular orbital theory, which of the following correctly lists these hydrogen species in terms of increasing bond order? (a) He2 < He 2+ < He22+ (b) He2+ < He 2 < He22+ (c) He22+ < He 2+ < He2 (d) He22+ < He 2 < He2+
32.
33.
According to molecular orbital theory, which of the following species is unlikely to exist? (a) H2 (b) H2+ (c) He2+ (d) He2
34.
According to the molecular orbital theory, which of the following correctly lists the following oxygen species in terms of increasing bond order? (a) O2+ < O2- < O 2 (b) O2+ < O2 < O 2(c) O2- < O2+ < O 2 (d) O2- < O2 < O 2+
35.
According to the molecular orbital theory, which of the following correctly lists these carbon species in terms of increasing bond length? (a) C 2+ < C 2- < C 2 (b) C 2+ < C 2 < C 2(c) C 2- < C 2+ < C 2 (d) C 2- < C 2 < C 2+
36.
According to molecular orbital theory, which of the following species is unlikely to exist? (a) Li2(b) Li2 (c) Be
2
(d)
Be
37.
According to the molecular orbital theory, which of the following molecules has a bond order of two? (a) Be2 (b) F2 (c) C2 (d) B2
38.
According to the molecular orbital theory, which of the following molecules has a bond order of three? (a) N2 (b) F2 (c) O2 (d) Be2
Prime Classes
UPS 6
39.
According to the molecular orbital theory, which of the following molecules is paramagnetic? (a) Be2 (b) F2 (c) C2 (d) B2
40.
Consider the simple molecule NO, nitrogen oxide. (i) What is the highest energy molecular orbital to which an electron or electrons have been assigned? _________ (ii) How many net sigma ( ) bonds are there ? _______ (iii) How many net pi ( ) bonds? _______ (iv) What is the NO bond order? _____________ (v) Is the molecular diamagnetic or paramagnetic? ____________________ (vi) If the molecule is oxidized to the nitrosonium ion, NO+ , the NO bond is (longer)(shorter) ____________ and it is (stronger)(weaker ) _____________than in NO. Assuming that the molecular orbital energy level diagram for a homonuclear diatomic molecule applies to a heteronuclear molecule such as NO, which of the following correctly lists these nitrogen oxide species in terms of increasing bond order? (a) NO+ < NO - < NO (b) NO+ < NO < NO+ (c) NO < NO < NO (d) NO- < NO < NO+ According to the molecular orbital energy level diagram given in the text, which of the following molecules has the highest bond order? (Assume the molecular orbital energy level diagram for a homonuclear diatomic molecule applies to heteronuclear diatomic molecules.) (a) OF (b) CO (c) NO (d) BN According to the molecular orbital energy level diagram given in the text, which of the following ions has the highest bond order? (Assume the molecular orbital energy level diagram for a homonuclear diatomic molecule applies to heteronuclear diatomic molecules.) (a) Ar2+ (b) OF(c) CN(d) NF2-
41.
42.
43.
44.
The elements called (a) metals (c) nonmetals
are characterized by the fact that the valence band is only partly filled. (b) semiconductors (d) allotropes
45.
What name is given to the highest filled energy level in a metal at absolute zero? (a) conduction band (b) antibonding orbital (c) band gap (d) Fermi level What do we call a material in which the band gap between the conduction band and the valence band is very large? (a) intrinsic semiconductor (b) conductor (c) insulator (d) extrinsic semiconductor
46.
Prime Classes
UPS 7
47.
What do we call a material such as silicon, in which the band gap between the conduction band and the valence band is small? (a) intrinsic semiconductor (b) conductor (c) insulator (d) extrinsic semiconductor Cysteine is one of the natural amino acids.
48.
carbon 1 H H S angle 1
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
H C
O C H
angle 2 OH carbon 2
H N H
angle 3
The molecule has ________ sigma ( ) bonds and _________pi ( ) bonds. Estimate the values of the indicated angles: Angle 1 = _____ Angle 2 = _____ Angle 3 = _____ Consider the SC bond. The orbital hybridization scheme used by the S atom is _________ and that used by the C atom (carbon 1) is _________. What is the hybrid orbital set used by carbon 2? ___________
49.
The compound C5H8O2 exists in two forms in equilibrium with one another. (Lone pairs are not shown.)
carbon 3 H3C C O H
(i)
H C C O angle 1 CH3 H H3C C C O C O H CH3
(ii)
Form A Form B What change occurs in the hybrid orbital set used by C atom 3? (a) changes from sp to sp 2 (b) changes from sp to sp 3 (c) changes from sp2 to sp3 (d) changes from sp3 to sp2 What change occurs in angle 1? (a) changes from 120 to 109(b) changes from 180 to 109 (c) changes from 109 to 120 (d) changes from 120 to 90
Prime Classes
UPS 8
50.
The molecule below is used as a pesticide. (The molecule lies in the yz plane. Lone pairs are not shown.)
y N H3C
1
S
2
x z
C 2py orbital N H3 C C 2pz orbital
(i) (ii) (iii)
S y
The hybrid orbital set used by carbon atom 1 is _____ , by carbon 2 is ____, and by the N atom is ______. The CN=C bond angle is _______ and the N=C=S bond angle is _______. The CN=C=S framework is planar. Assume these atoms lie in the xy plane. Now consider the orbitals (2s, 2px, 2p y, and 2pz ) on carbon atom 2. The orbitals on this atom that are involved in hybrid orbital formation are ______, and the orbitals on C atom 2 that are used in bond formation with the neighboring N and S atoms are ____________. Which is the shorter carbon-nitrogen bond in the molecule, H3CN or C=N? Which is the weaker carbon-nitrogen bond in the molecule, H3CN or C=N?
(iv) (v)
Prime Classes
UPS 9
ANSWERS
1. 2. 3. 4.
a d c b
11. 12. 13. 14.
c c a b
21. 22. 23. 24.
a b c i = b, ii = b, iii = c, iv = c
5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
b b b d b c
15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20.
d d c c d c
25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30.
c c b b a d
31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38.
c a d d b c c a
41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48.
d b c a d c a i = 13. 1; ii = 109, 120, 109; iii = both sp ; iv = sp
3 2
39. 40.
d i = *; ii = 1; 50.
49.
3
i = c; ii = a
2
i = sp , sp, sp ; ii = 120, 180; iii = s, p ; p , p ; iv = C=N; v = H CN
x y z 3
iii = 1 1/2; iv = 2 1/2; v = paramagnetic; vi = shorter, stronger
Prime Classes
UPS 10
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- General ChemistryDocumento27 pagineGeneral ChemistryRick AndrewsNessuna valutazione finora
- Coordinate Geometry Booster For IIT JEE Main and Advanced PDFDocumento383 pagineCoordinate Geometry Booster For IIT JEE Main and Advanced PDFUday Prakash Sahu100% (5)
- Xi Chem WPT 18-03-24Documento27 pagineXi Chem WPT 18-03-24pinnaacleclasses salemNessuna valutazione finora
- Competency Test 1Documento15 pagineCompetency Test 1Uhu UhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Structure, Chemical Bonding and Transition MetalsDocumento13 pagineMolecular Structure, Chemical Bonding and Transition Metalsngah lidwineNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry I - Tutorial 2Documento13 pagineGeneral Chemistry I - Tutorial 2Duc Anh NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry I - Tutorials 2 and 3Documento15 pagineGeneral Chemistry I - Tutorials 2 and 3Duc Anh NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- شبتر9 أسئلةaDocumento25 pagineشبتر9 أسئلةaAnonymous WkiYwkZ100% (1)
- 10 Orbital Hybridization & Molecular OrbitalsDocumento2 pagine10 Orbital Hybridization & Molecular Orbitalserice12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Questions - Chapter 7 PDFDocumento4 pagineSample Questions - Chapter 7 PDFRasel IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- 215215Documento5 pagine215215Chandan V ChanduNessuna valutazione finora
- 64 Practice Problems For CH 14Documento10 pagine64 Practice Problems For CH 14Erwin CabangalNessuna valutazione finora
- G. Cape Chem Sample Mult-ChoiceDocumento9 pagineG. Cape Chem Sample Mult-ChoiceGervent GayleNessuna valutazione finora
- QPDocumento7 pagineQPA N K I T , CLASS X C 34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Term1 Class Xi QN Paper 2021Documento11 pagineTerm1 Class Xi QN Paper 2021Raj IgniteZ SisoudiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Test ChemistryDocumento9 pagineTest ChemistryBryan NozaledaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Term 1 Test 1 XIDocumento8 pagineChemistry Term 1 Test 1 XIrajneesh kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Ch. 8-9 Structures Polarity Review AnswersDocumento13 pagineAP Ch. 8-9 Structures Polarity Review AnswersJocelyn Jp PolanskyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ha 1Documento5 pagineHa 1Shubha MangalaNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ 21cyb101j Unit 1Documento10 pagineMCQ 21cyb101j Unit 1jjamunagandhiNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry II 102 PtsDocumento10 pagineGeneral Chemistry II 102 PtsXyleen GregolaNessuna valutazione finora
- 111A Exam3 Practice 04Documento5 pagine111A Exam3 Practice 04yash patelNessuna valutazione finora
- Half Yearly Practice Paper ChemistryDocumento9 pagineHalf Yearly Practice Paper ChemistrySOHAN DASNessuna valutazione finora
- Xi Chemistry QuestionDocumento5 pagineXi Chemistry QuestionBiswakrit SatapathyNessuna valutazione finora
- General Chemistry I - Tutorials 6 and 7Documento10 pagineGeneral Chemistry I - Tutorials 6 and 7Duc Anh NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Cem1a10 CT2 2010Documento10 pagineCem1a10 CT2 2010elllzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem Academy: Exercise - IDocumento16 pagineChem Academy: Exercise - IHamit Rana100% (1)
- Class 11 - ChemistryDocumento5 pagineClass 11 - ChemistryhowsonoobNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 5Documento3 pagineTutorial 5ts8166Nessuna valutazione finora
- Inorganic Tes 1Documento4 pagineInorganic Tes 1Indah SariNessuna valutazione finora
- Compartment 2 Chem QPDocumento5 pagineCompartment 2 Chem QPAAKASH BHATTNessuna valutazione finora
- Q1: Answer (T) For True Sentences or (F) For False Sentences: (One Mark For Each)Documento5 pagineQ1: Answer (T) For True Sentences or (F) For False Sentences: (One Mark For Each)Ahmed aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry: Chem 210: Training Set IDocumento17 pagineOrganic Chemistry: Chem 210: Training Set Imattyg35Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pearson Edexcel International IGCSE Examination: November 2021 ChemistryDocumento6 paginePearson Edexcel International IGCSE Examination: November 2021 ChemistryKim KatNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Bond ObjbDocumento9 pagineChemical Bond Objbalvin2282Nessuna valutazione finora
- E1 PPT PDFDocumento103 pagineE1 PPT PDFNammaacademyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry PQDocumento15 pagineChemistry PQKrishna Mani100% (1)
- Level-1: Single Correct Answer TypeDocumento8 pagineLevel-1: Single Correct Answer TypePrince ChaturvediNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 02 A1Documento4 pagineAssignment 02 A1sundusNessuna valutazione finora
- Test ReviewDocumento3 pagineTest ReviewgraceNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - Chemical Bonding - ExercisesDocumento6 pagineChapter 3 - Chemical Bonding - Exercisesphat.nguyendothinhNessuna valutazione finora
- Genchem Tamu II (102 Items)Documento10 pagineGenchem Tamu II (102 Items)Mark Ryan TripoleNessuna valutazione finora
- MODEL QUESTIONS REVISION SESSION SCH0201 JUNE 2022 INTAKE GoogleDocumento7 pagineMODEL QUESTIONS REVISION SESSION SCH0201 JUNE 2022 INTAKE GoogleMalindu WickramasingheNessuna valutazione finora
- Cucet 2018 ChemistryDocumento7 pagineCucet 2018 ChemistryAaloka GautamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sankalp Sanjeevani NEET: Chemical BondingDocumento10 pagineSankalp Sanjeevani NEET: Chemical BondingKey RavenNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Question Bank For HiighschoolDocumento221 pagineChemistry Question Bank For HiighschoolsakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Bonding - 2Documento10 pagineChemical Bonding - 2prexa indiaNessuna valutazione finora
- 20 Questions: CHM 101 Final ExamDocumento5 pagine20 Questions: CHM 101 Final ExamAdelon LeopoldNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry 8Th Edition Wade 0321768418 9780321768414 Full Chapter PDFDocumento36 pagineTest Bank For Organic Chemistry 8Th Edition Wade 0321768418 9780321768414 Full Chapter PDFclarence.kuhns728100% (12)
- Test Bank Chapter 2Documento8 pagineTest Bank Chapter 2teafNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 12 Isc Chemistry (MCQ)Documento5 pagineClass 12 Isc Chemistry (MCQ)ashishsanthosh7002Nessuna valutazione finora
- June 2011 UnsolvedDocumento22 pagineJune 2011 UnsolvedAamerNessuna valutazione finora
- Rajat Chemistry Cbse EM PT 2 22Documento3 pagineRajat Chemistry Cbse EM PT 2 22raghavendra jNessuna valutazione finora
- Neet 11Documento4 pagineNeet 11snehakar3011Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Questions - Chapter 9Documento3 pagineSample Questions - Chapter 9Rasel Islam100% (3)
- USM XI ChemistryDocumento7 pagineUSM XI ChemistryPriyanshu GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Geol P 20 Paper II CHEMISTRY PDFDocumento32 pagineGeol P 20 Paper II CHEMISTRY PDFRambo FeverNessuna valutazione finora
- 111Documento2 pagine111nahil ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- ChemistryforAIEEE CET2009 10Documento140 pagineChemistryforAIEEE CET2009 10Lokesh ChemistNessuna valutazione finora
- Main Group Metal Coordination Polymers: Structures and NanostructuresDa EverandMain Group Metal Coordination Polymers: Structures and NanostructuresNessuna valutazione finora
- Akash Neet Question Bank PDFDocumento440 pagineAkash Neet Question Bank PDFUday Prakash Sahu75% (4)
- ToDocumento2 pagineToUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.1 Multiple-Choice and Bimodal Questions: Diff: 3 Page Ref: Sec. 2.1Documento74 pagine2.1 Multiple-Choice and Bimodal Questions: Diff: 3 Page Ref: Sec. 2.1Uday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- 9th Maths Ch-03 Coordinate Geometry FinalDocumento20 pagine9th Maths Ch-03 Coordinate Geometry FinalUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Revised Internal Campus Bus ScheduleDocumento2 pagineRevised Internal Campus Bus ScheduleUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Rotary ActuatorDocumento20 pagineRotary ActuatorUday Prakash Sahu100% (1)
- Roadmap For Reactions of Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes, Alcohols & EthersDocumento5 pagineRoadmap For Reactions of Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes, Alcohols & EthersUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Collision and Mean Free Path 40 CDocumento2 pagineCollision and Mean Free Path 40 CUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Drum Press, Temp CalDocumento22 pagineDrum Press, Temp CalUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- CarbonylDocumento1 paginaCarbonylUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- E2 EliminationDocumento2 pagineE2 EliminationUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid Base RXNDocumento7 pagineAcid Base RXNUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Proforma For OBC NC CertificateDocumento1 paginaProforma For OBC NC CertificateUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Motion - ObjectiveDocumento28 pagineCircular Motion - ObjectiveUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry IJSO Stage-1Documento4 pagineChemistry IJSO Stage-1Uday Prakash Sahu0% (1)
- Test Paper TwelfthDocumento1 paginaTest Paper TwelfthUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Lecture KMDocumento44 pagine01 Lecture KMUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Optics 10Documento24 pagineOptics 10Uday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class-10 Sample PaperDocumento8 pagineScience Class-10 Sample PaperUday Prakash Sahu100% (1)
- Fluid MechanicsDocumento3 pagineFluid MechanicsUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- PaperDocumento3 paginePaperUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ambedkar Nagar: Prime Classes For IIT-JEE/PMT, Ambedkar NagarDocumento2 pagineAmbedkar Nagar: Prime Classes For IIT-JEE/PMT, Ambedkar NagarUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Pages From 10 Ct-22Documento1 paginaPages From 10 Ct-22Uday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ambedkar Nagar: Prime Classes For IIT-JEE/PMT, Ambedkar NagarDocumento2 pagineAmbedkar Nagar: Prime Classes For IIT-JEE/PMT, Ambedkar NagarUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 9 Oct 09Documento3 pagineClass 9 Oct 09Uday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Compressed Air System Design ManualDocumento26 pagineCompressed Air System Design ManualBadrul HishamNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz - Compressors and Compressed Air SystemsDocumento3 pagineQuiz - Compressors and Compressed Air SystemsUday Prakash Sahu100% (1)
- Atomic Bohrs ModelDocumento2 pagineAtomic Bohrs ModelUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Samudra ManthanDocumento4 pagineSamudra ManthanUday Prakash SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 007Documento55 pagineChap 007Joy-mileny Sepulveda100% (2)
- Corporate Finance: How To Value Bonds and StocksDocumento49 pagineCorporate Finance: How To Value Bonds and StocksMajumdar VijayNessuna valutazione finora
- Do 156 S2015 PDFDocumento86 pagineDo 156 S2015 PDFMarjs MayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Isomers and Stereochemistry: Essential Organic Chemistry (Bruice)Documento39 pagineIsomers and Stereochemistry: Essential Organic Chemistry (Bruice)tyron9520Nessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm Review 2017Documento3 pagineMidterm Review 2017JADFNessuna valutazione finora
- China Policy Financial Bonds PrimerDocumento39 pagineChina Policy Financial Bonds PrimerbondbondNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 101 Final Exam-B Fall 2014Documento13 pagineChemistry 101 Final Exam-B Fall 2014Kristopher Park SolivenNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometrical and Optical IsomerismDocumento17 pagineGeometrical and Optical Isomerismmahesh67% (3)
- AldehydesDocumento18 pagineAldehydesVibhor KaushikNessuna valutazione finora
- Interest Rate RiskDocumento41 pagineInterest Rate RiskPardeep Ramesh AgarvalNessuna valutazione finora
- Valuation of Bonds PDFDocumento6 pagineValuation of Bonds PDFMoud KhalfaniNessuna valutazione finora
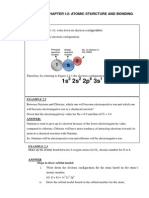
- TUTORIAL I-2 Atomic Structure and Bonding PDFDocumento6 pagineTUTORIAL I-2 Atomic Structure and Bonding PDFJack TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 Enzyme KineticsDocumento31 pagineLecture 2 Enzyme KineticsCarinaJongLeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Betting Against BetaDocumento25 pagineBetting Against BetamNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrogen Adsorption On Boron Nitride NanotubesDocumento16 pagineHydrogen Adsorption On Boron Nitride NanotubesSarathkumar SethunarayananNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry Question BankDocumento92 pagineOrganic Chemistry Question BankGpg Subhash100% (7)
- Macromolecular Structure and Analysis (Semester - 1) : Reg. NoDocumento6 pagineMacromolecular Structure and Analysis (Semester - 1) : Reg. NoJnanendra SenguptaNessuna valutazione finora
- I B Chem 1 Pract Test BondingDocumento7 pagineI B Chem 1 Pract Test BondingMuy TamNessuna valutazione finora
- SF 28 Affidavit of Individual SuretyDocumento2 pagineSF 28 Affidavit of Individual Suretyandy miller100% (1)
- How To Redeem A Savings Bond or NoteDocumento3 pagineHow To Redeem A Savings Bond or NoteShevis Singleton Sr.100% (2)
- Chapter 2 AlkanesDocumento6 pagineChapter 2 AlkanesShan TiNessuna valutazione finora
- Applications of The Olefin Metathesis Reaction Application of CADocumento273 pagineApplications of The Olefin Metathesis Reaction Application of CAGabriela Pinho Tavares RitterhaussenNessuna valutazione finora
- Recent Advances in Composite Resins ReviewDocumento5 pagineRecent Advances in Composite Resins ReviewChitrang KolawaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Difference Between Organic and Inorganic CompoundsDocumento3 pagineDifference Between Organic and Inorganic CompoundsBilal Khan100% (1)
- Guide Quiz #1Documento3 pagineGuide Quiz #1Rujual BainsNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 2.4 Redox Reactions Oxidation and Reduction Oxidising and Reducing Agents Redox ReactionsDocumento7 pagineTopic 2.4 Redox Reactions Oxidation and Reduction Oxidising and Reducing Agents Redox ReactionsranazikriaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM 556 Experiment 5Documento12 pagineCHM 556 Experiment 5Amar Safwan100% (1)
- Experiment 15: Exploring The World of PolymersDocumento6 pagineExperiment 15: Exploring The World of PolymersABDFERNessuna valutazione finora
- $834.67 Discount BondDocumento5 pagine$834.67 Discount BondLưu Gia Bảo0% (1)