Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Test-El-05-06-2012 - Q
Caricato da
Pratik SharmaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Test-El-05-06-2012 - Q
Caricato da
Pratik SharmaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Test5 - Electrostatics Date : 05-06-2012 MCQ (Single Correct) (+3, 1) qd Q1. A spherical conductor A contains two spherical cavities.
The total charge on the conductor itself is zero. However, there is a point charge qb at the centre of one cavity and qc at the centre of the other. A considerable distance r away from the centre of the spherical conductor, there is another charge qd. Force acting on qb, qc and qd are. qb qc F1 F2 and F3 respectively. [Assume all charges are positive] (B) F1 = F2 < F3 (A) F1 < F2 < F3 (D) F1 > F2 > F3 (C) F1 = F2 > F3 Q2. There are two concentric metal shells of radii r1 and r2 (>r1). If the outer shell has a charge q and the inner shell is grounded, the charge on the inner shell is (C) r1r2q (D) (A) zero (B) (r1/r2)q B Q3. A and B are two concentric spheres. If A is given a charge + + ++ Q while B is earthed as shown in figure, then + + A (A) the charge densities of A and B are same + + (B) the field inside and outside A is zero + + + the field between A and B is not zero (D) the field inside and outside B is zero Q4. A hollow conducting sphere of inner radius R and outer radius 2R is +Q B given a charge Q as shown in the figure, then the A O C (A) potential at A and B is different R (B) potential at O and B is different 2R (C) potential at O and C is different (D) potential at A, B, C and O is same Q A conducting sphere A of radius rA carries a charge Q. Another conducting sphere B of radius rB is rB uncharged initially. Both the spheres are separated rA S by a very large distance. Sphere A is connected B with sphere B through a long conducting wire of A zero resistance through a switch S as shown in the figure. At t = 0 switch S is closed. As soon as the current flow through the wire vanishes, switch S is opened, sphere A is again charged to a total charge Q and then switch S is again closed and the process is continued for infinite times. If q is the charge transferred to sphere B when the switch S is closed for the first time, then total charge on the sphere B after large number of such processes is r qQ (A) Q (B) (D) None (C) Q B Qq rA Two identical conducting sphere having unequal positive charges q1 and q2are separated by distance r. If they are made to touch each other and then separated again to the same distance, the electrostatic force between them in this case will be (A) less than before (B) same as before (C) more than before (D) zero A solid conducting sphere having a charge Q is surrounded by an uncharged concentric conducting spherical shell. Let the potential difference between the surface of the solid sphere and that of the outer surface of the shell be V. If the shell is now given a charge of - 3Q, the new potential difference between the same two surfaces will be (A) V (B) 2V (C) 4V (D) 2V
Q5.
Q6.
Q7.
Q8.
A uniform conducting sphere having charge +q and radius a is placed at the center of a spherical conducting shell of inner radius b and outer radius c. The outer shell carries a charge of q. Choose the incorrect statement ( A) The field E(r) at any point within the sphere (r < a) is zero ( B) The field E(r) at any point between the sphere and shell (a < r < b) is ( C) The field E(r) at any point outside the shell ( D) The field E(r) at any point outside the shell (r > c) is zero. 1 q (r > c) is 4 0 r 2
c b
1 q 4 0 r 2
Q9.
The conducting spherical shells shown in the figure are connected by a conductor. The capacitance of the system is (A) 4 0 ab (B) 4 0 a ba (D) 4 0 a2/b a (C) 4 0 b
a b
Q10.
Two concentric conducting spheres having radii a and b are charged to q1 and q2, respectively. The potential difference between 1 and 2 will be q2 q1 q2 q2 1 1 q1 (B) (A) 40a 40b 40 a b a 2 1 b q1 1 1 (D) none of these. (C) - 40 a b
Q11.
A charge +q is brought near an isolated metal cube having no charge initially (A) the cube becomes positively charged. (B) the cube becomes negatively charged. (C) the external surface becomes negatively charged and the interior becomes positively charged. (D) the Interior remains charge free and the surface gets non-uniform charge distribution. Assertion Reason type ( +3,-1) (A) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement -2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1. (B) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement -2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1. (C) Statement -1 is True, Statement-2 is False. (D) Statement -1 is False, Statement-2 is True. Q12. STATEMENT-1 The electric field inside a conductor is always zero. because STATEMENT-2 There are large numbers of free electrons in a conductor. Q13. STATEMENT-1: The tangential component of electrostatic field due to charged conductor at a point just above the surface is zero. because STATEMENT-2: Circulation of electrostatic field over a closed loop is zero.
Q14.
A spherical uncharged conducting shell of radius r is P r placed in front of point charge q at distance d from its centre O as shown. O STATEMENT-1 The potential at point P lying on the surface of the sphere will be equal q/40d. because STATEMENT-2 The potential inside the conducting shell is same. Integer Type(+3, 1) Q15. A charge is distributed over two concentric hollow spheres of radii r and R (>r) such that their surface densities are equal. Find the potential at their common centre. [ Given R = 2m , r = 1m r and = 2 S.I. Unit ] 0
q d
Q16.
Q17.
Q18.
Two isolated metallic solid spheres of radii R and 2R are charged such that both of these have same charge density . The spheres are located far away from each other, and connected by a thin conducting wire. If the new charge density n on the bigger sphere is , then the value of n is.. 6 In the arrangement shown in figure, three concentric conducting shells are shown. The charge on the shell of radius b is q0. If the innermost and outermost a shells are connected to the earth, the potential on b q0 the shell of radius b in terms of a and q0 is . c 8n0 a Given that a : b : c = 1 : 2 : 4. Find the value of n Figure shows three concentric thin spherical shells A, B and C B C of radii a, b and c, respectively. The shells A and C are b A given charge q and q, respectively, and shell B is earthed. a c [ Given q = 3 C, a : b : c = 1 : 2 : 3] Find the charges appearing on the outer face of surfaces B
Q19.
Five identical conducting plates 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 are fixed parallel plates equidistant from each other as shown in figure. Plates 2 and 5 are connected by a conductor while 1 and 3 are joined by another conductor. If the charge on plate 5 is the value of k.
5 4 3
v0
kCV0 .Find 3
2 1
Q20.
Four identical metal plates of large area A are arranged as shown in the diagram. The plates 1 and 3 are connected by a conducting wire. The charge on plate 2 is 2q and an plate 4 is q. If the potential 16 volt.. difference (in volts) between the plate 2 and 3 is k qd = 2 Find the value of k Given A 0
4d
2q 2d
d q
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Electric Charge Multiple Choice Questions for JEE Main and AdvancedDocumento14 pagineElectric Charge Multiple Choice Questions for JEE Main and Advancedbrm1shubhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatics Assignment: Gravity ClassesDocumento6 pagineElectrostatics Assignment: Gravity Classesjagan9912342495Nessuna valutazione finora
- Questions: D or 2d As Drawn, and A Central Point Is Shown MidwayDocumento4 pagineQuestions: D or 2d As Drawn, and A Central Point Is Shown MidwayFirdous ANessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatics: (Physics)Documento5 pagineElectrostatics: (Physics)Tom HollandNessuna valutazione finora
- NHGKJDocumento9 pagineNHGKJChandan V ChanduNessuna valutazione finora
- Electro Statics - 26-08-2020 PDFDocumento10 pagineElectro Statics - 26-08-2020 PDFPonharish kumar.JNessuna valutazione finora
- (IITExp1) - (JLD 3.0) - Electrostatics - 14th August.Documento43 pagine(IITExp1) - (JLD 3.0) - Electrostatics - 14th August.Debi prasad jenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics ch-1 McqsDocumento20 paginePhysics ch-1 McqstdcgxgchhcNessuna valutazione finora
- Minor-2 (Paper With Solution)Documento27 pagineMinor-2 (Paper With Solution)ayush.dubey.46557Nessuna valutazione finora
- Xii Physics - Chapter 2term 1Documento17 pagineXii Physics - Chapter 2term 1RahulNessuna valutazione finora
- PhysicsforAIEEE CET2009 10Documento224 paginePhysicsforAIEEE CET2009 10Vishwajeet Aman100% (1)
- Physics Electrostatics MCQDocumento8 paginePhysics Electrostatics MCQSrijan Chakraborty100% (1)
- PG Brainstormer - Physics Concepts in 60 MinutesDocumento6 paginePG Brainstormer - Physics Concepts in 60 MinutesHarsh VardhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric charges and fields explainedDocumento9 pagineElectric charges and fields explainedHari KrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Field and Charges MCQsDocumento9 pagineElectric Field and Charges MCQsArvita KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Dpp-2 ElectrostaticDocumento8 pagineDpp-2 ElectrostaticYash GhorpadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Test On ElectrostaticsDocumento4 pagineTest On ElectrostaticsHemendra PrasannaNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectrostaticPhy - DPP - 05Documento6 pagineElectrostaticPhy - DPP - 05Yash GhorpadeNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ ElectrostaticsDocumento11 pagineMCQ ElectrostaticsShravani NarodeNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ Physics 1,2,3Documento10 pagineMCQ Physics 1,2,3Sugaraj SamuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Class-12 Physics-Chapter-1 ASSIGNMENT-1 2024Documento3 pagineClass-12 Physics-Chapter-1 ASSIGNMENT-1 2024maryak3050Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatics Test 1 Marks 90 Time 1 hrDocumento4 pagineElectrostatics Test 1 Marks 90 Time 1 hrSanjay Kumar DokaniaNessuna valutazione finora
- PG Brainstormer - 1CDocumento5 paginePG Brainstormer - 1CAlkaChoudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Potential and Gauss Law (06-05-2023)Documento6 pagineElectric Potential and Gauss Law (06-05-2023)Epic NationNessuna valutazione finora
- Kvpy ElectrostaticDocumento9 pagineKvpy ElectrostaticUdbhav DikshitNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatic (QB) 13thDocumento15 pagineElectrostatic (QB) 13thRaju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Mcq-Chp-1-Electrostatics Class 12Documento8 pagineMcq-Chp-1-Electrostatics Class 12domahe7121100% (2)
- Electrostatics Problems and SolutionsDocumento3 pagineElectrostatics Problems and SolutionsAyushmaan SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 8417QUESTIONS BANK FOR 12 - 22-23 - FINAL - MODIFIED - 20 PagesDocumento20 pagine8417QUESTIONS BANK FOR 12 - 22-23 - FINAL - MODIFIED - 20 PagesAkshat Parmar. 11 cNessuna valutazione finora
- PH108 2014tut3Documento3 paginePH108 2014tut3ashwinagrawal198231Nessuna valutazione finora
- Innovation Tuition Class Class 12 Physics Test Q1Documento3 pagineInnovation Tuition Class Class 12 Physics Test Q1Hemant HemantNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatic DPP JP 02Documento8 pagineElectrostatic DPP JP 02Piyush GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- The ReformerDocumento10 pagineThe ReformerDanis LevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity & MagnetismDocumento39 pagineElectricity & MagnetismAditya KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics TestDocumento8 paginePhysics TestrajatiitdNessuna valutazione finora
- Class XII Level 1 AssignmentDocumento72 pagineClass XII Level 1 AssignmentK VIKASNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Electric Charges & FieldDocumento16 pagine1 - Electric Charges & FieldAawesh BackupsNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Work Sheet - Charges and FieldDocumento10 paginePractice Work Sheet - Charges and FieldShirley VeigasNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet - 01-Pages-27-72Documento46 pagineSheet - 01-Pages-27-72Hemant KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- B PH 1 S EnglishDocumento19 pagineB PH 1 S Englishnifty.vedNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 2Documento21 pagineCH 2terasaini77Nessuna valutazione finora
- PhysicsforAIEEE CET2009 10 PDFDocumento224 paginePhysicsforAIEEE CET2009 10 PDFPraveen KumarpillaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatics (JEE MAIN Online) PDFDocumento15 pagineElectrostatics (JEE MAIN Online) PDFAnanya DwivediNessuna valutazione finora
- Electro Statics - 27-08-2020 PDFDocumento12 pagineElectro Statics - 27-08-2020 PDFPonharish kumar.JNessuna valutazione finora
- Electromagnetism Practice SheetDocumento104 pagineElectromagnetism Practice Sheetsohammodi9030Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatics ExerciseDocumento20 pagineElectrostatics ExerciseUtkarsh Mittal86% (7)
- Arjuna - ElectrostaticsDocumento11 pagineArjuna - ElectrostaticsNeha JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Potential Capacitance Multiple Choice 2014-03-13Documento14 pagineElectric Potential Capacitance Multiple Choice 2014-03-13Zeeshan sharifNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatics (Question Paper)Documento6 pagineElectrostatics (Question Paper)anchlia12345Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatics: (Physics)Documento6 pagineElectrostatics: (Physics)Piyush GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 1: Electric Charges and FieldsDocumento7 pagineChapter - 1: Electric Charges and FieldsAkash SureshNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatics Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGDocumento20 pagineElectrostatics Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGSubhashChandraMishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Electromagnetism Practice Problems 1 4Documento18 pagineElectromagnetism Practice Problems 1 4Minh Trương PhúcNessuna valutazione finora
- Xii Phy CH1&2Documento3 pagineXii Phy CH1&2DEVIKAA ARUNNessuna valutazione finora
- PhysicsDocumento17 paginePhysicspaninikumar0000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ds Ds DS: Physics For XIIDocumento4 pagineDs Ds DS: Physics For XIIC.p. RawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 12 (2023) TESTDocumento12 pagineClass 12 (2023) TESTsubash murugaiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsDa EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyDa EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 6Documento10 pagineLec 6Pratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Task Scheduling Problem: A Scheduling System Model Consist of AnDocumento4 pagineTask Scheduling Problem: A Scheduling System Model Consist of AnPratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 5Documento6 pagineLec 5Pratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Paper 2 ElectrostaticsDocumento5 pagineTest Paper 2 ElectrostaticsPratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
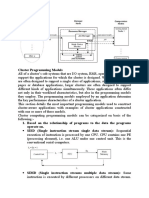
- Parallel Programming Models and ToolsDocumento4 pagineParallel Programming Models and ToolsPratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- ELECTROSTATICS-1 TITLEDocumento5 pagineELECTROSTATICS-1 TITLEPratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 3-4Documento4 pagineLec 3-4Pratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Cluster Computer and Its ArchitectureDocumento3 pagineA Cluster Computer and Its ArchitecturePratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Motivation Behind Why To Use Grid and Cluster ComputingDocumento7 pagineMotivation Behind Why To Use Grid and Cluster ComputingPratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Flux 1A Class WorkDocumento5 pagineFlux 1A Class WorkPratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Paper 1Documento1 paginaQuestion Paper 1Book WormNessuna valutazione finora
- Gateway 2010 Quiz FinalsDocumento49 pagineGateway 2010 Quiz FinalsPratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Code Wars 2010 PrelimDocumento2 pagineCode Wars 2010 PrelimPratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- All About Wiki .: Wikimedia Foundation, Inc. Is Headquartered inDocumento6 pagineAll About Wiki .: Wikimedia Foundation, Inc. Is Headquartered inPratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Access 2006 Junior Quiz PrelimsDocumento1 paginaAccess 2006 Junior Quiz PrelimsPratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Handa Ka Funda - Best of Tata CrucibleDocumento52 pagineHanda Ka Funda - Best of Tata CrucibleMrigank Gutgutia100% (1)
- It Quiz Study GuideDocumento172 pagineIt Quiz Study GuidePratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Al QaedaDocumento35 pagineHistory of Al QaedaPratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- QuadraticDocumento1 paginaQuadraticPratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategy For Combating TerrorismDocumento45 pagineStrategy For Combating TerrorismPratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Business BasicsDocumento43 pagineBusiness BasicsPratik SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 12th Physics ProjectDocumento21 pagine12th Physics ProjectPratik Sharma47% (19)
- Heat and Mass Transfer ProblemsDocumento3 pagineHeat and Mass Transfer ProblemsRiyasNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Operation-1: Prepared By: Mukhtiar AliDocumento12 pagineUnit Operation-1: Prepared By: Mukhtiar AliFarman AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Forms of EnergyDocumento15 pagineForms of EnergyTrajce StojanovNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Lifting Hook: Earth Fill Load (Dl2)Documento21 pagineDesign of Lifting Hook: Earth Fill Load (Dl2)Asaru DeenNessuna valutazione finora
- In A Sliding Pair Minimum Number of Degree of FreedomDocumento15 pagineIn A Sliding Pair Minimum Number of Degree of FreedomanuanwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Nonlinear Dynamics of A Duffing-Like Negative StifDocumento13 pagineNonlinear Dynamics of A Duffing-Like Negative StifPietro TestaNessuna valutazione finora
- Back Calculated P-Y Relation of Liquefied Soils From Large Shaking Table TestsDocumento7 pagineBack Calculated P-Y Relation of Liquefied Soils From Large Shaking Table TestsEmreNessuna valutazione finora
- Aircraft Center of Mass AnalysisDocumento18 pagineAircraft Center of Mass AnalysisOscar Oreste Salvador CarlosNessuna valutazione finora
- Base Plate Design For Fixed BaseDocumento59 pagineBase Plate Design For Fixed Basemoneoffice100% (2)
- Topic 1 (Introduction and Friction) Part 1Documento21 pagineTopic 1 (Introduction and Friction) Part 1Brix DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Rate and Temperature Dependent Strain Hardening of Polycarbonate by D. J. A. SandenDocumento14 pagineRate and Temperature Dependent Strain Hardening of Polycarbonate by D. J. A. SandenSamuel ManaluNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm c1161 13Documento19 pagineAstm c1161 13Taiana BonadioNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrodynamic Journal BearingDocumento4 pagineHydrodynamic Journal BearingEbe Nezer GNessuna valutazione finora
- Mauritius Metro Express Project - Engineering, Procurement and Construction WorksDocumento36 pagineMauritius Metro Express Project - Engineering, Procurement and Construction WorksmvssrajuNessuna valutazione finora
- PT Specialist training friction loss calculationDocumento28 paginePT Specialist training friction loss calculationVladimir SimeunovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Exam Questions For SS2 Second TermDocumento15 paginePhysics Exam Questions For SS2 Second TermShoon100% (3)
- Assignment 1 ThermodynamicsDocumento1 paginaAssignment 1 ThermodynamicsMarvin BayanayNessuna valutazione finora
- Boundary Layer Analysis PDFDocumento242 pagineBoundary Layer Analysis PDFSekhar SamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer Correlations for Flat PlatesDocumento13 pagineFluid Flow and Heat Transfer Correlations for Flat PlatesRiad El Abed100% (1)
- George Haller - Transport Barriers and Coherent Structures in Flow Data - Advective, Diffusive, Stochastic and Active Methods-Cambridge University Press (2023)Documento427 pagineGeorge Haller - Transport Barriers and Coherent Structures in Flow Data - Advective, Diffusive, Stochastic and Active Methods-Cambridge University Press (2023)Cesar RosalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Paper 3 TZ1 HLDocumento36 paginePhysics Paper 3 TZ1 HLd bNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamics of Rotors PDFDocumento386 pagineDynamics of Rotors PDFJon LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Report 16Documento5 pagineReport 16M AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- How Rebar Distribution Affects Concrete Beam Flexural StrengthDocumento10 pagineHow Rebar Distribution Affects Concrete Beam Flexural Strengthtoma97Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento28 pagineChapter 2Siti Hajar Mohd PodziNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 - Maneuvering Theory: Lecture Notes TTK 4190 Guidance and Control of Vehicles (T. I. Fossen)Documento27 pagineChapter 6 - Maneuvering Theory: Lecture Notes TTK 4190 Guidance and Control of Vehicles (T. I. Fossen)Cao Quang HưngNessuna valutazione finora
- EN 13706 Fiberglass Profile Standard SummaryDocumento2 pagineEN 13706 Fiberglass Profile Standard SummaryRohan BajNessuna valutazione finora
- Moment of A Force (With Worked Examples)Documento5 pagineMoment of A Force (With Worked Examples)A BarrettNessuna valutazione finora
- Column New EC2 LastDocumento81 pagineColumn New EC2 LastsuniljayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Elastic and viscoelastic properties of metals and their modelingDocumento11 pagineElastic and viscoelastic properties of metals and their modelinggunapalshettyNessuna valutazione finora