Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Procurement Process
Caricato da
Raks ThuruthiyilCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Procurement Process
Caricato da
Raks ThuruthiyilCopyright:
Formati disponibili
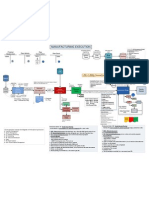
PROCUREMENT PROCESS
G / L: Consumption Raw 300 P/L Stock Raw 3000 Balance sheet Bank 3300
GR / IR
3300 3300
Reconciliation Vendor 3300 3300
Subledger Vendor 3300 3300
Material Management Integration: (FI) Financial Accounting: Purchasing and FI maintains data on the VENDOR master data (is a creditor account in FI) that contains account.+ procur. info (SD) Sales and Distribution: requirements that arrives to Sales can be passed on to Purchasing. when a P.Req. is created, it can be directly assigned to a Sales Order. Production Planning: and MM are linked through inventory needs. Inv. Mgt is responsible for assuring all components required for production. Plant Maintenance and MM are linked by BOM. Its possible to post a GR with ref to an equipment BOM and to withdraw part for maintenance orders too. Integration in Logistics: the Inv. Mgt system (manages Stock (Q) quantity + ($) value) can be extended by the WMS which manages storage (also Storage Bins)
Invoice Verification and Vendor Payment
Account Posting Good Receipt : Debit Stock, Credit GR/IR Invoice Receipt: Debit GR/IR, Credit Vendor (Recon.+Subledger) (=> acc. payable) Pay Vendor: Debit Vendor (Recon.+Subledger), Credit Bank/Cash
If there are variances between the PO or GR vs INVOICE, the system warns the user and blocks the invoice for payment. Posting the invoice completes the process of Invoice Verification. Types of Invoice Verification: Invoice items can be posted with reference to: Goods receipt based Invoice verification: invoices for quantities greater than the goods receipt cannot be posted. Purchase order based Invoice verification: you can settle all items, irrespective of whether there have been partial deliveries. The postings are automatically made to the corresponding G/L accounts. When an Invoice is posted, an open item is credited on the vendor account. Logistics: Invoice Verification: Effects FI - Accounting document is created PO History is updated Open Item is created in the vendors account
If invoice $ differs from the PO $, the stock value and the current moving price is recalculated and updated in the material master, for a material valuated with mov. aver. $.
Cost element
Vendor Account group
Info record
Material
Conditio n Condition types
Output Output types
Material type Industry sector
_ Account affected: .Provision in the GR/IR clearing account are reversed - debited .Reconc. Vendor is credited Account payable .Subledger Vendor is credited . NON Stock raw-consum. raw, Bank
Material Mgt, manages the procurement process until Invoice verif. Is an Internal document
Other Dpt (account) manage the payment and evaluation of invoices. Therefore, Inv. Verif. creates a link between Mat. Mgt and external (FI) or Internal account. (CO)
Manually by the Dep. Respons. Automatically by MRP
Purchase Requisition
Source of supply Info record Quotation Contract Source list
with / without reference
Purchase order
10
Org. level needed for a PO Plant Purch. Org. Vendor Storage loc not nec. until good
are not received.
Invoice/ Billing
Pay
10 20
Stock item Non-stock item Item Category
Header Data: Doc. # Date Vendor Terms of payment Currency
20
Item: Material # Delivery date Q, $, Text
MM Doc
FI Doc
FI Doc
Vendor (Recon.+Subledger) are debited, Bank/Cash is credited
Consumable Material: Are materials or services that are procured specifically for an account assignment object. (EX: office supplies; computer systems) Value is recorded in the cost element or asset accounts. When a material is procured directly for consumption, no material master record is necessary. In the case of consumable material with a master record: o Not subject to inventory management (on either quantity or value basis) o Subject to inventory management on a quantity, but not a value basis Account Assign. Objects A Asset C Cost Center P Project P Prod. Order S Sales Order
Item category: defines the process used to procure a material
or service.
Goods Receipt
S Standard: material procured externally S Stock transport order: mat. is transf. from 1 plant to another S Subcontracting: vendor manufacture a component C Consignment: Liability only when mat. is withdrawn from
consg. stock, no when the stock is placed in the consg. store
103
you enter goods receipt against production and purchase orders
101
Movement type: determines the kind of goods movements. What happens to the items, how they are handledkey to differentiate between goods movements (ex: GR, GI or transfer postings). (Inv. Mgt) Determines which stock or consumption accounts are updated (posted) in Financial Accounting. Determines the structure of the screen when entering documents and updating quantity fields.
T Third-party order: material order from a vendor with the
instruction to deliver the goods directly to a 3er party (customer)
Storage location Goods receipt area F - Unrestricted 105 Q Quality Insp. X Blocked Stock
Stock type
Documents generated
Posting a Goods Receipt by referencing to a Purchase Order has a 3 advantages: The goods receiving department can check whether the goods delivered are what was actually ordered. Data from PO is copied automatically to the GR transaction. PO history is updated upon GR creation.
MM Doc
MM Doc
FI Doc
CO Doc
When goods receipt to the warehouse is posted: A MM doc. is created: with info such as material delivered and quantity delivered; storage location and associated plant. An FI doc. is created: which record the effects the material movement has on the value of the stock.
Goods movements: A transaction that causes a stock change. Include both external and internal movements. You can distinguish between: Goods receipt (GR): is a goods movement in which the receipt of goods from both an external vendor and from production is posted. A GR leads to an increase of warehouse stock. Goods issue (GI): is a goods movement in which a material withdrawal, goods issue, material consumption, or goods shipment is posted to a customer. A GI leads to a decrease of warehouse stock. Stock trasfer: is removal of materials from particular storage location and placement into another storage location. Stock transfers can take place both within the same plant and between two plants. Transer posting: changes the stock identification or qualification of a material regardless of its a physical movement or not. (EX: release of the stock for quality inspection).
Effects of Goods Receipt: MM - Material document is created (quantity) FI - Accounting document is created (value) CO Cost Accounting document cost analysis purpose Material master is updated (here not in the inv. verif) _ Account affected: .Stock raw (+ Consumption Raw) is debited .Provision in the GR/IR is credited . NON Bank, Reconc. Vendor, Subdledger Vendor PO History for a PO items is updated (when a GR is
entered with reference to this item)
Quality Management (Inspection lot is created) Warehouse Management (Transfer Requir. is created) Output may be generated (GR slip)
Process of GR with Transfer Order GR posting is subject to WMS: checks for each PO item and generates: MM + FI docs for goods movt.: _MM doc.: Header + Item (q, descrip, stor.loc., plant), is identified by material document number and year. _FI doc.: Header + Item (G/L acc. #, $) records the effects of material movements on the accounts. Is identified by CC (of the plant); acc doc. #, fiscal year. Transfer requirement doc Incoming quantity of materials into the goods receiving area An Interim storage area in the receiving warehouse number A transfer order is used to move the items from the receiving area (in a put away process) the destination storage type, the storage section, storage bin are determined
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Implementing Integrated Business Planning: A Guide Exemplified With Process Context and SAP IBP Use CasesDa EverandImplementing Integrated Business Planning: A Guide Exemplified With Process Context and SAP IBP Use CasesNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Sales Order Management WWW - SapDocumento1 pagina4 Sales Order Management WWW - SapRajni SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sap MM OverviewDocumento26 pagineSap MM OverviewrameshbabualluriNessuna valutazione finora
- Procurement Process in SAP MM Chap.4Documento26 pagineProcurement Process in SAP MM Chap.4Priyanka BarotNessuna valutazione finora
- Procurement Process Cycle Procure To Pay Process P2PDocumento3 pagineProcurement Process Cycle Procure To Pay Process P2PSdev123Nessuna valutazione finora
- PURCHASE-TO-PAYMENT PROCESS ASSESSMENT REVIEWDocumento36 paginePURCHASE-TO-PAYMENT PROCESS ASSESSMENT REVIEWviswaja100% (1)
- ERP SAP MM Procure To Pay Process CycleDocumento1 paginaERP SAP MM Procure To Pay Process CycleBunty Jain100% (5)
- Purpose: IRCON - Global Business Process Master List (BPML)Documento24 paginePurpose: IRCON - Global Business Process Master List (BPML)AdityaNessuna valutazione finora
- SD MM FlowDocumento5 pagineSD MM Flowharish2912Nessuna valutazione finora
- Procure To Pay Cycle Process and Configuration From FI EndDocumento14 pagineProcure To Pay Cycle Process and Configuration From FI Endganesanmani1985Nessuna valutazione finora
- MH02 - MM Procure To Pay - Business BlueprintDocumento32 pagineMH02 - MM Procure To Pay - Business BlueprintwiesenerNessuna valutazione finora
- Purchasing ProcessDocumento2 paginePurchasing ProcessBriann BarriosNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Blueprint for Non-Hydrocarbon ProcurementDocumento22 pagineBusiness Blueprint for Non-Hydrocarbon ProcurementVincent ChangNessuna valutazione finora
- Imprest Funds & ReplenishmentsDocumento38 pagineImprest Funds & ReplenishmentsraghavNessuna valutazione finora
- Procure To Pay CycleDocumento9 pagineProcure To Pay CycleRajashree DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Table of Contents:-: Asset AccountingDocumento5 pagineTable of Contents:-: Asset AccountingsurendraNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding the Key Data and Process Flow in SAP MM ModuleDocumento40 pagineUnderstanding the Key Data and Process Flow in SAP MM ModuleexcelhelplineNessuna valutazione finora
- Sap MM Standard Business ProcessesDocumento65 pagineSap MM Standard Business ProcessesDipak BanerjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- BPML Draft1 08042013Documento9 pagineBPML Draft1 08042013ahsanNessuna valutazione finora
- End User Procedure For Sap MM PurchasingDocumento86 pagineEnd User Procedure For Sap MM PurchasingEduardo100% (1)
- Complete Procure to Pay Cycle in SAP MMDocumento8 pagineComplete Procure to Pay Cycle in SAP MMPavilionNessuna valutazione finora
- Rent Payment Process With Sap Mm1Documento14 pagineRent Payment Process With Sap Mm1Alfonso Herrera RojasNessuna valutazione finora
- SAP A/P Payments UnitDocumento49 pagineSAP A/P Payments Unittarunaggarwal11Nessuna valutazione finora
- BP-PP-Master Data-Routing & Rate RoutingDocumento9 pagineBP-PP-Master Data-Routing & Rate RoutingAhmed TalaatNessuna valutazione finora
- Purchase Requisition (PR) Document in SAP MM. Purchase Requisition (PR) Is An Internal Purchasing Document in SAPDocumento5 paginePurchase Requisition (PR) Document in SAP MM. Purchase Requisition (PR) Is An Internal Purchasing Document in SAPashwiniNessuna valutazione finora
- SAP FINANCE SYSTEM - Departmental User GuideDocumento126 pagineSAP FINANCE SYSTEM - Departmental User Guidesteinfatt1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Accounts PayableDocumento44 pagineAccounts Payablethat_glossmk100% (2)
- Questionnaire For ClientDocumento7 pagineQuestionnaire For ClientAnonymous hjPz1PYlrNessuna valutazione finora
- Period End ClosingDocumento4 paginePeriod End ClosingJose Luis Becerril BurgosNessuna valutazione finora
- Procure To Pay OverviewDocumento13 pagineProcure To Pay Overviewmohamedrizkibrahim100% (6)
- SAP Inventory Module ProcessDocumento37 pagineSAP Inventory Module ProcessRajesh ChalkeNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Overview - View Procurement DC: DC Stocking Flow ThroughDocumento10 pagineProcess Overview - View Procurement DC: DC Stocking Flow ThroughBessemNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Process Master List For CODocumento24 pagineBusiness Process Master List For COlionelkenethNessuna valutazione finora
- PDD Accounting For Bad Debts and Writeoffs (BDAR2160)Documento37 paginePDD Accounting For Bad Debts and Writeoffs (BDAR2160)SRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Procure To Pay Lifecycle - MarkedDocumento15 pagineProcure To Pay Lifecycle - MarkedYogesh SalviNessuna valutazione finora
- SAP-based process documentation for production maintenanceDocumento7 pagineSAP-based process documentation for production maintenanceNaveen BansalNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of SAP MM ModuleDocumento167 pagineOverview of SAP MM Modulevadamalaiathimoolam100% (2)
- Milky Mist Risk & Control Matrix - Procure To Pay: COSO Principle Process Name Control Activity No. Coso ComponentDocumento20 pagineMilky Mist Risk & Control Matrix - Procure To Pay: COSO Principle Process Name Control Activity No. Coso ComponentAswath S100% (1)
- Third Party ProcessingDocumento3 pagineThird Party ProcessingVishnu Kumar SNessuna valutazione finora
- Purchase Requisition in Sap The Process ManualDocumento31 paginePurchase Requisition in Sap The Process Manualrukometlas100% (1)
- Truebell - Fin - Ap - Config - Account PayableDocumento49 pagineTruebell - Fin - Ap - Config - Account PayableRajesh ChowdaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Audit of Accounts Payable and DisbursementDocumento10 pagineInternal Audit of Accounts Payable and DisbursementJoreseNessuna valutazione finora
- Mfg Operations MIS Reports Capacity Demand ForecastDocumento2 pagineMfg Operations MIS Reports Capacity Demand Forecastharish_inNessuna valutazione finora
- 010 Esker White Paper Accounts Payable SAP-USDocumento15 pagine010 Esker White Paper Accounts Payable SAP-USaaditya01Nessuna valutazione finora
- FI SD MM PP IntegrationDocumento2 pagineFI SD MM PP Integrationprakash_kumNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Blueprint Master Data (Procurement) : Central Public Works Department, Redevelopment Project Zone N. Delhi, IndiaDocumento18 pagineBusiness Blueprint Master Data (Procurement) : Central Public Works Department, Redevelopment Project Zone N. Delhi, IndiaAbhay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) For Vendor Creation in SAPDocumento2 pagineStandard Operating Procedure (SOP) For Vendor Creation in SAPMRL Accounts100% (1)
- SAP MM Notes - Master FileDocumento21 pagineSAP MM Notes - Master Filekurrysuchit100% (1)
- SAP RFQ and Sourcing in Purchasing ProceDocumento22 pagineSAP RFQ and Sourcing in Purchasing ProceAruni JayaweeraNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 - SAP - Order To CashDocumento25 pagine03 - SAP - Order To CashkeimmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sap Fundamental Guide Procurement ProcessDocumento39 pagineSap Fundamental Guide Procurement Processvmyreddy80% (5)
- SAP Sales Order ManagementDocumento1 paginaSAP Sales Order ManagementKarim Derouiche100% (2)
- Sales Order Management Process For Sap Terp10Documento1 paginaSales Order Management Process For Sap Terp10pbtg100% (1)
- ICAU Summary 2023Documento28 pagineICAU Summary 2023jesperjakobs01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Procurement Processes: EGS 5622 Enterprise Systems Integration Spring, 2018Documento42 pagineProcurement Processes: EGS 5622 Enterprise Systems Integration Spring, 2018nbhaskar bhaskarNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing ExecutionDocumento1 paginaManufacturing ExecutionShiji Shukla100% (1)
- IM 2 GoodsMovement GRDocumento18 pagineIM 2 GoodsMovement GRAnwar Bin Saleem MirzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sap Real Time IssuesDocumento4 pagineSap Real Time IssuessowmyanavalNessuna valutazione finora
- Sap FiDocumento10 pagineSap Firagz22Nessuna valutazione finora
- SAP MM - Practice Book - IV - 2018Documento37 pagineSAP MM - Practice Book - IV - 2018praneeth varmaNessuna valutazione finora
- SAPTERP10Documento37 pagineSAPTERP10Raks ThuruthiyilNessuna valutazione finora
- ERP Basics and Netweaver FundamentalsDocumento11 pagineERP Basics and Netweaver FundamentalsRaks ThuruthiyilNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Certification Test Number of Questions WWW - Sap Terp10.Com .Ar 1Documento1 pagina7 Certification Test Number of Questions WWW - Sap Terp10.Com .Ar 1Fernando VicenteNessuna valutazione finora
- SAP Oil Chapter2Documento20 pagineSAP Oil Chapter2Raks Thuruthiyil100% (1)
- SAP Oil Chapter 1Documento40 pagineSAP Oil Chapter 1Raks ThuruthiyilNessuna valutazione finora
- PFR CompiledDocumento91 paginePFR CompiledLyn Dela Cruz DumoNessuna valutazione finora
- Declaration - 13th Melaka International Youth DialogueDocumento6 pagineDeclaration - 13th Melaka International Youth DialogueBojan GrebenarNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Data Sheet: Zetpol 1020Documento8 pagineSafety Data Sheet: Zetpol 1020henrychtNessuna valutazione finora
- V2150 Mexico CAB MU920 MU610Documento2 pagineV2150 Mexico CAB MU920 MU610RubenL MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Anarchy (c.1)Documento33 pagineAnarchy (c.1)Hidde WeeversNessuna valutazione finora
- A&M Plastics v. OPSol - ComplaintDocumento35 pagineA&M Plastics v. OPSol - ComplaintSarah BursteinNessuna valutazione finora
- Key provisions of the Philippine Civil Code on laws and jurisprudenceDocumento7 pagineKey provisions of the Philippine Civil Code on laws and jurisprudenceIzay NunagNessuna valutazione finora
- Tenancy Agreemen2222Documento8 pagineTenancy Agreemen2222Samuel Chukwuma100% (1)
- Harvardian Colleges of San Fernando Pampanga, Inc. v. Country Bankers Insurance Corp. - IBP Zamboanga Del Norte ChapterDocumento3 pagineHarvardian Colleges of San Fernando Pampanga, Inc. v. Country Bankers Insurance Corp. - IBP Zamboanga Del Norte ChapterZainne Sarip BandingNessuna valutazione finora
- Achievements of Fatima JinnahDocumento5 pagineAchievements of Fatima JinnahmuhammadrafayNessuna valutazione finora
- Case StudyDocumento6 pagineCase StudyGreen Tree0% (1)
- Unified Soil Classification SystemDocumento4 pagineUnified Soil Classification SystemRoch battousai100% (1)
- ISPS Code Awareness TrainingDocumento57 pagineISPS Code Awareness Trainingdiegocely700615100% (1)
- Ibr 1950Documento5 pagineIbr 1950sebinNessuna valutazione finora
- MOA Establishes 50-Hectare Model Agroforestry FarmDocumento8 pagineMOA Establishes 50-Hectare Model Agroforestry FarmENRO NRRGNessuna valutazione finora
- Digest 25. Serrano de Agbayani vs. PNB, 38 SCRA 429Documento1 paginaDigest 25. Serrano de Agbayani vs. PNB, 38 SCRA 429Inez Monika Carreon PadaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cignal: Residential Service Application FormDocumento10 pagineCignal: Residential Service Application FormJUDGE MARLON JAY MONEVANessuna valutazione finora
- Bulletin No 18 August 16 2019 - PassDocumento770 pagineBulletin No 18 August 16 2019 - PassNithyashree T100% (1)
- Genetically Modified Foods: The Public Health Association of Australia Notes ThatDocumento4 pagineGenetically Modified Foods: The Public Health Association of Australia Notes ThatLe HuyNessuna valutazione finora
- Report on 5 Warehouses for LeaseDocumento6 pagineReport on 5 Warehouses for LeaseMirza MešanovićNessuna valutazione finora
- Contract of Usufruct.Documento4 pagineContract of Usufruct.MD LebriaNessuna valutazione finora
- United States Bankruptcy Court Southern District of New YorkDocumento21 pagineUnited States Bankruptcy Court Southern District of New YorkChapter 11 DocketsNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm Examination in Capital MarketsDocumento3 pagineMidterm Examination in Capital MarketsNekki Joy LangcuyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Larceny in The Heart-DraftDocumento159 pagineLarceny in The Heart-DraftChalcedon Foundation100% (1)
- BE Forms 1 and 1.1Documento4 pagineBE Forms 1 and 1.1Mel Joy NatadNessuna valutazione finora
- INTERNATIONAL ACCOUNTING FINAL TEST 2020Documento8 pagineINTERNATIONAL ACCOUNTING FINAL TEST 2020Faisel MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- U.S. vs. Macaspac, G.R. No. 3878, November 16, 1907-1Documento2 pagineU.S. vs. Macaspac, G.R. No. 3878, November 16, 1907-1Abby PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- MC 2021-086 General Guidelines On The International Organization For Standardization ISO Certification of The PNP Office Units Revised 2021Documento10 pagineMC 2021-086 General Guidelines On The International Organization For Standardization ISO Certification of The PNP Office Units Revised 2021Allysa Nicole OrdonezNessuna valutazione finora
- Bogigian v. BogigianDocumento1 paginaBogigian v. BogigiancrlstinaaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Download Understanding Human Sexuality 13th Edition Hyde Test BankDocumento13 pagineFull Download Understanding Human Sexuality 13th Edition Hyde Test Bankjosiah78vcra100% (29)