Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Basic Questions - Engineering
Caricato da
GanesanGovindarjTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Basic Questions - Engineering
Caricato da
GanesanGovindarjCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Basic Questions - Engineering.
1. Name some of the manufacturing process? a. Casting process. b. Plastic and composite process. c. Forming process. d. Machining process. e. Non Traditional Process. f. Fabrication Process. 2. Name of the Casting process. a. Sand casting. b. Shell casting. c. Gravity die casting. d. Investment mold casting. e. Ceramic Mold casting. 3. Name some of the Plastic and Composite process. a. Injection molding. b. Vacuum molding. c. Blow molding. 4. Name some of the forming process. a. Hot forging. b. Cold forging. c. Sheet metal shearing. d. Spinning. e. Powder metallurgy. 5. Name some of the machining Process.
a. Milling. b. Turning. c. Drilling. d. Grinding. e. Honing. f. Lapping. g. Planning and shaping. 6. Name some of the Non traditional Machining process. a. Electrical discharge machining.( EDM) b. Ultrasonic Machining. 7. Name some of the Fabrication and joining process. a. Tungsten inert - gas Welding (TIG) b. Metal insert gas welding. c. Gas welding. d. Brazing. e. Soldering. f. Mechanical Fastening. 8. Expand DFA? Design for Assembly. 9. Expand DFM? Design for Manufacturing. 10.Expand FMEA? Failure mode and Effects Analysis.
11.Expand QFD? Quality Function Deployment. 12. Expand DOE? Design of Experiments. 13. What are the uses of DFA? DFA techniques are capable of identifying opportunities for part count reduction and potential costs of manufacture and assembly. 14. Name some of the process selections parameters to be considered? a. Product quantity. b. Tooling Costs. c. Tolerance requirements. d. Surface finish needs. e. Bulk Treatment and Surface treatments. f. Processing times. g. Material Costs and availability. h. Material to Process capability. i. Component form and dimensions.
15. Name some of the materials which is found to be difficult for sand casting. Lead, Tin and Zinc alloys. 16. Some of the typical applications of sand Casting.
a. Engine blocks b. Machine tool bases. c. Pump housings. d. Cylinder heads. 17. Materials used for Gravity die casting. Usually non ferrous metals, for example: copper, Aluminum, Magnesium etc. 18. What are the two types of pressure die castings.? a. Cold Chamber die casting. Used for high melting temp metals. b. Hot Chamber die casting. Used for low melting temp metals (Zinc, Magnesium). 19. What are the uses of Investment casting. a. Very complex castings with unusual internal configurations Possible. b. High strength castings are produced. c. d. size. e. Complex shapes may be assembled from several simpler shapes. Practical way of producing threads in hard to machine materials, or where thread design is unusual. Minimum section ranges from 0.25 to 1.00mm depending upon
20. Explain Injection molding? Granules of Un polymerized material are heated and then forced, under pressure into the die cavity. 21. Materials used for injection molding?
Mostly thermo plastics, but thermosets, composites and elastomers are possible. 22. What are thermo plastics? Plastics which are re usable are called thermo plastics. 23. Applications for injection molding components? a. High precision, complex plastic components. b. Electrical Parts. c. Fittings. d. Containers. e. Housings. f. Tool handles.
24. What are the minimum wall thicknesses that can be molded in injection molding? Minimum 0.4 mm for thermo plastics and 1mm for thermo setting materials. 25. Expand the following? a. ABS - Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene. b. PMMA polymethylmethaacrylate. c. PC poly carbonate. d. PP poly propylene e. PVC poly vinyl chloride. f. PA poly amide. g. PETP polyethyleneteraphthalate.
26. Give some examples of Blow Molding? a. Pet bottles b. Hollow plastic parts with relatively thin walls. c. Bumpers. d. Ducting. 27. Minimum wall thickness in blow molding? 0.25mm 28. Hot forging examples? a. Connecting rods. b. Crank shafts. c. Axle shafts. d. Tool bodies. 29. Minimum wall thickness of hot forgings? 3mm 30. What is the basic Material property required for forging? Material must be ductile at forging temperatures.
31. Typical applications of cold forgings? a. Fasteners. b. Tool sockets. c. Gear blanks.
32. Name some of the sheet metal shearing? a. Cutting. b. Piercing. c. Blanking. d. Fine blanking. 33. Name some of the Sheet metal forming? a. Deep drawing. b. Bending. c. Stretch forming. d. Roll forming. 34. Strength of the powder metallurgical parts depends on? Product Strength determined by powder size, compacting pressure, sintering time and temperature. 35. What is CRCA? Cold Rolled cleared annealed. 36. What is HRCA? Hot rolled cleared annealed. 37. What are the types of bending? a. Air bending b. 3 point bending. c. Radius forming. d. Joggle. e. Offset forming.
38. What is the difference between piercing and blanking? In piercing operation, the component which is falling from the die is a waste. In blanking operation, the component which is on the die is a waste.
39. Surface roughness value achieved in turning operation? Ra = 0.32 to 25 microns. 40. How the machining time is is calculated in turning operation? Machining time = Length to be turned ________________ Feed per minute. 41. What are the types of lathes? a. Center lathe. b. Turret lathe. c. Computer Numerical control lathe. d. Vertical lathe. 42. What are the two types of milling process used in milling? a. Climb milling. (up milling) b. Down milling. (Down milling). 43. Name some of the Centre less grinding process components are used? a. Guide rods.
b. Shafts. 44. What are the parameters to be considered for a grinding wheel selection? a. Material to be ground. b. Type of bonds used for the grinding wheel. c. Structure of the grinding wheel. d. Hardness of the material to be ground. 45. What type of grinding wheels is used for grinding steel components? Aluminum oxide. 46. What type of grinding wheels is used for grinding steel components? Silicon Carbide. 47. What type of grinding wheels will be choosed for the following? a. Soft materials - hard wheels (coarser grains). b. Hard materials Soft wheels (finer grains). 48. What is the minimum amount of material removed during Lapping operation? 0.005 to 0.01mm 49. What is the material used for preparing the electrode in wire cutting Process? Copper wire. 50. What are the tolerances that can be achieved in wire cutting process?
0.005 to 0.125mm 51. What is the roughness value achieved in a wire cutting process? 0.05 to 12.5microns. 52. What is the material used for preparing the electrode in an EDM Process (Sparking)? Copper. 53. What is the roughness value achieved in a wire cutting process? 0.2 to 6.3microns. 54. Materials used for ultrasonic Welding? Brittle hard materials are preferred to Ductile. For Example: Ceramics, Plastics, Precious stones and glass. 55. Where is tig welding used? Most non ferrous material (except zinc), for example Aluminum,nickel, and magnesium. Dissimilar materials are difficult to weld. 56. Where is the tig welding used? Butt, Lap, fillet and edges. 57. Where is Mig welding used? Carbon, Low alloy steel and stainless Steels. Dissimilar materials are difficult to weld.
58. Where is Spot welding used? Low carbon steels. Not recommended for cast iron, Low melting points metals and high carbon steels. 59. What is minimum and Maximum sheet thickness required for spot welding? Minimum Sheet thickness 0.3mm ; Max - 6mm 60. Where is Gas welding used? Carbon, Low alloy steel, stainless Steels and Cast iron. Dissimilar materials are difficult to weld. 61. What is minimum and Maximum sheet thickness required for Gas welding? Minimum Sheet thickness 0.5mm (3mm for cast iron) ; Max - 30mm for carbon steel and cast iron). 62. What is Alpha iron? The body centered cubic form of pure iron, Stable below 1025Degree centigrade. 63. What is austenite? A sold solution of iron and carbon and some times other elements in which gamma iron, characterized by a face centered crystal structure, is the solvent. 64. What is cold rolled steel? Steel which has been passed through rollers at steel mills to size it accurately and smoothly.
65. What is a gray cast iron? A cast iron gives a gray fracture due to the presence of flake graphite. 66. What is high carbon steel? Steel that has more than 0.6% carbon. 67. What is low carbon steel? Steel containing less than 0.3% carbon. 68. What is Marten site? An unstable constituent that is formed by heating and quenching steel. 69. What is medium carbon steel? Steel containing between 0.3 to 0.6% carbon. 70. What is pig iron ? Iron produced from ore in the blast furnace, basic raw material from which all cast iron, wrought iron and steel are made. Usually contains about 4.5% carbon and impurities such as phosphorus , silicon and sulphur. 71. Material composition of stain less steel? Alloy steel containing iron, atleast 11% chromium , nickel molybdenum and 0.1 1% carbon. 72. Define brittleness?
The property of the materials does not deform under load, but to break suddenly, for example, cast iron and glass are brittle. Brittleness is opposite to Plasticity. 73. Define Compressive strength? The maximum stress that can be applied to a brittle material in compression without fracture. 74. Define Creep? Slow plastic deformation in steel and Most structural metals caused by prolonged stress under yield point at elevated temperature. 75. What is damping capacity? The ability to absorb vibration. More accurately defined as the amount of work dissipated into heat by a unit volume of material during a completely reverse cycle of unit stress. 76. Define Ductility? The property of a material to deform permanently or to exhibit plasticity, elongation or bending or twisting without rupture( Breaking or cracking) while under tension. 77. Define elasticity? The ability of a material to return to its original form after the load is removed. 78. Define Factor of Safety? The ratio of the damaging stress to working stress.
79. What is fatigue in metals? The tendency in a metal to fail, breaking or cracking under conditions of repeated cyclical stressing that takes place well below the ultimate tensile strength. 80. What is fatigue strength? The amount of stress that can applied to a metal without failure while it is subjected to ten million or more cycles of load reversals. In Mild steel, the fatigue strength is 50% of the tensile strength. 81. What is Hardenability? The property that determines the depth and distribution of hardness in a ferrous alloy induced by heating and quenching. 82. What is machinability? The relative ease of machining that is related to the hardness of the material to be cut. 83. What is malleability? In Metals, The property of being able to undergo mechanical deformation(flattened by rolling or hammering) without rupturing or developing a marked increase in resistance to change of shape. 84. What is modulus of Elasticity or Youngs modulus? A measure of the rigidity of metals. Ratio of stress, within propotional limit, to corresponding strain. 85. What is plasticity?
The quality of material such that it can be deformed without breaking. Clay is completely a plastic material. 86. What is permeability? In casting of metals, the term used to define the porosity of foundry sands in moulds and the ability of trapped gases to escape through the sand. 87. What is plastic deformation? Deformation that does or will remain permanent after the removal of load which caused it. 88. What is resilience? Ability of a material to store elastic energy without permanent deformation. 89. What is shear Load? A load that tends to force materials apart by application of side slip action. 90. What is stiffness? The ability of a metal or shape to resist elastic deformation. For identical shapes, the stiffness is proportional to the modulus of elasticity.
91. What is toughness?
Ability of a metal to absorb energy and deform plastically before fracturing. 92. What is annealing? A heat treatment in which metals are heated and then cooled very slowly for the purpose of decreasing hardness. Also used to remove stresses resulting from cold working and refine and make uniform the microscopic internal structures of metals. 93. What is anodizing? To Subject to metal to electrolytic action, as takes place at the anode of a cell, in order to coat it with a protective or decorative film. Used for non ferrous metals. 94. What is carburizing? A process that introduces carbon into a heated solid ferrous alloy by having it in contact with a carbonaceous material. 95. What is case hardening? Heating a steel in the presence of a solid, liquid or gs, rich in carbon. In order to enable the surface to be hardened, while retaining a tough, ductile core. 96. What is flame hardening? Process of hardening by which steel or cast iron is raised to a high temperature by a gas torch flame and immediately quenched. 97. What is induction hardening?
Heating the surface of cast iron or tool steel by means of electromagnetic currents followed by quench. 98. What is nitriding? A process of case hardening in which a special ferrous alloy is heated in an atmosphere of ammonia or is in contact with any other nitrogenous material. By this surface hardening is achieved the absorption of nitrogen with out quenching. 99. What is Normalising? Process applied to iron base alloys, such as steel, to refine the grain structure and remove the effects of previous processing for example hot rolling.
100.
What is sub zero treatment?
Method of heat treatment of steel, introducing a cooling period or periods at a temperature well below freezing point, the object being to ensure complete transformation of austenite to marten site. 101. What is tempering steel?
Heat treatment designed to relieve the stresses and brittleness set up in carbon or alloy steel tools and other parts after hardening and to restore the required degree of toughness and ductility to hardened steel.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Pro/ENGINEER Questions-IIIDocumento1 paginaPro/ENGINEER Questions-IIIGanesanGovindarjNessuna valutazione finora
- Intellectual Design and EngineeringDocumento5 pagineIntellectual Design and EngineeringGanesanGovindarjNessuna valutazione finora
- Metals Polymers Composites CeramicsDocumento23 pagineMetals Polymers Composites CeramicsGanesanGovindarjNessuna valutazione finora
- IDE Firm Work FlowDocumento1 paginaIDE Firm Work FlowGanesanGovindarjNessuna valutazione finora
- GopiDocumento2 pagineGopiGanesanGovindarjNessuna valutazione finora
- Intellectualde Industry 2003Documento20 pagineIntellectualde Industry 2003GanesanGovindarjNessuna valutazione finora
- Injection MoldingDocumento2 pagineInjection MoldingGanesanGovindarjNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced WeldingDocumento10 pagineAdvanced WeldingGanesanGovindarjNessuna valutazione finora
- Composite Tolerance GDTDocumento67 pagineComposite Tolerance GDTGanesanGovindarjNessuna valutazione finora
- Orientation Tolerance GDTDocumento30 pagineOrientation Tolerance GDTGanesanGovindarjNessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Lesson Plan: Effects of Human Activities To The AtmosphereDocumento7 pagineLesson Plan: Effects of Human Activities To The AtmosphereKATRINA MARIE AmayNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Procedure For Seismic Analysis of Liquid-Storage TanksDocumento5 pagineSimple Procedure For Seismic Analysis of Liquid-Storage TanksbcvdocuNessuna valutazione finora
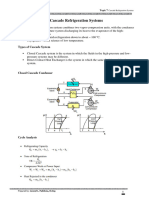
- Topic 7 Cascade Refrigeration SystemsDocumento6 pagineTopic 7 Cascade Refrigeration SystemsJanelle D. Puti-anNessuna valutazione finora
- RPT Chemistry F4 2023Documento9 pagineRPT Chemistry F4 2023Ajlaa SudfiijNessuna valutazione finora
- Liquid CrystalDocumento18 pagineLiquid CrystalNanditha ANessuna valutazione finora
- RanikhetDocumento2 pagineRanikhetAbhishikta BhattacharjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Bauchau Benchmark 16Documento20 pagineBauchau Benchmark 16Victor Hugo Garcia de CamposNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization of Labyrinth Seal For Screw Compressor Ht2007-32275Documento7 pagineOptimization of Labyrinth Seal For Screw Compressor Ht2007-32275api-3842143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Heavy-Duty Lubricant: FeaturesDocumento2 pagineHeavy-Duty Lubricant: Featuresarjun vsNessuna valutazione finora
- Combined Set12Documento159 pagineCombined Set12Nguyễn Sơn LâmNessuna valutazione finora
- Semiconductor PDFDocumento67 pagineSemiconductor PDFحسين النعيميNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Introduction To Reservoir Rock PropertiesDocumento20 pagine1 Introduction To Reservoir Rock PropertiesAram RafiqNessuna valutazione finora
- January 2014 (IAL) QP - Unit 5 Edexcel Physics A-LevelDocumento24 pagineJanuary 2014 (IAL) QP - Unit 5 Edexcel Physics A-LevelParalla ANessuna valutazione finora
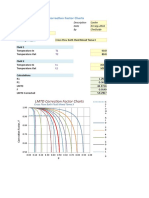
- LMTD ChartsDocumento1 paginaLMTD ChartsvinodNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation and Assessment of The Nfatigue in The Architectural Artwork On The Lighting Poles in The Anzac Drive BridgeDocumento29 pagineEvaluation and Assessment of The Nfatigue in The Architectural Artwork On The Lighting Poles in The Anzac Drive BridgeFabrizio BisernaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bubble ColumnDocumento34 pagineBubble ColumnAfroz MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy - Work - Resources of EnergyDocumento23 pagineEnergy - Work - Resources of EnergykhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 2 Thermo 1 & 2 PDFDocumento4 pagineActivity 2 Thermo 1 & 2 PDFonyxNessuna valutazione finora
- CBB Ts 161128 Babbitt TypesDocumento1 paginaCBB Ts 161128 Babbitt TypesAlejandro SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Primal Et Al. 2004Documento13 paginePrimal Et Al. 2004Francisco OppsNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper On Dymola Behavior ModelingDocumento9 paginePaper On Dymola Behavior ModelingDr Vijay BhatkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Diffusion Experiment Chemical Engineering Laboratories (ENCH 292)Documento4 pagineDiffusion Experiment Chemical Engineering Laboratories (ENCH 292)taj232Nessuna valutazione finora
- MEE NumericalsDocumento9 pagineMEE NumericalsenzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrochemistry: Electrochemistry Chemistry and Energy Relations Lecture Notes 12 Chemistry For EngineersDocumento46 pagineElectrochemistry: Electrochemistry Chemistry and Energy Relations Lecture Notes 12 Chemistry For EngineersAce Heart Rosendo AmanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Chimney SolvedDocumento2 pagineChimney SolvedJasem Abdurahman50% (4)
- Home Cmplab HTML Bbs Data Pds0085 1Documento9 pagineHome Cmplab HTML Bbs Data Pds0085 1呂昕儒Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cam Analysis ManualDocumento4 pagineCam Analysis ManualNishant B MayekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechyr1 Chapter 8::: Introduction To MechanicsDocumento22 pagineMechyr1 Chapter 8::: Introduction To MechanicsAgrata PouloseNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel Beam DesignDocumento8 pagineSteel Beam DesignKatracho2Nessuna valutazione finora