Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Ionic Bonding Vs Metallic Bonding
Caricato da
sakuraleeshaoranTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Ionic Bonding Vs Metallic Bonding
Caricato da
sakuraleeshaoranCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Ionic Bonding vs Metallic Bonding As proposed by the American chemist G.N.
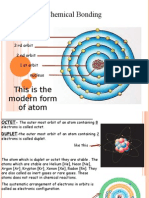
Lewis, atoms are stable when they contain eight electrons in their valence shell. Most of the atoms have less than eight electrons in their valence shells (except the noble gases in the group 18 of the periodic table); therefore, they are not stable. These atoms tend to react with each other to become stable. Thus, each atom can achieve a noble gas electronic configuration. This can be done by forming ionic bonds, covalent bonds or metallic bonds. Ionic Bonding Atoms can gain or lose electrons and form negative or positive charged particles respectively. These particles are called ions. There are electrostatic interactions between the ions. Ionic bonding is the attractive force between these oppositely charged ions. The strength of the electrostatic interactions is largely influenced by the electronegativities of the atoms in an ionic bond. Electronegativity gives a measurement of the atoms affinity for electrons. An atom with high electronegativity can attract electrons from an atom with low electronegativity to form an ionic bond. For example, sodium chloride has an ionic bond between sodium ion and chloride ion. Sodium is a metal, therefore, it has a very low electronegativity (0.9) compared to Chlorine (3.0). Because of this electronegativity difference, Chlorine can attract an electron from Sodium and form Cl- and Na+ ions. Because of this, both atoms gain the stable, noble gas electronic configuration. Cl- and Na+ are held together by attractive electrostatic forces, thus forming an ionic bond. Metallic Bonding Metals are atoms, which can form cations by removing electrons. Group 1, group 2 and transition elements are metals. Most of the time metals are in the solid phase. The type of bond forms between metal atoms is called metallic bonding. Metals release electrons in their outer shells, and these electrons are dispersed between metal cations. Therefore, they are known as a sea of delocalized electrons. The electrostatic interactions between the electrons and cations are called metallic bonding. The number of electrons released into the sea, and the size of the cation determines the strength of the metallic bond. Size of the cations is inversely proportional to the strength of the bond, and the number of electrons released is directly proportional to the metallic bond strength. The electrons can move, therefore metals have the ability to conduct electricity. Because of the metallic bonding metals have an ordered structure. High melting points and boiling points of metals are also due to this strong metallic bonding. Metals are strong and not brittle, due to the strength of metallic bonding. Whats the difference between Ionic Bonding and Metallic Bonding? - Ionic bonding takes place between positive and negative ions. Metallic bonding takes place between positive ions and electrons. - Since same type of atoms is participating in metallic bonding, there is no electron negativity difference between two atoms like in ionic bonding. - Ionic bonds are much stronger than metallic bonds. - Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity, unless they are in the molten form or dissolved in a solution. But metals can conduct electricity in the solid state.
Atoms are the basic building blocks of all types of matter. Atoms link to other atoms
through chemicals bonds resulting from the strong attractive forces that exist between the atoms. So what exactly is a chemical bond? It is a region that forms when electrons from different atoms interact with each other. The electrons that participate in chemical bonds are the valence electrons, which are the electrons found in an atom's outermost shell. When two atoms approach each other these outer electrons interact. Electrons repel each other, yet they are attracted to the protons within atoms. The interplay of forces results in some atoms forming bonds with each other and sticking together. The two main types of bonds formed between atoms are ionic bonds and covalent bonds. An ionic bond is formed when one atom accepts or donates one or more of its valence electrons to another atom. Acovalent bond is formed when atoms share valence electrons. The atoms do not always share the electrons equally, so a polar covalent bond may be the result. When electrons are shared by two metallic atoms a metallic bond may be formed. In a covalent bond, electrons are shared between two atoms. The electrons that participate in metallic bonds may be shared between any of the metal atoms in the region. If the electronegativity values of two atoms are: Answer: A molecule or compound is made when two or more atoms form a chemical bond, linking them together. The two types of bonds are ionic bonds and covalent bonds. In an ionic bond, the atoms are bound together by the attraction between oppositely-charged ions. For example, sodium and chloride form an ionic bond, to make NaCl, or table salt. In a covalent bond, the atoms are bound by shared electrons. If the electron is shared equally between the atoms forming a covalent bond, then the bond is said to be nonpolar. Usually, an electron is more attracted to one atom than to another, forming a polar covalent bond. For example, the atoms in water, H2O, are held together by polar covalent bonds. Do you understand? Test your comprehension with this quiz.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic BondingDocumento22 pagineChapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bondingapi-256257174100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding 2020Documento73 pagineChemical Bonding 2020HANNAH JULIA CAPUNGCONessuna valutazione finora
- Bond - Chemical Bond (10th-11th Grade)Documento42 pagineBond - Chemical Bond (10th-11th Grade)jv peridoNessuna valutazione finora
- Metallic Bonding: Chemical Bonding Is Different in Metals Than It Is in Ionic, Molecular and Covalent CompoundsDocumento7 pagineMetallic Bonding: Chemical Bonding Is Different in Metals Than It Is in Ionic, Molecular and Covalent CompoundsKenzy HamdyNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of Ionic and Covalent Compounds LabDocumento1 paginaProperties of Ionic and Covalent Compounds LabKevonSingh1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bohr Model and Electron ConfigurationDocumento33 pagineBohr Model and Electron ConfigurationLiviaAsriNessuna valutazione finora
- Iconic Bonding: The Evidence That Ions ExistDocumento12 pagineIconic Bonding: The Evidence That Ions ExistKingson_786Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 Shapes of Molecules and Intermolecular ForcesDocumento9 pagineChapter 6 Shapes of Molecules and Intermolecular Forcesnoreen doraniNessuna valutazione finora
- Mettalic BondDocumento32 pagineMettalic BondKim Paolo Armin Torcelino VINessuna valutazione finora
- What Is An Isotope in Chemistry?: Isotopes Are Atoms With The Same NumberDocumento56 pagineWhat Is An Isotope in Chemistry?: Isotopes Are Atoms With The Same NumberFrancez Anne GuanzonNessuna valutazione finora
- Earths InteriorDocumento50 pagineEarths InteriorJulius Memeg PanayoNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Lewis Dot Structure and Types of BondDocumento71 pagine4 Lewis Dot Structure and Types of BondEren Micaella100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding Test ReviewDocumento5 pagineChemical Bonding Test ReviewAlakh Jagtap100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding PowerpointDocumento46 pagineChemical Bonding PowerpointJohn GianneNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL chemNOV23Documento4 pagineDLL chemNOV23Rosallie Caaya-NuezNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectronConfiguration PPT 2 of 2 - 13Documento37 pagineElectronConfiguration PPT 2 of 2 - 13kassandra mae celis0% (1)
- (10E) Worksheet 1.2 - Electronic ConfigurationDocumento2 pagine(10E) Worksheet 1.2 - Electronic ConfigurationkrisnuNessuna valutazione finora
- Metallic BondingDocumento15 pagineMetallic Bondingwidya sariNessuna valutazione finora
- 0620 Properties of MetalsDocumento10 pagine0620 Properties of MetalsTadisa ChiwiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Timeline of The History of Atomic StructureDocumento16 pagineTimeline of The History of Atomic StructureIrena FengNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 1 Atomic StructureDocumento35 pagineChap 1 Atomic StructuregajenraoNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Theory PowerpointDocumento25 pagineAtomic Theory PowerpointRolly EgasNessuna valutazione finora
- Electron Configuration 123Documento34 pagineElectron Configuration 123Gelo AngelesNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 11 Liquids, Solids and Intermolecular Forces StudentDocumento113 pagineCH 11 Liquids, Solids and Intermolecular Forces StudentAneeqa YounasNessuna valutazione finora
- PAGASA Weather Bulletin August 27, 2012Documento1 paginaPAGASA Weather Bulletin August 27, 2012Angela JuliaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM 423 - Polymer Technology Module PDFDocumento3 pagineCHM 423 - Polymer Technology Module PDFGlory UsoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Bonds: Lecturer: Dr. Yayooo Course Title: Organic ChemistryDocumento50 pagineChemical Bonds: Lecturer: Dr. Yayooo Course Title: Organic Chemistryyayooo200450% (2)
- Corossion Lesson Plan EngDocumento22 pagineCorossion Lesson Plan EngadeliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Energi Kisi Dan Born HaberDocumento31 pagineEnergi Kisi Dan Born HaberNovi CherlyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Names and Formulas: Ionic CompoundsDocumento66 pagineChemical Names and Formulas: Ionic CompoundsKiao CODMNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic TrendsDocumento30 paginePeriodic TrendsMaureen GutierrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionic Bond NotesDocumento4 pagineIonic Bond Notesapi-197752333100% (1)
- 5) Percent CompositionDocumento11 pagine5) Percent CompositionRamona Esteves100% (1)
- Chemical BondingDocumento12 pagineChemical BondingdharanicrrNessuna valutazione finora
- 15.2 Born-Haber Cycle: 15.2.2 Explain How The Relative Sizes and The Charges of IonsDocumento16 pagine15.2 Born-Haber Cycle: 15.2.2 Explain How The Relative Sizes and The Charges of IonsGiselle PeachNessuna valutazione finora
- CH8 6 Volume and Moles Avogadros Laws GOB Structures 5th EdDocumento17 pagineCH8 6 Volume and Moles Avogadros Laws GOB Structures 5th EdJayr Linsangan100% (1)
- The Ozone LayerDocumento3 pagineThe Ozone LayerorionsalinasNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 4 BondingDocumento13 pagineTopic 4 Bondinglobna masadehNessuna valutazione finora
- Layers of The EarthDocumento42 pagineLayers of The EarthDrei BangateNessuna valutazione finora
- Gladie Lesson PlanDocumento6 pagineGladie Lesson PlanJustine MontemayorNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure of MatterDocumento35 pagineAtomic Structure of MatterJhon Vincent C. PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- The Particle Nature of MatterDocumento2 pagineThe Particle Nature of MatterJohn Van Dave TaturoNessuna valutazione finora
- SUBJECT: Science 9 Time Allotment: 1 Hour GRADE AND SECTION: Grade 9-Kyanite I. ObjectiveDocumento5 pagineSUBJECT: Science 9 Time Allotment: 1 Hour GRADE AND SECTION: Grade 9-Kyanite I. Objectiverose ann chavezNessuna valutazione finora
- Intermolecular Forces PPT AS AlevelsDocumento24 pagineIntermolecular Forces PPT AS AlevelsZaryab KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Origin of The UniverseDocumento37 pagine1 - Origin of The UniverseMa'am Geneizzel GotuatoNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystalline and Amorphous SolidsDocumento34 pagineCrystalline and Amorphous SolidsCx100% (1)
- Naming CompoundsDocumento27 pagineNaming CompoundsAtulya BharadwajNessuna valutazione finora
- 15 Unique Nature of CarbonDocumento17 pagine15 Unique Nature of CarbonlairinNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic Properties of The Elements: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDocumento48 paginePeriodic Properties of The Elements: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenCory Perrin100% (1)
- Lewis Dot Structures of Atoms and Ions: Valence Electrons Noble Gas StabilityDocumento6 pagineLewis Dot Structures of Atoms and Ions: Valence Electrons Noble Gas StabilityAndrew CabreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of Atom: Chemistry Chapter 2Documento8 pagineStructure of Atom: Chemistry Chapter 2Himanshi KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Nomenclature Binary Ternary and AcidsDocumento43 pagineNomenclature Binary Ternary and AcidsSofia PaganNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Co1Documento5 pagineFinal Co1michelle.patauegNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Definition in Chemistry F4Documento7 pagineList of Definition in Chemistry F4Lil' Nyeh100% (1)
- Atomic StructureDocumento28 pagineAtomic StructureJohn Vince Ramos PapNessuna valutazione finora
- Variation and Classification 2Documento33 pagineVariation and Classification 2Lina Na'ilahNessuna valutazione finora
- Yearly Lesson Plan Chemistry 2015 Form 4Documento15 pagineYearly Lesson Plan Chemistry 2015 Form 4suzi0108Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mole Concept Notes 2Documento43 pagineMole Concept Notes 2Gupta's StudioNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3. Basic Concepts of Crystal StructuresDocumento72 pagineUnit 3. Basic Concepts of Crystal StructuresClaresse NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- There Are Only Two Known Species ofDocumento7 pagineThere Are Only Two Known Species ofmuhammad aslamNessuna valutazione finora
- How Safe Are Color AdditivesDocumento3 pagineHow Safe Are Color AdditivessakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Products Claiming To Cure CancerDocumento4 pagineProducts Claiming To Cure CancersakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Stimulant Potentially Dangerous To HealthDocumento3 pagineStimulant Potentially Dangerous To HealthsakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Keep Listeria Out of Your KitchenDocumento3 pagineKeep Listeria Out of Your KitchensakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Is It Really 'FDA Approved?': Share Tweet Linkedin Email PrintDocumento6 pagineIs It Really 'FDA Approved?': Share Tweet Linkedin Email PrintsakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Infant Overdose Risk With Liquid Vitamin DDocumento2 pagineInfant Overdose Risk With Liquid Vitamin DsakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- My Dog Has CancerDocumento4 pagineMy Dog Has CancersakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is ListeriosisDocumento4 pagineWhat Is ListeriosissakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Tip-Offs To Rip-Offs: Don't Fall For Health Fraud Scams: Not Worth The RiskDocumento3 pagine6 Tip-Offs To Rip-Offs: Don't Fall For Health Fraud Scams: Not Worth The RisksakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaccines Protect Children From Harmful Infectious DiseasesDocumento3 pagineVaccines Protect Children From Harmful Infectious DiseasessakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- How People Become InfectedDocumento4 pagineHow People Become InfectedsakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Use Caution With Ayurvedic ProductsDocumento3 pagineUse Caution With Ayurvedic ProductssakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Help Stop The Spread of Coronavirus and Protect Your FamilyDocumento4 pagineHelp Stop The Spread of Coronavirus and Protect Your FamilysakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- How Do You Know If You Have ListeriosisDocumento1 paginaHow Do You Know If You Have ListeriosissakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- What You Need To KnowDocumento3 pagineWhat You Need To KnowsakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- What You Need To KnowDocumento3 pagineWhat You Need To KnowsakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Tips To Stay Safe in The SunDocumento4 pagineTips To Stay Safe in The Sunsakuraleeshaoran100% (1)
- Animal Cloning and Food SafetyDocumento3 pagineAnimal Cloning and Food SafetysakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- How Do You Know If You Have ListeriosisDocumento1 paginaHow Do You Know If You Have ListeriosissakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- FDA 101: Dietary Supplements: Share Tweet Linkedin Email PrintDocumento4 pagineFDA 101: Dietary Supplements: Share Tweet Linkedin Email PrintsakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Adding Folic Acid To Corn Masa Flour May Prevent Birth DefectsDocumento3 pagineAdding Folic Acid To Corn Masa Flour May Prevent Birth DefectssakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is ListeriosisDocumento4 pagineWhat Is ListeriosissakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- FDA Gives Latinas Tools To Fight DiabetesDocumento3 pagineFDA Gives Latinas Tools To Fight DiabetessakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Caution Bodybuilding ProductsDocumento3 pagineCaution Bodybuilding ProductssakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Beware of Products Promising Miracle Weight LossDocumento3 pagineBeware of Products Promising Miracle Weight LosssakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Chocolate LoversDocumento9 pagineChocolate LoverssakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- FDA 101 Health Fraud AwarenessDocumento5 pagineFDA 101 Health Fraud AwarenesssakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Avoiding Drug InteractionsDocumento4 pagineAvoiding Drug InteractionssakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Caution: Bodybuilding Products Can Be Risky: Share Tweet Linkedin Email PrintDocumento3 pagineCaution: Bodybuilding Products Can Be Risky: Share Tweet Linkedin Email PrintsakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Be Aware of Potentially Dangerous Products and Therapies That Claim To Treat AutismDocumento3 pagineBe Aware of Potentially Dangerous Products and Therapies That Claim To Treat AutismsakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- ACI Structural Journal - Mar-Apr 2014Documento258 pagineACI Structural Journal - Mar-Apr 2014Manuel Gutarra100% (2)
- CHEMISTRY#11Documento15 pagineCHEMISTRY#11SUNYNessuna valutazione finora
- Preview of 13.10-13.15: Kinetics of Particles: Energy and Momentum MethodsDocumento21 paginePreview of 13.10-13.15: Kinetics of Particles: Energy and Momentum MethodsAnonymous ANessuna valutazione finora
- Performance of Deck Ovens: Standard Test Method ForDocumento13 paginePerformance of Deck Ovens: Standard Test Method ForFrancisco GuerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Phys. 3341 Homework Solution Set #5: 1 Reif 3.3Documento4 paginePhys. 3341 Homework Solution Set #5: 1 Reif 3.3Daiver JuarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetism SC L1-3Documento24 pagineMagnetism SC L1-3Abhishek tiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Assessment Grade 10Documento7 paginePhysics Assessment Grade 10Steven ShemdoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Derivation of The Wave Equation F QeDocumento3 pagineDerivation of The Wave Equation F QegillNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermite Reaction Demo Lecture Slides - 0Documento17 pagineThermite Reaction Demo Lecture Slides - 0anilkumarmuntha868_5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Refrigeration System Operating With Solar Energy: - Design of Vapor-AbsorptionDocumento27 pagineRefrigeration System Operating With Solar Energy: - Design of Vapor-AbsorptionKedir MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- NVH Optimization Analysis of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor by Rotor SlottingDocumento16 pagineNVH Optimization Analysis of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor by Rotor Slottingreddy venkata krishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Meteorology Quiz 2 (Checked)Documento15 pagineMeteorology Quiz 2 (Checked)mahmoud deyaaNessuna valutazione finora
- SCIENCE 9 4th QUARTER SUMMATIVE TEST NO.2Documento3 pagineSCIENCE 9 4th QUARTER SUMMATIVE TEST NO.2Hellary Smith100% (1)
- Methods and Practice in Cantilever Retaining Wall DesignDocumento14 pagineMethods and Practice in Cantilever Retaining Wall DesignArdalan100% (2)
- Weld 3Documento1 paginaWeld 3canettijNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.1 - Resistance QP PDFDocumento16 pagine10.1 - Resistance QP PDFMuhammad Saif AmirNessuna valutazione finora
- Equations of Planes in The Form Ax + by + CZ DDocumento4 pagineEquations of Planes in The Form Ax + by + CZ DNagesh ThotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tribology-2021 Lecture - 6 - NEWDocumento28 pagineTribology-2021 Lecture - 6 - NEWAhmed Ayman AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical PropertiesDocumento11 pagineOptical PropertiesPallaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Concepts Rev 3 - 32 GuptaDocumento106 pagineConcepts Rev 3 - 32 GuptaSorabh Gupta100% (1)
- Strength of Materials - IDocumento2 pagineStrength of Materials - IJosephNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Loss From A Buried Oil PipeDocumento20 pagineHeat Loss From A Buried Oil PipeJuan Pablo ApazaNessuna valutazione finora
- RACE 2011 ProceedingDocumento680 pagineRACE 2011 Proceedingrace2590Nessuna valutazione finora
- Closed-Form PO-PTD Solution For Fast Electromagnetic Scattering PredictionDocumento4 pagineClosed-Form PO-PTD Solution For Fast Electromagnetic Scattering PredictionWesley GeorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Scilab Textbook Companion For Basic Electrical Engineering by A. Mittle and V. N. MittleDocumento212 pagineScilab Textbook Companion For Basic Electrical Engineering by A. Mittle and V. N. MittleRudra PratapNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Metrology Basics: Understand Basics of Metrology, Standards and Calculate Least Count of Measuring InstrumentsDocumento34 pagineChapter 1 Metrology Basics: Understand Basics of Metrology, Standards and Calculate Least Count of Measuring InstrumentsAswaja313Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rank Booster Test Series: 12 and 13 Students (PHYSICS (1) ) Target Iit - Jee - 2016Documento9 pagineRank Booster Test Series: 12 and 13 Students (PHYSICS (1) ) Target Iit - Jee - 2016ashu mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Motor SimulinkDocumento8 pagineDC Motor SimulinkMELVINNessuna valutazione finora
- Cfe Assignment Module5Documento3 pagineCfe Assignment Module5Nandan AnnamrajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (4)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDa EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (137)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDa EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Sodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyDa EverandSodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (21)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeDa EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (90)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideDa EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolDa EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisDa EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeDa EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsDa EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNessuna valutazione finora
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionDa EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Ingredients: A Visual Exploration of 75 Additives & 25 Food ProductsDa EverandIngredients: A Visual Exploration of 75 Additives & 25 Food ProductsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsDa EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityDa EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodDa EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (20)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsDa EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsDa EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (146)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsDa EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableDa EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (22)