Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
CHN
Caricato da
Michael BoadoDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CHN
Caricato da
Michael BoadoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CHN
2 Sectors of Dual Health Care Delivery System 1. Public Lgu, distric,regional and medical center (L.D.R.M) FOURMULA 1 FOR HEALTH - should be free sectors is the framework for implementation of HSRA > National Agencies -dept of health (lead sectors) is the roadmap for the health sectors reform > Local agencies(govt) regional, 2005-2010(medium term) provincial,district, rural and barangay(health single package designed to implement critical unit/system), puericultural clinics(lowest unit) (R.P. health intervention backed up by effective D.R and B, P) management infrastructur and financing 2. Private ngo, st lukes and medical centers (N.S.M) arrangements - in profit and non profit health providers - health clinics and center (H.C) GOAL OF F1 FOR HEALTH ( B.E.M) B etter health outcome ROLES AND FUNCTIONS OF DOH (E.0 102) E quitable health care financing L eadership in health M ore responsive delivered system E nabler and Capacity builder A dministrator of specific services National level - D.O.H R.A 7160 devolution of health services LEADERSHIP IN HEALTH ( L.A) local gov't code serves as an advocate in the adoption of health policies,plans and program to address national PREVENTION THAN CURE- CHN and sectoral concerns. 1. Primary Prevention health promotion and protection/maintenance ENABLER AND CAPACITY BUILDER ( I.HAS) 2. Secondary early detection/diagnosis innovate new strategies in health 3. Tertiary rehabilitation ensure the highest achievable standards of quality health care, health promotion and health PRIMARY HEALTH CARE protector at cost declared sept 6-12 -1978 by WHO in Alma Ata Russia ADMINISTRATOR OF SPECIFIC SERVICES (A.M.A) universally accessible (no race, no color, no age A dminister direct service for emergent health limit) concers client (ind., family, population groups, community) M anage selected national health facilities and GOAL: hospitals health for all by 2000 by LOI 949 by Pres A dminister health emergency responses Marcos Health in the hands of the services people by 2020 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH VISION OF D.O.H (V.L) - DO.H is the leader, a staunch advocate model in promoting HEALTH FOR ALL in the philippines MISSION OF D.O.H (G.E.S.Q) G - uarantee E - quitable S - ustainable Q - uality health care CONCEPT OF PHC partnership and empowerment (core strategy) in the effect of essential health services that are: ( C.A.S.A) C ommunity based A - ccessible S ustainable A- cceptable
S - ector R - eform A - genda
GOAL OF D.O.H (H.S.R.A) H - ealth
LOI 949 Health in the Hands of the People by 2020 (ELEMENTS) E ducation
L ocally endemic disease E xpanded Program Immunization M aternal and child health E ssential drugs N utrition T reatments of communicable disease and noncommunicable disease S afe water and sanitation
4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
Clinical Evaluation Laboratory and other Examination Referral System Prescription/Dispensing Health Education
4 COURNERSTONES/PILLARS IN THE PRIMARY HEALTH CARE (A.I.U.S) 1. 2. 3. 4. A ctive community participation I ntra and inter sectoral linkages U se of appropriate technology S - upport mecahnism made available
STEPS IN APPLYING BP CUFF (B.A.AK.P) 1. Bare clients arm 2. Apply cuff around the upper arm 2-3 cm. Abpve the brachial artery 3. Apply snugly with no creases 4. Keep the manometer at eye level 5. Palpate the brachial pulse correctly just below or slightly medial to the antecubital area
HOME VISITS family nurse-contact allows the health workers to assess the home and family situatioms in order to provide the necessary nsg care and health related activities BASIC PRIMARY HEALTH CARE TEAM STEPS: 1. Physician captain greet the patient and introduce self 2. PHN state the purpose of visit 3. Midwives observe the patient and determine the health needs 2 LEVELS OF PHC WORKERS put the bag in a convenient place then 1. Village/Brgy Health Workers (non process to perform the bag technique educated) trained community health perform nsg care needed and give health workers, volunteer,birth attendant or healer teaching 2. Intermediate Level Health Worker record all important data, observation and (educated) -M.D, PHN, Rural Sanitary Inspectors and Midwives care rendered make appointment for a return visit LEVELS OF HEALTH CARE AND REFERRAL SYSTEM *THE BAG TECHNIQUE (tool) 1. Primary Level Of Care developed to * PUBLIC HEALTH BAG (indispensable equipment) cities and municiapalities 2. Secondary Level Of Care given by ELEMENTS OF PRIMARY HEALTH CARE physicians, emergency district hospital 3. Tertiary Level Of Care rendered by Education specialist belief can behavior LEVELS OF HEALTH CARE SYSTEM health education is the process of assisting individuals acting *EPI ----> Nurses not M.D separately or collectively to make informed desicisions about matters affecting personal health and that of others NURSING PROCEDURES Clinic Visit (nurse-patient contact) -pt visits the clinic for consultation on matters that ailed them 1. Registration/Admission -ellicit and record the pt chief complaint and clinical history -perform physical exam 2. Waiting Time - first come, first served policy 3. Triaging -manage program-based cases D.O.H PROGRAM (I. E.C) -refer all non prog cases to the physicianI nformation provide ist aid treatment for emergency cases -provision of knowledge
-data interpreted= 38.5 -->fever E ducation -knowledge -skilss(put it in action) -attitiude(deals with nurse ans patientinterpersonal) C ommunications -facts -5 components ((1.sender or encoder,m2.receiver or decoder, 3.message, 4. medium/channel, 5.feedback) Data---->Information---->Knowledge---->Wisdom Locally Endemic Disease -study of occurerence and distribution of disease -Epidemologic (AGENT, HOST, ENVIRONMENTAHE) -Backbone HOST
DIFFERENT KINDS OF VITAL STATISTICS Morbidity Ill Mortality Death Crude/General Rates total living population Specific Rate 1. CBR- Crude Birth Rate -increase in population B(birth)/P(population) X 100 ex: 1000/15000 X 1000 CBR = 66.7 = 67 2. CDR Crude Death Rate D (death)/P X 1000 3. IMR - Infant Mortality Rate - index for general/med condition of com D(death)/B(birth)X 1000 4. MMR Maternal Mortality Rate - index of obstretical care - prenatal and postnatal care D/B X 1000 5. FDR Fetal Death Rate (abortion) - pregnancy wastage < 20 weeks D/B X 1000
AGENT ENVIRONMENT Agent-microorganism that causes the disease(What) ex: virus, bacteria,fungi,rickettsia,plasmodia etc. Host -organism that harbors the disease (Who) Environment cause the disease.Transmission (Where) DISTRIBUTION AND OCCURRENCE (S.E.E.P) S poradic -intermittent, few, isolated, unrelated cases, given locally ex: rabies E ndemic continous , a period of time, usual number ex: filiarisis, schistosomiasis E pidemic unuasually large, short period of time ex:birds flu P andemic globally epidemic, same disease in different countries ex: SARS H1N1,AIDS PUBLIC HEALTH SURVEILLANCE (disease watching) an on-going systematic collection, analysis, interpretation and dissemination of health data VITAL STATISTICS studies of imp that happened in a person's life such as birth, death and marriage indices of health and illness status of a community LINE GRAPH USED IN STATS
NEONATAL DEATH RATE measures of dying ist month of the life index of the effects of prenatal care and obstretrical management or newborn INCIDENCE IR- new cases PR- old cases EPI EXPANDED PROGRAM OF IMMUNIZATION objective: -decrease morbidity and decrease mortality among infants and young children -7 preventable disease BCG -Tb and meningitis DPT Anti Hepa B Anti Measles ELEMENTS OF EPI (T.I.C.A.S) T arget setting -child below 8 years old I nformation education and communication C old chain logistic management A ssessment and evaluation of overall performance S urveillance, studies and research
PRINCIPLES (B.M.I) B ased on epidimiological situation
M ass approach I ntegrated in the health care delivery system Legal Basis /Policies based on PD 996 -compulsary basic immunization for infants and children below 8 years old to have EPI 1. Safe and immunologically effective to administer all EPI vaccine in the same day at different site of the body 2. Measles vaccines as soon as child turns to 9 months( fully immunized at 9 months(85 % protection), 12 months (95 % protection) preferred to be protected at 9 months 3. Vaccination should not be restarted Hepa B1 at birth Hepa B1 and Hepa B2 = 6 weeks Hepa B2 and Hepa B3 = 8 weeks 4. Moderate fever, malnutrition, mild respiratory, cough and diarrhea and vomiting are not contraindicated to vaccination 5. Safe and effective with mild S/E bec of vaccination ( give paracetamol) NOTE: ABSOLUTE CONTRAINDICATION Do not give BCG to a child who is immnocompromised because it causes malignancy Do not give DPT2 or DPT3 to a child who had convulsion or shock REMEMBER EPI before 1st Birthday FULLY IMMUNIZED CHILD REQUIREMENT (BM) BCG Measles 1 dose with diluents because of powder BCG at birth Measles 9 months 85 % protection (DOH) Diptheria, OPV, Hepa B DPT and OPV 6 weeks, 3 dosage and 4 weeks interval DPT severe pertusis OPV -polio free philippines (BO-BO) All EPI Vaccines is given 0.5 ml except B cg 0.05 ml O pv 2 gtts (BOM) All EPI Vaccines is given IM except B ID O by mouth M SQ
M easeles freezed dried -25 degree celcius O PV -15 degree celcius Least Sensitive + 2 to 8 degree celcius BCG D weakened toxins P atay killed bacteria T weakened toxins TT1 -anytime early pregnancy TT2 4 weeks 80 % 3 years TT3 6 months 95 % 5 years TT4 1 year 99 % 10 years TT5 1 year 99 % Lifetime Maternal Mortality Rate IMPROVE MATERNAL HEALTH GOALS: Strategic trust for 2005-2010 -launch and implement the basic obstretic care -normal prenatal check up visit = atleast 4 visits -Postpartum 1st visit = ist week post partum (3-5 days) 2nd visit = 6 weeks post partum POST PARTUM Normal(Clinic/Hospital) 1st 1st week (3-5 days) 2nd 6 weeks 3rd none Home Delivery 1st within 24 hours 2nd 1 week 3rd 2-4 weeks ESSENTIAL HEALTH SERVICES LEAKAGES 1. Antenatal Registration ist -as early in pregnancy as possible before four months 2. Tetanus Toxoid - 2 doses of TT one month before delivery Vitamin Vitamin A Dose Schedule 10,000 I.U 2x a week start on the 4th month of preg Remarks Do not give Vit A before the 4th month of preg. It might cause congenital prob in the baby
Iron MOst Sensitive -15 to -25 degree celcius Remember M O st
60 mg/400 ug daily
Treatment of Disease and Other Conditions 3 C'S =clean hands, clean surface, clean cord
Child Health -giving birth ? R.A 9288 new born screening law METABOLIC DISORDERS CH- Congenital Hypothyroidism CAH Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia GAL Galactosemia PKU Phynel Ketunuria G6PD Glucose 6 Phosphate Dehydrogenase National Plan of Action for 2005-2010 for infants and young child feeding * initiate feeding within 1 hour after birth B est For Babies R educe allergy E conomical A vailable STFEE DING Laws in MCN E051 milk code, milk substitute R.A.7600 rooming in and breastfeeding act of 1992 R.A 8976 food fortification law, staple food such as rice, floor and bread COPAR -COMMUNITY ORGANIZING PARTICIPATORY ACTION RESEARCH COPAR -self reliant -imarginalized -underserved A. PHC -community dev -5 years B. RESEARCH -NARS -RN HEALS= new prog
PARTICIPATORY ACTION RESEARCH a strategy used in implementing the primary health care delivery in the depressed and underserved communities to become self reliant COPAR PROCESS 1. Pre- entry 2. Entry 3. Community Diagnosis 4. Community Organization 5. Community Action Phase 6. Sustenance and Strengthening PRE-ENTRY PHASE -an initial phase of the org process where the community/organizer looks for communities to serve/help 1. consultation/dialogues(call barangay officer via telephonecourtesy) 2. Development of criteria for site selection 3. Site selection (check for accessibility) 4. Preliminary social investigation (PSI) 5. Networking with LGU'S, NGO etc( ask help from prominent people) SELECTION OF PSI - site must be socio-economically depressed and underserved community with majority of the population belonging to the poor sector - health services in the site are inaccessible - the area must have relative peace and order -acceptance of the program by the community to ensure their participation in the activities planned ENTRY PHASE -sometimes called the social preparation phase signal the actual entry of the community worker/organizer into com. 1. Integration with the community 2. Continuing social investigation 3. Coordination with other community organization 4. Core group formation 5. Self- awareness and leadership training action plan (salt) COMMUNITY STUDY/DIAGNOSIS PHASE -is a comprehensive documentation of the data about the community gathered through social investigation 1. Selection of the research team(potential leader) 2. Training on data collection methods 3. Data gathering 4. Data Validation 5. Presentation of the community study and recommendations
COMMUNITY ORGANIZING a process whereby community members develop the capability to assess their health needs and problem, plan and implement action to solve these prob, put up and sustain organizational structure which will support and monitor COMMUNITY ORGANIZATION AND CAPABILITY implementation of health initiatives BUILDING PHASE
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Community meetings Election of officers Team Building Organization of working committes Training of the community leaders
COMMUNITY ACTION PHASE 1. Organization and training of community health workers COLOR CODE CLASSIFICATION 2. Setting up of linkages/referral system Pink- severe classification -refer to hospital 3. initial identification and implementation of resource Yellow moderate classification to be done in mobilization schemes rural health unit (RHU) Green -mild- home treatment SUSTENANCE AND STRENGTHENING 1. Formulation and ratification of constitution and by PINK CATEGORY (A.C.I.T.R) laws pre-referral treatment first 2. Identification and development of secondary leaders A ssess 3. Setting p of financing scheme for community halth C lassify program I dentify 4. Formalizing of linkages and referral system T - reat 5. Development and implementation of viable R - efer management system IMCI -INTEGRATED MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD ILLNESS Major Childhood Illness (ADM3) 1. Acute Respiratory Infection 2. Diarheal Disease 3. Measles 4. Malaria 5. Malnutrition IMCI was initiated jointly in 1992 by DOH, WHO and UNICEF IMCI MAJOR OBJECTIVES to decrease morbidity and mortality in developing countries IMCI PROCESS (A.C.I.T.C.G) A - ssessment C lassification I identify the treatment T reat the child C- ounsel the mother G- ive follow up ASSESSMENT Check general danger signs (CLUV) C -onvulsion L ethargy U unable to drink V omiting For All Sick Children Age 1 week to 5 Years Old Who Are Bought To The Clinic Ask The Child's Age --->if from 1 week up to 2 months-->use the chart and assess, classify and treat the sick Ask The Child's Age--> if the chilkd is from 2 months up to 5 years-->assess and classify, treat child and counsel mother Acute Respiratory System( ARI ) Nose-->Pharynx-->Larynx-->Trachea-->Bronchus->Bronchioles-->Alveoli PNEUMONIA -infectionof the lungs, caused by bacteria. -stiffening of the lungs-->Fast breathing-->stiffer (pneumonia)( fail treatment) -chest indrawing--> severe pneumonia -fast breathing and chest indrawing(2 sign of pneumonia) ASSESSMENT -ask for how long? COUNT THE RR -if the child has fast breathing -2 months up to 12 months -50 breaths or more -12 months- 5 years 40 breaths or more LOOK FOR CHEST INDRAWING LOOK AND LISTEN FOR STRIDOR -harsh sound heard during inspiration
D iarrhea C ough Assess (F.I.M) F eeding problem I mmunization sched M- alnutrition Check- other problems
Assess main symptoms (F.E.D.C) F ever E ar problem
CLASSIFICATION Pink Severe Pneumonia
S/SX GDS,stridor, chest indrawing
Yellow-Pneumonia Green- No Pneumonia
Fast Breathing Cough or cold
< 14 days persistent diarrhea CLASSIFICATION (Dehydration) Pink severe dehydration Yellow some dehydration Green no dehydration SEVERE DEHYDRATION Signs : any 2 of the following abnormally sleepy or difficult to awaken sunken eyes not able to drink or drink slowly skin pinch goes back very slowly MANAGEMENT Plan C: 2 sings in pink row IV theraphy (best LR NSS) 2 pink + 1 pink not plan c management (refer urgently) with sips of Oral Rehydrstion Solution (ORS) on the way give antibiotic for cholera if there's an outbreak to a child 2 years old? SOME DEHYDRATION Signs: any 2 of the following Restless, irritable sunken eyes drinkng eagerly, thirsty skin pinch goes back slowly 2 yellow (Plan B ORS) 2 yellow + 1 pink (refer urgently to the nearest hospital) MANAGEMENT Give ORS, zinc supplement and food for some dehydrstion (Plan B) 2 yellow + 1 pink Refer urgently to hospital Advised mother to continue breastfeeding Advised mother when to return immediately Follow up in 5 days if not improving NO DEHYDRATION Give ORS, zinc supplementations and foor to treat the diarrhea at home (Plan A) Advised mother when to return immediately Follow up in 5 days if not improving Continue breastfeeding
Treatment (Severe Pneumonia) Give the first dose of an appropriate antibiotic( IM antibiotic fore severe pneumonia-benzyl penicillin and gentamycin is the drug of choice) Give vitamin A (capsule for)to boost the immune system( 6 months onwards) If chest indrawing and wheezing (salbutamol 3x with interval of 15 minutes) Treat the child to prevent low blood sugar Give inhaled salbutamol for wheezing Treatment (Pneumonia) Give appropriate antibiotic for 3 days( amoxixillin first if not effective give contrioxizole) If wheezing give inhaled bronchodilators for 5 days Soothe the throat and relieve the cough with safe remedy ( gatas ng ina, kalamansi or ginger) If cough is more tha 3 weeks-- refer for asssessment for TB or asthma Advised the mother when to refer Follow uo for 2 days Treatment (No Pneumonia) If wheezing( even if it disappeared after rapid acting bronchodilators) give an inhaled bronchodilators for 5 days > 30 days-->refer assessment( chronic cough signs for asthma, TB) DIARRHEA -3 or more loose bowel in 24 hours -more water than formed elements ASSESSMENT Table Table 2 Dehydration Persistent Diarrhea Table 3 Dysentery
Assessment Parameters Gen Conditions -lethargic/unconcious -restless/irritable Sunken eyes Offered water -drinking eager/does not drink at all Pinch test >2 secs- very slowly < 2 secs slowly/immediately
14 Day Rule > 14 days severe persistent diarrhea
PLAN B: Treat Dehydrations with ORS? PLAN A: Give extra fluid Give zinc supplement ( 20 mg tab) Contunue feeding Advised when to return DYSYNTERIA (with blood < 14 days) -classify a child with diarrhea -give ciprofloxacin for 3 days -follow up in 2 days FEVER = 37 degree celcius(malaria, measle dengue) MALARIA -caused by parasites in the blood called plasmodia Ask about ( as measure) fever in all sick children Ask:- does the child have a fever - check to see if the child has a history of fever Decide the malaria risk Ask:- does the child live in malaria area - has the child visited/travelled or stated overnight in a malaria area in the past 4 weeks - If yes, obtain a blood smear to check the pathognomonic agent in the blood Ask: - for how long? If more than 7 days, has fever been present everyday for more than 7 days can mean the child has a more severe disease such as typhoid fever CLASSIFICATION Pink: Any DGS (CLUV), stiff neck very severe febrile disease Management: ist dose of quinine should be under medical supervision or if the hospital is not accessible within 4 hours give first dose of an appropriate antibiotic treat the child of an appropriate antibiotic give one dose of paracetamol in health center for high fever 38.5 degree celcius or above----> refer urgently to the hospital send a blood smear with the patient Yellow: + blood smear If blod smear is not done patient should have no: runny nose, no measles, no other cause of fever Management: Treat the child with an oral antimalarial Give one dose of paracetamol in health center for high fever )38.5 degree celcius or above) Advised the mother when to return immediately
Follow up in 2 days if fever persists If fever is present everyday for more than 7 days, refer for assessment Green: fever- malaria unlikely Measles Other cause of fever Management Give one dose of paracetamol in clinic for high fever ( 38.5 degree celcius or above) Advised mother when to return immediately Follow up in 2 days if fever persists If fever is present everyday for more than 7 days refer for assessment MEASLES Ask: has the child had a measles within the 3 months? -measles damage the child's immune system -give vitamin A(All Color) Signs of Suggesting Measles -generalized rash or any of the ff: cough, runny nose, or red eyes Complications Of Measles diarrhea, pneumonia, stridor, mouth ulcer Look: for mouth ulcer, are they deep or extensive mouth ulcer for puss draining from the eye (sign for conjunctivitis) for clouding of the cornea ( if untreated due to Vit A deficiency-treat to prevent blindness) DENGUE Pink: severe dengue hemorrhagic fever bleeding from the nose and mouth bleeding from the stools or vomitus black stools or vomitus skin petechia cold clammy extremities capillary refill for more than 3 sec persistent vomiting positive tourniquet test Management if persistent vomiting or persistent pain or skin petchiae or positive tourniquet test re
the only positive signs, give ORS (Plan B) If any other sign?? Ear Infection Pink : Mastoiditis Yellow: acute ear infection (oral antibiotic, paracetamol, dry) pus is seen from the ear folow up in 5 days discharge for fewer than 14 days chronic ear infection (drying wicking)
2. 3.
Validate improvements in nursing Make a health care efficient as well as cost effective ( the more the research/er the cheaper would be the service in hospital)
RESEARCH Research ( testing for a theory, testing theory, solving a prob) to solve the prob (systematic) ADOPIE nsg process is synonymous to scientific method there should be a problem to be assessed validate and invalidate a theory a systematic of inquiry that uses disciplined methods to answer questions or solve problems Nsg Research can be utilized by: nsg service/practice nsg education community Importance of Research In Nursing - the reason why we do research is to: Adopt Evidece-Based Practice ( EBP) -the use of the best clinical evidence in making patient care descision (not a book based) -try to modify the practice -gumawa o humanap ng diskarte -actions are clinically appropriate and cost effective
MAJOR STEPS/PROCESS IN NURSING RESEARCH
C-onceptual D- esign and Planning A- nalytical D-issemination
CONCEPTUAL PHASE -Always start with an idea -read in the newspaper etc to get idea -formulation of problem -review or related literature -define framework -formulate hypothesis *RESEARCH PROBLEM IS THE HEART OF THE RESEARCH Characteristics Of A Research Problem(GReFINS)
G General Applicability should be helpful or applicable to all Re researchable -collectable and abundant data to be researched F- feasible/Immesurable KANGAROO CARE - 1990's only a minority of NICU'S -time,money/cost, participants, instruments, offered kangaroo care options experience, good ethics of research I - important MAIN PURPOSE OF NSG RESEARCH -dapat may patutunguhan 1. General -something that will give value to nursing profession a. Basic N- novelty - out of curiosity -original to avoid plagiarism -gusto lang malaman -dapat hindi nangopya -walang pinatunguhan -something that is new S- significant b. Applied/Technological -quality of life Sources Of Research Problem C.L.I.E.N.T -focus on finding solutions to the problem C ONCEPT 2. Specific -ideas that are group together -to identify -pinagusapan yung idea at naging concept -describe( acute or chronic) L ITERATURE -explore ( go beyond what is known already) -can get the research problem in the book -explain I SSUES -predict or control variables of relevance to -issues in the school nursing poblem -awayan ng stud-stud, student prob -issues should be relevant and concerns in the nursing world NEEDS OR NURSING RESEARCH E SSAYS 1. Build body of nursing knowledge -from journal can be also source of a research ( to improve or negate wrong ideas)
N- URSING PROBS T- HEORIES -utilized NIGHTINGALE THEORY
Statement Of The Problem -focus of the study and all questions should be categorically answer -it consists of main problem and sub-problems Literature -refers to all the writings -comes from the books, newspaper, pamphlets
Step 4: Formulating Hypothesis -a statement of predicted relationship bet 2 or more variables
Variable ( makakaapekto sa research) -characteristic which has 2 or more traits/characteristics -ex :demographic data: Age: 0-15 below 10 y.o Related 6-10 11- 21 y.o -main purpose is to know what is known and 11- 15 22- 31 y.o unknown 16- 20 -implies that the literature reviewed have some income, revenue,degree of connections,relations to the problems or concern malnutrition, sex: gender m/f under investigation Variable Independent Variable Reason For Having Review Of Related Literature -this is the cause -it provides the researcher knowledge and Dependent Variable background on the subject under study -this is the effect -it enables the researcher to avoid duplicating Intervening Variable what has been studies already -can be found in dependent and independent variable -if a study on the same topic has been conducted Exogenous Variable before, it provides the researcher information about -outside variable and not included in the study but the aspects of the problem which have not been can afect the study investigated or explore before. ex: climate Example: Sources Of Related Literature Relationship of self motivation and passing the NLE Libraries among the Nov 2009 board exam Internet Independent: Pubmed - all papers that have ben -self motivation reviewed already are published in this site Dependent -uses search engine(yahoo, google etc) -passing the NLE Graduate school file of theses Personal file of books and other printed matter FORMS OF HYPOTHESIS Newspaper, magazines, pamphlets etc Null Hypothesis -the independent variable does not affect the dependent variable. It is a statement of denial of Step 3: Framework relationship, difference or an effort -helps organize the study Alternate Hypothesis -provide a background or foundation for a study -the independent variable affects the dependent variable FRAMEWORK 1. Conceptual -idea -IPO -helps explain the relationship between concepts -comes from the idea that have been refined or from other works 2. Theoretical -theory/theories USES OF HYPOTHESIS provide direction to the research indicate the major independent and variable being considered suggest the types of data that must be collected suggest the type of analyses that must be made Hypothesis --->statistically tested -t-test, ANOVA,
Chi-Square, F- Test, Z- Test, Pearson
-representation of different areas 5. Quasi Experimental handpick your subject no randomization
TYPES OF HYPOTHESIS Simple -predicts the relationship one independent and one dependent -performance in the college of nursing is the related to the success in the nurses licensure examination -1 IV and 1 DV Complex -predicts the relationship of 2 or more IV and 2 or more DV Directional -species the direction of the relationship between variable being studied ex: people who smoke are more prone to lung cancer than those who do not smoke -may patutunguhan,does not give a complete thought Non- Directional -predicts only that there is a relationship between variable being studied but does not specify what it is. Ex: there is a difference in the level of anxiety of pre-op patients who received teachings than those who do not received such teachings -does not give a complete thought/sentence PHASE 2: DESIGN AND PLANNING PHASE Step 1: selecting a research design Step 2: identification of the research Step 3: selection of the research sample RESEARCH DESIGN I. Quantitative Research -numbers, data collated rather than the respondent -associated with quantity -more concerned on data collected than the respondents A. Experimental 1. True M anipulation E - xperimental/comtrol group R - andomization 2 . Pre- Test Post- Test Experimental group vs control group 3. Post Test -no pre test 4. Solomon Four -segregate by number (1,2,3,4) -all number 1 and 2 = experimental group -all number 3 and 4 = control group
B. Non- Experimental -does not manipulate the Independent Variable I. Correlational-relationship -strength of relation ex: relationship of gender and salary II. Comparative -examine the different bet in tact groups on some dependent variable of interest ex: a comparative study between male and female in their lifestyle III. Methodological -concerned with the development, testing and evaluation of research instruments and methods ex: wong and baker pain scale used in pedia IV. Survey -data gather from relatively large number of cases at a particular time ex: conduct a study who is favorite commedienne of brgy pinyahan, 50 % dolphy, 30 % michael v, 20 % vic sotto II. Qualitative Research C.H.E.P.G -associated with the naturalistic inquiry explores human feelings and experience -focus on insights and understanding of individual perceptions on the phenomenon under study C ase Study H- istorical E ethnographic P henomelogical G rounded theory CASE STUDY - in depth or extensive of an individual and group ex: Anton researches on AIDS.Its transmission, causative agent and factors, sign and symptoms, treatment and medical HISTORICAL -PAST ex: Ace is to perform a study hpw the nurses performed aseptic technique during world war 2 ETHNOGRAPHIC - culture, feelings PHENOMELOGICAL
- feeling lived experiences GROUNDED THEORY -collection, validation for making theory
METHODOLOGY VALIDITY -extent to which a measurement does what it is supposed to measure -valid data--> not only reliable but also sound and true -researcher must select a design that will yield a true and accurate information SAMPLING -the process of selecting a portion of the population to represent the entire population
3. 4.
5. 6. 7. 8.
-weakest type -accidental, incidental,chunk -selection of the most readily available people or objects for the study -No way to determine representativeness -Save Time 2. Snowball -networking, referral Quota Sampling Purposive -a.k.a judegementa/expert choice of sampling -handpicked by expert -very specific Cross-cultural -sample from different tribes Longitudinal -development for a period (long time Cross Section -one period only ( 6 months) Quota Sampling -10, 50, 100
sample representation Determine the sample size Slovin's Formula n = N/(1 + Ne 2) where n = sample N = population c = desired margin of error ( allowable error) SAMPLING STRATEGIES I. PROBABILITY 1. Simple Random(strongest type) a. Table Of Random Numbers b. Lottery, Systematic, Stratified, Cluster Sampling (Fishbowl) -have equal chance of being selected as respondents 2. Systematic -nth, 5th, 15th, 20th is being selected 3. Stratified -per layer, still randomized II. NON-PROBABILITY -does not have equal chance 1. Convenience or accidental 2. Snowball or networking 3. Judgemental or Purposive 4. Cross- Cultural 5. Longitudinal 6. Cross Section 7. Quota Sampling 1. Convenience
PHASE 3: EMPIRICAL PHASE Step 1: Collecting the data Step 2: Prepare data for analysis RELIABILITY Mean add and then divide = average 75+80+65+70+90=380/5 =76 % Median middle -most value arrange from highest to lowest 22,32,33,27,30,30,28 25,27,28,30,30,32,33 (N +1)/2 = 7 +1/2=4( odd number) Find the median 124,120,118,122,125,121,122,120 arranged from highest to lowest 118,120,120,121,122,122,124,125 x = nth item/2 + (n/2 +1)nth item 2 - n/2 = 8/2 = 4th item (n/2 +1)=8/2 +1 = 5th item x = 4th item + 5th item / 2 x = 121 + 122 2 = 121.5 or 1. n/2 =8/2 = 4 = 4th item=121 2. n/2 + 1 = 8/2 + 1 = 5= 5th item=122 =121 + 122 = 243 2 2
= 121.5
Mode ?
PHASE 4 : ANALYTICAL Step 1 : Analytical Step 2 : Interpreting the result Types Of Graphical Method Bar Graph Line Graph or Frequency Polygon Circle Graph or Pie Graph Pictograph or Pictogram Table FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION -is the arrangement of the data showing frequency of occurrence of the variable Frequency number of observations or occurences of variable Sturges Rule
MATERNAL AND CHILD NURSING Male External Reproductive System Penis -tubular stucture composed of shaft and glans -soft and placcid (2.5-4 inches) -hard and erect ( 5.5 7 inches) -impregnante women -filipino 4-5 inches common -nitrate oxide cause dilation of blood vessels which increase blood flow Glans -has external urinary meatus -have sebaceous glands produce a waxy secretion called smegma -right age for circumsition is 10-12 years old due to easy to remove foreskin and less bleeding Scrotum -rugated(kulubot), skin covered muscular pouch -helps regulate the temp of sperm in the testes -main function is to lower body temp to 1-2 o F in order for the sperm to survive -left is lower to avoid friction -hot: dangling -cold: contracted Testes -witness -to ovid glands -composed of interstitial cells ( leydigs) which produce testosterone and seminiferous tubule produce sperm Male Internal Structures Epididymis -a tightly coiled tube -approx 20 feet long -12-20 days for the sperm to travel -64 days to reach maturity -responsible for conducting sperm from the testis to the vas deferens Ductus Deferens( Vas Deferens) -site for vasectomy -reservoir fro sperm bet ejeculations -ampula storage for matured spem then ready for ejaculation Ejaculatory Ducts -ejaculatory reflex or jerky movement -2 ejaculatory ducts pass through the prostrate and j oin in the seminal vessicles with the urethra Prostrate Gland -chestnut-size glans lies below the bladder -produce alkaline and gives calcium and other nutrients
Bulbourethral Glands -cowpers glands -produce small droplets of fluid during sexual activity which do not mix with sperm -counteract the acidity of urethra Urethra -part of the male reproductive organ Seminal Plasma -provides ergizing nutrients for the sperm such as from of sugar fructose, mucus,salts, water, base buffer and coagulators to aid the sperm Semen -thick, creamy wgite fluid -2- 6 ml/ ejaculation -fertile man will dispel 20 to 160 million sperm per ejaculation - only 1 sperm is needed to dertilized the egg
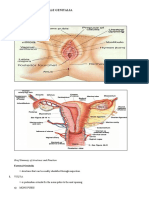
Female Reprodcutive System Mons Veneris/Mons Pubis -protect the junction of the pubic bone from trauma Labia Majora -2 rounded folds of fatty tissue -analogous to scrotum Labia Minora -napupunit during sexual intercourse and delivery -thin, pale pink in color -it turns dark red or dark pink when stimulated Clitoris -increased in size when stimulated -also produce smegma when stimulated by londo -for argasm Paraurethral/Skenes Glands -near urethral orifice -susceptible for gonorrheal infection -homologous to male prostrate Vulvovaginal/Bartholin's Glands -near vaginal orifice -lubrication during intercourse(clear, viscid mucus) Hymen -tough but elastic semicicle of tissue that covers the opening to the vagina in childhood - 2 3 time of sexual activity before the hymen worned out -broken also through strenous physical activities or masturbation Perinium -muscular area that's easily stretched during childbirth to allow enlargement of the vagine and the passage of the fetal head -most common site for laceration -forchette-episiotomy -stretch and very thin during delivery Ovary -produce mature and discharge ova or egg cells and produce hormones Hormone: FSH: Estrogen, LH: Progesterone
Graafian Follicle matured ovum menopause = menarch(first menstration) + 37 -contains 200,000- 400,000 follicles Fallopina Tube -transport matured ovum from the ovary to the uterus -3 days for an egg to travel but unfertilized egg lives only 24 hours -interstitial portion the -isthmus(sterlization, ligation) -ampulala(fetilization -meet the sperm and ovum) -( fertilization takes place) Uterus -house and nurture a pregnancy -bahay bata implantation -responsible in expelling fetus by contraction -thickening of endometrium during menstration - 3 divisions -body or corpus contain the growing fetus * fundus -portion can be palpated to measure the uterine growth and the force of uterine contraction during labor Isthmus short segment bet the body and cervix - for C.S Cervix lowest portion of the uterus - Layers of the uterus Perimetrium part of visceral peritnoneum Myometrium bulk of uterus, layers of muscles contract under influence of oxytocin during labor Endometrium deeper, permanent layer Vagina -passageway for sperm nd menstrual flow -receptacle for penis during intercourse -inferior portion of birth canal
Hypothalamus stimulates APG to begin
production of gonadotropic hormones
Pituitary Gland under the influence of
Luteneizing Hormone Releasing Hormones (LHRH), the anterior pituitary gland produces 2 hormones that acts on the ovaries to further influence menstruation - FSH hormone that is active early in a cycle and is responsible for mauration of ovum - LH - hormone that becomes most active at midpoint of the cycle and is responsible for ovulation or release of the matured egg cell from the ovary, and growth of uterine lining Ovaries one ovum is discharge in one or the other ovaries and is discharge from its month Uterus - stimulation from the hormones produced by the ovaries causes specific monthly efffects on the uterus Estrogen - hormone for women -proliferate or make the endometriam lining thicken -stimulate the growth,development, and maintenance of female reproductive structures, secondary sex characteristics and the breast -lower blood cholesterol -spinnbarkeit and ferning (main function of the breast is for lactation and indication women is o vulating. =smaller breast =more milk Progesterone -maintains the thickens of endometrium lining -responsible for mood swing -produced by corpus luteum( structure left b graafian follicle) and works with estrogen to prepare the endometrium for implantation and mammary glands for lactation -hormone of the mother, responsible for the mood swings of the mother -mammary gland for development -Decrease G.I motility and increase permeability of kidney to lactose and dextrose OVARIAN CYCLE The Follicular Phase: Days 1 through 13 -in response to FSH released from PG, ultimately 1 egg matures Ovaluation: Day 14 -in response to surge LH, the egg is released from the ovary -the egg travels through the fallopian tube toward the uterus Luteal Phase: Days 14 through 28 -the remains of the follicle becomes the corpus luteum which releases progesteron
MENSTUATION -monthly period as early as teen years and end around at the age of 50 years -about once a month the uterus grows a new, thickened lining( endometrium) that can hold a fertilized egg - when there is no fertilized egg to start a pregnancy, the uterus sheds its lining - menstrual cycle is measure from the first day of menstrual bleeding(day 1) up to the day 1 of the next menstuation -normal blood loss every menstual period is 30-80ml -5- 10 %= 28 day cycle -3 days = common menstruation - 1 pad = 30 ml of blood loss Organs Involved In Menstruation
UTERINE CYCLE Proliferative Phase: Days 5- 14 -hormone responsible is estrogen -uterine lining increases rapidly in thickness, and the uterine glands and proliferate and grow
69 chromosomes; sperm carries the gender; y = male, x =female; deep positioning to get a baby boy
SIGNS OF PREGNANCY PRESUMPTIVE SIGNS (MACFUQ) Secretory Phase: Days 14 through 28 -subjective data -when the egg is not fertilized, corpus luteum - M orning Sickness gradually disappears, estrogen and progesterone - A menorhhea levels drop, and the thickened uterine lining is - C hanges in Breast shed .This is your menses(your period) -tenderness, tingling sensation(ovulation) Time of Ovulation - F atigue -tme of ovulation for women with regular cycles is to - U rinary Frequency subtract 16 from the number of days in the cycle then - 1st and 3rd trimester (compressed bladder) add 4.This will calculate the span of days in which Q uickening (18th - 20th week) ovulation is most likely to occur -fetal movement felt by the mother Signs And Symptoms Of Ovulation Mittleschmerz abdominal tenderness on PROBABLE SIGNS (CHUPBOGS) left/right iliac regions, brought by about changes observed by the examiner peritoneal irritation due to blood coming out -objectives from graafian follicle - C hadwicks sign Spinbarkeit vaginal secretions is clear and - bluish discoloration due to increase transparent blood flow Change in vaginal mucus H egars sign Goodle's sign changes in cervix -softening of the lower utering (Uterus) Mood changes - U terine enlargment (12 weeks) Breast Tenderness - fundus can be palpated above the Increase levels of Progesterone symphisis pubis Changes in basal body temp .3. 6, temp - P ositive pregnancy test before the ovum is released - presence of HCG - B - allotement ANTEPARTAL PERIOD - rebound movement through I.E Process of Fertilization - O utlining of the fetal body - through leopolds maneuver Ferilization (Conception, Fecundation) - G oodle sign -is the union of an ovum and a spermatozoon - softening of the cervix -usually occurs in the outer third fallopian tube - S ouffle contraction and braxton hicks (28 Apposition the blastocyst brushes against the rich weeks painless contraction uterine endometrium occurs approx 8 10 days after - other, echo which can be heard by the fertilization examiner -naghahanap ng lugar kung san iimplant si zygote POSITIVE SIGNS Adhesion it attaches to the surface of the -definitive signs of pregnancy endometrium HEARTBEAT -nakakita na ng place -12 weeks by droppler Invasion the blastocyst settles down into its soft -18-20 weeks by auscultation folds Movement felt by the examiner usually 20 Once the zygote is implanted it becomes an weeks EMBRYO Terms BIOPHYSICAL ADAPTATION OF PREGNANCY Ovum from ovulation to fertilization REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Zygote from fertilization to implantation 1. Uterus Embryo from implantation to 5- 8 weeks > Hegars Sign softening of the lower uterine Fetus 5 8 weeks until term segments Conceptus developing embryo or fetus and placental > Goodell's Sign -softening of the cervix sructure throughout the pregnancy 2. Vagina Chromosomes 23 (sperm) + 23(ovum) = 46 + 23=
> Chadwicks Sign increase vascularity causes causes change of color from light pink to deep purple Breast - tender and tingle in the early weeks of pregnancy -increased in size, larger nipple, more pigmented INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Striae Gravidarum -reddish slightly depressed streaks in the abdominal wall, breast and thighs (stretch mark), from dark to silvery white Linea Nigra -line of dark pigment extending from the umbillicus down the midline to the symphisis pubis (tyan ng nanay) Chloasma - mask of pregnancy are brownish patches of pigment in the face METABOLIC SYSTEM Weight Gain -ave wt gain 24-28 lbs -fetus : 3400 grams -placenta 450 grams -amniotic fluid 900 -uterus 1100 grams -breast tissue 1400grams -blood volume 1800 grams -matenal stores 1800 3600 grams Iron requirments increased to 20-40 mg daily and during on the last half of pregnancy, iron is transferred to the fetus and stroed to the liver ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Adrenal Glands -increased level helps to reduce the possibility of the woman's body to rejecting the foreign protein of the fetus -help regulate glucose metabolism -the body does not reject the foreign protein of the fetus Parathyroid Glands -necessary for the metabolism of calcium which is important in for fetal growth Pancreas -increase production of insulin -the maternal glucose level is usually at a higher than normal level CIRCULATORY SYSTEM increase HR by 10 bpm. Cardiac increase on the 2nd trimester Heart murmurs are audible because of the altered heart position Easy Fatugability/shortness of breath and epistaxis Edema on the lower extemities bec of poor 3.
circulation. Management: raised leg above hip level, compress blood vessle in lower extremities -varicosities on lower extremities can occur. Management: wear elastic stockings to promote varicose flows thus preventing stasis on the lower extremities GASTROINTESTINAL 1. Morning Sickness -naglilihi -nausea and vomiting during pregnancy due to increased HCG, increased production of gastric acid or it can be due to emotional factor -1 3 months (normal) Management: -small frequent meals -eat dry toast crackers 30 minutes before arising in the morning - Hyperemesis Gravidarum excessive nausea and vomiting which persists beyond 3 months may result in dehydration, starvation and alkalosis Management: D10 NSS, 3000 cc in 24 hours and CBR 2. Constipation and Flatulence -are due to displacement of the stomach and intestines thus allowing peristalsis and gastric emptying time; may also to increase progesterone which inhibits gastric motility Management: - increased fluid and roughage in the diet - establish ellimination time - avoid enema and suppository (may lead to labor) - mineral oil should not be taken bec it interferes with absorption of fat soluble vitamins Hemorrhoids: are due to pressure of enlarge uterus on the intestine Management: Cold compress with hazel salt, sitz bath Heartburn: due to increased progesterone which decreased gastric motility and thereby causing reverse peristaltic waves which lead to regurgitation of acid in stomach into stomach into the esophagus,causing irritation Management: - avoid fried and fatty foods - small and frequent meal and taken slowly
- take antacid(milk of magnesia) - never take sodium bicarbonate because they promote fluid retention RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Marked congestion or stuffiness of the nasopharynx, a reponse to increase estrogen level Breathing is rapid than normal Management: side lying, lateral expansion of the chest URINARY SYSTEM Urinary frequency =seen during 1st and 3rd trimester. 1St tri due to blood supply in the kidney, 3rd tri due to pressure of enlarge uterus on the bladder MUSCULOSKELETAL Because of the woman's attempt to change on gravity, she makes ambulation easier by standing more straight and taller LORDOSIS/Pride Of Pregnancy = Liyad -Management: advise to use low healed shoes after the first trimester Leg Cramps - are caused by increased pressure of gravid on lower extremities and low calcium in the body -Management: - frequent rest period with legs elevated, increase calcium intake. Cheese and milk are good for calcium PSYCHOLOGICAL RESPONSE First Trimester -mother is ambivalent (uncertain/unsure) -some degree of rejection/disbelief -implication: when giving health teachings, emphasize the body changes in pregnancy Second Trimester -mother accepts the pregnancy -fantasized appearance of the baby Third Trimester -the best time to talk about infant feeding feeding method -fear of death is prominent that's why its its better to let the mother listen to fetal heart sound E051: milk code 7600: rooming in PRENATAL VISIT
Definition of Terms Gestation from lmp to weeks Abortion termination of pregnancy Term- 38-42 weeks Stillbirth Viable ability of the baby to survive 2024 weeks Gravida no of pregnancy irreagardless of abortion, term Parity- number of delivery that reach the age of viability Ex: GTPAL -Len Victor is pregnant for the fourth time. At home she has a child who was born at term. Her second pregnancy ended at 10 weeks gestation. She then gave birth to twins at 35 weeks.One twin died soon after birth. At her antepartal assessment, the nurse records her obstetric history as: Answer: G4T1P1A1L2 Prenatal Visits are scheduled once a month up to 7 months( 28 weeks) Every 2 weeks at the 8 months Once a week from the 9th month until delivery OBSTETRIC HISTORY Nagele's Rule > if lmp bet jan- march + 9 +7 + 0 > if lm bet april dec -3 + 7 + 1 Mc Donalds Rule > fundic height(cm)x2/7 =AOG in lunar months 22x2/7 = 6 months >fundic height(cm)x8/7=AOG in weeks 22x8/7 = 25 weeks Bartholomew's Rule > 36 weeks = xiphoid process > 20 weeks = navel >12 weeks = symphisis pubis Johnson's Rule -is used to calculate fetal weight in grams -fundic height(cm) N x K =fetal weight - K = 155(constant) - N = 12 if engaged ( do leopold to find out) - N = 11 if not engaged LEOPOLDS MANEUVER Cardinal Rule in Leopolds Maneuver Instruct the woman to empty her bladder first Place in dorsal recumbent position, supine with knees flexed to relax abdominal muscles.Place a small pillow under the head for comfort Drape properly to maintain privacy Explain procedure to gain patient'c cooperation Warm hands first by rubbing them together before placing them over the woman's abdomen Use the palm for palpaltion not fingers
First Manuever = Fundal grip = presenting part of the fundus = hard(breech) Second Maneuver = umbilical grip = locate fetal back to assess fetal heart rate Third Manuever = pawlicks grip = check for engagement = 0 station Fourth Manuever = pelvic grip = facing the feet of the mother = determine the fetal attitude = relationship of one body part to another
LABOR AND DELIVERY Stages Of Labor FIRST STAGE Begins witht the onset of true labor contraction and ends with full or complete cervical dilatation Provide privacy Provide reaasurance Establish Rapport Nsg Management: Hospital Admission : Inform patient of labor progress : Check for show/rupture BOW; if rupture BOW, perform: Nitrazine Paper Test: bluegreen to deep blue: alkaline -amniotic fluid, Fern Test- (+) ferning test amniotic fluid Observe after BOW COLOR: Yellow -stained blood incompatibility Green-Stained meconium staining Physical Examination Maternal V/S = Temp; ruptured membranes : every 2 hours, intact membranes : every 4 hours, bp, pr, rr as needed in latent phase, every 30 minutes fo active phase Fetal Assessment: Fetal Electronic Monitoring: Normal: 120 - 160 bpm > Fetal distress: fetal bradycardia : <100 bpm, fetal tachycardia: > 100 bpm Health Teachings 1. Ambulation 2. Breathing Technique - panting during contraction (reduce tension and prevent hyperventilation 3. Diet : NPO - digestion is delayed during labor - full stomach interferes with proper bearing
down - aspiration 4. Enema -to increase space for passage -to decrease possibility of fecal contamination during 2nd stage of labor -to provide confort to the patient -not a routine procedure and contraindicated in the ff:vaginal bleeding, crowning, rupture membranes, abdominal fetal presentation, premature labor 5. Ellimination -Encourage to void every 2-3 hours by offering a bedpan Perineal shaving and preparation Pain relief: administer analgesic as ordered (demerol -meperidine HCL) -give only when cervix is already 5-8 cms dilated (25-100 mg/ml) -antidote : Narcan or Nalline(narcotic antagonist) 8. Anestesia: Regional: low spinal - usually xylocaine given at the 5th lumbar but monitor BP( can cause hypotension - post-spinal headache due to leakage of CSF (keep patient flat on bed for 13 hours - patient kept on NPO with IVF of glucose -watch out for hypotension 9. Danger Signs Mother: BP > 140/90 Falling BP: with accompanying signs of cold, clammy skin, pallor,restlessness, apprehension, increase RR -hypovelemic shock SECOND STAGE Stage Of Expulsion Period from full dilattation and cervical effacement to birth of Infant Uncomplicated birth, it last about 1 hour ED FIRE ERE E - Engagement D Descent F Flexion IR Internal Rotation ER External Rotation E - Expulsion NSG MANAGEMENT Prepare the lace of birth Positioning of birth Promoting effective second stage of pushing Perineal Cleaning Episiotomy (lidocaine is given) Birth (EDFIRERE),
Ritgens Manuever to support the perineum and prevent laceration Place the newborn below the level of the mother's vulva for a few second Wrap the baby on the mother's abdomen Show the baby to the mother, inform the sex and time of delivery Suctioning Cutting And Clamping Of The Cord -delay cutting until pulsation ceases and maintaining the infant at a uterine level as much as 100 ml of blood to pass from placenta into the fetus -late clumping of the cord can cause overinfusion with placental blood -clamp is placed 8- 10 inches from the infants umbilicus THIRD STAGE Placental Stage Begins with the birth of the infant and ends with the delivery of the placenta Signs Of Placental Separation: -Lengtening Of The Cord -Sudden Gush Of Blood -Change In the Size Of The Uterus -Firm Contraction Of The Uterus -Appearance Of The Placenta At The Vaginal Opening Types Of Placenta Schultz -shiny -80 % of placenta separation -placenta separate first at its center and lastly to its edge, it tends to fold on itself like an umbrella Duncan -dirty -separate first at its edge, it slides along the uterine surface -raw, red and irregular NURSING MANAGEMENT Brandth Andrews Maneuver Do not hurry the delivery of the placenta ( up to 20 minutes) Timing of placental delivery Care of placental delivery -Inspection of the placenta completeness of cotyledos 18- 22 cotyledons -Determine the degree of uterine contraction by palpating the uterus -Adminster Oxytocin agents
Inspection Of The perineum for lacerations -1st degree laceration vaginal mucuos membrane and skin of perineum -2nd degree laceration -plus the levator of muscle -3rd degree laceration -plus the external sphincter of the rectum -4th degree laceration -plus mucous membrane of the rectum -3rd and 4th degree laceration is only repaired by the physicians Care During And After Perineal Repair -administration of xylocaine/lidocaine -episioraphy -vaginal packing is sometimes inserted to prevent bleeding but must be removed after 24 hours Estimation Of Blood Loss
FOURTH STAGE Recovery Stage Fist 2 hours of Post Partum most critical stage Monitor Signs of Hemorrage and other complications Nsg Responsibilities Assess: Fundus checked every 15 minutes for 1 hour and every 30 minutes for 4 hours Lochia should be moderate in amount Lochia -Lochia Rubra - 3-4 days post partum. Red, made up of blood, endometrial decidua, fetal lanugo, vernix -Lochia Serosa after 3rd day, placental site exudes serous material and lochia becomes dark and thinner -Lochia Alba - 3rd week and thereafter , lochia decreases and gray white color * oxytocin- causes contraction let down reflex
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Sample Questions 2Documento6 pagineSample Questions 2Filipino Nurses CentralNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer NCP 5Documento9 pagineAnswer NCP 5Mar Ble100% (1)
- Community Health Nursing Examination Part I Answer KeyDocumento7 pagineCommunity Health Nursing Examination Part I Answer KeyMhaye HasschaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bullets Funda2Documento89 pagineBullets Funda2Jek NevadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Practice 1 QuestionDocumento12 pagineNursing Practice 1 QuestiongranfrancoNessuna valutazione finora
- C. Palpate Neck For Air Bubble Popping SensationDocumento4 pagineC. Palpate Neck For Air Bubble Popping SensationNom NomNessuna valutazione finora
- DOH PowerpointDocumento232 pagineDOH PowerpointEmmanuel ApuliNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Surgical Nurse Practice TestDocumento4 pagineMedical Surgical Nurse Practice Testazazelshine0% (1)
- Med Surg Exam 3 ReviewDocumento2 pagineMed Surg Exam 3 ReviewLynn KimNessuna valutazione finora
- NLEDocumento18 pagineNLEKeij AranetaNessuna valutazione finora
- MS Practice Questions With RationaleDocumento13 pagineMS Practice Questions With RationaleRey Gil Flee GabonadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Draw The Shear and Moment Diagrams For The Beam Shown in Fig. 6-4aDocumento15 pagineDraw The Shear and Moment Diagrams For The Beam Shown in Fig. 6-4aAmyHuiNessuna valutazione finora
- FluidDocumento3 pagineFluidcruzjuan58Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nars and RN HealsDocumento2 pagineNars and RN HealsSanibat EcnalNessuna valutazione finora
- Drills-1 Np4 AquinoDocumento11 pagineDrills-1 Np4 AquinoSolah SalvatoreNessuna valutazione finora
- TB and LeprosyDocumento39 pagineTB and LeprosyCharise Ligores100% (1)
- Philippines Sentrong Sigla MovementDocumento13 paginePhilippines Sentrong Sigla Movementronell villamilNessuna valutazione finora
- M S N 3Documento23 pagineM S N 3Muhammad YusufNessuna valutazione finora
- HeheezjghDocumento7 pagineHeheezjghDemiar Madlansacay QuintoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 01: Professional Nursing Practice Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10th EditionDocumento5 pagineChapter 01: Professional Nursing Practice Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10th EditionKenyia CheatumNessuna valutazione finora
- NP1Documento12 pagineNP1Bruce EstilloteNessuna valutazione finora
- QuestionsDocumento6 pagineQuestionsLorvic Andrew Juanson UmaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 19Documento16 pagineChapter 19missy23pap100% (1)
- Med SurgDocumento23 pagineMed SurgReymart AcalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fabs and Onco Post TestDocumento20 pagineFabs and Onco Post TestJe KirsteneNessuna valutazione finora
- Scope of This Nursing Test I Is Parallel To The NP1 NLE CoverageDocumento15 pagineScope of This Nursing Test I Is Parallel To The NP1 NLE CoverageHanah Kanashiro AlcoverNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Practice IVDocumento11 pagineNursing Practice IVapi-3718174100% (1)
- Nursing ExamsDocumento5 pagineNursing ExamsPedialy AvilesNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Diagnostic ExamDocumento28 pagineFinal Diagnostic ExamAlfred Benjamin CajitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health Nursing Practice Questions With AnswersDocumento7 pagineCommunity Health Nursing Practice Questions With AnswersDaimin TevesNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Nursing Letter AnswersDocumento1 paginaFundamentals of Nursing Letter AnswersEpaphras Joel MilitarNessuna valutazione finora
- EXCELLEROLYMPICSDocumento53 pagineEXCELLEROLYMPICSJoya Jimenea GenzolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health NursingDocumento40 pagineCommunity Health NursingBONGNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Mist TentDocumento3 paginePediatric Mist Tentleo90_wyattNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Surgical Nursing IDocumento11 pagineMedical Surgical Nursing IAJ DalawampuNessuna valutazione finora
- Documentation in Psychiatric Nursing PracticeDocumento25 pagineDocumentation in Psychiatric Nursing PracticeRichelle TalaguitNessuna valutazione finora
- Iloilo Psyche 2Documento7 pagineIloilo Psyche 2stoto_arenNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Leadership and Management: Ethicomoral/ Legal Aspects of Health Care and Nursing PracticeDocumento271 pagineNursing Leadership and Management: Ethicomoral/ Legal Aspects of Health Care and Nursing PracticeRonnie De Vera II100% (1)
- Nursing Practice IDocumento3 pagineNursing Practice IななみけんとNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Nursing - DX Exam 50 Items Without RatioDocumento3 pagineFundamentals of Nursing - DX Exam 50 Items Without RatioDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RM100% (1)
- Tutorials On GenitourinaryDocumento15 pagineTutorials On Genitourinaryabangjojo123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pasar Rbe CutieDocumento11 paginePasar Rbe CutieElla RetizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Disorder PREBOARDS 4BSNDocumento8 pagineCardiac Disorder PREBOARDS 4BSNJayson Mherl GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- GYNECOLOGICALNURSINGDocumento4 pagineGYNECOLOGICALNURSINGSheana TmplNessuna valutazione finora
- Impac & Project EntreprenurseDocumento3 pagineImpac & Project EntreprenurseCharles Anthony Lopez EstebanNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health Nursing Sample TestDocumento45 pagineCommunity Health Nursing Sample TestPaulo Tiangson MejiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nle 2019Documento4 pagineNle 2019Jackie AbarraNessuna valutazione finora
- ABGDocumento22 pagineABGRaja Najwa Raja IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Maternal and PediaDocumento11 pagineTest Maternal and PediaDefensor Pison GringgoNessuna valutazione finora
- Haad QuestionDocumento20 pagineHaad QuestionNimraj PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Which Activities Are The Circulating NurseDocumento12 pagineWhich Activities Are The Circulating NurseDENNIS N. MUÑOZNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 27 - Management of Patients With Dysrhythmias and ConductionDocumento8 pagineChapter 27 - Management of Patients With Dysrhythmias and ConductionMichael Boado100% (1)
- NP1 NotesDocumento59 pagineNP1 NotesBrianMarBeltranNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALDocumento13 paginePractice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALFilipino Nurses CentralNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundation of PROFESSIONAL Nursing Practice: Practice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALDocumento19 pagineFoundation of PROFESSIONAL Nursing Practice: Practice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALFilipino Nurses CentralNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health Nursing - PresentationDocumento91 pagineCommunity Health Nursing - PresentationLaca SaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHN HandoutsDocumento7 pagineCHN HandoutsTrisha ArizalaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHN NotesDocumento5 pagineCHN NotesVinceNessuna valutazione finora
- Investigation, Primary Health Care (PHC)Documento77 pagineInvestigation, Primary Health Care (PHC)api-3710926Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dianne Gay Leaño 23 Years Old FSUU Batch 2017 November 2017 PNLE (85.20)Documento213 pagineDianne Gay Leaño 23 Years Old FSUU Batch 2017 November 2017 PNLE (85.20)Matt AndreyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 29 - Management of Patients With Structural, Infectious, andDocumento6 pagineChapter 29 - Management of Patients With Structural, Infectious, andMichael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultrasound To Pregnant WomanDocumento2 pagineUltrasound To Pregnant WomanMichael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 30 - Management of Patients With Complications From Heart DiseaseDocumento7 pagineChapter 30 - Management of Patients With Complications From Heart DiseaseMichael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdominal HerniaDocumento2 pagineAbdominal HerniaMichael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Adeno Carcinoma-Lanuza Karla BernadineDocumento7 pagineAdeno Carcinoma-Lanuza Karla BernadineMichael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 21 - Assessment of Respiratory FunctionDocumento6 pagineChapter 21 - Assessment of Respiratory FunctionMichael Boado100% (3)
- What Causes A FractureDocumento2 pagineWhat Causes A FractureMichael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 37 - Management of Patients With Gastric and Duodenal DisordersDocumento5 pagineChapter 37 - Management of Patients With Gastric and Duodenal DisordersMichael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 30 - Management of Patients With Complications From Heart DiseaseDocumento7 pagineChapter 30 - Management of Patients With Complications From Heart DiseaseMichael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular 2011 108Documento36 pagineCardiovascular 2011 108Michael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 39 - Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersDocumento6 pagineChapter 39 - Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersMichael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 38 - Management of Patients With Intestinal and Rectal DisordersDocumento7 pagineChapter 38 - Management of Patients With Intestinal and Rectal DisordersMichael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- LMpart 2Documento21 pagineLMpart 2Michael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- LMpart 2Documento21 pagineLMpart 2Michael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 37 - Management of Patients With Gastric and Duodenal DisordersDocumento5 pagineChapter 37 - Management of Patients With Gastric and Duodenal DisordersMichael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 34 - Assessment of Digestive and Gastrointestinal FunctionDocumento3 pagineChapter 34 - Assessment of Digestive and Gastrointestinal FunctionMichael Boado100% (1)
- Chapter 35 - Management of Patients With Oral and Esophageal DisordersDocumento6 pagineChapter 35 - Management of Patients With Oral and Esophageal DisordersMichael Boado100% (1)
- Chapter 32 - Assessment and Management of Patients With HypertensionDocumento6 pagineChapter 32 - Assessment and Management of Patients With HypertensionMichael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 33 - Assessment and Management of Patients With HematologicDocumento8 pagineChapter 33 - Assessment and Management of Patients With HematologicMichael Boado100% (1)
- Chapter 27 - Management of Patients With Dysrhythmias and ConductionDocumento8 pagineChapter 27 - Management of Patients With Dysrhythmias and ConductionMichael Boado100% (1)
- Chapter 31 - Assessment and Management of Patients With Vascular DisordersDocumento7 pagineChapter 31 - Assessment and Management of Patients With Vascular DisordersMichael Boado100% (1)
- Chapter 33 - Assessment and Management of Patients With HematologicDocumento8 pagineChapter 33 - Assessment and Management of Patients With HematologicMichael Boado100% (1)
- Chapter 28 - Management of Patients With Coronary Vascular DisordersDocumento10 pagineChapter 28 - Management of Patients With Coronary Vascular DisordersMichael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Treatment 07 (1) .PPT 0Documento27 pagineMycobacterium Tuberculosis Treatment 07 (1) .PPT 0Michael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes Mellitus RPTDocumento17 pagineDiabetes Mellitus RPTMichael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 24 - Management of Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocumento8 pagineChapter 24 - Management of Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseMichael Boado100% (3)
- Cardiovascular: Common Lab Tests For Cardiovascular DisordersDocumento49 pagineCardiovascular: Common Lab Tests For Cardiovascular Disordersesruneitak100% (1)
- Endocrine System RevisedDocumento31 pagineEndocrine System RevisedMichael BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Course in The WardDocumento4 pagineFinal Course in The WardMichael Boado100% (1)
- Human Reroduction by Digambar Mali.Documento22 pagineHuman Reroduction by Digambar Mali.Surge E-Solution Pvt.Ltd.100% (1)
- Augmentation and IOLDocumento24 pagineAugmentation and IOLBlessy MadhuriNessuna valutazione finora
- The Endocrine SystemDocumento18 pagineThe Endocrine Systemadelina.jianu9991Nessuna valutazione finora
- NP2 RatioDocumento13 pagineNP2 RatioArnie Jude CaridoNessuna valutazione finora
- Erythromycin Use During PregnancyDocumento3 pagineErythromycin Use During Pregnancydrg Muh Rahman BurhanuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Cer 217 Infertility Final Report PDFDocumento418 pagineCer 217 Infertility Final Report PDFSara Al-FerkhNessuna valutazione finora
- (Imp) Ras, Basmas Constipation, Draksharishta, Sukhavirechanavati, Swarnakravyadarasa, TriphalachurnaDocumento10 pagine(Imp) Ras, Basmas Constipation, Draksharishta, Sukhavirechanavati, Swarnakravyadarasa, TriphalachurnaPraveen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine SystemDocumento4 pagineEndocrine SystemKirsten GomezNessuna valutazione finora
- Com Diagnosis With HTDocumento7 pagineCom Diagnosis With HTRoan-Lhieyne Sagli Diad VenancioNessuna valutazione finora
- Hubungan Psikologis Ibu Hamil Dengan Kejadian Hiperemesis GravidarumDocumento6 pagineHubungan Psikologis Ibu Hamil Dengan Kejadian Hiperemesis GravidarumAlfaridziNessuna valutazione finora
- SCI-Down SyndromeDocumento1 paginaSCI-Down SyndromeCharleson Kurt OngNessuna valutazione finora
- Infanticide A Concept PDFDocumento5 pagineInfanticide A Concept PDFHafizul AkbarNessuna valutazione finora
- Prof. Veni Hadju - Nutrition Deficiency During PregnancyDocumento22 pagineProf. Veni Hadju - Nutrition Deficiency During Pregnancyati sangajiNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System Group 1Documento26 pagineEndocrine System Group 1Jayson Kier AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ang 071457Documento19 pagineAng 071457Théophile NAMOINENessuna valutazione finora
- Manejo Cancer in Pregnancy Fetal and Neonatal OutcomesDocumento17 pagineManejo Cancer in Pregnancy Fetal and Neonatal OutcomesLaura LealNessuna valutazione finora
- Crude Death RateDocumento2 pagineCrude Death RatemanojrkmNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm NutriDietDocumento10 pagineMidterm NutriDietKristaMaeC.LazoNessuna valutazione finora
- English Project FinalDocumento27 pagineEnglish Project FinalVirendra NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Child Psychology Psychiatry - 2022 - Chronis Tuscano - ADHD in Girls and Women A Call To Action Reflections On HinshawDocumento3 pagineChild Psychology Psychiatry - 2022 - Chronis Tuscano - ADHD in Girls and Women A Call To Action Reflections On HinshawOana OrosNessuna valutazione finora
- Cephalo Pelvic DisproportionDocumento28 pagineCephalo Pelvic DisproportionSashmi ManandharNessuna valutazione finora
- Hirsutism: Diagnosis and TreatmentDocumento6 pagineHirsutism: Diagnosis and TreatmentAnonymous ysrxggk21cNessuna valutazione finora
- END-IAP Exam Question Paper - March-JulyDocumento3 pagineEND-IAP Exam Question Paper - March-JulyLinus JohannesNessuna valutazione finora
- Comprehensive Exam in Nursing Part 1Documento36 pagineComprehensive Exam in Nursing Part 1Ariane-Gay Cristobal DuranNessuna valutazione finora
- Student's Copy - Benedict's and Acetic Acid TestDocumento14 pagineStudent's Copy - Benedict's and Acetic Acid TestRonel ResurricionNessuna valutazione finora
- Metritis and Endometritis in High Yielding Dairy Cows PDFDocumento9 pagineMetritis and Endometritis in High Yielding Dairy Cows PDFfranky100% (1)
- Percentage of Women in Prevalence Study of Varicose VeinsDocumento3 paginePercentage of Women in Prevalence Study of Varicose Veinsjinni0926Nessuna valutazione finora
- Antepartum HemorrhageDocumento43 pagineAntepartum HemorrhageashwiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of Female Genitalia 1Documento13 pagineAssessment of Female Genitalia 1Cristine SyNessuna valutazione finora
- Anemia 2021Documento40 pagineAnemia 2021Gwyneth FisherNessuna valutazione finora
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDa EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (29)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDDa EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsDa EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNessuna valutazione finora
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDa EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (404)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDa EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (81)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDa EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsDa EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (170)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Da EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDa EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDa EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDa EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeValutazione: 2 su 5 stelle2/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (42)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDa EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (328)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDa EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Da EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (110)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (8)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceDa EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (51)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDa EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlDa EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (58)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryDa EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeDa EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (253)