Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Small Business
Caricato da
Al AminTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Small Business
Caricato da
Al AminCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Executive Summary This report is to critically review the traits and characteristics of an entrepreneur who can entail the
entrepreneurship opportunity within the small business, social enterprise, and large organization sectors. Entrepreneurship is a process of action an entrepreneur undertakes to establish his enterprise. It is a creative and innovative response to the environment. The entrepreneur creates or invents opportunities and exploits them to the benefit of the society which in turn brings prosperity to the innovator and his organization. The entrepreneur can entail the creation of a new enterprise within the small business, or social enterprise, or large organization. An entrepreneur works as a coordinating person. She or he coordinates all the inputs of the production process and make an arrangement of those inputs in a way so as to achieve the ultimate goal of the organization. In this regard, the entrepreneur brings together all the inputs namely land, labor and capital and put them into the production process. Again, the entrepreneur remains responsible mainly for any outcome of the organization. She or he has to bear all the risk regarding future uncertainty. She or he is the leader of the organization. Therefore, in order to be succeeded, an entrepreneur has to possess certain characteristics such as the urge to be succeeded, the motivation to work with full level of diligence, skill to perform all the required activities of the organization properly. Since an entrepreneur is a pioneer of doing business in an uncertain business environment, she or he must have the willingness to take risk.
Table of Contents Contents 1. Introduction 2. Traits and Characteristics of Entrepreneurs 2.1 Traits of Entrepreneurs 2.2 Characteristics of Entrepreneurs 3. Conclusion 4. Reference and Bibliography Page No 03 05 06 08 11 12-13
1. Introduction Entrepreneurship is an important aspect in contemporary business world. According to Dollinger (2009), entrepreneurship refers to the activity of creating an organization adaptive to the continuously changing economic environment. He further stressed that entrepreneurship also indicates to the activity of creating an economic organization or network of organization, the purpose of which is to meet the future uncertainty of the business environment. Rwigema and Venter (2004:6) describe the process of entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship is the process and
through innovation in order to propel the growth of a business opportunity into a highly nurtured venture in a completely uncertain environment. Entrepreneurship is the process of creating a new enterprise and that new enterprise can be a small business organization, social enterprise or a large enterprise (Bartol and Martin, 2008). As the terminology Entrepreneurship has numerous aspects of its definition, small enterprise also has numerous definitions (Culkin and Smith, 2000). The definition of Small firm given by one researcher is often a cloudy concept to another researcher. Hence, Very few of the researchers can agree on a certain definition of small firm. On the other hand, the term small has different interpretations in different industry. With a view to reducing the controversy regarding the definition of Small firm, Department of Trade and Industry in the UK (Culkin and Smith, 2000) gave the definitions and also classifications of business enterprises based on their different size. Those classifications are provided as followsFirms having 0 to 9 employees are known as Micro firm. Firms having 0 to 99 employees are known as small firm. This will also include micro enterprise. Firms having 50 to 249 employees are known as medium firm. Finally, firms having over 250 employees are known as large firms. Social enterprises are those enterprises the purpose of which is to serve the society and improve the societal environment without any motive for profit. Social Enterprise Coalition website, (April 2011) states that there are around 250,000 social enterprises in the UK and those enterprises are contributing over 24 billion to the economy of the UK. Although social enterprises have no legal aspect to be identified or defined in a precise way, but the model of these enterprises are highly encouraged by the government of the UK and also an increasingly popular concept over the last 10 years. Social enterprises are non-profit organizations. In order to achieve cherished social change, these enterprises follow the principles and methods of profit-oriented business organizations. The motto of these enterprises is to bring about a positive change in the society. Gillian Somers, Julie Cain, Megan Jeffery (2011) clarified the concept of organization and also defined that. They stated that an organization is a formal structure where more than two people work simultaneously in order to achieve a common goal. Often, the goal is to maximize their wealth. The inherent process regarding any organization is to convert the inputs into output that will maximize the wealth and attain their goal. An entrepreneur works as a coordinating person. She or he coordinates all the inputs of the production process and make an arrangement of those inputs in a way so as to achieve the ultimate goal of the organization. She or he is the leader of the organization. Therefore, in order to be succeeded, an entrepreneur has to possess certain characteristics such as the urge to be succeeded, the motivation to work with full level of diligence, skill to perform all the required activities of the organization properly. Since an entrepreneur is a pioneer of doing business in an uncertain business environment, she or he must have the willingness to take risk. Hence, entrepreneurship can also be defined as a new way of doing operations of the business organizations. It can be seen as process described as follows-
_Pic1
Figure: Basics of an entrepreneur In the above diagram, it can be observed that to manage an organization effectively and efficiently, the person responsible namely the entrepreneur should have the characteristics described above. Those features are- urge, skill, vision, growth, innovation, risk, and finally the ability to enterprise the organization. 2. Traits and Characteristics of Entrepreneurs Holt (1992) described the characteristics an entrepreneur must have to possess in order to be succeeded. He stressed that the entrepreneur is that person who can bring about new ideas in an organization, can establish an enterprise successfully and finally can provide the society with added features that gives value. Holt further said that the entrepreneurs can be referred to as value adding persons because with their innovative capabilities, they add value to the society. Holt (1992) stated that an entrepreneur must be self-confident, self-dependent, optimistic, and also diligent. Successful entrepreneurs are reality oriented, hard working and strive for the successful completion of their organizational task (Welsh and White, 1981). In accordance with Meredith, et al, (1982), an entrepreneur should have a list of entrepreneurial characteristics namely they should be practical, future-oriented, risk taker and emotionally stable etc. Meredith further said that it is not compulsory for an entrepreneur to have all the characteristics described above but the more features she or he possesses, the more probability of her or his performing of entrepreneurial functions properly and the also the more probability of entrepreneurial success. Khanka (1999) identified three broad categories of an entrepreneur. Such categories are- risk taking, origination and innovation. Again, an entrepreneur is that person who innovates new ways to do business and bears concerned risk and enjoys the return (Hisrich and Peters, 1998). Kirzner 1983) stressed the fact that a successful entrepreneur must invent new opportunities for performing organizational activity; she or he must be benefitted from the managerial training program, and further importance is not given on innovation. Tripathi (1997) argued that there are three stages in the entrepreneurial process. Those stages are- ability to recognize new opportunity to earn profit, establish an effective organization to perceive those opportunities, and instant reactive response to the changes in order to exploit those opportunities. Timmons (1999) explained that although it is said that an entrepreneur is an inborn entrepreneur, but training program, congenial environment are also important for a person to become a successful entrepreneur and also to drive an entrepreneur to achieve success. Hence, it is clear that all the entrepreneurs are not inborn; any person can be a successful entrepreneur if she or he strives to attain that. Therefore, from the above discussion, it is obvious that an entrepreneur must have certain characteristics which are described as follows2.1 Traits of Entrepreneurs Mental Ability: A successful entrepreneur must have sound mental ability which means
that she or he must be intelligent and creative thinker. Since s/he has to identify the potential opportunity and threat for her/his business environment, s/he must have the capability to exploit the opportunity and cope up with the threat. Therefore, her/his intelligence is a must one. On the other hand, an entrepreneur has to think creatively to identify new ways of operating her/his business organization. S/he also has to identify new source of collecting raw materials to produce the goods or services, to train her/his employees, to motivate them, to invent new technology for the production process etc. Hence, the power to think creatively is obviously required for an entrepreneur to be succeeded. In case small business, an entrepreneur is intelligent enough to exploit the opportunities required to attain the success of the organization. S/he thinks creatively to identify new source of getting raw materials cheaply. In a social enterprise, an entrepreneur thinks to go ahead for the betterment of the society whereas in a large organization, the entrepreneurs think to identify new source of funding extended line of business. Clear Objectives: As it is commonly said that planning means the work done half way. Hence, an entrepreneur must plan to do business properly and work accordingly. In a small business, entrepreneurs have to plan for short and medium term because during this time period, they can achieve their goal whereas in a social enterprise, the entrepreneurs plan according to the situation of the society, the level of standard of citizens lives, the political stability etc. On the other hand, in a large organization, an entrepreneur does plan for long term because they believe in the going concern of their business. And in this case, the task of preparing planning program is a complex one. For instance, Steve jobs, the founder of Apple, one of the largest business organizations in the world, had successfully prepared the business plan and clarified the objectives of his business and ultimately at present, the eventual motto of the business has been achieved. Business Secrecy: Keeping the policies of the business secret is important to sustain in the competitive world. In case of small firm, entrepreneurs maintain this as part of their business policy whereas in case of social enterprise, entrepreneurs do not maintain this so strictly. While in case of large organization, this policy is very important because competition is very severe in this level. Human Relations Ability: Humans are very important resource of any organization. In case of small firm, since owner/s is/are the main entrepreneur/s of the organization, limited number of employees are needed. Many employees are needed in case of social enterprise for properly functioning. Again, in a large firm, many employees are required and in this case, human relationship management is very important. For example, Merck Zuckerburk, the founder of Facebook, one of the most popular social networking sites in the world, created this site realizing the importance of keeping social networking alive. Effective Communication: Since in a small firm, there are few employees, extensive communication is not required. In a social enterprise, to be operated properly, communication is required to the level greater than that of small firm. On the other hand, in a large firm, as there are many line of products, huge number of employees, communication process must be effective. Technical Knowledge: The small firm often produces small number of products or provides limited number of services; hence extensive technical knowledge is not needed. In a social enterprise, there is minimum requirement for technical knowledge but in case of large organization, it is a must to possess extensive technical knowledge. Decision-Making: In case of small firm, the owner or the entrepreneur is the only responsible person for making decision. In case of social enterprise, as there are many entrepreneurs, all of them together make any decision. Again, in a large firm, as there are many hierarchy, decision making process is very complex and often bureaucracy exists in the decision making process. Risk-Bearing: The entrepreneur or the owner is only the risk bearer in a small firm. All the entrepreneurs are responsible for any risk in a social enterprise and all the owners are the ultimate risk bearer in a large firm. Entrepreneurs take fairly large risks and are not afraid to do so. For example Zappos, the largest on-line footwear retailer. When a customer orders a pair of shoes, Zappos sends the customers three pairs, (one size smaller, one size larger and the ordered size). Why? To enable the customer to select the size that fits best. The
other two pairs should be returned by the customer to a designated courier company. Zappos pays for the courier charges of returning the extra pairs. This is what entrepreneurial marketing and risk taking is all about. Networking: Entrepreneurs or small business owners do not have the resources of big businesses. For example, research & development units, headed by scientists and researchers. Hence, they overcome this by creating a virtual organization that is perpetually networked. For e.g. entrepreneurs would encourage students in universities to conduct research projects on their organizations. In this manner, they obtain research inputs virtually free of charge!! Many small and medium scale business owners (SMEs) in Sri Lanka have a great thirst for knowledge and attend appropriate seminars to acquire same. This also gives them opportunities to network. Self-Confidence: Entrepreneurs must be self-confident. This quality is widely needed in a small firm hence she or he is alone to bear any risk and cannot share the risk with others or even with the employees. Social workers also have to be self-confident to be succeeded. Owners and also the employees of a large firm also have to be self-confident.
2.2 Characteristics of Entrepreneurs An ideal entrepreneur has the following featuresVision: Vision means the future prospect of any situation. An entrepreneur must be visionary about the future success of her or his organization. S/he has to make an appropriate plan to be succeeded and has to work accordingly. Market Demands Soicio- Economic Technological Environment Knowledge: As knowledge is the basis of becoming success in any case. To achieve the ultimate goal, an entrepreneur must have knowledge. Again, s/he has to acquire knowledge on the continuous basis. A small firm can be operated without extensive knowledge, a social enterprise can be operated with a certain level of knowledge but a large organization has to be operated with extensive knowledge of organizational management. Desire to succeed: Desire to succeed means having urged to achieve any goal. It is needed in all the business organizations. For instance, Dr. Muhammed Yunus, the founder of a social enterprise namely Grameen Bank and Nobel laureate in peace, has possessed the strong desire to achieve the goal of his organization, to alleviate poverty. Independence: To make decision quickly, independence is a must which is very available in a small and social enterprise. On the contrary, due to many hierarchies in a large organization, there is limited independence to make any organizational decision. Optimism: Optimism means having hopes to be succeeded in the future. This is an equally important concept in a small, social enterprise and also in a large organization. Value Addition: Entrepreneurs have the desire to create something new. They want to add value to the societal work. In all the levels of business namely small, social enterprise or in a large organization, all the entrepreneurs always try to add more value. Leadership: Leadership is one of the most important characteristics of a successful entrepreneur. This feature is also equally important to the all levels of business organizations. Hardworking: An entrepreneur has to be hard working whether she or he belongs to a small firm, social enterprise or a large organization. Without extensive diligence, an entrepreneur cannot be successful. For example, Muhammed Johurul Islam, one of the most successful entrepreneurs of large organizations in Bangladesh was extremely hard working and this hard work brought him about his success. Risk-Taking Ability: An entrepreneur is a risk taker. In case of a small firm, the
entrepreneur is the only owner of the business organization; hence s/he has to take the risk of the business fully. In a social enterprise, there does not exist unlimited risk while in case of a large organization, the risk of uncertainty is limited to the proportional ownership of the owners. So, the risk is not unlimited in a large organization. Ability to Find and Explore Opportunities: An important characteristic of a successful entrepreneur is to identify new opportunities and ways of exploiting those opportunities. For example, Ranada Prashad Saha, one of the successful entrepreneurs of large business improved his ability to identify new opportunities of expanding new line of business and at last, became a successful entrepreneur. Motivator: An entrepreneur is the motivator of the employees of her/his organization. This is equally important in all the levels of business organization. Customer focus: An entrepreneur should focus on the customers. Smaller businesses are more focused on providing excellent service to their customers. Why? Since they have fewer customers than bigger players and value these customers. For example, Virgin Atlantic Airlines. They provide great customer service when compared with much bigger airlines such as British Airways and Air Canada. This customer focuses gives SMEs a great competitive edge and builds up customer loyalty and even customer intimacy. Creativity: The bigger a business becomes, creativity is lost in many instances. Why? Processes, systems, rules and regulations take over. In smaller entrepreneurial businesses, the culture is entrepreneurial and hence creativity is always encouraged. For example of Titan the Indian watch maker. They are significantly smaller than the larger timekeepers in Switzerland and Japan. However, Titan was the first brand to create the worlds slimmest watch The Edge. Further, Titan was the first brand to create matching watches for him and her. (Gifting solution) The Titan Raga collection. Future Oriented: All the entrepreneurs of all the business organizations have to be future oriented, they have to forecast the future situation. Interpersonal Skills: Interpersonal skills mean entrepreneurs ability to communicate with the others in a proper way. Entrepreneurs in a small firm, social organization or in a large organization need to be interpersonally skilled.
3. Conclusion Entrepreneurship is a process of action an entrepreneur undertakes to establish his enterprise. It is a creative and innovative response to the environment. The entrepreneur creates or invents opportunities and exploits them to the benefit of the society which in turn brings prosperity to the innovator and his organization. The entrepreneur can entail the creation of a new enterprise within the small business, or social enterprise, or large organization. An entrepreneur works as a coordinating person. She or he coordinates all the inputs of the production process and make an arrangement of those inputs in a way so as to achieve the ultimate goal of the organization. In this regard, the entrepreneur brings together all the inputs namely land, labor and capital and put them into the production process. Again, the entrepreneur remains responsible mainly for any outcome of the organization. She or he has to bear all the risk regarding future uncertainty. She or he is the leader of the organization. Therefore, in order to be succeeded, an entrepreneur has to possess certain characteristics such as the urge to be succeeded, the motivation to work with full level of diligence, skill to perform all the required activities of the organization properly. Since an entrepreneur is a pioneer of doing business in an uncertain business environment, she or he must have the willingness to take risk. An entrepreneur must be self-confident, self-dependent, optimistic, and also diligent. Successful entrepreneurs are reality oriented, hard working and strive for the successful completion of their organizational task. An entrepreneur should have a list of entrepreneurial characteristics namely they should be practical, future-oriented, risk taker and emotionally stable etc. Meredith further said that it is not compulsory for an entrepreneur to have all the characteristics described above but the more features she or he possesses, the more probability of her or his performing of entrepreneurial functions properly and the also the more
probability of entrepreneurial success. Hence, it is clear that all the entrepreneurs are not inborn; any person can be a successful entrepreneur if she or he strives to attain such traits and characteristics.
4. Reference and Bibliography v. Alvord, S. H., Brown, L. D., & Letts, C. W. (2004). Social entrepreneurship and social transformation: An exploratory study. The Journal of Applied Behavioral Science, 40, 260282. v. BARTOL, K.M. and MARTIN, D.C. 1998. Management, 3rd edition. New York: McGraw-Hill. v. CULKIN, N. and SMITH, D. 2000. An emotional business: A guide to understanding the motivations of small business takers, Qualitative Market Research: An International Journal, 3(3): 145-157. v. Dixon, S. E. A., & Clifford, A. (2007). Ecopreneurship-a new approach to managing the triple bo om line. Journal of Organiza nal Change Management, 20(3), 326-345. vi. DOLLINGER, M.J. 1999. Entrepreneurship: Strategies and resources, 2nd edition. New Jersey: Prentice Hall. v. European Commission (2011). Communication on Social Business Initiative. Creating a favourable climate for social enterprises, key stakeholders in the social economy and innovation. COM (2011) 682 final. http://eurlex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do? uri=COM:2011: 0682:FIN:EN:PDF v. Gillian Somers, Julie Cain, Megan Jeffery (2011). Large Scale organization. Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-1-107-63549-4 v. HISRICH, R.D. and PETERS, M.P. 1998. Entrepreneurship, 4th edition. New York: McGraw-Hill. v. HISRICH, R.D. and PETERS, M.P. 2002. Entrepreneurship, 5th edition. New York: McGraw-Hill. v. Khanka, S.S. (1999), Entrepreneurial Development, 1st edition, S. Chand & Company Ltd., India. v. Kirzner, I. M. (1983), Perception, Opportunity and Profit: Studies in the Theory of Entrepreneurship, 1st edition 1979, Chicago: University of Chicago Press. v. Meredith, G.G., Nelson, R.E., Neck, P.A. (1982), The Practice of Entrepreneurship, Geneva: International Labour Office. v. Welsh, J. A. and White, J. F. (1981), Converging on Characteristics of Entrepreneurs, Frontiers of Entrepreneurship Research, pp. 504-510. v. Timmons, J.A, (1999), Characteristics and Role Demands of Entrepreneurship, American Journal of Small Business, 3, 1, p. 5-17. v. Yunus, M. (2004), Grameen Bank o Amar Jibon (in Bengali), Maola Brothers, Dhaka.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Research Title The Introduction of Total Quality Management (TQM) Culture in Hotel-A Case Study of Accor Hotel in Central LondonDocumento21 pagineResearch Title The Introduction of Total Quality Management (TQM) Culture in Hotel-A Case Study of Accor Hotel in Central LondonAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- How Effective Motivation and Employee Satisfaction On Organizational Growth.-A Case Study On Travelodge HotelDocumento44 pagineHow Effective Motivation and Employee Satisfaction On Organizational Growth.-A Case Study On Travelodge HotelAl Amin100% (4)
- Stragegic MKT 2Documento17 pagineStragegic MKT 2Al AminNessuna valutazione finora
- PROPOSAL EmpowermentDocumento18 paginePROPOSAL EmpowermentAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Hotel MarketingDocumento5 pagineHotel MarketingAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- The Relationship Between Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction: A Case Study of Pizza HutDocumento9 pagineThe Relationship Between Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction: A Case Study of Pizza HutAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Employee Motivation in The Competitive Retail Super Market IndustryDocumento9 pagineEmployee Motivation in The Competitive Retail Super Market IndustryAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- A Critical Analysis of Online Marketing in Retail Industry in The Uk, A Case Study of TescoDocumento10 pagineA Critical Analysis of Online Marketing in Retail Industry in The Uk, A Case Study of TescoAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Marketing Communications in Consumer Markets - A Case Study of Pizza HutDocumento12 pagineMobile Marketing Communications in Consumer Markets - A Case Study of Pizza HutAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Impact of Online Marketing on Consumer Buying DecisionsDocumento10 pagineImpact of Online Marketing on Consumer Buying DecisionsAl Amin100% (1)
- International and Comparative Human Resource ManagementDocumento8 pagineInternational and Comparative Human Resource ManagementAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- The Marketing Efficiency of Online Retailing Division of Marks & Spencer in London: A Case StudyDocumento9 pagineThe Marketing Efficiency of Online Retailing Division of Marks & Spencer in London: A Case StudyAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- The Role of 'Scientific Racism' in Western Imperialist ThinkingDocumento6 pagineThe Role of 'Scientific Racism' in Western Imperialist ThinkingAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment MISDocumento10 pagineAssignment MISAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Role of Information Technology in Personalization and Standardization of A BPO Company (A Case Study On Juriscape Legal Research Company of Ahmadabad, India)Documento48 pagineRole of Information Technology in Personalization and Standardization of A BPO Company (A Case Study On Juriscape Legal Research Company of Ahmadabad, India)Al AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Marketing Communications in Consumer Markets - A Case Study of Pizza HutDocumento38 pagineMobile Marketing Communications in Consumer Markets - A Case Study of Pizza HutAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Wal MartDocumento11 pagineWal MartAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- "It's A Journey, Not A Destination" Harley-Davidson's Mantra Clearly Suggests The Image and TheDocumento13 pagine"It's A Journey, Not A Destination" Harley-Davidson's Mantra Clearly Suggests The Image and TheAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Marketing Communications in Consumer Markets - A Case Study of Pizza HutDocumento12 pagineMobile Marketing Communications in Consumer Markets - A Case Study of Pizza HutAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Small BusinessDocumento8 pagineSmall BusinessAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- E CRMDocumento10 pagineE CRMAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Impact of Brand Image On The Clothing Buying Behavior - A Case Study of Marks & SpencerDocumento12 pagineImpact of Brand Image On The Clothing Buying Behavior - A Case Study of Marks & SpencerAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Training is vital for high performance organizationsDocumento6 pagineTraining is vital for high performance organizationsAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Management of Coca ColaDocumento11 pagineStrategic Management of Coca ColaAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Management of TescoDocumento14 pagineStrategic Management of TescoAl Amin100% (1)
- Strategic Management of TescoDocumento14 pagineStrategic Management of TescoAl Amin100% (1)
- Business Law AssignmentDocumento8 pagineBusiness Law AssignmentAl AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Operation Management of Coca ColaDocumento11 pagineOperation Management of Coca ColaAl Amin100% (1)
- Finance AssignmentDocumento13 pagineFinance AssignmentAl Amin0% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Design of A Neural Network Function Block For Insertion Into The Function Block Library of A Programmable Logic ControllerDocumento4 pagineDesign of A Neural Network Function Block For Insertion Into The Function Block Library of A Programmable Logic ControllerArmando Fermin PerezNessuna valutazione finora
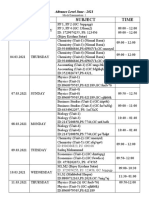
- Mock Examination Routine A 2021 NewDocumento2 pagineMock Examination Routine A 2021 Newmufrad muhtasibNessuna valutazione finora
- Everything You Need to Know About TimberDocumento63 pagineEverything You Need to Know About TimberAkxzNessuna valutazione finora
- Synopsis Sagar Project - A Study On The Need of CRM in OrganizatonDocumento3 pagineSynopsis Sagar Project - A Study On The Need of CRM in OrganizatonViraja GuruNessuna valutazione finora
- Collection of Books To Read Preparing For ACM ICPCDocumento1 paginaCollection of Books To Read Preparing For ACM ICPCJia Hong100% (2)
- Rexroth HABDocumento20 pagineRexroth HABeleceng1979Nessuna valutazione finora
- Curios AllianceDocumento32 pagineCurios AllianceyesterowNessuna valutazione finora
- #1 Introduction To C LanguageDocumento6 pagine#1 Introduction To C LanguageAtul SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocumento3 pagineGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridaySheilaMarB.Esteban100% (1)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Social MediaDocumento2 pagineAdvantages and Disadvantages of Social MediaCeleste GalvanNessuna valutazione finora
- Determination of The Molecular Weight of Polymers From Viscosity MeasurementsDocumento10 pagineDetermination of The Molecular Weight of Polymers From Viscosity MeasurementsAbdullah MunawarNessuna valutazione finora
- Temp Gradient For Warping Stress in Rigid PavementDocumento9 pagineTemp Gradient For Warping Stress in Rigid PavementAmul KotharkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Guide VLSI Aspirants FAQ Physical DesignDocumento3 pagineEssential Guide VLSI Aspirants FAQ Physical DesignRohith RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Elon Musk: AI Is A Fundamental Risk To The Existence of Human CivilizationDocumento19 pagineElon Musk: AI Is A Fundamental Risk To The Existence of Human CivilizationBDApp StarNessuna valutazione finora
- DLookup Function - Access - Microsoft OfficeDocumento2 pagineDLookup Function - Access - Microsoft OfficevinahackNessuna valutazione finora
- BS en 12583 - 2014 - Gas Infrastructure. Compressor Stations. Functional Requirements.Documento56 pagineBS en 12583 - 2014 - Gas Infrastructure. Compressor Stations. Functional Requirements.SDP02Nessuna valutazione finora
- Perfect Secrecy: Chester Rebeiro IIT MadrasDocumento50 paginePerfect Secrecy: Chester Rebeiro IIT MadrasDr. Jayanthi V.S.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gr07 S DanceDocumento17 pagineGr07 S DanceMaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Gradient of A Scalar Field and Its Geometrical InterpretationDocumento3 pagineGradient of A Scalar Field and Its Geometrical InterpretationMichael100% (1)
- H07RN-F, Enhanced Version: Product InformationDocumento5 pagineH07RN-F, Enhanced Version: Product InformationDarwin YupaNessuna valutazione finora
- English Test 03Documento6 pagineEnglish Test 03smkyapkesbi bjbNessuna valutazione finora
- MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT - Copy (Repaired)Documento10 pagineMECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT - Copy (Repaired)Wan Mohd AfnanNessuna valutazione finora
- 20752-Reservoir Management Training An Lntegrated ApproachDocumento6 pagine20752-Reservoir Management Training An Lntegrated ApproachdanonninoNessuna valutazione finora
- Wheel Radial Fatigue Test MachineDocumento1 paginaWheel Radial Fatigue Test MachineAlex NuñezNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5: Attention and PerformanceDocumento10 pagineChapter 5: Attention and Performancerebela29Nessuna valutazione finora
- NB-CPR 14-612r7 Issuance of Certificates Under CPRDocumento13 pagineNB-CPR 14-612r7 Issuance of Certificates Under CPRÜmit BUCAKNessuna valutazione finora
- Mastercam Book 5 Axis Bai 1Documento31 pagineMastercam Book 5 Axis Bai 1tuanvn76100% (3)
- Practical File Class XDocumento5 paginePractical File Class XJaiNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 - The Geological Interpretation of Well LogsDocumento292 pagine10 - The Geological Interpretation of Well LogsLorenza LorenzanaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3D Technical Data Package Configuration Management, Modeling and Drawing ProcedureDocumento175 pagine3D Technical Data Package Configuration Management, Modeling and Drawing Procedurejesse_w_petersNessuna valutazione finora