Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
MODULE B-2 D Transformation
Caricato da
M.Saravana Kumar..M.ECopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
MODULE B-2 D Transformation
Caricato da
M.Saravana Kumar..M.ECopyright:
Formati disponibili
M.SARAVANA KUMAR M.
E Engineering Design 2 D GEOMETRIC TRANSFORMATIONS
BASIC TRANSFORMATION
Animations are produced by moving the 'camera' or the objects in a scene along animation paths. Changes in orientation, size and shape are accomplished with geometric transformations that alter the coordinate descriptions of the objects. The basic geometric transformations are translation, rotation, and scaling. Other transformations that are often applied to objects include reflection and shear. Use of transformations in CAD In mathematics, "Transformation" is the elementary term used for a variety of operation such as rotation, translation, scaling, reflection, shearing etc. CAD is used throughout the engineering process from conceptual design and layout, through detailed engineering and analysis of components to definition of manufacturing methods. Every aspect of modeling in CAD is dependent on the transformation to view model from different directions we need to perform rotation operation. To move an object to a different location translation operation is done. Similarly Scaling operation is done to resize the object. Coordinate Systems In CAD three types of coordinate systems are needed in order to input, store and display model geometry and graphics. These are the Model Coordinate System (MCS), the World Coordinate System (WCS) and the Screen Coordinate System (SCS). Model Coordinate System The MCS is defined as the reference space of the model with respect to which all the model geometrical data is stored. The origin of MCS can be arbitrary chosen by the user.
World Coordinate System As discussed above every object have its own MCS relative to which its geometrical data is stored. In case of multiple objects in the same working space then there is need of a World Coordinate System which relates each MCS to each other with respect to the orientation of the WCS. It can be seen by the picture shown below.
Screen Coordinate System In contrast to the MCS and WCS the Screen Coordinate System is defined as a two dimensional device-dependent coordinate system whose origin is usually located at the lower left corner of the graphics display as shown in the picture below. A transformation operation from MCS coordinates to SCS coordinates is performed by the software before displaying the model views and graphics.
Viewing Transformations As discussed that the objects are modeled in WCS, before these object descriptions can be projected to the view plane, they must be transferred to viewing coordinate system. The view plane or the projection plane is set up perpendicular to the viewing zv axis. The World coordinate positions in the scene are transformed to viewing coordinates, and then viewing coordinates are projected onto the view plane. The transformation sequence to align WCS with Viewing Coordinate System is. 1. Translate the view reference point to the origin of the world coordinate system. 2. Apply rotations to align xv, yv, and zv with the world xw, yw and zw axes, respectively.
TRANSLATION A translation is applied to an object by repositioning it along a straight line path from one coordinate location to another. We translate a two-dimensional point by adding translation distances, tx and ty, to the original coordinate position (x,y) to move the point to a new position (x',y')
TRANSLATION
A translation is applied to an object by repositioning it along a straight line path from one coordinate location to another. We translate a two-dimensional point by adding translation distances, tx and ty, to the original coordinate position (x,y) to move the point to a new position (x',y')
The translation distance pair (tx, ty) is called translation vector or shift vector Matrix representation of translation
This allows us to write the two-dimensional translation equations in the matrix form:
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- M208 HandbookDocumento112 pagineM208 HandbookAwf Awf100% (3)
- DSP1 - Practice Homework With SolutionsDocumento9 pagineDSP1 - Practice Homework With Solutionsdania alamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan DemoDocumento4 pagineSemi Detailed Lesson Plan DemoGeraldine Dela Vega Quines100% (2)
- M.saravana Kumar Updated Co StatementDocumento5 pagineM.saravana Kumar Updated Co StatementM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
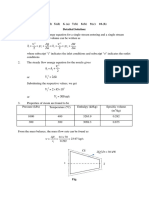
- Strength of Materials - Unit 2 - Week 1Documento3 pagineStrength of Materials - Unit 2 - Week 1M.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- 2 & 3 - Institutional Vision, Mision, PO, PSO, PEODocumento4 pagine2 & 3 - Institutional Vision, Mision, PO, PSO, PEOM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Effective Engineering Teaching in PracticeDocumento4 pagineEffective Engineering Teaching in PracticeM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Thermodynamics - Unit 2 - Week 1 - SI Unit, Definitions & ConceptsDocumento4 pagineEngineering Thermodynamics - Unit 2 - Week 1 - SI Unit, Definitions & ConceptsM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Solution - Assignment - Laws of Thermodynamics - 3rd WeekDocumento5 pagineSolution - Assignment - Laws of Thermodynamics - 3rd WeekM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- IAT2 Key PDFDocumento8 pagineIAT2 Key PDFM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Details Dr. V KhalkarDocumento1 paginaDetails Dr. V KhalkarM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- NDT Syallbus Anna University ScribdDocumento2 pagineNDT Syallbus Anna University ScribdM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Thermodynamics - Unit 4 - Week 3 - Properties of Pure SubstancesDocumento4 pagineEngineering Thermodynamics - Unit 4 - Week 3 - Properties of Pure SubstancesM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Design Subject SyallbusDocumento8 pagineDesign Subject SyallbusM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Thermodynamics - Unit 6 - Week 5 - First Law of Thermodynamics For Non-Flow ProcessesDocumento4 pagineEngineering Thermodynamics - Unit 6 - Week 5 - First Law of Thermodynamics For Non-Flow ProcessesM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Latha MathavanDocumento3 pagineLatha MathavanM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Scholar List MechDocumento152 pagineScholar List MechM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Laws of Thermodynamics - Unit 3 - Week 2 PDFDocumento3 pagineLaws of Thermodynamics - Unit 3 - Week 2 PDFM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- WEEK 1 SolutionsDocumento5 pagineWEEK 1 SolutionsM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Laws of Thermodynamics - Unit 3 - Week 2Documento3 pagineLaws of Thermodynamics - Unit 3 - Week 2M.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics of Solids - Unit 2 - Week 01 - Introduction To Mechanics of SolidsDocumento5 pagineMechanics of Solids - Unit 2 - Week 01 - Introduction To Mechanics of SolidsM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Laws of Thermodynamics - Unit 5 - Week 4Documento3 pagineLaws of Thermodynamics - Unit 5 - Week 4M.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics of Solids - Unit 5 - Week 4 - Force Displacement Relationship and Introduction To Concept of StressDocumento4 pagineMechanics of Solids - Unit 5 - Week 4 - Force Displacement Relationship and Introduction To Concept of StressM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Thermodynamics - Unit 3 - Week 2 - SI Unit, Definitions & ConceptsDocumento5 pagineEngineering Thermodynamics - Unit 3 - Week 2 - SI Unit, Definitions & ConceptsM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Strength of Materials - Unit 6 - Week 5Documento3 pagineStrength of Materials - Unit 6 - Week 5M.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Strength of Materials - Unit 3 - Week 2Documento4 pagineStrength of Materials - Unit 3 - Week 2M.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- DTS 06Documento18 pagineDTS 06M.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- MT-1 Full NotesDocumento56 pagineMT-1 Full NotesM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Abrasive Jet MachiningDocumento12 pagineAbrasive Jet MachiningM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Anna University Manufacturing Technology1 Previous Year Question Papers CollectionDocumento20 pagineAnna University Manufacturing Technology1 Previous Year Question Papers CollectioneurekaNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabi GATE2017 PDFDocumento73 pagineSyllabi GATE2017 PDFAnkit Kumar AJNessuna valutazione finora
- ME-1 Section MCQ and NAT Type Exam ResultsDocumento2 pagineME-1 Section MCQ and NAT Type Exam ResultsM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- Gate PlanDocumento1 paginaGate PlanM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENessuna valutazione finora
- HL Paper1Documento2 pagineHL Paper1GIANLUCA CICCO BILBAO-AlumnoNessuna valutazione finora
- Soal Latihan - Tes 3Documento4 pagineSoal Latihan - Tes 3Mochamad Syahrial100% (1)
- Sample Solution Manual For Orbital Mechanics For Engineer 3rd CurtisDocumento16 pagineSample Solution Manual For Orbital Mechanics For Engineer 3rd CurtisSumon SwiftNessuna valutazione finora
- Moment of InertiaDocumento7 pagineMoment of InertiaNazir AbdulmajidNessuna valutazione finora
- Quick review of index notationDocumento5 pagineQuick review of index notationFrank SandorNessuna valutazione finora
- 2-D Cylindrical Roller ContactDocumento51 pagine2-D Cylindrical Roller ContactDan Wolf100% (1)
- MathematicsDocumento9 pagineMathematicsJohn Eivhon FestijoNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Crystal Structures-2 PDFDocumento135 pagineSimple Crystal Structures-2 PDFRoslina ShariffNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics ReportDocumento9 pagineMathematics ReportShivaraj Subramaniam0% (1)
- UTM Coordinate SystemDocumento13 pagineUTM Coordinate SystemErick JumaNessuna valutazione finora
- 07 04ChapGereDocumento31 pagine07 04ChapGereZero Yip100% (1)
- Edited Week 1Documento5 pagineEdited Week 1Rhea DonaNessuna valutazione finora
- O Level Mathematics SyllabusDocumento14 pagineO Level Mathematics SyllabusOttone Chipara Ndlela50% (8)
- Teaching GeometryDocumento17 pagineTeaching Geometryanglo phile100% (1)
- k6 Maths SylDocumento201 paginek6 Maths Syldrwho01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alberta Competition AnswersDocumento53 pagineAlberta Competition AnswersBogus AccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Innovative Aviation Training Services: TrigonometryDocumento11 pagineInnovative Aviation Training Services: TrigonometrynathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Richard Long - Lines of Thought - EntrevistaDocumento7 pagineRichard Long - Lines of Thought - EntrevistacarolillanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2021: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Mathematics B (4MB1) Paper 02Documento30 pagineMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2021: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Mathematics B (4MB1) Paper 02Fairooz Sadaf Susan100% (1)
- TALLER N - 2 Funciones Vectoriales (II)Documento5 pagineTALLER N - 2 Funciones Vectoriales (II)miguel rojas tonuscoNessuna valutazione finora
- DDA Line DrawingDocumento13 pagineDDA Line DrawingMazharulislamNessuna valutazione finora
- G2 Physics 1Documento37 pagineG2 Physics 1Carlina FerreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Surface Areas and Volumes of Similar SolidsDocumento4 pagineSurface Areas and Volumes of Similar SolidsTaha YousafNessuna valutazione finora
- Sokolnikoff Theory of ElasticityDocumento491 pagineSokolnikoff Theory of ElasticityAdam Taylor88% (8)
- Trial Melaka Spm2021Documento66 pagineTrial Melaka Spm2021Hafiz HakimiiNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 12 Maths Marking Scheme 2020Documento10 pagineCBSE Class 12 Maths Marking Scheme 2020Kiran PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- S3 Paper MTCDocumento4 pagineS3 Paper MTCIshimwe Jasha100% (2)