Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Monitoring cerebral perfusion in stroke patient
Caricato da
Karel LuDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Monitoring cerebral perfusion in stroke patient
Caricato da
Karel LuCopyright:
Formati disponibili
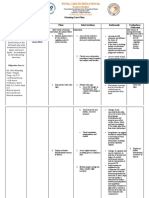
DATE
CUES
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
RATIONALE
OBJECTIVES OF CARE
NURSING INTERVENTIONS 1. Determine factors related to individual situation/cause for coma/decreased cerebral perfusion.
EVALUTAION
D E C E M B E R
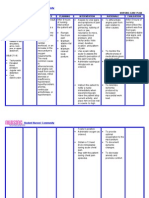
Subjective: Ineffective Cerebral tissue Nastroke siya as verbalized by the patients watcher perfusion r/t interruption of blood flow secondary to hemorrhage Too much pressure in the vessels can cause it to rupture and thus leads to hemorrhage. If Objective: hemorrhage occurs in the Speech brain, there would be increased intracranial
After several Nursing Interventions, the client will be able to:
After several Nursing interventions, the patient was able to demonstrate increased perfusion as evidenced by: -warm skin -strong pulse noted VS within
Demonstrate increased perfusion as individually appropriate such as warm skin, strong pulse present/VS
R: Influences choice of interventions. 2. Monitor/document neurological status frequently and compare with
2 0 1
abnormality noted
Changes in motor
pressure and the brain will swell. Therefore there would be no enough blood flow and oxygenation in the brain.
within normal range.
baseline. R: Assesses trends in level of consciousness (LOC) and potential for increased ICP and is useful in
normal range: BP=120/90 mm Hg PR= 80 RR= 20 Temp= 36.9
response; extremity
5:00 PM
weakness; paralysis
GCS of 11
determining location, extent, and
VS taken as noted: BP= 130/90 mm Hg Source: Textbook of Medical
progression/resoluti on of CNS damage. 3.
RR= 20 cpm PR= 89 bpm Temp= 37.0
Surgical 12th edition by Brunner and Suddhart pg 563
Monitored vital signs. R: Fluctuations in pressure may occur because of cerebral pressure/injury in vasomotor area of the brain.
4. Evaluate pupils, noting size, shape, equality, light reactivity. R: Pupil reactions are regulated by the oculomotor (III)
cranial nerve and are useful in determining whether the brainstem is intact. Pupil size/equality is determined by balance between parasympathetic and sympathetic enervation. Response to light reflects combined function of the optic (II) and oculomotor
(III) cranial nerves.
5. Document changes in vision, e.g., reports of blurred vision, alterations in visual field/depth perception. R: Specific visual alterations reflect area of brain involved, indicate safety concerns, and influence
choice of interventions. 6. Position with head slightly elevated and in neutral position. R: Reduces arterial pressure by promoting venous drainage and may improve cerebral circulation/perfusio n. 7. Maintain bedrest; provided quiet environment;
Provided rest periods between care activities, limit duration of procedures. R: Continual stimulation/activity can increase ICP. Absolute rest and quiet may be needed to prevent rebleeding in the case of hemorrhage.
8. Administer medications as indicated such as Manitol, Citicholine and Neuroaid. R: To promote pharmacologic treatment regimen.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 pagineTissue PerfusionMichael John LeandichoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM 118L/ 119L (Related Learning Experience) Day 3-ActivityDocumento4 pagineNCM 118L/ 119L (Related Learning Experience) Day 3-ActivityNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 pagineIneffective Tissue Perfusionsyderman999Nessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceDocumento2 pagineNCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceAngelyn ArdinesNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: by The Wife During InterviewDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan: by The Wife During InterviewJayson SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP CKDDocumento3 pagineNCP CKDRiel TumandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPDocumento4 pagineNursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPderic100% (2)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPDocumento2 pagineNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPpa3kmedina100% (1)
- Ineffective Renal Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 pagineIneffective Renal Tissue PerfusionHendra Tanjung100% (4)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento3 pagineNursing Care PlanJayalakshmi David50% (2)
- Compartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)Documento2 pagineCompartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)eunica16Nessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento3 pagineNCPJezza RequilmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento11 pagineNursing Care Planaycee0316100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 pagineNursing Diagnosis: Ineffective Tissue PerfusionIan RamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning ImplementationDocumento4 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Planning ImplementationMG PolvorosaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Cva Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento1 paginaNCP Cva Ineffective Tissue Perfusionexcel21121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 pagineIneffective Tissue PerfusionDiane ReyNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento1 paginaNCP Impaired Physical MobilityCharmaine SolimanNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessing and Managing Cerebral Perfusion IssuesDocumento3 pagineAssessing and Managing Cerebral Perfusion IssuesMicaela CrisostomoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion R/T Space Occupying Lesion (Neuroblastoma On Frontal Lobe)Documento4 pagineNCP - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion R/T Space Occupying Lesion (Neuroblastoma On Frontal Lobe)Carl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (4)
- NCP AneurysmDocumento4 pagineNCP AneurysmJanielle Christine Monsalud100% (1)
- NCP AnginaDocumento3 pagineNCP AnginaShie LA100% (1)
- Ate Gara NCP (Activity Intolerance)Documento2 pagineAte Gara NCP (Activity Intolerance)Kimsha ConcepcionNessuna valutazione finora
- CVA Activity IntoleranceDocumento1 paginaCVA Activity IntoleranceNursesLabs.com75% (4)
- NCP-fluid Volume DeficitDocumento4 pagineNCP-fluid Volume DeficitChrissa Mae Aranilla MayoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento2 pagineNCPLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNessuna valutazione finora
- Decrease Cardiac OutputDocumento6 pagineDecrease Cardiac OutputGerardeanne ReposarNessuna valutazione finora
- As Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Documento4 pagineAs Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Nicole GumolonNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Pain Assessment and Nursing InterventionsDocumento1 paginaAcute Pain Assessment and Nursing InterventionsAi RouNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Confusion Nursing DiagnosisDocumento4 pagineAcute Confusion Nursing Diagnosisasmika danaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 pagineIneffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care Planrois romaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7Documento2 pagineIneffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7dana100% (4)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation for Impaired Gas ExchangeDocumento2 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation for Impaired Gas ExchangeCharissa Magistrado De LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- "Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient'sDocumento4 pagine"Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient'sAllisson BeckersNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento2 pagineImpaired Physical MobilityAl-Qadry NurNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For Mi PainDocumento2 pagineNCP For Mi PainKahMallariNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Ineffective Cardiopulmonary PerfusionDocumento3 pagineNCP Ineffective Cardiopulmonary PerfusionjamiemapanaoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Tissue PerfusionDocumento4 pagineNCP Tissue PerfusionLisa Tandog100% (1)
- Rufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Documento6 pagineRufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For CTTDocumento1 paginaNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Icu-CcuDocumento6 pagineNCP Icu-CcuJohn CenasNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain Injury Nursing CareDocumento1 paginaBrain Injury Nursing CareEm Castillo50% (2)
- Nursing Diagnosis Scientific ExplanationDocumento9 pagineNursing Diagnosis Scientific ExplanationMarisol Dizon100% (1)
- A Nursing Care Plan VaDocumento3 pagineA Nursing Care Plan VaArianne Paola QuindoyNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento3 pagineNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- NCP 1Documento7 pagineNCP 1Roldan VidadNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP (Riskforimpairedskinintegrity)Documento3 pagineNCP (Riskforimpairedskinintegrity)Ma Kaye Gelizabeth Corpuz-DauloNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For StokeDocumento5 pagineNCP For StokeMemedNessuna valutazione finora
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDocumento3 pagineDisturbed Sensory PerceptionJoenna GaloloNessuna valutazione finora
- Deficit)Documento2 pagineDeficit)Lee DeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocumento3 pagineImpaired Urinary EliminationDenise Republika100% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 pagineIneffective Tissue PerfusionClaidelyn De Leyola100% (1)
- Chicken-Pox Concept MapDocumento4 pagineChicken-Pox Concept MapElle0% (1)
- Risk For Impaired SwallowingDocumento3 pagineRisk For Impaired SwallowingCalimlim Kim100% (1)
- Block 2 Assignment Edited Catherine Ruguru SamsonDocumento12 pagineBlock 2 Assignment Edited Catherine Ruguru Samsonmoses karituNessuna valutazione finora
- Jade R. Dinolan BSN-4: Diagnosi SDocumento5 pagineJade R. Dinolan BSN-4: Diagnosi SJhade Relleta100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 pagineNCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionAngelo ︻╦̵̵͇̿̿̿̿╤── Bulacan50% (6)
- Maintaining normal intracranial pressure through physiological mechanismsDocumento25 pagineMaintaining normal intracranial pressure through physiological mechanismsRAFNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocumento3 pagineIneffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionHanya Bint Potawan88% (25)
- Brain DeathDocumento6 pagineBrain DeathmohamedelsayedelmenyawyNessuna valutazione finora
- Xix RecommendationsDocumento2 pagineXix RecommendationsKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- Cva PADocumento6 pagineCva PAKarel Lu100% (1)
- Member's Data Form (MDF) PAG-IBIGDocumento3 pagineMember's Data Form (MDF) PAG-IBIGSimplyIreneNessuna valutazione finora
- Instrumentation FinalDocumento1 paginaInstrumentation FinalKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypertension CKD AnemiaDocumento128 pagineHypertension CKD AnemiaKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- MercuryDocumento2 pagineMercuryKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study D5W2Documento3 pagineDrug Study D5W2Girlie Jane Sevillano RN100% (2)
- The Renal Plays A Pivotal Role in The Clearance and Degradation of Circulating Insulin and Is Also An Important Site of Insulin ActionDocumento11 pagineThe Renal Plays A Pivotal Role in The Clearance and Degradation of Circulating Insulin and Is Also An Important Site of Insulin ActionKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- Leadership ReadingDocumento5 pagineLeadership ReadingKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- JasonfileDocumento7 pagineJasonfileKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Be An Effective Charge NurseDocumento4 pagineHow To Be An Effective Charge NurseKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- Komunidad 3,4,5,6 REVISEDDocumento7 pagineKomunidad 3,4,5,6 REVISEDKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic Syndrome-PathoDocumento6 pagineNephrotic Syndrome-PathoKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- Woman's Symptoms and Hospital Treatment for Abdominal PainDocumento2 pagineWoman's Symptoms and Hospital Treatment for Abdominal PainKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Exam Ch2Documento12 pagineSample Exam Ch2wikidoggNessuna valutazione finora
- Stress GASDocumento6 pagineStress GASKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- The Human Brain Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento14 pagineThe Human Brain Anatomy and PhysiologyKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM 103 Endo, Meta, GI SyllabusDocumento8 pagineNCM 103 Endo, Meta, GI Syllabusjongmartinez100% (1)
- Hepatic DisordersDocumento5 pagineHepatic DisordersKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- Hung Ting TonDocumento6 pagineHung Ting TonKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lung ActivitiesDocumento5 pagineLung ActivitiesKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- CataractDocumento6 pagineCataractKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- EtiologyDocumento2 pagineEtiologyKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- CVA Drug StudyDocumento51 pagineCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP AgnDocumento2 pagineNCP AgnMichael Vincent DuroNessuna valutazione finora
- Nicard I PineDocumento3 pagineNicard I PineKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- CVD Atlas 01 Types PDFDocumento1 paginaCVD Atlas 01 Types PDFroykelumendekNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 205 Lecture 5: Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids (Derived From Voet, 2011)Documento37 pagineChem 205 Lecture 5: Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids (Derived From Voet, 2011)Rab BaloloyNessuna valutazione finora
- Trimestral Exam First GradeDocumento3 pagineTrimestral Exam First Gradeemmanuel espinozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Mechanical Ventilation 7th Edition J M CairoDocumento11 pagineTest Bank For Mechanical Ventilation 7th Edition J M CairoJohnCampbellyacer100% (27)
- Biological Level of Analysis Research GuideDocumento45 pagineBiological Level of Analysis Research GuidePhiline Everts100% (2)
- Four Directions Tai-Chi Form Aka Five Elements Tai-ChiDocumento21 pagineFour Directions Tai-Chi Form Aka Five Elements Tai-ChiDiana IleaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz ReviewerDocumento8 pagineQuiz ReviewerCai PascualNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine - FRCEM SuccessDocumento110 pagineEndocrine - FRCEM SuccessskNessuna valutazione finora
- UQU SLE CORRECTED FILE by DR Samina FidaDocumento537 pagineUQU SLE CORRECTED FILE by DR Samina Fidaasma .sassi100% (1)
- CurcuminaDocumento60 pagineCurcuminaLuis Armando BuenaventuraNessuna valutazione finora
- HEMOLYTIC ANEMIAS AND ACUTE BLOOD LOSS: CAUSES, SIGNS, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENTDocumento4 pagineHEMOLYTIC ANEMIAS AND ACUTE BLOOD LOSS: CAUSES, SIGNS, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENTAjay Pal NattNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9 &10 - Gene ExpressionDocumento4 pagineChapter 9 &10 - Gene ExpressionMahmOod GhNessuna valutazione finora
- Jump Height Loss As An Indicator of Fatigue During Sprint TrainingDocumento11 pagineJump Height Loss As An Indicator of Fatigue During Sprint TrainingLevyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Ontogenetic Basic of Human AnatomyDocumento18 pagineThe Ontogenetic Basic of Human AnatomymeseniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Q and A DactylosDocumento56 pagineQ and A DactylosJUNN REE MONTILLA100% (2)
- 4 - Subphylum UrochordataDocumento12 pagine4 - Subphylum UrochordataStudent 365Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pathological Postpartum Breast Engorgement Prediction, Prevention, and ResolutionDocumento6 paginePathological Postpartum Breast Engorgement Prediction, Prevention, and ResolutionHENINessuna valutazione finora
- Rhopalocera (Butterfly) : FunctionsDocumento18 pagineRhopalocera (Butterfly) : FunctionsChris Anthony EdulanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Importance of Anaerobic ExerciseDocumento13 pagineThe Importance of Anaerobic Exerciseapi-357421918Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Motor System and Its Disorders LectureDocumento51 pagineThe Motor System and Its Disorders LectureKaito Noburu ShinNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Examination ChecklistDocumento5 paginePhysical Examination Checklistsamhie21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Microtome and ultrastructure microscopy guideDocumento360 pagineMicrotome and ultrastructure microscopy guidesquishyboitae33% (3)
- Renal Arteries PDFDocumento18 pagineRenal Arteries PDFServo LedNessuna valutazione finora
- Nontoxic Nodular GoiterDocumento7 pagineNontoxic Nodular GoiterKayshey Christine ChuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Full PDFDocumento399 pagineFull PDFTeresa Marie Yap CorderoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mphil Bio-Chemistry ProjectDocumento98 pagineMphil Bio-Chemistry ProjectBalaji Rao NNessuna valutazione finora
- 7/23/2016 Cristina S. Nebres Mindanao State University at Naawan 1Documento32 pagine7/23/2016 Cristina S. Nebres Mindanao State University at Naawan 1Laila UbandoNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 Bartek Janacek Summative ProfileDocumento4 pagine2022 Bartek Janacek Summative Profilenavishana MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Illusions The Magic Eye of PerceptionDocumento12 pagineIllusions The Magic Eye of PerceptionArctic Illusion100% (2)
- Surya NamaskarDocumento2 pagineSurya NamaskarDipkumar Patel100% (2)
- General Biology 2 Organs and Organ System: APRIL 13, 2021Documento6 pagineGeneral Biology 2 Organs and Organ System: APRIL 13, 2021Patrick VerroyaNessuna valutazione finora