Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
MS Office 2007 - Notes
Caricato da
manuDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
MS Office 2007 - Notes
Caricato da
manuCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Hardware concepts
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PRIMARY COMPONENTS OF COMPUTER SYSTEM
INPUT DEVICES
PROCESSING
MOTHERBOARD
MEMORY
SECONDARY STORAGE DEVICES
OUTPUT DEVICES
SOFTWARE
SHORTCUT KEY
Hardware concepts
- 2 -
Introduction to Computers
The computer as we know it is a group of pieces of hardware put together
to get a job done faster. To accomplish its various tasks, the computer is made of
different parts, each serving a particular purpose almost independent of, or in
conjunction with, other parts. You don't necessarily need to know how these parts
operate, at least not at this time, but you should be aware of their co-dependence to
take advantage of their various characteristics.
The "computer" is an ensemble of different machines that you will be using to
get your job done. A computer is primarily made of the Central Processing Unit
(usually referred to as the computer), the monitor, the keyboard, and the mouse.
Other pieces of hardware, commonly referred to as peripherals, can enhance or
improve your experience with the computer.
To use the computer, the first thing you should find is the power switch that is
used to put the unit on. Nowadays, it is usually located in front of the computer.
Pushing it would start the computer. Therefore, before using a computer, you must
first turn it on.
Practical Learning: Starting a Computer
To turn the computer on, find its Power button and press it
When the computer starts, it will show welcome screen
Click on Trainees
BASICS OF COMPUTERS
O Hardware Devices
O Software Program/instructions
O Heart ware-- Users or Personnel
Data is a collection of facts figures supplied to the computer to generate meaningful
information.
Data cycle- Input Data Processing Meaningful Information
Computer Hardware consists of the devices & the equipment that make up a
computer system. Stated simply, if you can touch it, it is computer Hardware.
The three primary functions of a computer system are INPUT, PROCESS &
OUTPUT. Before information can be processed & output, the data must be entered
into the system. This data before it is processed is referred to as input data.
Hardware concepts
- 3 -
Since the input data is the beginning point for the processing, the output can be no
more accurate than the input. Bad input data gives us the term GIGO Garbage in
Garbage out. If you input Garbage or incorrect data into the computer system you
should expect garbage or incorrect information as output from the computer system.
INPUT DEVICES
Input devices allow you to enter raw data into the computer system. The function of
any input device is to convert an electronic form that can be understood by the
computer. Input devices can be divided into three major categories: -
(I) The first category is touch devices
1. Keyboard: is used to for typing
2. Mouse: The mouse is one of several pieces of hardware you will be using
when interacting with the computer. It works by its pointing on the screen.
A mouse is primarily made of three parts: the buttons, the handling area, and the
rolling object. By default, a mouse has two buttons: left and right. Most mice
nowadays are also equipped with a wheel on top:
a. Left mouse button : For normal selection
b. Right Mouse button : For context sensitive menu options
Mouse movement
a) Click Selection of object
b) Double click - Object / window opened
c) Drag & Drop - For dragging the object & fix up at other place.
3) Touch Screen
4) Light pen
(II) Visual or optical devices
a) Bar code Scanner
b) Optical mark readers (OMR)
c) Magnetic ink character Recognition (MICR)
(III) Sound devices
d) Microphone
PROCESSING
The key to all the processing that occurs is the Central Processing Unit
(CPU); which is often referred to as a "Computer on a chip" because it is contained
on an electronic circuit chip. The CPU is housed in the system unit. The system unit
Hardware concepts
- 4 -
is a cabinet that houses many electronic components & serves as the main
connecting point for other devices.
C.P.U.
The most important part, also called the Central Processing Unit or CPU. It is
made up of two components; the control unit & the Arithmetic logical unit. These
pieces, inside of the box, perform the jobs of the computer. One of the assignments
of this unit is to join all the other pieces connected to it. Another job of this unit is to
perform calculations, exactly the same types of calculations you were performing in
primary school, except that this box can handle them very (extremely) fast, so fast
that there is no human being who can match that speed. Besides the calculations,
this unit also performs other assignments that it receives from various sources
including you and the external units that are connected to the CPU.
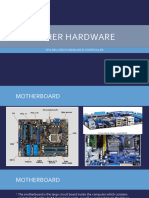
THE MOTHER BOARD
The main electronic circuit board, located in the system unit cabinet called the
motherboard. The C.P.U. chip is plugged into a special socket on the main electronic
circuit board and it is connected to every device installed in the system because the
C.P.U. handles all operations in the computer.
The Motherboard also provides connection for the Computer's keyboard, disk
drives, monitor and other devices. It also provided various expansions socket on the
main electronic circuit board and it is connected to every device installed in the
system because the C.P.U. handles all operations in the Computer.
The Motherboard also provided connection for the computer's keyboard, disk
drives, monitor and other devices. It also provides various expansions socket or
ports that allow you to plug in special devices such as a mouse or printer. It also
provides special sockets where additional memory or primary storage can be added.
MEMORY
It is the place or area that holds programme & the data being manipulated while
they are being used. There are two types of memory:-
- Primary or Main Memory.
- Secondary or permanent memory.
Primary or Main Memory: There are two types of primary memory.
1. RAM (Random Access Memory)
It is volatile or temporary memory. It will lose its contents when the computer's
power is shut off. The purpose of RAM is to hold programs & data while they are in
use. It is also known as Read/Write memory.
Hardware concepts
- 5 -
2. ROM (Read only Memory)
It is non-volatile or permanent memory. It always holds same data, the data in
them cannot be changed. The data in these chips can only be read & used.
Computer needs ROM so that it knows what to do when the power is first turned on
ROM contains a set of startup instructions, which ensure that the rest of memory is
functioning properly, check for hardware devices & check for an operating system
on the Computer's disk drivers.
3. Cache Memory
It is a special type of high-speed memory that resides between the CPU &
RAM in a computer. It stores data and instructions that the CPU is likely to need
next. The CPU can retrieve data or instructions more quickly from cache that it can
from RAM or a disk.
SECONDARY MEMORY:
Once data is input it needs to be storage of data requires two components:
the storage device & the storage media. The most common storage devices are
floppy drives & Hard disk drives & CD.
1. Hard Disk
The primary object used to hold information in a computer is called the hard
drive. Hard disk is non-flexible, non-removable secondary storage device. They are
built into the computer. They can store very large amount of data & are also much
faster than floppy.
It is made of a pack of aluminum platters and every platter has read/write
head associated. Hard disk is enclosed in a metallic box which has vacuum inside.
It is not portable
2. Floppy Disk
Floppy disks are small & portable. There are two sizes in which a floppy
comes.
5 Capacity 1.22 MB
3 Capacity 1.44 MB
It is made up of myler flexible plastic & it is coated with iron oxide (Fe
2
O) and
enclosed in a plastic jacket. Floppy disk made up of tracks (80) and sectors to store
data.
3. CD
CD Stands for Compact Disk. The primary use of this type of media is for
storing huge amount of pre-recorded data. It can hold 700 MB of data
Hardware concepts
- 6 -
4. DVD
DVD is Short for digital versatile disc or digital video disc, a type of optical
disk technology similar to the CD-ROM. A DVD holds a minimum of 4.7GB and
maximum 17 GB of data, enough for a full-length movie. DVDs are commonly used
as a medium for digital representation of movies and other multimedia presentations
that combine sound with graphics.
5. USB flash drive
It is a small, portable flash memory card that plugs into a computers USB port
and functions as a portable hard drive. USB flash drives are touted as being easy-to-
use as they are small enough to be carried in a pocket and can plug into any
computer with a USB drive. USB flash drives have less storage capacity than an
external hard drive, but they are smaller and more durable because they do not
contain any internal moving parts.
USB flash drives also are called thumb drives, jump drives, pen drives, key
drives, tokens, or simply USB drives.
STORAGE CAPACITY
Bit - 0 or 1
8 bits 1 byte
1024 bytes 1 KB
1024 KB 1 MB
1024 MB 1 GB
C: Parent folder or Root folder represents Hard Disk
A: folder for floppy 3
B: Second floppy 5
D: Folder for CD-ROM
OUTPUT DEVICES
Output is the third step in the Input-Process-Output cycle. In order to output
information you must have an output device. There are many different types of
output devices. We will group these output devices into three categories:-
- Visual, touch & sound
1. VISUAL
a) Monitor
O CRT (Cathode Ray Tube)
O LCD (Liquid Crystal Display).
Hardware concepts
- 7 -
CRT model requires continues supply of electricity whereas LCD are used in
laptop, palmtops etc and power is given by battery. It is portable.
PROPERTIES
1. Size- Two commonly used sizes are 15'' & 17'' diagonally.17'' are required for
designing software.
2. Resolution No. of pixels on the screen. Pixel is the Phosphor dot on
screen.
3. Refresh rate No. of times the electron gun strikes at phosphor dot.
Monitor communicates to the CPU using video controller card called VGA (Video
Graphic Adapter)
b) Screen Image Projectors: Are used to display the computers images on a
void projection screen. These devices are excellent for presentations &
demonstrations.
2) TOUCH
a) Printer: Are commonly used Output device. They provide information in a
permanent readable form. They produce printed output of results, programs & data.
Printers are classified as follows:
1. Character printer that prints one character of the text at a time.
2. Line printer that prints one line of the text at a time.
3. Page printer that prints one page of a text at a time.
There is one more classification, which depends on the technology used in the
manufacture.
1. Impact printers Use electro mechanical mechanism that causes hammers
or pins to strike against a ribbon and paper to print the text. Speed
measured on the basis of dpi dots per inch
2. Non Impact Printers Use thermal chemical electro static laser beam or
ink jet technology for printing the text. Speed measured in PPM pages per
minute. They are faster than impact printer but can produce single copy of
the text where as impact printer produces multiple copy of the text.
b) Plotters
They are use to produce precise a good quality graphics and drawings under
computers control. They use ink pen or inkjet to draw graphics or drawings.
Plotters are used by engineers, Drafters, Mapmakers, architects & other
professionals who require precise detail in their graphic output.
Hardware concepts
- 8 -
3. Sound
a. Speaker
SOFTWARE
Are the electronic instructions that tell the Computer what to do? There are two types
of software
1. System software
2. Application software
The system software includes operating system, which is a collection of
programs, which controls the overall operation of a computer. These programs
written to assist humans in the use of the Computer system. These programs are
general programs.
An operating system is a collection of programs that helps the computer
manage its resources and that acts as the interface between the user and the
computer. The three main functions of an operating system are to control hardware
manage information and run application software. Hardware control consists of
coordinating the different parts of the computer system so that all parts work
together, this includes coordinating the flow of data (to and from the system unit and
to and from input and output devices like the keyboard and the display screen,
information, management consists of controlling computer system resources and
includes providing the means to manage and store information on the computer
running application software consists of loading programs designed for specific uses,
such as Word Processing, Graphics and spreadsheet analysis. Ex: DOS, Window
98, Windows NT, UNIX, Linux, OS/2.
System software user interface E.g. O.S. Dos, windows, UNIX, Linux
Application software E.g. MS Office, AutoCAD, Adobe Photoshop
OPERATING SYSTEM UTILITIES:
1. User interface
2. Memory management
3. Handling system interrupts
4. I/O Device management
Application Software: is designed for specific uses or applications such as word
processing, graphics or spreadsheet analysis.
MICROSOFT WINDOWS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
FILES & FOLDERS OVERVIEW
DESKTOP COMPONENTS
CONTROL PANEL
CREATE FILE & FOLDER
COPYING AND MOVING
RENAMING & DELETING
CREATING SHORTCUTS
CONTROL PANEL
SEARCH FEATURE
Windows
- 10 -
With Windows you have faster access to information, and you are able to accomplish
tasks more quickly and easily.
Windows makes it easier to:
Work with files.
Find information.
Personalize your computing environment.
Work on the Web.
Work remotely.
FILES AND FOLDERS OVERVIEW
Most Windows tasks involve working with files and folders. File: A complete,
named collection of information, such as a program, a set of data used by a
program, or a user-created document. A file is the basic unit of storage that enables
a computer to distinguish one set of information from another. It is a collection of
data that a user can retrieve, change, delete, save, or send to an output device, such
as a printer or e-mail program. Folder: - A container for programs and files in
graphical user interfaces, symbolized on the screen by a graphical image (icon) of a
file folder. A folder is a means of organizing programs and documents on a disk and
can hold both files and additional folders
Windows uses folders to provide a storage system for the files on your
computer, just as you use manila folders to organize information in a filing cabinet.
Folders can contain many different types of files, such as documents, music,
pictures, videos, and programs. You can copy and move files from other locations,
such as another folder, computer, or the Internet, to folders you create. You can
even create folders within folders.
The work you do with files and folders falls into three categories:
Organizing and managing files and folders
You can perform basic file and folder tasks, such as creating, deleting, copying, and
moving files and folders, and more advanced tasks, such as changing file and folder
properties and managing shared folders
Searching for files and folders
You can narrow the focus of your file and folder searches by including additional
search criteria, such as the date, type, file size, or case sensitivity. You can also
broaden the scope of your file searches by using wildcard characters, and specifying
literal text or regular expressions.
DESKTOP- is the first screen in Windows OS
Windows
- 11 -
DESKTOP COMPONENTS-
My computer My Computer is used to explore the content of your computer and to
do other routine things.
My documents - is the default folder for all the application files.
Recycle Bin- When you get rid of (delete) some things on your computer (folders or
files), they go to an area called the Recycle Bin where you still have a chance of
recalling (retrieving or restoring) them.
My Network Places: You use My Network Places to communicate with other
computers if yours is part of a network.
Internet explorer- It is a Web Browser to view and explore websites.
TASK BAR: - It shows how many programs are opened or the tasks in hand. You can
click the taskbar buttons to switch between programs. Task bar is movable by
dragging it with mouse pointer.
TO OPEN AN EXISTING FILE OR FOLDER
1. Open My Computer (Right Click on its Icon Click on Open)
2. Right-click the drive that contains the file Click on Open
3. Right-click the file or folder you want to open Click on Open
TO CREATE A NEW FOLDER
1. Open My Computer (Right Click on its Icon click on Open)
2. Open desired drive (Right click on it (D: or E:) Click on Open)
3. Right click on blank area, go to New
4. Click on Folder
5. Type a name for the new folder
6. Press ENTER key
TO CREATE NEW FILE
1. Open your own folder
2. Right click on blank area
3. Go to New
Windows
- 12 -
4. Click on Microsoft Office Word OR Microsoft Office Excel OR Microsoft Office
PowerPoint
5. Type appropriate name for the file
6. Press ENTER key
TO COPY OR MOVE A FILE OR FOLDER
1. Open My Computer (Right Click on its Icon Click on Open)
2. Open desired drive (Right click on it Click on Open)
3. Right Click the file or folder you want to copy or move.
4. Click Copy ( or Press Ctrl + C) OR Cut (or Press Ctrl + X)
5. Right click the folder or disk where you want to copy or move the item.
6. Click Paste.
Notes
To select consecutive files or folders to copy or move, click the first item,
press and hold down SHIFT, and then click the last item.
To select files or folders that are not consecutive, press and hold down CTRL,
and then click each item.
You can also move a file or folder by dragging it to the desired location.
TO COPY A FILE OR FOLDER TO A FLOPPY DISK OR PEN DRIVE
1. Insert the floppy disk into the disk drive or attach Pen drive in appropriate port
2. Open My Computer or Windows Explorer.
3. Right click the file or folder you want to copy.
4. Point to Send To
5. Click 3 Floppy (A) or USBPRO (pen drive)
To copy CDs or Pen Drives or Floppys contents to your Hard disk:
1. Insert CD in CD Drive OR Floppy in Floppy Drive OR attach Pen Drive to
appropriate USB Port and Open My Computer
2. Right click on CD drive OR Floppy Drive OR Pen Drive and Click on Open
3. Right click on desired folder(s) or file(s) to be copied
4. Click on Copy (or Press Ctrl + C to copy)
5. Switch to Hard disc (D: or E:)
Windows
- 13 -
6. Right click on destination folder
7. Click on Paste ( or Press Ctrl + V to paste copied item)
TO CHANGE THE NAME OF A FILE OR FOLDER
1. Open My Computer
2. Right click the file or folder you want to rename.
3. Click Rename.
4. Type the new name, and then press ENTER.
Notes
You do not need to open the file or folder to rename it.
A file name can contain up to 255 characters, including spaces. However, it is
not recommended that you create file names with 255 characters. Most
programs cannot interpret extremely long file names. File names cannot
contain the following characters: \ /: *? " < > |
TO DELETE A FILE OR FOLDER
1. Open My computer
2. Right click the file or folder you want to delete.
3. Click Delete (or select the file to be deleted and press delete key)
4. Click on Yes or press Enter
Note: - When you delete a file or folder it will go to Recycle Bin.
TO DELETE OR RESTORE FILES IN THE RECYCLE BIN
1. On the desktop, Right click on Recycle Bin Click on open
2. Do one of the following:
To restore an item, right-click it, and then click Restore.
To delete an item, right-click it, and then click Delete.
To delete all of the items, on the File menu, click Empty Recycle Bin.
Notes:
Deleting an item from the Recycle Bin permanently removes it from your
computer. Items deleted from the Recycle Bin cannot be restored.
Restoring an item in the Recycle Bin returns that item to its original location.
Windows
- 14 -
To retrieve several items at once, hold down CTRL, and then click each item
that you want to retrieve. When you have finished selecting the items that you
want to retrieve, on the File menu, click Restore.
If you restore a file that was originally located in a deleted folder, the folder is
recreated in its original location, and then the file is restored in that folder.
TO SEARCH FOR A FILE OR FOLDER
1. Click Start
2. Click Search.
3. Click All files and folders.
4. Type All or part of file or folder name, or type a Word or phrase that is in the
file.
5. If you do not know either piece of information or want to narrow your search
further, select one or more of the remaining options:
a. In Look in, click the drive, folder, or network you want to search.
b. Click When was it modified? to look for files that were created or
modified on or between specific dates.
c. Click What size is it? to look for files of a specific size.
6. Click Search.
Notes: If you get too many results, try using additional search criteria to make your
search more specific.
CREATING A SHORTCUT
A shortcut is a quick way to start a program or open a file or folder without
having to go to its permanent location in Windows Explorer. Shortcuts are especially
useful for programs, files, and folders you use frequently
TO PUT A SHORTCUT ON THE DESKTOP
1. In My Computer or Windows Explorer, click the item, such as a file or folder for
which you want to create a shortcut
2. Right Click on its Icon
3. Click on Send to
4. Click on Desktop (Create Shortcut)
TO CREATE PROGRAMS OR APPLICATIONS SHORTCUT:
1. Click on Start Button
Windows
- 15 -
2. Go to All Programs
3. Point to desired program of which you want to create shortcut.
4. Right click on it
5. Click on Send to
6. Click on Desktop(create shortcut)
CONTROL PANEL: It manages Date& Time settings, Regional Settings, add/Removes
Hardware and soft wares.
Start Control Panel OR Start Settings Control Panel
TO CHANGE DATE FORMAT FROM CONTROL PANEL:
1. Click Start button
2. Click Control Panel
3. Double click Regional and Language Options
4. Click on Customize button
5. Click on Date heading
6. Select Short Date Format and if needed change it according to your
requirement.
7. Select Long Date Format and if needed change it according to your
requirement.
8. Click on Apply button
9. Click on OK
10. Again click on OK
TASK MANAGER:
Task Manager provides information about programs and processes running on your
computer. You can end running task which are not responding due to which your
computer stops working (Hang).
USING TASK MANAGER:
1. Press Ctrl + Alt + Del OR
Right click on Taskbars blank area and then click on Task Manager
2. The Windows Task Managers window will appear
Windows
- 16 -
3. Click on Application tab, the list and status of running programs will be
displayed
4. Click on program name which is not responding under Task heading
5. Click on End Task button at the bottom of Task Managers window
6. Close the Task Manager
WINDOWS TERMS:
Graphical User Interface:- A design that uses graphical objects called ICONS,
Which represent the items you can select to activate the feature.
Abbreviated GUI (pronounced GOO-ee). A program interface that takes advantage
of the computer's graphics capabilities to make the program easier to use. Well-
designed graphical user interfaces can free the user from learning complex
command languages.
Graphical user interfaces feature the following basic components:
- Desktop : The area on the display screen where icons are grouped is often
referred to as the desktop because the icons are intended to represent real
objects on a real desktop.
- Windows: You can divide the screen into different areas. In each window,
you can run a different program or display a different file. You can move
windows around the display screen, and change their shape and size at will.
- Menus : Most graphical user interfaces let you execute commands by
selecting a choice from a menu.
- Insertion Point or Cursor:- A solid blinking vertical line that is displayed in
areas where you enter text. It shows you where the next character you type
will appear.
- Multitasking:- The capability of the operating system to run multiple
application and inserted or stored in another application.
- Clipboard:- An area of memory that temporarily stores information to be
copied or moved within or between files and applications.
Windows
- 17 -
KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS
GENERAL KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS
Press To
CTRL+C Copy.
CTRL+X Cut.
CTRL+V Paste.
CTRL+Z Undo.
DELETE Delete.
SHIFT+DELETE
Delete selected item permanently without
placing the item in the Recycle Bin.
CTRL while dragging an item Copy selected item.
CTRL+RIGHT ARROW
Move the insertion point to the beginning of the
next word.
CTRL+LEFT ARROW
Move the insertion point to the beginning of the
previous word.
CTRL+DOWN ARROW
Move the insertion point to the beginning of the
next paragraph.
CTRL+UP ARROW
Move the insertion point to the beginning of the
previous paragraph.
CTRL+SHIFT with any of the
arrow keys
Highlight a block of text.
SHIFT with any of the arrow
keys
Select more than one item in a window or on the
desktop, or select text within a document.
CTRL+A Select all.
F3 Search for a file or folder.
ALT+F4 Close the active item, or quit the active program.
CTRL+F4
Close the active document in programs that
allow you to have multiple documents open
simultaneously.
ALT+TAB Switch between open items.
F6
Cycle through screen elements in a window or
on the desktop.
CTRL+ESC Display the Start menu.
ALT+Underlined letter in a
menu name
Display the corresponding menu.
Underlined letter in a command
name on an open menu
Carry out the corresponding command.
F10 Activate the menu bar in the active program.
Windows
- 18 -
RIGHT ARROW
Open the next menu to the right, or open a
submenu.
LEFT ARROW
Open the next menu to the left, or close a
submenu.
BACKSPACE
View the folder one level up in My Computer or
Windows Explorer.
ESC Cancel the current task.
WINDOWS EXPLORER KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS
Press To
END
Display the bottom of the active
window.
HOME Display the top of the active window.
NUM LOCK+ASTERISK on
numeric keypad (*)
Display all subfolders under the
selected folder.
NUM LOCK+PLUS SIGN on
numeric keypad (+)
Display the contents of the selected
folder.
NUM LOCK+MINUS SIGN on
numeric keypad (-)
Collapse the selected folder.
LEFT ARROW
Collapse current selection if it's
expanded, or select parent folder.
RIGHT ARROW
Display current selection if it's
collapsed, or select first subfolder.
MICROSOFT WORD 2007
TABLE OF CONTENTS
BASIC FILE OPERATIONS
CREATING, SAVING, CLOSING AND OPENING A FILE
EDITING A DOCUMENT
CUT, COPY, PASTE, SPELLING & GRAMMAR CHECK,
FIND AND REPLACE AND CHANGE CASE
FORMATTING
FONT, PARAGRAPH AND PAGE FORMATTING
WORKING WITH TABLES
MAIL MERGE
VIEWS IN WORD
PASSWORD PROTECTION
PRINTING
Microsoft Word is a word processing
*
application used to create, edit, format & print
a document. MS Word file is commonly known as document file and extension of
document file is .docx
*Word Processing includes typing in text and manipulating it, so as to give a very
systematic and organized look to your document.
MS Word provides many features in word processing like correcting spelling
mistakes and grammatical errors, align text within the margins offers a variety of font
styles and font sizes, shows a preview of the text that you have typed in or wanted to
print.
HOW TO OPEN MS WORD:
1. Click Start button
2. Point to All Programs
3. Point to Microsoft Office
4. Click Microsoft Office Word 2007
Introducing the new interface
There is a new look for Office Word 2007, the new Office Fluent user interface,
which replaces menus, toolbars, and most of the task panes from earlier versions of
Word with a single mechanism that is simple and discoverable. The new Office
Fluent user interface is designed to help you be more productive in Word, more
easily find the right features for various tasks, discover new functionality, and be
more efficient.
Office Fluent user interface
The primary replacement for menus and toolbars in Office Word 2007 is the Ribbon,
a component of the Office Fluent user interface. Designed for easy browsing, the
Ribbon consists of tabs that are organized around specific scenarios or objects. The
controls on each tab are further organized into several groups. The Office Fluent
Ribbon can host richer content than menus and toolbars can, including buttons,
galleries, and dialog box content.
1. Tabs are designed to be task-oriented.
2. Groups within each tab break a task into subtasks.
3. Command buttons in each group carry out a command or display a menu of
commands.
Tabs that appear only when you need them
In addition to the standard set of tabs that you see on the Ribbon whenever you start
Office Word 2007, there are two other kinds of tabs, which appear in the interface
only when they are useful for the type of task that you are currently performing.
Contextual tools Contextual tools enable you to work with an object that you
select on the page, such as a table, picture, or drawing. When you click the object,
the pertinent set of contextual tabs appears in an accent color next to the standard
tabs.
Program tabs Program tabs replace the standard set of tabs when you switch to
certain authoring modes or views, including Print Preview.
Menus, toolbars and other familiar elements
In addition to tabs, groups, and commands, Office Word 2007 uses other elements
that also provide paths for accomplishing your tasks. The following elements are
more like the menus and toolbars that you are already familiar with from earlier
versions of Word.
Microsoft Office Button: This button is located in the upper-left corner of the Word
window and opens the menu shown here.
Quick Access Toolbar The Quick Access Toolbar is located by default at the top
of the Word window and provides quick access to tools that you use frequently. You
can customize the Quick Access Toolbar by adding commands to it.
Dialog Box Launchers Dialog Box Launchers are small icons that appear in some
groups. Clicking a Dialog Box Launcher opens a related dialog box or task pane,
providing more options related to that group.
Horizontal ruler or scale to set left & right page margins and Indents (Paragraph
margins)
Text area: blank area for writing text or inserting other elements like pictures, tables
etc. Text area has vertical blinking bar called Cursor or Insertion point where the
typed text appears.
Vertical ruler at the left side of Text area
Vertical scroll bar at the right side of Text area used to scroll a document upward
and downward.
Status bar at the bottom most of Words window: displays information about current
position of Cursor in a document and on/off status of some keys.
TO CREATE NEW FILE:
The following procedure creates a new, blank document.
1. Click the Microsoft Office Button, and then click New.
2. Click on Blank Document
3. Click on Create button at the bottom right
OR
1. Press Ctrl + N
TO SAVE A FILE IN YOUR OWN FOLDER:
1. Press Ctrl + S OR Click the Microsoft Office Button, Click Save As, the Save
As window will appears
2. Type appropriate name for the file inside File Name Box at the bottom
3. Click inside Save in Box at the top, Click desired drive letter C: or D:
4. Double click on your own folder
5. Click on Save Button at the Bottom left
TO CLOSE A FILE CURRENT FILE:
1. Click the Microsoft Office Button, Click Close
OR
1. Click on button at the upper right of the window
TO OPEN AN EXISTING FILE:
1. Press Ctrl + O OR Click the Microsoft Office Button, Click Open, the open
window will appears
2. Click inside Look in box at the top, click desired drive letter C: or D:
3. Double click on your own folder
4. Double click on File name to be opened
EDITING
Making corrections in an existing document is called editing. Like deleting existing
text, inserting new text between words, spelling and grammar checking, find old
words and replace new words in place of old words, copy or move block of text to
another location in a document.
You can undo the very last action you took by just clicking Undo on the Quick
Access toolbar or press Ctrl + Z.
If you later decide you didn't want to undo an action, click Redo on the Quick
Access toolbar or press Ctrl + Y.
INSERTING TEXT
There are two modes of inserting text
1. Insert mode: insert new characters between existing text
2. Overtype mode: replaces existing characters as you type
The OVR indicator in Status bar at the bottom indicates the type of mode using the
insert key on the keyboard, we can switch between the modes using Insert key.
COPY OR MOVE TEXT
Copy command is used to create duplicate of selected text and Cut command is
used to move selected text from its original location to another location.
TO COPY OR MOVE TEXT:
1. Select desired text (text to be copied) using mouse or Shift and Four arrow
keys (left, right, up & down)
2. Click HOME Tab
3. In the CLIPBOARD Group, Click Copy / Cut OR Press Ctrl + C to Copy and Ctrl
+ X to Cut
4. Place the cursor where you want to Paste the specified text.
5. Click Paste tool OR Press Ctrl + V
CHECK SPELLING AND GRAMMAR ALL AT ONCE
You can check spelling and grammar automatically as you type or all at once.
When the spelling checker encounters a word it doesn't recognize, it
determines which words in its dictionary are similarly spelled and displays a list of
those words, with the most likely match highlighted. The contents of the list are
determined only by spelling, so any instances of terms that seem inappropriate in
context are completely coincidental.
Note: MS Word indicates spelling mistakes with Red Wavy Underline and Grammar
mistakes with Green Wavy Underline.
1. Select the desired text (text to be checked).
2. Click REVIEW Tab
3. In the PROOFING group click on Spelling and Grammar command button OR
Press F7 function key.
4. Spelling and Grammar window will appears, Misspelled word and grammar
error will displayed and also the correct nearest suggestions. It also displays type
of mistake.
5. Select the word from the Suggestions list
6. Either click Change. (If you want to fix the error by using one of the suggested
words.)
OR
Click Ignore Once (I want to ignore this misspelled word and move on to
the next misspelled word.)
OR
Click Add to Dictionary. (The misspelled word is actually a real word that
I use. I want all of the Microsoft Office programs
to recognize this word and not treat it as a
misspelling.)
7. Click No
FIND AND REPLACE TEXT
1. Click HOME Tab
2. In the EDITING group click Replace.
3. Type desired word in Find What box.
4. In the Replace with box, enter the replacement text.
5. Click Find Next, It will highlights the specified word, click Replace to replace
highlighted occurrence or click Find Next, or Click Replace All to replace
specified word in the entire document at one click.
CHANGING CASE
To change the case of selected text does the following
1. Select the text that you want to change the case of.
2. Click on HOME tab, in the FONT group, click Change Case command button, and
then click the capitalization option that you want.
Note: You can use Shift + F3 to switch between cases.
FORMATTING
Enhancing the appearance of a document to make it more attractive and readable is
called formatting. Formatting is last stage of document development. There are three
types of formatting in MS Word:-
(a) Font or Character formatting
(b) Paragraph formatting
(c) Page formatting.
Font or Character formatting
You can change looks or appearance of single character. Font formatting includes
Type of character, Color, Size and Styles of a character.
TO APPLY FONT FORMATTING:
1. Click on HOME tab
2. In the FONT group
FONT TYPE:
1) Select desired text using mouse or keyboard
2) + Click drop down arrow to displays list of Fonts
3) Click desired font to apply on selected text
FONT SIZE:
1) Select desired text using mouse or keyboard
2) + Click drop down arrow to display list of font size no.
3) Click desired no to apply on selected text
FONT STYLES:
1) Select desired text using mouse or keyboard
2) Click to bold , Click to Italic & Click
FONT COLOR:
1) Select desired text using mouse or keyboard
2) Click + to display color library
3) Click on desired color
PARAGRAPH FORMATTING
Paragraph is the total matter written without pressing enter. To create a paragraph
press enter key. Paragraph formatting means formatting apply to the entire
paragraph.
ALIGNMENT: Alignment is how text is positioned between margins. There are four
types of alignments:
1. Left Alignment - it aligns selected paragraph(s) from left side only.
2. Centre Alignment - it centers the entire paragraph between margins.
3. Right Alignment - it aligns the entire paragraph from right margin.
4. Justify - It aligns paragraph from both the sides.
TO APPLY ALIGNMENT
1. Select desired paragraph(s)
2. Click on HOME tab
3. In the PARAGRAPH group
4. Click on desired alignment command button
INDENTS: Paragraph Margins
Paragraph margins are called indents. There are four types of indents. By default all
the four paragraph margins are set at 0 on horizontal ruler.
1. Left: Indents the entire paragraph from the left page margin.
2. Right: Indents the entire paragraph from the right page margin.
3. First Line: Indents only the first line of a paragraph from the left page margin
leaving all the following lines aligned with left page margin.
4. Hanging: Indent all the following lines from the left page margin except the
first line of a paragraph.
CREATE A FIRST-LINE INDENT
1. Select the paragraph you want to indent.
2. Click on HOME tab / PAGE LAYOUT tab
3. Click the Paragraph Dialog Box Launcher of PARAGRAPH group, the
paragraph window will appear
4. Click on drop down arrow under Indent Special heading
5. Click on First line
6. Increase or decrease no. according to your requirement
7. Click on OK button at the bottom right
INCREASE OR DECREASE THE LEFT INDENT OF AN ENTIRE PARAGRAPH
1. Select the paragraph you want to change.
2. Click on HOME tab
3. In the PARAGRAPH group, click Increase Indent or Decrease Indent
Microsoft Word increases or decreases the indent by one tab stop.
OR
1. Select the paragraph you want to indent.
2. Click on PAGE LAYOUT tab
3. In the PARAGRAPH group, under Indent option increase or decrease indents
according to your requirement
BULLETS & NUMBERING
Bullets & Numbering is used to create ordered or itemized list and unordered list.
Bullets are used for unordered list. We can customize the bullet size, color and
indent. Numbering is used for ordered list to make the sequence of events. We can
continue the numbering or restart at any time.
Found on HOME tab PARAGRAPH group
To start Ordered list Click on numbering tool
To start unordered list click on bullets tool
TO FORMAT NUMBERED LIST OR BULLETED LIST
1. Select desired list
2. Click on HOME tab
3. In the PARAGRAPH group
4. Click drop down arrow of Bullets & Numbering tool
5. The Bullets or Numbers Library will appear, click desired style
ADJUSTING LINE SPACING
Line spacing is vertical distance between lines of text of a paragraph. By default line
spacing is single. You can increase line spacing that suits your need.
TO INCREASE OR DECREASE LINE SPACING:
1. Select desired paragraphs
2. Click HOME tab
3. In the PARAGRAPH group click on drop down arrow of Line spacing tool
4. Click on desired spacing
OR
1. Expand the PARAGRAPH group by clicking on Paragraph Dialog Box Launcher,
the Paragraph window will appears
2. Type value for Line Spacing inside At Text box
3. Click on OK
PAGE FORMATTING
PAGE BREAK
When you fill a page with text or graphics, Microsoft Word inserts an automatic page
break (the point at which one page end and another begins) and starts a new page.
To force a page break at a specific location, you can insert a manual page break.
To Insert New Page
1. Place the cursor at the end of the document
2. Press Ctrl + Enter
OR
1. Click where you want to start a new page
2. On the INSERT Tab
3. In the PAGES group click on Page Break command button
TO REMOVE PAGE BREAK
1. Click on VIEW tab
2. In the DOCUMENTS VIEWS group click on Draft command button
3. Page break is indicated by dotted line.
4. Click on dotted line & press delete key
GO TO A SPECIFIC PAGE
1. Click on HOME tab
2. In the EDITING group, click Find, click Go to
3. Enter desired page no in appropriate box
4. Click on Go To button OR press Enter key
5. Click on Close button
PAGE SETUP : MARGINS, PAGE ORIENTATION & PAPER SIZE
Page margins are the blank space around the edges of the page. In general, you
insert text and graphics in the printable area inside the margins (Margin: The blank
space outside the printing area on a page.). However, you can position some items
in the margins for example, headers, footers, and page numbers.
1. Click PAGE LAYOUT tab
2. In the PAGE SETUP group, Click on MARGINS command button
3. Either click on preset margin option or click on Custom Margins, the Page
Setup window will appear
4. Set Top, Bottom, Left & Right Margins that suits your requirement.
5. Change page orientation from Portrait to Landscape if required. (By default
Orientation is Portrait )
6. Click on Paper / Paper Size Tab & from the Paper Size drop down list select
required paper size.
7. Click OK
HEADER & FOOTER
Header is a line or several lines of text that automatically appears on every page in
Top Margin.
Footer is a line or several lines of text that automatically appears on every page in
Bottom Margin.
TO INSERT HEADER & FOOTER:
1. Click INSERT tab
2. In the HEADER & FOOTER group click Header / Footer
3. Either select built-in style OR click on Edit header/footer
4. The dotted line for Header / Footer will appears in Top & Bottom Margins
5. Type desired text in Header / Footer.
Note: To switch between Header & Footer Up / Down arrow can be used.
WORKING WITH TABLES
Table is a grid of Row & Columns. Table displays information in horizontal rows and
vertical columns. Intersection row & column is called cell.
To jump to the next cell Press Tab or Mouse click or Direction keys & to the previous
cell Shift + Tab.
Microsoft Word offers a number of ways to make a table. The best way depends on
how you like to work.
TO INSERT TABLE:
1. Click INSERT tab
2. In the TABLES group click on TABLE command button
3. Select no. of rows and no. of columns.
The four-headed arrow appears at the top left corner of the table to move the table &
the square box appear at the bottom right corner of the table. Both the options
appear only when the mouse pointer is over the table.
TO INSERT ROWS
1. Select no. of rows to be inserted
2. Click LAYOUT tab
3. In the ROWS & COLUMNS group
4. Click Insert above / Insert below command button
TO INSERT COLUMNS
1. Select no. of columns to be inserted
2. Click LAYOUT tab
3. In the ROWS & COLUMNS group
4. Click Insert Left / Insert Right command button
TO DELETE ROW / COLUMNS
1. Select no. of Rows / Columns to be deleted
2. Click LAYOUT tab
3. In the ROWS & COLUMNS group
4. Click DELETE command button
5. Click Columns/ Rows
TO INCREASE OR DECREASE COLUMN WIDTH
Click, hold and drag grey boxes found on horizontal Ruler
TO INCREASE OR DECREASE ROW HEIGHT
Click, hold and drag grey boxes found on vertical Ruler
Note: To move between Table cells Tab key or Mouse click or Direction keys are
used.
TABLE PROPERTIES
To change a column width to a specific measurement,
1. Select desired columns to be resized.
2. Click LAYOUT tab
3. In the CELL SIZE group
4. Fix desired value in 2
nd
tool (for column width)
To change a row height to a specific measurement
1. Select desired columns to be resized.
2. Click LAYOUT tab
3. In the CELL SIZE group
4. Fix desired value in 1
st
tool (for row height)
Merge cells into one cell in a table
You can combine two or more cells (cell: A box formed by the intersection of a row
and column in a worksheet or a table, in which you enter information.) in the same
row or column into a single cell. For example, you can merge several cells
horizontally to create a table heading that spans several columns.
1. Select the cells you want to merge.
2. Click LAYOUT tab
3. In the MERGE group click on MERGE CELLS command button
To select:
A cell
Click the left edge of the cell
A row
Click to the left of the row.
A column
Click the column's top gridline or border.
Multiple cells, rows, or columns
Drag across the cell, row, or column.
Note: You can also select rows, columns, or the entire table by clicking in the table
and then using the Select command on the Layout tab, Table group.
To Split cells in multiple rows and columns:
1. Click in a cell, or select multiple cells that you want to split.
2. Click LAYOUT tab
3. In the MERGE group click SPLIT CELLS command button
4. Select the number of columns or rows you want to split the selected cells into.
5. Click OK
To change text alignment in a cell
By default, Microsoft Word aligns text in a table to the upper left of a cell. You can
change the alignment of text in a cell both the vertical alignment (top, center, or
bottom) and the horizontal alignment (left, center, or right).
1. Select desired cells
2. Click LAYOUT tab
3. In the ALIGNMENT group
4. Click on desired cell alignment command button
AUTOMATICALLY FORMAT A TABLE
You can quickly give your table a professional design by using any of the built-in
table formats.
1. Click the table.
2. Click on DESIGN tab
3. In the TABLE STYLES group, click the format you want.
REPEAT A TABLE HEADING ON SUBSEQUENT PAGES
When you work with a very long, it must be divided where a page break occurs. You
can make adjustments to the table to make sure than the information appears as you
want it to when the table spans multiple pages.
Repeated table headings are visible only in print layout view or when you print the
document.
1. Select the heading row or rows. The selection must include the first row of the
table.
2. Click LAYOUT tab
3. In the DATA group click REPEAT. HEADER ROWS command button
Note: Microsoft Word automatically repeats table headings on new pages that result
from automatic page breaks.
MAIL MERGE
When you want to send a letter to several persons at the same time, you can
perform this task very quickly and easily using Mail Merge technique. For this you
have to create two different files (1) Data source: It contains address of recipients in
the form of Table only. (2) Main document: It contains actual message to be send to
all the recipients.
STEPS TO PERFORM MAIL MERGE:
1. Open Main document (Seminar Invitation)
2. Click on Mailing Tab
3. In Start Mail Merge group, click on Start Mail Merge command button
4. Click on Letters option
5. In Start Mail Merge group, click on Select Recipients
6. Click on Use Existing List, the Select Data Source window will appear
7. Select desired data source file by double clicking (My computer, D:, Your own
folder, Data Source file (Address diary))
8. Place the cursor where you want to insert recipients address
9. In the Write & Insert Fields group, Click on Insert Merge field command
button
10. Click on desired field name. Repeat step 9
th
and 10
th
to insert all the fields.
11. In the Finish group, click on Finish & Merge
12. Click on Edit Individual Documents, the Merge to New Document window
will appear
13. Click on OK
VIEW IN MS WORD
Microsoft Word has different ways for you to get a good view of your work,
depending on the task at hand.
Draft View: Work in normal view for typing, editing, and formatting text. Normal view
shows text formatting but simplifies the layout of the page so that you can type and
edit quickly. In normal view, page boundaries, headers and footers, backgrounds,
drawing objects, and pictures do not appear.
Print Layout: Work in print layout view to see how text, graphics, and other
elements will be positioned on the printed page. This view is useful for editing
headers and footers, for adjusting margins, and for working with columns and
drawing objects.
Print Preview: In print preview (print preview: A view of a document as it will appear
when you print it.), you can display multiple pages of a document in a reduced size.
In this view, you can see page breaks and you can make editing or formatting
changes before you print the document.
To switch to print preview
1. Click the Microsoft Office Button
2. Point to the arrow next to Print, and then click Print Preview.
To close print preview
1) Click Close Print Preview command button on print preview ribbon
Note: You can add Print preview command button to Quick Access toolbar.
INSERTING EXCEL'S WORKSHEET WITHIN A WORD DOCUMENT
When you create a new worksheet within a document, the worksheet is inserted in
the document as an embedded object.
1. Place the insertion point where you want to create the worksheet.
2. Click INSERT tab
3. In the TABLES group, click Table, and then click Excel Spreadsheet.
Note:- When you are working inside the worksheet the screen elements(Tabs,
Command buttons)automatically change to Excel's screen elements.
TO PROTECT AN ACTIVE FILE:
1. Click the Microsoft Office Button
2. Point to Prepare Click Encrypt document
3. Type Password to open
4. Click on OK
5. Again type same password for confirmation
6. Click OK
PRINTING
1) Click the Microsoft Office Button
2) Click on Print
3) The print window will appears
4) Select name of the printer from Printers name drop down list (the printer you are
using to print your document)
5) Select Page range means the no of pages to be print.
6) Select no of copies to be print
7) Click OK
TO CANCEL PRINTING
In case you want to cancel current print job
1) Turn off the printer (Power off)
2) Click on Start button
3) Point to Settings
4) Click on Printers and Faxes
5) Double click printers icon(current), it will displays jobs in queue
6) Right click on job to be canceled
7) Click Cancel printing
KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS
COMMON TASKS DONE IN A MICROSOFT WORD DOCUMENT
CTRL+B Make letters bold
CTRL+I Make letters italic
CTRL+U Make letters underline
CTRL+SHIFT+< Decrease font size
CTRL+SHIFT+> Increase font size
CTRL+C Copy the selected text or object
CTRL+X Cut the selected text or object
CTRL+V Paste text or an object
CTRL+Z Undo the last action
CTRL+Y Redo the last action
CREATE, VIEW, AND SAVE DOCUMENTS
CTRL+N
Create a new document of the same
type as the current or most recent
document
CTRL+O Open a document
CTRL+W Close a document
CTRL+S Save a document
FIND, REPLACE, AND BROWSE THROUGH TEXT
CTRL+F Find text, formatting, and special items
CTRL+H
Replace text, specific formatting, and
special items
CTRL+G Go to a page
EDITING AND MOVING TEXT AND GRAPHICS
DELETE TEXT AND GRAPHICS
BACKSPACE Delete one character to the left
CTRL+BACKSPACE Delete one word to the left
DELETE Delete one character to the right
CTRL+DELETE Delete one word to the right
INSERT SPECIAL CHARACTERS
SHIFT+ENTER A line break (within same paragraph)
CTRL+ENTER A page break
CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER A column break
SELECT TEXT AND GRAPHICS
Select text by holding down SHIFT and pressing the key that moves the
insertion point.
SELECT MULTIPLE AREAS THAT AREN'T NEXT TO EACH OTHER
After making your first selection, hold down CTRL, and then select any other
items you want.
EXTEND A SELECTION
SHIFT+RIGHT ARROW One character to the right
SHIFT+LEFT ARROW One character to the left
CTRL+SHIFT+RIGHT ARROW To the end of a word
CTRL+SHIFT+LEFT ARROW To the beginning of a word
SHIFT+END To the end of a line
SHIFT+HOME To the beginning of a line
SHIFT+DOWN ARROW One line down
SHIFT+UP ARROW One line up
CTRL+SHIFT+DOWN ARROW To the end of a paragraph
CTRL+SHIFT+UP ARROW To the beginning of a paragraph
SHIFT+PAGE DOWN One screen down
SHIFT+PAGE UP One screen up
CTRL+SHIFT+HOME To the beginning of a document
CTRL+SHIFT+END To the end of a document
CTRL+A To select the entire document
MOVE THE INSERTION POINT
LEFT ARROW One character to the left
RIGHT ARROW One character to the right
CTRL+LEFT ARROW One word to the left
CTRL+RIGHT ARROW One word to the right
CTRL+UP ARROW One paragraph up
CTRL+DOWN ARROW One paragraph down
SHIFT+TAB One cell to the left (in a table)
TAB One cell to the right (in a table)
UP ARROW Up one line
DOWN ARROW Down one line
END To the end of a line
HOME To the beginning of a line
ALT+CTRL+PAGE UP To the top of the window
ALT+CTRL+PAGE DOWN To the end of the window
PAGE UP Up one screen (scrolling)
PAGE DOWN Down one screen (scrolling)
CTRL+PAGE DOWN To the top of the next page
CTRL+PAGE UP To the top of the previous page
CTRL+END To the end of a document
CTRL+HOME To the beginning of a document
SHIFT+F5
To the location of the insertion point
when the document was last closed
CHARACTER AND PARAGRAPH FORMATTING
APPLY CHARACTER FORMATS
CTRL+EQUAL SIGN
Apply subscript formatting (automatic
spacing)
CTRL+SHIFT+PLUS SIGN
Apply superscript formatting (automatic
spacing)
SET LINE SPACING
CTRL+1 Single-space lines
CTRL+2 Double-space lines
CTRL+5 Set 1.5-line spacing
ALIGN PARAGRAPHS
CTRL+E Center a paragraph
CTRL+J Justify a paragraph
CTRL+L Left align a paragraph
CTRL+R Right align a paragraph
CTRL+M Indent a paragraph from the left
FUNCTION KEYS
F1 Get Help or the Office Assistant
F3
Insert an AutoText entry (after
Microsoft Word displays the entry)
F4 Repeat the last action
F5 Choose the Go To command
F7
Choose the Spelling command (Tools
menu)
F8 Extend a selection
F9 Update selected fields
F12
Choose the Save As command (File
menu)
MICROSOFT EXCEL 2007
TABLE OF CONTENTS
O INTRODUCTION OF EXCELS SCREEN ELEMENTS
O BASIC FILE OPERATIONS
O TYPES OF ENTRIES
O AUTOFILL
O FORMATTING WORKSHEET
O SPREADSHEET COMPONENT
O FUNCTIONS
O DATABASE COMPONENTS
o SORTING
o SUBTOTALS
o FILTERS
O CHART
O PASSWORD PROTECTION
O PRINTING
Excel is used to analyze business, personal, or financial data and create reports in a
table format that is used for sorting, organizing and manipulating data. It provides
many features like calculation, graphics tools, pivot tables, creating different types of
charts etc.
TO START MS EXCEL
1. Click on Start button
2. Point to All Programs
3. Point to Microsoft Office
4. Click on Microsoft Office Excel 2007
Excel file is commonly known as Workbook and extension of Excel 2007s file
is .xlsx. Workbook consists of Worksheets.
Worksheet is the work area for entering and calculating data made up of
columns and rows separated by gridlines. Also called a spreadsheet. The
Office Excel 2007 grid is 1,048,576 rows by 16,384 columns. The rows are
Elements of Excels screen:
Cell: A cell is the intersection of a column and a row on a worksheet.
Active cell: The active cell contains the cell pointer a dark outline around the cell.
Name box: It identifies the selected cell, chart item, or drawing object. In other
words it displays name of current selection.
Formula Bar: A bar that you use to enter or edit values or formulas in cells or charts.
It displays the constant value or formula stored in the active cell.
Sheet Navigation buttons (tab scrolling buttons): Buttons that appear at the
bottom of the workbook window. If you don't see the tab that you want, click the tab
scrolling buttons to display the tab.
Sheet tabs: Tabs that appear at the bottom of the workbook window, which displays
the name of each worksheet.
TO CREATE NEW WORKBOOK:
1. Click the Microsoft Office Button, and then click New.
2. Click on Blank Workbook
3. Click on Create button at the bottom right
OR
1. Press Ctrl + N
TO SAVE A FILE IN YOUR OWN FOLDER:
1. Press Ctrl + S OR Click the Microsoft Office Button, Click Save As, the Save
As window will appears
2. Type appropriate name for the file inside File Name Box at the bottom
3. Click inside Save in Box at the top, Click desired drive letter C: or D:
4. Double click on your own folder
5. Click on Save Button at the Bottom left
TO CLOSE A FILE CURRENT FILE:
1. Click the Microsoft Office Button, Click Close
OR
1. Click on 2nd button at the upper right of the window
TO OPEN AN EXISTING WORKBOOK
1. Press Ctrl + O OR Click the Microsoft Office Button, Click Open, the open
window will appears
2. Click inside Look in box at the top, click desired drive letter C: or D:
3. Double click on your own folder
4. Double click on File name to be opened
THERE ARE THREE TYPES OF ENTRIES IN MS EXCEL:
1. Text: It includes A - Z alphabets, 0 - 9 digits & Special characters. By default
Text entry is left aligned in cell.
2. Number or Numeric: It includes 0 - 9 digits & arithmetic operators. By default
Numbers are right aligned in cell. It is constant entry.
3. Formula: It is used to perform calculations. It is always start with = signs. It is
variable value.
SELECTING CELLS:
1. Selecting Row: Click on Row Heading once.
2. Selecting Column: Click On Column Heading Once.
3. Selecting Entire Sheet: Press Ctrl+A, Right clicks on the Sheet Tab, then
select All Sheets.
4. For non-consecutive selection of cells: Hold down the Ctrl key and click on
cells.
5. Press ESC to cancel the previous entry.
CHANGE THE WIDTH OF COLUMNS / HEIGHT OF ROWS BY USING THE MOUSE
To change the width of one column, drag the boundary on the right side of the
column heading until the column is the width that you want.
To change the row height of one row, drag the boundary below the row
heading until the row is the height that you want.
TO INCREASE OR DECREASE ROW(S) HEIGHT /COLUMN(S) WIDTH
1. Select Row(s)/Column(s) to be resized
2. Click on HOME tab
3. In the CELLS group Click on Format command button
4. Click on Height/Width
5. Type desired value
6. Click on OK
TO INSERT ROW(S)/ COLUMN(S)
1. Select no. of Row(s)/Column(s) to be inserted
2. Click on HOME tab
3. In the CELLS group Click on Insert command button
4. Click on Insert sheet rows/ Insert sheet columns option
TO DELETE ROW(S)/ COLUMN(S)
1. Select no. of Row(s)/ Column(s) to be deleted
2. Click HOME tab
3. In the CELLS group Click on Delete command button
4. Click on Delete sheet rows/ Delete sheet columns option
AUTO FILL
Using the fill handle the formula or the value of selected cell can be copied to
adjacent cells. The fill handle is available at the bottom right corner of the cell. The
mouse pointer normally appears as (broad plus sign). But the fill handle appears as
thin dark + sign. Auto fill feature can be used to generate odd no. series, even no.
series, and names of days, months etc.
Fill in a series of numbers, dates, or other built-in series items
1. Select the first cell in the range that you want to fill.
2. Type the starting value for the series.
3. Type a value in the next cell to establish a pattern called increment value.
For example, if you want the series 1, 2, 3, 4, 5..., type 1 and 2 in the first two
cells. If you want the series 2, 4, 6, 8..., type 2 and 4.
4. Select the cell or cells that contain the starting values.
5. Drag the fill handle across the range that you want to fill.
To fill in increasing order, drag down or to the right. To fill in decreasing order,
drag up or to the left.
Tips
You can also specify the type of series by using the right mouse button to drag
the fill handle over the range and then clicking the appropriate command on the
shortcut menu (shortcut menu: A menu that shows a list of commands relevant
to a particular item. To display a shortcut menu, right-click an item or press
SHIFT+F10.). For example, if the starting value is the date JAN-2007, click Fill
Months for the series FEB-2007, MAR-2007, and so on; or click Fill Years for
the series JAN-2007, JAN-2008, and so on.
If the selection contains numbers, you can control the type of series that you
want to create.
CELL FORMATTING
The format of a cell determines how that cells contents are displayed. When you
change a cells format, you change its appearance.
CHANGING NUMBER FORMATS
You can format the numbers in a cell by using the Currency Style, Percent Style, and
Comma Style buttons on the Formatting Toolbars or selecting the Format Cells
option.
ADDING CURRENCY STYLE
1. Select the cells to be formatted
2. Click the Currency Style button on the HOME tab NUMBER group
Note: Currency Style includes Currency sign & Comma Style & Decimal point & two
decimal places. For example, if you apply the Currency Style to the number 25000 it
is displayed as $25,000.00
TO CHANGE CURRENCY FROM CONTROL PANEL:
1. Click Start button
2. Click Control Panel
3. Double click Regional and Language Options
4. Click on Customize button
5. Click on Currency heading
6. Type Rs. as currency symbol
7. Click on Apply button
8. Click on OK
9. Again click on OK
ADDING PERCENT STYLE
Note: Percent style when applied multiplies the cell value with 100 and displays the
result with percentage sign.
1. Select the cells to be formatted to the Percent Style
2. Click the Percent Style button on the HOME tab NUMBER group
APPLYING COMMA STYLE
1. Select the cells
2. Click on the Comma Style command button on the Number group.
Note: Comma style includes comma and two decimal places
INCREASING AND DECREASING DECIMAL PLACES
The number of places after the decimal point can be increased or decreased by
1. Selecting cell
2. Clicking on Increase decimal command button or Click Decrease decimal
command button on Home tab Number group
CELL ALIGNMENT
ROTATE TEXT IN A CELL
1. Select desired Cells
2. Click Home tab
3. In the Alignment group
4. Click on Orientation command button, click on desired option
WRAP TEXT: Wrap text in multiple lines in a cell within fixed column width.
1. Select desired Cells
2. Click Home tab
3. In the Alignment group
4. Click on Wrap Text command button
MERGE CELLS
To combine or merge multiple cells in a single cell
1. Select cells horizontally or vertically to be merged
2. Click Merge & Center command button on Home tab Alignment group
SPREADSHEET COMPONENTS
TO INSERT WORKSHEET:
To quickly insert a new worksheet at the end of the existing worksheets, click the
Insert Worksheet tab at the bottom of the screen.
TO DELETE CURRENT WORKSHEET:
1. Right click on Sheet tab to be deleted
2. Click on Delete
3. It will displays confirmation message
4. Click on OK
TO RENAME CURRENT SHEET:
1. Right click on Sheet tab to be renamed
2. Click on Rename
3. The Sheet Tab at the bottom will be highlighted
4. Type new name
5. Press Enter
TO CREATE A DUPLICATE OF CURRENT SHEET WITHIN WORKBOOK:
1. Right click on sheet tab to be duplicated OR Click on Edit Menu
2. Click on Move or Copy Sheet at the bottom
3. Check Create a Copy
4. Click on OK
FUNCTIONS
Function is prewritten formula used to perform certain types of calculations
automatically. Function simplifies formula. Like formula function is always start with =
sign and always return in proper format called syntax. In function spaces are not
allowed.
=FunctionName(Arguments or Range)
Range:- Range is a group of cells. There are two types of range Adjacent & Non
Adjacent. Adjacent range is group of adjoining cells and expressed by Colon (:)
sign. Non-Adjacent range is group of random or non-consecutive cell and expressed
by Comma (,) sign.
Cell addressing or Cell referencing: The reference of the cell that appears at the
intersection of column B and row 3 is B3.
There are mainly two types of Cell References:-
1. Relative: If the cell address changes with the fill handle. By default, new
formulas use relative references. For example, if you copy a relative
reference in cell B2 to cell B3, it automatically adjusts from =A1 to =A2.
2. Absolute or Fix: If the cell address does not change with the fill handle it is
absolute or fix address. By default, new formulas use relative references, and
you need to switch them to absolute references by pressing F4 function key.
For example, if you copy a absolute reference in cell B2 to cell B3, it stays the
same in both cells =$A$1.
STEPS TO INVOKE FUNCTION WIZARD:
1. Click on cell where you want the result.
2. Click on fx command button on the left of formula bar
OR
Click on Formula tab, in the Function Library group click on Insert Function
command button
3. In the window that appears, select the category and the function.
4. Click on OK.
5. Enter all the parameters in respective text boxes.
6. Finally click on OK.
SUM
It adds given numbers
=Sum(A1:A10) - Adjacent Range
=Sum(A1,C6,G9,R7) - Non Adjacent Range
PRODUCT
It multiplies given numbers
=Product(A1:A10)
=Product(A1,C6,G9,R7)
ROUND
Rounds a number to a specified number of digits.
ROUND(number,num_digits)
Number is the number you want to round.
Num_digits specifies the number of digits to which you want to round number.
Examples
=ROUND(2.15, 1) equals 2.2
=ROUND(2.149, 1) equals 2.1
=ROUND(-1.475, 2) equals -1.48
SUMIF Adds the cells specified by a given criteria.
=SumIf(Criteria Range, Criteria, Sum Range)
=SumIf(A1:A6,">200",B1:B6)
=SumIf(A1:A5,"MP",B1:B5)
AVERAGE
It calculates average of given numbers.
=Average(A1:A10)
=Average(A1,C6,G9,R7)
MAX
To find highest no. of given range.
=Max(A1:A10)
=Max(A1,C6,G9,R7)
MIN
To find lowest no. of given range.
=Min(A1:A10)
=Min(A1,C6,G9,R7)
COUNT
Counts the number of cells that contain numbers within the range.
=COUNT(value1,value2,...)
=COUNT(A2:A8) Counts the number of cells that contain numbers in the list
COUNTA
Counts the number of cells that are not empty and the values within the list of
arguments.
=COUNTA(value1,value2,...)
=COUNTA(A2:A8) Counts the number of nonblank cells in the list
COUNTIF
The COUNTIF worksheet function counts the number of number of cells of a given
range that meets specified criteria.
=COUNTIF(range, criteria)
=CountIf(A1:A10,">=40%")
The IF worksheet function
It is used to determine which one of two values to use, based on a condition that is
either true or false.
If the condition is true, the function returns one value; if the condition is false, the
function returns another value.
=IF(logical_test,value_if_true,value_if_false)
For any salesperson's $8,000 invoice, the function (in cell C4) looks like this:
=IF(B4<10000,10%,15%)
If the invoice amount is less than $10,000 (the logical_test argument), the bonus is
10 percent (the value_if_true argument). If the invoice amount is $10,000 or greater,
the bonus is 15 percent (the value _if_false argument).
TODAY
Returns current Date
=Today()
NOW
Returns the current date and time.
=Now( )
Using Auto functions to perform calculation:
1. Click in the cell where you want the result.
2. Click on Home tab
3. In the Editing group, Click on drop down arrow besides Autosum command
button
OR
1. Click Formula tab
2. In the Function Library group Click on drop down arrow besides Autosum
command button, click on desired function
3. Select range to be calculated
4. Finally press Enter.
DATABASE COMPONENTS
SORTING
Sorting is rearranging of worksheet data in ascending or descending order.
To sort data on single field:
1. Select field on which you want to sort the entire table.
2. Click on Home tab
3. In the Editing group click on Sort/Filter command button
OR
1. Click on Data tab
2. In the Sort & Filter group
3. Click to sort table in ascending order or Click to sort table in descending
order.
SUBTOTALS
1. First sort the table on which field you want to generate subtotals (Sorting is
must before subtotaling).
2. Click a cell in the list.
3. Click on Data tab
4. In the Outline group, click on Subtotals command button
5. In the At each change in box, select the sorted field name on which you want
to generate subtotals.
6. From "Use Function" drop down list select desired function.
7. Check required fields in "Add Subtotals to". Fields to be calculated.
8. Clear the Replace current subtotals check box, and then click OK.
REMOVE SUBTOTALS FROM A LIST
When you remove subtotals from a list, Microsoft Excel also removes the outline and
all page breaks that were inserted into the list when you inserted the subtotals.
1. Click a cell in the list that contains subtotals.
2. Click on Data tab
3. In the Outline group, click on Subtotals command button
4. Click on Remove All button at the bottom left
DATA FILTER
Filtering is a quick and easy way to temporarily hides rows you do not want
displayed. A filtered list displays only the rows that meet the criteria. A criterion is
conditions you specify to limit which records are included in the result set filter. For
example, the following criterion selects records for which the value for the Order
Amount field is greater than 30,000: Order Amount > 30000.
Microsoft Excel provides two commands for filtering lists:
AutoFilter, which includes filter by selection, for simple criteria
Advanced Filter, for more complex criteria
TO USE AUTOFILTER
1. Click any single item of the list
2. Click on Home tab
3. In the Editing group, click on Sort/Filter command button
OR
1. Click on Data tab
2. In the Sort & Filter group, click on Filter command button
3. A dropdown arrow appears with every field, Click the arrow in the column
header and select the desired criteria value to be filtered.
4. Only those records that match the given criteria will be shown.
TO REMOVE AUTO FILTER
1. Click on single item
2. Click any single item of the list
3. Click on Home tab
4. In the Editing group, click on Sort/Filter command button
5. Click on Filter option again
OR
1. Click on Data tab
2. In the Sort & Filter group, click on Clear command button
CHART COMPONENT
Charts are used to display series of numeric data in a graphical format to make it
easier to understand large quantities of data and the relationship between different
series of data.
EXCEL PROVIDES MANY TYPES OF CHART:-
1. AREA CHART This chart is used to show the magnitude of change over time. It
is a stacked line chart with area between them filled with colors.
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
180
1st Qtr 2nd Qtr 3rd Qtr 4th Qtr
North
West
East
2. BAR CHART-
i. Clustered bar chart - Relative comparison of two or more items
represented with horizontal bars.
ii. Stacked bar chart Data series bar are stacked over the other or
multiple segments represented with a single bar.
0 20 40 60 80 100
1st Qtr
2nd Qtr
3rd Qtr
4th Qtr
North
West
East
0 50 100 150 200
1st Qtr
2ndQtr
3rdQtr
4thQtr
East
West
North
3. COLUM CHART Series of vertical column that allows relative comparison.
0
20
40
60
80
100
1st
Qtr
2nd
Qtr
3rd
Qtr
4th
Qtr
East
West
North
4. LINE (GRAPH) CHART - This is used to show trends. Each of the data series is
equally spaced and it is used to produce a line on the chart.
0
50
100
150
200
1st Qtr 2nd Qtr 3rd Qtr 4th Qtr
5. PIE CHART This is circular chart divided into sectors, illustrating percents. In a
pie chart, the arc length of each sector (and consequently its central angle
and area), is proportional to the quantity it represents.
6. EXPLODED PIE CHART - A chart with one or more sectors separated from the rest
of the disk is known as an exploded pie chart. This effect is used to either
highlight a sector, or to highlight smaller segments of the chart with small
proportions.
7. DOUGHNUT CHART- A doughnut chart displays category groups, series groups,
and values series as doughnut slices. The size of the slice is determined by
the series value as a percentage of the total of all values.
- Note: All the above charts can also be created with a three dimensional effect in
Excel, named as 3D charts like 3D Column chart, 3D Pie chart etc.
STEPS TO CREATE CHART:-
1. Select only Series data including its heading.
2. Click Insert tab
3. In Charts group click desired chart type command button, the chart subtypes
will appear
4. Click appropriate Chart Sub type
5. The chart will be inserted in same worksheet
- Note: When you create a chart, the chart tools become available and the
Design, Layout, and Format tabs are displayed. You can use the commands
on these tabs to modify the chart so that it presents the data the way that you
want.
6. On Design tab In Data group, click on Select data command button, the
Select data source window will appear
7. Under Horizontal(category) X axis labels click on Edit button, the Axis labels
window will appear
8. Select Category data excluding its heading
9. Click on OK
10. Again click on OK
Formatting the chart
Change the layout of chart elements manually
1. Click a chart to display the Chart Tools, adding the Design, Layout, and
Format tabs.
Chart title:
On the Layout tab, in the Labels group, click the Chart title command
button and select desired layout
Type text for chart title (the text will appear in formula bar)
Press Enter key
X and Y Axis titles
Click the Axis title command button, point to Primary Horizontal Axis
Title and select desired layout
Type text for axis title (the text will appear in formula bar)
Press Enter key
Click the Axis title command button again, point to Primary Vertical
Axis Title and select desired layout
Type text for axis title (the text will appear in formula bar)
Press Enter key
Click the Legend command button and select the desired position
Click the Data Labels command button and click on show
Click the Data Table command button and click on desired layout
To change chart location
1. Click a chart
2. Click Design tab
3. In the Location group, click Move chart command button, the move chart
window will appear
4. Click New sheet
5. Click OK
Use Page Layout view to fine-tune pages before printing
Before you print a Microsoft Office Excel worksheet that contains large amounts of
data or charts, you can quickly fine-tune it in the new Page Layout view to achieve
professional-looking results. In this view, you can change the layout and format of
data the way that you can in Normal view. But you can also use the rulers to
measure the width and height of the data, change the page orientation, add or
change page headers and footers, set margins for printing, and hide or display row
and column headers.
NOTE: Page Layout view is useful to get your data ready for printing. Page breaks
are more easily adjusted in Page Break Preview view. For an exact preview of how
the data will be printed, you can preview the worksheet pages in Print Preview view.
Use rulers in Page Layout view
In Page Layout view, Excel provides a horizontal ruler and a vertical ruler, so that
you can take precise measurements of cells, ranges, objects, and page margins.
Rulers can help you to position objects and to view or edit page margins directly on
the worksheet.
Change page orientation in Page Layout view
1. Click View tab
2. In the Workbook Views group, click Page Layout View.
TIP: You can also click Page Layout View on the status bar.
3. Click Page Layout tab
4. In the Page Setup group, click Orientation
5. Click Portrait or Landscape.
Add or change page headers and footers in Page Layout view
1. Click View tab
2. In the Workbook Views group, click Page Layout View.
TIP: You can also click Page Layout View on the status bar.
3. To change a header or footer, click the header or footer text box at the top of
the worksheet page or at the bottom of the worksheet page that contains
header or footer text, and then type the desired text that.
To close the headers or footers, click anywhere in the worksheet, or press
ESC.
Set page margins
1. Click Page Layout tab
2. In the Page Setup group, click Margins
3. Click Normal, Narrow, or Wide.
TIP: For more options, click Custom Settings, and then on the Margins tab,
choose the margin sizes that you want.
TO PROTECT AN ACTIVE FILE:
1. Click the Microsoft Office Button
2. Point to Prepare Click Encrypt document
3. Type Password to open
4. Click on OK
5. Again type same password for confirmation
6. Click OK
PRINTING IN EXCEL
PRINT AREA- We can define the selection as print area to take the printout .The sheet
is quite big so to take printout of a range we define the print area.
Steps to define Print Area-
1. Select the range
2. Click on Page layout tab
3. In the Page setup group click on Print area command button
4. Click on Set print area
5. Click on Office button , click on Print, the print dialog box will appear
6. Select printer name and click on OK
To clear the print area-
1. Click on Page layout tab
2. In the Page setup group click on Print area command button
3. Click on Clear print area
KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS
WORK WITH WORKSHEETS
SHIFT+F11 or ALT+SHIFT+F1 Insert a new worksheet.
CTRL+PAGE DOWN Move to the next sheet in the workbook.
CTRL+PAGE UP Move to the previous sheet in the workbook.
MOVE AND SCROLL WITHIN WORKSHEETS
Arrow keys Move one cell up, down, left, or right.
HOME Move to the beginning of the row.
CTRL+HOME Move to the beginning of the worksheet.
CTRL+END
Move to the last cell on the worksheet, in the
bottom-most used row of the rightmost used
column.
PAGE DOWN Move down one screen.
PAGE UP Move up one screen.
KEYS FOR SELECTING DATA AND CELLS
SELECT CELLS, ROWS AND COLUMNS, AND OBJECTS
CTRL+SPACEBAR Select the entire column.
SHIFT+SPACEBAR Select the entire row.
CTRL+A Select the entire worksheet.
EXTEND A SELECTION
SHIFT+ arrow key Extend the selection by one cell.
SHIFT+HOME
Extend the selection to the beginning of the
row.
CTRL+SHIFT+HOME
Extend the selection to the beginning of the
worksheet.
CTRL+SHIFT+END
Extend the selection to the last used cell on
the worksheet (lower-right corner).
SHIFT+PAGE DOWN Extend the selection down one screen.
SHIFT+PAGE UP Extend the selection up one screen.
KEYS FOR ENTERING, EDITING, FORMATTING, AND CALCULATING DATA
ENTER DATA
ENTER
Complete a cell entry and select the cell
below.
ALT+ENTER Start a new line in the same cell.
ESC Cancel a cell entry.
Arrow keys Move one character up, down, left, or right.
HOME Move to the beginning of the line.
CTRL+; (semicolon) Enter the date.
CTRL+SHIFT+: (colon) Enter the time.
ALT+= (equal sign)
Insert an AutoSum formula with the SUM
function.
CTRL+` (single left quotation mark)
Alternate between displaying cell values and
displaying formulas.
EDIT DATA
F2
Edit the active cell and position the insertion
point at the end of the cell contents.
ALT+ENTER Insert new line in same cell
CTRL+DELETE Delete text to the end of the line.
FORMAT DATA
CTRL+9 Hide the selected rows.
CTRL+SHIFT+( (opening parenthesis) Unhide any hidden rows within the selection.
CTRL+0 (zero) Hide the selected columns.
CTRL+SHIFT+) (closing parenthesis)
Unhide any hidden columns within the
selection.
MICROSOFT POWERPOINT 2007
TABLE OF CONTENTS
COMMON TERMS OF POWERPOINT
SLIDE LAYOUTS
ORGANIZATION CHART
DIFFERENT VIEW OF POWERPOINT
SLIDE BACKGROUND AND THEMES
HEADER & FOOTER
ABOUT MASTERS
ADD TRANSITIONS TO A SLIDE SHOW
ANIMATE TEXT AND OBJECTS
PACKAGE A PRESENTATION
PRINTING
SHORTCUT KEYS
Microsoft PowerPoint
82
POWERPOINT is a presentation graphics program that lets you create slide shows that
can be shown with a projector, a computer screen, or as a Web page. You can use a
presentation to supplement a speech or lecture.
PowerPoint presentations consist of a number of individual pages or "slides". The
"slide" analogy is a reference to the slide projector, a device that can be seen as
obsolete, within the context of widespread use of PowerPoint and other presentation
software. Slides may contain text, graphics, movies, and other objects, which may be
arranged freely on the slide. PowerPoint, however, facilitates the use of a consistent
style in a presentation using a template or "Slide Master".
PowerPoint provides three types of movements:
1. Entrance, emphasis, and exit of elements on a slide itself are controlled by
what PowerPoint calls Custom Animations
2. Transitions, on the other hand are movements between slides. These can be
animated in a variety of ways
3. Custom animation can be used to create small story boards by animating
pictures to enter, exit or move
Terms:
Presentation is a set of slides or handouts that contain information you want
to convey to an audience.
Slide is an individual page of a presentation. By default slide layouts are set
up in landscape orientation.
Slide layouts Pre-determined sets of placeholders for various types of slide
content.
Placeholder Designated areas in PowerPoint layouts that can be used to
easily insert text, graphics, or multimedia objects.
Placeholder border A screened area around the edge of a placeholder, used
to move a placeholder. You can also click on a placeholder to select the text
or apply font changes.
Clipart Pre-drawn artwork that you can insert into your files.
WordArt A feature used to transform text into a picture object.
Object An item other than text, such as a table, chart, clipart, WordArt, or
worksheet.
AutoShapes A set of tools that make drawing common geometric shapes fast
and easy.
Microsoft PowerPoint
83
Views PowerPoint offers several different ways you can view the presentation
as you work on it. Each view has its own advantages and features.
TO INSERT NEW SLIDE:
1. Press Ctrl + M OR
2. Click Home tab
3. In the Slides group, click New Slide command button
ABOUT LAYOUTS
"Layout" refers to the way things are arranged on a slide. A layout contains
placeholders (placeholders: Boxes with dotted or hatch-marked borders that are part
of most slide layouts. These boxes hold title and body text or objects such as charts,
tables, and pictures.), which in turn hold text such as titles and bulleted lists and slide
content such as tables, charts, pictures, shapes, and clip art.
When you start a new presentation or add a slide to a presentation, it will appear
with a default slide layout. You can use that layout, or select a new layout.
TO CHANGE LAYOUT OF A SLIDE:
1. Click on HOME tab
2. In the SLIDES GROUP Click on LAYOUT command button, Slide Auto layouts will
appear below
3. Click on desired auto layout
ORGANIZATION CHART
An organization chart graphically represents the management structure of an
organization, such as department managers and non management employees within
a company. It helps to show the hierarchy of any Organization. We can have
different levels:
1. Manager
2. Co Worker
3. Subordinate
Create an organization chart
1. Click on Insert tab
2. In the Illustrations group, click SmartArt.
Microsoft PowerPoint
84
3. In the Choose a SmartArt Graphic gallery, click Hierarchy, click an
organization chart layout (such as Organization Chart), and then click OK.
4. To enter your text, do one of the following:
Click in a shape in the SmartArt graphic, and then type your text.
Click [Text] in the Text pane, and then type your text.
Copy text from another location or program, click [Text] in the Text pane,
and then paste your text.
Add a shape to your organization chart
1. Click the SmartArt graphic that you want to add a shape to.
2. Click the existing shape that is located closest to where you want to add the
new shape.
3. Under SmartArt Tools, on the Design tab, in the Create Graphic group, click
the arrow under Add Shape, and then do one of the following:
To insert a shape at the same level as the selected shape but following it,
click Add Shape After.
To insert a shape at the same level as the selected shape but before it,
click Add Shape Before.
To insert a shape one level above the selected shape, click Add Shape
Above.
The new shape takes the position of the selected shape, and the selected
shape and all of the shapes directly below it are each demoted one level.
To insert a shape one level below the selected shape, click Add Shape
Below.
The new shape is added after the other shapes at the same level.
To add an assistant shape, click Add Assistant.
The assistant shape is added above the other shapes at the same level in
the SmartArt graphic, but it is displayed in the Text pane after the other
shapes at the same level.
Microsoft PowerPoint
85
Add Assistant is available only for organization chart layouts. It is not
available for hierarchy layouts, such as Hierarchy.
Change the hanging layout of your organization chart
A hanging layout affects the layout of all shapes below the selected shape.
1. Click the shape in the organization chart that you want to apply a hanging layout
to.
2. Under SmartArt Tools, on the Design tab, in the Create Graphic group, click
Layout, and then do one of the following:
To center all of the shapes below the selected shape, click Standard.
To center the selected shape above the shapes below it and arrange the
shapes below it horizontally with two shapes in each row, click Both.
To arrange the selected shape to the right of the shapes below it and left-
align the shapes below it vertically, click Left Hanging.
To arrange the selected shape to the left of the shapes below it and right-
align the shapes below it vertically, click Right Hanging.
Change the colors of your organization chart
You can apply color combinations that are derived from the theme colors (theme
colors: A set of colors that is used in a file. Theme colors, theme fonts, and theme
effects compose a theme.) to the shapes in your SmartArt graphic.
1. Click the SmartArt graphic whose color you want to change.
2. Under SmartArt Tools, on the Design tab, in the SmartArt Styles group, click
Change Colors.
3. Click the color combination that you want.
TIP When you place your pointer over a thumbnail, you can see how the colors
affect your SmartArt graphic.
Apply a SmartArt Style to your organization chart
Microsoft PowerPoint
86
A SmartArt Style is a combination of various effects, such as line style, bevel, or 3-D,
that you can apply to the shapes in your SmartArt graphic to create a unique and
professionally designed look.
1. Click the SmartArt graphic whose SmartArt Style you want to change.
2. Under SmartArt Tools, on the Design tab, in the SmartArt Styles group, click
the SmartArt Style that you want.
To see more SmartArt Styles, click the More button
OVERVIEW OF POWERPOINT 2007 VIEWS
The views in Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007 that you can use to edit, print, and
deliver in your presentation are:
Normal view
Slide Sorter view
Notes Page view
Slide Show view (which includes Presenter view)
Master views: Slide, Handout, and Notes
You can find PowerPoint views in two places:
On the View tab, in the Presentations Views group, where all views are
available.
On an easy-accessible bar at the bottom of the PowerPoint Window where
the main views (Normal, Slide Sorter, and Slide Show) are available.
VIEWS FOR DELIVERING YOUR PRESENTATION
There are many views in PowerPoint that can help you to create a professional
presentation.
NORMAL VIEW
Normal view is the main editing view, which you use to write and design your
presentation. The view has three working areas: on the left, tabs that alternate
between an outline of your slide text (Outline tab) and your slides displayed as
Microsoft PowerPoint
87
thumbnails (Slides tab); on the right, the slide pane, which displays a large view of
the current slide; and on the bottom, the notes pane (notes pane: The pane in
normal view in which you type notes that you want to accompany a slide. You print
these notes as notes pages or have them display when you save a presentation as a
Web page.).
SLIDE SORTER VIEW
Slide sorter view is an exclusive view of your slides in thumbnail form. When you are
finished creating and editing your presentation, slide sorter gives you an overall
picture of it making it easy to reorder, add, or delete slides and preview your
transition and animation effects.
NOTES PAGE VIEW
The Notes pane is located just below the Slide pane. You can type notes that apply
to the current slide. Later, you can print your notes and refer to them when you give
your presentation. You can also print notes to hand out to your audience or include
the notes in a presentation that you send to the audience or post on a Web page.
When you want to view and work with your notes in full page format, on the View
tab, in the Presentation Views group, click Notes Page.
MASTER VIEWS
The master views include, Slide, Handout, and Notes view. They are the main slides
that store information about the presentation, including background, color, fonts,
effects, placeholder sizes and positions. The key benefit to working in a master view
is that on the slide master, notes master, or handout master, you can make universal
style changes to every slide, notes page, or handout associated with your
presentation.
VIEWS FOR DELIVERING YOUR PRESENTATION
SLIDE SHOW VIEW
Slide show view takes up the full computer screen, like an actual slide show
presentation. In this full-screen view, you see your presentation the way your
audience will. You can see how your graphics, timings, movies, animated elements,
and transition effects will look in the actual show.
TO DELETE SLIDE:
1. Select slides to be deleted (you can select multiple slides by holding down Ctrl
key while clicking on it)
2. Press Delete key
OR
On the Home tab, in Slides group click on Delete slide command button
Microsoft PowerPoint
88
TO MOVE SLIDE WITHIN PRESENTATION
1. Switch to Slide Sorter view
2. Click, hold and drag the desired slide to the new position
HIDE OR SHOW A SLIDE
If there is a slide that you need in your presentation, but you do not want it to appear
in the slide show, you can hide the slide.
This is particularly useful when you have added slides to a presentation that provide
different levels of detail on the subject matter, perhaps for different audiences. You
can mark these slides as hidden so that they are not displayed in your main slide
show, but you can still access them if you need to.
NOTE When you hide a slide, the slide remains in the file even though it is hidden
when you run the presentation in Slide Show view. You can switch the Hide Slide
option on and off individually for any slide in the presentation.
To hide a slide
1. Right-click the slide that you want to hide
2. Click Hide Slide.
The hidden slide icon appears with the slide number inside, next to the slide
that you have hidden.
To show a slide or unhide a slide
1. Right-click the slide that you want to show
2. Click Hide Slide.
NOTE: If you are in Slide Show view and you decide that you want to show a slide
that you previously hid, you can right-click the current slide, click Go to slide, and
then click the slide that you want to show.
TO CHANGE THE APPEARANCE OF A BLANK PRESENTATION-
Following are the options:
1. Background
Microsoft PowerPoint
89
2. Themes
BACKGROUND:
Background styles are displayed in thumbnails in the Background Styles gallery.
When you place your pointer over a background style thumbnail, you can preview
how the background style will affect your presentation. If you like the background
style, you can then click to apply it. You can also use a picture or a texture for a slide
background.
ADD A BACKGROUND STYLE TO YOUR PRESENTATION
1. Click the slide or slides that you want to add a background style to.
To select multiple slides, click the first slide, and then press and hold CTRL
while you click the other slides.
2. Click on Design tab
3. In the Background group, click the arrow next to Background Styles.
4. Right-click the background style that you want, and then do one of the following:
To apply the background style to the selected slides, click Apply to
Selected Slides.
To apply the background style to all of the slides in your presentation, click
Apply to All Slides.
THEMES:
PowerPoint 2007 themes replace used in earlier versions of PowerPoint. Microsoft
Office PowerPoint 2007 contains several built-in themes (theme: A combination of
theme colors, theme fonts, and theme effects. A theme may be applied to a file as a
single selection.), which include theme colors (theme colors: A set of colors that is
used in a file. Theme colors, theme fonts, and theme effects compose a theme.),
theme fonts (theme fonts: A set of major and minor fonts that is applied to a file, and
theme effects (theme effects: A set of visual attributes that is applied to elements in a
file. Whether you use an existing built-in theme, create a new theme, or modify an
existing built-in theme
APPLY A THEME TO YOUR PRESENTATION
1. Click Design tab
2. In the Themes group, click More.
3. To apply a built-in theme, under Built-In, click the theme that you want.
Microsoft PowerPoint
90
TO DISPLAY HEADER & FOOTER
1. Click on Insert tab
2. In the Text group, click Header & Footer command button
3. Click the options for Date and Slide no.
4. Click on Apply to all
ABOUT THE SLIDE MASTER
The slide master is an element of the design template that stores information about
the template, including font styles, placeholder sizes and positions, background
design, and color schemes.
The slide master's purpose is to let you make a global change such as replacing
the font style and have that change reflected on all the slides in your presentation.
You would typically go to the slide master to do the following:
Change the font or bullets
Insert art such as a logo that you want to appear on multiple slides
Change placeholder positions, size, and formatting
To see the slide master, you display master view. You can make changes to the
slide master just as you would change any slide, except remember that the text on
the master is only for styling; actual slide text, such as titles and lists, should be
typed on the slide in normal view or, for headers and footers, in the Header and
Footer dialog box. When you change the slide master, changes you have made to
individual slides are preserved.
1. Click on View tab
2. In the Presentation Views group, click on Slide Master command button,
PowerPoint switched to master view
3. After making desired formatting click on Close Master View command to go
back to Normal View
THERE ARE TWO EFFECTS IN POWERPOINT
- SLIDE TRANSITION: The visual effect used when one slide moves off of the
screen and another moves onto the screen. These are the effects given to
slide as a whole. We can allot timings, effects and sound to the advancement
of slide. You can apply transitions in any view.
Microsoft PowerPoint
91
- ANIMATE: To apply movement to text or an object. You can animate text on
slices to add interest to your presentation or to emphasize special points. For
example, text might fly onto the screen from the left or drop in from above.
o Custom Animation
Every slide can have different Transition effect. Using Apply to All we can apply
same transition for all the slides.
STEPS TO APPLY TRANSITION-
1. Select desired slide
2. Click on Animation tab
3. In the Transition to this slide group
4. Select desired transition
5. Select the speed slow, medium or fast.
6. To assign timings check automatically after how many seconds.
7. Click on Apply to All, if you want to apply to the entire presentation.
ANIMATE TEXT AND OBJECTS
Animation effects give motion to text, pictures, and other content on your slides.
Besides adding action, they help you steer audience focus, emphasize important
points. For example, you can have your text bullet points fly in from the left, one word
at a time, or hear the sound of applause when a picture is uncovered
APPLY A CUSTOM ANIMATION
1. In normal view, display the slide that has the text or objects you want to animate.
2. Select the object you want to animate.
3. On the Animations tab, click Custom Animation.
4. In the Custom Animation task pane, click , and do one or more of
the following:
If you want to make the text or object enter the slide show presentation with an
effect, point to Entrance and then click an effect.
If you want to add an effect to text or an object that is on the slide, point to
Emphasis and then click an effect.
If you want to add an effect to text or an object that makes it leave the slide at
some point, point to Exit and then click an effect.
If you want to add an effect that makes an object move in a specified pattern,
point to Motion Paths and then click an effect.
Microsoft PowerPoint
92
5. Icon that indicates the timing of the animation event in relation to the other
events on the slide. Choices include:
Start on click: Animation event begins on click of the mouse on the
slide.
Start with previous: Animation sequence begins at the same time as
the previous item in the list (that is, one click executes 2 animation
effects).
Start after previous: Animation sequence begins immediately after the
previous item in the list if finished playing (that is, no additional click is
required to make the next sequence start).
6. Specify Speed of the animation (Slow, Medium, Fast)
7. Click on Play button to see the given effects in Normal View
Note: - To preview animations work, click the Slide Show button.
Remove one or more animation effects from your presentation
1. Click on Animation tab
2. In the Animations group, click Custom Animation.
3. In the slide window, click the text or object with one or more animation
effects applied to it that you want to remove.
4. In the Custom Animation list, click an animation effect, and then click
Remove. To select more than one animation effect applied to a single
instance of text or an object, press and hold CTRL while you click each
animation effect that you want to remove.
PACKAGE A PRESENTATION TO RUN ON ANOTHER COMPUTER
STEPS:
1. Click Microsoft Office Button
2. Point to the arrow next to Publish
3. Click on Package for CD.
4. In the Package for CD dialog box, in the Name the CD box, type a name
for the CD or the folder that you want to copy your presentation to.
5. Click on Copy to Folder folder button at the bottom left
6. Type Folder name you want to create
7. Click on Browse button, the choose location window will appear
8. Choose the drive and folder where you want to create above specified folder.
9. Click on Select button, the selected path will be displayed in Location box
Microsoft PowerPoint
93
10. Click on OK button, the selected presentation will be packed in specified
location.
11. Click on Close button
12. Open folder where you have packed presentation
13. Right click on presentation to be showed
14. Click on Open, now you can run the presentation
OR
1. You can go to specified location and copy the packed presentation folder in
your removable secondary storage device.
2. If you use other computer to run your presentation, first Copy the packed
presentation folder to that computer
3. Open the folder and Right click on presentation to be showed
4. Click on Open, now you can run the presentation OR If the computer dont
have PowerPoint installed Right click on PPTView Click on Open, the
PowerPoint Viewer window will appear
5. Locate and Select the presentation to be showed
6. Click on Open button at the bottom right.
PRINT HANDOUTS
Handout prints multiple slides on one page
1. Open the presentation that you want to print.
2. On the File menu, click Print Preview.
3. To choose the page orientation, click Portrait or Landscape on the
4. To set headers and footers, click the arrow on the Options button, and then click
Header and Footer.
5. On the Print Preview toolbar, in the Print What box, click the Handout layout
option you want.
6. On the Print Preview toolbar, click Print.
Microsoft PowerPoint
94
KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS
MOVE BETWEEN PANES
F6
Move clockwise among panes of
normal view
CTRL+SHIFT+TAB
Switch between Slides and Outline
tabs of the Outline and Slides pane in
normal view
CREATE AND EDIT PRESENTATIONS
CTRL+N Create a new presentation
CTRL+M Insert a new slide
CTRL+D Make a copy of the selected slide
CTRL+O Open a presentation
CTRL+W Close a presentation
CTRL+P Print a presentation
CTRL+S Save a presentation
F5 Run a presentation
ALT+F4 Quit PowerPoint
WORK IN AN OUTLINE
ALT+SHIFT+LEFT ARROW Promote a paragraph
ALT+SHIFT+RIGHT ARROW Demote a paragraph
ALT+SHIFT+UP ARROW Move selected paragraphs up
ALT+SHIFT+DOWN ARROW Move selected paragraphs down
RUN A SLIDE SHOW PRESENTATION
You can use the following shortcut keys while running your slide show presentation
in full-screen mode.
N, ENTER, PAGE DOWN, RIGHT
ARROW, DOWN ARROW, or the
SPACEBAR (or click the mouse)
Perform the next animation or advance
to the next slide
P, PAGE UP, LEFT ARROW, UP
ARROW, or BACKSPACE
Perform the previous animation or
return to the previous slide
Microsoft PowerPoint
95
Number + ENTER Go to slide number
S or PLUS SIGN Stop or restart an automatic slide show
ESC, CTRL+BREAK, or HYPHEN End a slide show
H Go to the next hidden slide
SHIFT+F10 (or right-click) Display the shortcut menu
TAB
Go to the first or next hyperlink on a
slide
SHIFT+TAB
Go to the last or previous hyperlink on
a slide
Microsoft Word
- 96 -
INTERNET
WHAT IS INTERNET?
The term Internet has been coined from two terms, interconnection and network. A
network is simply a group of computers that are connected together for sharing
information and resources. Several such networks have been joined together across
the world to form what is called as the Internet. Thus, it is a network of networks.
APPLICATIONS OF THE INTERNET
In the simplest terms, you can do following three things on the Internet
1. Communicate with other people
2. Get information
3. Connect to other computer systems
Communicating with other people
There are many ways by which you can communicate with people on the Internet.
Some of them are as follows.
E-mail
The most common use of the Internet is electronic mail (popularly known as e-mail).
Using e-mail a user can send text, pictures, sounds, programs or even movies to
other person on the Internet anywhere in the world. Each user on the Internet has a
unique address. This address helps you in identifying a user to whom you wish to
send e-mail.
username@domain is the format of email address Eg-ram@sancharnet.in
Chatting and conferencing
Another method of communicating on the Internet is known as internet Relay Chat
(IRC). Using IRC you can speak to other users around the world virtually in real time
as though you were in the same room.
Nowadays you can also have audio and videoconference using appropriate
software.
Getting Information
Internet provides a tremendous wealth of information. With thousands of systems
connected on the Internet, there are millions of computer programs and data that
have been made available to the users. These may be text files, graphics files,
sound files, full motion video files or even programs files.
There are number of ways in which you can obtain the desired information
FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
One of the methods of getting information via internet is File Transfer Protocol (FTP).
Using FTP a user can copy computer files (Games, utility programs, etc.) from a
remote computer to his computer. This process is called file downloading. Similarly,
Microsoft Word
- 97 -
a user can also send files from his computers to a remote computer. This is known
as file uploading. FTP is a standard protocol, i.e. it consists of a standard set of
commands for file downloading and uploading.
WWW
There is another approach to offering information on the computers on the internet,
the most popular one at that, and it is called World Wide Web (WWW).
A WWW computer system consists of a computer called web server. The information
that is to be offered is stored on the web servers in the form of web pages. A user
can view these web pages using a web browser.
Internet Terminology
Modem
The term modem stands for MOdulator/DEModulator. A modem is a device that
enables a computer to transmit data over telephone lines. Computer information is
store digitally, whereas information transmitted over telephone lines is transmitted in
the form of analog waves. A modem converts between these two forms.
Network
A network is a group of computer connected to each other, for communicating and
sharing resources. Networks can either be local (Local Area Networks or LAN),
which are generally contained within one building, or quite dispersed (Wide Area
Networks or WAN), which are computers that are connected to each other over long
distances. Internet can be thought of as a huge Wide Area Network.
Client
Client is a computer or program that requests a service of another computer or
program.
Server
Server is a computer or program that provides services to other computers or
programs.
Baud Rate
The baud rate is the speed at which your modem can transfer data. The higher the
baud rate the faster your modem works. For example, a 300 bps modem is very slow
as compared to a 28800 bps (i.e. 28.8 kbps) modem.
TCP/IP
A protocol can be defined as a standard set of rules to be followed by all computers
wanting to talk to each other. This enables different types of computers running
Microsoft Word
- 98 -
different types of operating system to communicate efficiently. The de-facto standard
today is TCP/IP. TCP/IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet
Protocol. It is a standard set of protocols that lets networked computers
communicate with each other, regardless of the type of computer connected to the
network.
Hypertext Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
This is a protocol that World Wide Web clients and servers use to communicate
(Popularly known as HTTP). All web clients and servers must use HTTP in order to
send and receive hypermedia documents. For this reason, Web servers are often
called HTTP servers.
Universal Resources Locator (URL)
Uniform or Universal Resource Locator are the most common and efficient method
for identifying specific resources on the internet. An URL specifies the location of
something on the internet. It is possible to represent almost any file or service on the
Internet with a URL. A URL looks like
http://www.microsoft.com
The first part of the URL (before the two slashes) specifies the method of access.
The second is typically the address of the computer on which the information or
service is to be located. Further parts may specify the names of files, the port to
connect to, or the text to search for in a database. A URL is always a single line with
no spaces.
GETTING CONNECTED
Hardware Requirements
A computer
A Modem any speed will work, but the higher the baud rate, the better it is.
A 28.8 or a 33.6 KBPS modem is just fine.
A Phone Line you do not need a separate phone line to use your modem.
The regular line will work just fine.
Software Requirements
Communication Software- this is just a computer program that lets your
computer talk to your modem.
Microsoft Word
- 99 -
If you want to access World Wide Web, you need a browse program.
Netscape Navigator, Microsoft Internet Explorer and Mosaic are the most
popular web browsers.
E-mail software that will help you in sending and receiving e-mail. The
browsers such Netscape Navigator and Internet Explorer have built-in mail
program.
In addition to these softwares you may also need FTP software and IRC
software.
Internet Service Provider (ISP): is an organization that provides access to the
Internet. For a monthly/yearly fee, the service provider gives you a username,
password and access phone number. Using the modem you can then connect to the
Internet.
There are many ways in which you can connect to the Internet. However the two
main ways are:
Dial-Up Access
Direct or Dedicated Access
Dial-Up-Access
This type of Internet connection is by far the most common way that individuals use
to connect to the Internet. In this type of connection you connect to the Internet via a
modem and regular telephone line.
The major advantage of a dial-up connection is that it is less expensive as compared
to the dedicated connection. Another advantage of a dial-up connection is that it
required very modest hardware and software resources.
The major disadvantage is their slow speed and low reliability.
Direct or Dedicated Connections
This options provides full Internet access by dedicating a leased phone line between
your network (or individual PC) and an Internet Service Provider. An Internet
Service Provider (ISP) is an organization that provides access to the Internet. For a
monthly/yearly fee, the service provider gives you a username, password and
access phone number. Using the modem, you can then connect to the Internet.
Videsh Sanchar Nigam Limited (VSNL), Department of Telecommunication (DOT),
Mantra Online & Satyam Online are popular ISPs of India.
The dedicated connection has many advantages. The major advantage is the fast
speed and better reliability. With a direct connection, you can have many users of
your local area network connected to the Internet through a single leased line. You
Microsoft Word
- 100 -
do not need a modem on each individual computer that is connected to your LAN.
This means that you do not have to dial to connect to the Internet. The computer on
your desktop is always connected to the Internet.
The only disadvantage of dedicated connections is that the cost of communication is
too high. Also a dedicated connection is more complex and difficult to maintain.
Introduction to Domain and Address
Every computer connected to the Internet is identified by a unique address. The term
unique means that no two computers connected to the Internet can have the same
address. There are two types of addresses Domain Names and IP Addresses- that
help in locating a computer on the Internet.
The Domain Name System
A domain name helps in locating a computer on the Internet. A typical domain name
indicates the country in which the computer is located and which organization owns
it. The term Domain Name System (DNS) refers to the systematic hierarchical
organization of domain names.
How does a domain name help in locating a computer?
The hierarchical organization of domain names help in locating a computer on the
Internet. These domain names are organized either on the basis geographical
regions or on the basis of type of the organization that owns the computer.
The following table lists some geographical domain names.
Domain type Indicates this country
.in India
.au Australia
.us United States of America
.pk Pakistan
.uk United Kingdom
.ch Switzerland
Some of the common non geographical domain types are listed as follows:
Domain Type Description
.com A Commercial Organization
.net A Network Service Provider Organization
.edu An Academic Organization
.gov A government Organization
Microsoft Word
- 101 -
.int International Organization
.mil Military Operations
.org Noncommercial Organization
USING THE WORLD WIDE WEB
The World Wide Web is a collection of documents and other types of files that are
stored on computers all around the world. The documents and files on the WWW are
called pages and the things used to connect these pages are called links. A
hyperlink is an element in an electronic document that links to another place in the
same document or to an entirely different document.
A Web Page is a hypermedia document. These web pages are created using the
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML), which is very easy to use.
Browser is client software that enables the client computer to gain access to a web
server or other Internet Servers. A browser also interprets and display documents.
Three of the most popular browsers are Netscape Navigator, Microsoft Internet
Explorer and Mosaic.
SEARCHING FOR INFORMATION ON THE INTERNET
There are some special web-sites on the Internet, known as Search Engines, which
allow you to search for the desired information on the Internet. Some popular search
engines are Yahoo, Google, Alta vista, Infoseek, Webcrawler and Lycos. A search
engine maintains a database of keywords. When you request the search engine for
information, it attempts to locate the specified information in its database of
keywords. If the search engine finds a match, it displays these references.
HISTORY OF THE INTERNET
In 1969, the ARPA (Advanced Research Project Agency) created ARPANET to help
the researchers communicate with each other. ARPAs task was to develop a
geographically dispersed, reliable communication network for military use that would
not be disrupted in case of partial destruction from a nuclear attack. They
accomplished this by splitting the data being transmitted into small packets, which
could take different routes to their destination.
Other private networks came up soon following the design of ARPANET. In 1986 the
NSF (National Science Foundation) created NSFNET, a network with five
supercomputers to help establish effective communication amongst universities. In
19990, the ARPANET was dismantled and other networks came up to substitute for
it.
Microsoft Word
- 102 -
To provide services to Internet users, and in an attempt to standardize the working
on the Internet, NSF created an organization called InterNIC in 1993.
GETTING TO KNOW YOUR BROWSER
The program you use to browse or explore the Web is called a Web browser.
To start Internet Explorer
1. Click on Start button
2. Go to All Programs
3. Click on Internet Explorer OR
1. Click the Launch Internet Explorer Browser button in the Windows XP Quick
Launch toolbar. OR
1. Click the Internet Explorer icon on your Windows desktop
Windows Internet Explorer will start and probably take you to your default home
page.
Title Bar: - Displays the title of the page youre viewing at that moment (if any) and
also holds the standard Maximize, Minimize, and close buttons.
Menu Bar: - Plays the same role it does in all programs; just click any menu item to
view its pull-down menu.
Toolbar: - Contains navigation buttons, Explorer bar buttons, and other tools.
Address Bar: - Shows the URL (address- the www.whatever.com thing) of the page
youre viewing. Also allows you to visit other pages.
Document area: - When you view a Web page, it will appear in the document area.
Status bar: - Whenever you point your Web browser to a new URL, the status bar
will display messages to keep you informed of its progress in loading the page.
Going to a Specific Site
If you already know a Web sites URL, you can visit that site by following these
simple steps:
1. Click the URL thats currently in the Address bar to select it.
2. Type in the new URL
3. Press the Enter key on your keyboard
4. Wait the status bar will keep you posted.
Microsoft Word
- 103 -
Navigating Through Visited Sites
Several buttons in Internet Explorers toolbar, shown below, help you navigate
through recently visited sites.
Back: Takes you back to the page you visited before the one you are currently on (if
there is one)
Forward: Takes you to the page you just backed out of (again, if there is one)
Stop: If its taking too long for a page to appear on your screen, you can click the
Stop button to step the transfer. You can then navigate to some other page.
Refresh: Reloads the page from the Web server, ensuring that you have the
absolute latest copy of the page.
Home: Takes you back to your default home page.
Using the History Explorer Bar
Internet Explorer also keeps track of sites youve visited in its history lists. The
Address bar itself contains a short history list, which you can view by clicking the
down-pointing arrow at the right edge of the Address bar, as shown below. To revisit
any listed there, just click the sites URL.
Internet Explorer also maintains a more complete history list, which you can view in
Internet Explorers Explorer Bar.
To view that large history list, do either of the following:
Click the History button in the toolbar.
Choose View Explorer Bar History.
The History Explorer Bar opens on the left edge of the screen
To delete History
If you share your computer and dont want other people seeing where youve been
on the Web, you can remove any URL from the list by
1. Right-clicking it
2. Choosing delete.
You can clear the entire history list, erasing all traces of where youve been.
To Empty the History list
1. Click Tools menu
2. Click Internet Options
Microsoft Word
- 104 -
3. Click on General Tab
4. Click the Clear History button
5. Click on Yes
6. Click on OK
SEARCHING
Using Search Engine:- Google
Doing a search on Google is easy. Simply type one or more search terms
(the words or phrase that best describe the information you want to find) into the
search box and hit the 'Enter' key or click on the Google Search button.
In response, Google produces a results page: a list of web pages related to
your search terms, with the most relevant page appearing first, then the next, and
so on.
"I'm Feeling Lucky"
After you've entered your search terms, you might want to try the "I'm
Feeling Lucky" button, which takes you straight to the most relevant website that
Google found for your query. You won't see the search results page at all, but if
you did, the "I'm Feeling Lucky" site would be listed on top.
For example, if you're looking for the Stanford University homepage, just
enter Stanford and click "I'm Feeling Lucky" instead of the Google Search
button. Google will take you directly to "www.stanford.edu."
FAVORITES
As you explore the Web, youre likely to come across some pages that you
might like to visit again in the future. Microsoft refers to such pages as Favorites and
provides tools for organizing and keeping track of them. You can also subscribe to
sites to receive notification of when something in the site has changed.
Keeping Track of Favorite Sites
1. While visiting a page that youd like to add to your favorites, click Favorites
menu
2. Add to Favorites, The dialog box shown below appears.
3. If you want to add current page in your own folder under Favorite folder, Click
on Create in button
4. If the desired folder is not exist in folders list, select folder in which you want
to create new folder
Microsoft Word
- 105 -
5. Click on New folder
6. Type name for the folder
7. Click on OK
8. Click on OK
Using Favorites Folders
1. Click Favorites in Internet Explorers menu bar. The Favorites menu that
opens will include any new folders youve created.
2. Point to (or click) the folder that contains the favorite site you want to revisit.
Sites within that folder appear to the right.
3. Click the name of the site you want to visit.
Making pages available for offline viewing
When you make a Web page available offline, you can read its content when
your computer is not connected to the Internet. For example, you can view Web
pages on your laptop computer when you don't have a network or Internet
connection. Or you can read Web pages at home without tying up a phone line.
You can specify how much content you want available, such as just a page, or
a page and its entire links, and choose how you want to update that content on your
computer.
If you just want to view a Web page offline, and you don't need to update the
content, you can save the page on your computer. There are several ways you can
save the Web page, from just saving the text to saving all of the images and text
needed to display that page as it appears on the Web.
To make the current Web page available offline
1. On the Favorites menu, click Add to Favorites.
2. Select the Make available offline check box.
3. Click OK
Note
Before you go offline, make sure you have the latest version of your pages by
clicking the Tools menu and then clicking Synchronize.
You can also make Web pages available offline without adding them to your
Favorites list, by saving the pages on your computer.
Microsoft Word
- 106 -
When you choose to work offline, Internet Explorer will always start in Offline
mode until you click Work Offline again to clear the check mark.
To save a Web page on your computer
1. On the File menu, click Save As.
2. Double-click the folder you want to save the page in.
3. In the File name box, type a name for the page.
4. In the Save as type box, select a file type.
5. Do one of the following:
o To save all of the files needed to display this page, including graphics,
frames, and style sheets, click Web Page, complete. This option
saves each file in its original format.
o To save just the text from the current Web page, click Text Only. This
option saves the information on the Web page in straight text format.
Notes
With Web Page, complete and Web Archive, you can view all of the Web
page offline, without adding the page to your Favorites list and marking it for
offline viewing.
ELECTRONIC MAIL
Creating E-mail Account on Yahoo.com
1. Open Yahoos Mail Page by typing www.mail.yahoo.com in Internet Explorers
Address bar.
2. Click on Sign Up to register with yahoo.
3. Yahoo will display registration form, fill the form carefully.
4. Click on I Agree button at the bottom of the form.
5. If yahoo will satisfy with all the information filled by you, it will complete the
registration and displays some information about your account, write down the
information in your diary if required.
6. Locate continue button and click on it.
7. Yahoo will take you to your e-mail account you have created.
Microsoft Word
- 107 -
8. To help protect the privacy of your account, be sure to click the "Sign Out"
link on the left-hand navigation bar.
9. And then the "Sign Out Completely" link at the end of each Yahoo! Mail
session.
Using e-mail account to send and receives messages:
1. Open Yahoos Mail Page by typing www.mail.yahoo.co.in in Internet
Explorers Address bar.
1. Type your Yahoo ID you have provided, type Password and click on Sign in
button.
2. Yahoo will take you to your e-mail account you have created.
3. To check mails you have received click on Inbox option. The list of incoming
mails will be displayed.
4. Click on the subject of the message you would like to read.
To write mail:-
1. Click on Compose option or click on Mail Compose, the window where you
can type your e-mail message and recipients e-mail addresses will appear.
2. In the "To:" field, specify the recipient's email address. To send your message
to more than one person, add additional email addresses in the "To:" field
separated by commas (e.g., jaybhatt@yahoo.co.in, jayaroy@yahoo.co.in,
etc.).
3. In the "Subject" field, enter the subject of your message.
4. In the "Cc:" field, enter the email addresses of those to whom you would like
to send a "carbon copy" of your message.
5. In the "Bcc:" field, enter the email addresses of those to whom you would like
to send a "blind carbon copy" of your message.
6. Use the large text box to enter the contents of your message.
7. Check the spelling of your message by clicking the Spell Check button. Any
words that may be mis-spelled will then be outlined on your screen. Click the
"?" button to the right of an outlined word to access the dictionary. When you
have finished checking your spelling, click the Done button to return to the
"Compose Mail" window.
Microsoft Word
- 108 -
8. To attach a file to your message, click on Attach File button, click on the
Browse button and select a file. When you've selected a file, click the "Attach"
link to attach it to your message.
9. Once you have completed the above steps, click the Send button to send the
message.
What do Cc: and Bcc: mean?
Cc: stands for "carbon copy." Anyone listed in the "Cc:" field of a message will
receive a copy of that message when you send it. All other recipients of that
message will be able to see that the person you designated as a "Cc:" recipient has
received a copy of the message.
Bcc: stands for "blind carbon copy." This is nearly identical to the "Cc:" feature,
except that "Bcc:" recipients are invisible to the "To:" and "Cc:" recipients of the
message as well as to each other. For example, if you send a message "To:"
jaybhatt@yahoo.co.in with a "Bcc:" to jayaroy@yahoo.co.in, then jaybhatt will see
himself as the message's only recipient, while jayaroy will see that you have also
sent the message "To:" jaybhatt. There is a limit of 10 "Bcc:" addresses per
message.
Add an attachment to a message
You can send all types of files as attachments, including word-processor or
spreadsheet documents, audio files, image files(.bmp, .jpg, .gif, etc.), web pages
saved as HTML files, and more.
1. Click the Attach file button to open the Attachment window.
2. Click the Browse button and select a file.
3. To add multiple attachments, repeat step 2.
4. To delete an attachment, click the Remove option
5. After selecting desired files to be attached, click on Attach file button. It will
take few minutes to attach files depending on their size.
6. Click on Continue to Message button
Once the files are attached, you can address, compose and send the message as
you normally would.
Microsoft Word
- 109 -
About Draft folder
To save an unfinished email composition without sending it, click the "Save Draft"
button near the top of the Compose Mail window.
Once you have saved a draft, you can open it at any time by doing the following:
1. Click the "Folders" link on the left-hand navigation bar.
2. Choose the Draft folder on the right.
3. Click on the message you wish to continue composing.
Reply to a message
To reply to a message that you have received in your Yahoo! Mail account, you must
first open the message on your screen. When the message is open:
1. Reply: Click the "Reply" button at the top of the message window to reply only
to the sender of the message.
2. Reply All: If you would like to send your reply to all of the other recipients of
the message in addition to the sender, click the "Reply All" button.
3. A Compose Mail window will appear. If you clicked the "Reply" button, the
sender's email address will appear in the "To:" field. If you clicked the "Reply
All" button, then in addition to the sender's address, the addresses of all of the
other recipients will appear in the "To:" and/ or "Cc:" fields, according to the
way they were listed in the original message. You can also add new email
addresses if you wish.
4. Depending on your "Preferences" setting*, in the large text window you will
see quoted all, part, or none of the sender's message. A quoted message will
be set off by ">" symbols on the left margin.
5. Type your reply. If you have quoted the sender's message, you can type in
the area above the sender's message as well within the sender's message
itself.
6. Click the "Send" button to send your reply.
Saving a message in Sent folder
By default, Yahoo! Mail does not automatically save a copy of messages you send
into your Sent folder.
To enable this option for a single message, check the "Save copy of outgoing
message to Sent folder" checkbox in the Compose Mail window before clicking the
"Send" button.
Microsoft Word
- 110 -
To enable this option for all messages that you send:
1. Click the "Options" link on the left-hand navigation bar.
2. Click the "Preferences" link on the right.
3. Place a check in the box next to "Save Sent Messages into the Sent folder."
4. Click the "Save Settings" button near the bottom of the window to put your
new settings into effect.
Yahoo! Mail will then save a copy of each outgoing message into your Sent folder.
Forward a message
When forwarding a message, you have the option to forward either as an
"attachment" or as "inline text". If you forward as an attachment, your recipient will
need to save or open the attachment in order to view the message. If you forward as
inline text, the text of the message will appear quoted within the body of the
message that you send, set off by ">" characters on the left margin.
To forward a message which itself includes an attachment, choose the "attachment"
option rather than "inline text." Forwarding as an attachment will preserve the whole
of the original message, including all of its attachments.
To forward a message, begin by opening the message on your screen. When you
have the message open:
1. Choose whether you would like to forward the message as an attachment or
as inline text. ("Attachment" is the default setting and appears next to the
Forward button near the top of the "Read Message" window. Click the down
arrow to the right of "attachment" to choose "inline text."*)
2. Click the Forward button. This will open a Compose Mail window. If you have
chosen to forward as an attachment, the Compose Mail window will be blank.
If you have chosen "inline text," the Compose Mail window will contain the text
of the forwarded message.
3. In the "To:", "Cc:" and "Bcc:" fields, enter the email addresses of your
intended recipients.
4. In the message window, type any additional text you would like to include.
5. Click the Send button.
*If you would like to set "inline text" as your default rather than "attachment," click the
Options link on the left-hand navigation bar, choose Preferences, scroll down to the
Forwarding header, and select "inline text." Be sure to click the Save Settings button
at the bottom of the Preferences window to put your new settings into effect.
Microsoft Word
- 111 -
Add a contact
There are a number of ways to add contacts to your Yahoo! Address Book:
1. Click on Addresses Tab
2. Click on Add Contact, the Add contact form will appear
3. Enter the information in the fields provided (Name and Email address) and
click on Save or Save and add another
Inserting address from contact list:
If you have already started composing an email
1. Click on Insert address option
2. In the window, locate recipients and check the appropriate boxes (To:, Cc:, or
Bcc:) to the left of their names.
3. Click on Insert checked contacts
4. The recipients' email addresses will appear in the To:, Cc:, and Bcc: fields.
5. Compose and send your message.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Consumer Behaviour of Titan WatchesDocumento57 pagineConsumer Behaviour of Titan Watchesmanu100% (1)
- Lab 5 - Batch FilesDocumento10 pagineLab 5 - Batch FilesArthur RiversNessuna valutazione finora
- Training and Placement at Krishna HondaDocumento68 pagineTraining and Placement at Krishna Hondamanu0% (3)
- Assignment On Hair SalonDocumento14 pagineAssignment On Hair SalonmanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Project On SunsilkDocumento27 pagineFull Project On Sunsilkmanu89% (9)
- MS Office 2007 ExcelDocumento38 pagineMS Office 2007 ExcelJames DapiawenNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Microsoft Windows 98Documento5 pagineIntroduction To Microsoft Windows 98usman6484Nessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Manual: (Computer Networks)Documento27 pagineLaboratory Manual: (Computer Networks)anon_547570183Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computer PeripheralsDocumento23 pagineComputer PeripheralsscribdNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 2.6.1: Topology Orientation and Building A Small N Etw OrkDocumento32 pagineLab 2.6.1: Topology Orientation and Building A Small N Etw OrkPatronovski PatronNessuna valutazione finora
- Hardware Function - CpuDocumento42 pagineHardware Function - CpumyzalNessuna valutazione finora
- Packet Tracer - Creating A New TopologyDocumento18 paginePacket Tracer - Creating A New TopologyManishNessuna valutazione finora
- Motherboard PDFDocumento17 pagineMotherboard PDFPriyanka BadicharNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Assembly Language and ProgrammingDocumento85 pagineChapter 4 Assembly Language and ProgrammingPetra Kalasa100% (1)
- Value Learning Chip Level SyllabusDocumento5 pagineValue Learning Chip Level SyllabusVenkatareddy MulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Input and Output in JavaDocumento28 pagineInput and Output in JavaCHANDRA BHUSHANNessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Word - Screen Element - Mrs - Lucy David - 14610Documento3 pagineMicrosoft Word - Screen Element - Mrs - Lucy David - 14610Game of AttitudeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 3.5.2 IP Addresses and Network Communication: ObjectivesDocumento5 pagineLab 3.5.2 IP Addresses and Network Communication: Objectivesnunna_vaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Computer System (2) (1) - 1629266582Documento61 pagineUnit 1 Computer System (2) (1) - 1629266582Nischal ChaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Laptop Chip Level Training Full Day Module and Day Wise Course ContentDocumento23 pagineLaptop Chip Level Training Full Day Module and Day Wise Course ContentJawad AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 9 Computer Applications (Finals 20-21)Documento5 pagineClass 9 Computer Applications (Finals 20-21)Aditya PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Binary Codes Lecture NotesDocumento7 pagineBinary Codes Lecture NotesPatrick SerandonNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.1 RaidDocumento14 pagine5.1 Raidgidum2007100% (1)
- Processor Socket and Slot TypesDocumento2 pagineProcessor Socket and Slot TypesdudungNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Planet: Tomorrow's Technology and You: Hardware BasicsDocumento20 pagineDigital Planet: Tomorrow's Technology and You: Hardware BasicsHannah Esey Aquino PaquinNessuna valutazione finora
- FOSS Lab - V Prasad, 2013Documento51 pagineFOSS Lab - V Prasad, 2013prasad94400246610% (2)
- Cs 105 Week 4 AssignmentDocumento3 pagineCs 105 Week 4 AssignmentGrantham University100% (1)
- Lab Exercise For C ProgrammingDocumento51 pagineLab Exercise For C ProgrammingAhmed NUR HUSIEN100% (1)
- Storage Devices and Multimedia DevicesDocumento25 pagineStorage Devices and Multimedia DevicesJoevertVillartaBentulanNessuna valutazione finora
- Terminology Mouse Clicks Menus File Extensions Hardware: Windows BasicsDocumento7 pagineTerminology Mouse Clicks Menus File Extensions Hardware: Windows BasicsTimothy John SomcioNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Parts of A Computer: - Monitor - Keyboard - Mouse - System UnitDocumento35 pagineBasic Parts of A Computer: - Monitor - Keyboard - Mouse - System UnitShenny CariscalNessuna valutazione finora
- Ms-Office (Theory) : Max. Marks: 100Documento3 pagineMs-Office (Theory) : Max. Marks: 100bhagathnagarNessuna valutazione finora
- CL X Practical File 2022-23Documento9 pagineCL X Practical File 2022-23Krrish HingoraniNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.3.3.3 Lab - Building A Simple NetworkDocumento13 pagine2.3.3.3 Lab - Building A Simple NetworkDaisy Galvan33% (3)
- Windows API For Visual Basic and REALbasicDocumento34 pagineWindows API For Visual Basic and REALbasicLuis Argenis ZabalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ms WordDocumento29 pagineMs WordXerofishNessuna valutazione finora
- Adv Dip in Computer Hardware and Netwark ManagementDocumento20 pagineAdv Dip in Computer Hardware and Netwark ManagementALLWYNPALNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cpu: Central Processing UnitDocumento26 pagineThe Cpu: Central Processing Unitjim_finn_1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Excel Project FinalDocumento38 pagineExcel Project FinalhimanshiNessuna valutazione finora
- PHP and Mysql: Tiji ThomasDocumento83 paginePHP and Mysql: Tiji ThomasMoazzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Bca-Vi Sem-Pc HW and Network-SylDocumento6 pagineBca-Vi Sem-Pc HW and Network-Syllo leeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chip Level Laptop Repairing InstituteDocumento6 pagineChip Level Laptop Repairing InstituteMagzoub NourNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual - Basic Computer Skills - Windows 7 PDFDocumento27 pagineManual - Basic Computer Skills - Windows 7 PDFMay ann argenioNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networks Lab (CL307) Lab Session 06: National University of Computer & Emerging ScienceDocumento15 pagineComputer Networks Lab (CL307) Lab Session 06: National University of Computer & Emerging Sciencesnooker masterNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamental Laptops and Portable DevicesDocumento45 pagineFundamental Laptops and Portable Deviceshani100% (1)
- Computer Interfacing - Lecture1Documento22 pagineComputer Interfacing - Lecture1mohamed faragNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit2 Input OutputDocumento10 pagineUnit2 Input OutputDeepak KumbharNessuna valutazione finora
- Assembly Programming Tutorial: What Is Assembly Language?Documento75 pagineAssembly Programming Tutorial: What Is Assembly Language?Bhagya Gaddam100% (1)
- MS DOS CommandsDocumento3 pagineMS DOS CommandsNaveenNessuna valutazione finora
- RdbmsDocumento88 pagineRdbmsVigneshwaranSankaran100% (1)
- 01 Computer LiteracyDocumento19 pagine01 Computer LiteracyGadi Fosta100% (1)
- Otherhardware Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3Documento54 pagineOtherhardware Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3somerandomhedgehog100% (1)
- Familiarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and PeripheralsDocumento98 pagineFamiliarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and Peripheralsjuliet brusola100% (1)
- Data BaseDocumento9 pagineData BaseElias PetrosNessuna valutazione finora
- Charusat Android Practical List.Documento95 pagineCharusat Android Practical List.programmerNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE - VI - Computer Studies - OpenShot Video EditorDocumento23 pagineCBSE - VI - Computer Studies - OpenShot Video EditorAhaan DoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- X86 AssemblyDocumento123 pagineX86 AssemblyVIV0411Nessuna valutazione finora
- Microprocessors & InterfacingDocumento43 pagineMicroprocessors & Interfacingshubhang2392Nessuna valutazione finora
- CPP Questions BankDocumento4 pagineCPP Questions BankRishikesh MahajanNessuna valutazione finora
- E2900 - Status Chs ComponentDocumento5 pagineE2900 - Status Chs ComponentKang AmengNessuna valutazione finora
- Investor's Perception Towards The Reliance Mutual FundsDocumento83 pagineInvestor's Perception Towards The Reliance Mutual FundsmanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Investment in Systematic Investment Plan in Satna CityDocumento71 pagineInvestment in Systematic Investment Plan in Satna CitymanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance Appraisal With Reference To UclDocumento52 paginePerformance Appraisal With Reference To UclmanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Customer Satisfaction Towards Mahindra Company Automobile SectorDocumento63 pagineCustomer Satisfaction Towards Mahindra Company Automobile Sectormanu100% (1)
- Customer Satisfaction Towards Mahindra Company Automobile SectorDocumento63 pagineCustomer Satisfaction Towards Mahindra Company Automobile Sectormanu100% (1)
- From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: BuckwheatDocumento13 pagineFrom Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: BuckwheatmanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Of Sales and Promotion GhariDocumento67 pagineOf Sales and Promotion GharimanuNessuna valutazione finora
- General Introduction ToDocumento15 pagineGeneral Introduction TomanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Vivo Quality Dialysis CertificateDocumento1 paginaVivo Quality Dialysis CertificatemanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Tricks Book TypeDocumento57 pagineMath Tricks Book TypemanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Knotweeds of Medicinal UsesDocumento2 pagineKnotweeds of Medicinal UsesmanuNessuna valutazione finora
- RKT Conc UsionDocumento1 paginaRKT Conc UsionmanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Customer Satisfaction Towards WhatsappDocumento40 pagineCustomer Satisfaction Towards WhatsappmanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Report ON "Comparative Study Between Amazon and Flipkart"Documento49 pagineResearch Report ON "Comparative Study Between Amazon and Flipkart"manuNessuna valutazione finora
- Coal Mining in India 2015 PDFDocumento6 pagineCoal Mining in India 2015 PDFmanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Management at Maruti SuzukiDocumento77 pagineFinancial Management at Maruti Suzukimanu100% (1)