Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
TRANSPORT SYSTEMS-suggested Textbook Answers
Caricato da
someone4630Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
TRANSPORT SYSTEMS-suggested Textbook Answers
Caricato da
someone4630Copyright:
Formati disponibili
TRANSPORT SYSTEMS [Chapter 12] Further questions 1a The leaves of fresh vegetables wilt after being picked because
water continues to be lost by transpiration from the leaves, but no water is drawn into the plants via the stems. When plants lose too much water the cells lose their turgidity and the plant wilts. Wilting can be minimised by limiting water loss by evaporation. This could be achieved by placing the fresh vegetable into an airtight plastic bag or container and keeping it in the dark so that the stomata stay closed. Wilting can also be minimised by replacing the water that is lost; that is, by placing the stems in water so that water lost by transpiration is replaced by water drawn up through the xylem. Cooling will reduce metabolic rate. 1b Celery stalks curl because the cut surfaces take up the water causing increased turgidity of the cells. This means that cells near the cut surface expand and because the strings remain the same length the stalks curl. 2 Xylem is dead tissue and water movement is by a mechanical process only. If the flowers continue to lose water by transpiration then water will be drawn up the xylem. 3 Type of tissue Energy source Pathway Transpiration Xylem Sun causing evaporation of water from leaves Xylem throughout the plant: leaves, stems and roots Water containing mineral salts Translocation Phloem Active transport using glucose in the plant Phloem throughout the plant: leaves, stems and roots Glucose and other chemicals such as hormones produced within the plant Very important. The means by which glucose and chemicals such as hormones are distributed throughout the plant Root pressure Xylem Sun causing evaporation of water from leaves Xylem throughout the plant: leaves, stems and roots Water containing mineral salts
Material transported
Relative importance
Very important. The means by which water is taken in and distributed throughout the plant
One factor contributing to transpiration
4a Aphloem; Bxylem 4b Type of vascular tissue Process involved in transport Main direction of flow Sucrose Phloem Transpiration Upwards from roots to leaves Water Xylem Translocation Movement can be in either direction. Glucose from photosynthesis is carried from the leaves to other plant parts, ususally downwards. Glucose from stores (such as roots) will be carried up to growing tips of stems or down to growing tips of roots Glucose. Translocation is active transport
Source of energy for the
Suns energy causing
process
evaporation
5 Insects do not rely on the circulatory system to deliver oxygen to cells during flight. The oxygen is supplied by the tracheal system; the oxygen from the air is brought directly to the active muscles. 6a Multicellular organisms need a transport system because they have a small surface area-to-volume ratio and materials are not able to move through the organism by diffusion quickly enough to meet its needs. 6b The heart has two sides and they pump blood to different parts of the body. First the right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs. Then the blood returns to the left side of the heart from which it is pumped out to the rest of the body. The blood from the two sides of the heart do not mix, therefore it can be thought of a two separate pumps or a double pump. 6c Pump A comprises the right atrium and the right ventricle. Pump B comprises the left atrium and left ventricle. 6d The walls of the right ventricle are thinner than the walls of the left ventricle. The right ventricle does not have to pump the blood as fas as does the left ventricle therefore the walls do not need as much muscle tissue. 6ei O: pulmonary artery; P: pulmonary vein 6eii The pulmonary artery (O) has a lower oxygen concentration than the pulmonary vein (P). 6fi P and M are both veins and will contain valves. 6fii Valves in the veins prevent the backwards flow of blood. They are necessary because the blood in the veins is not under pressure from the pumping of the heart the same way that the arterial blood in under pressure. 7a Blood pressure tends to increase with age because arteries tend to harden with increased age. 7b The lower incidence of deaths from coronary heart disease in females compared with males may be related to: gender (e.g. hormonal differences) behaviour (e.g. less aggressive, less stress) culture (e.g. more weight conscious). Men and women in Japan have a lower incidence of coronary heart disease when compared with men and women in the USA, Australia and the UK. This could be due to: racially inherited factors cultural differences (e.g. diet). 7c If there is significant blood loss the blood pressure becomes so low that circulation round the body cannot be maintained. 8a
8b Red blood cells are biconcave in shape rather than spherical. This shape gives red blood cells a greater surface area to carry oxygen, thus increasing the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. 8c The advantages for red blood cells of not having a nucleus are: it can be biconcave in shape which increases the SA : V ratio it can hold a greater amount of haemoglobin. However, the nucleus controls all the activities of the cell, including maintenance and repair. The disadvantage for red blood cells of not having a nucleus is that the cells cannot repair the damage done to them as they move through the circulatory system. 8d Red blood cells are slightly larger than the capillaries, so as they move through the capillaries they fold over to squeeze through, increasing the surface in close contact with the capillary wall thus reducing the distance for gaseous exchange. 9 After vigorous exercise, a persons skin becomes flushed and they sweat; these are mechanisms of body temperature control. The redness in the skin is due to the dilation of blood vessels close to the skin which allows heat to be lost by radiation and convection. Evaporation of sweat from the skin also enables heat to be lost by evaporative cooling. 10 Affirmative: saves lives, improves the quality of some peoples lives, allows people to become organ donors. Negative: costs a lot of money, long waiting list, anti-rejection drugs needed, moral and ethical considerations, may create a black market for organs. 11a The diagram shown represents a vein; this is indicated by the presence of valves. 11b The direction of blood flow would be from the left-hand side of the page to the right-hand side of the page. 11ci Blood moves along veins towards the heart, largely as a result of the local compression of thinwalled veins by muscles during body movements. Standing motionless for long periods of time limits the blood flow through the veins back to the heart and thus to the lungs to obtain oxygen. Reduced levels of oxygen in the blood may cause fainting. 11cii To overcome this problem, individuals should contract muscles, particularly in their legs, periodically. 12 Estimate the volume of your blood using this method. Approximately 8% of your body weight is blood. Weight yourself and calculate the weight of blood in your body. Assuming one litre of blood weighs approximately one kilogram, calculate how many litres of blood in your body. For a person weighing 55 kg, 4.4 kg would be blood, i.e. 4.4 L.
13 You can donate blood at hospitals or mobile units. It only takes about 10 minutes but allow about an hour for the whole process, which includes a personal interview and refreshments. Your blood will be grouped, tested for anaemia, and screened for viruses such as HIV, hepatitis. There are many blood products, e.g. red cell (boosts the oxygen-carrying capacity), platelet (blood clotting) and white cell concentrates (bolster immune system), plasma (boost blood volume) and cryoprecipitate (for severe haemorrhage). You can donate 470 mL of whole blood every 12 weeks but you can donate plasma every two weeks. 14 Passengers on long plane trips often suffer swollen feet as a result of being in a sitting position for a long period of time without exercising. The lymphatic system relies on the activity of skeletal movement to move lymphatic fluid. With little muscular movement, the fluid settles in the body tissues resulting in swelling. Also, blood may accumulate in the veins. Exercise would help to move the lymphatic fluid back towards the heart by squeezing the thin-walled vessels. 15 The disadvantages of the old method of treating snake bite include: sucking the blood could result in ingestion of venom cutting open the bite will increase blood flow to the area and may increase the rate at which the venom moves throughout the body applying a tight tourniquet could actually prevent blood flow to an area below the bite and this may cause further damage to tissue. The reasons for using the method of pressureimmobilisation include: the pressure bandage will reduce blood flow in the area immobilisation of the bitten body part reduces blood flow in the veins towards the heart. 16 Reduced blood flow to the lungs for oxygenation due to the narrowed pulmonary artery and reduced oxygenation of blood due to the blood flow across the ventricular septum. Blood low in oxygen is pumped around the body from the right ventricle via the aorta. Therefore there would be low levels of oxygen in the tissues, and tiredness due to low energy production by cellular respiration. Also the heart is enlarged and overworking because the right ventricle is pumping blood into a narrowed pulmonary artery and the aorta. Heart attack is possible due to low levels of oxygen in the coronary vessels. Corrective measures would involve heart surgery to attach the aorta to the left ventricle only, repair the hole in the septum and correct the narrowing of the pulmonary artery (insert a stent, replace narrowed section etc.).
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- 15 Day Detox ChallengeDocumento84 pagine15 Day Detox ChallengeDanii Supergirl Bailey100% (4)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Measurement Assignment EssayDocumento31 pagineMeasurement Assignment EssayBihanChathuranga100% (2)
- Anatomy of the pulp cavity กย 2562-1Documento84 pagineAnatomy of the pulp cavity กย 2562-1IlincaVasilescuNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm B19Documento6 pagineAstm B19Davor IbarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Training For Humans Guide: FAQ's How Many Sets/reps Should I Do Per Exercise?Documento28 pagineTraining For Humans Guide: FAQ's How Many Sets/reps Should I Do Per Exercise?Paulo Pires100% (1)
- Case Study 2Documento5 pagineCase Study 2api-247285537100% (1)
- Daedric Quests Found in SkyrimDocumento6 pagineDaedric Quests Found in Skyrimsomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- Issue: Older Woman Opting To Have The Test For Down 'S SyndromeDocumento1 paginaIssue: Older Woman Opting To Have The Test For Down 'S Syndromesomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- Daedric Quests Found in SkyrimDocumento6 pagineDaedric Quests Found in Skyrimsomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- Consumerism WorksheetDocumento3 pagineConsumerism Worksheetsomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cotton BollwormDocumento3 pagineCotton Bollwormsomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- The History of Contact LensesDocumento1 paginaThe History of Contact Lensessomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- GlossaryDocumento4 pagineGlossarysomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- DanteDocumento65 pagineDantesomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- Keeping A Research JournalDocumento1 paginaKeeping A Research Journalsomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- DanteDocumento65 pagineDantesomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- EpidermisDocumento2 pagineEpidermissomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- Model For ERT On MaterialsDocumento10 pagineModel For ERT On Materialssomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- Exchange RatesDocumento2 pagineExchange Ratessomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- SpeedDocumento1 paginaSpeedsomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- LyssavirusDocumento2 pagineLyssavirussomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- Infertility, ART, and The Reproductive SystemDocumento5 pagineInfertility, ART, and The Reproductive Systemsomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- Glass Vs HydrogelDocumento4 pagineGlass Vs Hydrogelsomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- NutritionDocumento3 pagineNutritionsomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Excretory SystemDocumento19 pagineThe Excretory Systemsomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ophelia's PoemDocumento1 paginaOphelia's Poemsomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- Components of BloodDocumento1 paginaComponents of Bloodsomeone4630Nessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Title: Learning Targets: Reference (S)Documento5 pagineActivity Title: Learning Targets: Reference (S)Jhev LeopandoNessuna valutazione finora
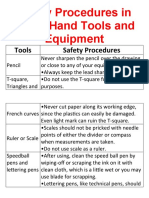
- Safety Procedures in Using Hand Tools and EquipmentDocumento12 pagineSafety Procedures in Using Hand Tools and EquipmentJan IcejimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Lamentation of The Old Pensioner FinalDocumento17 pagineLamentation of The Old Pensioner FinalRahulNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 Closing The Gap ReportDocumento64 pagine2016 Closing The Gap ReportAllan ClarkeNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Post - Exploring The Intersection of Work and Well-Being - A Guide To Occupational Health PsychologyDocumento3 pagineHealth Post - Exploring The Intersection of Work and Well-Being - A Guide To Occupational Health PsychologyihealthmailboxNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics (Cheg6121) : Review of Basic ThermodynamicsDocumento74 pagineAdvanced Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics (Cheg6121) : Review of Basic ThermodynamicsetayhailuNessuna valutazione finora
- The Influence of Irish Monks On Merovingian Diocesan Organization-Robbins BittermannDocumento15 pagineThe Influence of Irish Monks On Merovingian Diocesan Organization-Robbins BittermanngeorgiescuNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Biology EducationDocumento13 pagineJournal of Biology EducationFarah ArrumyNessuna valutazione finora
- World Insurance Report 2017Documento36 pagineWorld Insurance Report 2017deolah06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biblical World ViewDocumento15 pagineBiblical World ViewHARI KRISHAN PALNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Resume For Supply Chain Logistics PersonDocumento2 pagineSample Resume For Supply Chain Logistics PersonAmmar AbbasNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Exploration: Inclined Plane - Simple MachineDocumento9 pagineStudent Exploration: Inclined Plane - Simple MachineLuka MkrtichyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment of Chemistry For B.sc-B.ed First Semester Session 2019-2023-1Documento2 pagineAssignment of Chemistry For B.sc-B.ed First Semester Session 2019-2023-1Payal sahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 140322224412 Phpapp02Documento26 pagineQuiz 140322224412 Phpapp02Muhammad Mubeen Iqbal PuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Pityriasis VersicolorDocumento10 paginePityriasis Versicolorketty putriNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Profession - Educational PhilosophyDocumento23 pagineTeaching Profession - Educational PhilosophyRon louise PereyraNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 Mable Parker Mclean Scholarship ApplicationDocumento2 pagine2022 Mable Parker Mclean Scholarship Applicationapi-444959661Nessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation About GyroscopesDocumento24 paginePresentation About GyroscopesgeenjunkmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Economic Review English 17-18Documento239 pagineEconomic Review English 17-18Shashank SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Comp PPT 1Documento12 pagineCloud Comp PPT 1Kanishk MehtaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2014 - A - Levels Actual Grade A Essay by Harvey LeeDocumento3 pagine2014 - A - Levels Actual Grade A Essay by Harvey Leecherylhzy100% (1)
- Man and Historical ActionDocumento4 pagineMan and Historical Actionmama.sb415Nessuna valutazione finora
- Jakub - BaZi CalculatorDocumento3 pagineJakub - BaZi Calculatorpedro restinxNessuna valutazione finora
- KsDocumento5 pagineKsnurlatifahNessuna valutazione finora