Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Carbohydrates Monosacharide Compostion Biological Function
Caricato da
Donnabelle VaronaDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Carbohydrates Monosacharide Compostion Biological Function
Caricato da
Donnabelle VaronaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CARBOHYDRATES 1. Sucrose 2. Lactose 3. Maltose 4. 5. 6. 7.
Starch Glycogen Cellulose Chitin
MONOSACHARIDE COMPOSTION Glucose + Tructose Glucose + Galactose Glucose + Glucose Glucose Glucose (found in liver) Glucose Glucose
BIOLOGICAL FUNCTION Transplant sugar in plants In milk, energy source Digestive breakdown product of starch Energy storage in plants Energy storage in animals Plant structure, cell wall Exoskeleton in crabs, lobsters, insects BIOLOGICAL FUNCTION Long term energy storage Protective cuticle to prevent loss of water in plants Plasma membrane, structure and properties
LIPID Fats and Oils Waxes
MONOSACHARIDE COMPOSTITION 3 fatty acids + glycerol Long chain fatty acid and long chain alcohol Glycerol + 2 fatty acids + phosphate group
Phospholipids
Starch- made of amylose and amylopectin Saturated= single bond Unsaturated= double bond (fruits. Vegetables) Glycerol= hydrophilic polar (water loving)
Triacylglycerol= hydrophobic (no water) Metabolism= totality of all the chemical reaction a. Catabolism= cut form bigger to small (chewing) b. Anabolism = from smaller to big (photosynthesis plants) Glucose= monomer of carbohydrates
Acidity: more Hydrogen Hydrolysis= add water molecule to break a bond (shorter polymer) Dehydration= removes a water molecule forming a new bond (longer polymer) Glycosidic Linkage= linkage in carbon bonds Ester Linkage= Fat monomer HDL (High Density Lipoprotein)= good cholesterol Sources: Palm oil, olive oil, vegetable oil LDL (Low Density Lipoprotein)= bad cholesterol, single bonded, saturated Sources: fats from animals, red meat, beef, horse meat, pork
Simple Lipids= Oil a. Components: Triacylglycerol b. Fatty acids= tails H H C H C H C H C H
DISEASES: Arteriosclerosis= thickness of fat Atherosclerosis= brittleness Stroke= head Hypertension= lower
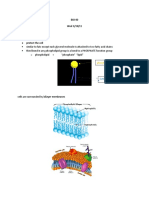
H H H H Dehydrogenation= if double bond process through this process, it will be single bonded. Phospholipids a. Head= Choline, Phosphate, Glycerol (Hydrophilic) b. 2 Tails= Fatty Acids (Hydrophobic) c. Source= Phospholipid bilayer (found in the cell wall) (2 Layers) Acc. Singer and Nicolson = proposed a model of phospholipid bilayer. = Fluid Mosaic Model = found in soap Steroid= makes bones brittle Protein = building blocks of protein is Amino Acid NH2
Amino GROUP (NH2) SUGAR BASES STRANDS HELIX DNA Deoxyribose A,T,G,C 2 RNA Ribose A,U,G,C Single
Carboxyl Group
FUNCTION OF PROTEINS Enzymatic Protein Selective acceleration of chemical reaction Support Storage of amino acid Transport other substances Coordination of an organisms activities Response of cell to chemical stimuli Tag/identification of cell Speeds up/catalyse hydrolysis of polymer in food Silk fibers, collagen, elastin, keratin Ovalbumin (protein of egg) Hemoglobin (4 iron, pechay, kangkong) Insulin, (pancreas) regulate the concentration of sugar in blood. Receptors built into the membrane of a nerve cell
Structural Proteins Storage Proteins Transport Protein Hormonal Protein
Receptor Proteins MHC (Major Histocompatibility Complex) Defensive Protein Contractile and Motor Proteins
Protection against diseases movement
Antibodies Actin and myosin are responsible for the movement.
ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS P- hehylalamine V- aline T- ryptophah M E T-ionine H- istioline I- soleucine L- ysine L-eucine Peptide Bond- linkage in proteins. ex. Milk, Nuts
LEVELS OF PROTEIN STRUCTURE 1. 2. 3. 4. Primary Structure- Amino Acid + Peptide Bond Secondary Protein- a-helix and beta pleated sheet Tertiary bonds Quaternary Structure- collagen, hemoglobin
Sickle- Cell Disease- when the cell only brings 2 irons instead of 4. Pattern: a. Normal: Val, His, Leu, Thr, Pro, Glu, Glu b. Abnormal: Val, His, Leu, Thr, Pro, Val, Glu Denaturation= loses the body structure Renature= tightens X-ray crystallography= Linus Pauling, Rosalind Franklin, Maurice Wilkins Nucleotide=monomer of nucleic acid = building blocks of nucleic acid Components: a. Phosphate Group PO4 b. Pentose Sugar = 5 Carbon sugar/ribose c. Nitrogenious Base 2 BASES = Purine: Adenine and Guanine = 2 rings = Pyrimidines: single ring. Rhyamine, Urasil, Cytosine Phosphodiester Linkage= nucleotide to nucleotide Anti-parallel-different direction Hydrgoen bond- joins one strand/bases Semi-conservative model= DNA replication Nucleotide- phosphate, sugar base Nucleoside- nitrogenous base, sugar
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 2021 Physician Compensation Report - Updated 0821Documento24 pagine2021 Physician Compensation Report - Updated 0821Michael Knapp100% (3)
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDa EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- End-of-the-Year Test - Grade 3Documento16 pagineEnd-of-the-Year Test - Grade 3nachNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers To Competency Assessment SectionDocumento16 pagineAnswers To Competency Assessment Sectionapi-209542414100% (1)
- Electro Acupuncture TherapyDocumento16 pagineElectro Acupuncture TherapyZA IDNessuna valutazione finora
- The Structure and Function of Macromolecules: AP Biology Chapter 5Documento48 pagineThe Structure and Function of Macromolecules: AP Biology Chapter 5iksingh78Nessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Reference For Water Conservation in Cooling TowersDocumento41 pagineTechnical Reference For Water Conservation in Cooling TowersDorn GalamarNessuna valutazione finora
- Extraction of Total Lipids From Chicken Egg Yolk and Column Chromatography of LipidsDocumento6 pagineExtraction of Total Lipids From Chicken Egg Yolk and Column Chromatography of LipidsJea CansinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Macromolecules. Monomers: Bio 11O Topic 5 - BiomoleculesDocumento8 pagineMacromolecules. Monomers: Bio 11O Topic 5 - BiomoleculesYda TolentinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lipid Chemistry - Bio Synthesis of Fatty AcidDocumento92 pagineLipid Chemistry - Bio Synthesis of Fatty AcidDonna Dominique GuariñoNessuna valutazione finora
- YuzurtDocumento2 pagineYuzurtFranco Ascari100% (1)
- BiomoleculesDocumento52 pagineBiomoleculesTrixie Rose Ebona CortezNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Science Biological MacromoleculesDocumento49 paginePhysical Science Biological MacromoleculesHannah Lee JudillaNessuna valutazione finora
- HMPE1 (Catering MGT.)Documento17 pagineHMPE1 (Catering MGT.)Rysyl Mae MoquerioNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulverizers: By: G. RamachandranDocumento140 paginePulverizers: By: G. Ramachandranshivshankar prajapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- ASNT QuestionsDocumento3 pagineASNT Questionsshabbir626100% (1)
- Chapter 2Documento8 pagineChapter 2Kate Wen GuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Zoology 1Documento53 pagineZoology 1Nouran SamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Basis of LifeDocumento26 pagineChemical Basis of LifeEla SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition 2011 EAMDocumento38 pagineNutrition 2011 EAMJayson BasiagNessuna valutazione finora
- MicronutrientsDocumento21 pagineMicronutrientsJohn Paolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes-1 BiomoleculesDocumento4 pagineNotes-1 BiomoleculesMa.Catherine NoblezaNessuna valutazione finora
- l3 Biological Molecules - Without DnaDocumento16 paginel3 Biological Molecules - Without Dnaapi-239537002Nessuna valutazione finora
- There Are 4 Main Biomolecules/macromoleculesDocumento2 pagineThere Are 4 Main Biomolecules/macromoleculesWendi SchroederNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbohydrate Lipids: Saturated Fatty Acid Unsaturated Fatty AcidsDocumento53 pagineCarbohydrate Lipids: Saturated Fatty Acid Unsaturated Fatty AcidsSyamila YusofNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 10 Biological MacromoleculesDocumento38 pagineLesson 10 Biological MacromoleculesKit ivy LituañasNessuna valutazione finora
- Draft Sooca Case 1 2014Documento22 pagineDraft Sooca Case 1 2014Hafdzi MaulanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological MacromoleculesDocumento92 pagineBiological MacromoleculesAilen Rose SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5 NutritionDocumento24 pagineUnit 5 Nutritionyarutewelde5.yaredteweldeNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomolecules: Chemical Compounds of The Living SystemDocumento89 pagineBiomolecules: Chemical Compounds of The Living SystemAriane DionisioNessuna valutazione finora
- To The Point New Ch1,2Documento7 pagineTo The Point New Ch1,2m.mansoor3377Nessuna valutazione finora
- Carbohydrates and LipidsDocumento11 pagineCarbohydrates and LipidsCarlene OretaNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Nutrition LectureDocumento66 pagineAnimal Nutrition Lecturemovie nightsNessuna valutazione finora
- MoleculesDocumento60 pagineMoleculesCharlize Jeneah MedinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomolecules (KH, Lemak, Protein) - Topik 3 FBS 1Documento47 pagineBiomolecules (KH, Lemak, Protein) - Topik 3 FBS 1Teofilus Dani PNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 60 NotesDocumento12 pagineBio 60 NotesLauraLBCCNessuna valutazione finora
- IJSO Biology Module - 3Documento207 pagineIJSO Biology Module - 3Ikhbaat Atiqur RehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3 - Molecules of LifeDocumento65 pagineLesson 3 - Molecules of Lifemariaeloisacarlos.pgpcsNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymes in Biotechnology: It IsDocumento26 pagineEnzymes in Biotechnology: It IsAnthony Farquhar WuNessuna valutazione finora
- BiomoleculesDocumento11 pagineBiomoleculesHarrish SandeevNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 LipidsDocumento59 pagine4 LipidsDESIGNERICLELYN SORONIONessuna valutazione finora
- Chem of Life 1 PDFDocumento14 pagineChem of Life 1 PDFJester LabanNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 17-Animal NutritionDocumento18 pagineWeek 17-Animal NutritionEugine Paul RamboyonNessuna valutazione finora
- Fat MetabolismDocumento30 pagineFat Metabolismborn2dive 9702Nessuna valutazione finora
- Aureus Penicillin G (Parenterally) and Penicillin V (Oral)Documento22 pagineAureus Penicillin G (Parenterally) and Penicillin V (Oral)jeffreyNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestive SystemDocumento102 pagineDigestive Systemkavya nandhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbohydrates SlidesDocumento75 pagineCarbohydrates SlidesShiva PratheekNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Revision 1st SecDocumento2 pagineFinal Revision 1st SecdhwbmmjgyzNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 Notes Part 1Documento10 pagineUnit 2 Notes Part 1calimagandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer in Biology Protein-A Large Macromolecules Consists of One or More Long Chains of Amino AcidsDocumento9 pagineReviewer in Biology Protein-A Large Macromolecules Consists of One or More Long Chains of Amino AcidsDanilo PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 11. Blood Biochemistry. Erythrocytes Metabolism. HemoglobinDocumento27 pagineLecture 11. Blood Biochemistry. Erythrocytes Metabolism. HemoglobinВіталій Михайлович НечипорукNessuna valutazione finora
- As 252 DR Victoria - ARCDocumento120 pagineAs 252 DR Victoria - ARCSuhuyineNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 1 Lesson 4Documento28 pagineBio 1 Lesson 4sattNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Enzymes, Nucleic Acids, ATP and MicronutrientsDocumento109 pagineOrganic Macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Enzymes, Nucleic Acids, ATP and MicronutrientsFENessuna valutazione finora
- Biology LectureDocumento28 pagineBiology LecturePhương Ngô VănNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemical MoleculesDocumento4 pagineBiochemical MoleculesValeria OlmedoNessuna valutazione finora
- Final LipdsDocumento90 pagineFinal LipdsEstrera Ruschelle A.Nessuna valutazione finora
- BIOMOLECULESDocumento22 pagineBIOMOLECULESNothing ToseehereNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology NotesDocumento30 pagineBiology NotesnadineNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOMOLECULESDocumento38 pagineBIOMOLECULESReflecta123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ap Cell Tour 2 EnergyDocumento39 pagineAp Cell Tour 2 Energyapi-235744933Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hormone Synthesis, Release and TransportDocumento24 pagineHormone Synthesis, Release and TransportRommanah AzmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology NotesDocumento16 pagineBiology NotesSarah Jane O Farrell100% (1)
- Animal AnatomyDocumento11 pagineAnimal AnatomyTimothee KazunguNessuna valutazione finora
- Lipid ChemistryDocumento37 pagineLipid ChemistryAnna KhurshidNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Molecular Biology IDocumento26 pagineLecture Molecular Biology ImartinmulingeNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal NutritionDocumento112 pagineAnimal NutritionJessa PalbanNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Science q3 Week 4 v2 RecoveredDocumento9 paginePhysical Science q3 Week 4 v2 Recoveredjensenearl934Nessuna valutazione finora
- Earth Sci Long TestDocumento1 paginaEarth Sci Long TestDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- Math STEM Tutorials Summary 2Documento1 paginaMath STEM Tutorials Summary 2Donnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus 1 Tutor - Worksheet 8 - Curve Sketching Using DerivativesDocumento17 pagineCalculus 1 Tutor - Worksheet 8 - Curve Sketching Using DerivativesDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 6 Review Conics Circles ParabolasDocumento4 pagineUnit 6 Review Conics Circles ParabolasDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- LiteratureDocumento3 pagineLiteratureDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- TrigoDocumento32 pagineTrigoDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Chapter 8 - Cell CommunicationDocumento8 pagineBiology Chapter 8 - Cell CommunicationDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost Estimate (Conct Fence VARONA)Documento2 pagineCost Estimate (Conct Fence VARONA)Donnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- EOCT Analytic Geometry Study Guide Revised January 2014Documento215 pagineEOCT Analytic Geometry Study Guide Revised January 2014jastillero1Nessuna valutazione finora
- BIOLOGY CHAPTER 11 - Nucleic Acids DNA and RNADocumento12 pagineBIOLOGY CHAPTER 11 - Nucleic Acids DNA and RNADonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bohol Earthquake 2013: EarthquakesDocumento12 pagineBohol Earthquake 2013: EarthquakesDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 - Leeuwenhoek September 1, 2016 Group 2Documento1 pagina11 - Leeuwenhoek September 1, 2016 Group 2Donnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pe10 LM U2Documento58 paginePe10 LM U2Donnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- Health ReportDocumento3 pagineHealth ReportDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- C Multi Dimensional ArraysDocumento2 pagineC Multi Dimensional ArraysDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- HealthDocumento3 pagineHealthDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- ArithmeticDocumento1 paginaArithmeticDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- Crea WriDocumento2 pagineCrea WriDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- DepEd Order No. 35, S. 2003Documento23 pagineDepEd Order No. 35, S. 2003Donnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- Literature and SocietyDocumento5 pagineLiterature and SocietyDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fandoms: Maria Beatriz B. VaronaDocumento24 pagineFandoms: Maria Beatriz B. VaronaDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- HumaDocumento1 paginaHumaDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- C ArraysDocumento3 pagineC ArraysDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- PR OJ EC T: Submitted To: Mr. Oliver Gatmen Teacher Submitted By: Maria Beatriz B. Varona 6 - CharityDocumento1 paginaPR OJ EC T: Submitted To: Mr. Oliver Gatmen Teacher Submitted By: Maria Beatriz B. Varona 6 - CharityDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- لآٌُِDocumento1 paginaلآٌُِDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- FranceDocumento4 pagineFranceDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bioluminescent Bacteria To Reduce Cancer CellsDocumento4 pagineBioluminescent Bacteria To Reduce Cancer CellsDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotechnology ReviewerDocumento5 pagineBiotechnology ReviewerDonnabelle VaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2 WaterDocumento32 pagine2.2 WaterHelena GlanvilleNessuna valutazione finora
- (Complete) BLC 201 Assignment Intro Logistics SCM Sep 2021 - McdonaldDocumento12 pagine(Complete) BLC 201 Assignment Intro Logistics SCM Sep 2021 - McdonaldHf CreationNessuna valutazione finora
- Yume Beauty Price ListDocumento1 paginaYume Beauty Price ListjessicaelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurology and Special Senses: High-Yield SystemsDocumento72 pagineNeurology and Special Senses: High-Yield SystemsMahmoud Abu MayalehNessuna valutazione finora
- BS 5422 2001 Method For Specifying Thermal Insulating Materials For Pipes, Tanks, Vessels, DuctDocumento60 pagineBS 5422 2001 Method For Specifying Thermal Insulating Materials For Pipes, Tanks, Vessels, DuctRamiAl-fuqahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cen-Tech 63759Documento8 pagineCen-Tech 63759GregNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 2: College of EngineeringDocumento3 pagineActivity 2: College of EngineeringMa.Elizabeth HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Medication Dosing GuildelinesDocumento2 paginePediatric Medication Dosing GuildelinesMuhammad ZeeshanNessuna valutazione finora
- I. Choose The Meaning of The Underlined Words Using Context CluesDocumento4 pagineI. Choose The Meaning of The Underlined Words Using Context CluesMikko GomezNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Nursing?: What Exactly Do Nurses Do?Documento3 pagineWhat Is Nursing?: What Exactly Do Nurses Do?mabel yapuraNessuna valutazione finora
- 2006 SM600Documento2 pagine2006 SM600Ioryogi KunNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Different Fruit Peels FormulationsDocumento3 pagineApplication of Different Fruit Peels FormulationsYvette GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiation Hazards & Radiation ProtectionDocumento62 pagineRadiation Hazards & Radiation ProtectionGurupada JanaNessuna valutazione finora
- E GarageDocumento36 pagineE GarageLidijaSpaseskaNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Diagnosis of Parasitic DiseasesDocumento57 pagineLaboratory Diagnosis of Parasitic DiseasesAmanuel MaruNessuna valutazione finora
- Handover Paper Final 22 3 16 BJNDocumento13 pagineHandover Paper Final 22 3 16 BJNsisaraaah12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Normal Microflora of Human BodyDocumento14 pagineNormal Microflora of Human BodySarah PavuNessuna valutazione finora
- All About Ocean Life-Rachel BladonDocumento6 pagineAll About Ocean Life-Rachel BladonRichard TekulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet 2 - TLC - Updated Summer 2021Documento4 pagineWorksheet 2 - TLC - Updated Summer 2021Bria PopeNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemorrhagic Shock (Anestesi)Documento44 pagineHemorrhagic Shock (Anestesi)Dwi Meutia IndriatiNessuna valutazione finora
- 8DJ - 8DH Katalog en PDFDocumento32 pagine8DJ - 8DH Katalog en PDFJosue Espinoza YachachinNessuna valutazione finora
- Goat AnatomyDocumento8 pagineGoat AnatomyLochi GmNessuna valutazione finora