Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
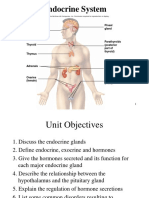
Hormones
Caricato da
Tang Tiong Min 郑中铭Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Hormones
Caricato da
Tang Tiong Min 郑中铭Copyright:
Formati disponibili
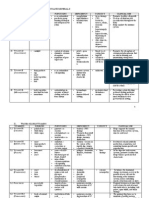
Hormone
Neck
Gland which produces it
Position in the body
Diagram of gland
Target organs
Response of the Abnormal body functions
Controls basic metabolism and growth rate Lack: Dwarfism, mental retardation Excess: Hyperactivity
Thyroxine
Thyroid
/
liver liver Increases levels of sugar in blood Decreases level of sugar in blood
Insulin Pancreas Above kidneys
Islets of Langerhans
Pancreas
Lack: Diabetes mellitus Lack: Diabetes mellitus
Glucagon
Islets of Langerhans
Adrenaline
Adrenal gland
Vital organs, liver Fight or flight actions by increasing heartbeat & heart etc.
sugar level
Oestrogen
Ovary
Abdomen (dorsal wall) Abdomen (dorsal wall) In scrotum Pituitary gland
Female reproductive organs
Controls secondary sexual characteristics E.g. growth of hair, breasts, etc
Causes delay of these changes Prevents uterine wall When low contraction menstruation occurs
Progesterone
Ovary
Testosterone
Testis
Male reproductive Controls secondary sexual Causes delay of characteristics organs these changes
E.g. deepening of voice
TSH Part of the brain
Pituitary
Part of the brain
thyroid Ovaries, testes
Controls thyroid Follicles develop in the uterus, increase sperm production Ovaries, testes kidney Activity of other endocrine glands is effected if pituitary is not functioning properly.
FSH
Pituitary
LH
Pituitary
Part of the brain Part of the brain
ADH
Pituitary
Causes ovulation and testosterone release Lack: excessive loss of water Causes kidney to reabsorb wtaer
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- List of Hormones - Hypersecretion and HyposecretionDocumento11 pagineList of Hormones - Hypersecretion and HyposecretionAngeli Jean Koreen Corpuz88% (48)
- Endocrine SystemDocumento3 pagineEndocrine SystemAnne Jillian83% (6)
- Gland Hormone Target Tissue Principle Actions Chemical NatureDocumento4 pagineGland Hormone Target Tissue Principle Actions Chemical Naturernalfas100% (1)
- Hormone Summary ChartDocumento1 paginaHormone Summary ChartVDiesel990% (2)
- Hormones and Endocrine SystemsDocumento26 pagineHormones and Endocrine SystemsNikko Adhitama100% (4)
- Where Hormone Is Produced Hormone Secreted Chemical Class Target Cell Location Hormone FunctionDocumento3 pagineWhere Hormone Is Produced Hormone Secreted Chemical Class Target Cell Location Hormone FunctionRNStudent1100% (1)
- Hormones TableDocumento84 pagineHormones TableSaajid AmraNessuna valutazione finora
- Patho Immune System PathologyDocumento7 paginePatho Immune System PathologyCoy Nuñez100% (1)
- Allergy and HypersensitivityDocumento73 pagineAllergy and HypersensitivityAdi PomeranzNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Hormones and Their Functions: Balete, Berida, BorromeoDocumento88 pagineAnimal Hormones and Their Functions: Balete, Berida, BorromeoRessabela Juniper FayneNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Clinical Reproductive EndocrinologyDa EverandIntroduction to Clinical Reproductive EndocrinologyValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- Endocrine System: A Tutorial Study GuideDa EverandEndocrine System: A Tutorial Study GuideValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Oestrogen, Progesterone, AndrogensDocumento58 pagineOestrogen, Progesterone, AndrogensTandin SonamNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenocorticosteroids & Adrenocortical AntagonistsDocumento20 pagineAdrenocorticosteroids & Adrenocortical Antagonistsapi-3859918Nessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenal Hormones: HydrocortisoneDocumento4 pagineAdrenal Hormones: HydrocortisoneDyanne AguilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System (Pathophysiology)Documento18 pagineEndocrine System (Pathophysiology)roselle legson100% (1)
- Biochemistry of Hormones - Lecture NotesDocumento9 pagineBiochemistry of Hormones - Lecture NotesAyukafangha EtandoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Endocrine System: Presented By, MD Nasir Uddin Mahmood, Product Executive, Opsonin Pharma LimitedDocumento24 pagineThe Endocrine System: Presented By, MD Nasir Uddin Mahmood, Product Executive, Opsonin Pharma LimitedMd Nasir Uddin Mahmood100% (2)
- Endocrine HarmonyDocumento68 pagineEndocrine HarmonyafnanNessuna valutazione finora
- HormonesDocumento29 pagineHormonesCandy Chieng67% (3)
- Endocrine SystemDocumento20 pagineEndocrine SystemSheena Pasion100% (2)
- HormonesDocumento2 pagineHormonesMario IstrefiNessuna valutazione finora
- Major & Trace MineralsDocumento5 pagineMajor & Trace MineralsRhenier S. IladoNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin Mineral ChartDocumento4 pagineVitamin Mineral ChartAnonymous snSfklbI8p100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocumento96 pagineEndocrine SystemSandhya Kakkar100% (3)
- Reproductive HormonesDocumento43 pagineReproductive HormonesMunchkin CelinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hormones of Thyroid and Parathyroid GlandDocumento16 pagineHormones of Thyroid and Parathyroid Glandapi-25908492100% (1)
- Mechanism of Action of HormonesDocumento33 pagineMechanism of Action of HormonesMehwishNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin ChartDocumento5 pagineVitamin ChartHimNessuna valutazione finora
- The Hormone HandbookDocumento74 pagineThe Hormone Handbookvictoria100% (2)
- Medical Assisting: Powerpoint To AccompanyDocumento30 pagineMedical Assisting: Powerpoint To AccompanyJam Knows Right100% (1)
- Hormones and BehaviourDocumento367 pagineHormones and BehaviourRojo100% (3)
- Blood Test and Normal RangeDocumento40 pagineBlood Test and Normal Rangeethirukumaran0% (1)
- Liver As Endocrine - Stuart WhiteDocumento53 pagineLiver As Endocrine - Stuart WhitechicanahenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine SystemDocumento5 pagineEndocrine SystemKimberly Anne SP Padilla100% (2)
- List of Physiology PracticalsDocumento2 pagineList of Physiology PracticalsSeerat Ul irfanNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins and Minerals Study QuestionsDocumento14 pagineVitamins and Minerals Study QuestionsRaymond100% (3)
- HormonesDocumento43 pagineHormonesDontu Maria0% (1)
- Recommendations To Maintain Immune Health in Athletes Walsh 2018Documento13 pagineRecommendations To Maintain Immune Health in Athletes Walsh 2018Felipe Ricardo Garavito PeñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Microbiology PassnplexDocumento25 pagineMicrobiology PassnplexVerónica BezaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Return To The Medical Biochemistry PageDocumento8 pagineReturn To The Medical Biochemistry Pagevibhav82Nessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System Review Flashcards - QuizletDocumento5 pagineEndocrine System Review Flashcards - QuizletDani Anyika100% (1)
- GI HormonesDocumento23 pagineGI Hormonesriskyy1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins and Minerals TableDocumento4 pagineVitamins and Minerals TableEliza Paula Bacud100% (3)
- Understanding Lab Results - Lab Testing E-BookDocumento463 pagineUnderstanding Lab Results - Lab Testing E-BookBrent Hussong100% (2)
- Chapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine SystemDocumento8 pagineChapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine System123456789123456789hi100% (2)
- Water & Mineral MetabolismDocumento151 pagineWater & Mineral MetabolismSicilia Bunga Athifah ArnurNessuna valutazione finora
- Hormone Health:: How To Get Your Hormones Back in BalanceDocumento9 pagineHormone Health:: How To Get Your Hormones Back in BalanceHarindra DunuwilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine SystemDocumento59 pagineEndocrine SystemCharm Angeles100% (3)
- The Blood: Rubie Maranan-Causaren, MSDocumento73 pagineThe Blood: Rubie Maranan-Causaren, MSlady ann jimenez100% (3)
- B VitaminsDocumento7 pagineB VitaminsAppzStarNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestive SystemDocumento9 pagineDigestive SystemMemes only100% (3)
- Essential Amino Acids Functions: Patricia Anne Nicole C. Mansat Bs Nursing BiochemDocumento4 pagineEssential Amino Acids Functions: Patricia Anne Nicole C. Mansat Bs Nursing BiochembiologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Aging & Cell DeathDocumento94 pagineCell Aging & Cell Deathcholan1177% (13)
- Reproductive Hormones and Their FunctionsDocumento6 pagineReproductive Hormones and Their FunctionsOwolabi PetersNessuna valutazione finora
- Female HormonesDocumento28 pagineFemale Hormonesİlbey Kayra Özçelik100% (1)
- Microbiome Impact On Metabolism and Function of Sex, Thyroid, Growth and Parathyroid Hormones 2015Documento13 pagineMicrobiome Impact On Metabolism and Function of Sex, Thyroid, Growth and Parathyroid Hormones 2015Brenda FolkNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Important Blood Tests PART-1 PDFDocumento22 pagine10 Important Blood Tests PART-1 PDFDimple100% (3)
- Thyroid HormonesDocumento47 pagineThyroid Hormonesamalia100% (1)
- Urinary Organic Acids DR BralleyDocumento5 pagineUrinary Organic Acids DR BralleyMetametrixNessuna valutazione finora
- Myvi BrochureDocumento2 pagineMyvi BrochurePartiban SathiaseelanNessuna valutazione finora
- 四种爱 PDFDocumento12 pagine四种爱 PDFTang Tiong Min 郑中铭Nessuna valutazione finora
- "历史上"的耶稣Documento21 pagine"历史上"的耶稣Tang Tiong Min 郑中铭Nessuna valutazione finora
- Draw The Process of Mitosis and MeiosisDocumento4 pagineDraw The Process of Mitosis and MeiosisTang Tiong Min 郑中铭Nessuna valutazione finora
- Draw The Process of Mitosis and MeiosisDocumento4 pagineDraw The Process of Mitosis and MeiosisTang Tiong Min 郑中铭Nessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 6.8Documento2 pagineExperiment 6.8Tang Tiong Min 郑中铭Nessuna valutazione finora
- Topical Test-Quadratic Expressions and EquationsDocumento2 pagineTopical Test-Quadratic Expressions and EquationsTang Tiong Min 郑中铭Nessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 1 DietDocumento15 pagineUNIT 1 DietTang Tiong Min 郑中铭Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Klinefelter Syndrome ?: Genetic DiseasesDocumento5 pagineWhat Is Klinefelter Syndrome ?: Genetic DiseasesTang Tiong Min 郑中铭Nessuna valutazione finora
- Topical Test-Standard FormDocumento2 pagineTopical Test-Standard FormTang Tiong Min 郑中铭Nessuna valutazione finora
- Blue Bird PDFDocumento1 paginaBlue Bird PDFTang Tiong Min 郑中铭Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Biology Form 4 NotesDocumento2 pagineChapter 3 Biology Form 4 Notesanahusni100% (3)
- Hots Dalam Matematik Sesi Perbengkelan: Bahagian Pembangunan Kurikulum Kementerian Pelajaran MalaysiaDocumento3 pagineHots Dalam Matematik Sesi Perbengkelan: Bahagian Pembangunan Kurikulum Kementerian Pelajaran MalaysiaTang Tiong Min 郑中铭Nessuna valutazione finora
- Asking Effective QuestionsDocumento8 pagineAsking Effective Questionsjrogenski9000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Module Chemical Composition in The Cell: WaterDocumento16 pagineBiology Module Chemical Composition in The Cell: Waternorrmus71Nessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 3 Conditions Supporting LifeDocumento8 pagineUNIT 3 Conditions Supporting LifeTang Tiong Min 郑中铭Nessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 4 TransportDocumento16 pagineUNIT 4 TransportTang Tiong Min 郑中铭Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Nutrient Functions and Deficiency and Toxicity SymptomsDocumento16 paginePlant Nutrient Functions and Deficiency and Toxicity SymptomsTang Tiong Min 郑中铭Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sains - Biology Form 5Documento56 pagineSains - Biology Form 5Sekolah Portal100% (5)
- Biology Form 5: Chapter 5 - InheritanceDocumento3 pagineBiology Form 5: Chapter 5 - InheritanceTang Tiong Min 郑中铭Nessuna valutazione finora
- (24.01) Plant Essential ElementsDocumento33 pagine(24.01) Plant Essential ElementsTang Tiong Min 郑中铭Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biologyform5 Chapter6 130716042847 Phpapp01Documento2 pagineBiologyform5 Chapter6 130716042847 Phpapp01Sharmini RajagopalNessuna valutazione finora
- Biologyform5 Chapter6 130716042847 Phpapp01Documento2 pagineBiologyform5 Chapter6 130716042847 Phpapp01Sharmini RajagopalNessuna valutazione finora
- Tekanan UdaraDocumento5 pagineTekanan UdaraAini AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 4 - Biology NotesDocumento59 pagineForm 4 - Biology Notesshahmi200679% (28)
- Vitamin C ContentDocumento2 pagineVitamin C ContentTang Tiong Min 郑中铭Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 RevisionDocumento3 pagineChapter 1 RevisionTang Tiong Min 郑中铭Nessuna valutazione finora
- Calvin Institutes of The Christian ReligionDocumento944 pagineCalvin Institutes of The Christian ReligionTheologienNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise Introduction To ScienceDocumento17 pagineExercise Introduction To Science颜慧嘉Nessuna valutazione finora