Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Steam Power Plant
Caricato da
Karthikn AltocCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Steam Power Plant
Caricato da
Karthikn AltocCopyright:
Formati disponibili
POWER PLANT ENGINEERING
INTRODUCTION Power plays a greater role wherever man lives and works. Electricity is the only form of energy which is easy to produce, transport and easy to control. The types of power plants which is used to produce the electricity are thermal, nuclear, hydraulic, gas turbine and geothermal.
In the above said power plants, the thermal power plants generate more than 80% of the total electricity produced in the world. Fossil fuel like coal, fuel oil and natural gas are the energy sources and steam is the working fluid. Thermal power production cost in India is more when compared to nuclear power due to rise in oil prizes. Hydraulic power plants are essentially multi purposes. It is used for power generation as well as irrigation. Nuclear energy has enlarged the worlds power resources. The amount of energy released by burning one kilogram of uranium is equivalent to the energy obtained by burning 4500tonnes of high-grade coal. The renewable energy source like solar energy in India has ideal geographical situations. If the sunshine is bright for an average of 8hours/day, then the amount of heat equivalent is more than 200MW per square kilometer. In this unit, the various layouts of power plants are discussed. They are shown below as follows: 1. Steam or thermal power plant. 2. Hyde power plant. 3. Diesel power plant. 4. Magneto hydrodynarnic (MHD). 5. Nuclear and gas power plants.
POWER PLANT ENGINEERING
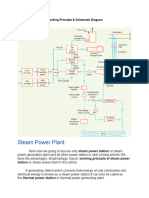
STEAM POWER PLANT
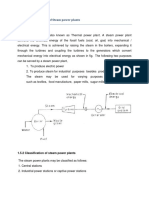
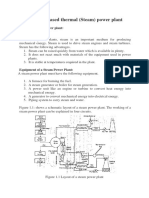
Introduction: Steam is an important medium for producing mechanical energy. A steam power plant continuously converts the energy stored in fossil fuels (coal, oil and natural gas). Steam has the advantage that it can be raised from water which is available in abundance. The steam power stations are very much suitable where coal is available in abundance. The pressure ranges from 10kg/cm2 to super critical pressure and temperature varies from 250C to 650C. Working Principle Steam or thermal power plant is using steam as working fluid. Steam is produced in a boiler using coal as fuel and used to drive the prime mover (Steam turbine).The heat energy is converted into mechanical energy by the steam turbine and that mechanical energy is used for generating power with the help of generator. The layout of the steam power plant consists of four main circuits as shown in below figure. The main circuits are given below as follows: 1. Coal and ash circuit. 2. Water and steam circuit. 3. Air and flue gas circuit. 4. Cooling water circuit.
POWER PLANT ENGINEERING 1. Coal and ash circuit: This circuit consists of coal storage, ash storage, coal handling and ash handling systems. Coal from mines is delivered by ships, rails or trucks to the power station. Coal received at coal yard. Coal is sized by crushers, breakers etc., the sized coal is stored in coal storage. From stock yard, the coal is transferred to the boiler furnace by means of conveyors, elevators etc. The coal is burnt in the boiler and ash is formed. Ash coming out of the furnace will be too hot, dusty and accompanied by poisonous gases. The ash is transferred to the ash storage. Generally the ash will be quenched to reduce the temperature and the dust content. The handling system consists of belt conveyors, screw conveyors etc. Coal from the storage yard is transferred to the boiler furnace by means of coal handling equipment as shown in below figure.
Ash resulting from the combustion of coal in the boiler furnace is removed to ash storage through ash handling. The Indian coal contains 30 to 40% of ash and a power plant of 100MW produces normally 20 to 25 tons of hot ash per hour. 2. Air and flue gas circuit: Air is taken from the atmosphere by the action of Forced Draft fan it is then passed to the air preheated; the dust from the air is removed by means of using air filter.
POWER PLANT ENGINEERING The air is preheated by the flue gases in the pre heater. This preheated air is supplied to the furnace to aid the combustion of fuel. Due to the combustion of fuel the flue gases are formed. The flue gases from the furnace pass over the boiler tubes and super heater tubes. Then the flue gases pass through economiser to heat the feed water. After that it passes through a dust collector. It is then exhausted to atmosphere through chimney. 3. Feed water and steam circuit: The steam generated in the boiler passes through super heater and is supplied to the steam turbine. Heat is transferred to the water by the burning of the coal. The steam is expanded in the steam turbine then passed to the condenser where it is condensed. The turbine drives generator to produce electric power. The condensate is heated in the HP and LP heaters using the steam tapped from different points of the turbine.
The feed water is passing through the economizer, where it is further heated by means of flue gases. Using the economizer, the feed water is heated by the feed water heaters and then it is fed into the boiler. Part of the steam and water are lost while passing through different components of the system. The expanded steam is then passed through the condenser. In the condenser, steam is condensed into water then re circulated. 4. Cooling water circuit: This circuit consists of circulating water pump, condenser, cooling water pumps and cooling tower. The exhaust steam from the turbine is condensed in the condenser. Adequate water supply is available from various sources like river or lake. In the condenser, the cold water is circulated to condense the steam into water. The steam is then condensed by losing its latent heat to the circulating the cold water. Hence the cold water gets heated.
POWER PLANT ENGINEERING The basic layout of the cooling water circuit is shown in below figure.
This hot water is then taken to a cooling tower. In cooling tower the water is sprayed in the form of droplets through nozzles. The atmospheric air enters the cooling tower from the openings provided at the bottom of the tower. This cold water is again circulated through the pump, condenser and the cooling. Some amount of water may be lost during circulation. Hence make up water is added to the pond by means of a pump. Characteristics of steam power plant: The characteristics of the steam power plant or thermal power plant is given below as follows: 1. Low cost as compared with hydro power plant. 2. High efficiency. 3. Reduced water requirement. 4. Higher reliability and availability. 5. Reduced environmental impact in terms of air pollution. Advantages of steam power plant: The advantages of the steam power plant or the thermal power plant is shown in below figure: 1. The power production does not depend on nature mercy. 2. Initial investment is low. 5
POWER PLANT ENGINEERING 3. The power plant can be located near load center, so the transmission cost and losses are considerably reduced. 4. The time requirement for construction and commissioning of thermal power plant require less period of time. 5. Life of plant is more (25-30 years ) compared to Diesel plant (2-5 years) 6. Repair and maintenance cost is low when compared to diesel plant. 7. Suitable for varying load conditions. 8. No radioactive harmful wastes are produced 9. Unskilled operators can operate the plant. 10. The power generation does not depend on the water storage. 11. There are no transmission losses, as they are located near load centers. Disadvantages of steam power plant: The disadvantage of the steam power plant is given below as follows: 1. As compared with hydro-electric power plant, life and efficiency are less. 2. Transportation of fuel is a major problem in this type of power plant. 3. Power generation cost is considerably high when compared to hydro-electric plant. 4. Air pollution is the major problem calling for additional investment. 5. It cannot be used as peak load plant. 6. Cooling water required is more. 7. Space required is more. 8. Storage required for the fuel is more. 9. Ash handling is a big problem 6. The coal (fuel) needed may be exhausted by gradual use. 7. Less efficient than diesel plants. 8. Starting up and bringing into service takes more time. 9. Not economical in areas which are remote from coal fields. 10. Manpower required is more. 11. For large units, the capital cost is more.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Introduction To Electrical Power Systems: by K.rajendraDocumento101 pagineIntroduction To Electrical Power Systems: by K.rajendrak rajendraNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit III Classification of Power PlantsDocumento21 pagineBasic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit III Classification of Power PlantsSiman NapstervkkNessuna valutazione finora
- Dry Cooling Systems1.2Documento40 pagineDry Cooling Systems1.2paragmishra1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Steam Power PlantDocumento20 pagineSteam Power PlantSiddi Sampath Kumar Reddy100% (1)
- PP 9th Meeting GENERATING STATIONS Thermal Power PlantDocumento5 paginePP 9th Meeting GENERATING STATIONS Thermal Power PlantJohn Kenneth LoricoNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Power PlantsDocumento24 pagineThermal Power Plantslakshmigsr6610100% (1)
- Steam Power PlantDocumento7 pagineSteam Power PlantsuganyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1.power Plant LayoutDocumento5 pagine1.1.power Plant LayoutBALAMBAL R100% (1)
- Thermal Power Plant - EeDocumento20 pagineThermal Power Plant - EePrabhat Chandra100% (1)
- Physics 4.Documento5 paginePhysics 4.SOLAIMANNessuna valutazione finora
- Steam Power Plant (PLTU)Documento5 pagineSteam Power Plant (PLTU)Aldi ErzanuariNessuna valutazione finora
- Report #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantDocumento41 pagineReport #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantKian TecsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Plant Engineering MTPP-1Documento13 paginePower Plant Engineering MTPP-1devendra pratapNessuna valutazione finora
- Selections of Powerplants LocationDocumento4 pagineSelections of Powerplants LocationMostafa GadelrabNessuna valutazione finora
- Rohini 86450143586Documento8 pagineRohini 86450143586Anksupriya BanerjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Power Plants (Steam Power Plants) : Instructor: Engr. Intisar Ali SajjadDocumento51 pagineThermal Power Plants (Steam Power Plants) : Instructor: Engr. Intisar Ali SajjadVishal PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- T Project ReportDocumento63 pagineT Project ReportArif AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Power Plant Project ReportDocumento63 pagineThermal Power Plant Project Reportasutoshjena28171% (24)
- Lecture No 3Documento4 pagineLecture No 3Musa KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Coal Fired Thermal Power Plant What Is A Thermal Power Plant?Documento6 pagineCoal Fired Thermal Power Plant What Is A Thermal Power Plant?carlo manabatNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal EngineeringDocumento10 pagineThermal Engineeringlokeshdhangar842Nessuna valutazione finora
- Me Lab 3Documento27 pagineMe Lab 3Jerome Vega AndesNessuna valutazione finora
- CoalDocumento48 pagineCoallekoringoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Power PlantDocumento6 pagineThermal Power PlantMasha Allah QasimiNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Power Plant Diagram All You Need To Know About ItDocumento7 pagineThermal Power Plant Diagram All You Need To Know About Itngoc hoangNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Visit Report On Siddhirganj 210MW Thermal Power StationDocumento14 pagineIndustrial Visit Report On Siddhirganj 210MW Thermal Power StationSaibNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Power PlantDocumento35 pagineThermal Power PlantAngelaa DassNessuna valutazione finora
- General Layout of A Thermal Power PlantDocumento87 pagineGeneral Layout of A Thermal Power PlantHarjith Vaibav100% (1)
- Thermal Power PlantDocumento16 pagineThermal Power PlantmudarNessuna valutazione finora
- EXP-1 Steam Power PlantDocumento7 pagineEXP-1 Steam Power PlantsejalNessuna valutazione finora
- Project ReportDocumento103 pagineProject ReportSeth CamachoNessuna valutazione finora
- Report of Electrical Wiring: Submitted To: Sir Urooj Uz ZafarDocumento21 pagineReport of Electrical Wiring: Submitted To: Sir Urooj Uz Zafarshrawan0908Nessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Power PlantDocumento31 pagineThermal Power PlantfefwerewNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To CFPPDocumento34 pagineIntroduction To CFPPVenkat CherukuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Steam Powerplant ReportDocumento14 pagineSteam Powerplant ReportAngeli Cascaño JoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Power Plant: Gaini Zail Singh Punjab Technical University Campus (Bathinda)Documento30 pagineThermal Power Plant: Gaini Zail Singh Punjab Technical University Campus (Bathinda)Sriram ramsNessuna valutazione finora
- Steam Power Plant: Boiler CondenserDocumento4 pagineSteam Power Plant: Boiler Condenserwajahat aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Power Plant: Shubham Thakur 13BME8149 5MEL3 Mechanical EngineeringDocumento34 pagineThermal Power Plant: Shubham Thakur 13BME8149 5MEL3 Mechanical EngineeringMos MohNessuna valutazione finora
- Steam Power PlantDocumento3 pagineSteam Power PlantRima SadekNessuna valutazione finora
- Table of Content: Page Number 1 3 2 Parts 6 3 Function Diagram 8 4 Function 9 5 Advantages 18 6 Disadvantages 20Documento20 pagineTable of Content: Page Number 1 3 2 Parts 6 3 Function Diagram 8 4 Function 9 5 Advantages 18 6 Disadvantages 20Utsav ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Plant Instrumentation Class Notes For Dr. Sanjeev Kumar Raghuwanshi Electronics Engineering Department IIT (ISM) DhanbadDocumento55 paginePower Plant Instrumentation Class Notes For Dr. Sanjeev Kumar Raghuwanshi Electronics Engineering Department IIT (ISM) DhanbadviratNessuna valutazione finora
- Gajendra KumarDocumento23 pagineGajendra KumarGAJENDRA KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Power PlantDocumento29 pagineThermal Power PlantSiri VenniNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Power Plant - Diagram, Layout, Working & ConstructionDocumento25 pagineThermal Power Plant - Diagram, Layout, Working & ConstructionACME NKSTPPNessuna valutazione finora
- Report On Jenco Thermal Power PlantDocumento18 pagineReport On Jenco Thermal Power PlantMuhammadAbbasJafriNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Training Report ON C & I Maintenance Division Unit-8 AT Panipat Thermal Power StationDocumento27 pagineIndustrial Training Report ON C & I Maintenance Division Unit-8 AT Panipat Thermal Power StationAbhishek AroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ukai Thermal Power Plant-Eman Refai Abdelkhaliq-Sec 3Documento13 pagineUkai Thermal Power Plant-Eman Refai Abdelkhaliq-Sec 3eman.refai13lcsNessuna valutazione finora
- NTPCDocumento33 pagineNTPCSubodh DuhanNessuna valutazione finora
- "Thermal Power Generation": Seminar Report OnDocumento10 pagine"Thermal Power Generation": Seminar Report OnAram Nasih MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Generation of Electric PowerDocumento108 pagineGeneration of Electric Powermausam sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Training Report NTPCDocumento30 pagineIndustrial Training Report NTPCTabish KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ppe NotesDocumento51 paginePpe NotesCharan PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Training AT: Submitted By: Rishikesh (11-1-6-002) NIT, SilcharDocumento26 pagineIndustrial Training AT: Submitted By: Rishikesh (11-1-6-002) NIT, SilcharRakesh Roshan KeshriNessuna valutazione finora
- Coal-Based Electricity ProductionDocumento11 pagineCoal-Based Electricity ProductionkirannainwalNessuna valutazione finora
- SIREreport 118ee0297Documento13 pagineSIREreport 118ee0297Bhabani sankar KishanNessuna valutazione finora
- Jagan Steam Power PlantDocumento101 pagineJagan Steam Power PlantMahender VangalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Plant EngineeringDocumento74 paginePower Plant EngineeringPranesh Ka100% (1)
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesDa EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningDa EverandThermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Waste Heat Recovery FactsheetDocumento2 pagineWaste Heat Recovery FactsheetMajid JafariNessuna valutazione finora
- Cround Source Heat PumpDocumento7 pagineCround Source Heat PumpVu Hai TruongNessuna valutazione finora
- GTL Technology Small Scale - by V.wanDocumento11 pagineGTL Technology Small Scale - by V.wanDebye101Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amine Gas SweeteningDocumento2 pagineAmine Gas SweeteningCeleste DopazoNessuna valutazione finora
- Fossil Energy: ASME Standards & Certification Energy-Related Products and ServicesDocumento1 paginaFossil Energy: ASME Standards & Certification Energy-Related Products and ServicesBayu TriwijayantaNessuna valutazione finora
- Compro Dakara Otto Mazurra BriketDocumento9 pagineCompro Dakara Otto Mazurra BriketSunMori IndustiralNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-MA Energy ResourcesDocumento8 pagine1-MA Energy Resources09joaquin.arcasNessuna valutazione finora
- PV System AnalysisDocumento5 paginePV System AnalysisklguuNessuna valutazione finora
- Syngas: 2.1 Steam Methane ReformingDocumento4 pagineSyngas: 2.1 Steam Methane ReformingthetreeoutthewindowNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydel Power: Meaning, Review and ExplainationDocumento25 pagineHydel Power: Meaning, Review and ExplainationAnirudhNessuna valutazione finora
- Green EnergyDocumento6 pagineGreen EnergyWAR FIRENessuna valutazione finora
- Terminal Blocks For PV ApplicationsDocumento1 paginaTerminal Blocks For PV ApplicationsSEO BDMNessuna valutazione finora
- Submittal Data Sheet: Ffq18Q2Vju / Rx18QmvjuDocumento2 pagineSubmittal Data Sheet: Ffq18Q2Vju / Rx18QmvjuEdNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Rooftop SolarDocumento6 pagineBasics of Rooftop SolarVasanth Kumar VNessuna valutazione finora
- SG Unit 1 PPT 2,3 H OurDocumento13 pagineSG Unit 1 PPT 2,3 H OurrajaramprathibaNessuna valutazione finora
- Company Profile MetalindoDocumento38 pagineCompany Profile MetalindoAngga PratamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Atlantis Solar Tech SpecsDocumento1 paginaAtlantis Solar Tech SpecsAditya GognaNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization of Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) Sizing For Solar Power Plant at Remote AreaDocumento7 pagineOptimization of Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) Sizing For Solar Power Plant at Remote AreaLuisito RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- OPEN ACCESS PPT 10-07-2021 v2Documento19 pagineOPEN ACCESS PPT 10-07-2021 v2JE Elec-Drg UBLNessuna valutazione finora
- NGL-PIAAP-00007-0712 Depropanizer PDFDocumento2 pagineNGL-PIAAP-00007-0712 Depropanizer PDFHairunnisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar Thermal PowerDocumento30 pagineSolar Thermal PowerMd Moinul Alom ShovonNessuna valutazione finora
- Reacting Gas MixturesDocumento2 pagineReacting Gas MixturesAxel Flores GonzalezNessuna valutazione finora
- Brochure Miscanthus en Low ResDocumento4 pagineBrochure Miscanthus en Low ResIuliana AndreiNessuna valutazione finora
- CBDMT - Market and Business Intelligence - White BiotechnologyDocumento1 paginaCBDMT - Market and Business Intelligence - White BiotechnologycbdmtNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete Project of Biomass Briquetting MachineDocumento23 pagineComplete Project of Biomass Briquetting MachineDeepi17100% (2)
- Lidetu Abu Thesis ProposalDocumento24 pagineLidetu Abu Thesis ProposalLîdé ÂbNessuna valutazione finora
- SRM TRP Engineering College - Lesson PlanDocumento3 pagineSRM TRP Engineering College - Lesson Planmaran2326Nessuna valutazione finora
- Torri FactionDocumento16 pagineTorri FactionhedayatinluvNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Feasibility Study of Hydrogen Production Using Electrolysis 3 PDFDocumento107 pagine3 Feasibility Study of Hydrogen Production Using Electrolysis 3 PDFJervisDeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Embodied EnergyDocumento10 pagineEmbodied Energyabhi krishNessuna valutazione finora