Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Quant Master Session - TGs Geometry II For CAT-12 PDF
Caricato da
Gunjan SolankiDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Quant Master Session - TGs Geometry II For CAT-12 PDF
Caricato da
Gunjan SolankiCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Quant Master
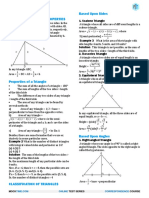
INRADIUS & CIRCUMRADIUS
Geometry Problems for CAT-12
Inradius (r) is radius of the incircle inscribed in a triangle which touches all the sides of the triangle. Circumradius (R) is radius of circumcircle passing through all the vertices of triangle. We have already mentioned the formulae to find r and R in terms of area of triangle. *If b, c are two sides of triangle and h is the altitude drawn from vertex common to b and c, then R = bc/2h. *For a right triangle with legs a, b and hypotenuse c, inradius r = (a + b c)/2
Congruent Triangles The two triangles, whose any three corresponding parameters (out of three sides and three angles) are identical are same to be congruent. There are three exceptions to this rule and they are AAA, SSA and ASS. Two congruent triangles are identical in all respects.
Similar Triangles The two triangles are said to be similar (I) if two of the angles of triangles are same AA, or (II) if two sides of a triangle are proportional to two sides of another triangle and angle included between the two sides in both the triangles is same SAS. Sides opposite to equal sides are said to be proportional sides and ratio of proportional sides is same. Area of two similar triangles is in the ratio of square of ratio of corresponding sides.
For any suggestions, corrections or improvements to this sheet and more of similar POWs, log on to our website
http://totagopinath.com
Quant Master
Geometry Problems for CAT-12
C. QUDRILATERALS Area of a quadrilateral
If side lengths of a quadrilateral are a, b, c, d, then its area is not constant. By changing internal angles, we can change area of the quadrilateral. For example take the case of a square with side length 5 whose area is 25 square units. Now keeping the side lengths constant, if we tilt it to turn it into a rhombus, area goes o decreasing which can ultimately minimised to zero when the sides overlap with each other. So, for a given set of four side lengths, Maximum Area is obtained for a cyclic quadrilateral which is given by
(s a)(s b)(s c )(s d ) (BRAHMGUPTAs formula) where s is semiperimeter i.e. (a + b + c + d)/2.
Remember that for every four side lengths which form a quadrilateral, a cyclic quadrilateral can be formed.
If D1 and D2 are the two diagonals of a quadrilateral which intersects at angle P, then its area is given by D1D2sinP. And this area will be largest when diagonals intersect at right angle.
Ptolemys inequality For a quadrilateral with side lengths a, b, c, d and diagonals of length D1 and D2, we have D1D2 ac + bd Equality arises in case of a cyclic quadrilateral.
If two diagonals divide a quadrilateral in four triangles, as shown, whose areas are A, B, C and D in order, then AC=BD
For any suggestions, corrections or improvements to this sheet and more of similar POWs, log on to our website
http://totagopinath.com
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Geometry: Triangles and Their Properties Based Upon SidesDocumento34 pagineGeometry: Triangles and Their Properties Based Upon SidesVaseem Raza Mirza100% (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDa EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (8)
- Math TermsDocumento6 pagineMath TermsChristelle Kaye BisnarNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- 4.2 Congruence of Triangles (Reflexive, Symetric, Transitive)Documento22 pagine4.2 Congruence of Triangles (Reflexive, Symetric, Transitive)MiiMii Imperial Ayuste100% (1)
- Salary Slip Sept 2014 PDFDocumento2 pagineSalary Slip Sept 2014 PDFGunjan SolankiNessuna valutazione finora
- Plane and Solid GeometryDocumento21 paginePlane and Solid Geometryrose FrondaNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus 8th Edition Stewart Solutions ManualDocumento35 pagineCalculus 8th Edition Stewart Solutions Manualsubbaseweasy0n3r100% (28)
- Tangent, SphericalDocumento9 pagineTangent, Sphericalfrawler22Nessuna valutazione finora
- MC35 Geometry Ch07 Handout-209Documento5 pagineMC35 Geometry Ch07 Handout-209SCARLETT CARSONNessuna valutazione finora
- All Math FormulasDocumento27 pagineAll Math FormulasMubassher Ahmed Shoaib100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Operation On IntegerDocumento12 pagineDetailed Lesson Plan in Operation On IntegerGladzangel Loricabv100% (10)
- Week 011angles in A Unit CircleDocumento7 pagineWeek 011angles in A Unit CircleJieann BalicocoNessuna valutazione finora
- Area & VolumeDocumento15 pagineArea & VolumeParthasarathi H RNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF Radius of Curvature CompressDocumento7 paginePDF Radius of Curvature CompressSollutions for techNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulas For Pre-Olympiad Competition Math: Eashan Gandotra 4 August 2017Documento11 pagineFormulas For Pre-Olympiad Competition Math: Eashan Gandotra 4 August 2017jehovisti100% (1)
- Formulas Pre OlympiadDocumento11 pagineFormulas Pre Olympiadbus9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Areas of Polygons and CirclesDocumento36 pagineAreas of Polygons and CirclesStevenzel Eala EstellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kurt Girstmair Napier400Memorial Napier - Spherical KLK 20160730Documento16 pagineKurt Girstmair Napier400Memorial Napier - Spherical KLK 20160730shyan berwaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths FormulaDocumento11 pagineMaths FormulaSajjad HameedNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry: 3. Solid BodiesDocumento40 pagineGeometry: 3. Solid BodiesEduardo Tello del PinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Radius of CurvatureDocumento7 pagineRadius of CurvatureYash LokhareNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet Area and Perimeter Answer KeyDocumento7 pagineGrade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet Area and Perimeter Answer Keygeetha100% (1)
- 1.1 Radian and Degree MeasureDocumento16 pagine1.1 Radian and Degree MeasureJOVANIE CLAVERONessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus NilDocumento7 pagineCalculus NilPushpak ShewaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Airline Tickets: Unit SquareDocumento1 paginaAirline Tickets: Unit SquareCarol LizardoNessuna valutazione finora
- General Organic and Biological Chemistry 2nd Edition Frost Test Bank 1Documento36 pagineGeneral Organic and Biological Chemistry 2nd Edition Frost Test Bank 1amynash23052000xne100% (30)
- AreaDocumento13 pagineAreaamitjustamitNessuna valutazione finora
- S - Geo Team SolutionsDocumento3 pagineS - Geo Team SolutionsJake ZengNessuna valutazione finora
- Rumus PrimoidalDocumento7 pagineRumus PrimoidaltsipilNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Notes Two AREASDocumento19 pagine4 Notes Two AREASfosuohenefrankjnrNessuna valutazione finora
- Primer Trig PhysicsDocumento13 paginePrimer Trig PhysicsjayNessuna valutazione finora
- Coc-Pen Math1 Study Guide of Trigonometry 01 Easy Way (How To Learn Trigonometry Faster)Documento9 pagineCoc-Pen Math1 Study Guide of Trigonometry 01 Easy Way (How To Learn Trigonometry Faster)Marlon AmpoNessuna valutazione finora
- GeometryDocumento28 pagineGeometryASHWIN .A.S.Nessuna valutazione finora
- D. Inverse Trigonometric Functions: One-To-One OntoDocumento69 pagineD. Inverse Trigonometric Functions: One-To-One Ontoabdullah naseerNessuna valutazione finora
- Transactions American Geophysical UnionDocumento6 pagineTransactions American Geophysical Unionlo5tboy5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7Documento16 pagineChapter 7Pyae Sone KyawNessuna valutazione finora
- The Many Faces of Gauss-Bonnet TheoremDocumento12 pagineThe Many Faces of Gauss-Bonnet TheoremFabian Correa QuinchiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Demystified GMAT Quant CapsuleDocumento14 pagineDemystified GMAT Quant CapsulePankaj DebnathNessuna valutazione finora
- GRE (Graduate Record Examination) Quant Formulas 1. SquareDocumento8 pagineGRE (Graduate Record Examination) Quant Formulas 1. SquareJeevitha BandiNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 103 Lecture Notes: Leah Keshet January 9, 2005Documento28 pagineMath 103 Lecture Notes: Leah Keshet January 9, 2005nagaraj108Nessuna valutazione finora
- TheoremDocumento8 pagineTheoremJoseph FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Orthogonal Curvilinear CoordinatesDocumento16 pagineOrthogonal Curvilinear CoordinatesstriaukasNessuna valutazione finora
- On The SAT - Triangles and CirclesDocumento13 pagineOn The SAT - Triangles and CirclesAnonymous 79okqFNessuna valutazione finora
- Celm 3Documento38 pagineCelm 3Nguyen Cac Diem DucNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of A RhombusDocumento4 pagineProperties of A Rhombusapi-150547803Nessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of A RhombusDocumento4 pagineProperties of A Rhombusapi-150547803Nessuna valutazione finora
- Celm 3Documento40 pagineCelm 3Xinrex NicolasNessuna valutazione finora
- Gre Math Review 6Documento11 pagineGre Math Review 6or tesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Formule Geometrijska TjelaDocumento1 paginaFormule Geometrijska TjelaFlorian KestenNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of A RhombusDocumento4 pagineProperties of A Rhombusapi-140032165Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cycloid Are AsDocumento5 pagineCycloid Are Aseduardopaiva9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Rules PDFDocumento21 pagineGeometry Rules PDFVadlamudiMohanKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- TrapeziumDocumento4 pagineTrapeziumPAWAN NAGALNessuna valutazione finora
- GeometryDocumento12 pagineGeometryJose Marviel JesoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Weatherwax Contest Problem BooksDocumento329 pagineWeatherwax Contest Problem BooksMkanNessuna valutazione finora
- Spherical Triangle PDFDocumento31 pagineSpherical Triangle PDFGiorgi BalkhamishviliNessuna valutazione finora
- Left-Right Symmetric Models From Higher Dimensional SpaceDocumento5 pagineLeft-Right Symmetric Models From Higher Dimensional SpaceIOSRjournalNessuna valutazione finora
- Last Perio Rev MathDocumento9 pagineLast Perio Rev MathDenniela Anica VergaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mensuration of Plane Figures (Quadrilateral)Documento10 pagineMensuration of Plane Figures (Quadrilateral)Danica AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE7 AreaComputationsDocumento17 pagineMODULE7 AreaComputationsMark Angelo LoceriagaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A CircleDocumento10 pagineWhat Is A Circlevalli rajuNessuna valutazione finora
- SDM - 2016-18 - Course OutlineDocumento22 pagineSDM - 2016-18 - Course OutlineGunjan SolankiNessuna valutazione finora
- Floor Pricing of "Plasto Cover" Floor Cover: 140 Price of "Plasto Cover" For Time of 5 Year in Case of Optimistic SellingDocumento4 pagineFloor Pricing of "Plasto Cover" Floor Cover: 140 Price of "Plasto Cover" For Time of 5 Year in Case of Optimistic SellingGunjan SolankiNessuna valutazione finora
- CASE 6: Hanover Bates Chemical Corporation: Group 5Documento1 paginaCASE 6: Hanover Bates Chemical Corporation: Group 5Gunjan SolankiNessuna valutazione finora
- 507419143 (1)Documento2 pagine507419143 (1)Gunjan Solanki0% (1)
- Mont BlancDocumento1 paginaMont BlancGunjan SolankiNessuna valutazione finora
- Body BoiloutDocumento1 paginaBody BoiloutGunjan SolankiNessuna valutazione finora
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Electrostatic PrecipitatorsDocumento9 pagineUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Electrostatic PrecipitatorsGunjan SolankiNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbonyl Sulfide / Carbon Dioxide at 1.00 Atm by SRK: Job: Reactor Date: 05/21/2014 Time: 00:17:30Documento1 paginaCarbonyl Sulfide / Carbon Dioxide at 1.00 Atm by SRK: Job: Reactor Date: 05/21/2014 Time: 00:17:30Gunjan SolankiNessuna valutazione finora
- State Bank of India ReciptDocumento1 paginaState Bank of India ReciptGunjan SolankiNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbonyl Sulfide / Carbon Dioxide at 1.00 Atm by SRK: Job: Reactor Date: 05/21/2014 Time: 00:17:30Documento1 paginaCarbonyl Sulfide / Carbon Dioxide at 1.00 Atm by SRK: Job: Reactor Date: 05/21/2014 Time: 00:17:30Gunjan SolankiNessuna valutazione finora
- CIRCLESDocumento2 pagineCIRCLESSabria SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Addition and Subtraction of Decimals and Mixed DecimalsDocumento15 pagineAddition and Subtraction of Decimals and Mixed DecimalsReynaldo B. LapakNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 8 Applications of IntegralsDocumento46 pagineNCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 8 Applications of IntegralsAarna BhardwajNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of Square2Documento4 pagineProperties of Square2MarkdanielRamiterreNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-Calculus Test On Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry Date: - Name: - PeriodDocumento3 paginePre-Calculus Test On Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry Date: - Name: - PeriodIshaan VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- FS - Paulino - Lesson PlanDocumento10 pagineFS - Paulino - Lesson PlanMarco SeəsonNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Miscellaneous QuestionsDocumento7 pagine03 Miscellaneous QuestionsRekha BhasinNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 6 Mathematics First Term Paper Practice PaperDocumento2 pagineGrade 6 Mathematics First Term Paper Practice PaperSiddhi Gupta100% (1)
- Math151 Module 2Documento11 pagineMath151 Module 2Yanni BarrientosNessuna valutazione finora
- Equation of A Tangent To A CurveDocumento7 pagineEquation of A Tangent To A CurvePaula FanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pascals TriangleDocumento4 paginePascals TriangleAmit kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- SR Maths - IiaDocumento12 pagineSR Maths - IiaNandhan MedaramittaNessuna valutazione finora
- HMMT Feb2020 C PDFDocumento20 pagineHMMT Feb2020 C PDFashrithNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry m3 Copy Ready MaterialsDocumento28 pagineGeometry m3 Copy Ready MaterialsOliver SevillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sec2Maths EndYrExamsDocumento135 pagineSec2Maths EndYrExamstuananh2410Nessuna valutazione finora
- Slope Equation: Problem 1 of 6Documento6 pagineSlope Equation: Problem 1 of 6Nilam DoctorNessuna valutazione finora
- Term1 GR9 Im P6Documento7 pagineTerm1 GR9 Im P6hitarth shahNessuna valutazione finora
- MathDocumento27 pagineMathRhoda MontesNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.1 Simplifying RadicalsDocumento8 pagine7.1 Simplifying RadicalsChinthaka Nayana Kumara RajapakshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet-5 Sequence & Series (V)Documento68 pagineWorksheet-5 Sequence & Series (V)tanishk goyalNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.5 Volume of Cube and CuboidsDocumento3 pagine4.5 Volume of Cube and Cuboidsbashirkaram177Nessuna valutazione finora
- Keamanan Informasi2 Pertemuan 4: Mohammad Hafiz Hersyah, M.T Rifki Suwandi, M.TDocumento72 pagineKeamanan Informasi2 Pertemuan 4: Mohammad Hafiz Hersyah, M.T Rifki Suwandi, M.TMuhammaf IrfanNessuna valutazione finora
- TriangleDocumento40 pagineTriangleZafar khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sumande - Field Work No.9 - Determination of The Height of A Remote PointDocumento14 pagineSumande - Field Work No.9 - Determination of The Height of A Remote PointCedrix SumandeNessuna valutazione finora
- fx-570ES PLUS fx-991ES PLUS: User's GuideDocumento46 paginefx-570ES PLUS fx-991ES PLUS: User's GuideHassanKMNessuna valutazione finora
- Loci in The Argand Diagram LESSONDocumento3 pagineLoci in The Argand Diagram LESSONMisum AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of Integers: 1 The Well-Ordering Principle: Mathematical InductionDocumento8 pagineProperties of Integers: 1 The Well-Ordering Principle: Mathematical Inductionb9902233Nessuna valutazione finora