Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Sba5s1a-1 D Handout
Caricato da
Meo MapTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Sba5s1a-1 D Handout
Caricato da
Meo MapCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Packet Tracer 4.
0 Troubleshooting Activity: SBA 5S1A-1_D Troubleshooting InterVLAN Routing
Objective
Use Packet Tracer to practice and develop the following skills: Troubleshoot connectivity between VLANs Verify trunking and Inter-VLAN routing functionality
Scenario
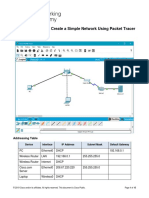
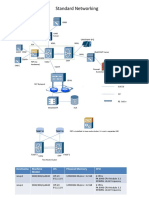
The network topology above represents a simple network that requires a router for communication between VLANs and for examining Inter-VLAN routing functionality. You are given a Class C network address of 192.168.1.0 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.224 (or 192.168.1.0 / 27). The three subnets starting with Subnet 1, are assigned to each VLAN.
Required Files
To complete this lab, you will need the following file: SBA5S1A-1_D.pka
Step 1 Open the Required File
1. Start Packet Tracer 4.0 2. Click on File > Open 3. Navigate to the correct directory/folder and open: SBA5S1A-1_D.pka
1-4 Packet Tracer 4.0 Activity Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc.
The following network topology and activity instructions should be displayed:
Step 2 Check Connectivity and Gather Information
1. Using the Packet Tracer Simple or Complex PDU feature in the Simulation mode, ping between the PCs in each VLAN, observe the packets, check the PDU info, and record the results. Attempt each ping twice. a. Ping between PC0 and PC1: b. Ping between PC0 and PC2: c. Ping between PC1 and PC2:
2. Using the Packet Tracer Inspection Tool or router CLI feature, examine the routing table of the router. a. What networks/subnetworks are in the routing table? 1) 2) 3)
2-4
Packet Tracer 4.0 Activity
Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc.
3. Examine the router configuration and record the IP addresses and interfaces to which they are assigned. a. b. c. 4. Using the Packet Tracer switch CLI feature, examine the switch configuration. a. Besides the default VLANs, what other VLANs are configured? 1) 2) 3) b. What ports are assigned to each VLAN? 1) 2) 3) 4) 5. Using the Packet Tracer PC Config or Desktop features, check the network settings for each PC and record. a. PC0: 1) IP Address and Subnet Mask: 2) Default Gateway: b. PC1: 1) IP Address and Subnet Mask: 2) Default Gateway: c. PC2: 1) IP Address and Subnet Mask: 2) Default Gateway:
Step 3 Examine and Analyze Information Collected and Identify Problem
1. Examine and analyze the information collected in the previous step. Briefly explain your findings and identify possible causes for the lack of connectivity between one VLAN and the other two.
3-4
Packet Tracer 4.0 Activity
Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Step 4 Determine a Plan of Action and Correct the Problem
1. Based upon the information collected and your examination and analysis, what course of action should be taken to correct the problem?
2. Using the Packet Tracer router CLI feature, make the changes necessary to correct the problem.
Step 5 Verify Trunking and Inter-VLAN Routing
1. Using the Packet Tracer Inspection Tool then CLI, examine the routing table on the router to verify the subnetworks have been installed correctly. 2. In the Packet Tracer Realtime mode, check end-to-end connectivity between the PCs with a simple PDU and a CLI ping between PCs.
Step 6 Examine the Routed Packets
1. In the Packet Tracer Simulation mode, check that only the ICMP event is selected in the Event Lists Filter at the bottom of the Simulation Panel. 2. Reset/clear all entries by clicking on the New button in the Scenario section of the Packet Tracer window. 3. Using the Simple PDU option, ping between PC0 and PC1, then ping between PC0 and PC2, then ping between PC1 and PC2, the click on the Auto Capture / Play button and observe the packets in the Event List window and topology. 4. When satisfied with your configuration, click on "Check Results".
4-4
Packet Tracer 4.0 Activity
Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Capstone 12 Stem ADocumento12 pagineCapstone 12 Stem ACashcade MercadejasNessuna valutazione finora
- Person Experiences Vigilance Decrement Due ToDocumento6 paginePerson Experiences Vigilance Decrement Due ToThrowaway TwoNessuna valutazione finora
- Local Media4030320246374826145Documento13 pagineLocal Media4030320246374826145Mae AbabonNessuna valutazione finora
- Pearl Dean Phil. v. Shoemart20210424-12-29t876Documento19 paginePearl Dean Phil. v. Shoemart20210424-12-29t876reese93Nessuna valutazione finora
- RIZKA NURUL OKTAVIANI - 120110180007 - TugasFinancialPlanningDocumento4 pagineRIZKA NURUL OKTAVIANI - 120110180007 - TugasFinancialPlanningRizka OktavianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 Service ManagementDocumento27 pagineModule 1 Service Managementkishore kNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Module 2Documento17 pagineCisco Module 2Froilan LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Processing of Fruit JamDocumento29 pagineProcessing of Fruit JamdavisdhunganaNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer - Amplitude ModulationDocumento11 pagineAnswer - Amplitude ModulationRichard RegidorNessuna valutazione finora
- Packet Tracer - Lab 1: Basic Switch Setup: Network DiagramDocumento3 paginePacket Tracer - Lab 1: Basic Switch Setup: Network DiagramjohnNessuna valutazione finora
- CaregivingDocumento35 pagineCaregivingJesusa AtienzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Q2-Module1 - G7 or 8 - Nail-Care - Bulaoen East NHS PDFDocumento9 pagineQ2-Module1 - G7 or 8 - Nail-Care - Bulaoen East NHS PDFRonna NicolasNessuna valutazione finora
- Southern Leyte Provincial Training Center: Housekeeping ScheduleDocumento24 pagineSouthern Leyte Provincial Training Center: Housekeeping ScheduleFrancis D. AlvarNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Sheet For 7.1.2.9 Lab - Converting IPv4 Addresses To BinaryDocumento4 pagineAnswer Sheet For 7.1.2.9 Lab - Converting IPv4 Addresses To Binaryرافد البركي78% (18)
- Sentential ConnectivesDocumento10 pagineSentential Connectivesmuhammad100% (2)
- Accounting Information System Course SyllabusDocumento10 pagineAccounting Information System Course Syllabusali alhussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networks SyllabusDocumento3 pagineComputer Networks SyllabuskrupeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Title: Barangay Profiling System With Analytics Author: Bernard Jacobe1, Mark Lester Pascua2, Billy Jay Tumbali3, Maria ClarissaDocumento8 pagineTitle: Barangay Profiling System With Analytics Author: Bernard Jacobe1, Mark Lester Pascua2, Billy Jay Tumbali3, Maria ClarissaBryan EstacioNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL Math7w5 - 2022 - 2023Documento9 pagineDLL Math7w5 - 2022 - 2023Rodel CaliniahanNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Lab IP Addressing Lab Student 1 enDocumento4 pagine3 Lab IP Addressing Lab Student 1 enDianka BodnarNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Model Canvas PDFDocumento1 paginaBusiness Model Canvas PDFFernando III PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networking: Ahmad Nadeem Ix Aster Comuter Networking Summer AssignmentDocumento36 pagineComputer Networking: Ahmad Nadeem Ix Aster Comuter Networking Summer AssignmentAhmad NadeemNessuna valutazione finora
- Students OrientationDocumento3 pagineStudents OrientationLomyr Jaine Ronda100% (1)
- NegoDocumento6 pagineNegoIvhy Cruz EstrellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3. Services Marketing (Quality Service Management)Documento11 pagineModule 3. Services Marketing (Quality Service Management)MARITONI MEDALLANessuna valutazione finora
- Packet Tracer Lab - Create A Simple Network Using Packet TracerDocumento15 paginePacket Tracer Lab - Create A Simple Network Using Packet TracerNam Nguyễn HoàngNessuna valutazione finora
- CO Food ProcessingDocumento25 pagineCO Food Processingchricyl mae leganadNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 Performance Task 1Documento2 pagine04 Performance Task 1jay elacoNessuna valutazione finora
- NSTP Final ExamDocumento6 pagineNSTP Final ExamJohn Carl AparicioNessuna valutazione finora
- Claret College of Isabela: Senior High SchoolDocumento5 pagineClaret College of Isabela: Senior High SchoolLatifah EmamNessuna valutazione finora
- Binary To DecimalDocumento8 pagineBinary To DecimalEmmanuel JoshuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Earthquake Detector Using Arduino: A Mini Project ReportDocumento20 pagineEarthquake Detector Using Arduino: A Mini Project ReportAbhishek DhadgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Final 01Documento129 pagineFinal 01Marveen TingkahanNessuna valutazione finora
- PNTC Colleges: Activity SheetDocumento10 paginePNTC Colleges: Activity SheetPagtakhan Mary JoyNessuna valutazione finora
- IP Addressing and SubnettingDocumento28 pagineIP Addressing and SubnettingIsmat Jahan NabilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Measure of Central TendencyDocumento18 pagineMeasure of Central Tendencyprince samNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking Essentials 2.0 Module2Documento35 pagineNetworking Essentials 2.0 Module2Hafiz Fachrezzy100% (1)
- Final Ccna3 ANSWERS TO ALL EXAMSDocumento357 pagineFinal Ccna3 ANSWERS TO ALL EXAMSDev TomarNessuna valutazione finora
- A Comparative Study On The Level of Awareness Towards Trial by PublicityDocumento85 pagineA Comparative Study On The Level of Awareness Towards Trial by PublicityChezka David PrejidoNessuna valutazione finora
- ICpEP CpE Challenge ProgrammingDocumento3 pagineICpEP CpE Challenge ProgrammingMorikidan YukizutoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tle9cookery q12Documento20 pagineTle9cookery q12Jayzi VicenteNessuna valutazione finora
- MARKET STUDY Chapter 34 1Documento51 pagineMARKET STUDY Chapter 34 1Steve HerobrineNessuna valutazione finora
- The Tuna Shanghai Roll and Its Effectiveness To Grade 11 and 12 Students of St. Augustine College of Las PinasDocumento4 pagineThe Tuna Shanghai Roll and Its Effectiveness To Grade 11 and 12 Students of St. Augustine College of Las PinasKim Porsha RitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Cookery12 q2 Module8Documento15 pagineFinal Cookery12 q2 Module8Junah SumalinogNessuna valutazione finora
- Uae QuestionnaireDocumento3 pagineUae QuestionnaireevahNessuna valutazione finora
- PharmAnal 3Documento84 paginePharmAnal 3Aaron Jhulian SimbitNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 10 DLL Quarter 3 Week 10Documento3 pagineMath 10 DLL Quarter 3 Week 10Mary Christine IgnacioNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL 1st Quarter Week 9Documento2 pagineDLL 1st Quarter Week 9Kareen GerminianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Creating Cross Over and Straight Through CablesDocumento2 pagineCreating Cross Over and Straight Through CablesRenz SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - Computer and Internet Crime 1Documento27 pagineChapter 3 - Computer and Internet Crime 1Benedicto Mendoza Quidem IIINessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Analysis and Reporting (Introduction)Documento5 pagineFinancial Analysis and Reporting (Introduction)Mariadel Yrog-irog100% (1)
- RAW Quarter 4 Week 3Documento33 pagineRAW Quarter 4 Week 3Lc CacaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ched-Marina Moa PDFDocumento45 pagineChed-Marina Moa PDFChes Vergara100% (1)
- CCNA1 Subnetting Practice 3 Answers Using PTDocumento4 pagineCCNA1 Subnetting Practice 3 Answers Using PTHace StevenNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Table of ContentsDocumento4 pagine2 Table of Contentssidereal28Nessuna valutazione finora
- DLL-TLE8-Caregiving Exploratory CourseDocumento5 pagineDLL-TLE8-Caregiving Exploratory CourseRenier SuarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Computerized Sales and Inventory System For 3K A.D Agliam Construction SupplyDocumento25 pagineComputerized Sales and Inventory System For 3K A.D Agliam Construction SupplyRica Jhoy De VeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Sycs CN DocumentationDocumento11 pagineSycs CN Documentationharshittiwari070401Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vlan 6Documento3 pagineVlan 6Emerson Emerson AemersonNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 2-3-PracticalDocumento6 pagineWeek 2-3-Practicalエンリコ エリカNessuna valutazione finora
- Nist SP 800-82 PDFDocumento156 pagineNist SP 800-82 PDFMeo MapNessuna valutazione finora
- Mesos Tech ReportDocumento14 pagineMesos Tech ReportMeo MapNessuna valutazione finora
- Daily Credit Report: Consumption CDR CNT #Load Rows #Processed #Error #Ignored #SuccessfulDocumento54 pagineDaily Credit Report: Consumption CDR CNT #Load Rows #Processed #Error #Ignored #SuccessfulMeo MapNessuna valutazione finora
- C1Lab08 PacketTracerConfigDocumento6 pagineC1Lab08 PacketTracerConfigMeo MapNessuna valutazione finora
- Python Design PatternDocumento82 paginePython Design PatternMeo Map100% (1)
- Schwarzkopf - Omega AlgorithmDocumento14 pagineSchwarzkopf - Omega AlgorithmMeo MapNessuna valutazione finora
- ICCLab Ceilometer CHOSUG PresentationDocumento23 pagineICCLab Ceilometer CHOSUG PresentationMeo MapNessuna valutazione finora
- System Analysis, Design & Implementation 1Documento16 pagineSystem Analysis, Design & Implementation 1Meo MapNessuna valutazione finora
- Minna II Answer MondaiDocumento58 pagineMinna II Answer MondaiMeo Map83% (178)
- System Analysis, Design & Implementation 2Documento93 pagineSystem Analysis, Design & Implementation 2Meo MapNessuna valutazione finora
- AIW425 Week00 OrientationDocumento13 pagineAIW425 Week00 OrientationMeo MapNessuna valutazione finora
- System Analysis, Design and ImplementationDocumento19 pagineSystem Analysis, Design and ImplementationMeo MapNessuna valutazione finora
- Programming: Information System Design and ImplementationDocumento22 pagineProgramming: Information System Design and ImplementationMeo MapNessuna valutazione finora
- FIT441 - AIW Tutorial Advanced Internet & Web ServicesDocumento3 pagineFIT441 - AIW Tutorial Advanced Internet & Web ServicesMeo MapNessuna valutazione finora
- EBZ Group AssignmentDocumento2 pagineEBZ Group AssignmentMeo MapNessuna valutazione finora
- CET437: Electronic Business: Week 4: E-Business Implementation, Infrastructure and ManagementDocumento44 pagineCET437: Electronic Business: Week 4: E-Business Implementation, Infrastructure and ManagementMeo MapNessuna valutazione finora
- Online SurveyDocumento1 paginaOnline SurveyMeo MapNessuna valutazione finora
- CET437: Electronic Business: Week 4: E-Business Implementation, Infrastructure and ManagementDocumento42 pagineCET437: Electronic Business: Week 4: E-Business Implementation, Infrastructure and ManagementMeo MapNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Case 9-30 Master BudgetDocumento6 pagineProject Case 9-30 Master Budgetleizalm29% (7)
- Workshop 6 - Project Time Management: Student: La Son Hai ID: 1c0901040025Documento5 pagineWorkshop 6 - Project Time Management: Student: La Son Hai ID: 1c0901040025Meo MapNessuna valutazione finora
- Project For MAT204Documento2 pagineProject For MAT204Meo MapNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 PreDCR - HelpManual PDFDocumento128 pagine1 PreDCR - HelpManual PDFJaydutt TailorNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.3.3.2 Lab - Troubleshoot LAN Traffic Using SPANDocumento6 pagine5.3.3.2 Lab - Troubleshoot LAN Traffic Using SPANYaser Samer0% (6)
- FiscalNote Whitepaper On Legislative TechDocumento9 pagineFiscalNote Whitepaper On Legislative TechJon OrtizNessuna valutazione finora
- Dataman 8050: Reference ManualDocumento44 pagineDataman 8050: Reference ManualFernando JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Web Design Principles and ElementsDocumento16 pagineWeb Design Principles and ElementsJacey Bautista MargalloNessuna valutazione finora
- Ccna 2 Module 11 v4.0Documento3 pagineCcna 2 Module 11 v4.0ccnaexploration4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Communication Systems Ii - LabmanualDocumento12 pagineCommunication Systems Ii - LabmanualpramodNessuna valutazione finora
- EEE 264-5: 3G Wireless NetworksDocumento102 pagineEEE 264-5: 3G Wireless NetworksSundus Ali100% (1)
- Huawei E5172 Kasutusjuhend ENGDocumento50 pagineHuawei E5172 Kasutusjuhend ENGGiancarlo Ortiz Benavides0% (1)
- Security PsAdminDocumento28 pagineSecurity PsAdminRiyaz AhamedNessuna valutazione finora
- CIS Controls v8 Mapping To Microsoft Azure Security Benchmarkv3 2 202Documento224 pagineCIS Controls v8 Mapping To Microsoft Azure Security Benchmarkv3 2 202Franck BNessuna valutazione finora
- Archimate Language Primer: Introduction To The Archimate Modelling Language For Enterprise ArchitectureDocumento27 pagineArchimate Language Primer: Introduction To The Archimate Modelling Language For Enterprise Architecturepeterche100% (2)
- ZTE UMTS Admission Control ParametersDocumento72 pagineZTE UMTS Admission Control ParametersAttila Kovács100% (2)
- IBM Spectrum Protect: Trusted Backup and Recovery Software SolutionsDocumento8 pagineIBM Spectrum Protect: Trusted Backup and Recovery Software Solutionsaldozp1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Huawei IN ArchitechtureDocumento4 pagineHuawei IN ArchitechtureNazmuz ZamanNessuna valutazione finora
- DSAM ManualDocumento362 pagineDSAM ManualMarco OchoaNessuna valutazione finora
- Website Analysis Overview Report: October 2019Documento5 pagineWebsite Analysis Overview Report: October 2019Anna FogarassyNessuna valutazione finora
- DGTL Brksec 2113Documento143 pagineDGTL Brksec 2113paulo_an7381Nessuna valutazione finora
- CIS Controls v8 Mapping To SOC2 Final 08-19-2021Documento105 pagineCIS Controls v8 Mapping To SOC2 Final 08-19-2021Ramon AlvarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Release ACOS 4.1.4-GR1-P10 IssuesDocumento241 pagineRelease ACOS 4.1.4-GR1-P10 IssuesdanielatellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Xspoc ManualDocumento175 pagineXspoc ManualANDEINessuna valutazione finora
- Aeronautical CommunicationsDocumento18 pagineAeronautical CommunicationsBibinMathewNessuna valutazione finora
- Matter EnabledDocumento7 pagineMatter Enabledsuraj kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Eltek Valere - Ethernet Controller - Operation Manual - V1.1Documento37 pagineEltek Valere - Ethernet Controller - Operation Manual - V1.1timmylau23Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wcs Installation GuideDocumento32 pagineWcs Installation GuideNamit SwarNessuna valutazione finora
- HoneywellDocumento78 pagineHoneywellAnonymous zMWvcTNessuna valutazione finora
- Specification: FeatureDocumento1 paginaSpecification: Featurenaveen643Nessuna valutazione finora
- Form ValidationDocumento4 pagineForm ValidationJASPER WESSLYNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Plan Guru99Documento9 pagineTest Plan Guru99saswataNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Parameter - Ue State HandlingDocumento39 pagineLTE Parameter - Ue State HandlingSatria Wibowo100% (5)