Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
GT8 - M - H&S Paper 1
Caricato da
Meet ShahTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
GT8 - M - H&S Paper 1
Caricato da
Meet ShahCopyright:
Formati disponibili
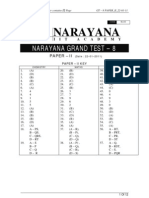
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
1 Of 20
CODE BLUE
NARAYANA
I I T A C A D E M Y
NARAYANA GRAND TEST 8
PAPER I (Dat e : 22012011)
PAPER I KEY
CHEMI STRY MATHS PHYSI CS
1. (C)
2. (C)
3. (C)
4. (B)
5. (A)
6. (A)
7. (D)
8. (B)
9. (A), (B), (D)
10. (A), (B), (C), (D)
11. (C), (D)
12. (A), (D)
13. (A), (C), (D)
14. (D)
15. (A)
16. (D)
17. (A)
18. (A)
19. 7
20. 3
21. 7
22. 5
23. 4
24. 4
25. 5
26. 6
27. 7
28. 4
29. (D)
30. (A)
31. (B)
32. (A)
33. (C)
34. (B)
35. (A)
36. (C)
37. (A, B, C)
38. (A, B, C, D)
39. (A, C)
40. (B, C, D)
41. (A, C)
42. (B)
43. (A)
44. (A)
45 (A)
46. (A)
47. (2)
48. (0)
49. (5)
50. (4)
51. (4)
52. (6)
53. (6)
54. (2)
55. (6)
56. (1)
57. (A)
58. (B)
59. (D)
60. (C)
61. (D)
62. (A)
63. (A)
64. (A)
65. (A), (B)
66. (A), (C), (D)
67. (B), (C)
68. (A), (B), (D)
69. (C), (D)
70. (A)
71. (A)
72. (C)
73. (C)
74. (A)
75. 7
76. 0
77. 8
78. 7
79. 6
80. 3
81. 2
82. 4
83. 8
84. 9
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
2 Of 20
HI NTS & SOLUTI ON
PAPER - I
CHEMISTRY
1. (C)
Extent of t bonding increases with increases the electronegativity.
2. (C)
Conceptual
3. (C)
Conceptual
4. (B)
It is not possible for the Mo.
5. (A)
6. (A)
If the difference in size of cation and anion is large then hydration energy will be
dominant.
7. (D)
(A) As K
SP
of hydroxides of Al
3+
, Fe
3+
& Cr
3+
are low and NH
4
Cl suppresses the
ionisation of NH
4
OH
(B) (NH
4
)
2
SO
4
+Ba
2+
BaSO
4
(white) + 2NH
4+
.
(C) SO
4
2
+Ba
2+
BaSO
4
(white) as it contains SO
4
2
as anion.
8. (B)
Average
1 2
1 v,m 2 v,m
v,m
1 2
3 5
2 R 2 R
nC n C
2 2
C 2R
n n 2 2
+
+
= = =
+ +
9. (A), (B), (D)
10. (A), (B), (C), (D)
11. (C), (D)
In complex bond order of O
2
+
is 2.5 whereas in KO
2
bonder order of O
2
is 1.5.
12. (A), (D)
The reaction in which chiral centre is produced racemic mixture is obtained due to
flipping in this compound.
13. (A), (C), (D)
14. (D)
Bottle 2 +bottle 3 colourless gas, carbon dioxide
sodiumcarbonate +acid
It suggests bottle 2 and 3 contains sodiumcarbonate and HCl.
Bottle 3 +4 blue precipitate confirms the Cu
2+
in either of bottle considering available
sulphate, chloride, nitrate and carbonate.
Precipitate must be carbonate.
Hence, 3 carbonate (sodiumcarbonate)
4 Cu
2+
2 HCl
15. (A)
Pb(NO
3
)
2
+Cu SO
4
Cu(NO
3
)
2
+ PbSO
4
Soluble white ppt.
Bottle 1 Bottle4
16. (D)
Bottle 4 CuSO
4
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
3 Of 20
Cu
2+
(aq) +4NH
3
(aq) [Cu(NH
3
)
4
]
2+
(aq)
Distinctive blue colour
19. 7
20. 3
O
H
H
H
O
H
H
O
H
H
O
H
H
21. 7
A = 8 (1/8) +4 (1/2) =3
B =12 (1/4) +1 =4
Total atoms =3 +4 =7
22. 5
0.3 =0.591 pH
pH =5.085
23. 4
(i) Boiling point : PH
3
<AsH
3
<NH
3
<SbH
3
(ii) Bond angle: H
2
O <OF
2
<OCl
2
(iii) Solubility: BeSO
4
>MgSO
4
>CaSO
4
>SrSO
4
>BaSO
4
(iv) Acidic strength: HCOOH >C
6
H
5
COOH >CH
3
COOH >C
6
H
5
OH >CH
3
OH >H
2
O
24. 4
2
4
CrO
,
2
2 7
Cr O
,
4
MnO
, Cu
2
O
25. 5
Three Hb between G and C
Two Hb between A and T
26. 6
2 log 4
27. 7
E(7 2) =E5
28. 4
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
4 Of 20
MATHEMATICS
29. (D)
By the property of inverse matrices a is true.
A
1
=A
1
I =A
1
(AB) =(A
1
A)B =IB =B b is true.
Similarly B
1
=A option c is true.
30. (A)
Let
n n n
1 2 n
S C sina C sin2a ...... C sinna = + + +
and
n n n n
0 1 2 n
C C C cosa C cos2a ........ C cosna = + + + +
( ) ( ) ( )
n n n
1 2 n
C iS 1 C cosa i sina C cos2a i sin2a ....... C cosna i sinna + = + + + + + + +
( )
n
n a a a
C iS 1 z ; z cosa i sina 2cos cos i sin
2 2 2
| |
+ = + = + = +
`
|
\ . )
n n
a na
S 2 cos .sin
2 2
| | | |
=
| |
\ . \ .
31. (B)
Required number of way = 480 2
4
4
5
1
6
= C C
32. (A)
Let f(x) =x
3
3x +a
f '(x) =3x
2
3 =0
x = 1
f(1) f(1) <0
(a +2) (a 2) <0
a e (2, 2)
fromgraph f(0).f(1) <0
a(a 2) <0
a e (0, 2)
y
1
1
x
a e (0, 2)
33. (C)
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
5 Of 20
Equation of circle
(x r 1)
2
+y
2
=r
2
(x r 1)
2
+4x =r
2
x
2
+(4 2(r +1))x +(2r +1) =0
D =0 4(1 r)
2
4(2r +1) =0
r =4
(r +1, 0)
(1, 0)
34. (B)
Period of f(x) is 2t, but f(x) is not defined for x e (t/2, 3t/2). Hence it suffices to
consider x e [t/2, t/2]. Further since f(x) is even, we consider x e [0, t/2].
Now ( ) x sin cos and ( ) x cos sin are decreasing functions for x e [0, t/2].
R
f
= ( ) ( ) | | 0 , 2 / f f t = | | 1 sin 1 , 1 cos +
35. (A)
Given differential equation is
(xy
2
+2x
2
y
3
)dx +(x
2
y x
3
y
2
) dy =0
dividing by x
3
y
3
0
1 1 2 1
2 2
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ dy
y xy
dx
x y x
0
2
2 2
=
1
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
dy
y
dx
x y x
xdy ydx
solution is
C y x
xy
= + | | log | | log 2
1
or 2log |x| log |y|
xy
1
=C
36. (C)
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) { }
o o o o o o o
1 tank 1 tan 45 k 1 tan45 1 tank tan 45 k tank tan 45 k + + = + +
=2
Hence,
( )( )( ) ( )
o o o o
1 tan1 1 tan2 1 tan3 ....... 1 tan25 + + + +
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
6 Of 20
( )( ) { } ( ) ( ) { } ( )( ) { }( )
o o o o o o o
1 tan1 1 tan44 1 tan2 1 tan43 ....... 1 tan22 1 tan23 1 tan45 = + + + + + + +
23
2 = n 23 =
37. (A), (B), (C)
(A) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
1
cos tan tan 4 cos 4 cos 4 cos4 0
t = t = t = >
(B) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
1
sin cot cot 4 sin 4 sin4 0
t = t = > (as sin 4 <0)
(C) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
1
tan cos cos 2 5 tan 2 5 tan5 0
t = t = > (as tan 5 <0)
(D) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
1
cot sin sin 4 cot 4 cot4 0
t = t = <
38. (A), (B), (C), (D)
a b
x y z 3
2
+ | |
+ + =
|
\ .
a b
15 3
2
+ | |
=
|
\ .
a +b =10 (1)
1 1
3
1 1 1 a b
x y z 2
| |
+
|
\ .
+ + =
( ) 3 a b 5 3 10
3 2ab 2ab
+
= =
ab =9 (2)
From(1) and (2), a =9, b =1 or a =1 and b =9.
Hence GM = ab =3, a +2b =11 or 19.
39. (A,C)
Number of triplets
( )( )
1 2
3 ,3 ,3 0 1
r r r
r n is n
+ +
s s
Number of triplets
( )( )
2 4
3 ,3 ,3 0 3
r r r
r n is n
+ +
s s
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
7 Of 20
------------------------------------------------------------
Number of triplets ( )
1
1
2
3 ,3 ,3 2
n
r
r r n
n odd is
+
+
| |
|
\ .
and no of triplets ( )
2
3 ,3 ,3 1
n
r
r r n
n even is
+
+
| |
|
\ .
If n is odd, the number of favourable outcomes
( ) ( )
2
1
1 3 .... 4 2
4
n
n n
= + + + + =
and if n is even, the number of favourable outcomes
( ) ( )
2
1 3 .... 3 1 / 4
2 2
n n
n n n = + + + + = =
Prob =
( )
( )
2
3
1 / 4
3/ 2
1
n
n
n C
=
+
if n is odd
( )
( )
2
2
3
/ 4 3
1 2 1
n n
n C n
= =
+
if n is even
40. (B), (C), (D)
( ) ( ) ( )
a b c d . a d 0 =
( ) ( )
acd b bcd a . a d 0
( (
=
acd bad 0
( (
=
Either c
or b
must lie in the plane of a
and d
41. (A), (C)
a
1
=0, b
1
=32, a
2
=a
1
+
3
2
b
1
=48,
1
2
b
b 16
2
= =
3 3
3 16
a 48 16 72,b 8
2 2
= + = = =
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
8 Of 20
X
X'
Y'
Y
O
32 48 72 80
So the three loops fromi =1 to i =3 are alike.
Now area of i
th
loop (square) = ( )
2 1
diagonal
2
( ) ( )
2
2
i i i
1
A 2b 2 b
2
= =
So,
( )
( )
2
i 1 i 1
2
i
i
2 b A 1
A 4
2 b
+ +
= =
So the area forma G. P. series
So, the sumof the G. P. upto infinite terms
= ( )
2
i
1 1
A 2 32
1
1 r
1
4
=
=2(32)
2
(4/3) =
8
3
(32)
2
square units.
42-44. Suppose degree of f(x) is n, then the degree of f ' is n - 1 and degree of f '' is n - 2.
So, n =(n - 1) +(n - 2) n =3
Hence, f(x) =
3 2
ax bx cx d + + +
From, ( ) ( ) ( ) f 2x f ' x .f '' x = , we have
( )( )
3 2 2
8ax 4bx 2cx d 3ax 2bx c 6ax 2b + + + = + + +
Comparing coefficient of terms, we have
a 4/ 9,b 0,c 0 = = = and d =0.
( )
3
4x
f x
9
=
(1) f(3) =12
(2) one-one and onto
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
9 Of 20
(3)
3
4x
x
9
= x =0,
3
2
45. (A)
Required probability =
1 1 1 1
1 0.728
2 2 4 2
| |
+ =
|
\ .
46. (A)
P(I/II) =
( ) ( )
( )
1 1
.
P I .P II / I
2 2
0.74
1 1 1
P II
.
2 8 2
= =
+
47. (2)
Let AD be the perpendicular fromA on BC. When AD is produced, it meets the
circumscribing circle at E. Fromquestion, DE =o.
A
B C
D
E
C B
Since angles in the same segment are equal, ZAEB =ZACB =ZC and ZAEC =ZABC
=ZB.
Fromright-angled triangle BDE, we get
tan C =
BD
DE
(1)
Fromthe right-angled triangle CDE, we get
tan B =
CD
DE
(2)
Adding (1) and (2),
BD CD BC a
tanB tanC
DE DE
+
+ = = =
o
(3)
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
10 Of 20
Similarly, tan C +tan A =
b
|
(4)
And tan A +tan B =
c
(5)
( )
a b c
2 tanA tanB tanC + + = + +
o |
48. (0)
Since cubic is divisible by both x
2
+ax +b and x
2
+bx +a. Therefore, x
2
+ax +b and x
2
+bx +a must have a common roots
x
2
+ax +b =0
x
2
+bx +a =0
subtract
x(a b) =(a b)
x =1
Therefore, common roots
for x
2
+ax +b =0 are 1 and o 1 . o =b o =b
for x
2
+bx +a =0 are 1 and | 1 . | =a | =a
roots of cubic be 1, a, b
1a b =72 (1)
and a +b +1 =0 (2) (fromx
2
+ax +b =0 put x =1)
a
72
1
a
=
a
2
+a 72 =0
(a +9)(a 8) =0
a =9, 8
Therefore roots are 1, 9, 8
49. (5)
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
11 Of 20
y'
y
x' x
A(z
1
)
B(z
2
)
C(z
3
)
O
P(z)
Let
i /2
1
2
z e ,
3
t
=
i /6
2
2
z e ,
3
t
=
i5 /6
3
2
z e
3
t
=
Clearly, the points lie on the circle
2
|z|
3
=
and AABC is equilateral
Centroid coincides with circumcentre
z
1
+z
2
+z
3
=0 and
1 2 3
z z z 0 + + =
Since the triangle is equilateral, inradius r =ID =
1
3
Equation of the incircle
1
|z|
3
=
Let P(z) be any point on the incircle
Now, AP
2
= ( )
2 2 2
1 1 1 1
|z z | |z| |z | zz zz = + +
Similarly, BP
2
= ( )
2 2
2 2 2
|z| |z | zz zz + +
and CP
2
= ( )
2 2
3 3 3
|z| |z | zz zz + +
AP
2
+BP
2
+CP
2
=
( ) ( )
2 2 2 2
1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3
3|z| |z | |z | |z | z z z z z z z z + + + + + + + =5
50. (4)
Hence, the continuity must be checked at x =1, 2, e, 3, 10, 11, 12,3.5
Further, f(1) =0 and
( ) ( ) | |
e
x 1 x 1
limf x limsgn x 2 log x 0
+ +
= =
Hence, f(x) is continuous at x =1
( ) ( ) | | ( )
e
x 2 x 2
limf x limsgn x 2 log x 1 0 0
= = =
( ) ( ) | | ( )
e
x 2 x 2
limf x limsgn x 2 log x 1 0 0
+ +
= = =
Hence, f(x) is continuous at x =2.
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
12 Of 20
( ) ( ) | |
e
x 3 x 3
limf x limsgn x 2 log x 1
= =
( ) { }
2
x 3 x 3
limf x lim x 0
+ +
= =
Hence, f(x) is discontinuous at x =3.
Also {x
2
} is discontinuous at x = 10, 11, 12
Therefore, ( ) { } ( )
2
x 3.5 x 3
limf x lim x 0.25 f 3.5
= = =
Hence, f(x) is discontinuous at x =3, 10, 11, 12
51. (4)
( )
( ) ( )
2 3
2 2
f x 3 4 x 1 4 x = + +
f(0)
3
0
1/3
t
2
Let t =
2
4 x , clearly 0 t 2 s s
F(t) =(3 t)
2
+(1 +t)
3
For maxima and minima,
( ) F' t 0 =
2(3 t) +3(1 +t)
2
=0
3t
2
+8t 3 =0
(3t 1)(t +3) =0
t =
1
3,
3
Also ( )
t 3
F'' t |
=
=10 maxima
And ( )
t 1/3
F'' t |
=
=+10 minima
As t 3 = , hence maximumvalue of F(t) will occur at the end points for which
F(0) =10, F(2) =28
Hence, maximumvalue of F(t) =28 for t =2
maximumvalue of f(x) =28 for x =0.
52. (6)
e
1
1 lnx
I dx
xlnx
+
=
}
Putting (x ln x) =t
2
, (ln x +1)dx =2tdt, we get
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
13 Of 20
e
0
2tdt
I 2 e
t
= =
}
53. (6)
The equation of the tangent at any point P(x, y) is Y y = ( )
dy
X x
dx
(1)
Given that intercept on the x-axis (putting Y =0) =2 (x coordinate of P)
dx
x y 2x
dy
=
dy dx
y x
=
Integrating, we get xy =c.
Since the curve passes through (1, 2), c =2.
Hence, the equation of the required curve is xy =2.
54. 2
Z
Y
X
O
M
C(0, 0, 1)
B(0, 1, 0)
A(1, 0, 0)
i
j
k
Let the edges OA, OB and OC of the unit cube be along OX, OY and OZ respectively.
Since OA =OB =OC =1 unit,
OA i,OB j,OC k = = =
.
Let CM be the perpendicular fromthe corner C on the diagonal OP. The vector equation
of OP is
( )
r i j k = + +
. Therefore, OM =projection of OC
on OP
=OC.OP
=
( )
i j k
1
k.
3 3
+ +
=
Now OC
2
=OM
2
+CM
2
2
2 2
1 2 2
CM OC OM 1 CM
3 3 3
= = = =
55. 6
We have five entries 1 and the remaining four entries are 0.
Since the matrix is symmetric, we must have an even number of zeros for i j = .
Hence, we have two cases :
(i) Two entries in the diagonal are zero.
We can select two places fromthree (in diagonal) in
3
C
2
ways.
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
14 Of 20
Now we have to select elements for the upper triangle.
For the upper triangle, we have three places of which one entry is 0 and two entries are 1.
One place fromthree can be selected in
3
C
1
ways.
Hence, the number of matrices is
3
C
2
3
C
1
=9.
(ii) If all the entries in the principal diagonal is 1, we have two 0 and one 1 in the upper
triangle.
Hence, the number of matrices is 3.
Thus, total matrices =12.
56. 1
S(x, y) =x
2
+y
2
x y 6 =0 (1)
has centre at
1 1
C ,
2 2
| |
|
\ .
According to the required conditions, the given point P(o - 1, o +1) must lie inside the
given circle.
i.e. S(o - 1, o +1) <0
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
2 2
1 1 1 1 6 0 o + o + o o + <
2
2 0 o o < , i.e., ( )( ) 2 1 0 o o+ <
1 2 < o < (2)
Also P and C must lie on the same side of the line (see figure)
x +y 2 =0
C
P
L (x, y) x y 2 0 + = (3)
i.e. L(1/2, ) and ( ) L 1, 1 o o+ must have the same sign.
Since
1 1
L ,
2 2
| |
|
\ .
=
1 1
2 0
2 2
+ <
( ) ( ) ( ) L 1, 1 1 1 2 0,i.e., 1 o o+ = o + o+ < o < (4)
Inequalities (2) and (4) together give the permissible values of o as 1 1 < o < .
PHYSICS
57. (A)
FromA to B,
V
T
is constant so pressure remains constant. FromC to D, V is constant P-
T graph will be straight line pressing trough origin
58. (B)
Apply gas law PV =nRT
2 2
C 0 D D
2 2 2
C D 0 0
P P P P
V V 2(4V ) PV
= =
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
15 Of 20
So
0
D
9P
P
8
=
A A D D
0
P V P V
RT RT
=
0 0 0 0
0
P V 9P (3V )
RT 8RT
=
0
27T
T
8
=
59. (D)
Use i 0 E = and series parallel combination.
i
B
: i
C
: i
D
=
B C D
1 1 1
: :
R R R
=
1 1 1
: :
6 3 2
=1 : 2 : 3
i
A
: i
B
: i
C
: i
D
: : 6 : 1 : 2 : 3
R
C
=3O
R
A
i
B
R
D
=6O
i R
D
=2O
i
A
60. (C)
P is a point on screen such that S
1
PS
2
P=constant, then P locus of P Will be circle with
center O.
S
1 S
2 O
P
61. (D)
( )
2 2
P P
KE
2m 2 4
o
o
= =
( )
( )
2 2
d
d
P P
KE
2m A 4
= =
o
( )
( )
d
KE
A 4
KE 4
o
| |
=
|
\ .
Also, A
o
=N
o
N
o
=A
o
/
A =A
o
e
t
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
16 Of 20
A
o
/n =A
o
e
t
n
-1
=e
-t
n =e
t
log n =t
t =log n /
62. (A)
max
o
hc hc
K =
max
o
3hc hc
nK =
Solving this we get
o
n 1
n 3
| |
=
|
\ .
63. (A)
a =A cost t, e =1
v =A sin t at t =t/2; v =A
=h/mA
64. (A)
0 0 AB
OA BC
l l B
B B (sin45 sin0 ) ( k)
2 4 a 4 2 a
= = = + =
t t
So net
0
Z OA
l
B 4B ( k)
2 a
= =
t
similarly
0
y
l
B ( j)
2 a
=
t
or
0
l
B ( j k)
2 a
=
t
65. (A), (B)
H
2
will decrease because water formed by ice will merge with water. H
1
will increase
66. (A), (C), (D)
Use relation P =hg at E and D.
P
A
=P
B
+L sin 30
o
g =P
B
+sin 30
o
g L =60 cm
Clearly, L is independent of h.
67. (B), (C)
Use B =
( )
2
o
3/2
2 2
iR
2 R x
+
68. (A), (B), (D)
Potential difference to be measured across external setup is
(A)
1
V
3
, when S
1
is closed
(B) 1 V, when S
2
is closed
(C)
1
V
3
, when both are closed
Potential difference across potentiometer wire is 2V.
69. (C), (D)
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
17 Of 20
3 1
V
i i i
2r
= = =
q =(V
A
V
B
).C =CV/2
70. (A)
2
1 1 1
2
1 2 2
L mr
L mr
e
=
e
, where r
1
and r
2
are respective distances fromCOM, such that m
1
r
1
=m
2
r
2
.
71. (A)
2 2 2
1 1 1 1 2
2 2 2
1 2 2 2 1
mv mr m
2
mv mr m
e
= = =
e
72. (C)
1 1 1 1
2 2 2 2
mv mr
1
mv mr
e
= =
e
73. (C)
Volume charge density =dQ/dv
or
R/2 R R/2 R
2 2
0 R/2 0 R/2
r
Q dv dV dV 4 r dr 2 1 4 r dr
R
| |
= = + = o t + o t
|
\ .
} } } } }
74. (A)
2
o
dv
1
E
4 r
=
tc
}
75. 7
FBD of the blocks are shown here,
10
A
N
1
T
f
1
10
B
N
2
f
1
F
f
2
N
1
10
C
N
3
f
2
T
N
2
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
18 Of 20
f
1
=2N, f
2
=4N, F 6 =1a, f
2
f
1
=2a a =1 m/s
2
, F =7 N
76. 0
( ) ( ) ( )
x y z
1 3 2 1 2 1
L' M L T LT ML T
=
0 1 0 x z 3x y 2z 2x y z
M L T M L T
+ + +
=
x +z =0; 2x y z =0 (3x +y) =0
77. 8
FBD of cylinder and block are as shown by Newtons laws
40 2T f
s
=8a (1)
T f
s
=4a/2 (2)
Subtracting equation (2) fromequation (1)
40 3T =6a
T =(40 6a)/3
Also, by t =Io, we get
T R +f
s
R =
3a
I
2R
T +f
s
=3Ia/2R
2
(40 6a)/3 +(40 12a)/3 =3Ia/2R
2
a =80/(18 +9I/2R
2
)
As t =Io =I (3a/2R)
t =Io =I (3a/2R)
2
3I 80
9I 2R
18
2R
t =
| |
+
|
\ .
3 80 80
N m
18 9 9
t = =
+
78. 7
Path difference at P =7/2
79. 6
E(MeV) =12375/(in ) =12.69
E
n
E
1
=13.6/n
2
+13.6 =12.69
13.6/n
2
=0.9 n
2
=13.6/0.9
Total number of lines =n(n 1)/2 =6
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
19 Of 20
80. 3
Angular width =/d =10
-3
(given)
Number of fringes within 0.12
o
will be n = | |
3
0.12
2.09
360 10
t
~
The number of bright spots will be three.
81. 2
First shift =
( )
1 1
1 t 1 9 3
g 3/ 2
| |
| |
= =
|
|
|
\ .
\ .
cm
Second shift
w
s
8
1 t 1 9 1cm
9
( (
= =
(
(
82. 4
Given =10 pm=100 10
-12
m
D =40 cm=40 10
-2
m
|=0.1 mm=0.1 10
-3
m
| =D/d
d =
12 2
3
D 100 10 40 10
10 0.1
=
|
=4 10
-7
m
83. 8
I =impulse by each of bigger
balls on smaller ball.
sin u =2/3,
5
cos
3
u =
By impulse momentum
theorem, for smaller ball
2I cos u =Mv
o
I =
o
3Mv
2 5
Now, I sin u =Mv (here v =
speed acquired by each of the
bigger balls after collision)
o o
3Mv v 2
v v
3 2 5M 5
= =
u
I
v
I
2Icosu
3R/2
u
I
Isinu
v
o
v
R
Applying law of conservation of energy, we get
2
2 o
o
v 1 1 M
M kx x v
2 2 5K 5
| |
= =
|
\ .
1.25
x 1.6
5 100
=
1.6
x
20
= m
x =8 cm
84. 9
This Key & Hints Paper contains 20 Page GT-8 PAPER-1_ 22_01_11
20 Of 20
For glass lens ( )
1 1 1
1.5 1
f R R
| |
= +
|
\ .
f =12 cm
For water lens
1 4 2
1
f 3 R
| || |
=
| |
\ .\ .
=
1 2
3 12
| |
|
\ .
f =18 cm
Now using
1 2 3
1 1 1 1
F f f f
= + +
1 2 1
F 12 18
=
1 3 1 2
F 18 18
= = F =9 cm
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1091)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Competetive Maths PDFDocumento464 pagineCompetetive Maths PDFTom McGovern100% (1)
- Sine Law WorksheetDocumento2 pagineSine Law Worksheetapi-297847828100% (1)
- Applied Linear AlgebraDocumento944 pagineApplied Linear AlgebraMatthew Flowers100% (2)
- Fiitjee AitsDocumento23 pagineFiitjee Aitsullasagw100% (6)
- Concept Recap Test Mains 6Documento22 pagineConcept Recap Test Mains 6Siddharth Gangal0% (1)
- ASMO 2020 Maths Grade 10-11Documento13 pagineASMO 2020 Maths Grade 10-11anthonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mca Vocab Chart GR 3-8mathDocumento4 pagineMca Vocab Chart GR 3-8mathapi-294805158Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basic MathDocumento87 pagineBasic MathHridoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Solving Word Problems in Geometry PDFDocumento3 pagineSolving Word Problems in Geometry PDFMiguel Xerxes VillacrucisNessuna valutazione finora
- MTAP Reviewer Grade 3Documento2 pagineMTAP Reviewer Grade 3Clarisa Ella Dapula100% (20)
- Cilk InstallationDocumento2 pagineCilk InstallationMeet ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Advance Recap Paper 1 Set 5 PDFDocumento18 pagineAdvance Recap Paper 1 Set 5 PDFPrateek GahlanNessuna valutazione finora
- Smith: Curriculum VitaeDocumento3 pagineSmith: Curriculum VitaeMeet ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Narayana Grand Test - 8Documento12 pagineNarayana Grand Test - 8Meet ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- QuestionDocumento20 pagineQuestionMeet ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Narayana Grand Test - 8Documento16 pagineNarayana Grand Test - 8Meet ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Gt8 - Final Paper 1Documento20 pagineGt8 - Final Paper 1Meet ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- 2014 H2 Maths Prelim Papers - JJC P1 Solution PDFDocumento12 pagine2014 H2 Maths Prelim Papers - JJC P1 Solution PDFcherylhzyNessuna valutazione finora
- Prekinder AADocumento6 paginePrekinder AAIT AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Groundbreaking Program Blanco EsDocumento2 pagineGroundbreaking Program Blanco EsPauline Erika Cagampang50% (2)
- DE Module 2 - The Study of CalculusDocumento72 pagineDE Module 2 - The Study of CalculusRaquel PanillosNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom Management Action PlanDocumento23 pagineClassroom Management Action Planapi-298602124100% (1)
- IntegralDocumento5 pagineIntegralRoselyn MatienzoNessuna valutazione finora
- German EducationDocumento5 pagineGerman Educationapi-282427998Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mock A I Me One SolutionsDocumento13 pagineMock A I Me One SolutionsPhan Thế HuyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Boarder CommunityDocumento3 pagineThe Boarder CommunityAnonymous ZLnwKn0g0xNessuna valutazione finora
- 16th PMO QualifyingDocumento5 pagine16th PMO QualifyingDaniel NicholsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Examen de Inglas 2021 de LIZ DAYANA SALCEDODocumento5 pagineExamen de Inglas 2021 de LIZ DAYANA SALCEDOlesliethNessuna valutazione finora
- Jim Green, SKSD Board Candidate QuestionnaireDocumento6 pagineJim Green, SKSD Board Candidate QuestionnaireStatesman JournalNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL Mathematics 5 q2 w8Documento8 pagineDLL Mathematics 5 q2 w8Quennee Ronquillo EscobilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics - Class 6 CH - 4Documento13 pagineMathematics - Class 6 CH - 4RUPali KUMARINessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching ResumeDocumento3 pagineTeaching Resumeapi-222315895Nessuna valutazione finora
- Report On Dolch Basic Sight Word Test For Grade Three Pupils (Pretest)Documento2 pagineReport On Dolch Basic Sight Word Test For Grade Three Pupils (Pretest)nelissa solinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Angles: Polygons: Edexcel GCSEDocumento8 pagineAngles: Polygons: Edexcel GCSEAddy The humanNessuna valutazione finora
- Variations of Sorsogon Dialects As Mother Tongue-Based Medium of Instruction in Grade School MathematicsDocumento8 pagineVariations of Sorsogon Dialects As Mother Tongue-Based Medium of Instruction in Grade School Mathematicsapjeas100% (1)
- List of Sheets - Engineering Drawing LabDocumento3 pagineList of Sheets - Engineering Drawing LabprashantattNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-Regional Mathematical Olympiad - PRMO Exam Booklet 2022Documento28 paginePre-Regional Mathematical Olympiad - PRMO Exam Booklet 2022Pratyusha RaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Helensburgh Hig: Celebrating 125 YearsDocumento6 pagineHelensburgh Hig: Celebrating 125 YearsSueDowlingNessuna valutazione finora
- Bks MaaHL 01uu ct00 XxaannDocumento5 pagineBks MaaHL 01uu ct00 XxaannAria ElectrobellNessuna valutazione finora