Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Eco 90984 Weebly Copy Assessment Scedule
Caricato da
api-220013388Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Eco 90984 Weebly Copy Assessment Scedule
Caricato da
api-220013388Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Assessment schedule: Economics 90984 Cadbury World Factory Tour - How Production Decisions Are Made at Cadbury
Evidence/Judgements for Achievement
The student demonstrates understanding of data that relates to producer decisions. The student correctly calculates the percentage change in production, calculates productivity from their input and output data, and presents their data and information clearly; their table is accurately labelled and measures the firms productivity using either natural, labour or capital inputs. The input and output figures match, either as dollar or number figures. The student explains the consequences for society of the production decisions. The student mentions some of the consequences and gives textbook-type answers for goals and for price and non-price competition, mostly using correct economic language. For example: Please note that the judgements are written for McDonalds not Cadburys to give you an idea of the Standards required. Production The production of the top 8 burgers increased by 3.62% from 2007 to 2008, and production of the top 8 burgers decreased by -1.98% from 2008 to 2009.
Evidence/Judgements for Achievement with Merit
The student demonstrates in-depth understanding of data that relates to producer decisions, provides detailed explanations of the producers decisions, and uses their data to support their explanations. The student correctly calculates the percentage change in production, calculates and shows changes in productivity from their input and output data, presents their data and information clearly and explains whether this is an improvement or a worsening of productivity. The data in their table is accurately labelled and measures the firms productivity using natural, labour or capital inputs. The input and output figures match, either in dollar or number figures. The student explains in detail the consequences for society of the production decisions. For example: Please note that the judgements are written for McDonalds not Cadburys to give you an idea of the Standards required. Production The production of the top 8 burgers increased by 3.62% from 2007 to 2008, and production of the top 8 burgers decreased by -1.98% from 2008 to 2009.
Evidence/Judgements for Achievement with Excellence
The student demonstrates comprehensive understanding of data that relates to producer decisions, provides detailed explanations of the producers decisions, and integrates the data into detailed explanations of the producers decisions. All the explanations are integrated by being linked to the information. Not all this information need be quantitative. Some of the information may be qualitative, and either type can be used as a means of linking supporting data or information to the explanations of producer decisions. The student correctly calculates the percentage change in production, calculates and shows changes in productivity from their input and output data, presents their data and information clearly and explains whether this is an improvement or a worsening of productivity. The student uses supporting data or information to justify the explanations of production decisions in a cohesive manner. The data is accurately labelled and measures the firms productivity using natural, labour or capital inputs. The student explains in detail the consequences for society of the production decisions and integrates their explanations of the consequences for society with their explanations of production decisions.
This resource is copyright Crown 2012
Page 1 of 5
Productivity of Labour The productivity of labour involved in producing the top 8 burgers for 2008 is 47,915,640/8000 (approx.) = 5989.455 per person (annually), or 115.18 per week (approx). If the staff levels remained about the same for 2009, the productivity of labour involved in producing the top 8 burgers would be 5870.64 annually or 112.89 per week approximately. Commercial and non-commercial goals The consequences of profit maximisation to some members of society is that franchisees have to pay fees to the company so will look at ways to control the cost of labour. Through business expansion, other smaller fast food businesses find it difficult to compete against the many McDonalds restaurants and their advertising campaigns,
Productivity of Labour The productivity of labour involved in producing the top 8 burgers for 2008 is 47,915,640/8000 (approx.) = 5989.455 per person (annually), or 115.18 per week (approx). It is likely there were fewer staff employed in 2007, and they have hired more part-time or casual, oncall staff to help with the increase in demand and the increase in production from 2007 to 2008. If the staff levels remained about the same for 2009, the productivity of labour involved in producing the top 8 burgers would have worsened (5870.64 annually or 112.89 per week approx.), so it is most likely fewer part-time and casual, on call staff were used in 2009 to counteract the decline in sales due to a decrease in demand. Commercial and non-commercial goals The consequences to some members of society of the focus on profit maximisation; franchisees have to pay fees to the company and so use casual, oncall staff as one way of controlling the cost of labour. Through business expansion (franchising), other smaller takeaway businesses find it difficult to compete against the many McDonalds restaurants, and their well-resourced advertising and marketing campaigns. One of the positive benefits of McDonalds purchasing off NZ suppliers is the income this provides for other businesses and their employees. The franchising arrangement means many local business people run the restaurants and help out local junior sports teams and other community events. Price and non-price strategies to increase
The student mentions micro consequences and uses textbook-type answers for goals and for price and non-price competition, and also gives a macro view of consequences, using appropriate economic language. The student provides a valid explanation of the payoffs and motives for McDonalds noncommercial goals, how these have affected producer decisions, and their impact on productivity. The student also provides an explanation of how McDonalds non-price marketing strategies, linking these production decisions to the consequences for society and vice versa, for example: the effect of unhealthy eating on society (due to price and non-price marketing) also impacts on producers as shown by the decision to expand their product range with healthier menu options. For example: Please note that the judgements are written for McDonalds not Cadburys to give you an idea of the Standards required. Production The production of the top 8 burgers increased by 3.62% from 2007 to 2008, and production of the top 8 burgers decreased by -1.98% from 2008 to 2009. The increase in production from 2007 to 2008 is likely due to the NZ economy being in a healthier business cycle stage, and more disposable income could be spent on fast food. It is perhaps also due to a successful marketing campaign, but towards the end of 2008 and through 2009, the NZ economy was in a recession, so less disposable income was spent on fast food resulting in the negative figure or
or:
One of the positive benefits of McDonalds purchasing off NZ suppliers is the income this provides for other businesses and their employees. Franchising means many local business people run the restaurants, and they help out local junior sports teams, and other community events. Price and non-price strategies to increase sales and market share The consequence for some members of society is that they eat more fast food than they should. The value-picks pricing makes it easier for students to afford the products, and the combo deals appeal to many consumers. and/or:
This resource is copyright Crown 2012
Page 2 of 5
The Breakfast menu, M selections range, McCafe, and Lighter choices are designed to attract new consumers who have different tastes and preferences and the income to match. They also cater for more health conscious consumers who will only eat low fat product. and/or: The company uses strategies like sponsorship and branding with trademarks on the names of their products, such as the golden arches and the McDonalds name. They use locations where there is maximum foot traffic. Packaging is used in attractive eye-catching colours. They used Sarah Ulmer and Hamish Carter to promote their new healthier products and get more consumers to buy their products.
sales and market share The consequence for some members of society is that they eat more fast food than they should or they make poor food choices. The value-picks pricing makes it easier for students to afford the products, and the combo deals appeal to many consumers. The product variation (Breakfast menu, M selections range, McCafe, and Lighter choices) is designed to attract new consumers who have different tastes and preferences and the income to match. It also attracts the more health conscious consumers who will only eat low fat products. The product differentiation strategies like sponsorship are widely used by this company, and branding is huge with trademarks on the names of their products. They use locations where there is maximum foot traffic, like mall food courts, beside service stations, and in central city sites. Packaging is used in the most attractive eyecatching colours and adapted to the products they sell. They use paper, light card, and most of the materials can be recycled. They have promotions and deals with other businesses that offer McDonalds vouchers or coupons. Advertising and marketing is huge. They used NZ sportspeople such as Sarah Ulmer and Hamish Carter to promote the Salads Plus and Lighter Choices.
decreased production between 2008 and 2009. Productivity of Labour The productivity of labour involved in producing the top 8 burgers for 2008 is 47,915,640/8000 (approx.) = 5989.455 per person (annually), or 115.18 per week (approx). It is likely there were fewer staff employed in 2007, and they have hired more part-time or casual, oncall staff to help with the increase in demand from consumers that led to the increase in production from 2007 to 2008. The decision to use casual, oncall staff means that they do not have to carry the cost of labour during the quiet times and only use extra staff for the busy shifts. Time management strategies used in the production process like the cooking times (36 seconds for a regular patty and a minimum of 101 seconds for a Quarter Pounder patty) and assembling of each product are also closely monitored to maximise efficiency, and cover health issues. If the staff levels remained about the same for 2009, the productivity of labour involved in producing the top 8 burgers would have worsened (5870.64 annually or 112.89 per week approx.), so it is most likely fewer part-time and casual, on-call staff were used in 2009 to counteract the decline in sales due to a decrease in demand, which was due to reduced disposable income. Commercial and non-commercial goals Goals are profit maximisation, sales maximisation, increased market share of the takeaways industry, and business expansion through selling more franchises. The consequences to some members of society are the focus on profit maximisation and the job uncertainty this creates; and the lack of set
This resource is copyright Crown 2012
Page 3 of 5
hours of employment. Hence personal income levels will fluctuate because franchisees have to pay fees to the company and so have to focus on profit margins. Other smaller takeaway businesses find it difficult to compete against the many McDonalds restaurants that spring up everywhere, with their well-resourced advertising and marketing campaigns. Some of the non-commercial goals are corporate responsibility (purchasing from mainly NZ suppliers). Community goals include helping to set up the Ronald McDonald House charities, supporting Variety-The childrens Charity; Al DunnAUT Northland Scholarships; Radio Network special Christmas parties; Olympic Games, and junior sport. Environmental goals include the 3Rsreduce, re-use, and recycle and supporting Clean up NZ week,
And
One of the positive benefits of McDonalds purchasing off NZ suppliers is the income this provides for other businesses in the NZ economy and for the consumers who work in these businesses. The franchising arrangement means many local business people run the restaurants and help out local junior sports teams and at other community events. The AUT scholarships assist Mori from Northland to attain tertiary qualifications. The special Christmas parties are for disadvantaged and disabled children around NZ. The environmental goals encourage reducing waste and support the clean up of NZ campaign in September every year. Price and non-price strategies to increase
This resource is copyright Crown 2012
Page 4 of 5
sales and market share The pricing strategies include value picks 6 items under $3 each, and combo deals. Non-price strategies include product variation (actual different products) including a Breakfast menu, M selections range, and McCafe to appeal to different tastes and preferences and income brackets, and lighter choices to try to capture the more health conscious consumers. Non-price strategies also include product differentiation (products that appear different) including community sponsorship, branding, promotions, location, packaging, advertising, service, and more innovative ones like buying a Happy Meal which includes a free toy, catering for childrens birthday parties, and promoting free range eggs being used in Christchurch and Dunedin restaurants. The consequences for some members of society is eating more fast food than they should or making poor food choices (choosing food with little nutritional value). Childhood obesity is a consequence as the value-picks pricing makes it easier for students to afford the products, and the combo deals appeal to many consumers who perceive they are getting more value for money. But for many consumers, McDonalds provides consistent food items that they like, anywhere in the country, clean premises, and are open very early to very late providing food for many shift workers and party-goers.
Final grades will be decided using professional judgement based on a holistic examination of the evidence provided against the criteria in the Achievement Standard.
This resource is copyright Crown 2012
Page 5 of 5
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- T R S A: HE Eview Chool of CcountancyDocumento12 pagineT R S A: HE Eview Chool of CcountancyNamnam KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Construction Estimate PDFDocumento40 pagineConstruction Estimate PDFCindy ArizoNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics For Managers 3rd Edition Farnham Test BankDocumento22 pagineEconomics For Managers 3rd Edition Farnham Test Bankcassandracruzpkteqnymcf100% (33)
- Test Bank For Labor Economics 8th Edition George BorjasDocumento36 pagineTest Bank For Labor Economics 8th Edition George Borjascist.publicaz6bt1100% (49)
- Child Labor in The Philippines (UP Study)Documento10 pagineChild Labor in The Philippines (UP Study)acabusay100% (3)
- Impact of Technology On JobsDocumento12 pagineImpact of Technology On JobsJuyee JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Level 3 Year Planner 2015Documento1 paginaLevel 3 Year Planner 2015api-220013388Nessuna valutazione finora
- Level 1 Year Planner 2015Documento2 pagineLevel 1 Year Planner 2015api-220013388Nessuna valutazione finora
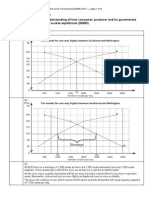
- Interpreting A Bar ChartDocumento1 paginaInterpreting A Bar Chartapi-220013388Nessuna valutazione finora
- Level 2 Year Planner 2015Documento1 paginaLevel 2 Year Planner 2015api-220013388Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cadbury Mark Schedule As 90988 1 6 2014Documento1 paginaCadbury Mark Schedule As 90988 1 6 2014api-2200133880% (1)
- Unemployment Internal Assessment As91225Documento7 pagineUnemployment Internal Assessment As91225api-220013388100% (1)
- As 90988 Cadbury Assessment 2015 - StudentDocumento10 pagineAs 90988 Cadbury Assessment 2015 - Studentapi-220013388Nessuna valutazione finora
- As 90987 Student Copy 2014Documento3 pagineAs 90987 Student Copy 2014api-220013388Nessuna valutazione finora
- Revised Mark Schedule As 90988 1 6 2014Documento1 paginaRevised Mark Schedule As 90988 1 6 2014api-220013388Nessuna valutazione finora
- HolocaustDocumento6 pagineHolocaustapi-220013388Nessuna valutazione finora
- As 90986 Marking Schedule 2011 Version 2Documento8 pagineAs 90986 Marking Schedule 2011 Version 2api-220013388Nessuna valutazione finora
- Important Geographic ConceptsDocumento1 paginaImportant Geographic Conceptsapi-220013388Nessuna valutazione finora
- As 90985 Exam 2013Documento8 pagineAs 90985 Exam 2013api-220013388Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mark Schedule As 90984Documento2 pagineMark Schedule As 90984api-220013388Nessuna valutazione finora
- Task 1 A B 90984Documento3 pagineTask 1 A B 90984api-220013388Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ncea As 90985 Marking Schedule 2011Documento6 pagineNcea As 90985 Marking Schedule 2011api-220013388Nessuna valutazione finora
- Extra Answers - Nov 2013Documento4 pagineExtra Answers - Nov 2013api-220013388Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Role of Women Empowerment in Economic ACTIVITY (In Case of Debremarkos Town)Documento18 pagineThe Role of Women Empowerment in Economic ACTIVITY (In Case of Debremarkos Town)tsegaw kebedeNessuna valutazione finora
- International EconomicsDocumento7 pagineInternational EconomicsJohn WarrenNessuna valutazione finora
- TB 14ComparativeAdvantageTradeDocumento8 pagineTB 14ComparativeAdvantageTradeLe Vu nguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Wipro Report - Report On Strike in Jhansi FacilityDocumento14 pagineWipro Report - Report On Strike in Jhansi FacilityRahul KhannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Speech 985Documento44 pagineSpeech 985TBP_Think_TankNessuna valutazione finora
- Ebook Economics 11Th Edition Michael Parkin Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocumento39 pagineEbook Economics 11Th Edition Michael Parkin Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFodilemelanie83au100% (10)
- 1 s2.0 S2214804322000908 MainDocumento15 pagine1 s2.0 S2214804322000908 MainPetronela NistorNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11Documento50 pagineChapter 11sidneyNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Macroeconomics Assignment: Apply Knowledge of UnemploymentDocumento2 pagineAP Macroeconomics Assignment: Apply Knowledge of UnemploymentSixPennyUnicorn0% (1)
- Microeconomics 9th Edition Parkin Test BankDocumento38 pagineMicroeconomics 9th Edition Parkin Test Banknbilojanoy100% (13)
- Problem of Farmers in Himachal PradeshDocumento9 pagineProblem of Farmers in Himachal PradeshRatnam SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Building WolisoDocumento30 pagineBuilding WolisoTarekegnNessuna valutazione finora
- Creative Labour HesmondalghDocumento7 pagineCreative Labour HesmondalghAinun NajibNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes Lecture 1 8 Notes History of Economic ThoughtrnDocumento39 pagineLecture Notes Lecture 1 8 Notes History of Economic ThoughtrnAurangzeb ChaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Economic Cost of Exclusion of LGBT PeopleDocumento25 pagineThe Economic Cost of Exclusion of LGBT PeopleADBGAD100% (1)
- Standard CostingDocumento21 pagineStandard CostingParth ParthNessuna valutazione finora
- Selected Questions Chapter 22Documento5 pagineSelected Questions Chapter 22Pranta SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson-2 5Documento22 pagineLesson-2 5Joana Marie LagmayNessuna valutazione finora
- The Failure of Federal Job Training, Cato Policy AnalysisDocumento13 pagineThe Failure of Federal Job Training, Cato Policy AnalysisCato Institute100% (1)
- Brazil's Case StudyDocumento27 pagineBrazil's Case StudyAndreea NeacsuNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro 0987 Syllabus 2023-2025Documento30 pagineIntro 0987 Syllabus 2023-2025Caesius ChenNessuna valutazione finora
- FM Chapter 3.1 Cash FlowDocumento24 pagineFM Chapter 3.1 Cash FlowBikila M. KejelaNessuna valutazione finora
- 12Documento14 pagine12Sarthak LakhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Economics Firms and Productions NotesDocumento13 pagineIGCSE Economics Firms and Productions Notesshaan.chauhan97Nessuna valutazione finora