Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Cocoa Solar Dryer Project
Caricato da
iky77Descrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Cocoa Solar Dryer Project
Caricato da
iky77Copyright:
Formati disponibili
4SOLAR DRYER FOR COCOA DRYING Introduction Cocoa production in Ghana has been a major source of foreign exchange
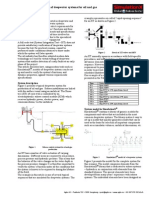
earner in Ghana. Ghana is also known to be the worlds second largest producer of cocoa after La Cote DIvoire. The country has also seen a study increase in cocoa production at a rate of 16% since 2001. This is as a result of Government subsidy on fertilizers for cocoa farmers and also spraying of the cocoa farms for farmers. This boom in cocoa production has brought about improvement in the living standards of cocoa farmers. The cocoa research institute and the Centre for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) have carried various research studies on how to develop ways by which cocoa beans could be dried. Cocoa is dried mainly using direct sun drying method in Ghana. It is by far the most convenient and traditional way of doing things. However, with increase in demand and production of cocoa beans there is the need to improved quality of cocoa beans produced in Ghana. An alternative way of drying cocoa and other food crops is using solar dryer technology. Solar energy is used directly for drying bulk of agriculture products in the country, especially cocoa beans. This technology has not been exploited much as a result of the cost of using it by farmers. Although the CSIR has done some research into the use and development of solar dryer technology there have been a few number of challenges. Objectives The overall aim of this project is to promote and develop the solar dryer technology using as much as possible local raw materials for food crop drying especially cocoa and other cash crops. The specific objectives include; Develop and promote the use of solar dryers by cocoa and cash crop farmers. Create employment for local fabricators of solar dryers. Improve the quality of cocoa beans produced in Ghana. The dryer will be a low cost, easy to fabricate and easy to operate equipment, using available local materials to make it suitable for most peasant farmers. Methodology The project will develop software which will be used to operate and control a solar system by regulating the amount of heat used to dry the cocoa beans. The capacity of the dryer is 250 kg which will have a collector area of approx. 25 m 2. The dryer will consist of 5 separate units each with a transparent collector area of 4.77m 2 and a capacity of approx 50 kg. Small dc fans will be use to distribute air evenly over the drying bed. The fans of thee dryer will be powered directly by PV panels in order to make the dryer independent of an often unreliable, missing or expensive grid. The components of the solar dryer are: 1. Solar Collector: Outer dimension is 4900 1070 mm 2. Transparent area 4.77 m2. Cover by a 10 mm double walled ribbed UV stabilized polycarbonate. Absorber will be made up of felt mat. Air intake at the back of the PV panels at both ends and air outlet in the middle at the back. Prepared by: Isaac Kuma Yeboah Page 1
2. Blower Fan: 300m2/h at 40 Pa 12 V dc motor with power of 12 W at 12 V. 3. PV: 2 panels of 12 V, 14 Wp. 4. Inlet Air Duct between collector and drying bed : metal ducting with the smallest cross section of 0.031m2. 5. Drying Bed Cabinet: 5 trays made of plastic, 600 400 278 mm3 of outer dimensions. 6. Heat Exchanger: These will contain gravels overlaid with a perforated plate 5 mm diameter holes, 10 mm apart to retain the beans and to facilitate convective heat flow from the gravels onto the beans during the rest periods of the sun. The solar dryer with it measured parameters and the illustration of the main components is shown below.
Prepared by: Isaac Kuma Yeboah
Page 2
The operation of the heat exchanger containing gravels overlaid with a perforated plate is shown below.
Budget The project will cost an amount of US$ 13944. The major costs of the solar dryer are the solar collector, drying trough and support structure. The estimated cost of there components are: PARAMETER AMOUNT (US $) Land clearing and flooring 300 Solar collector and accessories 2400 Dryer trough and frame 280 Duct heater, blower and ducts 2000 PV solar panel and accessories(3 pcs) 7200 Installation and labour costs 800 Transportation 300 Contingency (5%) 664 Total 13944 Project Schedule The project is expected to cover a period of six months during which a prototype will be developed and then mass production will commence. A much more detailed activity to be performed is below;
Prepared by: Isaac Kuma Yeboah
Page 3
Project Schedule Activities Month 1 1. Desktop and field study 2. Equipment procurements 3. Equipment installation and data collection 4. Data analysis and report writing 5. Presentation and training
2 3 4 5 6 7
Prepared by: Isaac Kuma Yeboah
Page 4
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Pulp and Paper Industry: Energy ConservationDa EverandPulp and Paper Industry: Energy ConservationValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Cacao Production: Horti 201: Advance Fruits and Plantation Crops ProductionDocumento30 pagineCacao Production: Horti 201: Advance Fruits and Plantation Crops ProductionJM RoxasNessuna valutazione finora
- Hot Pepper ProductionDocumento3 pagineHot Pepper ProductionAmeerah CabangalNessuna valutazione finora
- Sugar Mill Feasibility Report PDFDocumento23 pagineSugar Mill Feasibility Report PDFBaba YagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Voters List - Streams Per Polling StationDocumento425 pagineVoters List - Streams Per Polling Stationtnk67% (3)
- Corn Roadmap 2011-2017Documento32 pagineCorn Roadmap 2011-2017philmaize100% (5)
- Case Study - High-Tech FarmingDocumento15 pagineCase Study - High-Tech FarmingvaishnaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil PreparationDocumento48 pagineSoil PreparationVincent Paul BillonedNessuna valutazione finora
- Free Packaged Sachet Pure Water Startup Plan PDFDocumento24 pagineFree Packaged Sachet Pure Water Startup Plan PDFAlabi OlanrewajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Coconut ProductionDocumento14 pagineCoconut ProductionCharith LiyanageNessuna valutazione finora
- Rheang Proposal PDFDocumento8 pagineRheang Proposal PDFRhea Rose Varela SinadhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Duck Raising, Balot, Penoy, and Salted Eggs Production ProjectDocumento21 pagineDuck Raising, Balot, Penoy, and Salted Eggs Production Projectmarkgil1990Nessuna valutazione finora
- Farm Mechanization & Scope in IndiaDocumento4 pagineFarm Mechanization & Scope in IndiaSurjit Kumar GandhiNessuna valutazione finora
- An Overview of Groundnut Oil Extraction PDFDocumento14 pagineAn Overview of Groundnut Oil Extraction PDFAndriatsitohaina RabenaivoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cassava ProjectDocumento14 pagineCassava ProjectMark DeryNessuna valutazione finora
- Detailed Planning For Fish Farm ConstructionDocumento21 pagineDetailed Planning For Fish Farm ConstructionbashirmanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unido Cassava Value Chain Report FinalDocumento45 pagineUnido Cassava Value Chain Report FinalChima ChukwuNessuna valutazione finora
- projectproposal-RAYMUNDO G. AGRAVANTEDocumento6 pagineprojectproposal-RAYMUNDO G. AGRAVANTEJonafe Tapulgo-RodasNessuna valutazione finora
- Final PaperDocumento31 pagineFinal PaperSeila MolinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Feed Mill Design (ONIOT)Documento12 pagineFeed Mill Design (ONIOT)Rodel MarataNessuna valutazione finora
- Zee Proposal PiggeryDocumento11 pagineZee Proposal PiggeryMosunmola YetundeNessuna valutazione finora
- Agricultural MechanizationDocumento3 pagineAgricultural MechanizationSAMIA AKHTARNessuna valutazione finora
- Greenhouse Farming in India Beginner Guide 2018Documento11 pagineGreenhouse Farming in India Beginner Guide 2018amarNessuna valutazione finora
- Housing Systems of PoultryDocumento7 pagineHousing Systems of PoultryferdinandNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Proposal (Materials and Methods)Documento1 paginaResearch Proposal (Materials and Methods)Jorel F. Vanguardia0% (2)
- Coconut Oil MillingDocumento3 pagineCoconut Oil MillingRichwil John MagadanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulses MillDocumento2 paginePulses Millram100% (1)
- Ampalaya Production Per YearDocumento21 pagineAmpalaya Production Per YearRay Patrick Manigsaca100% (1)
- Business Cocoa PlanDocumento13 pagineBusiness Cocoa Planrita tamohNessuna valutazione finora
- Citronella Production EswarDocumento24 pagineCitronella Production EswarDr.Eswara Reddy SiddareddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cocoa Project ProposalDocumento3 pagineCocoa Project ProposalGAWII0% (1)
- CHAPTER I of Plant DesignDocumento8 pagineCHAPTER I of Plant DesignRehinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fish Cum Pig CultureDocumento18 pagineFish Cum Pig CultureMadhuban Bhattacharya50% (2)
- Paper and Pulp WastewaterDocumento36 paginePaper and Pulp WastewaterSandeep TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- PPT Sugar Cane IndustriesDocumento23 paginePPT Sugar Cane IndustriesVivek Kr TiwariiNessuna valutazione finora
- Maize Production Guide Ghana 2016Documento34 pagineMaize Production Guide Ghana 2016Selim Lukman100% (2)
- Peanut Processing PlantDocumento19 paginePeanut Processing PlantfaizkauNessuna valutazione finora
- Puff PlantDocumento9 paginePuff Planttauseef52Nessuna valutazione finora
- Brick Making Poverty Alleviation Project Business Plan 2005 Maluti A Phofung Local MunicipalityDocumento27 pagineBrick Making Poverty Alleviation Project Business Plan 2005 Maluti A Phofung Local MunicipalitySandeep PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Detailed Project Report On Rice Milling Unit at GelephuDocumento19 pagineDetailed Project Report On Rice Milling Unit at GelephuHarpy happyNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Plan For TillersDocumento15 pagineMarketing Plan For TillersBharat Veer Singh RathoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Chicken Housing: Brooder For ChicksDocumento3 pagineChicken Housing: Brooder For ChicksIdrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of A Modernized Cassava Peeling MachineDocumento9 pagineDesign of A Modernized Cassava Peeling MachineAnonymous lAfk9gNP100% (2)
- Cassava Grindier Project PDFDocumento9 pagineCassava Grindier Project PDFChuku EbubeNessuna valutazione finora
- Itik ChuchuDocumento34 pagineItik ChuchuJurie BalandacaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maize ProductionDocumento10 pagineMaize ProductionNsereko Ssekamatte100% (1)
- Design, Fabrication and Performance Evaluation of A Maize ShellerDocumento13 pagineDesign, Fabrication and Performance Evaluation of A Maize ShellerPeter AjewoleNessuna valutazione finora
- Aquaponics PresentationDocumento19 pagineAquaponics PresentationΡομίρ ΓιάνκκιλNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Report On Fresh Papaya FruitDocumento22 pagineProject Report On Fresh Papaya Fruitsachin89% (9)
- WarehousepropsalDocumento13 pagineWarehousepropsalKasandra NgNessuna valutazione finora
- Fertigrow Business Plan Group 3Documento69 pagineFertigrow Business Plan Group 3Elaiza May PatigayonNessuna valutazione finora
- Small RuminantsDocumento28 pagineSmall RuminantsAdnan Qaiser100% (1)
- Nursery PproposalDocumento5 pagineNursery PproposalAlfreda Enobio Te100% (1)
- Part-Ii: Bamboo Briquette Charcoal Making From Bamboo WasteDocumento7 paginePart-Ii: Bamboo Briquette Charcoal Making From Bamboo WasteNipan DekaNessuna valutazione finora
- Banana Farming ProjectDocumento3 pagineBanana Farming ProjectDmmi Fzco100% (1)
- Philippine Dried Fruit Marketing Plan PDFDocumento9 paginePhilippine Dried Fruit Marketing Plan PDFJordy Verdadero0% (1)
- Itlogan Sa Dabaw FarmDocumento15 pagineItlogan Sa Dabaw FarmMicka EllahNessuna valutazione finora
- Post Harvest Losses in HorticultureDocumento2 paginePost Harvest Losses in HorticultureInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- BE Project 2Documento14 pagineBE Project 2MithileshNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Project Solar Clothes DryerDocumento22 pagineDesign Project Solar Clothes DryerSaurav Kalita100% (1)
- AGSC PowerPoint Oral PresentationDocumento22 pagineAGSC PowerPoint Oral Presentationiky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- MSP430 DLL Developer's GuideDocumento30 pagineMSP430 DLL Developer's Guideiky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 7e Preliminary Design and Layout of An Embedded SystemDocumento2 pagineLab 7e Preliminary Design and Layout of An Embedded Systemiky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Digital ElectronicsDocumento41 pagineDigital Electronicsiky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Open Loop Amplifier Model and Parameters: The ComparatorDocumento1 paginaOpen Loop Amplifier Model and Parameters: The Comparatoriky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Labview DSP Module: Digital Signal Processing System-Level Design Using LabviewDocumento6 pagineLabview DSP Module: Digital Signal Processing System-Level Design Using Labviewiky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Agito Simulation of Deep Water SystemsDocumento3 pagineAgito Simulation of Deep Water Systemsiky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- "Have Thy Tools Ready. God Will Find Thee Work." - Sir James MurrayDocumento83 pagine"Have Thy Tools Ready. God Will Find Thee Work." - Sir James Murrayiky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 1e Fixed-Point Output Fall 2010 1e.1Documento8 pagineLab 1e Fixed-Point Output Fall 2010 1e.1iky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- IntroToPracticalElectronicsMicrocontrollersAndSoftwareDesign PDFDocumento1.014 pagineIntroToPracticalElectronicsMicrocontrollersAndSoftwareDesign PDFumar438098% (46)
- 1997-00 Listing of Working PapersDocumento16 pagine1997-00 Listing of Working Papersiky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Agito Simulation of Deep Water SystemsDocumento3 pagineAgito Simulation of Deep Water Systemsiky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 3e LCD Alarm Clock Page 3e.1Documento5 pagineLab 3e LCD Alarm Clock Page 3e.1iky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ghana Gas BrochureDocumento14 pagineGhana Gas Brochureiky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- OWA 2014 - Lo Res Brochure (KE)Documento24 pagineOWA 2014 - Lo Res Brochure (KE)iky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Blue BookDocumento20 pagineBlue BookCosmin DuceaNessuna valutazione finora
- OWA 2014 - Lo Res Brochure (KE)Documento24 pagineOWA 2014 - Lo Res Brochure (KE)iky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Interview Etiquettes: Do's and Don'tsDocumento32 pagineInterview Etiquettes: Do's and Don'tsiky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bascom 8051Documento316 pagineBascom 8051iky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Greenstone: A Comprehensive Open-Source Digital Library Software SystemDocumento9 pagineGreenstone: A Comprehensive Open-Source Digital Library Software Systemiky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 4 (1 3/4 Hours) : Configuring Collections: Part I - Working With Full Text DataDocumento4 pagineLab 4 (1 3/4 Hours) : Configuring Collections: Part I - Working With Full Text Dataiky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Greenstone: A Comprehensive Open-Source Digital Library Software SystemDocumento9 pagineGreenstone: A Comprehensive Open-Source Digital Library Software Systemiky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 2: Building Collections With The Librarian Interface: SnapshotsDocumento14 pagineLab 2: Building Collections With The Librarian Interface: Snapshotsiky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 3: Adding and Using Metadata: Snapshots: UNESCO Greenstone Workshop Nzdl/NcsiDocumento16 pagineLab 3: Adding and Using Metadata: Snapshots: UNESCO Greenstone Workshop Nzdl/Ncsiiky77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Refit ReadmeDocumento5 pagineRefit ReadmeAnakLabNessuna valutazione finora
- Ame 412 Lab ReportDocumento24 pagineAme 412 Lab ReportMd Masud RanaNessuna valutazione finora
- 200892619594143687Documento44 pagine200892619594143687ArunNessuna valutazione finora
- Tumble Dryers: Speed Queen 18 Digit Model Numbers With 3 and 5 in 13th Position Refer To Page 9 For Model IdentificationDocumento28 pagineTumble Dryers: Speed Queen 18 Digit Model Numbers With 3 and 5 in 13th Position Refer To Page 9 For Model IdentificationjavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Z160-250 Instruction ManualDocumento182 pagineZ160-250 Instruction ManualNMA Industrial ServicesNessuna valutazione finora
- Cab Heater: (AFTER OCT. 2008)Documento32 pagineCab Heater: (AFTER OCT. 2008)Juanjo Garcia JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Belt DryerDocumento14 pagineBelt DryerLyka ValdezNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Bed Drying PDFDocumento83 pagineFluid Bed Drying PDFsouhir gritliNessuna valutazione finora
- Washing Machine: Owner'S ManualDocumento83 pagineWashing Machine: Owner'S ManualMjhu NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- AE Reviewer Volume IIvvvvDocumento90 pagineAE Reviewer Volume IIvvvvFaith YilmazNessuna valutazione finora
- LG Electronics DLEX9500K LG Signature 9-Cu FT Electric Dryer (Black Stainless Steel)Documento108 pagineLG Electronics DLEX9500K LG Signature 9-Cu FT Electric Dryer (Black Stainless Steel)Trần Quang TuyênNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar DryingDocumento15 pagineSolar Dryingasprilla100% (1)
- CHE471Documento7 pagineCHE471MaizatulAkmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Freeze Dryer dc401Documento2 pagineFreeze Dryer dc401Dolphy LantiguaNessuna valutazione finora
- Compressed Air Drying PDFDocumento29 pagineCompressed Air Drying PDFmaddukuri jagadeesh babu100% (1)
- Ingersoll Rand Dryer O&M Manual 80442833-EnDocumento48 pagineIngersoll Rand Dryer O&M Manual 80442833-EnBill BrighamNessuna valutazione finora
- Instruction Manual MB45 Moisture AnalyzerDocumento70 pagineInstruction Manual MB45 Moisture AnalyzerAulia AdimNessuna valutazione finora
- Product Price List-FeehlaDocumento18 pagineProduct Price List-Feehlawizdom20032001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Adhiparasakthi Engineering College Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocumento27 pagineAdhiparasakthi Engineering College Department of Mechanical EngineeringKms BasheerNessuna valutazione finora
- TS5A-DB00000762-011705-spare Parts BookDocumento36 pagineTS5A-DB00000762-011705-spare Parts BookramonNessuna valutazione finora
- AEN 4 Laboratory Exercise 8Documento3 pagineAEN 4 Laboratory Exercise 8Jonel JacoboNessuna valutazione finora
- Asphalt Plant: Manual and MS-22 Principles of Construction of Hot-Mix Asphalt Pavements Contain Much MoreDocumento10 pagineAsphalt Plant: Manual and MS-22 Principles of Construction of Hot-Mix Asphalt Pavements Contain Much MoreAnonymous Jcr1ES8QYuNessuna valutazione finora
- HVAC Chapters 1 5Documento57 pagineHVAC Chapters 1 5Mcilwaine Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Hazard Analysis and Risk Assessment (HARA) Report For New ProductDocumento11 pagineHazard Analysis and Risk Assessment (HARA) Report For New ProductIJRASETPublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Instruction Manual Edc 2: Compressed Air DryersDocumento17 pagineInstruction Manual Edc 2: Compressed Air DryersTamNessuna valutazione finora
- Lennox Mini Split Air Conditioner Heat Pump Error CodesDocumento55 pagineLennox Mini Split Air Conditioner Heat Pump Error Codesjhon manuel de jesus100% (1)
- GX 2 5 Aib 20158004Documento70 pagineGX 2 5 Aib 20158004AR COMPRESSORESNessuna valutazione finora
- Siempelkamp Biomass Power Plant EngDocumento8 pagineSiempelkamp Biomass Power Plant EngWasim AshfaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Processing For Drying, Heating and CoolingDocumento8 pagineThermal Processing For Drying, Heating and Coolingamamùra maamarNessuna valutazione finora
- IN - 438917566EN - TD6-16 Compass Pro - ENDocumento44 pagineIN - 438917566EN - TD6-16 Compass Pro - ENBozo CovicNessuna valutazione finora