Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Human Body Systems - Skeletal, Muscular, Integumentary, Nervous
Caricato da
IndigoCat6Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Human Body Systems - Skeletal, Muscular, Integumentary, Nervous
Caricato da
IndigoCat6Copyright:
Formati disponibili
1
File>DownloadAs...NoneedtohighlightORFile>Print ConceptualLearningObjectivesforHumanBodySystemsUnit1 Skeletal,Muscle,Integumentary,&NervousSystems
Themesofunit: Recognizethatthebodyssystemsinteracttomaintainhomeostasis.Beableto distinguishdifferentformsofhomeostaticimbalanceandhowdisruptionof specificanatomicalstructureleadstothelossofspecificphysiologicalfunctions. Homeostasisisthenormalfunctioningofthehumanbody,orofanyofitssystemsororgans. Homeostaticimbalancecanoccurduetoillness,orduetophysicalailmentssuchasabroken boneoracutorbruise.Anatomyisthestructureofanorganismanditsparts,physiologyisthe studyofwhatthepartsdo,andhowtheydoit.Thisiswhydisruptionofanatomicalstructurecan leadtodisruptionofphysiologicalfunctions. Explainhowthemuscular/skeletalsystem(skeletal,smoothandcardiacmuscles, bones,cartilage,ligaments,tendons)workswithothersystemstosupportthe bodyandallowformovement.Recognizethatbonesproducebloodcells. Theskeletonisthesturdyframeofthebody,andmusclesaretheorganswhichmovethe skeletonthroughjoints,tendons,andligaments.Jointsconnectdifferentbonesandallow movementwiththehelpofmuscles(pivot,ballandsocket,gliding,hingejoints).Ligamentsarea connectivetissuethatholdbonesintothemovablejoints.Tendonsareanothertypeof connectivetissuethatconnectmusclestobones.Anexceptionistheeyeligament. Nameanddescribethe6mainfunctionsoftheskeletalsystem. Theskeletonprovidesastrongframeforthebody.Ithousesandprotectsthesoftorgansofthe body,suchastheheart,lungs,andbrain.Theskeletonalsoaidsinmovement,givingmusclesa placetoattachto.Theskeletonhelpsmaintainmineralhomeostasis,releasingcalciumand phosphorusintothebloodwhenneeded.Theskeletonproducesnewredbloodcellsthroughred bonemarrow.Yellowbonemarrowservesasstorageforfatsandlipids.So,thesixmain functionsaresupport,protection,movement,mineralhomeostasis,bloodcellproduction,and storage.Babiesaremostlymadeofcartilagethough.
Describetheanatomyofatypicallongbone(suchasafemur). Boneisasolidnetworkoflivingcellsandfibersthataresupportedbybonematrix.Bonematrix ismadeofthehardmineralmadeofcalciumphosphateandflexiblefibersoftheprotein collagen.Asheetoffibrousconnectivetissuesurroundstheboneandhelpsithealfroma fracture.Cartilagecushionsthejoints.Theshaftofthebonehasacentralcavityfilledwithyellow bonemarrow.Yellowbonemarrowstoresfat.Spongyboneislocatedattheendsofthebone andcontainsredbonemarrow,whichproducesnewbloodcells. Distinguishthedifferenttypesofbonecellsandtheirspecificfunctions. Therearefourtypesofbonecells.First,Osteocytes.Thesecellsmaintainthemineraland proteincontentoftheboneisintheinsideandcompactboneontheoutside.Thelongerpartis thePeriosteumandbonemarrowliesontheinsidesurroundingbone,theycannotdivide,and participateintherepairofdamagedbone.OsteoblastsproducemoreOsteocytesinaprocess calledOsteogenesis.OsteoprogenitorcellsarestemcellsthatdivideintoOsteoblasts.They maintainthenumberofOsteoblastsandaidintherepairofdamagedbone.Osteoclastsremove andrecyclebonematter.theydothisbysecretingacidsandenzymestodissolvethebonein orderfornewbonemattertobeproduced.ThisProcessiscalledOsteolysis.Sotorecap,the fourcellsareOsteocytes,Osteoblasts,Osteoprogenitors,andOsteoclasts. Explainhowskeletonsareheldtogetherandhowbonesconnecttomuscles. Bonesareheldtogetherwithjoints.somejointsallowfornomovementsuchasthejointsofthe ribsandspine,orthebonesintheskull.otherjointsallowforsomerangeofmotion,suchasthe jointintheknee,orthejointintheshoulderorpelvis.Inthesejointsthebonesareheldtogether byafibrousconnectivetissuecalledaligament.Boneshavebumpsonthem,whereadifferent connectivetissuecalledatendonattachesthebonetothemuscle. Distinguishbetweenthethreetypesofmuscle.
Thethreetypesofmuscleareskeletal,smooth,andcardiac.Skeletalmusclesare attachedtotheskeleton,andforthemost part,areunderconsciouscontrol(voluntarymuscles).Smoothmusclesurroundssoftorgans suchasthestomach,andtheintestines.Cardiacmuscleisthemusclethatpumpstheheart. Smoothandcardiacmusclesdonotrequireconsciouscontroltofunction(involuntarymuscles). Skeletalmusclecellsarelongandcylindershaped,withstriationsduetothesarcomeres. Smoothmuscleshavespindleshapedcells,beingtaperedattheend.Cardiacmusclecells
3 makebranchingconnectionswitheachother. Explainwhathappenswhenamusclecontracts.
Inamuscle,thefunctionalunitisthesarcomere.Thesarcomereiscomposedoftwotypesof filaments,thinandthick.thethinfilamentiscomposedoftheproteinactin,whilethethick filamentsarecomposedoftheproteinmyosin.Firstthemyosinheadsbindtothethinfilaments, thenthemyosinheadsbend,pullingthethinfilamentstowardsthecenterofthesarcomere.ATP thenbindstoeachmyosinhead,releasingitfromthethinfilament.themyosinheadcannow attachtoanewspotfurtherdownthethinfilamentandpullitfartheralong.creatingacontraction. Distinguishbetweenabductionandadduction. Abductionismusclemovementawayfromthebodyandadductionismovementtowardsthe body.Forexample,liftingyourarmisadduction,andputtingitdownisabduction. Explainhowtheskinisconstructedofmultiplelayersoftissueandfunctionsasa barrierbetweenthebodysinternalandexternalenvironment. Skinisconstructedinthreelayers.Fromoutsidetoinside:theepidermis,thedermis,andthe hypodermis.Itfunctionsasabarrierbetweentheinternalandexternalenvironmentbyactingas abarriertoinfections,aregulatorofbodytemperature,aremoverofwasteproducts(sweat), andaprotectoragainstUVradiation. describethe4majorfunctionsoftheIntegumentarysystem. Theintegumentarysystemisyourbodysoutercoveringthatphysicallyseparatesthebodyfrom theexternalenvironment.Ithelpsregulatebodytemperaturethroughsweatingandinsulating,it protectsfromUVradiation(hair),italsoactsasabarriertoinfection(physicalbarrierofskin), anditisaremoverofwasteproduct. Distinguishbetweenthe3differentlayersofskin.
EpidermisOutermostlayer,mostlydeadcellsthatflakeoffasnewcellsreplacethem DermisMiddlelayer,containshairfollicles,oilandsweatglands,muscles,nerves,andblood vessels. Hypodermisinnermostlayer,fatstoringcellsandbloodvessels. Explainhowthebodyregulatestemperature. Inordertoregulatetemperaturethebody,whenhot,thebodydilatesthebloodvesselsandthe bloodtemperaturedecreases,thebloodsignalsthebrain,whichsignalstheskinvianervesto
4 openupporesinordertoreleasesweat.Whenairblowsoverthesweat,itleavesacooling sensation.Whencold,bloodtemperatureincreases,bloodvesselsconstrictandthissignalsthe skintoclosetheporeswhicharelettingoutsweat.Alsothemusclesstartcontractingrapidly (shivering)inordertogenerateheat. Explainhowthenervoussystem(brain,spinalcord,sensoryneurons,motor neurons)mediatescommunicationamongdifferentpartsofthebodyand mediatesthebodysinteractionswiththeenvironment.Identifythebasicunitof thenervoussystem,theneuron,andexplaingenerallyhowitworks. ThisanswermayormaynotbecompleteBS...wellthatdoesntmakemeconfident...Nerve cellsarelocatedinthedermisoftheskin,aswellasinvariousothertissuetypes.Receptors sensingheat(thermoreceptors),chemicals(chemoreceptors),touch(mechanoreceptors),light (photoreceptors),pain(painreceptors)receiveenvironmentalsignals,andtransmitthese signalstothebrainthroughaseriesofactionpotentials.Thebrain,inturn,willsendsignalsto themotordivisionofthebodypartthatsentthesignaltoperformsomeactiontorespondtothe stimulus.Thebrainsresponsetothisstimulusdependsonthefrequencyofthestimulus(higher frequency=morepowerfulstimulus).Inthisway,thenervoussystemisabletocommunicate signalsthroughoutthebody. Theneuronsbasicpartsarethecellbody(withanucleus),dendrites,andanaxon.Dendrites receiveimpulsesfromotherneuronsandcarrythemtothecellbody.Axonscarryimpulsesfrom thecellbodytootherneurons.Axonsaresurroundedbymanymyelinsheathswithspacesin betweencallednodes.Actionpotentialscannottravelacrossmyelinsheaths,sotheyjump betweennodes.Thisspeedsthetransmissionofsignalsbecausetheactionpotentialdoesnt havetomoveacrossagreatdealmoreaxontogetwhereitneedstogo. Explain,ingeneralterms,thefunctionsofthemajorpartsofthebrain. Cerebrumisthemostcomplexitregulatesmemory,andlongtermstorageofinformationitis alsothebrainsmainprocessor.Itisdividedintotwohemispheres:theleftcontrolstherightside ofthebody,andviceversa.Leftsidecontrolslogicalthinking,rightsidecontrolscreative thinking. Hypothalamuscontrolsbodytemperature,thirst,hunger,waterbalance,andemotions. BrainStem(pons/medullaoblongata)thispartregulatesbodyprocessesthatareinvoluntary andarenotconsciouslycontrolled,liketheheartbeating.(smoothandcardiacmuscle) Cerebellumcontrolsallvoluntarybodymovement(skeletalmuscle)
5 Thalamussortsallinformationcomingintothebrain Diagramthemainsensoryandmotorpathwaysinvolvedinareflexarc.
Identifythepartsofaneuronandshowthedirectioninwhichanerve impulsepasses.
Thefirstpartofaneuronisthecellbodyandthenucleus.Branchingfromthecellbodyarethe dendriteswhichcarrysignalstowardthecellbody.Axonsthencarrythesesignals(action potentials)awayfromthecellbody.Theaxonsareinsulatedbymyelinsheaths,whichallowsthe signaltohopfromnodetonodespeedingthetransmissionprocessandcarryingthesignalto thenextneuronfaster(wedidntlearnthis,butthemyelinsheathscoverthingscalledSchwann cells,orneurolemmocytes).Thecellbodyisnucleated. Explainthetransmissionofnerveimpulsesalonganeuron. Therearemorepositiveionsoutsidethecellthaninside,creatingpotentialenergy.Whenthecell ishitbyastimulus,themembraneofthecellbecomesmorepermeableandmoreNA+ions diffuseintothecell,causingdepolarizationandthenmoreNA+ionsareletintothecellby channelgates,whichcausesactionpotential.Thisisabigchainreactionwhichmovesacross theaxontowardsothercells.K+arepotassiumionswhileNA+aresodiumions. Describehownerveimpulsescrossasynapse. 1.actionpotentialcausesvesiclestoreleasechemicalsignalscalledneurotransmitters. 2.neurotransmitterscrossthroughthetinyspacecalledthesynapticcleft 3.receptormoleculesonthereceivingneuronaccepttheneurotransmitterandmaycreatea newactionpotential,butthesynapsehasbeencrossed. Explainhowthehumaneyeworks. Lightenterstheeyethroughthecornea,nextthroughtheaqueoushumor,thenthroughthepupil
6 whichisahole.Thepupilgetslargerandsmallerbasedontheavailabilityoflight.Itis surroundedbytheIriswhichisthecoloredpartofaneye.Thelightnexthitsyourlens,which directsandbendsthelighttoyourretinawhichreceivesthesignalanddeliversittotheoptic nerve.Theopticnervethensendsittothebrain.Whenlightiscloserthelensismorebentand whenitsfartherawaythelensflattensout.Conesintheeyerespondtoblue,redandgreen. Rodsaremoresensitiveandhelpyouseeinthedark,howevercannotdistinguishbetween colors. Explainhowthehumanearworks. Sound,whichconsistsofsoundwaves,makesitswaytotheear,thesoundcomesinthrough theearcanaltravelsdowntotheeardrum,whichmakestheeardrumvibrate.Thisvibration passesthroughtheossicles(earbones)andintothecochlea.Inthecochlea,thevibrationspass throughthefluidandthatmakesthehaircellsmove.Thehairmovementinthecochleamakes anelectricsignalpassthroughtheauditorynerveandtothebrain.Thesemicircularcanalsaidin balancebecausethearelocatedintheX,YandZplanes,sowhentheheadtiltsacertainway, thehaircellsdetectthemovement. Integumentarysystem:coversthebodyandprotectsitfrominjury,infection,excessiveheator cold,anddryingout. Skeletalsystem:providesbodysupport,protectscertainorganssuchasthebrainandlungs, andworksw/themuscularsysteminbodymovements. Muscularsystem:enablesbodymovementandfacialexpressionsessentialtohuman communication. Nervoussystem:coordinatesbodysactivitiesbydetectingstimulianddirectingthebodys responses. Anatomy:studyofanorganism'sstructure. Physiology:studyoffunctionsorprocessesinanorganism. Tissue:cooperatingunitofmanysimilarcellsthatperformaspecificfunction.
7 Organ:unitconsistingofseveraltissuesthattogetherperformaspecifictask. Organsystem:unitofmultipleorgansthattogetherperformavitalbodyfunction. Epithelialtissue:sheetsofcloselypackedcellsthatcoverthesurfaceofthebodyandlinethe internalorgans. Connectivetissue:groupsofcellsthatholdtogetherandsupportothertissuesandcushion, insulate,andconnectorgans. Nervoustissue:tissuethattransmitssignalsinthebodyinresponsetochangesinthe environment. Neuron:nervecellbasicunitofnervoustissue. Skeletalmuscle:voluntarymuscleattachedtotheskeletonthatallowsmovementofthebody. Theyarecomposedofskeletalmuscletissue. Cardiacmuscle:involuntarymusclethatcausesthehearttopumpblood. Smoothmuscle:involuntarymusclefoundinmostorgansofthebody. Homeostasis:internalstabilityor"steadystate"maintainedbythebody. Hormone:signalmoleculereleasedintothebloodstreamthattriggersparticularresponses. Interstitialfluid:aqueoussolutionthatfillsthegapsbetweencellsinatissue. Integumentarysystem:outercoveringthatphysicallyseparatesthebodyfromtheexternal environment. Epidermis:outermostlayerofskin. Melanin:pigmentedproteinthatgivesskinitscolor. Dermis:layerofskinbeneathandsupportingtheepidermis,madeupmostlyoffibrous connectivetissuethatgivestheskinitsstrengthandelasticity. Hypodermis:tissuelayerbeneaththedermiscontainsadiposetissue,aconnectivetissuethat includesfatstoringcellsandbloodvessels. Vertebra:segmentofthebackboneenclosesandprotectsthenervecord. Cartilage:typeofconnectivetissuesofterthanbone. Marrow:specializedtissuefoundinboneyellowbonemarrowconsistsofstoredfatthatserves asanenergyreserveredbonemarrowmakescellsthatdevelopintobloodcells. Joint:areawhereonebonemeetsanother. Ligament:strongfibrousconnectivetissuethatholdstogetherthebonesinmovablejoints. Arthritis:groupofskeletaldisorderscharacterizedbyinflamedjoints. Osteoporosis:disorderinwhichbonesbecomethinner,moreporous,andmoreeasilybroken.
8 Tendon:denseconnectivetissuethatattachesamuscletoabone. Musclefiber:single,longcylindricalmusclecellcontainingmanynuclei. Myofibril:unitofmusclefibermadeupofsmallerunitsthatcontract(sarcomeres). Sarcomere:unitofcontractioninamusclefiber. Actin:twisted,thinfilamentinamusclefiber. Myosin:thickfilamentinamusclefiberhasbumplikeprojections. Centralnervoussystem(CNS):thebody'sprimaryinformationprocessingsystemincludes thebrainandspinalcord. Peripheralnervoussystem(PNS):networkofnervescarryingsignalsintoandoutofthe centralnervoussystem(nervetissueoutsidetheCNS). Nerve:bundleorbundlesofneuronfiberssurroundedbyconnectivetissue. Stimulus:environmentalchangethattriggersaresponse. Sensoryneuron:nervecellthatcarriesinformationfromtheenvironmenttothecentralnervous system. Sensoryreceptor:specializedcellthattransmitssignalstosensoryneurons. Interneuron:nervecelllocatedentirelyinthecentralnervoussystemthatintegratessensory informationandsendsmotorcommands. Motorneuron:nervecellthatcarriessignalsfromthecentralnervoussystemtomuscleor glandcells. Reflex:rapid,automaticresponsetoastimulus. Dendrite:neuronfiberthatreceivessignalsandcarriesthemtowardthecellbody. Axon:neuronfiberthatcarrieselectricimpulsesawayfromthecellbodyandtowardothercells. Myelinsheath:thickcoatofmaterialthatsurroundsandinsulatestheaxonofsomeneurons. Node:uninsulatedspacesbetweenthe"beads"ofamyelinsheathwhereanactionpotentialcan betransmitted. Restingpotential:voltageacrosstheplasmamembraneofarestingneuron. Depolarization:voltagechangethatoccurswhenthedifferenceinchargeacrossamembrane decreases. Threshold:minimumchangeinamembrane'svoltagethatmustoccurtogenerateanaction potential. Actionpotential:changeinvoltageacrosstheplasmamembraneofaneuronresultingina nervesignal.
9 Synapse:junctionbetweentwoneuronsoraneuronandanothercellwhereelectricalor chemicalsignalsarerelayed. Synapticcleft:tinyspaceseparatingaknobofatransmittingneuronfromareceivingneuronor othercell. Neurotransmitter:chemicalmessengerthatcarriesinformationfromoneneurontoanotheror toanothercell(small,nitrogencontainingorganiccompound). Somaticnervoussystem:subdivisionofthemotordivisionoftheperipheralnervoussystem thatcontrolsthevoluntarymovementofskeletalmuscles. Autonomicnervoussystem:subdivisionofthemotordivisionoftheperipheralnervoussystem thatregulatestheinternalenvironment. Sympatheticdivision:divisionoftheautonomicnervoussystemthatgenerallypreparesthe bodyforenergyconsumingactivities.Basically,ifyoufindyourselfinasituationwhichrequires quickresponsesandreactions,thesympatheticnervoussystemlowersdigestivefunctions,etc. andtheliverconvertsglycogenintoglucoseforusebythebody.Thebodyalsobeginsto producemoreadrenalinetoheightenawarenessofthesurroundings.FightorFlight Parasympatheticdivision:divisionoftheautonomicnervoussystemthatconservesenergy. ThisisasopposedtothesympatheticNS.TheparasympatheticNScalmsthebodydown, restartsbodymaintenancefunctions,andreducesadrenalinelevelsinthebloodstream. Cerebrum:largestandmostcomplexpartofthebrain,madeupoftheleftandright hemispheres. Corpuscallosum:bandofnervefibersthatsupportcommunicationbetweenthetwocerebral hemispheres. Cerebralcortex:outerregionofcerebrumcontainingintegrationcentersforhigherbrain functions. Cerebellum:partofthebrainlocatedbelowthecerebrumandabovethespinalcordplanning centerthatcoordinatesbodymovement. Brainstem:lowersectionofthebrainincludingthemedullaoblongata,pons,andmidbrainthat filtersinformationgoingtoandfromthebrain. Thalamus:brainregionthatsortsandexertssomecontroloverinformationgoingtoandfrom thecerebralcortex. Hypothalamus:regionofthebrainthatisthe"mastercontrolcenter"oftheendocrinesystem functionsinmaintaininghomeostasisbyregulatingtemperature,bloodpressure,andother
10 conditions. Limbicsystem:systemofregionsofthebrainthatinteractwiththecerebralcortexinemotion andmemory.Involvesseveraldifferentareasthatintegrateandrelayinfo,includingthe amygdala,hippocampus,andpartsofthecerebralcortex,hypothalamus,andthalamus. Sensation:awarenessofsensorystimuli. Perception:meaningfulinterpretationofsensorydatabythecentralnervoussystem. Cornea:transparentareaatthefrontoftheeyethroughwhichlightenters. Iris:coloredpartoftheeyecontrolstheamountoflightthatenterstheeyebyregulatingthesize ofthepupil. Pupil:openingintheiristhatadmitslightintotheeye. Retina:innersurfaceoftheeyethatislinedwithmillionsofphotoreceptorcells. Cone:photoreceptorcellintheretinathatisstimulatedinbrightlight,enablingcolorvision. Rod:photoreceptorintheretinathatenablesvisionindimlight. Auditorycanal:partoftheouterearthatchannelssoundsfromtheoutsidetotheeardrum. Eardrum:sheetoftissueseparatingtheouterearfromthemiddleearthatvibrateswhen stimulatedbysoundwaves. Auditorytube:airpassagebetweenthemiddleearandthroatthatequalizesairpressureon eithersideoftheeardrumalsocalledtheEustachiantube. Cochlea:coiledtubeintheinnerearcontaininghairlikeprojectionsthatfunctioninhearing. Tolerance:resistancetoadrug'seffectssuchthatmoreofthedrugisneededtoproducethe sameeffect. Addiction:uncontrollabledependenceonadrug. Withdrawal:psychologicaland/orphysicalsymptomsexperiencedwhenapersonstopstaking adrugtowhichheorsheisaddicted. Stimulant:drug,suchascaffeine,nicotine,andcocaine,whichgenerallyincreasesactivityin thecentralnervoussystem. Depressant:drugsuchasalcoholortranquilizersthat,ingeneral,slowscentralnervous systemactivity. Marijuana:drugmadefromdriedpiecesofthehempplant. Opiate:narcotic,suchasmorphineorheroin,whichisderivedfromopiumpoppies. Hallucinogen:drugthatcausesapersontosee,hear,andperceivethingsthatdonotexist. Ecstasy:syntheticdrugthatcausesstimulantlikeandhallucinogeniclikeeffectsintheuser.
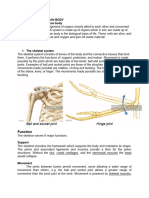
11 Inhalant:substance,suchascertainaerosols,whosevaporsproducemindalteringeffects. SourcesofHomeostaticImbalance TraumaAcuteinjuries,suchasacarcrash,orrepetitiveinjuries,such astendonitis,leadtodamagedtissue. EnvironmentalInfluencesSolarRadiationorahighsugardietcan damagetissuesorstressbodysystems GeneticVariationSomegenes,suchassicklecelltrait,alteroxygen capacity,butprovideformalariaresistance.Others,likeCysticFibrosis, providenobenefit. Parasites&VirusesParasitesliketapewormsorbacterialinfections consumehumantissuesforenergy.Virusesturncellsintovirus factories.Inbothcases,tissuesaredamagedandenergyislost. DesignCompromises&EvolutionaryLegaciesHumansarebipedal whichallowsforusingtheirhandsforcarryingobjects,butpredisposesus tobackpain.Unlikemostothermammals,humansarenotableto manufactureVitaminCandthereforemustconsumeitregularly.These evolutionaryvestigesleavehumansvulnerabletohomeostaticimbalance. Joints BallandSocketJoint(shoulder)bonescanrotatebackandforthandsidetoside HingeJoint(knee)allowsmovementbackandforthinoneplane PivotJoint(topofneckandbaseofskull)onebonerotatesaroundanother ImmovableJoint(bonesofskull,ribs,pelvis)bonesarefusedtogetherandcantmove.
12
13
AnatomyofanEar Auditorycanalthetubethroughwhichsoundtravelstotheeardrum. Eardrumathinmembranethatvibrateswhensoundwavesreachit. Hammeratinybonethatpassesvibrationsfromtheeardrumtotheanvil. Anvilatinybonethatpassesvibrationsfromthehammertothestirrup. Stirrupatiny,Ushapedbonethatpassesvibrationsfromthestirruptothecochlea.Thisisthe smallestboneinthehumanbody. Cochleaaspiralshaped,fluidfilledinnerearstructureitislinedwithcilia(tinyhairs)that movewhenvibratedandcauseanerveimpulsetoform. Auditorynervesthesecarryelectrochemicalsignalsfromtheinnerear(thecochlea)tothe brain. Auditorytubeatubethatconnectsthemiddleeartothebackofthenoseitequalizesthe pressurebetweenthemiddleearandtheairoutside.Whenyou"pop"yourearsasyouchange altitude(goingupamountainorinanairplane),youareequalizingtheairpressureinyourmiddle ear.AlsoknownastheEustachiantube Semicircularcanalsthreeloopsoffluidfilledtubesthatareattachedtothecochleainthe innerear.Theyhelpusmaintainoursenseofbalance.
14
AnatomyofanEye Scleratoughlayerofconnectivetissueformingtheouterwhitecoveringoftheeye. Corneatheclear,domeshapedtissuecoveringthefrontoftheeye. Iristhecoloredpartoftheeyeitcontrolstheamountoflightthatenterstheeyebychanging thesizeofthepupil. Lensacrystallinestructurelocatedjustbehindtheirisitfocuseslightontotheretina. Opticnervethenervethattransmitselectricalimpulsesfromtheretinatothebrain. Pupiltheopeninginthecenteroftheirisitchangessizeastheamountoflightchanges(the morelight,thesmallerthehole). Retinasensorytissuethatlinesthebackoftheeye.Itcontainsmillionsofphotoreceptorsthat convertlightraysintoelectricalimpulsesthatarerelayedtothebrainviatheopticnerve. RodsPhotoreceptorsintheretinathatsensered,green,andbluelight. ConesPhotoreceptorsintheretinathatareverysensitivetolight,allowingyoutoseepretty wellinthedark,butonlyingrayscale. Ligamentsintheeyeconnectmuscletomuscle,unlikeotherligamentswhichconnectbonesto bones.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Ns Elec 4 - Muscular SystemDocumento4 pagineNs Elec 4 - Muscular SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ns Elec 4 - Muscular SystemDocumento5 pagineNs Elec 4 - Muscular SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Anatomy and Physiology: An Overview of the Musculoskeletal SystemDocumento15 pagineBasics of Anatomy and Physiology: An Overview of the Musculoskeletal SystemCharmainne Kathlene ArellanoNessuna valutazione finora
- HCP MODULE 11 Musculoskeletal SystemDocumento9 pagineHCP MODULE 11 Musculoskeletal SystemLHYRA KATHLEEN LOPEZNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular-System-Handouts - BiologyDocumento7 pagineMuscular-System-Handouts - BiologyApril Joy T. GrijaldoNessuna valutazione finora
- Textos I Medicina Level I 2020Documento18 pagineTextos I Medicina Level I 2020Valeria DonzelliNessuna valutazione finora
- PE 11-Pathfit 1 - Worksheet 3Documento2 paginePE 11-Pathfit 1 - Worksheet 3MJ RHONNA TABO-TABONessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle Structure and Exercise Physiology PDFDocumento11 pagineMuscle Structure and Exercise Physiology PDFGabriel Zaharia100% (3)
- T1 Condicion Fisica 4º EsoDocumento6 pagineT1 Condicion Fisica 4º EsoMartín Benítez del HoyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology Module 1Documento13 pagineAnatomy and Physiology Module 1JayR Mendones100% (2)
- AnatomyDocumento8 pagineAnatomyK WangNessuna valutazione finora
- PE Part 1Documento34 paginePE Part 1MitchNessuna valutazione finora
- Justine May Arcos: TypesDocumento2 pagineJustine May Arcos: TypesJenniferFajutnaoArcosNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.1 HomeostasisDocumento13 pagine3.1 HomeostasisHAFSA RASHEDNessuna valutazione finora
- What Do You Call The Arrowed Part?Documento13 pagineWhat Do You Call The Arrowed Part?Earl GenodipaNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 11 7chapter-7 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento13 pagineClass 11 7chapter-7 Anatomy and PhysiologyImportant IdNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 3 - Basic Human Anatomy, Physiology & Fitness ConceptsDocumento30 pagineWeek 3 - Basic Human Anatomy, Physiology & Fitness ConceptsJohn Cailen Barceñas IINessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 6 - Musculoskeletal SystemDocumento30 pagineLesson 6 - Musculoskeletal Systemapi-307592530100% (1)
- Structure of Human BodyDocumento19 pagineStructure of Human BodyWimrod CanenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal TissuesDocumento10 pagineAnimal TissuesAlvin PaboresNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Musculoskeletal SystemDocumento11 pagineHuman Musculoskeletal SystemMuhammad NaqibNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 2 (Chapter 2.1)Documento12 pagineMODULE 2 (Chapter 2.1)Malapitan, Kiana Blanca A.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Human Anatomy 1Documento55 pagineBasic Human Anatomy 1ZzzNessuna valutazione finora
- Make-Up of The Human BodyDocumento7 pagineMake-Up of The Human BodyMariam GamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 2 FIT MEDocumento7 pagineTopic 2 FIT MESleepy HeadNessuna valutazione finora
- Osteosarcoma-Ana and PhysiologyDocumento4 pagineOsteosarcoma-Ana and PhysiologyNeirfla WassabiNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading 4 The Muscular SystemDocumento16 pagineReading 4 The Muscular Systemlephuongvy1406Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2304 Intro AnatomyDocumento6 pagine2304 Intro AnatomyLiezel CauilanNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento2 pagineAnatomy and PhysiologyMichelle BilayaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Musculoskeletal System: Structure and Movement in 38 CharactersDocumento30 pagineThe Musculoskeletal System: Structure and Movement in 38 CharactersJosee50% (2)
- Definition of Terms Anatomy - Physiology - : Weeks 1-3 Module: Learning ContentDocumento37 pagineDefinition of Terms Anatomy - Physiology - : Weeks 1-3 Module: Learning ContentShana AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Analec Week 1-3Documento17 pagineAnalec Week 1-3Ferndale AlimondoNessuna valutazione finora
- Relationship Between Anatomy & Physiology ExplainedDocumento16 pagineRelationship Between Anatomy & Physiology ExplainedMailin RipauNessuna valutazione finora
- Mascular Skeletal System p7Documento17 pagineMascular Skeletal System p7joseph kunikinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Co2 Lesson 1.1 Human Anatomy Week 4Documento10 pagineCo2 Lesson 1.1 Human Anatomy Week 4accfor everythingNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 NBHS1113 T1 PDFDocumento23 pagine05 NBHS1113 T1 PDFnaem nadzriNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain Anatomy and FunctionDocumento24 pagineBrain Anatomy and FunctionAdamu GudinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Competency 11Documento26 pagineCompetency 11Charis RebanalNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology Organ SystemsDocumento35 pagineAnatomy and Physiology Organ SystemsFebz CanutabNessuna valutazione finora
- MusculoskeletalDocumento5 pagineMusculoskeletalharleens204Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cult Certified Fitness Trainer Yoga Level 0 AnatomyDocumento34 pagineCult Certified Fitness Trainer Yoga Level 0 Anatomymanoj maharNessuna valutazione finora
- Submitted By: John Benedict Vocales Bsed 3-2Documento3 pagineSubmitted By: John Benedict Vocales Bsed 3-2John Benedict VocalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 1 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento9 paginePart 1 Anatomy and Physiologyzy- SBGNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Map - Muscle Types & FunctionsDocumento2 pagineBody Map - Muscle Types & FunctionsFani Try Utami BoedaxRed'waterzzNessuna valutazione finora
- MS System SummaryDocumento16 pagineMS System SummaryChelo Jan GeronimoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Musculoskeletal System Is Composed of Two SystemsDocumento3 pagineThe Musculoskeletal System Is Composed of Two SystemsKomang AyudhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- MUSCLESDocumento6 pagineMUSCLESTishonna DouglasNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle Ligaments & TendonsDocumento5 pagineMuscle Ligaments & TendonsMahnoor JawadNessuna valutazione finora
- NAW-5 Aspects of FitnessDocumento34 pagineNAW-5 Aspects of Fitnessganesh pNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan in Muscular System: Semi Detailed, With Lesson ContentsDocumento19 pagineLesson Plan in Muscular System: Semi Detailed, With Lesson ContentsToffee Perez85% (26)
- 1st Year Basic BSC Nursing Anatomy Word Notes in DetailsDocumento2 pagine1st Year Basic BSC Nursing Anatomy Word Notes in DetailsShreyas WalvekarNessuna valutazione finora
- A&P Chapter 1 Overview: Anatomy, Physiology, and Structural OrganizationDocumento10 pagineA&P Chapter 1 Overview: Anatomy, Physiology, and Structural OrganizationRustin John ReaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaphy LectureDocumento5 pagineAnaphy Lecturealthea jade villadongaNessuna valutazione finora
- MS 316 Lec Merge YarnDocumento73 pagineMS 316 Lec Merge YarnMARIA STEPHANY DELA CRUZNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.3 Bones Muscles and JointsDocumento5 pagine9.3 Bones Muscles and JointsDerick NKANDU KALUBANessuna valutazione finora
- The Human Organism: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento7 pagineThe Human Organism: Anatomy and PhysiologyGem Rose UretaNessuna valutazione finora
- TX Bio Ch30Documento48 pagineTX Bio Ch30Mario Alberto Mora OrtizNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaphy ReviewerDocumento12 pagineAnaphy ReviewerRuby Jane LaquihonNessuna valutazione finora
- AssignmentFile 18 06032024133208Documento15 pagineAssignmentFile 18 06032024133208kartikbansal232007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Motivation and EmotionDocumento77 pagineMotivation and EmotionWaqas MazharNessuna valutazione finora
- OCR Biology Practical Guide BookDocumento4 pagineOCR Biology Practical Guide BookFatima ImranNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of ApraxiaDocumento12 pagineOverview of ApraxiaMaheswarNessuna valutazione finora
- New Text DocumentDocumento3 pagineNew Text DocumentshamshadNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study CVDDocumento49 pagineCase Study CVDzerpthederpNessuna valutazione finora
- Developmental Neurology and Neuro RehabilitationDocumento2 pagineDevelopmental Neurology and Neuro RehabilitationClaudia MicuNessuna valutazione finora
- Proses Berkemih: Moganasivan S 1301-1211-3074Documento10 pagineProses Berkemih: Moganasivan S 1301-1211-3074Nuansa Chalid AwaluddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Neural-Networks ..Documento114 pagineLecture Neural-Networks ..Jaya ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basal Ganglia Circuits As Targets For Neuromodulation in Parkinson DiseaseDocumento7 pagineBasal Ganglia Circuits As Targets For Neuromodulation in Parkinson DiseaseSebastián GallegosNessuna valutazione finora
- Guillain - Barre Syndrome: Icu / PicuDocumento23 pagineGuillain - Barre Syndrome: Icu / PicuchellczyNessuna valutazione finora
- Antipsychotic Agents: Conventional vs AtypicalDocumento18 pagineAntipsychotic Agents: Conventional vs AtypicalmengakuNessuna valutazione finora
- Edelman, Gerald - Neural DarwinismDocumento8 pagineEdelman, Gerald - Neural DarwinismcdmemfgambNessuna valutazione finora
- Outcome Measure PresentationDocumento11 pagineOutcome Measure Presentationapi-547954700Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hindi Ocd BookletDocumento20 pagineHindi Ocd BookletAnonymous zNHxbrsETT100% (2)
- Psychy Supplement For Regular & Foundation 2020 PDFDocumento2 paginePsychy Supplement For Regular & Foundation 2020 PDFRAM KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- SchizophreniaDocumento34 pagineSchizophreniaSarasija NatarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Third Nerve Palsy Analysis of 1400 Personally Examined InpatientsDocumento9 pagineThird Nerve Palsy Analysis of 1400 Personally Examined Inpatientstenthousand hoursNessuna valutazione finora
- Dementia Diagnosis and EvaluationDocumento32 pagineDementia Diagnosis and EvaluationShary AlickNessuna valutazione finora
- The Evolutionary Basis of Strabismus and Nystagmus in ChildrenDocumento244 pagineThe Evolutionary Basis of Strabismus and Nystagmus in ChildrenComan MihaelaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Building of A BrainDocumento173 pagineThe Building of A BrainAvanish KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Facial Palsy Guide by NeurologistDocumento25 pagineFacial Palsy Guide by NeurologistMahad abuukarNessuna valutazione finora
- OMT Evaluation 6Documento34 pagineOMT Evaluation 6aza bellaNessuna valutazione finora
- NBME Neuro 2Documento2 pagineNBME Neuro 2naimNessuna valutazione finora
- Opposite Effects of Dopamine and Serotonin On Resting-State Networks: Review and Implications For Psychiatric DisordersDocumento12 pagineOpposite Effects of Dopamine and Serotonin On Resting-State Networks: Review and Implications For Psychiatric DisordersMae PNessuna valutazione finora
- PEDS Exam 2 - OutlineDocumento67 paginePEDS Exam 2 - OutlineBonquisha OrgamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Long Test No. 4 (Nervous System) Ready To PrintDocumento3 pagineLong Test No. 4 (Nervous System) Ready To Printjayrald cruzada100% (1)
- Arterial Supply of The Thalamus - A Comprehensive ReviewDocumento9 pagineArterial Supply of The Thalamus - A Comprehensive Reviewمحمد رؤوف خير الدينNessuna valutazione finora
- Mri Brain SequencesDocumento13 pagineMri Brain SequencesRisa MarissaNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Advances in The Cognitive Neuroscience of MusicDocumento21 pagineCurrent Advances in The Cognitive Neuroscience of MusicBen Blum100% (3)
- Autism Spectrum Disorders - From Genotypes To Phenotypes PDFDocumento95 pagineAutism Spectrum Disorders - From Genotypes To Phenotypes PDFMariaAndreaNessuna valutazione finora