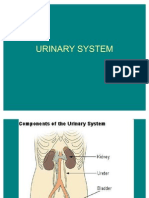
Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Preboard C Nurselabs
Caricato da
roldanDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Preboard C Nurselabs
Caricato da
roldanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
NP 1 1.
The nurse In-charge in labor and delivery unit administered a dose of terbutaline to a client without checking the clients pulse. The standard that would be used to determine if the nurse was negligent is: a. The physicians orders. b. The action of a clinical nurse specialist who is recognized expert in the field. c. The statement in the drug literature about administration of terbutaline. d. The actions of a reasonably prudent nurse with similar education and experience. 2. Nurse Trish is caring for a female client with a history of GI bleeding, sickle cell disease, and a platelet count of 22,000/l. The female client is dehydrated and receiving dextrose 5% in halfnormal saline solution at 150 ml/hr. The client complains of severe bone pain and is scheduled to receive a dose of morphine sulfate. In administering the medication, Nurse Trish should avoid which route? a. I.V b. I.M c. Oral d. S.C 3. Dr. Garcia writes the following order for the client who has been recently admitted Digoxin .125 mg P.O. once daily. To prevent a dosage error, how should the nurse document this order onto the medication administration record? a. Digoxin .1250 mg P.O. once daily b. Digoxin 0.1250 mg P.O. once daily c. Digoxin 0.125 mg P.O. once daily d. Digoxin .125 mg P.O. once daily 4. A newly admitted female client was diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis. Which nursing diagnosis should receive the highest priority? a. Ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion related to venous congestion. b. Risk for injury related to edema. c. Excess fluid volume related to peripheral vascular disease. d. Impaired gas exchange related to increased blood flow. 5. Nurse Betty is assigned to the following clients. The client that the nurse would see first after endorsement? a. A 34 year-old post operative appendectomy client of five hours who is complaining of pain. b. A 44 year-old myocardial infarction (MI) client who is complaining of nausea. c. A 26 year-old client admitted for dehydration whose intravenous (IV) has infiltrated. d. A 63 year-old post operatives abdominal hysterectomy client of three days whose incisional dressing is saturated with serosanguinous fluid. 6. Nurse Gail places a client in a four-point restraint following orders from the physician. The client care plan should include: a. Assess temperature frequently. b. Provide diversional activities. c. Check circulation every 15-30 minutes. d. Socialize with other patients once a shift. 7. A male client who has severe burns is receiving H2 receptor antagonist therapy. The nurse Incharge knows the purpose of this therapy is to: a. Prevent stress ulcer b. Block prostaglandin synthesis c. Facilitate protein synthesis. d. Enhance gas exchange
8. The doctor orders hourly urine output measurement for a postoperative male client. The nurse Trish records the following amounts of output for 2 consecutive hours: 8 a.m.: 50 ml; 9 a.m.: 60 ml. Based on these amounts, which action should the nurse take? a. Increase the I.V. fluid infusion rate b. Irrigate the indwelling urinary catheter c. Notify the physician d. Continue to monitor and record hourly urine output 9. Tony, a basketball player twist his right ankle while playing on the court and seeks care for ankle pain and swelling. After the nurse applies ice to the ankle for 30 minutes, which statement by Tony suggests that ice application has been effective? a. My ankle looks less swollen now. b. My ankle feels warm. c. My ankle appears redder now. d. I need something stronger for pain relief 10.The physician prescribes a loop diuretic for a client. When administering this drug, the nurse anticipates that the client may develop which electrolyte imbalance? a. Hypernatremia b. Hyperkalemia c. Hypokalemia d. Hypervolemia 11.She finds out that some managers have benevolent-authoritative style of management. Which of the following behaviors will she exhibit most likely? a. Have condescending trust and confidence in their subordinates. b. Gives economic and ego awards. c. Communicates downward to staffs. d. Allows decision making among subordinates. 12. Nurse Amy is aware that the following is true about functional nursing a. Provides continuous, coordinated and comprehensive nursing services. b. One-to-one nurse patient ratio. c. Emphasize the use of group collaboration. d. Concentrates on tasks and activities. 13.Which type of medication order might read Vitamin K 10 mg I.M. daily 3 days? a. Single order b. Standard written order c. Standing order d. Stat order 14.A female client with a fecal impaction frequently exhibits which clinical manifestation? a. Increased appetite b. Loss of urge to defecate c. Hard, brown, formed stools d. Liquid or semi-liquid stools 15.Nurse Linda prepares to perform an otoscopic examination on a female client. For proper visualization, the nurse should position the clients ear by: a. Pulling the lobule down and back b. Pulling the helix up and forward c. Pulling the helix up and back d. Pulling the lobule down and forward 16. Which instruction should nurse Tom give to a male client who is having external radiation therapy:
a. Protect the irritated skin from sunlight. b. Eat 3 to 4 hours before treatment. c. Wash the skin over regularly. d. Apply lotion or oil to the radiated area when it is red or sore. 17.In assisting a female client for immediate surgery, the nurse In-charge is aware that she should: a. Encourage the client to void following preoperative medication. b. Explore the clients fears and anxieties about the surgery. c. Assist the client in removing dentures and nail polish. d. Encourage the client to drink water prior to surgery. 18. A male client is admitted and diagnosed with acute pancreatitis after a holiday celebration of excessive food and alcohol. Which assessment finding reflects this diagnosis? a. Blood pressure above normal range. b. Presence of crackles in both lung fields. c. Hyperactive bowel sounds d. Sudden onset of continuous epigastric and back pain. 19. Which dietary guidelines are important for nurse Oliver to implement in caring for the client with burns? a. Provide b. Provide c. Monitor d. Provide high-fiber, high-fat diet high-protein, high-carbohydrate diet. intake to prevent weight gain. ice chips or water intake.
c. Place the client in high-Fowlers position. d. Stop the total parenteral nutrition. 25.Nurse May attends an educational conference on leadership styles. The nurse is sitting with a nurse employed at a large trauma center who states that the leadership style at the trauma center is taskoriented and directive. The nurse determines that the leadership style used at the trauma center is: a. Autocratic. b. Laissez-faire. c. Democratic. d. Situational 26.The physician orders DS 500 cc with KCl 10 mEq/liter at 30 cc/hr. The nurse in-charge is going to hang a 500 cc bag. KCl is supplied 20 mEq/10 cc. How many ccs of KCl will be added to the IV solution? a. .5 cc b. 5 cc c. 1.5 cc d. 2.5 cc 27.A child of 10 years old is to receive 400 cc of IV fluid in an 8 hour shift. The IV drip factor is 60. The IV rate that will deliver this amount is: a. 50 cc/ hour b. 55 cc/ hour c. 24 cc/ hour d. 66 cc/ hour 28.The nurse is aware that the most important nursing action when a client returns from surgery is: a. Assess the IV for type of fluid and rate of flow. b. Assess the client for presence of pain. c. Assess the Foley catheter for patency and urine output d. Assess the dressing for drainage. 29. Which of the following vital sign assessments that may indicate cardiogenic shock after myocardial infarction? a. BP 80/60, Pulse 110 irregular b. BP 90/50, Pulse 50 regular c. BP 130/80, Pulse 100 regular d. BP 180/100, Pulse 90 irregular 30.Which is the most appropriate nursing action in obtaining a blood pressure measurement? a. Take the proper equipment, place the client in a comfortable position, and record the appropriate information in the clients chart. b. Measure the clients arm, if you are not sure of the size of cuff to use. c. Have the client recline or sit comfortably in a chair with the forearm at the level of the heart. d. Document the measurement, which extremity was used, and the position that the client was in during the measurement. 31.Asking the questions to determine if the person understands the health teaching provided by the nurse would be included during which step of the nursing process? a. Assessment b. Evaluation c. Implementation d. Planning and goals 32.Which of the following item is considered the single most important factor in assisting the health professional in arriving at a diagnosis or determining the persons needs? a. Diagnostic test results b. Biographical date
20.Nurse Hazel will administer a unit of whole blood, which priority information should the nurse have about the client? a. Blood pressure and pulse rate. b. Height and weight. c. Calcium and potassium levels d. Hgb and Hct levels. 21. Nurse Michelle witnesses a female client sustain a fall and suspects that the leg may be broken. The nurse takes which priority action? a. Takes a set of vital signs. b. Call the radiology department for X-ray. c. Reassure the client that everything will be alright. d. Immobilize the leg before moving the client. 22.A male client is being transferred to the nursing unit for admission after receiving a radium implant for bladder cancer. The nurse in-charge would take which priority action in the care of this client? a. Place client on reverse isolation. b. Admit the client into a private room. c. Encourage the client to take frequent rest periods. d. Encourage family and friends to visit. 23.A newly admitted female client was diagnosed with agranulocytosis. The nurse formulates which priority nursing diagnosis? a. Constipation b. Diarrhea c. Risk for infection d. Deficient knowledge 24.A male client is receiving total parenteral nutrition suddenly demonstrates signs and symptoms of an air embolism. What is the priority action by the nurse? a. Notify the physician. b. Place the client on the left side in the Trendelenburg position.
c. History of present illness d. Physical examination 33.In preventing the development of an external rotation deformity of the hip in a client who must remain in bed for any period of time, the most appropriate nursing action would be to use: a. Trochanter roll extending from the crest of the ileum to the midthigh. b. Pillows under the lower legs. c. Footboard d. Hip-abductor pillow 34.Which stage of pressure ulcer development does the ulcer extend into the subcutaneous tissue? a. Stage I b. Stage II c. Stage III d. Stage IV 35.When the method of wound healing is one in which wound edges are not surgically approximated and integumentary continuity is restored by granulations, the wound healing is termed a. Second intention healing b. Primary intention healing c. Third intention healing d. First intention healing 36.An 80-year-old male client is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of pneumonia. Nurse Oliver learns that the client lives alone and hasnt been eating or drinking. When assessing him for dehydration, nurse Oliver would expect to find: a. Hypothermia b. Hypertension c. Distended neck veins d. Tachycardia 37.The physician prescribes meperidine (Demerol), 75 mg I.M. every 4 hours as needed, to control a clients postoperative pain. The package insert is Meperidine, 100 mg/ml. How many milliliters of meperidine should the client receive? a. 0.75 b. 0.6 c. 0.5 d. 0.25 38. A male client with diabetes mellitus is receiving insulin. Which statement correctly describes an insulin unit? a. Its a common measurement in the metric system. b. Its the basis for solids in the avoirdupois system. c. Its the smallest measurement in the apothecary system. d. Its a measure of effect, not a standard measure of weight or quantity. 39.Nurse Oliver measures a clients temperature at 102 F. What is the equivalent Centigrade temperature? a. 40.1 C b. 38.9 C c. 48 C d. 38 C 40.The nurse is assessing a 48-year-old client who has come to the physicians office for his annual physical exam. One of the first physical signs of aging is: a. Accepting limitations while developing assets. b. Increasing loss of muscle tone. c. Failing eyesight, especially close vision. d. Having more frequent aches and pains.
41.The physician inserts a chest tube into a female client to treat a pneumothorax. The tube is connected to water-seal drainage. The nurse incharge can prevent chest tube air leaks by: a. Checking and taping all connections. b. Checking patency of the chest tube. c. Keeping the head of the bed slightly elevated. d. Keeping the chest drainage system below the level of the chest. 42.Nurse Trish must verify the clients identity before administering medication. She is aware that the safest way to verify identity is to: a. Check the clients identification band. b. Ask the client to state his name. c. State the clients name out loud and wait a client to repeat it. d. Check the room number and the clients name on the bed. 43.The physician orders dextrose 5 % in water, 1,000 ml to be infused over 8 hours. The I.V. tubing delivers 15 drops/ml. Nurse John should run the I.V. infusion at a rate of: a. 30 drops/minute b. 32 drops/minute c. 20 drops/minute d. 18 drops/minute 44.If a central venous catheter becomes disconnected accidentally, what should the nurse incharge do immediately? a. Clamp the catheter b. Call another nurse c. Call the physician d. Apply a dry sterile dressing to the site. 45.A female client was recently admitted. She has fever, weight loss, and watery diarrhea is being admitted to the facility. While assessing the client, Nurse Hazel inspects the clients abdomen and notice that it is slightly concave. Additional assessment should proceed in which order: a. Palpation, auscultation, and percussion. b. Percussion, palpation, and auscultation. c. Palpation, percussion, and auscultation. d. Auscultation, percussion, and palpation. 46. Nurse Betty is assessing tactile fremitus in a client with pneumonia. For this examination, nurse Betty should use the: a. Fingertips b. Finger pads c. Dorsal surface of the hand d. Ulnar surface of the hand 47. Which type of evaluation occurs continuously throughout the teaching and learning process? a. Summative b. Informative c. Formative d. Retrospective 48.A 45 year old client, has no family history of breast cancer or other risk factors for this disease. Nurse John should instruct her to have mammogram how often? a. Twice per year b. Once per year c. Every 2 years d. Once, to establish baseline 49.A male client has the following arterial blood gas values: pH 7.30; Pao2 89 mmHg; Paco2 50 mmHg; and HCO3 26mEq/L. Based on these values, Nurse Patricia should expect which condition?
a. Respiratory acidosis b. Respiratory alkalosis c. Metabolic acidosis d. Metabolic alkalosis 50.Nurse Len refers a female client with terminal cancer to a local hospice. What is the goal of this referral? a. To help the client find appropriate treatment options. b. To provide support for the client and family in coping with terminal illness. c. To ensure that the client gets counseling regarding health care costs. d. To teach the client and family about cancer and its treatment. 51.When caring for a male client with a 3-cm stage I pressure ulcer on the coccyx, which of the following actions can the nurse institute independently? a. Massaging the area with an astringent every 2 hours. b. Applying an antibiotic cream to the area three times per day. c. Using normal saline solution to clean the ulcer and applying a protective dressing as necessary. d. Using a povidone-iodine wash on the ulceration three times per day. 52.Nurse Oliver must apply an elastic bandage to a clients ankle and calf. He should apply the bandage beginning at the clients: a. Knee b. Ankle c. Lower thigh d. Foot 53.A 10 year old child with type 1 diabetes develops diabetic ketoacidosis and receives a continuous insulin infusion. Which condition represents the greatest risk to this child? a. Hypernatremia b. Hypokalemia c. Hyperphosphatemia d. Hypercalcemia 54.Nurse Len is administering sublingual nitrglycerin (Nitrostat) to the newly admitted client. Immediately afterward, the client may experience: a. Throbbing headache or dizziness b. Nervousness or paresthesia. c. Drowsiness or blurred vision. d. Tinnitus or diplopia. 55.Nurse Michelle hears the alarm sound on the telemetry monitor. The nurse quickly looks at the monitor and notes that a client is in a ventricular tachycardia. The nurse rushes to the clients room. Upon reaching the clients bedside, the nurse would take which action first? a. Prepare for cardioversion b. Prepare to defibrillate the client c. Call a code d. Check the clients level of consciousness 56.Nurse Hazel is preparing to ambulate a female client. The best and the safest position for the nurse in assisting the client is to stand: a. On the unaffected side of the client. b. On the affected side of the client. c. In front of the client. d. Behind the client. 57.Nurse Janah is monitoring the ongoing care given to the potential organ donor who has been diagnosed with brain death. The nurse determines
that the standard of care had been maintained if which of the following data is observed? a. Urine output: 45 ml/hr b. Capillary refill: 5 seconds c. Serum pH: 7.32 d. Blood pressure: 90/48 mmHg 58. Nurse Amy has an order to obtain a urinalysis from a male client with an indwelling urinary catheter. The nurse avoids which of the following, which contaminate the specimen? a. Wiping the port with an alcohol swab before inserting the syringe. b. Aspirating a sample from the port on the drainage bag. c. Clamping the tubing of the drainage bag. d. Obtaining the specimen from the urinary drainage bag. 59.Nurse Meredith is in the process of giving a client a bed bath. In the middle of the procedure, the unit secretary calls the nurse on the intercom to tell the nurse that there is an emergency phone call. The appropriate nursing action is to: a. Immediately walk out of the clients room and answer the phone call. b. Cover the client, place the call light within reach, and answer the phone call. c. Finish the bed bath before answering the phone call. d. Leave the clients door open so the client can be monitored and the nurse can answer the phone call. 60. Nurse Janah is collecting a sputum specimen for culture and sensitivity testing from a client who has a productive cough. Nurse Janah plans to implement which intervention to obtain the specimen? a. Ask the client to expectorate a small amount of sputum into the emesis basin. b. Ask the client to obtain the specimen after breakfast. c. Use a sterile plastic container for obtaining the specimen. d. Provide tissues for expectoration and obtaining the specimen. 61. Nurse Ron is observing a male client using a walker. The nurse determines that the client is using the walker correctly if the client: a. Puts all the four points of the walker flat on the floor, puts weight on the hand pieces, and then walks into it. b. Puts weight on the hand pieces, moves the walker forward, and then walks into it. c. Puts weight on the hand pieces, slides the walker forward, and then walks into it. d. Walks into the walker, puts weight on the hand pieces, and then puts all four points of the walker flat on the floor. 62.Nurse Amy has documented an entry regarding client care in the clients medical record. When checking the entry, the nurse realizes that incorrect information was documented. How does the nurse correct this error? a. Erases the error and writes in the correct information. b. Uses correction fluid to cover up the incorrect information and writes in the correct information. c. Draws one line to cross out the incorrect information and then initials the change. d. Covers up the incorrect information completely using a black pen and writes in the correct information 63.Nurse Ron is assisting with transferring a client from the operating room table to a stretcher. To provide safety to the client, the nurse should:
a. Moves the client rapidly from the table to the stretcher. b. Uncovers the client completely before transferring to the stretcher. c. Secures the client safety belts after transferring to the stretcher. d. Instructs the client to move self from the table to the stretcher. 64.Nurse Myrna is providing instructions to a nursing assistant assigned to give a bed bath to a client who is on contact precautions. Nurse Myrna instructs the nursing assistant to use which of the following protective items when giving bed bath? a. Gown and goggles b. Gown and gloves c. Gloves and shoe protectors d. Gloves and goggles 65. Nurse Oliver is caring for a client with impaired mobility that occurred as a result of a stroke. The client has right sided arm and leg weakness. The nurse would suggest that the client use which of the following assistive devices that would provide the best stability for ambulating? a. Crutches b. Single straight-legged cane c. Quad cane d. Walker 66.A male client with a right pleural effusion noted on a chest X-ray is being prepared for thoracentesis. The client experiences severe dizziness when sitting upright. To provide a safe environment, the nurse assists the client to which position for the procedure? a. Prone with head turned toward the side supported by a pillow. b. Sims position with the head of the bed flat. c. Right side-lying with the head of the bed elevated 45 degrees. d. Left side-lying with the head of the bed elevated 45 degrees. 67.Nurse John develops methods for data gathering. Which of the following criteria of a good instrument refers to the ability of the instrument to yield the same results upon its repeated administration? a. Validity b. Specificity c. Sensitivity d. Reliability 68.Harry knows that he has to protect the rights of human research subjects. Which of the following actions of Harry ensures anonymity? a. Keep the identities of the subject secret b. Obtain informed consent c. Provide equal treatment to all the subjects of the study. d. Release findings only to the participants of the study 69.Patients refusal to divulge information is a limitation because it is beyond the control of Tifanny. What type of research is appropriate for this study? a. Descriptive- correlational b. Experiment c. Quasi-experiment d. Historical 70.Nurse Ronald is aware that the best tool for data gathering is? a. Interview schedule b. Questionnaire c. Use of laboratory data d. Observation
71.Monica is aware that there are times when only manipulation of study variables is possible and the elements of control or randomization are not attendant. Which type of research is referred to this? a. Field study b. Quasi-experiment c. Solomon-Four group design d. Post-test only design 72.Cherry notes down ideas that were derived from the description of an investigation written by the person who conducted it. Which type of reference source refers to this? a. Footnote b. Bibliography c. Primary source d. Endnotes 73.When Nurse Trish is providing care to his patient, she must remember that her duty is bound not to do doing any action that will cause the patient harm. This is the meaning of the bioethical principle: a. Non-maleficence b. Beneficence c. Justice d. Solidarity 74.When a nurse in-charge causes an injury to a female patient and the injury caused becomes the proof of the negligent act, the presence of the injury is said to exemplify the principle of: a. Force majeure b. Respondeat superior c. Res ipsa loquitor d. Holdover doctrine 75.Nurse Myrna is aware that the Board of Nursing has quasi-judicial power. An example of this power is: a. The Board can issue rules and regulations that will govern the practice of nursing b. The Board can investigate violations of the nursing law and code of ethics c. The Board can visit a school applying for a permit in collaboration with CHED d. The Board prepares the board examinations 76. When the license of nurse Krina is revoked, it means that she: a. Is no longer allowed to practice the profession for the rest of her life b. Will never have her/his license re-issued since it has been revoked c. May apply for re-issuance of his/her license based on certain conditions stipulated in RA 9173 d. Will remain unable to practice professional nursing 77.Ronald plans to conduct a research on the use of a new method of pain assessment scale. Which of the following is the second step in the conceptualizing phase of the research process? a. Formulating the research hypothesis b. Review related literature c. Formulating and delimiting the research problem d. Design the theoretical and conceptual framework 78. The leader of the study knows that certain patients who are in a specialized research setting tend to respond psychologically to the conditions of the study. This referred to as : a. Cause and effect b. Hawthorne effect c. Halo effect d. Horns effect
79.Mary finally decides to use judgment sampling on her research. Which of the following actions of is correct? a. Plans to include whoever is there during his study. b. Determines the different nationality of patients frequently admitted and decides to get representations samples from each. c. Assigns numbers for each of the patients, place these in a fishbowl and draw 10 from it. d. Decides to get 20 samples from the admitted patients 80. The nursing theorist who developed transcultural nursing theory is: a. Florence Nightingale b. Madeleine Leininger c. Albert Moore d. Sr. Callista Roy 81.Marion is aware that the sampling method that gives equal chance to all units in the population to get picked is: a. Random b. Accidental c. Quota d. Judgment 82.John plans to use a Likert Scale to his study to determine the: a. Degree of agreement and disagreement b. Compliance to expected standards c. Level of satisfaction d. Degree of acceptance 83.Which of the following theory addresses the four modes of adaptation? a. Madeleine Leininger b. Sr. Callista Roy c. Florence Nightingale d. Jean Watson 84.Ms. Garcia is responsible to the number of personnel reporting to her. This principle refers to: a. Span of control b. Unity of command c. Downward communication d. Leader 85.Ensuring that there is an informed consent on the part of the patient before a surgery is done, illustrates the bioethical principle of: a. Beneficence b. Autonomy c. Veracity d. Non-maleficence 86.Nurse Reese is teaching a female client with peripheral vascular disease about foot care; Nurse Reese should include which instruction? a. Avoid wearing cotton socks. b. Avoid using a nail clipper to cut toenails. c. Avoid wearing canvas shoes. d. Avoid using cornstarch on feet. 87.A client is admitted with multiple pressure ulcers. When developing the clients diet plan, the nurse should include: a. Fresh orange slices b. Steamed broccoli c. Ice cream d. Ground beef patties 88.The nurse prepares to administer a cleansing enema. What is the most common client position used for this procedure?
a. Lithotomy b. Supine c. Prone d. Sims left lateral 89.Nurse Marian is preparing to administer a blood transfusion. Which action should the nurse take first? a. Arrange for typing and cross matching of the clients blood. b. Compare the clients identification wristband with the tag on the unit of blood. c. Start an I.V. infusion of normal saline solution. d. Measure the clients vital signs. 90.A 65 years old male client requests his medication at 9 p.m. instead of 10 p.m. so that he can go to sleep earlier. Which type of nursing intervention is required? a. Independent b. Dependent c. Interdependent d. Intradependent 91.A female client is to be discharged from an acute care facility after treatment for right leg thrombophlebitis. The Nurse Betty notes that the clients leg is pain-free, without redness or edema. The nurses actions reflect which step of the nursing process? a. Assessment b. Diagnosis c. Implementation d. Evaluation 92.Nursing care for a female client includes removing elastic stockings once per day. The Nurse Betty is aware that the rationale for this intervention? a. To increase blood flow to the heart b. To observe the lower extremities c. To allow the leg muscles to stretch and relax d. To permit veins in the legs to fill with blood. 93.Which nursing intervention takes highest priority when caring for a newly admitted client whos receiving a blood transfusion? a. Instructing the client to report any itching, swelling, or dyspnea. b. Informing the client that the transfusion usually take 1 to 2 hours. c. Documenting blood administration in the client care record. d. Assessing the clients vital signs when the transfusion ends. 94.A male client complains of abdominal discomfort and nausea while receiving tube feedings. Which intervention is most appropriate for this problem? a. Give the feedings at room temperature. b. Decrease the rate of feedings and the concentration of the formula. c. Place the client in semi-Fowlers position while feeding. d. Change the feeding container every 12 hours. 95.Nurse Patricia is reconstituting a powdered medication in a vial. After adding the solution to the powder, she nurse should: a. Do nothing. b. Invert the vial and let it stand for 3 to 5 minutes. c. Shake the vial vigorously. d. Roll the vial gently between the palms. 96.Which intervention should the nurse Trish use when administering oxygen by face mask to a female client?
a. Secure the elastic band tightly around the clients head. b. Assist the client to the semi-Fowler position if possible. c. Apply the face mask from the clients chin up over the nose. d. Loosen the connectors between the oxygen equipment and humidifier. 97.The maximum transfusion time for a unit of packed red blood cells (RBCs) is: a. 6 hours b. 4 hours c. 3 hours d. 2 hours 98.Nurse Monique is monitoring the effectiveness of a clients drug therapy. When should the nurse Monique obtain a blood sample to measure the trough drug level? a. 1 hour before administering the next dose. b. Immediately before administering the next dose. c. Immediately after administering the next dose. d. 30 minutes after administering the next dose. 99.Nurse May is aware that the main advantage of using a floor stock system is: a. The nurse can implement medication orders quickly. b. The nurse receives input from the pharmacist. c. The system minimizes transcription errors. d. The system reinforces accurate calculations. 100. Nurse Oliver is assessing a clients abdomen. Which finding should the nurse report as abnormal? a. Dullness over the liver. b. Bowel sounds occurring every 10 seconds. c. Shifting dullness over the abdomen. d. Vascular sounds heard over the renal arteries. NP 2 1. May arrives at the health care clinic and tells the nurse that her last menstrual period was 9 weeks ago. She also tells the nurse that a home pregnancy test was positive but she began to have mild cramps and is now having moderate vaginal bleeding. During the physical examination of the client, the nurse notes that May has a dilated cervix. The nurse determines that May is experiencing which type of abortion? a. Inevitable b. Incomplete c. Threatened d. Septic 2. Nurse Reese is reviewing the record of a pregnant client for her first prenatal visit. Which of the following data, if noted on the clients record, would alert the nurse that the client is at risk for a spontaneous abortion? a. Age 36 years b. History of syphilis c. History of genital herpes d. History of diabetes mellitus 3. Nurse Hazel is preparing to care for a client who is newly admitted to the hospital with a possible diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy. Nurse Hazel develops a plan of care for the client and determines that which of the following nursing actions is the priority? a. Monitoring weight b. Assessing for edema c. Monitoring apical pulse d. Monitoring temperature
4. Nurse Oliver is teaching a diabetic pregnant client about nutrition and insulin needs during pregnancy. The nurse determines that the client understands dietary and insulin needs if the client states that the second half of pregnancy require: a. Decreased caloric intake b. Increased caloric intake c. Decreased Insulin d. Increase Insulin 5. Nurse Michelle is assessing a 24 year old client with a diagnosis of hydatidiform mole. She is aware that one of the following is unassociated with this condition? a. Excessive fetal activity. b. Larger than normal uterus for gestational age. c. Vaginal bleeding d. Elevated levels of human chorionic gonadotropin. 6. A pregnant client is receiving magnesium sulfate for severe pregnancy induced hypertension (PIH). The clinical findings that would warrant use of the antidote , calcium gluconate is: a. Urinary output 90 cc in 2 hours. b. Absent patellar reflexes. c. Rapid respiratory rate above 40/min. d. Rapid rise in blood pressure. 7. During vaginal examination of Janah who is in labor, the presenting part is at station plus two. Nurse, correctly interprets it as: a. Presenting part is 2 cm above the plane of the ischial spines. b. Biparietal diameter is at the level of the ischial spines. c. Presenting part in 2 cm below the plane of the ischial spines. d. Biparietal diameter is 2 cm above the ischial spines. 8. A pregnant client is receiving oxytocin (Pitocin) for induction of labor. A condition that warrant the nurse in-charge to discontinue I.V. infusion of Pitocin is: a. Contractions every 1 minutes lasting 70-80 seconds. b. Maternal temperature 101.2 c. Early decelerations in the fetal heart rate. d. Fetal heart rate baseline 140-160 bpm. 9. Calcium gluconate is being administered to a client with pregnancy induced hypertension (PIH). A nursing action that must be initiated as the plan of care throughout injection of the drug is: a. Ventilator assistance b. CVP readings c. EKG tracings d. Continuous CPR 10. A trial for vaginal delivery after an earlier caesareans, would likely to be given to a gravida, who had: a. First low transverse cesarean was for active herpes type 2 infections; vaginal culture at 39 weeks pregnancy was positive. b. First and second caesareans were for cephalopelvic disproportion. c. First caesarean through a classic incision as a result of severe fetal distress. d. First low transverse caesarean was for breech position. Fetus in this pregnancy is in a vertex presentation. 11.Nurse Ryan is aware that the best initial approach when trying to take a crying toddlers temperature is:
a. Talk to the mother first and then to the toddler. b. Bring extra help so it can be done quickly. c. Encourage the mother to hold the child. d. Ignore the crying and screaming. 12.Baby Tina a 3 month old infant just had a cleft lip and palate repair. What should the nurse do to prevent trauma to operative site? a. Avoid touching the suture line, even when cleaning. b. Place the baby in prone position. c. Give the baby a pacifier. d. Place the infants arms in soft elbow restraints. 13. Which action should nurse Marian include in the care plan for a 2 month old with heart failure? a. Feed the infant when he cries. b. Allow the infant to rest before feeding. c. Bathe the infant and administer medications before feeding. d. Weigh and bathe the infant before feeding. 14.Nurse Hazel is teaching a mother who plans to discontinue breast feeding after 5 months. The nurse should advise her to include which foods in her infants diet? a. Skim milk and baby food. b. Whole milk and baby food. c. Iron-rich formula only. d. Iron-rich formula and baby food. 15.Mommy Linda is playing with her infant, who is sitting securely alone on the floor of the clinic. The mother hides a toy behind her back and the infant looks for it. The nurse is aware that estimated age of the infant would be: a. 6 months b. 4 months c. 8 months d. 10 months 16.Which of the following is the most prominent feature of public health nursing? a. It involves providing home care to sick people who are not confined in the hospital. b. Services are provided free of charge to people within the catchments area. c. The public health nurse functions as part of a team providing a public health nursing services. d. Public health nursing focuses on preventive, not curative, services. 17.When the nurse determines whether resources were maximized in implementing Ligtas Tigdas, she is evaluating a. Effectiveness b. Efficiency c. Adequacy d. Appropriateness 18.Vangie is a new B.S.N. graduate. She wants to become a Public Health Nurse. Where should she apply? a. Department of Health b. Provincial Health Office c. Regional Health Office d. Rural Health Unit 19.Tony is aware the Chairman of the Municipal Health Board is: a. Mayor b. Municipal Health Officer c. Public Health Nurse d. Any qualified physician
20.Myra is the public health nurse in a municipality with a total population of about 20,000. There are 3 rural health midwives among the RHU personnel. How many more midwife items will the RHU need? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. The RHU does not need any more midwife item. 21.According to Freeman and Heinrich, community health nursing is a developmental service. Which of the following best illustrates this statement? a. The community health nurse continuously develops himself personally and professionally. b. Health education and community organizing are necessary in providing community health services. c. Community health nursing is intended primarily for health promotion and prevention and treatment of disease. d. The goal of community health nursing is to provide nursing services to people in their own places of residence. 22.Nurse Tina is aware that the disease declared through Presidential Proclamation No. 4 as a target for eradication in the Philippines is? a. Poliomyelitis b. Measles c. Rabies d. Neonatal tetanus 23.May knows that the step in community organizing that involves training of potential leaders in the community is: a. Integration b. Community organization c. Community study d. Core group formation 24.Beth a public health nurse takes an active role in community participation. What is the primary goal of community organizing? a. To educate the people regarding community health problems b. To mobilize the people to resolve community health problems c. To maximize the communitys resources in dealing with health problems. d. To maximize the communitys resources in dealing with health problems. 25.Tertiary prevention is needed in which stage of the natural history of disease? a. Pre-pathogenesis b. Pathogenesis c. Prodromal d. Terminal 26.The nurse is caring for a primigravid client in the labor and delivery area. Which condition would place the client at risk for disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)? a. Intrauterine fetal death. b. Placenta accreta. c. Dysfunctional labor. d. Premature rupture of the membranes. 27.A fullterm client is in labor. Nurse Betty is aware that the fetal heart rate would be: a. 80 to 100 beats/minute b. 100 to 120 beats/minute c. 120 to 160 beats/minute d. 160 to 180 beats/minute 28.The skin in the diaper area of a 7 month old infant is excoriated and red. Nurse Hazel should instruct the mother to:
a. Change the diaper more often. b. Apply talc powder with diaper changes. c. Wash the area vigorously with each diaper change. d. Decrease the infants fluid intake to decrease saturating diapers. 29.Nurse Carla knows that the common cardiac anomalies in children with Down Syndrome (trisomy 21) is: a. Atrial septal defect b. Pulmonic stenosis c. Ventricular septal defect d. Endocardial cushion defect 30.Malou was diagnosed with severe preeclampsia is now receiving I.V. magnesium sulfate. The adverse effects associated with magnesium sulfate is: a. Anemia b. Decreased urine output c. Hyperreflexia d. Increased respiratory rate 31.A 23 year old client is having her menstrual period every 2 weeks that last for 1 week. This type of menstrual pattern is bets defined by: a. Menorrhagia b. Metrorrhagia c. Dyspareunia d. Amenorrhea 32.Jannah is admitted to the labor and delivery unit. The critical laboratory result for this client would be: a. Oxygen saturation b. Iron binding capacity c. Blood typing d. Serum Calcium 33.Nurse Gina is aware that the most common condition found during the second-trimester of pregnancy is: a. Metabolic alkalosis b. Respiratory acidosis c. Mastitis d. Physiologic anemia 34.Nurse Lynette is working in the triage area of an emergency department. She sees that several pediatric clients arrive simultaneously. The client who needs to be treated first is: a. A crying 5 year old child with a laceration on his scalp. b. A 4 year old child with a barking coughs and flushed appearance. c. A 3 year old child with Down syndrome who is pale and asleep in his mothers arms. d. A 2 year old infant with stridorous breath sounds, sitting up in his mothers arms and drooling. 35.Maureen in her third trimester arrives at the emergency room with painless vaginal bleeding. Which of the following conditions is suspected? a. Placenta previa b. Abruptio placentae c. Premature labor d. Sexually transmitted disease 36.A young child named Richard is suspected of having pinworms. The community nurse collects a stool specimen to confirm the diagnosis. The nurse should schedule the collection of this specimen for: a. Just before bedtime b. After the child has been bathe
c. Any time during the day d. Early in the morning 37.In doing a childs admission assessment, Nurse Betty should be alert to note which signs or symptoms of chronic lead poisoning? a. Irritability and seizures b. Dehydration and diarrhea c. Bradycardia and hypotension d. Petechiae and hematuria 38.To evaluate a womans understanding about the use of diaphragm for family planning, Nurse Trish asks her to explain how she will use the appliance. Which response indicates a need for further health teaching? a. I should check the diaphragm carefully for holes every time I use it b. I may need a different size of diaphragm if I gain or lose weight more than 20 pounds c. The diaphragm must be left in place for atleast 6 hours after intercourse d. I really need to use the diaphragm and jelly most during the middle of my menstrual cycle. 39.Hypoxia is a common complication of laryngotracheobronchitis. Nurse Oliver should frequently assess a child with laryngotracheobronchitis for: a. Drooling b. Muffled voice c. Restlessness d. Low-grade fever 40.How should Nurse Michelle guide a child who is blind to walk to the playroom? a. Without touching the child, talk continuously as the child walks down the hall. b. Walk one step ahead, with the childs hand on the nurses elbow. c. Walk slightly behind, gently guiding the child forward. d. Walk next to the child, holding the childs hand. 41.When assessing a newborn diagnosed with ductus arteriosus, Nurse Olivia should expect that the child most likely would have an: a. Loud, machinery-like murmur. b. Bluish color to the lips. c. Decreased BP reading in the upper extremities d. Increased BP reading in the upper extremities. 42.The reason nurse May keeps the neonate in a neutral thermal environment is that when a newborn becomes too cool, the neonate requires: a. Less oxygen, and the newborns metabolic rate increases. b. More oxygen, and the newborns metabolic rate decreases. c. More oxygen, and the newborns metabolic rate increases. d. Less oxygen, and the newborns metabolic rate decreases. 43.Before adding potassium to an infants I.V. line, Nurse Ron must be sure to assess whether this infant has: a. Stable blood pressure b. Patant fontanelles c. Moros reflex d. Voided 44.Nurse Carla should know that the most common causative factor of dermatitis in infants and younger children is: a. Baby oil b. Baby lotion
c. Laundry detergent d. Powder with cornstarch 45.During tube feeding, how far above an infants stomach should the nurse hold the syringe with formula? a. 6 inches b. 12 inches c. 18 inches d. 24 inches 46. In a mothers class, Nurse Lhynnete discussed childhood diseases such as chicken pox. Which of the following statements about chicken pox is correct? a. The older one gets, the more susceptible he becomes to the complications of chicken pox. b. A single attack of chicken pox will prevent future episodes, including conditions such as shingles. c. To prevent an outbreak in the community, quarantine may be imposed by health authorities. d. Chicken pox vaccine is best given when there is an impending outbreak in the community. 47.Barangay Pinoy had an outbreak of German measles. To prevent congenital rubella, what is the BEST advice that you can give to women in the first trimester of pregnancy in the barangay Pinoy? a. Advice them on the signs of German measles. b. Avoid crowded places, such as markets and movie houses. c. Consult at the health center where rubella vaccine may be given. d. Consult a physician who may give them rubella immunoglobulin. 48.Myrna a public health nurse knows that to determine possible sources of sexually transmitted infections, the BEST method that may be undertaken is: a. Contact tracing b. Community survey c. Mass screening tests d. Interview of suspects 49.A 33-year old female client came for consultation at the health center with the chief complaint of fever for a week. Accompanying symptoms were muscle pains and body malaise. A week after the start of fever, the client noted yellowish discoloration of his sclera. History showed that he waded in flood waters about 2 weeks before the onset of symptoms. Based on her history, which disease condition will you suspect? a. Hepatitis A b. Hepatitis B c. Tetanus d. Leptospirosis 50.Mickey a 3-year old client was brought to the health center with the chief complaint of severe diarrhea and the passage of rice water stools. The client is most probably suffering from which condition? a. Giardiasis b. Cholera c. Amebiasis d. Dysentery 51.The most prevalent form of meningitis among children aged 2 months to 3 years is caused by which microorganism? a. Hemophilus influenzae b. Morbillivirus c. Steptococcus pneumoniae d. Neisseria meningitidis
52.The student nurse is aware that the pathognomonic sign of measles is Kopliks spot and you may see Kopliks spot by inspecting the: a. Nasal mucosa b. Buccal mucosa c. Skin on the abdomen d. Skin on neck 53.Angel was diagnosed as having Dengue fever. You will say that there is slow capillary refill when the color of the nailbed that you pressed does not return within how many seconds? a. 3 seconds b. 6 seconds c. 9 seconds d. 10 seconds 54.In Integrated Management of Childhood Illness, the nurse is aware that the severe conditions generally require urgent referral to a hospital. Which of the following severe conditions DOES NOT always require urgent referral to a hospital? a. Mastoiditis b. Severe dehydration c. Severe pneumonia d. Severe febrile disease 55.Myrna a public health nurse will conduct outreach immunization in a barangay Masay with a population of about 1500. The estimated number of infants in the barangay would be: a. 45 infants b. 50 infants c. 55 infants d. 65 infants 56.The community nurse is aware that the biological used in Expanded Program on Immunization (EPI) should NOT be stored in the freezer? a. DPT b. Oral polio vaccine c. Measles vaccine d. MMR 57.It is the most effective way of controlling schistosomiasis in an endemic area? a. Use of molluscicides b. Building of foot bridges c. Proper use of sanitary toilets d. Use of protective footwear, such as rubber boots 58.Several clients is newly admitted and diagnosed with leprosy. Which of the following clients should be classified as a case of multibacillary leprosy? a. 3 skin lesions, negative slit skin smear b. 3 skin lesions, positive slit skin smear c. 5 skin lesions, negative slit skin smear d. 5 skin lesions, positive slit skin smear 59.Nurses are aware that diagnosis of leprosy is highly dependent on recognition of symptoms. Which of the following is an early sign of leprosy? a. Macular lesions b. Inability to close eyelids c. Thickened painful nerves d. Sinking of the nosebridge 60.Marie brought her 10 month old infant for consultation because of fever, started 4 days prior to consultation. In determining malaria risk, what will you do? a. Perform a tourniquet test. b. Ask where the family resides. c. Get a specimen for blood smear. d. Ask if the fever is present everyday.
61.Susie brought her 4 years old daughter to the RHU because of cough and colds. Following the IMCI assessment guide, which of the following is a danger sign that indicates the need for urgent referral to a hospital? a. Inability to drink b. High grade fever c. Signs of severe dehydration d. Cough for more than 30 days 62.Jimmy a 2-year old child revealed baggy pants. As a nurse, using the IMCI guidelines, how will you manage Jimmy? a. Refer the child urgently to a hospital for confinement. b. Coordinate with the social worker to enroll the child in a feeding program. c. Make a teaching plan for the mother, focusing on menu planning for her child. d. Assess and treat the child for health problems like infections and intestinal parasitism. 63.Gina is using Oresol in the management of diarrhea of her 3-year old child. She asked you what to do if her child vomits. As a nurse you will tell her to: a. Bring the child to the nearest hospital for further assessment. b. Bring the child to the health center for intravenous fluid therapy. c. Bring the child to the health center for assessment by the physician. d. Let the child rest for 10 minutes then continue giving Oresol more slowly. 64.Nikki a 5-month old infant was brought by his mother to the health center because of diarrhea for 4 to 5 times a day. Her skin goes back slowly after a skin pinch and her eyes are sunken. Using the IMCI guidelines, you will classify this infant in which category? a. No signs of dehydration b. Some dehydration c. Severe dehydration d. The data is insufficient. 65.Chris a 4-month old infant was brought by her mother to the health center because of cough. His respiratory rate is 42/minute. Using the Integrated Management of Child Illness (IMCI) guidelines of assessment, his breathing is considered as: a. Fast b. Slow c. Normal d. Insignificant 66.Maylene had just received her 4th dose of tetanus toxoid. She is aware that her baby will have protection against tetanus for a. 1 year b. 3 years c. 5 years d. Lifetime 67.Nurse Ron is aware that unused BCG should be discarded after how many hours of reconstitution? a. 2 hours b. 4 hours c. 8 hours d. At the end of the day 68.The nurse explains to a breastfeeding mother that breast milk is sufficient for all of the babys nutrient needs only up to: a. 5 months b. 6 months
c. 1 year d. 2 years 69.Nurse Ron is aware that the gestational age of a conceptus that is considered viable (able to live outside the womb) is: a. 8 weeks b. 12 weeks c. 24 weeks d. 32 weeks 70.When teaching parents of a neonate the proper position for the neonates sleep, the nurse Patricia stresses the importance of placing the neonate on his back to reduce the risk of which of the following? a. Aspiration b. Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) c. Suffocation d. Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) 71.Which finding might be seen in baby James a neonate suspected of having an infection? a. Flushed cheeks b. Increased temperature c. Decreased temperature d. Increased activity level 72.Baby Jenny who is small-for-gestation is at increased risk during the transitional period for which complication? a. Anemia probably due to chronic fetal hyposia b. Hyperthermia due to decreased glycogen stores c. Hyperglycemia due to decreased glycogen stores d. Polycythemia probably due to chronic fetal hypoxia 73.Marjorie has just given birth at 42 weeks gestation. When the nurse assessing the neonate, which physical finding is expected? a. A sleepy, lethargic baby b. Lanugo covering the body c. Desquamation of the epidermis d. Vernix caseosa covering the body 74.After reviewing the Myrnas maternal history of magnesium sulfate during labor, which condition would nurse Richard anticipate as a potential problem in the neonate? a. Hypoglycemia b. Jitteriness c. Respiratory depression d. Tachycardia 75.Which symptom would indicate the Baby Alexandra was adapting appropriately to extrauterine life without difficulty? a. Nasal flaring b. Light audible grunting c. Respiratory rate 40 to 60 breaths/minute d. Respiratory rate 60 to 80 breaths/minute 76. When teaching umbilical cord care for Jennifer a new mother, the nurse Jenny would include which information? a. Apply peroxide to the cord with each diaper change b. Cover the cord with petroleum jelly after bathing c. Keep the cord dry and open to air d. Wash the cord with soap and water each day during a tub bath. 77.Nurse John is performing an assessment on a neonate. Which of the following findings is considered common in the healthy neonate? a. Simian crease b. Conjunctival hemorrhage
c. Cystic hygroma d. Bulging fontanelle 78.Dr. Esteves decides to artificially rupture the membranes of a mother who is on labor. Following this procedure, the nurse Hazel checks the fetal heart tones for which the following reasons? a. To determine fetal well-being. b. To assess for prolapsed cord c. To assess fetal position d. To prepare for an imminent delivery. 79.Which of the following would be least likely to indicate anticipated bonding behaviors by new parents? a. The parents willingness to touch and hold the new born. b. The parents expression of interest about the size of the new born. c. The parents indication that they want to see the newborn. d. The parents interactions with each other. 80.Following a precipitous delivery, examination of the clients vagina reveals a fourth-degree laceration. Which of the following would be contraindicated when caring for this client? a. Applying cold to limit edema during the first 12 to 24 hours. b. Instructing the client to use two or more peripads to cushion the area. c. Instructing the client on the use of sitz baths if ordered. d. Instructing the client about the importance of perineal (kegel) exercises. 81. A pregnant woman accompanied by her husband, seeks admission to the labor and delivery area. She states that shes in labor and says she attended the facility clinic for prenatal care. Which question should the nurse Oliver ask her first? a. Do you have any chronic illnesses? b. Do you have any allergies? c. What is your expected due date? d. Who will be with you during labor? 82.A neonate begins to gag and turns a dusky color. What should the nurse do first? a. Calm the neonate. b. Notify the physician. c. Provide oxygen via face mask as ordered d. Aspirate the neonates nose and mouth with a bulb syringe. 83. When a client states that her water broke, which of the following actions would be inappropriate for the nurse to do? a. Observing the pooling of straw-colored fluid. b. Checking vaginal discharge with nitrazine paper. c. Conducting a bedside ultrasound for an amniotic fluid index. d. Observing for flakes of vernix in the vaginal discharge. 84. A baby girl is born 8 weeks premature. At birth, she has no spontaneous respirations but is successfully resuscitated. Within several hours she develops respiratory grunting, cyanosis, tachypnea, nasal flaring, and retractions. Shes diagnosed with respiratory distress syndrome, intubated, and placed on a ventilator. Which nursing action should be included in the babys plan of care to prevent retinopathy of prematurity? a. Cover his eyes while receiving oxygen. b. Keep her body temperature low. c. Monitor partial pressure of oxygen (Pao2) levels. d. Humidify the oxygen.
85. Which of the following is normal newborn calorie intake? a. 110 to 130 calories per kg. b. 30 to 40 calories per lb of body weight. c. At least 2 ml per feeding d. 90 to 100 calories per kg 86. Nurse John is knowledgeable that usually individual twins will grow appropriately and at the same rate as singletons until how many weeks? a. 16 to 18 weeks b. 18 to 22 weeks c. 30 to 32 weeks d. 38 to 40 weeks 87. Which of the following classifications applies to monozygotic twins for whom the cleavage of the fertilized ovum occurs more than 13 days after fertilization? a. conjoined twins b. diamniotic dichorionic twins c. diamniotic monochorionic twin d. monoamniotic monochorionic twins 88. Tyra experienced painless vaginal bleeding has just been diagnosed as having a placenta previa. Which of the following procedures is usually performed to diagnose placenta previa? a. Amniocentesis b. Digital or speculum examination c. External fetal monitoring d. Ultrasound 89. Nurse Arnold knows that the following changes in respiratory functioning during pregnancy is considered normal: a. Increased tidal volume b. Increased expiratory volume c. Decreased inspiratory capacity d. Decreased oxygen consumption 90. Emily has gestational diabetes and it is usually managed by which of the following therapy? a. Diet b. Long-acting insulin c. Oral hypoglycemic d. Oral hypoglycemic drug and insulin 91. Magnesium sulfate is given to Jemma with preeclampsia to prevent which of the following condition? a. Hemorrhage b. Hypertension c. Hypomagnesemia d. Seizure 92. Cammile with sickle cell anemia has an increased risk for having a sickle cell crisis during pregnancy. Aggressive management of a sickle cell crisis includes which of the following measures? a. Antihypertensive agents b. Diuretic agents c. I.V. fluids d. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) for pain 93. Which of the following drugs is the antidote for magnesium toxicity? a. Calcium gluconate (Kalcinate) b. Hydralazine (Apresoline) c. Naloxone (Narcan) d. Rho (D) immune globulin (RhoGAM) 94. Marlyn is screened for tuberculosis during her first prenatal visit. An intradermal injection of purified protein derivative (PPD) of the tuberculin
bacilli is given. She is considered to have a positive test for which of the following results? a. An indurated wheal under 10 mm in diameter appears in 6 to 12 hours. b. An indurated wheal over 10 mm in diameter appears in 48 to 72 hours. c. A flat circumcised area under 10 mm in diameter appears in 6 to 12 hours. d. A flat circumcised area over 10 mm in diameter appears in 48 to 72 hours. 95. Dianne, 24 year-old is 27 weeks pregnant arrives at her physicians office with complaints of fever, nausea, vomiting, malaise, unilateral flank pain, and costovertebral angle tenderness. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely? a. Asymptomatic bacteriuria b. Bacterial vaginosis c. Pyelonephritis d. Urinary tract infection (UTI) 96. Rh isoimmunization in a pregnant client develops during which of the following conditions? a. Rh-positive maternal blood crosses into fetal blood, stimulating fetal antibodies. b. Rh-positive fetal blood crosses into maternal blood, stimulating maternal antibodies. c. Rh-negative fetal blood crosses into maternal blood, stimulating maternal antibodies. d. Rh-negative maternal blood crosses into fetal blood, stimulating fetal antibodies. 97. To promote comfort during labor, the nurse John advises a client to assume certain positions and avoid others. Which position may cause maternal hypotension and fetal hypoxia? a. Lateral position b. Squatting position c. Supine position d. Standing position 98. Celeste who used heroin during her pregnancy delivers a neonate. When assessing the neonate, the nurse Lhynnette expects to find: a. Lethargy 2 days after birth. b. Irritability and poor sucking. c. A flattened nose, small eyes, and thin lips. d. Congenital defects such as limb anomalies. 99. The uterus returns to the pelvic cavity in which of the following time frames? a. 7th to 9th day postpartum. b. 2 weeks postpartum. c. End of 6th week postpartum. d. When the lochia changes to alba. 100. Maureen, a primigravida client, age 20, has just completed a difficult, forceps-assisted delivery of twins. Her labor was unusually long and required oxytocin (Pitocin) augmentation. The nurse whos caring for her should stay alert for: a. Uterine inversion b. Uterine atony c. Uterine involution d. Uterine discomfort NP 3 1. Nurse Michelle should know that the drainage is normal 4 days after a sigmoid colostomy when the stool is: a. Green liquid b. Solid formed
c. Loose, bloody d. Semiformed 2. Where would nurse Kristine place the call light for a male client with a right-sided brain attack and left homonymous hemianopsia? a. On the clients right side b. On the clients left side c. Directly in front of the client d. Where the client like 3. A male client is admitted to the emergency department following an accident. What are the first nursing actions of the nurse? a. Check respiration, circulation, neurological response. b. Align the spine, check pupils, and check for hemorrhage. c. Check respirations, stabilize spine, and check circulation. d. Assess level of consciousness and circulation. 4. In evaluating the effect of nitroglycerin, Nurse Arthur should know that it reduces preload and relieves angina by: a. Increasing contractility and slowing heart rate. b. Increasing AV conduction and heart rate. c. Decreasing contractility and oxygen consumption. d. Decreasing venous return through vasodilation. 5. Nurse Patricia finds a female client who is postmyocardial infarction (MI) slumped on the side rails of the bed and unresponsive to shaking or shouting. Which is the nurse next action? a. Call for help and note the time. b. Clear the airway c. Give two sharp thumps to the precordium, and check the pulse. d. Administer two quick blows. 6. Nurse Monett is caring for a client recovering from gastro-intestinal bleeding. The nurse should: a. Plan care so the client can receive 8 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night. b. Monitor vital signs every 2 hours. c. Make sure that the client takes food and medications at prescribed intervals. d. Provide milk every 2 to 3 hours. 7. A male client was on warfarin (Coumadin) before admission, and has been receiving heparin I.V. for 2 days. The partial thromboplastin time (PTT) is 68 seconds. What should Nurse Carla do? a. Stop the I.V. infusion of heparin and notify the physician. b. Continue treatment as ordered. c. Expect the warfarin to increase the PTT. d. Increase the dosage, because the level is lower than normal. 8. A client undergone ileostomy, when should the drainage appliance be applied to the stoma? a. 24 hours later, when edema has subsided. b. In the operating room. c. After the ileostomy begin to function. d. When the client is able to begin self-care procedures. 9. A client undergone spinal anesthetic, it will be important that the nurse immediately position the client in: a. On the side, to prevent obstruction of airway by tongue. b. Flat on back. c. On the back, with knees flexed 15 degrees. d. Flat on the stomach, with the head turned to the side.
10.While monitoring a male client several hours after a motor vehicle accident, which assessment data suggest increasing intracranial pressure? a. Blood pressure is decreased from 160/90 to 110/70. b. Pulse is increased from 87 to 95, with an occasional skipped beat. c. The client is oriented when aroused from sleep, and goes back to sleep immediately. d. The client refuses dinner because of anorexia. 11.Mrs. Cruz, 80 years old is diagnosed with pneumonia. Which of the following symptoms may appear first? a. Altered mental status and dehydration b. Fever and chills c. Hemoptysis and Dyspnea d. Pleuritic chest pain and cough 12. A male client has active tuberculosis (TB). Which of the following symptoms will be exhibit? a. Chest and lower back pain b. Chills, fever, night sweats, and hemoptysis c. Fever of more than 104F (40C) and nausea d. Headache and photophobia 13. Mark, a 7-year-old client is brought to the emergency department. Hes tachypneic and afebrile and has a respiratory rate of 36 breaths/minute and has a nonproductive cough. He recently had a cold. Form this history; the client may have which of the following conditions? a. Acute asthma b. Bronchial pneumonia c. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) d. Emphysema 14. Marichu was given morphine sulfate for pain. She is sleeping and her respiratory rate is 4 breaths/minute. If action isnt taken quickly, she might have which of the following reactions? a. Asthma attack b. Respiratory arrest c. Seizure d. Wake up on his own 15. A 77-year-old male client is admitted for elective knee surgery. Physical examination reveals shallow respirations but no sign of respiratory distress. Which of the following is a normal physiologic change related to aging? a. Increased elastic recoil of the lungs b. Increased number of functional capillaries in the alveoli c. Decreased residual volume d. Decreased vital capacity 16. Nurse John is caring for a male client receiving lidocaine I.V. Which factor is the most relevant to administration of this medication? a. Decrease in arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) when measured with a pulse oximeter. b. Increase in systemic blood pressure. c. Presence of premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) on a cardiac monitor. d. Increase in intracranial pressure (ICP). 17. Nurse Ron is caring for a male client taking an anticoagulant. The nurse should teach the client to: a. Report incidents of diarrhea. b. Avoid foods high in vitamin K c. Use a straight razor when shaving. d. Take aspirin to pain relief.
18. Nurse Lhynnette is preparing a site for the insertion of an I.V. catheter. The nurse should treat excess hair at the site by: a. Leaving the hair intact b. Shaving the area c. Clipping the hair in the area d. Removing the hair with a depilatory. 19. Nurse Michelle is caring for an elderly female with osteoporosis. When teaching the client, the nurse should include information about which major complication: a. Bone fracture b. Loss of estrogen c. Negative calcium balance d. Dowagers hump 20. Nurse Len is teaching a group of women to perform BSE. The nurse should explain that the purpose of performing the examination is to discover: a. Cancerous lumps b. Areas of thickness or fullness c. Changes from previous examinations. d. Fibrocystic masses 21. When caring for a female client who is being treated for hyperthyroidism, it is important to: a. Provide extra blankets and clothing to keep the client warm. b. Monitor the client for signs of restlessness, sweating, and excessive weight loss during thyroid replacement therapy. c. Balance the clients periods of activity and rest. d. Encourage the client to be active to prevent constipation. 22. Nurse Kris is teaching a client with history of atherosclerosis. To decrease the risk of atherosclerosis, the nurse should encourage the client to: a. Avoid focusing on his weight. b. Increase his activity level. c. Follow a regular diet. d. Continue leading a high-stress lifestyle. 23. Nurse Greta is working on a surgical floor. Nurse Greta must logroll a client following a: a. Laminectomy b. Thoracotomy c. Hemorrhoidectomy d. Cystectomy. 24. A 55-year old client underwent cataract removal with intraocular lens implant. Nurse Oliver is giving the client discharge instructions. These instructions should include which of the following? a. Avoid lifting objects weighing more than 5 lb (2.25 kg). b. Lie on your abdomen when in bed c. Keep rooms brightly lit. d. Avoiding straining during bowel movement or bending at the waist. 25. George should be taught about testicular examinations during: a. when sexual activity starts b. After age 69 c. After age 40 d. Before age 20. 26. A male client undergone a colon resection. While turning him, wound dehiscence with evisceration occurs. Nurse Trish first response is to: a. Call the physician b. Place a saline-soaked sterile dressing on the
wound. c. Take a blood pressure and pulse. d. Pull the dehiscence closed. 27. Nurse Audrey is caring for a client who has suffered a severe cerebrovascular accident. During routine assessment, the nurse notices CheyneStrokes respirations. Cheyne-strokes respirations are: a. A progressively deeper breaths followed by shallower breaths with apneic periods. b. Rapid, deep breathing with abrupt pauses between each breath. c. Rapid, deep breathing and irregular breathing without pauses. d. Shallow breathing with an increased respiratory rate. 28. Nurse Bea is assessing a male client with heart failure. The breath sounds commonly auscultated in clients with heart failure are: a. Tracheal b. Fine crackles c. Coarse crackles d. Friction rubs 29. The nurse is caring for Kenneth experiencing an acute asthma attack. The client stops wheezing and breath sounds arent audible. The reason for this change is that: a. The attack is over. b. The airways are so swollen that no air cannot get through. c. The swelling has decreased. d. Crackles have replaced wheezes. 30. Mike with epilepsy is having a seizure. During the active seizure phase, the nurse should: a. Place the client on his back remove dangerous objects, and insert a bite block. b. Place the client on his side, remove dangerous objects, and insert a bite block. c. Place the client o his back, remove dangerous objects, and hold down his arms. d. Place the client on his side, remove dangerous objects, and protect his head. 31. After insertion of a cheat tube for a pneumothorax, a client becomes hypotensive with neck vein distention, tracheal shift, absent breath sounds, and diaphoresis. Nurse Amanda suspects a tension pneumothorax has occurred. What cause of tension pneumothorax should the nurse check for? a. Infection of the lung. b. Kinked or obstructed chest tube c. Excessive water in the water-seal chamber d. Excessive chest tube drainage 32. Nurse Maureen is talking to a male client, the client begins choking on his lunch. Hes coughing forcefully. The nurse should: a. Stand him up and perform the abdominal thrust maneuver from behind. b. Lay him down, straddle him, and perform the abdominal thrust maneuver. c. Leave him to get assistance d. Stay with him but not intervene at this time. 33. Nurse Ron is taking a health history of an 84 year old client. Which information will be most useful to the nurse for planning care? a. General health for the last 10 years. b. Current health promotion activities. c. Family history of diseases. d. Marital status. 34. When performing oral care on a comatose client, Nurse Krina should:
a. Apply lemon glycerin to the clients lips at least every 2 hours. b. Brush the teeth with client lying supine. c. Place the client in a side lying position, with the head of the bed lowered. d. Clean the clients mouth with hydrogen peroxide. 35. A 77-year-old male client is admitted with a diagnosis of dehydration and change in mental status. Hes being hydrated with L.V. fluids. When the nurse takes his vital signs, she notes he has a fever of 103F (39.4C) a cough producing yellow sputum and pleuritic chest pain. The nurse suspects this client may have which of the following conditions? a. Adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) b. Myocardial infarction (MI) c. Pneumonia d. Tuberculosis 36. Nurse Oliver is working in a out patient clinic. He has been alerted that there is an outbreak of tuberculosis (TB). Which of the following clients entering the clinic today most likely to have TB? a. A 16-year-old female high school student b. A 33-year-old day-care worker c. A 43-yesr-old homeless man with a history of alcoholism d. A 54-year-old businessman 37. Virgie with a positive Mantoux test result will be sent for a chest X-ray. The nurse is aware that which of the following reasons this is done? a. To confirm the diagnosis b. To determine if a repeat skin test is needed c. To determine the extent of lesions d. To determine if this is a primary or secondary infection 38. Kennedy with acute asthma showing inspiratory and expiratory wheezes and a decreased forced expiratory volume should be treated with which of the following classes of medication right away? a. Beta-adrenergic blockers b. Bronchodilators c. Inhaled steroids d. Oral steroids 39. Mr. Vasquez 56-year-old client with a 40-year history of smoking one to two packs of cigarettes per day has a chronic cough producing thick sputum, peripheral edema and cyanotic nail beds. Based on this information, he most likely has which of the following conditions? a. Adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) b. Asthma c. Chronic obstructive bronchitis d. Emphysema Situation: Francis, age 46 is admitted to the hospital with diagnosis of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. 40. The treatment for patients with leukemia is bone marrow transplantation. Which statement about bone marrow transplantation is not correct? a. The patient is under local anesthesia during the procedure b. The aspirated bone marrow is mixed with heparin. c. The aspiration site is the posterior or anterior iliac crest. d. The recipient receives cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) for 4 consecutive days before the procedure. 41. After several days of admission, Francis becomes disoriented and complains of frequent headaches. The nurse in-charge first action would be:
a. Call the physician b. Document the patients status in his charts. c. Prepare oxygen treatment d. Raise the side rails 42. During routine care, Francis asks the nurse, How can I be anemic if this disease causes increased my white blood cell production? The nurse in-charge best response would be that the increased number of white blood cells (WBC) is: a. Crowd red blood cells b. Are not responsible for the anemia. c. Uses nutrients from other cells d. Have an abnormally short life span of cells. 43. Diagnostic assessment of Francis would probably not reveal: a. Predominance of lymhoblasts b. Leukocytosis c. Abnormal blast cells in the bone marrow d. Elevated thrombocyte counts 44. Robert, a 57-year-old client with acute arterial occlusion of the left leg undergoes an emergency embolectomy. Six hours later, the nurse isnt able to obtain pulses in his left foot using Doppler ultrasound. The nurse immediately notifies the physician, and asks her to prepare the client for surgery. As the nurse enters the clients room to prepare him, he states that he wont have any more surgery. Which of the following is the best initial response by the nurse? a. Explain the risks of not having the surgery b. Notifying the physician immediately c. Notifying the nursing supervisor d. Recording the clients refusal in the nurses notes 45. During the endorsement, which of the following clients should the on-duty nurse assess first? a. The 58-year-old client who was admitted 2 days ago with heart failure, blood pressure of 126/76 mm Hg, and a respiratory rate of 22 breaths/minute. b. The 89-year-old client with end-stage right-sided heart failure, blood pressure of 78/50 mm Hg, and a do not resuscitate order c. The 62-year-old client who was admitted 1 day ago with thrombophlebitis and is receiving L.V. heparin d. The 75-year-old client who was admitted 1 hour ago with new-onset atrial fibrillation and is receiving L.V. dilitiazem (Cardizem) 46. Honey, a 23-year old client complains of substernal chest pain and states that her heart feels like its racing out of the chest. She reports no history of cardiac disorders. The nurse attaches her to a cardiac monitor and notes sinus tachycardia with a rate of 136beats/minutes. Breath sounds are clear and the respiratory rate is 26 breaths/minutes. Which of the following drugs should the nurse question the client about using? a. Barbiturates b. Opioids c. Cocaine d. Benzodiazepines 47. A 51-year-old female client tells the nurse incharge that she has found a painless lump in her right breast during her monthly self-examination. Which assessment finding would strongly suggest that this clients lump is cancerous? a. Eversion of the right nipple and mobile mass b. Nonmobile mass with irregular edges c. Mobile mass that is soft and easily delineated d. Nonpalpable right axillary lymph nodes 48. A 35-year-old client with vaginal cancer asks the nurse, What is the usual treatment for this type of cancer? Which treatment should the nurse name?
a. Surgery b. Chemotherapy c. Radiation d. Immunotherapy 49. Cristina undergoes a biopsy of a suspicious lesion. The biopsy report classifies the lesion according to the TNM staging system as follows: TIS, N0, M0. What does this classification mean? a. No evidence of primary tumor, no abnormal regional lymph nodes, and no evidence of distant metastasis b. Carcinoma in situ, no abnormal regional lymph nodes, and no evidence of distant metastasis c. Cant assess tumor or regional lymph nodes and no evidence of metastasis d. Carcinoma in situ, no demonstrable metastasis of the regional lymph nodes, and ascending degrees of distant metastasis 50. Lydia undergoes a laryngectomy to treat laryngeal cancer. When teaching the client how to care for the neck stoma, the nurse should include which instruction? a. Keep the stoma uncovered. b. Keep the stoma dry. c. Have a family member perform stoma care initially until you get used to the procedure. d. Keep the stoma moist. 51. A 37-year-old client with uterine cancer asks the nurse, Which is the most common type of cancer in women? The nurse replies that its breast cancer. Which type of cancer causes the most deaths in women? a. Breast cancer b. Lung cancer c. Brain cancer d. Colon and rectal cancer 52. Antonio with lung cancer develops Horners syndrome when the tumor invades the ribs and affects the sympathetic nerve ganglia. When assessing for signs and symptoms of this syndrome, the nurse should note: a. miosis, partial eyelid ptosis, and anhidrosis on the affected side of the face. b. chest pain, dyspnea, cough, weight loss, and fever. c. arm and shoulder pain and atrophy of arm and hand muscles, both on the affected side. d. hoarseness and dysphagia. 53. Vic asks the nurse what PSA is. The nurse should reply that it stands for: a. prostate-specific antigen, which is used to screen for prostate cancer. b. protein serum antigen, which is used to determine protein levels. c. pneumococcal strep antigen, which is a bacteria that causes pneumonia. d. Papanicolaou-specific antigen, which is used to screen for cervical cancer. 54. What is the most important postoperative instruction that nurse Kate must give a client who has just returned from the operating room after receiving a subarachnoid block? a. Avoid drinking liquids until the gag reflex returns. b. Avoid eating milk products for 24 hours. c. Notify a nurse if you experience blood in your urine. d. Remain supine for the time specified by the physician. 55. A male client suspected of having colorectal cancer will require which diagnostic study to confirm the diagnosis?
a. Stool Hematest b. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) c. Sigmoidoscopy d. Abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan 56. During a breast examination, which finding most strongly suggests that the Luz has breast cancer? a. Slight asymmetry of the breasts. b. A fixed nodular mass with dimpling of the overlying skin c. Bloody discharge from the nipple d. Multiple firm, round, freely movable masses that change with the menstrual cycle 57. A female client with cancer is being evaluated for possible metastasis. Which of the following is one of the most common metastasis sites for cancer cells? a. Liver b. Colon c. Reproductive tract d. White blood cells (WBCs) 58. Nurse Mandy is preparing a client for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to confirm or rule out a spinal cord lesion. During the MRI scan, which of the following would pose a threat to the client? a. The client lies still. b. The client asks questions. c. The client hears thumping sounds. d. The client wears a watch and wedding band. 59. Nurse Cecile is teaching a female client about preventing osteoporosis. Which of the following teaching points is correct? a. Obtaining an X-ray of the bones every 3 years is recommended to detect bone loss. b. To avoid fractures, the client should avoid strenuous exercise. c. The recommended daily allowance of calcium may be found in a wide variety of foods. d. Obtaining the recommended daily allowance of calcium requires taking a calcium supplement. 60. Before Jacob undergoes arthroscopy, the nurse reviews the assessment findings for contraindications for this procedure. Which finding is a contraindication? a. Joint pain b. Joint deformity c. Joint flexion of less than 50% d. Joint stiffness 61. Mr. Rodriguez is admitted with severe pain in the knees. Which form of arthritis is characterized by urate deposits and joint pain, usually in the feet and legs, and occurs primarily in men over age 30? a. Septic arthritis b. Traumatic arthritis c. Intermittent arthritis d. Gouty arthritis 62. A heparin infusion at 1,500 unit/hour is ordered for a 64-year-old client with stroke in evolution. The infusion contains 25,000 units of heparin in 500 ml of saline solution. How many milliliters per hour should be given? a. 15 ml/hour b. 30 ml/hour c. 45 ml/hour d. 50 ml/hour 63. A 76-year-old male client had a thromboembolic right stroke; his left arm is swollen. Which of the following conditions may cause swelling after a stroke?
a. Elbow contracture secondary to spasticity b. Loss of muscle contraction decreasing venous return c. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) due to immobility of the ipsilateral side d. Hypoalbuminemia due to protein escaping from an inflamed glomerulus 64. Heberdens nodes are a common sign of osteoarthritis. Which of the following statement is correct about this deformity? a. It appears only in men b. It appears on the distal interphalangeal joint c. It appears on the proximal interphalangeal joint d. It appears on the dorsolateral aspect of the interphalangeal joint. 65. Which of the following statements explains the main difference between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis? a. Osteoarthritis is gender-specific, rheumatoid arthritis isnt b. Osteoarthritis is a localized disease rheumatoid arthritis is systemic c. Osteoarthritis is a systemic disease, rheumatoid arthritis is localized d. Osteoarthritis has dislocations and subluxations, rheumatoid arthritis doesnt 66. Mrs. Cruz uses a cane for assistance in walking. Which of the following statements is true about a cane or other assistive devices? a. A walker is a better choice than a cane. b. The cane should be used on the affected side c. The cane should be used on the unaffected side d. A client with osteoarthritis should be encouraged to ambulate without the cane 67. A male client with type 1 diabetes is scheduled to receive 30 U of 70/30 insulin. There is no 70/30 insulin available. As a substitution, the nurse may give the client: a. 9 U regular insulin and 21 U neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH). b. 21 U regular insulin and 9 U NPH. c. 10 U regular insulin and 20 U NPH. d. 20 U regular insulin and 10 U NPH. 68. Nurse Len should expect to administer which medication to a client with gout? a. aspirin b. furosemide (Lasix) c. colchicines d. calcium gluconate (Kalcinate) 69. Mr. Domingo with a history of hypertension is diagnosed with primary hyperaldosteronism. This diagnosis indicates that the clients hypertension is caused by excessive hormone secretion from which of the following glands? a. Adrenal cortex b. Pancreas c. Adrenal medulla d. Parathyroid 70. For a diabetic male client with a foot ulcer, the doctor orders bed rest, a wetto- dry dressing change every shift, and blood glucose monitoring before meals and bedtime. Why are wet-to-dry dressings used for this client? a. They contain exudate and provide a moist wound environment. b. They protect the wound from mechanical trauma and promote healing. c. They debride the wound and promote healing by secondary intention. d. They prevent the entrance of microorganisms and minimize wound discomfort.
71. Nurse Zeny is caring for a client in acute addisonian crisis. Which laboratory data would the nurse expect to find? a. Hyperkalemia b. Reduced blood urea nitrogen (BUN) c. Hypernatremia d. Hyperglycemia 72. A client is admitted for treatment of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH). Which nursing intervention is appropriate? a. Infusing I.V. fluids rapidly as ordered b. Encouraging increased oral intake c. Restricting fluids d. Administering glucose-containing I.V. fluids as ordered 73. A female client tells nurse Nikki that she has been working hard for the last 3 months to control her type 2 diabetes mellitus with diet and exercise. To determine the effectiveness of the clients efforts, the nurse should check: a. urine glucose level. b. fasting blood glucose level. c. serum fructosamine level. d. glycosylated hemoglobin level. 74. Nurse Trinity administered neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin to a diabetic client at 7 a.m. At what time would the nurse expect the client to be most at risk for a hypoglycemic reaction? a. 10:00 am b. Noon c. 4:00 pm d. 10:00 pm 75. The adrenal cortex is responsible for producing which substances? a. Glucocorticoids and androgens b. Catecholamines and epinephrine c. Mineralocorticoids and catecholamines d. Norepinephrine and epinephrine 76. On the third day after a partial thyroidectomy, Proserfina exhibits muscle twitching and hyperirritability of the nervous system. When questioned, the client reports numbness and tingling of the mouth and fingertips. Suspecting a lifethreatening electrolyte disturbance, the nurse notifies the surgeon immediately. Which electrolyte disturbance most commonly follows thyroid surgery? a. Hypocalcemia b. Hyponatremia c. Hyperkalemia d. Hypermagnesemia 77. Which laboratory test value is elevated in clients who smoke and cant be used as a general indicator of cancer? a. Acid phosphatase level b. Serum calcitonin level c. Alkaline phosphatase level d. Carcinoembryonic antigen level 78. Francis with anemia has been admitted to the medical-surgical unit. Which assessment findings are characteristic of iron-deficiency anemia? a. Nights sweats, weight loss, and diarrhea b. Dyspnea, tachycardia, and pallor c. Nausea, vomiting, and anorexia d. Itching, rash, and jaundice 79. In teaching a female client who is HIV-positive about pregnancy, the nurse would know more teaching is necessary when the client says:
a. The baby can get the virus from my placenta. b. Im planning on starting on birth control pills. c. Not everyone who has the virus gives birth to a baby who has the virus. d. Ill need to have a C-section if I become pregnant and have a baby. 80. When preparing Judy with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) for discharge to the home, the nurse should be sure to include which instruction? a. Put on disposable gloves before bathing. b. Sterilize all plates and utensils in boiling water. c. Avoid sharing such articles as toothbrushes and razors. d. Avoid eating foods from serving dishes shared by other family members. 81. Nurse Marie is caring for a 32-year-old client admitted with pernicious anemia. Which set of findings should the nurse expect when assessing the client? a. Pallor, bradycardia, and reduced pulse pressure b. Pallor, tachycardia, and a sore tongue c. Sore tongue, dyspnea, and weight gain d. Angina, double vision, and anorexia 82. After receiving a dose of penicillin, a client develops dyspnea and hypotension. Nurse Celestina suspects the client is experiencing anaphylactic shock. What should the nurse do first? a. Page an anesthesiologist immediately and prepare to intubate the client. b. Administer epinephrine, as prescribed, and prepare to intubate the client if necessary. c. Administer the antidote for penicillin, as prescribed, and continue to monitor the clients vital signs. d. Insert an indwelling urinary catheter and begin to infuse I.V. fluids as ordered. 83. Mr. Marquez with rheumatoid arthritis is about to begin aspirin therapy to reduce inflammation. When teaching the client about aspirin, the nurse discusses adverse reactions to prolonged aspirin therapy. These include: a. weight gain. b. fine motor tremors. c. respiratory acidosis. d. bilateral hearing loss. 84. A 23-year-old client is diagnosed with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). After recovering from the initial shock of the diagnosis, the client expresses a desire to learn as much as possible about HIV and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When teaching the client about the immune system, the nurse states that adaptive immunity is provided by which type of white blood cell? a. Neutrophil b. Basophil c. Monocyte d. Lymphocyte 85. In an individual with Sjgrens syndrome, nursing care should focus on: a. moisture replacement. b. electrolyte balance. c. nutritional supplementation. d. arrhythmia management. 86. During chemotherapy for lymphocytic leukemia, Mathew develops abdominal pain, fever, and horse barn smelling diarrhea. It would be most important for the nurse to advise the physician to order:
a. enzyme-linked immunosuppressant assay (ELISA) test. b. electrolyte panel and hemogram. c. stool for Clostridium difficile test. d. flat plate X-ray of the abdomen. 87. A male client seeks medical evaluation for fatigue, night sweats, and a 20-lb weight loss in 6 weeks. To confirm that the client has been infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the nurse expects the physician to order: a. E-rosette immunofluorescence. b. quantification of T-lymphocytes. c. enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). d. Western blot test with ELISA. 88. A complete blood count is commonly performed before a Joe goes into surgery. What does this test seek to identify? a. Potential hepatic dysfunction indicated by decreased blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels b. Low levels of urine constituents normally excreted in the urine c. Abnormally low hematocrit (HCT) and hemoglobin (Hb) levels d. Electrolyte imbalance that could affect the bloods ability to coagulate properly 89. While monitoring a client for the development of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), the nurse should take note of what assessment parameters? a. Platelet count, prothrombin time, and partial thromboplastin time b. Platelet count, blood glucose levels, and white blood cell (WBC) count c. Thrombin time, calcium levels, and potassium levels d. Fibrinogen level, WBC, and platelet count 90. When taking a dietary history from a newly admitted female client, Nurse Len should remember that which of the following foods is a common allergen? a. Bread b. Carrots c. Orange d. Strawberries 91. Nurse John is caring for clients in the outpatient clinic. Which of the following phone calls should the nurse return first? a. A client with hepatitis A who states, My arms and legs are itching. b. A client with cast on the right leg who states, I have a funny feeling in my right leg. c. A client with osteomyelitis of the spine who states, I am so nauseous that I cant eat. d. A client with rheumatoid arthritis who states, I am having trouble sleeping. 92. Nurse Sarah is caring for clients on the surgical floor and has just received report from the previous shift. Which of the following clients should the nurse see first? a. A 35-year-old admitted three hours ago with a gunshot wound; 1.5 cm area of dark drainage noted on the dressing. b. A 43-year-old who had a mastectomy two days ago; 23 ml of serosanguinous fluid noted in the Jackson-Pratt drain. c. A 59-year-old with a collapsed lung due to an accident; no drainage noted in the previous eight hours. d. A 62-year-old who had an abdominal-perineal resection three days ago; client complaints of chills.
93. Nurse Eve is caring for a client who had a thyroidectomy 12 hours ago for treatment of Graves disease. The nurse would be most concerned if which of the following was observed? a. Blood pressure 138/82, respirations 16, oral temperature 99 degrees Fahrenheit. b. The client supports his head and neck when turning his head to the right. c. The client spontaneously flexes his wrist when the blood pressure is obtained. d. The client is drowsy and complains of sore throat. 94. Julius is admitted with complaints of severe pain in the lower right quadrant of the abdomen. To assist with pain relief, the nurse should take which of the following actions? a. Encourage the client to change positions frequently in bed. b. Administer Demerol 50 mg IM q 4 hours and PRN. c. Apply warmth to the abdomen with a heating pad. d. Use comfort measures and pillows to position the client. 95. Nurse Tina prepares a client for peritoneal dialysis. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? a. Assess for a bruit and a thrill. b. Warm the dialysate solution. c. Position the client on the left side. d. Insert a Foley catheter 96. Nurse Jannah teaches an elderly client with right-sided weakness how to use cane. Which of the following behaviors, if demonstrated by the client to the nurse, indicates that the teaching was effective? a. The client holds the cane with his right hand, moves the can forward followed by the right leg, and then moves the left leg. b. The client holds the cane with his right hand, moves the cane forward followed by his left leg, and then moves the right leg. c. The client holds the cane with his left hand, moves the cane forward followed by the right leg, and then moves the left leg. d. The client holds the cane with his left hand, moves the cane forward followed by his left leg, and then moves the right leg. 97. An elderly client is admitted to the nursing home setting. The client is occasionally confused and her gait is often unsteady. Which of the following actions, if taken by the nurse, is most appropriate? a. Ask the womans family to provide personal items such as photos or mementos. b. Select a room with a bed by the door so the woman can look down the hall. c. Suggest the woman eat her meals in the room with her roommate. d. Encourage the woman to ambulate in the halls twice a day. 98. Nurse Evangeline teaches an elderly client how to use a standard aluminum walker. Which of the following behaviors, if demonstrated by the client, indicates that the nurses teaching was effective? a. The client slowly pushes the walker forward 12 inches, then takes small steps forward while leaning on the walker. b. The client lifts the walker, moves it forward 10 inches, and then takes several small steps forward. c. The client supports his weight on the walker while advancing it forward, then takes small steps while balancing on the walker. d. The client slides the walker 18 inches forward, then takes small steps while holding onto the walker for balance.
99. Nurse Deric is supervising a group of elderly clients in a residential home setting. The nurse knows that the elderly are at greater risk of developing sensory deprivation for what reason? a. Increased sensitivity to the side effects of medications. b. Decreased visual, auditory, and gustatory abilities. c. Isolation from their families and familiar surroundings. d. Decrease musculoskeletal function and mobility. 100. A male client with emphysema becomes restless and confused. What step should nurse Jasmine take next? a. Encourage the client to perform pursed lip breathing. b. Check the clients temperature. c. Assess the clients potassium level. d. Increase the clients oxygen flow rate. NP 4 1. Randy has undergone kidney transplant, what assessment would prompt Nurse Katrina to suspect organ rejection? a. Sudden weight loss b. Polyuria c. Hypertension d. Shock 2. The immediate objective of nursing care for an overweight, mildly hypertensive male client with ureteral colic and hematuria is to decrease: a. Pain b. Weight c. Hematuria d. Hypertension 3. Matilda, with hyperthyroidism is to receive Lugols iodine solution before a subtotal thyroidectomy is performed. The nurse is aware that this medication is given to: a. Decrease the total basal metabolic rate. b. Maintain the function of the parathyroid glands. c. Block the formation of thyroxine by the thyroid gland. d. Decrease the size and vascularity of the thyroid gland. 4. Ricardo, was diagnosed with type I diabetes. The nurse is aware that acute hypoglycemia also can develop in the client who is diagnosed with: a. Liver disease b. Hypertension c. Type 2 diabetes d. Hyperthyroidism 5. Tracy is receiving combination chemotherapy for treatment of metastatic carcinoma. Nurse Ruby should monitor the client for the systemic side effect of: a. Ascites b. Nystagmus c. Leukopenia d. Polycythemia 6. Norma, with recent colostomy expresses concern about the inability to control the passage of gas. Nurse Oliver should suggest that the client plan to: a. Eliminate foods high in cellulose. b. Decrease fluid intake at meal times. c. Avoid foods that in the past caused flatus. d. Adhere to a bland diet prior to social events. 7. Nurse Ron begins to teach a male client how to perform colostomy irrigations. The nurse would
evaluate that the instructions were understood when the client states, I should: a. Lie on my left side while instilling the irrigating solution. b. Keep the irrigating container less than 18 inches above the stoma. c. Instill a minimum of 1200 ml of irrigating solution to stimulate evacuation of the bowel. d. Insert the irrigating catheter deeper into the stoma if cramping occurs during the procedure. 8. Patrick is in the oliguric phase of acute tubular necrosis and is experiencing fluid and electrolyte imbalances. The client is somewhat confused and complains of nausea and muscle weakness. As part of the prescribed therapy to correct this electrolyte imbalance, the nurse would expect to: a. Administer Kayexalate b. Restrict foods high in protein c. Increase oral intake of cheese and milk. d. Administer large amounts of normal saline via I.V. 9. Mario has burn injury. After Forty48 hours, the physician orders for Mario 2 liters of IV fluid to be administered q12 h. The drop factor of the tubing is 10 gtt/ml. The nurse should set the flow to provide: a. 18 gtt/min b. 28 gtt/min c. 32 gtt/min d. 36 gtt/min 10.Terence suffered form burn injury. Using the rule of nines, which has the largest percent of burns? a. Face and neck b. Right upper arm and penis c. Right thigh and penis d. Upper trunk 11. Herbert, a 45 year old construction engineer is brought to the hospital unconscious after falling from a 2-story building. When assessing the client, the nurse would be most concerned if the assessment revealed: a. Reactive pupils b. A depressed fontanel c. Bleeding from ears d. An elevated temperature 12. Nurse Sherry is teaching male client regarding his permanent artificial pacemaker. Which information given by the nurse shows her knowledge deficit about the artificial cardiac pacemaker? a. take the pulse rate once a day, in the morning upon awakening b. May be allowed to use electrical appliances c. Have regular follow up care d. May engage in contact sports 13.The nurse is ware that the most relevant knowledge about oxygen administration to a male client with COPD is a. Oxygen at 1-2L/min is given to maintain the hypoxic stimulus for breathing. b. Hypoxia stimulates the central chemoreceptors in the medulla that makes the client breath. c. Oxygen is administered best using a nonrebreathing mask d. Blood gases are monitored using a pulse oximeter. 14.Tonny has undergoes a left thoracotomy and a partial pneumonectomy. Chest tubes are inserted, and one-bottle water-seal drainage is instituted in the operating room. In the postanesthesia care unit Tonny is placed in Fowlers position on either his
right side or on his back. The nurse is aware that this position: a. Reduce incisional pain. b. Facilitate ventilation of the left lung. c. Equalize pressure in the pleural space. d. Increase venous return 15.Kristine is scheduled for a bronchoscopy. When teaching Kristine what to expect afterward, the nurses highest priority of information would be: a. Food and fluids will be withheld for at least 2 hours. b. Warm saline gargles will be done q 2h. c. Coughing and deep-breathing exercises will be done q2h. d. Only ice chips and cold liquids will be allowed initially. 16.Nurse Tristan is caring for a male client in acute renal failure. The nurse should expect hypertonic glucose, insulin infusions, and sodium bicarbonate to be used to treat: a. hypernatremia. b. hypokalemia. c. hyperkalemia. d. hypercalcemia. 17.Ms. X has just been diagnosed with condylomata acuminata (genital warts). What information is appropriate to tell this client? a. This condition puts her at a higher risk for cervical cancer; therefore, she should have a Papanicolaou (Pap) smear annually. b. The most common treatment is metronidazole (Flagyl), which should eradicate the problem within 7 to 10 days. c. The potential for transmission to her sexual partner will be eliminated if condoms are used every time they have sexual intercourse. d. The human papillomavirus (HPV), which causes condylomata acuminata, cant be transmitted during oral sex. 18.Maritess was recently diagnosed with a genitourinary problem and is being examined in the emergency department. When palpating the her kidneys, the nurse should keep which anatomical fact in mind? a. The left kidney usually is slightly higher than the right one. b. The kidneys are situated just above the adrenal glands. c. The average kidney is approximately 5 cm (2) long and 2 to 3 cm ( to 1-1/8) wide. d. The kidneys lie between the 10th and 12th thoracic vertebrae. 19.Jestoni with chronic renal failure (CRF) is admitted to the urology unit. The nurse is aware that the diagnostic test are consistent with CRF if the result is: a. Increased pH with decreased hydrogen ions. b. Increased serum levels of potassium, magnesium, and calcium. c. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 100 mg/dl and serum creatinine 6.5 mg/ dl. d. Uric acid analysis 3.5 mg/dl and phenolsulfonphthalein (PSP) excretion 75%. 20. Katrina has an abnormal result on a Papanicolaou test. After admitting that she read her chart while the nurse was out of the room, Katrina asks what dysplasia means. Which definition should the nurse provide? a. Presence of completely undifferentiated tumor cells that dont resemble cells of the tissues of their origin. b. Increase in the number of normal cells in a
normal arrangement in a tissue or an organ. c. Replacement of one type of fully differentiated cell by another in tissues where the second type normally isnt found. d. Alteration in the size, shape, and organization of differentiated cells. 21. During a routine checkup, Nurse Mariane assesses a male client with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) for signs and symptoms of cancer. What is the most common AIDS-related cancer? a. Squamous cell carcinoma b. Multiple myeloma c. Leukemia d. Kaposis sarcoma 22.Ricardo is scheduled for a prostatectomy, and the anesthesiologist plans to use a spinal (subarachnoid) block during surgery. In the operating room, the nurse positions the client according to the anesthesiologists instructions. Why does the client require special positioning for this type of anesthesia? a. To prevent confusion b. To prevent seizures c. To prevent cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage d. To prevent cardiac arrhythmias 23.A male client had a nephrectomy 2 days ago and is now complaining of abdominal pressure and nausea. The first nursing action should be to: a. Auscultate bowel sounds. b. Palpate the abdomen. c. Change the clients position. d. Insert a rectal tube. 24.Wilfredo with a recent history of rectal bleeding is being prepared for a colonoscopy. How should the nurse Patricia position the client for this test initially? a. Lying on the right side with legs straight b. Lying on the left side with knees bent c. Prone with the torso elevated d. Bent over with hands touching the floor 25.A male client with inflammatory bowel disease undergoes an ileostomy. On the first day after surgery, Nurse Oliver notes that the clients stoma appears dusky. How should the nurse interpret this finding? a. Blood supply to the stoma has been interrupted. b. This is a normal finding 1 day after surgery. c. The ostomy bag should be adjusted. d. An intestinal obstruction has occurred. 26.Anthony suffers burns on the legs, which nursing intervention helps prevent contractures? a. Applying knee splints b. Elevating the foot of the bed c. Hyperextending the clients palms d. Performing shoulder range-of-motion exercises 27.Nurse Ron is assessing a client admitted with second- and third-degree burns on the face, arms, and chest. Which finding indicates a potential problem? a. Partial pressure of arterial oxygen (PaO2) value of 80 mm Hg. b. Urine output of 20 ml/hour. c. White pulmonary secretions. d. Rectal temperature of 100.6 F (38 C). 28. Mr. Mendoza who has suffered a cerebrovascular accident (CVA) is too weak to move on his own. To help the client avoid pressure ulcers, Nurse Celia should:
a. Turn him frequently. b. Perform passive range-of-motion (ROM) exercises. c. Reduce the clients fluid intake. d. Encourage the client to use a footboard. 29.Nurse Maria plans to administer dexamethasone cream to a female client who has dermatitis over the anterior chest. How should the nurse apply this topical agent? a. With a circular motion, to enhance absorption. b. With an upward motion, to increase blood supply to the affected area c. In long, even, outward, and downward strokes in the direction of hair growth d. In long, even, outward, and upward strokes in the direction opposite hair growth 30.Nurse Kate is aware that one of the following classes of medication protect the ischemic myocardium by blocking catecholamines and sympathetic nerve stimulation is: a. Beta -adrenergic blockers b. Calcium channel blocker c. Narcotics d. Nitrates 31.A male client has jugular distention. On what position should the nurse place the head of the bed to obtain the most accurate reading of jugular vein distention? a. High Fowlers b. Raised 10 degrees c. Raised 30 degrees d. Supine position 32.The nurse is aware that one of the following classes of medications maximizes cardiac performance in clients with heart failure by increasing ventricular contractility? a. Beta-adrenergic blockers b. Calcium channel blocker c. Diuretics d. Inotropic agents 33.A male client has a reduced serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL) level and an elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL) level. Which of the following dietary modifications is not appropriate for this client? a. Fiber intake of 25 to 30 g daily b. Less than 30% of calories form fat c. Cholesterol intake of less than 300 mg daily d. Less than 10% of calories from saturated fat 34. A 37-year-old male client was admitted to the coronary care unit (CCU) 2 days ago with an acute myocardial infarction. Which of the following actions would breach the client confidentiality? a. The CCU nurse gives a verbal report to the nurse on the telemetry unit before transferring the client to that unit b. The CCU nurse notifies the on-call physician about a change in the clients condition c. The emergency department nurse calls up the latest electrocardiogram results to check the clients progress. d. At the clients request, the CCU nurse updates the clients wife on his condition 35. A male client arriving in the emergency department is receiving cardiopulmonary resuscitation from paramedics who are giving ventilations through an endotracheal (ET) tube that they placed in the clients home. During a pause in compressions, the cardiac monitor shows narrow QRS complexes and a heart rate of beats/minute with a palpable pulse. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
a. Start an L.V. line and administer amiodarone (Cardarone), 300 mg L.V. over 10 minutes. b. Check endotracheal tube placement. c. Obtain an arterial blood gas (ABG) sample. d. Administer atropine, 1 mg L.V. 36. After cardiac surgery, a clients blood pressure measures 126/80 mm Hg. Nurse Katrina determines that mean arterial pressure (MAP) is which of the following? a. 46 mm Hg b. 80 mm Hg c. 95 mm Hg d. 90 mm Hg 37. A female client arrives at the emergency department with chest and stomach pain and a report of black tarry stool for several months. Which of the following order should the nurse Oliver anticipate? a. Cardiac monitor, oxygen, creatine kinase and lactate dehydrogenase levels b. Prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time, fibrinogen and fibrin split product values. c. Electrocardiogram, complete blood count, testing for occult blood, comprehensive serum metabolic panel. d. Electroencephalogram, alkaline phosphatase and aspartate aminotransferase levels, basic serum metabolic panel 38. Macario had coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery 3 days ago. Which of the following conditions is suspected by the nurse when a decrease in platelet count from 230,000 ul to 5,000 ul is noted? a. Pancytopenia b. Idiopathic thrombocytopemic purpura (ITP) c. Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) d. Heparin-associated thrombosis and thrombocytopenia (HATT) 39. Which of the following drugs would be ordered by the physician to improve the platelet count in a male client with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)? a. Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) b. Corticosteroids c. Methotrezate d. Vitamin K 40. A female client is scheduled to receive a heart valve replacement with a porcine valve. Which of the following types of transplant is this? a. Allogeneic b. Autologous c. Syngeneic d. Xenogeneic 41. Marco falls off his bicycle and injuries his ankle. Which of the following actions shows the initial response to the injury in the extrinsic pathway? a. Release of Calcium b. Release of tissue thromboplastin c. Conversion of factors XII to factor XIIa d. Conversion of factor VIII to factor VIIIa 42. Instructions for a client with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) would include information about which of the following blood dyscrasias? a. Dresslers syndrome b. Polycythemia c. Essential thrombocytopenia d. Von Willebrands disease 43. The nurse is aware that the following symptoms is most commonly an early indication of stage 1 Hodgkins disease?
a. Pericarditis b. Night sweat c. Splenomegaly d. Persistent hypothermia 44. Francis with leukemia has neutropenia. Which of the following functions must frequently assessed? a. Blood pressure b. Bowel sounds c. Heart sounds d. Breath sounds 45. The nurse knows that neurologic complications of multiple myeloma (MM) usually involve which of the following body system? a. Brain b. Muscle spasm c. Renal dysfunction d. Myocardial irritability 46. Nurse Patricia is aware that the average length of time from human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection to the development of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)? a. Less than 5 years b. 5 to 7 years c. 10 years d. More than 10 years 47. An 18-year-old male client admitted with heat stroke begins to show signs of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Which of the following laboratory findings is most consistent with DIC? a. Low platelet count b. Elevated fibrinogen levels c. Low levels of fibrin degradation products d. Reduced prothrombin time 48. Mario comes to the clinic complaining of fever, drenching night sweats, and unexplained weight loss over the past 3 months. Physical examination reveals a single enlarged supraclavicular lymph node. Which of the following is the most probable diagnosis? a. Influenza b. Sickle cell anemia c. Leukemia d. Hodgkins disease 49. A male client with a gunshot wound requires an emergency blood transfusion. His blood type is AB negative. Which blood type would be the safest for him to receive? a. AB Rh-positive b. A Rh-positive c. A Rh-negative d. O Rh-positive Situation: Stacy is diagnosed with acute lymphoid leukemia (ALL) and beginning chemotherapy. 50. Stacy is discharged from the hospital following her chemotherapy treatments. Which statement of Stacys mother indicated that she understands when she will contact the physician? a. I should contact the physician if Stacy has difficulty in sleeping. b. I will call my doctor if Stacy has persistent vomiting and diarrhea. c. My physician should be called if Stacy is irritable and unhappy. d. Should Stacy have continued hair loss, I need to call the doctor. 51. Stacys mother states to the nurse that it is hard to see Stacy with no hair. The best response for the nurse is:
a. Stacy looks very nice wearing a hat. b. You should not worry about her hair, just be glad that she is alive. c. Yes it is upsetting. But try to cover up your feelings when you are with her or else she may be upset. d. This is only temporary; Stacy will re-grow new hair in 3-6 months, but may be different in texture. 52. Stacy has beginning stomatitis. To promote oral hygiene and comfort, the nurse in-charge should: a. Provide frequent mouthwash with normal saline. b. Apply viscous Lidocaine to oral ulcers as needed. c. Use lemon glycerine swabs every 2 hours. d. Rinse mouth with Hydrogen Peroxide. 53. During the administration of chemotherapy agents, Nurse Oliver observed that the IV site is red and swollen, when the IV is touched Stacy shouts in pain. The first nursing action to take is: a. Notify the physician b. Flush the IV line with saline solution c. Immediately discontinue the infusion d. Apply an ice pack to the site, followed by warm compress. 54. The term blue bloater refers to a male client which of the following conditions? a. Adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) b. Asthma c. Chronic obstructive bronchitis d. Emphysema 55. The term pink puffer refers to the female client with which of the following conditions? a. Adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) b. Asthma c. Chronic obstructive bronchitis d. Emphysema 56. Jose is in danger of respiratory arrest following the administration of a narcotic analgesic. An arterial blood gas value is obtained. Nurse Oliver would expect the paco2 to be which of the following values? a. 15 mm Hg b. 30 mm Hg c. 40 mm Hg d. 80 mm Hg 57. Timothys arterial blood gas (ABG) results are as follows; pH 7.16; Paco2 80 mm Hg; Pao2 46 mm Hg; HCO3- 24mEq/L; Sao2 81%. This ABG result represents which of the following conditions? a. Metabolic acidosis b. Metabolic alkalosis c. Respiratory acidosis d. Respirator y alkalosis 58. Norma has started a new drug for hypertension. Thirty minutes after she takes the drug, she develops chest tightness and becomes short of breath and tachypneic. She has a decreased level of consciousness. These signs indicate which of the following conditions? a. Asthma attack b. Pulmonary embolism c. Respiratory failure d. Rheumatoid arthritis Situation: Mr. Gonzales was admitted to the hospital with ascites and jaundice. To rule out cirrhosis of the liver: 59. Which laboratory test indicates liver cirrhosis? a. Decreased red blood cell count b. Decreased serum acid phosphate level
c. Elevated white blood cell count d. Elevated serum aminotransferase 60.The biopsy of Mr. Gonzales confirms the diagnosis of cirrhosis. Mr. Gonzales is at increased risk for excessive bleeding primarily because of: a. Impaired clotting mechanism b. Varix formation c. Inadequate nutrition d. Trauma of invasive procedure 61. Mr. Gonzales develops hepatic encephalopathy. Which clinical manifestation is most common with this condition? a. Increased urine output b. Altered level of consciousness c. Decreased tendon reflex d. Hypotension 62. When Mr. Gonzales regained consciousness, the physician orders 50 ml of Lactose p.o. every 2 hours. Mr. Gozales develops diarrhea. The nurse best action would be: a. Ill see if your physician is in the hospital. b. Maybe your reacting to the drug; I will withhold the next dose. c. Ill lower the dosage as ordered so the drug causes only 2 to 4 stools a day. d. Frequently, bowel movements are needed to reduce sodium level. 63. Which of the following groups of symptoms indicates a ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm? a. Lower back pain, increased blood pressure, decreased re blood cell (RBC) count, increased white blood (WBC) count. b. Severe lower back pain, decreased blood pressure, decreased RBC count, increased WBC count. c. Severe lower back pain, decreased blood pressure, decreased RBC count, decreased RBC count, decreased WBC count. d. Intermitted lower back pain, decreased blood pressure, decreased RBC count, increased WBC count. 64. After undergoing a cardiac catheterization, Tracy has a large puddle of blood under his buttocks. Which of the following steps should the nurse take first? a. Call for help. b. Obtain vital signs c. Ask the client to lift up d. Apply gloves and assess the groin site 65. Which of the following treatment is a suitable surgical intervention for a client with unstable angina? a. Cardiac catheterization b. Echocardiogram c. Nitroglycerin d. Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) 66. The nurse is aware that the following terms used to describe reduced cardiac output and perfusion impairment due to ineffective pumping of the heart is: a. Anaphylactic shock b. Cardiogenic shock c. Distributive shock d. Myocardial infarction (MI) 67. A client with hypertension ask the nurse which factors can cause blood pressure to drop to normal levels?
a. Kidneys excretion to sodium only. b. Kidneys retention of sodium and water c. Kidneys excretion of sodium and water d. Kidneys retention of sodium and excretion of water 68. Nurse Rose is aware that the statement that best explains why furosemide (Lasix) is administered to treat hypertension is: a. It dilates peripheral blood vessels. b. It decreases sympathetic cardioacceleration. c. It inhibits the angiotensin-coverting enzymes d. It inhibits reabsorption of sodium and water in the loop of Henle. 69. Nurse Nikki knows that laboratory results supports the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is: a. Elavated serum complement level b. Thrombocytosis, elevated sedimentation rate c. Pancytopenia, elevated antinuclear antibody (ANA) titer d. Leukocysis, elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels 70. Arnold, a 19-year-old client with a mild concussion is discharged from the emergency department. Before discharge, he complains of a headache. When offered acetaminophen, his mother tells the nurse the headache is severe and she would like her son to have something stronger. Which of the following responses by the nurse is appropriate? a. Your son had a mild concussion, acetaminophen is strong enough. b. Aspirin is avoided because of the danger of Reyes syndrome in children or young adults. c. Narcotics are avoided after a head injury because they may hide a worsening condition. d. Stronger medications may lead to vomiting, which increases the intracarnial pressure (ICP). 71. When evaluating an arterial blood gas from a male client with a subdural hematoma, the nurse notes the Paco2 is 30 mm Hg. Which of the following responses best describes the result? a. Appropriate; lowering carbon dioxide (CO2) reduces intracranial pressure (ICP) b. Emergent; the client is poorly oxygenated c. Normal d. Significant; the client has alveolar hypoventilation 72. When prioritizing care, which of the following clients should the nurse Olivia assess first? a. A 17-year-old clients 24-hours postappendectomy b. A 33-year-old client with a recent diagnosis of Guillain-Barre syndrome c. A 50-year-old client 3 days postmyocardial infarction d. A 50-year-old client with diverticulitis 73. JP has been diagnosed with gout and wants to know why colchicine is used in the treatment of gout. Which of the following actions of colchicines explains why its effective for gout? a. Replaces estrogen b. Decreases infection c. Decreases inflammation d. Decreases bone demineralization 74. Norma asks for information about osteoarthritis. Which of the following statements about osteoarthritis is correct? a. Osteoarthritis is rarely debilitating b. Osteoarthritis is a rare form of arthritis c. Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis d. Osteoarthritis afflicts people over 60
75. Ruby is receiving thyroid replacement therapy develops the flu and forgets to take her thyroid replacement medicine. The nurse understands that skipping this medication will put the client at risk for developing which of the following lifethreatening complications? a. Exophthalmos b. Thyroid storm c. Myxedema coma d. Tibial myxedema 76. Nurse Sugar is assessing a client with Cushings syndrome. Which observation should the nurse report to the physician immediately? a. Pitting edema of the legs b. An irregular apical pulse c. Dry mucous membranes d. Frequent urination 77. Cyrill with severe head trauma sustained in a car accident is admitted to the intensive care unit. Thirty-six hours later, the clients urine output suddenly rises above 200 ml/hour, leading the nurse to suspect diabetes insipidus. Which laboratory findings support the nurses suspicion of diabetes insipidus? a. Above-normal urine and serum osmolality levels b. Below-normal urine and serum osmolality levels c. Above-normal urine osmolality level, belownormal serum osmolality level d. Below-normal urine osmolality level, abovenormal serum osmolality level 78. Jomari is diagnosed with hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome (HHNS) is stabilized and prepared for discharge. When preparing the client for discharge and home management, which of the following statements indicates that the client understands her condition and how to control it? a. I can avoid getting sick by not becoming dehydrated and by paying attention to my need to urinate, drink, or eat more than usual. b. If I experience trembling, weakness, and headache, I should drink a glass of soda that contains sugar. c. I will have to monitor my blood glucose level closely and notify the physician if its constantly elevated. d. If I begin to feel especially hungry and thirsty, Ill eat a snack high in carbohydrates. 79. A 66-year-old client has been complaining of sleeping more, increased urination, anorexia, weakness, irritability, depression, and bone pain that interferes with her going outdoors. Based on these assessment findings, the nurse would suspect which of the following disorders? a. Diabetes mellitus b. Diabetes insipidus c. Hypoparathyroidism d. Hyperparathyroidism 80. Nurse Lourdes is teaching a client recovering from addisonian crisis about the need to take fludrocortisone acetate and hydrocortisone at home. Which statement by the client indicates an understanding of the instructions? a. Ill take my hydrocortisone in the late afternoon, before dinner. b. Ill take all of my hydrocortisone in the morning, right after I wake up. c. Ill take two-thirds of the dose when I wake up and one-third in the late afternoon. d. Ill take the entire dose at bedtime. 81. Which of the following laboratory test results would suggest to the nurse Len that a client has a corticotropin-secreting pituitary adenoma?
a. High corticotropin and low cortisol levels b. Low corticotropin and high cortisol levels c. High corticotropin and high cortisol levels d. Low corticotropin and low cortisol levels 82. A male client is scheduled for a transsphenoidal hypophysectomy to remove a pituitary tumor. Preoperatively, the nurse should assess for potential complications by doing which of the following? a. Testing for ketones in the urine b. Testing urine specific gravity c. Checking temperature every 4 hours d. Performing capillary glucose testing every 4 hours 83. Capillary glucose monitoring is being performed every 4 hours for a client diagnosed with diabetic ketoacidosis. Insulin is administered using a scale of regular insulin according to glucose results. At 2 p.m., the client has a capillary glucose level of 250 mg/dl for which he receives 8 U of regular insulin. Nurse Mariner should expect the doses: a. onset to be at 2 p.m. and its peak to be at 3 p.m. b. onset to be at 2:15 p.m. and its peak to be at 3 p.m. c. onset to be at 2:30 p.m. and its peak to be at 4 p.m. d. onset to be at 4 p.m. and its peak to be at 6 p.m. 84. The physician orders laboratory tests to confirm hyperthyroidism in a female client with classic signs and symptoms of this disorder. Which test result would confirm the diagnosis? a. No increase in the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) level after 30 minutes during the TSH stimulation test b. A decreased TSH level c. An increase in the TSH level after 30 minutes during the TSH stimulation test d. Below-normal levels of serum triiodothyronine (T3) and serum thyroxine (T4) as detected by radioimmunoassay 85. Rico with diabetes mellitus must learn how to self-administer insulin. The physician has prescribed 10 U of U-100 regular insulin and 35 U of U-100 isophane insulin suspension (NPH) to be taken before breakfast. When teaching the client how to select and rotate insulin injection sites, the nurse should provide which instruction? a. Inject insulin into healthy tissue with large blood vessels and nerves. b. Rotate injection sites within the same anatomic region, not among different regions. c. Administer insulin into areas of scar tissue or hypotrophy whenever possible. d. Administer insulin into sites above muscles that you plan to exercise heavily later that day. 86. Nurse Sarah expects to note an elevated serum glucose level in a client with hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome (HHNS). Which other laboratory finding should the nurse anticipate? a. Elevated serum acetone level b. Serum ketone bodies c. Serum alkalosis d. Below-normal serum potassium level 87. For a client with Graves disease, which nursing intervention promotes comfort? a. Restricting intake of oral fluids b. Placing extra blankets on the clients bed c. Limiting intake of high-carbohydrate foods d. Maintaining room temperature in the low-normal range
88. Patrick is treated in the emergency department for a Colles fracture sustained during a fall. What is a Colles fracture? a. Fracture of the distal radius b. Fracture of the olecranon c. Fracture of the humerus d. Fracture of the carpal scaphoid 89. Cleo is diagnosed with osteoporosis. Which electrolytes are involved in the development of this disorder? a. Calcium and sodium b. Calcium and phosphorous c. Phosphorous and potassium d. Potassium and sodium 90. Johnny a firefighter was involved in extinguishing a house fire and is being treated to smoke inhalation. He develops severe hypoxia 48 hours after the incident, requiring intubation and mechanical ventilation. He most likely has developed which of the following conditions? a. Adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) b. Atelectasis c. Bronchitis d. Pneumonia 91. A 67-year-old client develops acute shortness of breath and progressive hypoxia requiring right femur. The hypoxia was probably caused by which of the following conditions? a. Asthma attack b. Atelectasis c. Bronchitis d. Fat embolism 92. A client with shortness of breath has decreased to absent breath sounds on the right side, from the apex to the base. Which of the following conditions would best explain this? a. Acute asthma b. Chronic bronchitis c. Pneumonia d. Spontaneous pneumothorax 93. A 62-year-old male client was in a motor vehicle accident as an unrestrained driver. Hes now in the emergency department complaining of difficulty of breathing and chest pain. On auscultation of his lung field, no breath sounds are present in the upper lobe. This client may have which of the following conditions? a. Bronchitis b. Pneumonia c. Pneumothorax d. Tuberculosis (TB) 94. If a client requires a pneumonectomy, what fills the area of the thoracic cavity? a. The space remains filled with air only b. The surgeon fills the space with a gel c. Serous fluids fills the space and consolidates the region d. The tissue from the other lung grows over to the other side 95. Hemoptysis may be present in the client with a pulmonary embolism because of which of the following reasons? a. Alveolar damage in the infracted area b. Involvement of major blood vessels in the occluded area c. Loss of lung parenchyma d. Loss of lung tissue 96. Aldo with a massive pulmonary embolism will have an arterial blood gas analysis performed to
determine the extent of hypoxia. The acid-base disorder that may be present is? a. Metabolic acidosis b. Metabolic alkalosis c. Respiratory acidosis d. Respiratory alkalosis 97. After a motor vehicle accident, Armand an 22year-old client is admitted with a pneumothorax. The surgeon inserts a chest tube and attaches it to a chest drainage system. Bubbling soon appears in the water seal chamber. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the bubbling? a. Air leak b. Adequate suction c. Inadequate suction d. Kinked chest tube 98. Nurse Michelle calculates the IV flow rate for a postoperative client. The client receives 3,000 ml of Ringers lactate solution IV to run over 24 hours. The IV infusion set has a drop factor of 10 drops per milliliter. The nurse should regulate the clients IV to deliver how many drops per minute? a. 18 b. 21 c. 35 d. 40 99. Mickey, a 6-year-old child with a congenital heart disorder is admitted with congestive heart failure. Digoxin (lanoxin) 0.12 mg is ordered for the child. The bottle of Lanoxin contains .05 mg of Lanoxin in 1 ml of solution. What amount should the nurse administer to the child? a. 1.2 ml b. 2.4 ml c. 3.5 ml d. 4.2 ml 100. Nurse Alexandra teaches a client about elastic stockings. Which of the following statements, if made by the client, indicates to the nurse that the teaching was successful? a. I will wear the stockings until the physician tells me to remove them. b. I should wear the stockings even when I am sleep. c. Every four hours I should remove the stockings for a half hour. d. I should put on the stockings before getting out of bed in the morning. NP 5 1. Mr. Marquez reports of losing his job, not being able to sleep at night, and feeling upset with his wife. Nurse John responds to the client, You may want to talk about your employment situation in group today. The Nurse is using which therapeutic technique? a. Observations b. Restating c. Exploring d. Focusing 2. Tony refuses his evening dose of Haloperidol (Haldol), then becomes extremely agitated in the dayroom while other clients are watching television. He begins cursing and throwing furniture. Nurse Oliver first action is to: a. Check the clients medical record for an order for an as-needed I.M. dose of medication for agitation. b. Place the client in full leather restraints. c. Call the attending physician and report the behavior. d. Remove all other clients from the dayroom.
3. Tina who is manic, but not yet on medication, comes to the drug treatment center. The nurse would not let this client join the group session because: a. The client is disruptive. b. The client is harmful to self. c. The client is harmful to others. d. The client needs to be on medication first. 4. Dervid, an adolescent boy was admitted for substance abuse and hallucinations. The clients mother asks Nurse Armando to talk with his husband when he arrives at the hospital. The mother says that she is afraid of what the father might say to the boy. The most appropriate nursing intervention would be to: a. Inform the mother that she and the father can work through this problem themselves. b. Refer the mother to the hospital social worker. c. Agree to talk with the mother and the father together. d. Suggest that the father and son work things out. 5. What is Nurse John likely to note in a male client being admitted for alcohol withdrawal? a. Perceptual disorders. b. Impending coma. c. Recent alcohol intake. d. Depression with mutism. 6. Aira has taken amitriptyline HCL (Elavil) for 3 days, but now complains that it doesnt help and refuses to take it. What should the nurse say or do? a. Withhold the drug. b. Record the clients response. c. Encourage the client to tell the doctor. d. Suggest that it takes awhile before seeing the results. 7. Dervid, an adolescent has a history of truancy from school, running away from home and barrowing other peoples things without their permission. The adolescent denies stealing, rationalizing instead that as long as no one was using the items, it was all right to borrow them. It is important for the nurse to understand the psychodynamically, this behavior may be largely attributed to a developmental defect related to the: a. Id b. Ego c. Superego d. Oedipal complex 8. In preparing a female client for electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), Nurse Michelle knows that succinylcoline (Anectine) will be administered for which therapeutic effect? a. Short-acting anesthesia b. Decreased oral and respiratory secretions. c. Skeletal muscle paralysis. d. Analgesia. 9. Nurse Gina is aware that the dietary implications for a client in manic phase of bipolar disorder is: a. Serve the client a bowl of soup, buttered French bread, and apple slices. b. Increase calories, decrease fat, and decrease protein. c. Give the client pieces of cut-up steak, carrots, and an apple. d. Increase calories, carbohydrates, and protein. 10.What parental behavior toward a child during an admission procedure should cause Nurse Ron to suspect child abuse? a. Flat affect b. Expressing guilt
c. Acting overly solicitous toward the child. d. Ignoring the child. 11.Nurse Lynnette notices that a female client with obsessive-compulsive disorder washes her hands for long periods each day. How should the nurse respond to this compulsive behavior? a. By designating times during which the client can focus on the behavior. b. By urging the client to reduce the frequency of the behavior as rapidly as possible. c. By calling attention to or attempting to prevent the behavior. d. By discouraging the client from verbalizing anxieties. 12.After seeking help at an outpatient mental health clinic, Ruby who was raped while walking her dog is diagnosed with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Three months later, Ruby returns to the clinic, complaining of fear, loss of control, and helpless feelings. Which nursing intervention is most appropriate for Ruby? a. Recommending a high-protein, low-fat diet. b. Giving sleep medication, as prescribed, to restore a normal sleepwake cycle. c. Allowing the client time to heal. d. Exploring the meaning of the traumatic event with the client. 13.Meryl, age 19, is highly dependent on her parents and fears leaving home to go away to college. Shortly before the semester starts, she complains that her legs are paralyzed and is rushed to the emergency department. When physical examination rules out a physical cause for her paralysis, the physician admits her to the psychiatric unit where she is diagnosed with conversion disorder. Meryl asks the nurse, Why has this happened to me? What is the nurses best response? a. Youve developed this paralysis so you can stay with your parents. You must deal with this conflict if you want to walk again. b. It must be awful not to be able to move your legs. You may feel better if you realize the problem is psychological, not physical. c. Your problem is real but there is no physical basis for it. Well work on what is going on in your life to find out why its happened. d. It isnt uncommon for someone with your personality to develop a conversion disorder during times of stress. 14.Nurse Krina knows that the following drugs have been known to be effective in treating obsessivecompulsive disorder (OCD): a. benztropine (Cogentin) and diphenhydramine (Benadryl). b. chlordiazepoxide (Librium) and diazepam (Valium) c. fluvoxamine (Luvox) and clomipramine (Anafranil) d. divalproex (Depakote) and lithium (Lithobid) 15.Alfred was newly diagnosed with anxiety disorder. The physician prescribed buspirone (BuSpar). The nurse is aware that the teaching instructions for newly prescribed buspirone should include which of the following? a. A warning about the drugs delayed therapeutic effect, which is from 14 to 30 days. b. A warning about the incidence of neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS). c. A reminder of the need to schedule blood work in 1 week to check blood levels of the drug. d. A warning that immediate sedation can occur with a resultant drop in pulse.
16.Richard with agoraphobia has been symptomfree for 4 months. Classic signs and symptoms of phobias include: a. Insomnia and an inability to concentrate. b. Severe anxiety and fear. c. Depression and weight loss. d. Withdrawal and failure to distinguish reality from fantasy. 17.Which medications have been found to help reduce or eliminate panic attacks? a. Antidepressants b. Anticholinergics c. Antipsychotics d. Mood stabilizers 18.A client seeks care because she feels depressed and has gained weight. To treat her atypical depression, the physician prescribes tranylcypromine sulfate (Parnate), 10 mg by mouth twice per day. When this drug is used to treat atypical depression, what is its onset of action? a. 1 to 2 days b. 3 to 5 days c. 6 to 8 days d. 10 to 14 days 19. A 65 years old client is in the first stage of Alzheimers disease. Nurse Patricia should plan to focus this clients care on: a. Offering nourishing finger foods to help maintain the clients nutritional status. b. Providing emotional support and individual counseling. c. Monitoring the client to prevent minor illnesses from turning into major problems. d. Suggesting new activities for the client and family to do together. 20.The nurse is assessing a client who has just been admitted to the emergency department. Which signs would suggest an overdose of an antianxiety agent? a. Combativeness, sweating, and confusion b. Agitation, hyperactivity, and grandiose ideation c. Emotional lability, euphoria, and impaired memory d. Suspiciousness, dilated pupils, and increased blood pressure 21.The nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with antisocial personality disorder. The client has a history of fighting, cruelty to animals, and stealing. Which of the following traits would the nurse be most likely to uncover during assessment? a. History of gainful employment b. Frequent expression of guilt regarding antisocial behavior c. Demonstrated ability to maintain close, stable relationships d. A low tolerance for frustration 22.Nurse Amy is providing care for a male client undergoing opiate withdrawal. Opiate withdrawal causes severe physical discomfort and can be lifethreatening. To minimize these effects, opiate users are commonly detoxified with: a. Barbiturates b. Amphetamines c. Methadone d. Benzodiazepines 23.Nurse Cristina is caring for a client who experiences false sensory perceptions with no basis in reality. These perceptions are known as: a. Delusions b. Hallucinations
c. Loose associations d. Neologisms 24. Nurse Marco is developing a plan of care for a client with anorexia nervosa. Which action should the nurse include in the plan? a. Restricts visits with the family and friends until the client begins to eat. b. Provide privacy during meals. c. Set up a strict eating plan for the client. d. Encourage the client to exercise, which will reduce her anxiety. 25.Tim is admitted with a diagnosis of delusions of grandeur. The nurse is aware that this diagnosis reflects a belief that one is: a. Highly important or famous. b. Being persecuted c. Connected to events unrelated to oneself d. Responsible for the evil in the world. 26.Nurse Jen is caring for a male client with manic depression. The plan of care for a client in a manic state would include: a. Offering a high-calorie meals and strongly encouraging the client to finish all food. b. Insisting that the client remain active through the day so that hell sleep at night. c. Allowing the client to exhibit hyperactive, demanding, manipulative behavior without setting limits. d. Listening attentively with a neutral attitude and avoiding power struggles. 27.Ramon is admitted for detoxification after a cocaine overdose. The client tells the nurse that he frequently uses cocaine but that he can control his use if he chooses. Which coping mechanism is he using? a. Withdrawal b. Logical thinking c. Repression d. Denial 28.Richard is admitted with a diagnosis of schizotypal personality disorder. Which signs would this client exhibit during social situations? a. Aggressive behavior b. Paranoid thoughts c. Emotional affect d. Independence needs 29. Nurse Mickey is caring for a client diagnosed with bulimia. The most appropriate initial goal for a client diagnosed with bulimia is to: a. Avoid shopping for large amounts of food. b. Control eating impulses. c. Identify anxiety-causing situations d. Eat only three meals per day. 30.Rudolf is admitted for an overdose of amphetamines. When assessing the client, the nurse should expect to see: a. Tension and irritability b. Slow pulse c. Hypotension d. Constipation 31.Nicolas is experiencing hallucinations tells the nurse, The voices are telling me Im no good. The client asks if the nurse hears the voices. The most appropriate response by the nurse would be: a. It is the voice of your conscience, which only you can control. b. No, I do not hear your voices, but I believe you can hear them. c. The voices are coming from within you and only
you can hear them. d. Oh, the voices are a symptom of your illness; dont pay any attention to them. 32.The nurse is aware that the side effect of electroconvulsive therapy that a client may experience: a. Loss of appetite b. Postural hypotension c. Confusion for a time after treatment d. Complete loss of memory for a time 33.A dying male client gradually moves toward resolution of feelings regarding impending death. Basing care on the theory of Kubler-Ross, Nurse Trish plans to use nonverbal interventions when assessment reveals that the client is in the: a. Anger stage b. Denial stage c. Bargaining stage d. Acceptance stage 34.The outcome that is unrelated to a crisis state is: a. Learning more constructive coping skills b. Decompensation to a lower level of functioning. c. Adaptation and a return to a prior level of functioning. d. A higher level of anxiety continuing for more than 3 months. 35.Miranda a psychiatric client is to be discharged with orders for haloperidol (haldol) therapy. When developing a teaching plan for discharge, the nurse should include cautioning the client against: a. Driving at night b. Staying in the sun c. Ingesting wines and cheeses d. Taking medications containing aspirin 36.Jen a nursing student is anxious about the upcoming board examination but is able to study intently and does not become distracted by a roommates talking and loud music. The students ability to ignore distractions and to focus on studying demonstrates: a. Mild-level anxiety b. Panic-level anxiety c. Severe-level anxiety d. Moderate-level anxiety 37.When assessing a premorbid personality characteristics of a client with a major depression, it would be unusual for the nurse to find that this client demonstrated: a. Rigidity b. Stubbornness c. Diverse interest d. Over meticulousness 38.Nurse Krina recognizes that the suicidal risk for depressed client is greatest: a. As their depression begins to improve b. When their depression is most severe c. Before nay type of treatment is started d. As they lose interest in the environment 39.Nurse Kate would expect that a client with vascular dementis would experience: a. Loss of remote memory related to anoxia b. Loss of abstract thinking related to emotional state c. Inability to concentrate related to decreased stimuli d. Disturbance in recalling recent events related to cerebral hypoxia.
40.Josefina is to be discharged on a regimen of lithium carbonate. In the teaching plan for discharge the nurse should include: a. Advising the client to watch the diet carefully b. Suggesting that the client take the pills with milk c. Reminding the client that a CBC must be done once a month. d. Encouraging the client to have blood levels checked as ordered. 41.The psychiatrist orders lithium carbonate 600 mg p.o t.i.d for a female client. Nurse Katrina would be aware that the teaching about the side effects of this drug were understood when the client state, I will call my doctor immediately if I notice any: a. Sensitivity to bright light or sun b. Fine hand tremors or slurred speech c. Sexual dysfunction or breast enlargement d. Inability to urinate or difficulty when urinating 42.Nurse Mylene recognizes that the most important factor necessary for the establishment of trust in a critical care area is: a. Privacy b. Respect c. Empathy d. Presence 43.When establishing an initial nurse-client relationship, Nurse Hazel should explore with the client the: a. Clients perception of the presenting problem. b. Occurrence of fantasies the client may experience. c. Details of any ritualistic acts carried out by the client d. Clients feelings when external; controls are instituted. 44.Tranylcypromine sulfate (Parnate) is prescribed for a depressed client who has not responded to the tricyclic antidepressants. After teaching the client about the medication, Nurse Marian evaluates that learning has occurred when the client states, I will avoid: a. Citrus fruit, tuna, and yellow vegetables. b. Chocolate milk, aged cheese, and yogurt c. Green leafy vegetables, chicken, and milk. d. Whole grains, red meats, and carbonated soda. 45.Nurse John is a aware that most crisis situations should resolve in about: a. 1 to 2 weeks b. 4 to 6 weeks c. 4 to 6 months d. 6 to 12 months 46. Nurse Judy knows that statistics show that in adolescent suicide behavior: a. Females use more dramatic methods than males b. Males account for more attempts than do females c. Females talk more about suicide before attempting it d. Males are more likely to use lethal methods than are females 47. Dervid with paranoid schizophrenia repeatedly uses profanity during an activity therapy session. Which response by the nurse would be most appropriate? a. Your behavior wont be tolerated. Go to your room immediately. b. Youre just doing this to get back at me for making you come to therapy. c. Your cursing is interrupting the activity. Take time out in your room for 10 minutes.
d. Im disappointed in you. You cant control yourself even for a few minutes. 48.Nurse Maureen knows that the nonantipsychotic medication used to treat some clients with schizoaffective disorder is: a. phenelzine (Nardil) b. chlordiazepoxide (Librium) c. lithium carbonate (Lithane) d. imipramine (Tofranil) 49.Which information is most important for the nurse Trinity to include in a teaching plan for a male schizophrenic client taking clozapine (Clozaril)? a. Monthly blood tests will be necessary. b. Report a sore throat or fever to the physician immediately. c. Blood pressure must be monitored for hypertension. d. Stop the medication when symptoms subside. 50.Ricky with chronic schizophrenia takes neuroleptic medication is admitted to the psychiatric unit. Nursing assessment reveals rigidity, fever, hypertension, and diaphoresis. These findings suggest which lifethreatening reaction: a. Tardive dyskinesia. b. Dystonia. c. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome. d. Akathisia. 51.Which nursing intervention would be most appropriate if a male client develop orthostatic hypotension while taking amitriptyline (Elavil)? a. Consulting with the physician about substituting a different type of antidepressant. b. Advising the client to sit up for 1 minute before getting out of bed. c. Instructing the client to double the dosage until the problem resolves. d. Informing the client that this adverse reaction should disappear within 1 week. 52.Mr. Cruz visits the physicians office to seek treatment for depression, feelings of hopelessness, poor appetite, insomnia, fatigue, low selfesteem, poor concentration, and difficulty making decisions. The client states that these symptoms began at least 2 years ago. Based on this report, the nurse Tyfany suspects: a. Cyclothymic disorder. b. Atypical affective disorder. c. Major depression. d. Dysthymic disorder. 53. After taking an overdose of phenobarbital (Barbita), Mario is admitted to the emergency department. Dr. Trinidad prescribes activated charcoal (Charcocaps) to be administered by mouth immediately. Before administering the dose, the nurse verifies the dosage ordered. What is the usual minimum dose of activated charcoal? a. 5 g mixed in 250 ml of water b. 15 g mixed in 500 ml of water c. 30 g mixed in 250 ml of water d. 60 g mixed in 500 ml of water 54.What herbal medication for depression, widely used in Europe, is now being prescribed in the United States? a. Ginkgo biloba b. Echinacea c. St. Johns wort d. Ephedra 55.Cely with manic episodes is taking lithium. Which electrolyte level should the nurse check before administering this medication?
a. Calcium b. Sodium c. Chloride d. Potassium 56.Nurse Josefina is caring for a client who has been diagnosed with delirium. Which statement about delirium is true? a. Its characterized by an acute onset and lasts about 1 month. b. Its characterized by a slowly evolving onset and lasts about 1 week. c. Its characterized by a slowly evolving onset and lasts about 1 month. d. Its characterized by an acute onset and lasts hours to a number of days. 57.Edward, a 66 year old client with slight memory impairment and poor concentration is diagnosed with primary degenerative dementia of the Alzheimers type. Early signs of this dementia include subtle personality changes and withdrawal from social interactions. To assess for progression to the middle stage of Alzheimers disease, the nurse should observe the client for: a. Occasional irritable outbursts. b. Impaired communication. c. Lack of spontaneity. d. Inability to perform self-care activities. 58.Isabel with a diagnosis of depression is started on imipramine (Tofranil), 75 mg by mouth at bedtime. The nurse should tell the client that: a. This medication may be habit forming and will be discontinued as soon as the client feels better. b. This medication has no serious adverse effects. c. The client should avoid eating such foods as aged cheeses, yogurt, and chicken livers while taking the medication. d. This medication may initially cause tiredness, which should become less bothersome over time. 59.Kathleen is admitted to the psychiatric clinic for treatment of anorexia nervosa. To promote the clients physical health, the nurse should plan to: a. Severely restrict the clients physical activities. b. Weigh the client daily, after the evening meal. c. Monitor vital signs, serum electrolyte levels, and acid-base balance. d. Instruct the client to keep an accurate record of food and fluid intake. 60.Celia with a history of polysubstance abuse is admitted to the facility. She complains of nausea and vomiting 24 hours after admission. The nurse assesses the client and notes piloerection, pupillary dilation, and lacrimation. The nurse suspects that the client is going through which of the following withdrawals? a. Alcohol withdrawal b. Cannibis withdrawal c. Cocaine withdrawal d. Opioid withdrawal 61.Mr. Garcia, an attorney who throws books and furniture around the office after losing a case is referred to the psychiatric nurse in the law firms employee assistance program. Nurse Beatriz knows that the clients behavior most likely represents the use of which defense mechanism? a. Regression b. Projection c. Reaction-formation d. Intellectualization 62.Nurse Anne is caring for a client who has been treated long term with antipsychotic medication. During the assessment, Nurse Anne checks the
client for tardive dyskinesia. If tardive dyskinesia is present, Nurse Anne would most likely observe: a. Abnormal movements and involuntary movements of the mouth, tongue, and face. b. Abnormal breathing through the nostrils accompanied by a thrill. c. Severe headache, flushing, tremors, and ataxia. d. Severe hypertension, migraine headache, 63.Dennis has a lithium level of 2.4 mEq/L. The nurse immediately would assess the client for which of the following signs or symptoms? a. Weakness b. Diarrhea c. Blurred vision d. Fecal incontinence 64.Nurse Jannah is monitoring a male client who has been placed inrestraints because of violent behavior. Nurse determines that it will be safe to remove the restraints when: a. The client verbalizes the reasons for the violent behavior. b. The client apologizes and tells the nurse that it will never happen again. c. No acts of aggression have been observed within 1 hour after the release of two of the extremity restraints. d. The administered medication has taken effect. 65.Nurse Irish is aware that Ritalin is the drug of choice for a child with ADHD. The side effects of the following may be noted by the nurse: a. Increased attention span and concentration b. Increase in appetite c. Sleepiness and lethargy d. Bradycardia and diarrhea 66.Kitty, a 9 year old child has very limited vocabulary and interaction skills. She has an I.Q. of 45. She is diagnosed to have Mental retardation of this classification: a. Profound b. Mild c. Moderate d. Severe 67.The therapeutic approach in the care of Armand an autistic child include the following EXCEPT: a. Engage in diversionary activities when acting -out b. Provide an atmosphere of acceptance c. Provide safety measures d. Rearrange the environment to activate the child 68.Jeremy is brought to the emergency room by friends who state that he took something an hour ago. He is actively hallucinating, agitated, with irritated nasal septum. a. Heroin b. Cocaine c. LSD d. Marijuana 69.Nurse Pauline is aware that Dementia unlike delirium is characterized by: a. Slurred speech b. Insidious onset c. Clouding of consciousness d. Sensory perceptual change 70.A 35 year old female has intense fear of riding an elevator. She claims As if I will die inside. The client is suffering from: a. Agoraphobia b. Social phobia
c. Claustrophobia d. Xenophobia 71.Nurse Myrna develops a counter-transference reaction. This is evidenced by: a. Revealing personal information to the client b. Focusing on the feelings of the client. c. Confronting the client about discrepancies in verbal or non-verbal behavior d. The client feels angry towards the nurse who resembles his mother. 72.Tristan is on Lithium has suffered from diarrhea and vomiting. What should the nurse in-charge do first: a. Recognize this as a drug interaction b. Give the client Cogentin c. Reassure the client that these are common side effects of lithium therapy d. Hold the next dose and obtain an order for a stat serum lithium level 73.Nurse Sarah ensures a therapeutic environment for all the client. Which of the following best describes a therapeutic milieu? a. A therapy that rewards adaptive behavior b. A cognitive approach to change behavior c. A living, learning or working environment. d. A permissive and congenial environment 74.Anthony is very hostile toward one of the staff for no apparent reason. He is manifesting: a. Splitting b. Transference c. Countertransference d. Resistance 75.Marielle, 17 years old was sexually attacked while on her way home from school. She is brought to the hospital by her mother. Rape is an example of which type of crisis: a. Situational b. Adventitious c. Developmental d. Internal 76. Nurse Greta is aware that the following is classified as an Axis I disorder by the Diagnosis and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Text Revision (DSM-IV-TR) is: a. Obesity b. Borderline personality disorder c. Major depression d. Hypertension 77.Katrina, a newly admitted is extremely hostile toward a staff member she has just met, without apparent reason. According to Freudian theory, the nurse should suspect that the client is experiencing which of the following phenomena? a. Intellectualization b. Transference c. Triangulation d. Splitting 78.An 83year-old male client is in extended care facility is anxious most of the time and frequently complains of a number of vague symptoms that interfere with his ability to eat. These symptoms indicate which of the following disorders? a. Conversion disorder b. Hypochondriasis c. Severe anxiety d. Sublimation 79. Charina, a college student who frequently visited the health center during the past year with multiple vague complaints of GI symptoms before
course examinations. Although physical causes have been eliminated, the student continues to express her belief that she has a serious illness. These symptoms are typically of which of the following disorders? a. Conversion disorder b. Depersonalization c. Hypochondriasis d. Somatization disorder 80. Nurse Daisy is aware that the following pharmacologic agents are sedativehypnotic medication is used to induce sleep for a client experiencing a sleep disorder is: a. Triazolam (Halcion) b. Paroxetine (Paxil)\ c. Fluoxetine (Prozac) d. Risperidone (Risperdal) 81. Aldo, with a somatoform pain disorder may obtain secondary gain. Which of the following statement refers to a secondary gain? a. It brings some stability to the family b. It decreases the preoccupation with the physical illness c. It enables the client to avoid some unpleasant activity d. It promotes emotional support or attention for the client 82. Dervid is diagnosed with panic disorder with agoraphobia is talking with the nurse in-charge about the progress made in treatment. Which of the following statements indicates a positive client response? a. I went to the mall with my friends last Saturday b. Im hyperventilating only when I have a panic attack c. Today I decided that I can stop taking my medication d. Last night I decided to eat more than a bowl of cereal 83. The effectiveness of monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor drug therapy in client with posttraumatic stress disorder can be demonstrated by which of the following client self reports? a. Im sleeping better and dont have nightmares b. Im not losing my temper as much c. Ive lost my craving for alcohol d. Ive lost my phobia for water 84. Mark, with a diagnosis of generalized anxiety disorder wants to stop taking his lorazepam (Ativan). Which of the following important facts should nurse Betty discuss with the client about discontinuing the medication? a. Stopping the drug may cause depression b. Stopping the drug increases cognitive abilities c. Stopping the drug decreases sleeping difficulties d. Stopping the drug can cause withdrawal symptoms 85. Jennifer, an adolescent who is depressed and reported by his parents as having difficulty in school is brought to the community mental health center to be evaluated. Which of the following other health problems would the nurse suspect? a. Anxiety disorder b. Behavioral difficulties c. Cognitive impairment d. Labile moods 86. Ricardo, an outpatient in psychiatric facility is diagnosed with dysthymic disorder. Which of the following statement about dysthymic disorder is true?
a. It involves a mood range from moderate depression to hypomania b. It involves a single manic depression c. Its a form of depression that occurs in the fall and winter d. Its a mood disorder similar to major depression but of mild to moderate severity 87. The nurse is aware that the following ways in vascular dementia different from Alzheimers disease is: a. Vascular dementia has more abrupt onset b. The duration of vascular dementia is usually brief c. Personality change is common in vascular dementia d. The inability to perform motor activities occurs in vascular dementia 88. Loretta, a newly admitted client was diagnosed with delirium and has history of hypertension and anxiety. She had been taking digoxin, furosemide (Lasix), and diazepam (Valium) for anxiety. This clients impairment may be related to which of the following conditions? a. Infection b. Metabolic acidosis c. Drug intoxication d. Hepatic encephalopathy 89. Nurse Ron enters a clients room, the client says, Theyre crawling on my sheets! Get them off my bed! Which of the following assessment is the most accurate? a. The client is experiencing aphasia b. The client is experiencing dysarthria c. The client is experiencing a flight of ideas d. The client is experiencing visual hallucination 90. Which of the following descriptions of a clients experience and behavior can be assessed as an illusion? a. The client tries to hit the nurse when vital signs must be taken b. The client says, I keep hearing a voice telling me to run away c. The client becomes anxious whenever the nurse leaves the bedside d. The client looks at the shadow on a wall and tells the nurse she sees frightening faces on the wall. 91. During conversation of Nurse John with a client, he observes that the client shift from one topic to the next on a regular basis. Which of the following terms describes this disorder? a. Flight of ideas b. Concrete thinking c. Ideas of reference d. Loose association 92. Francis tells the nurse that her coworkers are sabotaging the computer. When the nurse asks questions, the client becomes argumentative. This behavior shows personality traits associated with which of the following personality disorder? a. Antisocial b. Histrionic c. Paranoid d. Schizotypal 93. Which of the following interventions is important for a Cely experiencing with paranoid personality disorder taking olanzapine (Zyprexa)? a. Explain effects of serotonin syndrome b. Teach the client to watch for extrapyramidal adverse reaction c. Explain that the drug is less affective if the client smokes
d. Discuss the need to report paradoxical effects such as euphoria 94. Nurse Alexandra notices other clients on the unit avoiding a client diagnosed with antisocial personality disorder. When discussing appropriate behavior in group therapy, which of the following comments is expected about this client by his peers? a. Lack of honesty b. Belief in superstition c. Show of temper tantrums d. Constant need for attention 95. Tommy, with dependent personality disorder is working to increase his selfesteem. Which of the following statements by the Tommy shows teaching was successful? a. Im not going to look just at the negative things about myself b. Im most concerned about my level of competence and progress c. Im not as envious of the things other people have as I used to be d. I find I cant stop myself from taking over things other should be doing 96. Norma, a 42-year-old client with a diagnosis of chronic undifferentiated schizophrenia lives in a rooming house that has a weekly nursing clinic. She scratches while she tells the nurse she feels creatures eating away at her skin. Which of the following interventions should be done first? a. Talk about his hallucinations and fears b. Refer him for anticholinergic adverse reactions c. Assess for possible physical problems such as rash d. Call his physician to get his medication increased to control his psychosis 97. Ivy, who is on the psychiatric unit is copying and imitating the movements of her primary nurse. During recovery, she says, I thought the nurse was my mirror. I felt connected only when I saw my nurse. This behavior is known by which of the following terms? a. Modeling b. Echopraxia c. Ego-syntonicity d. Ritualism 98. Jun approaches the nurse and tells that he hears a voice telling him that hes evil and deserves to die. Which of the following terms describes the clients perception? a. Delusion b. Disorganized speech c. Hallucination d. Idea of reference 99. Mike is admitted to a psychiatric unit with a diagnosis of undifferentiated schizophrenia. Which of the following defense mechanisms is probably used by mike? a. Projection b. Rationalization c. Regression d. Repression 100. Rocky has started taking haloperidol (Haldol). Which of the following instructions is most appropriate for Ricky before taking haloperidol? a. Should report feelings of restlessness or agitation at once b. Use a sunscreen outdoors on a year-round basis c. Be aware youll feel increased energy taking this drug
d. This drug will indirectly control essential hypertension
6. Answer: (C) Check circulation every 15-30 minutes. Rationale: Restraints encircle the limbs, which place the client at risk for circulation being restricted to the distal areas of the extremities. Checking the clients circulation every 15-30 minutes will allow the nurse to adjust the restraints before injury from decreased blood flow occurs. 7. Answer: (A) Prevent stress ulcer Rationale: Curlings ulcer occurs as a generalized stress response in burn patients. This results in a decreased production of mucus and increased secretion of gastric acid. The best treatment for this prophylactic use of antacids and H2 receptor blockers. 8. Answer: (D) Continue to monitor and record hourly urine output Rationale: Normal urine output for an adult is approximately 1 ml/minute (60 ml/hour). Therefore, this clients output is normal. Beyond continued evaluation, no nursing action is warranted. 9. Answer: (B) My ankle feels warm. Rationale: Ice application decreases pain and swelling. Continued or increased pain, redness, and increased warmth are signs of inflammation that shouldnt occur after ice application 10. Answer: (B) Hyperkalemia Rationale: A loop diuretic removes water and, along with it, sodium and potassium. This may result in hypokalemia, hypovolemia, and hyponatremia. 11. Answer:(A) Have condescending trust and confidence in their subordinates Rationale: Benevolent-authoritative managers pretentiously show their trust and confidence to their followers. ANSWERS NP 1 1. Answer: (D) The actions of a reasonably prudent nurse with similar education and experience. Rationale: The standard of care is determined by the average degree of skill, care, and diligence by nurses in similar circumstances. 2. Answer: (B) I.M Rationale: With a platelet count of 22,000/l, the clients tends to bleed easily. Therefore, the nurse should avoid using the I.M. route because the area is a highly vascular and can bleed readily when penetrated by a needle. The bleeding can be difficult to stop. 3. Answer: (C) Digoxin 0.125 mg P.O. once daily Rationale: The nurse should always place a zero before a decimal point so that no one misreads the figure, which could result in a dosage error. The nurse should never insert a zero at the end of a dosage that includes a decimal point because this could be misread, possibly leading to a tenfold increase in the dosage. 4. Answer: (A) Ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion related to venous congestion. Rationale: Ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion related to venous congestion takes the highest priority because venous inflammation and clot formation impede blood flow in a client with deep vein thrombosis. 5. Answer: (B) A 44 year-old myocardial infarction (MI) client who is complaining of nausea. Rationale: Nausea is a symptom of impending myocardial infarction (MI) and should be assessed immediately so that treatment can be instituted and further damage to the heart is avoided. 12. Answer: (A) Provides continuous, coordinated and comprehensive nursing services. Rationale: Functional nursing is focused on tasks and activities and not on the care of the patients. 13. Answer: (B) Standard written order Rationale: This is a standard written order. Prescribers write a single order for medications given only once. A stat order is written for medications given immediately for an urgent client problem. A standing order, also known as a protocol, establishes guidelines for treating a particular disease or set of symptoms in special care areas such as the coronary care unit. Facilities also may institute medication protocols that specifically designate drugs that a nurse may not give. 14. Answer: (D) Liquid or semi-liquid stools Rationale: Passage of liquid or semi-liquid stools results from seepage of unformed bowel contents around the impacted stool in the rectum. Clients with fecal impaction dont pass hard, brown, formed stools because the feces cant move past the impaction. These clients typically report the urge to defecate (although they cant pass stool) and a decreased appetite. 15. Answer: (C) Pulling the helix up and back Rationale: To perform an otoscopic examination on an adult, the nurse grasps the helix of the ear and pulls it up and back to straighten the ear canal. For a child, the nurse grasps the helix and pulls it down to straighten the ear canal. Pulling the lobule in any direction wouldnt straighten the ear canal for visualization. 16. Answer: (A) Protect the irritated skin from sunlight. Rationale: Irradiated skin is very sensitive and must be protected with clothing or sunblock. The priority approach is the avoidance of strong sunlight.
17. Answer: (C) Assist the client in removing dentures and nail polish. Rationale: Dentures, hairpins, and combs must be removed. Nail polish must be removed so that cyanosis can be easily monitored by observing the nail beds. 18. Answer: (D) Sudden onset of continuous epigastric and back pain. Rationale: The autodigestion of tissue by the pancreatic enzymes results in pain from inflammation, edema, and possible hemorrhage. Continuous, unrelieved epigastric or back pain reflects the inflammatory process in the pancreas. 19. Answer: (B) Provide high-protein, highcarbohydrate diet. Rationale: A positive nitrogen balance is important for meeting metabolic needs, tissue repair, and resistance to infection. Caloric goals may be as high as 5000 calories per day. 20. Answer: (A) Blood pressure and pulse rate. Rationale: The baseline must be established to recognize the signs of an anaphylactic or hemolytic reaction to the transfusion. 21. Answer: (D) Immobilize the leg before moving the client. Rationale: If the nurse suspects a fracture, splinting the area before moving the client is imperative. The nurse should call for emergency help if the client is not hospitalized and call for a physician for the hospitalized client. 22. Answer: (B) Admit the client into a private room. Rationale: The client who has a radiation implant is placed in a private room and has a limited number of visitors. This reduces the exposure of others to the radiation. 23. Answer: (C) Risk for infection Rationale: Agranulocytosis is characterized by a reduced number of leukocytes (leucopenia) and neutrophils (neutropenia) in the blood. The client is at high risk for infection because of the decreased body defenses against microorganisms. Deficient knowledge related to the nature of the disorder may be appropriate diagnosis but is not the priority. 24. Answer: (B) Place the client on the left side in the Trendelenburg position. Rationale: Lying on the left side may prevent air from flowing into the pulmonary veins. The Trendelenburg position increases intrathoracic pressure, which decreases the amount of blood pulled into the vena cava during aspiration. 25. Answer: (A) Autocratic. Rationale: The autocratic style of leadership is a task-oriented and directive. 26. Answer: (D) 2.5 cc Rationale: 2.5 cc is to be added, because only a 500 cc bag of solution is being medicated instead of a 1 liter. 27. Answer: (A) 50 cc/ hour Rationale: A rate of 50 cc/hr. The child is to receive 400 cc over a period of 8 hours = 50 cc/hr. 28. Answer: (B) Assess the client for presence of pain. Rationale: Assessing the client for pain is a very important measure. Postoperative pain is an indication of complication. The nurse should also assess the client for pain to provide for the clients comfort. 29. Answer: (A) BP 80/60, Pulse 110 irregular Rationale: The classic signs of cardiogenic shock are low blood pressure, rapid and weak irregular pulse, cold, clammy skin, decreased urinary output, and cerebral hypoxia.
30. Answer: (A) Take the proper equipment, place the client in a comfortable position, and record the appropriate information in the clients chart. Rationale: It is a general or comprehensive statement about the correct procedure, and it includes the basic ideas which are found in the other options 31. Answer: (B) Evaluation Rationale: Evaluation includes observing the person, asking questions, and comparing the patients behavioral responses with the expected outcomes. 32. Answer: (C) History of present illness Rationale: The history of present illness is the single most important factor in assisting the health professional in arriving at a diagnosis or determining the persons needs. 33. Answer: (A) Trochanter roll extending from the crest of the ileum to the mid-thigh. Rationale: A trochanter roll, properly placed, provides resistance to the external rotation of the hip. 34. Answer: (C) Stage III Rationale: Clinically, a deep crater or without undermining of adjacent tissue is noted. 35. Answer: (A) Second intention healing Rationale: When wounds dehisce, they will allowed to heal by secondary intention 36. Answer: (D) Tachycardia Rationale: With an extracellular fluid or plasma volume deficit, compensatory mechanisms stimulate the heart, causing an increase in heart rate. 37. Answer: (A) 0.75 Rationale: To determine the number of milliliters the client should receive, the nurse uses the fraction method in the following equation. 75 mg/X ml = 100 mg/1 ml To solve for X, cross-multiply: 75 mg x 1 ml = X ml x 100 mg 75 = 100X 75/100 = X 0.75 ml (or ml) = X 38. Answer: (D) Its a measure of effect, not a standard measure of weight or quantity. Rationale: An insulin unit is a measure of effect, not a standard measure of weight or quantity. Different drugs measured in units may have no relationship to one another in quality or quantity. 39. Answer: (B) 38.9 C Rationale: To convert Fahrenheit degreed to Centigrade, use this formula C = (F 32) 1.8 C = (102 32) 1.8 C = 70 1.8 C = 38.9 40. Answer: (C) Failing eyesight, especially close vision. Rationale: Failing eyesight, especially close vision, is one of the first signs of aging in middle life (ages 46 to 64). More frequent aches and pains begin in the early late years (ages 65 to 79). Increase in loss of muscle tone occurs in later years (age 80 and older). 41. Answer: (A) Checking and taping all connections Rationale: Air leaks commonly occur if the system isnt secure. Checking all connections and taping them will prevent air leaks. The chest drainage system is kept lower to promote drainage not to prevent leaks. 42. Answer: (A) Check the clients identification band. Rationale: Checking the clients identification band
is the safest way to verify a clients identity because the band is assigned on admission and isnt be removed at any time. (If it is removed, it must be replaced). Asking the clients name or having the client repeated his name would be appropriate only for a client whos alert, oriented, and able to understand what is being said, but isnt the safe standard of practice. Names on bed arent always reliable 43. Answer: (B) 32 drops/minute Rationale: Giving 1,000 ml over 8 hours is the same as giving 125 ml over 1 hour (60 minutes). Find the number of milliliters per minute as follows: 125/60 minutes = X/1 minute 60X = 125 = 2.1 ml/minute To find the number of drops per minute: 2.1 ml/X gtt = 1 ml/ 15 gtt X = 32 gtt/minute, or 32 drops/minute 44. Answer: (A) Clamp the catheter Rationale: If a central venous catheter becomes disconnected, the nurse should immediately apply a catheter clamp, if available. If a clamp isnt available, the nurse can place a sterile syringe or catheter plug in the catheter hub. After cleaning the hub with alcohol or povidone-iodine solution, the nurse must replace the I.V. extension and restart the infusion. 45. Answer: (D) Auscultation, percussion, and palpation. Rationale: The correct order of assessment for examining the abdomen is inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation. The reason for this approach is that the less intrusive techniques should be performed before the more intrusive techniques. Percussion and palpation can alter natural findings during auscultation. 46. Answer: (D) Ulnar surface of the hand Rationale: The nurse uses the ulnar surface, or ball, of the hand to asses tactile fremitus, thrills, and vocal vibrations through the chest wall. The fingertips and finger pads best distinguish texture and shape. The dorsal surface best feels warmth. 47. Answer: (C) Formative Rationale: Formative (or concurrent) evaluation occurs continuously throughout the teaching and learning process. One benefit is that the nurse can adjust teaching strategies as necessary to enhance learning. Summative, or retrospective, evaluation occurs at the conclusion of the teaching and learning session. Informative is not a type of evaluation. 48. Answer: (B) Once per year Rationale: Yearly mammograms should begin at age 40 and continue for as long as the woman is in good health. If health risks, such as family history, genetic tendency, or past breast cancer, exist, more frequent examinations may be necessary. 49. Answer: (A) Respiratory acidosis Rationale: The client has a below-normal (acidic) blood pH value and an above-normal partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide (Paco2) value, indicating respiratory acidosis. In respiratory alkalosis, the pH value is above normal and in the Paco2 value is below normal. In metabolic acidosis, the pH and bicarbonate (Hco3) values are below normal. In metabolic alkalosis, the pH and Hco3 values are above normal. 50. Answer: (B) To provide support for the client and family in coping with terminal illness. Rationale: Hospices provide supportive care for terminally ill clients and their families. Hospice care doesnt focus on counseling regarding health care costs. Most client referred to hospices have been
treated for their disease without success and will receive only palliative care in the hospice. 51. Answer: (C) Using normal saline solution to clean the ulcer and applying a protective dressing as necessary. Rationale: Washing the area with normal saline solution and applying a protective dressing are within the nurses realm of interventions and will protect the area. Using a povidone-iodine wash and an antibiotic cream require a physicians order. Massaging with an astringent can further damage the skin. 52. Answer: (D) Foot Rationale: An elastic bandage should be applied form the distal area to the proximal area. This method promotes venous return. In this case, the nurse should begin applying the bandage at the clients foot. Beginning at the ankle, lower thigh, or knee does not promote venous return. 53. Answer: (B) Hypokalemia Rationale: Insulin administration causes glucose and potassium to move into the cells, causing hypokalemia. 54. Answer: (A) Throbbing headache or dizziness Rationale: Headache and dizziness often occur when nitroglycerin is taken at the beginning of therapy. However, the client usually develops tolerance55. Answer: (D) Check the clients level of consciousness Rationale: Determining unresponsiveness is the first step assessment action to take. When a client is in ventricular tachycardia, there is a significant decrease in cardiac output. However, checking the unresponsiveness ensures whether the client is affected by the decreased cardiac output. 56. Answer: (B) On the affected side of the client. Rationale: When walking with clients, the nurse should stand on the affected side and grasp the security belt in the midspine area of the small of the back. The nurse should position the free hand at the shoulder area so that the client can be pulled toward the nurse in the event that there is a forward fall. The client is instructed to look up and outward rather than at his or her feet. 57. Answer: (A) Urine output: 45 ml/hr Rationale: Adequate perfusion must be maintained to all vital organs in order for the client to remain visible as an organ donor. A urine output of 45 ml per hour indicates adequate renal perfusion. Low blood pressure and delayed capillary refill time are circulatory system indicators of inadequate perfusion. A serum pH of 7.32 is acidotic, which adversely affects all body tissues. 58. Answer: (D ) Obtaining the specimen from the urinary drainage bag. Rationale: A urine specimen is not taken from the urinary drainage bag. Urine undergoes chemical changes while sitting in the bag and does not necessarily reflect the current client status. In addition, it may become contaminated with bacteria from opening the system. 59. Answer: (B) Cover the client, place the call light within reach, and answer the phone call. Rationale: Because telephone call is an emergency, the nurse may need to answer it. The other appropriate action is to ask another nurse to accept the call. However, is not one of the options. To maintain privacy and safety, the nurse covers the client and places the call light within the clients reach. Additionally, the clients door should be closed or the room curtains pulled around the bathing area. 60. Answer: (C) Use a sterile plastic container for obtaining the specimen. Rationale: Sputum specimens for culture and
sensitivity testing need to be obtained using sterile techniques because the test is done to determine the presence of organisms. If the procedure for obtaining the specimen is not sterile, then the specimen is not sterile, then the specimen would be contaminated and the results of the test would be invalid. 61. Answer: (A) Puts all the four points of the walker flat on the floor, puts weight on the hand pieces, and then walks into it. Rationale: When the client uses a walker, the nurse stands adjacent to the affected side. The client is instructed to put all four points of the walker 2 feet forward flat on the floor before putting weight on hand pieces. This will ensure client safety and prevent stress cracks in the walker. The client is then instructed to move the walker forward and walk into it. 62. Answer: (C) Draws one line to cross out the incorrect information and then initials the change. Rationale: To correct an error documented in a medical record, the nurse draws one line through the incorrect information and then initials the error. An error is never erased and correction fluid is never used in the medical record. 63. Answer: (C) Secures the client safety belts after transferring to the stretcher. Rationale: During the transfer of the client after the surgical procedure is complete, the nurse should avoid exposure of the client because of the risk for potential heat loss. Hurried movements and rapid changes in the position should be avoided because these predispose the client to hypotension. At the time of the transfer from the surgery table to the stretcher, the client is still affected by the effects of the anesthesia; therefore, the client should not move self. Safety belts can prevent the client from falling off the stretcher. 64. Answer: (B) Gown and gloves Rationale: Contact precautions require the use of gloves and a gown if direct client contact is anticipated. Goggles are not necessary unless the nurse anticipates the splashes of blood, body fluids, secretions, or excretions may occur. Shoe protectors are not necessary. 65. Answer: (C) Quad cane Rationale: Crutches and a walker can be difficult to maneuver for a client with weakness on one side. A cane is better suited for client with weakness of the arm and leg on one side. However, the quad cane would provide the most stability because of the structure of the cane and because a quad cane has four legs. 66. Answer: (D) Left side-lying with the head of the bed elevated 45 degrees. Rationale: To facilitate removal of fluid from the chest wall, the client is positioned sitting at the edge of the bed leaning over the bedside table with the feet supported on a stool. If the client is unable to sit up, the client is positioned lying in bed on the unaffected side with the head of the bed elevated 30 to 45 degrees. 67. Answer: (D) Reliability Rationale: Reliability is consistency of the research instrument. It refers to the repeatability of the instrument in extracting the same responses upon its repeated administration. 68. Answer: (A) Keep the identities of the subject secret Rationale: Keeping the identities of the research subject secret will ensure anonymity because this will hinder providing link between the information given to whoever is its source.
69. Answer: (A) Descriptive- correlational Rationale: Descriptive- correlational study is the most appropriate for this study because it studies the variables that could be the antecedents of the increased incidence of nosocomial infection. 70. Answer: (C) Use of laboratory data Rationale: Incidence of nosocomial infection is best collected through the use of biophysiologic measures, particularly in vitro measurements, hence laboratory data is essential. 71. Answer: (B) Quasi-experiment Rationale: Quasi-experiment is done when randomization and control of the variables are not possible. 72. Answer: (C) Primary source Rationale: This refers to a primary source which is a direct account of the investigation done by the investigator. In contrast to this is a secondary source, which is written by someone other than the original researcher. 73. Answer: (A) Non-maleficence Rationale: Non-maleficence means do not cause harm or do any action that will cause any harm to the patient/client. To do good is referred as beneficence. 74. Answer: (C) Res ipsa loquitor Rationale: Res ipsa loquitor literally means the thing speaks for itself. This means in operational terms that the injury caused is the proof that there was a negligent act. 75. Answer: (B) The Board can investigate violations of the nursing law and code of ethics Rationale: Quasi-judicial power means that the Board of Nursing has the authority to investigate violations of the nursing law and can issue summons, subpoena or subpoena duces tecum as needed. 76. Answer: (C) May apply for re-issuance of his/her license based on certain conditions stipulated in RA 9173 Rationale: RA 9173 sec. 24 states that for equity and justice, a revoked license maybe re-issued provided that the following conditions are met: a) the cause for revocation of license has already been corrected or removed; and, b) at least four years has elapsed since the license has been revoked. 77. Answer: (B) Review related literature Rationale: After formulating and delimiting the research problem, the researcher conducts a review of related literature to determine the extent of what has been done on the study by previous researchers. 78. Answer: (B) Hawthorne effect Rationale: Hawthorne effect is based on the study of Elton Mayo and company about the effect of an intervention done to improve the working conditions of the workers on their productivity. It resulted to an increased productivity but not due to the intervention but due to the psychological effects of being observed. They performed differently because they were under observation. 79. Answer: (B) Determines the different nationality of patients frequently admitted and decides to get representations samples from each. Rationale: Judgment sampling involves including samples according to the knowledge of the investigator about the participants in the study. 80. Answer: (B) Madeleine Leininger Rationale: Madeleine Leininger developed the theory on transcultural theory based on her observations on the behavior of selected people within a culture.
81. Answer: (A) Random Rationale: Random sampling gives equal chance for all the elements in the population to be picked as part of the sample. 82. Answer: (A) Degree of agreement and disagreement Rationale: Likert scale is a 5-point summated scale used to determine the degree of agreement or disagreement of the respondents to a statement in a study 83. Answer: (B) Sr. Callista Roy Rationale: Sr. Callista Roy developed the Adaptation Model which involves the physiologic mode, selfconcept mode, role function mode and dependence mode. 84. Answer: (A) Span of control Rationale: Span of control refers to the number of workers who report directly to a manager. 85. Answer: (B) Autonomy Rationale: Informed consent means that the patient fully understands about the surgery, including the risks involved and the alternative solutions. In giving consent it is done with full knowledge and is given freely. The action of allowing the patient to decide whether a surgery is to be done or not exemplifies the bioethical principle of autonomy. 86. Answer: (C) Avoid wearing canvas shoes. Rationale: The client should be instructed to avoid wearing canvas shoes. Canvas shoes cause the feet to perspire, which may, in turn, cause skin irritation and breakdown. Both cotton and cornstarch absorb perspiration. The client should be instructed to cut toenails straight across with nail clippers. 87. Answer: (D) Ground beef patties Rationale: Meat is an excellent source of complete protein, which this client needs to repair the tissue breakdown caused by pressure ulcers. Oranges and broccoli supply vitamin C but not protein. Ice cream supplies only some incomplete protein, making it less helpful in tissue repair. 88. Answer: (D) Sims left lateral Rationale: The Sims left lateral position is the most common position used to administer a cleansing enema because it allows gravity to aid the flow of fluid along the curve of the sigmoid colon. If the client cant assume this position nor has poor sphincter control, the dorsal recumbent or right lateral position may be used. The supine and prone positions are inappropriate and uncomfortable for the client. 89. Answer: (A) Arrange for typing and cross matching of the clients blood. Rationale: The nurse first arranges for typing and cross matching of the clients blood to ensure compatibility with donor blood. The other options, although appropriate when preparing to administer a blood transfusion, come later. 90. Answer: (A) Independent Rationale: Nursing interventions are classified as independent, interdependent, or dependent. Altering the drug schedule to coincide with the clients daily routine represents an independent intervention, whereas consulting with the physician and pharmacist to change a clients medication because of adverse reactions represents an interdependent intervention. Administering an already-prescribed drug on time is a dependent intervention. An intradependent nursing intervention doesnt exist. 91. Answer: (D) Evaluation Rationale: The nursing actions described constitute evaluation of the expected outcomes. The findings
show that the expected outcomes have been achieved. Assessment consists of the clients history, physical examination, and laboratory studies. Analysis consists of considering assessment information to derive the appropriate nursing diagnosis. Implementation is the phase of the nursing process where the nurse puts the plan of care into action. 92. Answer: (B) To observe the lower extremities Rationale: Elastic stockings are used to promote venous return. The nurse needs to remove them once per day to observe the condition of the skin underneath the stockings. Applying the stockings increases blood flow to the heart. When the stockings are in place, the leg muscles can still stretch and relax, and the veins can fill with blood. 93. Answer:(A) Instructing the client to report any itching, swelling, or dyspnea. Rationale: Because administration of blood or blood products may cause serious adverse effects such as allergic reactions, the nurse must monitor the client for these effects. Signs and symptoms of lifethreatening allergic reactions include itching, swelling, and dyspnea. Although the nurse should inform the client of the duration of the transfusion and should document its administration, these actions are less critical to the clients immediate health. The nurse should assess vital signs at least hourly during the transfusion. 94. Answer: (B) Decrease the rate of feedings and the concentration of the formula. Rationale: Complaints of abdominal discomfort and nausea are common in clients receiving tube feedings. Decreasing the rate of the feeding and the concentration of the formula should decrease the clients discomfort. Feedings are normally given at room temperature to minimize abdominal cramping. To prevent aspiration during feeding, the head of the clients bed should be elevated at least 30 degrees. Also, to prevent bacterial growth, feeding containers should be routinely changed every 8 to 12 hours. 95. Answer: (D) Roll the vial gently between the palms. Rationale: Rolling the vial gently between the palms produces heat, which helps dissolve the medication. Doing nothing or inverting the vial wouldnt help dissolve the medication. Shaking the vial vigorously could cause the medication to break down, altering its action. 96. Answer: (B) Assist the client to the semi-Fowler position if possible. Rationale: By assisting the client to the semi-Fowler position, the nurse promotes easier chest expansion, breathing, and oxygen intake. The nurse should secure the elastic band so that the face mask fits comfortably and snugly rather than tightly, which could lead to irritation. The nurse should apply the face mask from the clients nose down to the chin not vice versa. The nurse should check the connectors between the oxygen equipment and humidifier to ensure that theyre airtight; loosened connectors can cause loss of oxygen. 97. Answer: (B) 4 hours Rationale: A unit of packed RBCs may be given over a period of between 1 and 4 hours. It shouldnt infuse for longer than 4 hours because the risk of contamination and sepsis increases after that time. Discard or return to the blood bank any blood not given within this time, according to facility policy. 98. Answer: (B) Immediately before administering the next dose. Rationale: Measuring the blood drug concentration helps determine whether the dosing has achieved the therapeutic goal. For measurement of the trough, or lowest, blood level of a drug, the nurse
draws a blood sample immediately before administering the next dose. Depending on the drugs duration of action and half-life, peak blood drug levels typically are drawn after administering the next dose. 99. Answer: (A) The nurse can implement medication orders quickly. Rationale: A floor stock system enables the nurse to implement medication orders quickly. It doesnt allow for pharmacist input, nor does it minimize transcription errors or reinforce accurate calculations. 100. Answer: (C) Shifting dullness over the abdomen. Rationale: Shifting dullness over the abdomen indicates ascites, an abnormal finding. The other options are normal abdominal findings. NP 2 1. Answer: (A) Inevitable Rationale: An inevitable abortion is termination of pregnancy that cannot be prevented. Moderate to severe bleeding with mild cramping and cervical dilation would be noted in this type of abortion. 2. Answer: (B) History of syphilis Rationale: Maternal infections such as syphilis, toxoplasmosis, and rubella are causes of spontaneous abortion. 3. Answer: (C) Monitoring apical pulse Rationale: Nursing care for the client with a possible ectopic pregnancy is focused on preventing or identifying hypovolemic shock and controlling pain. An elevated pulse rate is an indicator of shock. 4. Answer: (B) Increased caloric intake Rationale: Glucose crosses the placenta, but insulin does not. High fetal demands for glucose, combined with the insulin resistance caused by hormonal changes in the last half of pregnancy can result in elevation of maternal blood glucose levels. This increases the mothers demand for insulin and is referred to as the diabetogenic effect of pregnancy. 5. Answer: (A) Excessive fetal activity. Rationale: The most common signs and symptoms of hydatidiform mole includes elevated levels of human chorionic gonadotropin, vaginal bleeding, larger than normal uterus for gestational age, failure to detect fetal heart activity even with sensitive instruments, excessive nausea and vomiting, and early development of pregnancyinduced hypertension. Fetal activity would not be noted. 6. Answer: (B) Absent patellar reflexes Rationale: Absence of patellar reflexes is an indicator of hypermagnesemia, which requires administration of calcium gluconate. 7. Answer: (C) Presenting part in 2 cm below the plane of the ischial spines. Rationale: Fetus at station plus two indicates that the presenting part is 2 cm below the plane of the ischial spines. 8. Answer: (A) Contractions every 1 minutes lasting 70-80 seconds. Rationale: Contractions every 1 minutes lasting 70-80 seconds, is indicative of hyperstimulation of the uterus, which could result in injury to the mother and the fetus if Pitocin is not discontinued. 9. Answer: (C) EKG tracings Rationale: A potential side effect of calcium gluconate administration is cardiac arrest. Continuous monitoring of cardiac activity (EKG) throught administration of calcium gluconate is an essential part of care.
10. Answer: (D) First low transverse caesarean was for breech position. Fetus in this pregnancy is in a vertex presentation. Rationale: This type of client has no obstetrical indication for a caesarean section as she did with her first caesarean delivery. 11. Answer: (A) Talk to the mother first and then to the toddler. Rationale: When dealing with a crying toddler, the best approach is to talk to the mother and ignore the toddler first. This approach helps the toddler get used to the nurse before she attempts any procedures. It also gives the toddler an opportunity to see that the mother trusts the nurse. 12. Answer: (D) Place the infants arms in soft elbow restraints. Rationale: Soft restraints from the upper arm to the wrist prevent the infant from touching her lip but allow him to hold a favorite item such as a blanket. Because they could damage the operative site, such as objects as pacifiers, suction catheters, and small spoons shouldnt be placed in a babys mouth after cleft repair. A baby in a prone position may rub her face on the sheets and traumatize the operative site. The suture line should be cleaned gently to prevent infection, which could interfere with healing and damage the cosmetic appearance of the repair. 13. Answer: (B) Allow the infant to rest before feeding. Rationale: Because feeding requires so much energy, an infant with heart failure should rest before feeding. 14. Answer: (C) Iron-rich formula only. Rationale: The infants at age 5 months should receive iron-rich formula and that they shouldnt receive solid food, even baby food until age 6 months. 15. Answer: (D) 10 months Rationale: A 10 month old infant can sit alone and understands object permanence, so he would look for the hidden toy. At age 4 to 6 months, infants cant sit securely alone. At age 8 months, infants can sit securely alone but cannot understand the permanence of objects. 16. Answer: (D) Public health nursing focuses on preventive, not curative, services. Rationale: The catchments area in PHN consists of a residential community, many of whom are well individuals who have greater need for preventive rather than curative services. 17. Answer: (B) Efficiency Rationale: Efficiency is determining whether the goals were attained at the least possible cost. 18. Answer: (D) Rural Health Unit Rationale: R.A. 7160 devolved basic health services to local government units (LGUs ). The public health nurse is an employee of the LGU. 19. Answer: (A) Mayor Rationale: The local executive serves as the chairman of the Municipal Health Board. 20. Answer: (A) 1 Rationale: Each rural health midwife is given a population assignment of about 5,000. 21. Answer: (B) Health education and community organizing are necessary in providing community health services. Rationale: The community health nurse develops the health capability of people through health education and community organizing activities. 22. Answer: (B) Measles Rationale: Presidential Proclamation No. 4 is on the Ligtas Tigdas Program.
23. Answer: (D) Core group formation Rationale: In core group formation, the nurse is able to transfer the technology of community organizing to the potential or informal community leaders through a training program. 24. Answer: (D) To maximize the communitys resources in dealing with health problems. Rationale: Community organizing is a developmental service, with the goal of developing the peoples self-reliance in dealing with community health problems. A, B and C are objectives of contributory objectives to this goal. 25. Answer: (D) Terminal Rationale: Tertiary prevention involves rehabilitation, prevention of permanent disability and disability limitation appropriate for convalescents, the disabled, complicated cases and the terminally ill (those in the terminal stage of a disease). 26. Answer: (A) Intrauterine fetal death. Rationale: Intrauterine fetal death, abruptio placentae, septic shock, and amniotic fluid embolism may trigger normal clotting mechanisms; if clotting factors are depleted, DIC may occur. Placenta accreta, dysfunctional labor, and premature rupture of the membranes arent associated with DIC. 27. Answer: (C) 120 to 160 beats/minute Rationale: A rate of 120 to 160 beats/minute in the fetal heart appropriate for filling the heart with blood and pumping it out to the system. 28. Answer: (A) Change the diaper more often. Rationale: Decreasing the amount of time the skin comes contact with wet soiled diapers will help heal the irritation. 29. Answer: (D) Endocardial cushion defect Rationale: Endocardial cushion defects are seen most in children with Down syndrome, asplenia, or polysplenia. 30. Answer: (B) Decreased urine output Rationale: Decreased urine output may occur in clients receiving I.V. magnesium and should be monitored closely to keep urine output at greater than 30 ml/hour, because magnesium is excreted through the kidneys and can easily accumulate to toxic levels. 31. Answer: (A) Menorrhagia Rationale: Menorrhagia is an excessive menstrual period. 32. Answer: (C) Blood typing Rationale: Blood type would be a critical value to have because the risk of blood loss is always a potential complication during the labor and delivery process. Approximately 40% of a womans cardiac output is delivered to the uterus, therefore, blood loss can occur quite rapidly in the event of uncontrolled bleeding. 33. Answer: (D) Physiologic anemia Rationale: Hemoglobin values and hematocrit decrease during pregnancy as the increase in plasma volume exceeds the increase in red blood cell production. 34. Answer: (D) A 2 year old infant with stridorous breath sounds, sitting up in his mothers arms and drooling. Rationale: The infant with the airway emergency should be treated first, because of the risk of epiglottitis. 35. Answer: (A) Placenta previa Rationale: Placenta previa with painless vaginal bleeding.
36. Answer: (D) Early in the morning Rationale: Based on the nurses knowledge of microbiology, the specimen should be collected early in the morning. The rationale for this timing is that, because the female worm lays eggs at night around the perineal area, the first bowel movement of the day will yield the best results. The specific type of stool specimen used in the diagnosis of pinworms is called the tape test. 37. Answer: (A) Irritability and seizures Rationale: Lead poisoning primarily affects the CNS, causing increased intracranial pressure. This condition results in irritability and changes in level of consciousness, as well as seizure disorders, hyperactivity, and learning disabilities. 38. Answer: (D) I really need to use the diaphragm and jelly most during the middle of my menstrual cycle. Rationale: The woman must understand that, although the fertile period is approximately midcycle, hormonal variations do occur and can result in early or late ovulation. To be effective, the diaphragm should be inserted before every intercourse. 39. Answer: (C) Restlessness Rationale: In a child, restlessness is the earliest sign of hypoxia. Late signs of hypoxia in a child are associated with a change in color, such as pallor or cyanosis. 40. Answer: (B) Walk one step ahead, with the childs hand on the nurses elbow. Rationale: This procedure is generally recommended to follow in guiding a person who is blind. 41. Answer: (A) Loud, machinery-like murmur. Rationale: A loud, machinery-like murmur is a characteristic finding associated with patent ductus arteriosus. 42. Answer: (C) More oxygen, and the newborns metabolic rate increases. Rationale: When cold, the infant requires more oxygen and there is an increase in metabolic rate. Non-shievering thermogenesis is a complex process that increases the metabolic rate and rate of oxygen consumption, therefore, the newborn increase heat production. 43. Answer: (D) Voided Rationale: Before administering potassium I.V. to any client, the nurse must first check that the clients kidneys are functioning and that the client is voiding. If the client is not voiding, the nurse should withhold the potassium and notify the physician. 44. Answer: (c) Laundry detergent Rationale: Eczema or dermatitis is an allergic skin reaction caused by an offending allergen. The topical allergen that is the most common causative factor is laundry detergent. 45. Answer: (A) 6 inches Rationale: This distance allows for easy flow of the formula by gravity, but the flow will be slow enough not to overload the stomach too rapidly. 46. Answer: (A) The older one gets, the more susceptible he becomes to the complications of chicken pox. Rationale: Chicken pox is usually more severe in adults than in children. Complications, such as pneumonia, are higher in incidence in adults. 47. Answer: (D) Consult a physician who may give them rubella immunoglobulin. Rationale: Rubella vaccine is made up of attenuated German measles viruses. This is contraindicated in pregnancy. Immune globulin, a specific prophylactic against German measles, may be given to pregnant women.
48. Answer: (A) Contact tracing Rationale: Contact tracing is the most practical and reliable method of finding possible sources of person-to-person transmitted infections, such as sexually transmitted diseases. 49. Answer: (D) Leptospirosis Rationale: Leptospirosis is transmitted through contact with the skin or mucous membrane with water or moist soil contaminated with urine of infected animals, like rats. 50. Answer: (B) Cholera Rationale: Passage of profuse watery stools is the major symptom of cholera. Both amebic and bacillary dysentery are characterized by the presence of blood and/or mucus in the stools. Giardiasis is characterized by fat malabsorption and, therefore, steatorrhea. 51. Answer: (A) Hemophilus influenzae Rationale: Hemophilus meningitis is unusual over the age of 5 years. In developing countries, the peak incidence is in children less than 6 months of age. Morbillivirus is the etiology of measles. Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis may cause meningitis, but age distribution is not specific in young children. 52. Answer: (B) Buccal mucosa Rationale: Kopliks spot may be seen on the mucosa of the mouth or the throat. 53. Answer: (A) 3 seconds Rationale: Adequate blood supply to the area allows the return of the color of the nailbed within 3 seconds. 54. Answer: (B) Severe dehydration Rationale: The order of priority in the management of severe dehydration is as follows: intravenous fluid therapy, referral to a facility where IV fluids can be initiated within 30 minutes, Oresol or nasogastric tube. When the foregoing measures are not possible or effective, then urgent referral to the hospital is done. 55. Answer: (A) 45 infants Rationale: To estimate the number of infants, multiply total population by 3%. 56. Answer: (A) DPT Rationale: DPT is sensitive to freezing. The appropriate storage temperature of DPT is 2 to 8 C only. OPV and measles vaccine are highly sensitive to heat and require freezing. MMR is not an immunization in the Expanded Program on Immunization. 57. Answer: (C) Proper use of sanitary toilets Rationale: The ova of the parasite get out of the human body together with feces. Cutting the cycle at this stage is the most effective way of preventing the spread of the disease to susceptible hosts. 58. Answer: (D) 5 skin lesions, positive slit skin smear Rationale: A multibacillary leprosy case is one who has a positive slit skin smear and at least 5 skin lesions. 59. Answer: (C) Thickened painful nerves Rationale: The lesion of leprosy is not macular. It is characterized by a change in skin color (either reddish or whitish) and loss of sensation, sweating and hair growth over the lesion. Inability to close the eyelids (lagophthalmos) and sinking of the nosebridge are late symptoms. 60. Answer: (B) Ask where the family resides. Rationale: Because malaria is endemic, the first question to determine malaria risk is where the clients family resides. If the area of residence is not a known endemic area, ask if the child had traveled
within the past 6 months, where she was brought and whether she stayed overnight in that area. 61. Answer: (A) Inability to drink Rationale: A sick child aged 2 months to 5 years must be referred urgently to a hospital if he/she has one or more of the following signs: not able to feed or drink, vomits everything, convulsions, abnormally sleepy or difficult to awaken. 62. Answer: (A) Refer the child urgently to a hospital for confinement. Rationale: Baggy pants is a sign of severe marasmus. The best management is urgent referral to a hospital. 63. Answer: (D) Let the child rest for 10 minutes then continue giving Oresol more slowly. Rationale: If the child vomits persistently, that is, he vomits everything that he takes in, he has to be referred urgently to a hospital. Otherwise, vomiting is managed by letting the child rest for 10 minutes and then continuing with Oresol administration. Teach the mother to give Oresol more slowly. 64. Answer: (B) Some dehydration Rationale: Using the assessment guidelines of IMCI, a child (2 months to 5 years old) with diarrhea is classified as having SOME DEHYDRATION if he shows 2 or more of the following signs: restless or irritable, sunken eyes, the skin goes back slow after a skin pinch. 65. Answer: (C) Normal Rationale: In IMCI, a respiratory rate of 50/minute or more is fast breathing for an infant aged 2 to 12 months. 66. Answer: (A) 1 year Rationale: The baby will have passive natural immunity by placental transfer of antibodies. The mother will have active artificial immunity lasting for about 10 years. 5 doses will give the mother lifetime protection. 67. Answer: (B) 4 hours Rationale: While the unused portion of other biologicals in EPI may be given until the end of the day, only BCG is discarded 4 hours after reconstitution. This is why BCG immunization is scheduled only in the morning. 68. Answer: (B) 6 months Rationale: After 6 months, the babys nutrient needs, especially the babys iron requirement, can no longer be provided by mothers milk alone. 69. Answer: (C) 24 weeks Rationale: At approximately 23 to 24 weeks gestation, the lungs are developed enough to sometimes maintain extrauterine life. The lungs are the most immature system during the gestation period. Medical care for premature labor begins much earlier (aggressively at 21 weeks gestation) 70. Answer: (B) Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) Rationale: Supine positioning is recommended to reduce the risk of SIDS in infancy. The risk of aspiration is slightly increased with the supine position. Suffocation would be less likely with an infant supine than prone and the position for GER requires the head of the bed to be elevated. 71. Answer: (C) Decreased temperature Rationale: Temperature instability, especially when it results in a low temperature in the neonate, may be a sign of infection. The neonates color often changes with an infection process but generally becomes ashen or mottled. The neonate with an infection will usually show a decrease in activity level or lethargy.
72. Answer: (D) Polycythemia probably due to chronic fetal hypoxia Rationale: The small-for-gestation neonate is at risk for developing polycythemia during the transitional period in an attempt to decrease hypoxia. The neonates are also at increased risk for developing hypoglycemia and hypothermia due to decreased glycogen stores. 73. Answer: (C) Desquamation of the epidermis Rationale: Postdate fetuses lose the vernix caseosa, and the epidermis may become desquamated. These neonates are usually very alert. Lanugo is missing in the postdate neonate. 74. Answer: (C) Respiratory depression Rationale: Magnesium sulfate crosses the placenta and adverse neonatal effects are respiratory depression, hypotonia, and bradycardia. The serum blood sugar isnt affected by magnesium sulfate. The neonate would be floppy, not jittery. 75. Answer: (C) Respiratory rate 40 to 60 breaths/minute Rationale: A respiratory rate 40 to 60 breaths/minute is normal for a neonate during the transitional period. Nasal flaring, respiratory rate more than 60 breaths/minute, and audible grunting are signs of respiratory distress. 76. Answer: (C) Keep the cord dry and open to air Rationale: Keeping the cord dry and open to air helps reduce infection and hastens drying. Infants arent given tub bath but are sponged off until the cord falls off. Petroleum jelly prevents the cord from drying and encourages infection. Peroxide could be painful and isnt recommended. 77. Answer: (B) Conjunctival hemorrhage Rationale: Conjunctival hemorrhages are commonly seen in neonates secondary to the cranial pressure applied during the birth process. Bulging fontanelles are a sign of intracranial pressure. Simian creases are present in 40% of the neonates with trisomy 21. Cystic hygroma is a neck mass that can affect the airway. 78. Answer: (B) To assess for prolapsed cord Rationale: After a client has an amniotomy, the nurse should assure that the cord isnt prolapsed and that the baby tolerated the procedure well. The most effective way to do this is to check the fetal heart rate. Fetal well-being is assessed via a nonstress test. Fetal position is determined by vaginal examination. Artificial rupture of membranes doesnt indicate an imminent delivery. 79. Answer: (D) The parents interactions with each other. Rationale: Parental interaction will provide the nurse with a good assessment of the stability of the familys home life but it has no indication for parental bonding. Willingness to touch and hold the newborn, expressing interest about the newborns size, and indicating a desire to see the newborn are behaviors indicating parental bonding. 80. Answer: (B) Instructing the client to use two or more peripads to cushion the area Rationale: Using two or more peripads would do little to reduce the pain or promote perineal healing. Cold applications, sitz baths, and Kegel exercises are important measures when the client has a fourth-degree laceration. 81. Answer: (C) What is your expected due date? Rationale: When obtaining the history of a client who may be in labor, the nurses highest priority is to determine her current status, particularly her due date, gravidity, and parity. Gravidity and parity affect the duration of labor and the potential for labor complications. Later, the nurse should ask about chronic illnesses, allergies, and support persons.
82. Answer: (D) Aspirate the neonates nose and mouth with a bulb syringe. Rationale: The nurses first action should be to clear the neonates airway with a bulb syringe. After the airway is clear and the neonates color improves, the nurse should comfort and calm the neonate. If the problem recurs or the neonates color doesnt improve readily, the nurse should notify the physician. Administering oxygen when the airway isnt clear would be ineffective. 83. Answer: (C) Conducting a bedside ultrasound for an amniotic fluid index. Rationale: It isnt within a nurses scope of practice to perform and interpret a bedside ultrasound under these conditions and without specialized training. Observing for pooling of strawcolored fluid, checking vaginal discharge with nitrazine paper, and observing for flakes of vernix are appropriate assessments for determining whether a client has ruptured membranes. 84. Answer: (C) Monitor partial pressure of oxygen (Pao2) levels. Rationale: Monitoring PaO2 levels and reducing the oxygen concentration to keep PaO2 within normal limits reduces the risk of retinopathy of prematurity in a premature infant receiving oxygen. Covering the infants eyes and humidifying the oxygen dont reduce the risk of retinopathy of prematurity. Because cooling increases the risk of acidosis, the infant should be kept warm so that his respiratory distress isnt aggravated. 85. Answer: (A) 110 to 130 calories per kg. Rationale: Calories per kg is the accepted way of determined appropriate nutritional intake for a newborn. The recommended calorie requirement is 110 to 130 calories per kg of newborn body weight. This level will maintain a consistent blood glucose level and provide enough calories for continued growth and development. 86. Answer: (C) 30 to 32 weeks Rationale: Individual twins usually grow at the same rate as singletons until 30 to 32 weeks gestation, then twins dont gain weight as rapidly as singletons of the same gestational age. The placenta can no longer keep pace with the nutritional requirements of both fetuses after 32 weeks, so theres some growth retardation in twins if they remain in utero at 38 to 40 weeks. 87. Answer: (A) conjoined twins Rationale: The type of placenta that develops in monozygotic twins depends on the time at which cleavage of the ovum occurs. Cleavage in conjoined twins occurs more than 13 days after fertilization. Cleavage that occurs less than 3 day after fertilization results in diamniotic dicchorionic twins. Cleavage that occurs between days 3 and 8 results in diamniotic monochorionic twins. Cleavage that occurs between days 8 to 13 result in monoamniotic monochorionic twins. 88. Answer: (D) Ultrasound Rationale: Once the mother and the fetus are stabilized, ultrasound evaluation of the placenta should be done to determine the cause of the bleeding. Amniocentesis is contraindicated in placenta previa. A digital or speculum examination shouldnt be done as this may lead to severe bleeding or hemorrhage. External fetal monitoring wont detect a placenta previa, although it will detect fetal distress, which may result from blood loss or placenta separation. 89. Answer: (A) Increased tidal volume Rationale: A pregnant client breathes deeper, which increases the tidal volume of gas moved in and out of the respiratory tract with each breath. The expiratory volume and residual volume decrease as the pregnancy progresses. The inspiratory capacity
increases during pregnancy. The increased oxygen consumption in the pregnant client is 15% to 20% greater than in the nonpregnant state. 90. Answer: (A) Diet Rationale: Clients with gestational diabetes are usually managed by diet alone to control their glucose intolerance. Oral hypoglycemic drugs are contraindicated in pregnancy. Long-acting insulin usually isnt needed for blood glucose control in the client with gestational diabetes. 91. Answer: (D) Seizure Rationale: The anticonvulsant mechanism of magnesium is believes to depress seizure foci in the brain and peripheral neuromuscular blockade. Hypomagnesemia isnt a complication of preeclampsia. Antihypertensive drug other than magnesium are preferred for sustained hypertension. Magnesium doesnt help prevent hemorrhage in preeclamptic clients. 92. Answer: (C) I.V. fluids Rationale: A sickle cell crisis during pregnancy is usually managed by exchange transfusion oxygen, and L.V. Fluids. The client usually needs a stronger analgesic than acetaminophen to control the pain of a crisis. Antihypertensive drugs usually arent necessary. Diuretic wouldnt be used unless fluid overload resulted. 93. Answer: (A) Calcium gluconate (Kalcinate) Rationale: Calcium gluconate is the antidote for magnesium toxicity. Ten milliliters of 10% calcium gluconate is given L.V. push over 3 to 5 minutes. Hydralazine is given for sustained elevated blood pressure in preeclamptic clients. Rho (D) immune globulin is given to women with Rh-negative blood to prevent antibody formation from RH-positive conceptions. Naloxone is used to correct narcotic toxicity. 94. Answer: (B) An indurated wheal over 10 mm in diameter appears in 48 to 72 hours. Rationale: A positive PPD result would be an indurated wheal over 10 mm in diameter that appears in 48 to 72 hours. The area must be a raised wheal, not a flat circumcised area to be considered positive. 95. Answer: (C) Pyelonephritis Rational: The symptoms indicate acute pyelonephritis, a serious condition in a pregnant client. UTI symptoms include dysuria, urgency, frequency, and suprapubic tenderness. Asymptomatic bacteriuria doesnt cause symptoms. Bacterial vaginosis causes milky white vaginal discharge but no systemic symptoms. 96. Answer: (B) Rh-positive fetal blood crosses into maternal blood, stimulating maternal antibodies. Rationale: Rh isoimmunization occurs when Rhpositive fetal blood cells cross into the maternal circulation and stimulate maternal antibody production. In subsequent pregnancies with Rhpositive fetuses, maternal antibodies may cross back into the fetal circulation and destroy the fetal blood cells. 97. Answer: (C) Supine position Rationale: The supine position causes compression of the clients aorta and inferior vena cava by the fetus. This, in turn, inhibits maternal circulation, leading to maternal hypotension and, ultimately, fetal hypoxia. The other positions promote comfort and aid labor progress. For instance, the lateral, or side-lying, position improves maternal and fetal circulation, enhances comfort, increases maternal relaxation, reduces muscle tension, and eliminates pressure points. The squatting position promotes comfort by taking advantage of gravity. The standing position also takes advantage of gravity and aligns the fetus with the pelvic angle.
98. Answer: (B) Irritability and poor sucking. Rationale: Neonates of heroin-addicted mothers are physically dependent on the drug and experience withdrawal when the drug is no longer supplied. Signs of heroin withdrawal include irritability, poor sucking, and restlessness. Lethargy isnt associated with neonatal heroin addiction. A flattened nose, small eyes, and thin lips are seen in infants with fetal alcohol syndrome. Heroin use during pregnancy hasnt been linked to specific congenital anomalies. 99. Answer: (A) 7th to 9th day postpartum Rationale: The normal involutional process returns the uterus to the pelvic cavity in 7 to 9 days. A significant involutional complication is the failure of the uterus to return to the pelvic cavity within the prescribed time period. This is known as subinvolution. 100. Answer: (B) Uterine atony Rationale: Multiple fetuses, extended labor stimulation with oxytocin, and traumatic delivery commonly are associated with uterine atony, which may lead to postpartum hemorrhage. Uterine inversion may precede or follow delivery and commonly results from apparent excessive traction on the umbilical cord and attempts to deliver the placenta manually. Uterine involution and some uterine discomfort are normal after delivery. NP 3 1. Answer: (C) Loose, bloody Rationale: Normal bowel function and soft-formed stool usually do not occur until around the seventh day following surgery. The stool consistency is related to how much water is being absorbed. 2. Answer: (A) On the clients right side Rationale: The client has left visual field blindness. The client will see only from the right side. 3. Answer: (C) Check respirations, stabilize spine, and check circulation Rationale: Checking the airway would be priority, and a neck injury should be suspected. 4. Answer: (D) Decreasing venous return through vasodilation. Rationale: The significant effect of nitroglycerin is vasodilation and decreased venous return, so the heart does not have to work hard. 5. Answer: (A) Call for help and note the time. Rationale: Having established, by stimulating the client, that the client is unconscious rather than sleep, the nurse should immediately call for help. This may be done by dialing the operator from the clients phone and giving the hospital code for cardiac arrest and the clients room number to the operator, of if the phone is not available, by pulling the emergency call button. Noting the time is important baseline information for cardiac arrest procedure. 6. Answer: (C) Make sure that the client takes food and medications at prescribed intervals. Rationale: Food and drug therapy will prevent the accumulation of hydrochloric acid, or will neutralize and buffer the acid that does accumulate. 7. Answer: (B) Continue treatment as ordered. Rationale: The effects of heparin are monitored by the PTT is normally 30 to 45 seconds; the therapeutic level is 1.5 to 2 times the normal level. 8. Answer: (B) In the operating room. Rationale: The stoma drainage bag is applied in the operating room. Drainage from the ileostomy contains secretions that are rich in digestive enzymes and highly irritating to the skin. Protection of the skin from the effects of these enzymes is begun at once. Skin exposed to these enzymes
even for a short time becomes reddened, painful, and excoriated. 9. Answer: (B) Flat on back. Rationale: To avoid the complication of a painful spinal headache that can last for several days, the client is kept in flat in a supine position for approximately 4 to 12 hours postoperatively. Headaches are believed to be causes by the seepage of cerebral spinal fluid from the puncture site. By keeping the client flat, cerebral spinal fluid pressures are equalized, which avoids trauma to the neurons. 10. Answer: (C) The client is oriented when aroused from sleep, and goes back to sleep immediately. Rationale: This finding suggest that the level of consciousness is decreasing. 11. Answer: (A) Altered mental status and dehydration Rationale: Fever, chills, hemortysis, dyspnea, cough, and pleuritic chest pain are the common symptoms of pneumonia, but elderly clients may first appear with only an altered lentil status and dehydration due to a blunted immune response. 12. Answer: (B) Chills, fever, night sweats, and hemoptysis Rationale: Typical signs and symptoms are chills, fever, night sweats, and hemoptysis. Chest pain may be present from coughing, but isnt usual. Clients with TB typically have low-grade fevers, not higher than 102F (38.9C). Nausea, headache, and photophobia arent usual TB symptoms. 13. Answer:(A) Acute asthma Rationale: Based on the clients history and symptoms, acute asthma is the most likely diagnosis. Hes unlikely to have bronchial pneumonia without a productive cough and fever and hes too young to have developed (COPD) and emphysema. 14. Answer: (B) Respiratory arrest Rationale: Narcotics can cause respiratory arrest if given in large quantities. Its unlikely the client will have asthma attack or a seizure or wake up on his own. 15. Answer: (D) Decreased vital capacity Rationale: Reduction in vital capacity is a normal physiologic changes include decreased elastic recoil of the lungs, fewer functional capillaries in the alveoli, and an increased in residual volume. 16. Answer: (C) Presence of premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) on a cardiac monitor. Rationale: Lidocaine drips are commonly used to treat clients whose arrhythmias havent been controlled with oral medication and who are having PVCs that are visible on the cardiac monitor. SaO2, blood pressure, and ICP are important factors but arent as significant as PVCs in the situation. 17. Answer: (B) Avoid foods high in vitamin K Rationale: The client should avoid consuming large amounts of vitamin K because vitamin K can interfere with anticoagulation. The client may need to report diarrhea, but isnt effect of taking an anticoagulant. An electric razor-not a straight razorshould be used to prevent cuts that cause bleeding. Aspirin may increase the risk of bleeding; acetaminophen should be used to pain relief. 18. Answer: (C) Clipping the hair in the area Rationale: Hair can be a source of infection and should be removed by clipping. Shaving the area can cause skin abrasions and depilatories can irritate the skin. 19. Answer: (A) Bone fracture Rationale: Bone fracture is a major complication of osteoporosis that results when loss of calcium and phosphate increased the fragility of bones. Estrogen
deficiencies result from menopause-not osteoporosis. Calcium and vitamin D supplements may be used to support normal bone metabolism, But a negative calcium balance isnt a complication of osteoporosis. Dowagers hump results from bone fractures. It develops when repeated vertebral fractures increase spinal curvature. 20. Answer: (C) Changes from previous examinations. Rationale: Women are instructed to examine themselves to discover changes that have occurred in the breast. Only a physician can diagnose lumps that are cancerous, areas of thickness or fullness that signal the presence of a malignancy, or masses that are fibrocystic as opposed to malignant. 21. Answer: (C) Balance the clients periods of activity and rest. Rationale: A client with hyperthyroidism needs to be encouraged to balance periods of activity and rest. Many clients with hyperthyroidism are hyperactive and complain of feeling very warm. 22. Answer: (B) Increase his activity level. Rationale: The client should be encouraged to increase his activity level. Maintaining an ideal weight; following a low-cholesterol, low sodium diet; and avoiding stress are all important factors in decreasing the risk of atherosclerosis. 23. Answer: (A) Laminectomy Rationale: The client who has had spinal surgery, such as laminectomy, must be log rolled to keep the spinal column straight when turning. Thoracotomy and cystectomy may turn themselves or may be assisted into a comfortable position. Under normal circumstances, hemorrhoidectomy is an outpatient procedure, and the client may resume normal activities immediately after surgery. 24. Answer: (D) Avoiding straining during bowel movement or bending at the waist. Rationale: The client should avoid straining, lifting heavy objects, and coughing harshly because these activities increase intraocular pressure. Typically, the client is instructed to avoid lifting objects weighing more than 15 lb (7kg) not 5lb. instruct the client when lying in bed to lie on either the side or back. The client should avoid bright light by wearing sunglasses. 25. Answer: (D) Before age 20. Rationale: Testicular cancer commonly occurs in men between ages 20 and 30. A male client should be taught how to perform testicular selfexamination before age 20, preferably when he enters his teens. 26. Answer: (B) Place a saline-soaked sterile dressing on the wound. Rationale: The nurse should first place salinesoaked sterile dressings on the open wound to prevent tissue drying and possible infection. Then the nurse should call the physician and take the clients vital signs. The dehiscence needs to be surgically closed, so the nurse should never try to close it. 27. Answer: (A) A progressively deeper breaths followed by shallower breaths with apneic periods. Rationale: Cheyne-Strokes respirations are breaths that become progressively deeper fallowed by shallower respirations with apneas periods. Biots respirations are rapid, deep breathing with abrupt pauses between each breath, and equal depth between each breath. Kussmauls respirations are rapid, deep breathing without pauses. Tachypnea is shallow breathing with increased respiratory rate. 28. Answer: (B) Fine crackles Rationale: Fine crackles are caused by fluid in the alveoli and commonly occur in clients with heart failure. Tracheal breath sounds are auscultated over the trachea. Coarse crackles are caused by
secretion accumulation in the airways. Friction rubs occur with pleural inflammation. 29. Answer: (B) The airways are so swollen that no air cannot get through Rationale: During an acute attack, wheezing may stop and breath sounds become inaudible because the airways are so swollen that air cant get through. If the attack is over and swelling has decreased, there would be no more wheezing and less emergent concern. Crackles do not replace wheezes during an acute asthma attack. 30. Answer: (D) Place the client on his side, remove dangerous objects, and protect his head. Rationale: During the active seizure phase, initiate precautions by placing the client on his side, removing dangerous objects, and protecting his head from injury. A bite block should never be inserted during the active seizure phase. Insertion can break the teeth and lead to aspiration. 31. Answer: (B) Kinked or obstructed chest tube Rationales: Kinking and blockage of the chest tube is a common cause of a tension pneumothorax. Infection and excessive drainage wont cause a tension pneumothorax. Excessive water wont affect the chest tube drainage. 32. Answer: (D) Stay with him but not intervene at this time. Rationale: If the client is coughing, he should be able to dislodge the object or cause a complete obstruction. If complete obstruction occurs, the nurse should perform the abdominal thrust maneuver with the client standing. If the client is unconscious, she should lay him down. A nurse should never leave a choking client alone. 33. Answer: (B) Current health promotion activities Rationale: Recognizing an individuals positive health measures is very useful. General health in the previous 10 years is important, however, the current activities of an 84 year old client are most significant in planning care. Family history of disease for a client in later years is of minor significance. Marital status information may be important for discharge planning but is not as significant for addressing the immediate medical problem. 34. Answer: (C) Place the client in a side lying position, with the head of the bed lowered. Rationale: The client should be positioned in a sidelying position with the head of the bed lowered to prevent aspiration. A small amount of toothpaste should be used and the mouth swabbed or suctioned to remove pooled secretions. Lemon glycerin can be drying if used for extended periods. Brushing the teeth with the client lying supine may lead to aspiration. Hydrogen peroxide is caustic to tissues and should not be used. 35. Answer: (C) Pneumonia Rationale: Fever productive cough and pleuritic chest pain are common signs and symptoms of pneumonia. The client with ARDS has dyspnea and hypoxia with worsening hypoxia over time, if not treated aggressively. Pleuritic chest pain varies with respiration, unlike the constant chest pain during an MI; so this client most likely isnt having an MI. the client with TB typically has a cough producing blood-tinged sputum. A sputum culture should be obtained to confirm the nurses suspicions. 36. Answer: (C) A 43-yesr-old homeless man with a history of alcoholism Rationale: Clients who are economically disadvantaged, malnourished, and have reduced immunity, such as a client with a history of alcoholism, are at extremely high risk for developing TB. A high school student, daycare worker, and businessman probably have a much low risk of contracting TB.
37. Answer: (C ) To determine the extent of lesions Rationale: If the lesions are large enough, the chest X-ray will show their presence in the lungs. Sputum culture confirms the diagnosis. There can be falsepositive and false-negative skin test results. A chest X-ray cant determine if this is a primary or secondary infection. 38. Answer: (B) Bronchodilators Rationale: Bronchodilators are the first line of treatment for asthma because broncho-constriction is the cause of reduced airflow. Beta adrenergic blockers arent used to treat asthma and can cause bronchoconstriction. Inhaled oral steroids may be given to reduce the inflammation but arent used for emergency relief. 39. Answer: (C) Chronic obstructive bronchitis Rationale: Because of this extensive smoking history and symptoms the client most likely has chronic obstructive bronchitis. Client with ARDS have acute symptoms of hypoxia and typically need large amounts of oxygen. Clients with asthma and emphysema tend not to have chronic cough or peripheral edema. 40. Answer: (A) The patient is under local anesthesia during the procedure Rationale: Before the procedure, the patient is administered with drugs that would help to prevent infection and rejection of the transplanted cells such as antibiotics, cytotoxic, and corticosteroids. During the transplant, the patient is placed under general anesthesia. 41. Answer: (D) Raise the side rails Rationale: A patient who is disoriented is at risk of falling out of bed. The initial action of the nurse should be raising the side rails to ensure patients safety. 42. Answer: (A) Crowd red blood cells Rationale: The excessive production of white blood cells crowd out red blood cells production which causes anemia to occur. 43. Answer: (B) Leukocytosis Rationale: Chronic Lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is characterized by increased production of leukocytes and lymphocytes resulting in leukocytosis, and proliferation of these cells within the bone marrow, spleen and liver. 44. Answer: (A) Explain the risks of not having the surgery Rationale: The best initial response is to explain the risks of not having the surgery. If the client understands the risks but still refuses the nurse should notify the physician and the nurse supervisor and then record the clients refusal in the nurses notes. 45. Answer: (D) The 75-year-old client who was admitted 1 hour ago with new-onset atrial fibrillation and is receiving L.V. dilitiazem (Cardizem) Rationale: The client with atrial fibrillation has the greatest potential to become unstable and is on L.V. medication that requires close monitoring. After assessing this client, the nurse should assess the client with thrombophlebitis who is receiving a heparin infusion, and then the 58- year-old client admitted 2 days ago with heart failure (his signs and symptoms are resolving and dont require immediate attention). The lowest priority is the 89year-old with end stage right-sided heart failure, who requires time-consuming supportive measures. 46. Answer: (C) Cocaine Rationale: Because of the clients age and negative medical history, the nurse should question her about cocaine use. Cocaine increases myocardial oxygen consumption and can cause coronary artery spasm, leading to tachycardia, ventricular
fibrillation, myocardial ischemia, and myocardial infarction. Barbiturate overdose may trigger respiratory depression and slow pulse. Opioids can cause marked respiratory depression, while benzodiazepines can cause drowsiness and confusion. 47. Answer: (B) Nonmobile mass with irregular edges Rationale: Breast cancer tumors are fixed, hard, and poorly delineated with irregular edges. A mobile mass that is soft and easily delineated is most often a fluid-filled benign cyst. Axillary lymph nodes may or may not be palpable on initial detection of a cancerous mass. Nipple retraction not eversion may be a sign of cancer. 48. Answer: (C) Radiation Rationale: The usual treatment for vaginal cancer is external or intravaginal radiation therapy. Less often, surgery is performed. Chemotherapy typically is prescribed only if vaginal cancer is diagnosed in an early stage, which is rare. Immunotherapy isnt used to treat vaginal cancer. 49. Answer: (B) Carcinoma in situ, no abnormal regional lymph nodes, and no evidence of distant metastasis Rationale: TIS, N0, M0 denotes carcinoma in situ, no abnormal regional lymph nodes, and no evidence of distant metastasis. No evidence of primary tumor, no abnormal regional lymph nodes, and no evidence of distant metastasis is classified as T0, N0, M0. If the tumor and regional lymph nodes cant be assessed and no evidence of metastasis exists, the lesion is classified as TX, NX, M0. A progressive increase in tumor size, no demonstrable metastasis of the regional lymph nodes, and ascending degrees of distant metastasis is classified as T1, T2, T3, or T4; N0; and M1, M2, or M3. 50. Answer: (D) Keep the stoma moist. Rationale: The nurse should instruct the client to keep the stoma moist, such as by applying a thin layer of petroleum jelly around the edges, because a dry stoma may become irritated. The nurse should recommend placing a stoma bib over the stoma to filter and warm air before it enters the stoma. The client should begin performing stoma care without assistance as soon as possible to gain independence in self-care activities. 51. Answer: (B) Lung cancer Rationale: Lung cancer is the most deadly type of cancer in both women and men. Breast cancer ranks second in women, followed (in descending order) by colon and rectal cancer, pancreatic cancer, ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, lymphoma, leukemia, liver cancer, brain cancer, stomach cancer, and multiple myeloma. 52. Answer: (A) miosis, partial eyelid ptosis, and anhidrosis on the affected side of the face. Rationale: Horners syndrome, which occurs when a lung tumor invades the ribs and affects the sympathetic nerve ganglia, is characterized by miosis, partial eyelid ptosis, and anhidrosis on the affected side of the face. Chest pain, dyspnea, cough, weight loss, and fever are associated with pleural tumors. Arm and shoulder pain and atrophy of the arm and hand muscles on the affected side suggest Pancoasts tumor, a lung tumor involving the first thoracic and eighth cervical nerves within the brachial plexus. Hoarseness in a client with lung cancer suggests that the tumor has extended to the recurrent laryngeal nerve; dysphagia suggests that the lung tumor is compressing the esophagus. 53. Answer: (A) prostate-specific antigen, which is used to screen for prostate cancer. Rationale: PSA stands for prostate-specific antigen, which is used to screen for prostate cancer. The other answers are incorrect.
54. Answer: (D) Remain supine for the time specified by the physician. Rationale: The nurse should instruct the client to remain supine for the time specified by the physician. Local anesthetics used in a subarachnoid block dont alter the gag reflex. No interactions between local anesthetics and food occur. Local anesthetics dont cause hematuria. 55. Answer: (C) Sigmoidoscopy Rationale: Used to visualize the lower GI tract, sigmoidoscopy and proctoscopy aid in the detection of two-thirds of all colorectal cancers. Stool Hematest detects blood, which is a sign of colorectal cancer; however, the test doesnt confirm the diagnosis. CEA may be elevated in colorectal cancer but isnt considered a confirming test. An abdominal CT scan is used to stage the presence of colorectal cancer. 56. Answer: (B) A fixed nodular mass with dimpling of the overlying skin Rationale: A fixed nodular mass with dimpling of the overlying skin is common during late stages of breast cancer. Many women have slightly asymmetrical breasts. Bloody nipple discharge is a sign of intraductal papilloma, a benign condition. Multiple firm, round, freely movable masses that change with the menstrual cycle indicate fibrocystic breasts, a benign condition. 57. Answer: (A) Liver Rationale: The liver is one of the five most common cancer metastasis sites. The others are the lymph nodes, lung, bone, and brain. The colon, reproductive tract, and WBCs are occasional metastasis sites. 58. Answer: (D) The client wears a watch and wedding band. Rationale: During an MRI, the client should wear no metal objects, such as jewelry, because the strong magnetic field can pull on them, causing injury to the client and (if they fly off) to others. The client must lie still during the MRI but can talk to those performing the test by way of the microphone inside the scanner tunnel. The client should hear thumping sounds, which are caused by the sound waves thumping on the magnetic field. 59. Answer: (C) The recommended daily allowance of calcium may be found in a wide variety of foods. Rationale: Premenopausal women require 1,000 mg of calcium per day. Postmenopausal women require 1,500 mg per day. Its often, though not always, possible to get the recommended daily requirement in the foods we eat. Supplements are available but not always necessary. Osteoporosis doesnt show up on ordinary X-rays until 30% of the bone loss has occurred. Bone densitometry can detect bone loss of 3% or less. This test is sometimes recommended routinely for women over 35 who are at risk. Strenuous exercise wont cause fractures. 60. Answer: (C) Joint flexion of less than 50% Rationale: Arthroscopy is contraindicated in clients with joint flexion of less than 50% because of technical problems in inserting the instrument into the joint to see it clearly. Other contraindications for this procedure include skin and wound infections. Joint pain may be an indication, not a contraindication, for arthroscopy. Joint deformity and joint stiffness arent contraindications for this procedure. 61. Answer: (D) Gouty arthritis Rationale: Gouty arthritis, a metabolic disease, is characterized by urate deposits and pain in the joints, especially those in the feet and legs. Urate deposits dont occur in septic or traumatic arthritis. Septic arthritis results from bacterial invasion of a joint and leads to inflammation of the synovial lining. Traumatic arthritis results from blunt trauma to a joint or ligament. Intermittent arthritis is a rare,
benign condition marked by regular, recurrent joint effusions, especially in the knees. 62. Answer: (B) 30 ml/hou Rationale: An infusion prepared with 25,000 units of heparin in 500 ml of saline solution yields 50 units of heparin per milliliter of solution. The equation is set up as 50 units times X (the unknown quantity) equals 1,500 units/hour, X equals 30 ml/hour. 63. Answer: (B) Loss of muscle contraction decreasing venous return Rationale: In clients with hemiplegia or hemiparesis loss of muscle contraction decreases venous return and may cause swelling of the affected extremity. Contractures, or bony calcifications may occur with a stroke, but dont appear with swelling. DVT may develop in clients with a stroke but is more likely to occur in the lower extremities. A stroke isnt linked to protein loss. 64. Answer: (B) It appears on the distal interphalangeal joint Rationale: Heberdens nodes appear on the distal interphalageal joint on both men and women. Bouchards node appears on the dorsolateral aspect of the proximal interphalangeal joint. 65. Answer: (B) Osteoarthritis is a localized disease rheumatoid arthritis is systemic Rationale: Osteoarthritis is a localized disease, rheumatoid arthritis is systemic. Osteoarthritis isnt gender-specific, but rheumatoid arthritis is. Clients have dislocations and subluxations in both disorders. 66. Answer: (C) The cane should be used on the unaffected side Rationale: A cane should be used on the unaffected side. A client with osteoarthritis should be encouraged to ambulate with a cane, walker, or other assistive device as needed; their use takes weight and stress off joints. 67. Answer: (A) a. 9 U regular insulin and 21 U neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH). Rationale: A 70/30 insulin preparation is 70% NPH and 30% regular insulin. Therefore, a correct substitution requires mixing 21 U of NPH and 9 U of regular insulin. The other choices are incorrect dosages for the prescribed insulin. 68. Answer: (C) colchicines Rationale: A disease characterized by joint inflammation (especially in the great toe), gout is caused by urate crystal deposits in the joints. The physician prescribes colchicine to reduce these deposits and thus ease joint inflammation. Although aspirin is used to reduce joint inflammation and pain in clients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, it isnt indicated for gout because it has no effect on urate crystal formation. Furosemide, a diuretic, doesnt relieve gout. Calcium gluconate is used to reverse a negative calcium balance and relieve muscle cramps, not to treat gout. 69. Answer: (A) Adrenal cortex Rationale: Excessive secretion of aldosterone in the adrenal cortex is responsible for the clients hypertension. This hormone acts on the renal tubule, where it promotes reabsorption of sodium and excretion of potassium and hydrogen ions. The pancreas mainly secretes hormones involved in fuel metabolism. The adrenal medulla secretes the catecholamines epinephrine and norepinephrine. The parathyroids secrete parathyroid hormone. 70. Answer: (C) They debride the wound and promote healing by secondary intention Rationale: For this client, wet-to-dry dressings are most appropriate because they clean the foot ulcer by debriding exudate and necrotic tissue, thus promoting healing by secondary intention. Moist, transparent dressings contain exudate and provide
a moist wound environment. Hydrocolloid dressings prevent the entrance of microorganisms and minimize wound discomfort. Dry sterile dressings protect the wound from mechanical trauma and promote healing. 71. Answer: (A) Hyperkalemia Rationale: In adrenal insufficiency, the client has hyperkalemia due to reduced aldosterone secretion. BUN increases as the glomerular filtration rate is reduced. Hyponatremia is caused by reduced aldosterone secretion. Reduced cortisol secretion leads to impaired glyconeogenesis and a reduction of glycogen in the liver and muscle, causing hypoglycemia. 72. Answer: (C) Restricting fluids Rationale: To reduce water retention in a client with the SIADH, the nurse should restrict fluids. Administering fluids by any route would further increase the clients already heightened fluid load. 73. Answer: (D) glycosylated hemoglobin level. Rationale: Because some of the glucose in the bloodstream attaches to some of the hemoglobin and stays attached during the 120-day life span of red blood cells, glycosylated hemoglobin levels provide information about blood glucose levels during the previous 3 months. Fasting blood glucose and urine glucose levels only give information about glucose levels at the point in time when they were obtained. Serum fructosamine levels provide information about blood glucose control over the past 2 to 3 weeks. 74. Answer: (C) 4:00 pm Rationale: NPH is an intermediate-acting insulin that peaks 8 to 12 hours after administration. Because the nurse administered NPH insulin at 7 a.m., the client is at greatest risk for hypoglycemia from 3 p.m. to 7 p.m. 75. Answer: (A) Glucocorticoids and androgens Rationale: The adrenal glands have two divisions, the cortex and medulla. The cortex produces three types of hormones: glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and androgens. The medulla produces catecholamines epinephrine and norepinephrine. 76. Answer: (A) Hypocalcemia Rationale: Hypocalcemia may follow thyroid surgery if the parathyroid glands were removed accidentally. Signs and symptoms of hypocalcemia may be delayed for up to 7 days after surgery. Thyroid surgery doesnt directly cause serum sodium, potassium, or magnesium abnormalities. Hyponatremia may occur if the client inadvertently received too much fluid; however, this can happen to any surgical client receiving I.V. fluid therapy, not just one recovering from thyroid surgery. Hyperkalemia and hypermagnesemia usually are associated with reduced renal excretion of potassium and magnesium, not thyroid surgery. 77. Answer: (D) Carcinoembryonic antigen level Rationale: In clients who smoke, the level of carcinoembryonic antigen is elevated. Therefore, it cant be used as a general indicator of cancer. However, it is helpful in monitoring cancer treatment because the level usually falls to normal within 1 month if treatment is successful. An elevated acid phosphatase level may indicate prostate cancer. An elevated alkaline phosphatase level may reflect bone metastasis. An elevated serum calcitonin level usually signals thyroid cancer. 78. Answer: (B) Dyspnea, tachycardia, and pallor Rationale: Signs of iron-deficiency anemia include dyspnea, tachycardia, and pallor as well as fatigue, listlessness, irritability, and headache. Night sweats, weight loss, and diarrhea may signal acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Nausea,
vomiting, and anorexia may be signs of hepatitis B. Itching, rash, and jaundice may result from an allergic or hemolytic reaction. 79. Answer: (D) Ill need to have a C-section if I become pregnant and have a baby. Rationale: The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is transmitted from mother to child via the transplacental route, but a Cesarean section delivery isnt necessary when the mother is HIVpositive. The use of birth control will prevent the conception of a child who might have HIV. Its true that a mother whos HIV positive can give birth to a baby whos HIV negative. 80. Answer: (C) Avoid sharing such articles as toothbrushes and razors. Rationale: The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which causes AIDS, is most concentrated in the blood. For this reason, the client shouldnt share personal articles that may be blood-contaminated, such as toothbrushes and razors, with other family members. HIV isnt transmitted by bathing or by eating from plates, utensils, or serving dishes used by a person with AIDS. 81. Answer: (B) Pallor, tachycardia, and a sore tongue Rationale: Pallor, tachycardia, and a sore tongue are all characteristic findings in pernicious anemia. Other clinical manifestations include anorexia; weight loss; a smooth, beefy red tongue; a wide pulse pressure; palpitations; angina; weakness; fatigue; and paresthesia of the hands and feet. Bradycardia, reduced pulse pressure, weight gain, and double vision arent characteristic findings in pernicious anemia. 82. Answer: (B) Administer epinephrine, as prescribed, and prepare to intubate the client if necessary. Rationale: To reverse anaphylactic shock, the nurse first should administer epinephrine, a potent bronchodilator as prescribed. The physician is likely to order additional medications, such as antihistamines and corticosteroids; if these medications dont relieve the respiratory compromise associated with anaphylaxis, the nurse should prepare to intubate the client. No antidote for penicillin exists; however, the nurse should continue to monitor the clients vital signs. A client who remains hypotensive may need fluid resuscitation and fluid intake and output monitoring; however, administering epinephrine is the first priority. 83. Answer: (D) bilateral hearing loss. Rationale: Prolonged use of aspirin and other salicylates sometimes causes bilateral hearing loss of 30 to 40 decibels. Usually, this adverse effect resolves within 2 weeks after the therapy is discontinued. Aspirin doesnt lead to weight gain or fine motor tremors. Large or toxic salicylate doses may cause respiratory alkalosis, not respiratory acidosis. 84. Answer: (D) Lymphocyte Rationale: The lymphocyte provides adaptive immunity recognition of a foreign antigen and formation of memory cells against the antigen. Adaptive immunity is mediated by B and T lymphocytes and can be acquired actively or passively. The neutrophil is crucial to phagocytosis. The basophil plays an important role in the release of inflammatory mediators. The monocyte functions in phagocytosis and monokine production. 85. Answer: (A) moisture replacement. Rationale: Sjogrens syndrome is an autoimmune disorder leading to progressive loss of lubrication of the skin, GI tract, ears, nose, and vagina. Moisture replacement is the mainstay of therapy. Though malnutrition and electrolyte imbalance may occur as a result of Sjogrens syndromes effect on the GI
tract, it isnt the predominant problem. Arrhythmias arent a problem associated with Sjogrens syndrome. 86. Answer: (C) stool for Clostridium difficile test. Rationale: Immunosuppressed clients for example, clients receiving chemotherapy, are at risk for infection with C. difficile, which causes horse barn smelling diarrhea. Successful treatment begins with an accurate diagnosis, which includes a stool test. The ELISA test is diagnostic for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and isnt indicated in this case. An electrolyte panel and hemogram may be useful in the overall evaluation of a client but arent diagnostic for specific causes of diarrhea. A flat plate of the abdomen may provide useful information about bowel function but isnt indicated in the case of horse barn smelling diarrhea. 87. Answer: (D) Western blot test with ELISA. Rationale: HIV infection is detected by analyzing blood for antibodies to HIV, which form approximately 2 to 12 weeks after exposure to HIV and denote infection. The Western blot test electrophoresis of antibody proteins is more than 98% accurate in detecting HIV antibodies when used in conjunction with the ELISA. It isnt specific when used alone. Erosette immunofluorescence is used to detect viruses in general; it doesnt confirm HIV infection. Quantification of T-lymphocytes is a useful monitoring test but isnt diagnostic for HIV. The ELISA test detects HIV antibody particles but may yield inaccurate results; a positive ELISA result must be confirmed by the Western blot test. 88. Answer: (C) Abnormally low hematocrit (HCT) and hemoglobin (Hb) levels Rationale: Low preoperative HCT and Hb levels indicate the client may require a blood transfusion before surgery. If the HCT and Hb levels decrease during surgery because of blood loss, the potential need for a transfusion increases. Possible renal failure is indicated by elevated BUN or creatinine levels. Urine constituents arent found in the blood. Coagulation is determined by the presence of appropriate clotting factors, not electrolytes. 89. Answer: (A) Platelet count, prothrombin time, and partial thromboplastin time Rationale: The diagnosis of DIC is based on the results of laboratory studies of prothrombin time, platelet count, thrombin time, partial thromboplastin time, and fibrinogen level as well as client history and other assessment factors. Blood glucose levels, WBC count, calcium levels, and potassium levels arent used to confirm a diagnosis of DIC. 90. Answer: (D) Strawberries Rationale: Common food allergens include berries, peanuts, Brazil nuts, cashews, shellfish, and eggs. Bread, carrots, and oranges rarely cause allergic reactions. 91. Answer: (B) A client with cast on the right leg who states, I have a funny feeling in my right leg. Rationale: It may indicate neurovascular compromise, requires immediate assessment. 92. Answer: (D) A 62-year-old who had an abdominal-perineal resection three days ago; client complaints of chills. Rationale: The client is at risk for peritonitis; should be assessed for further symptoms and infection. 93. Answer: (C) The client spontaneously flexes his wrist when the blood pressure is obtained. Rationale: Carpal spasms indicate hypocalcemia. 94. Answer: (D) Use comfort measures and pillows to position the client. Rationale: Using comfort measures and pillows to
position the client is a non-pharmacological methods of pain relief. 95. Answer: (B) Warm the dialysate solution. Rationale: Cold dialysate increases discomfort. The solution should be warmed to body temperature in warmer or heating pad; dont use microwave oven. 96. Answer: (C) The client holds the cane with his left hand, moves the cane forward followed by the right leg, and then moves the left leg. Rationale: The cane acts as a support and aids in weight bearing for the weaker right leg. 97. Answer: (A) Ask the womans family to provide personal items such as photos or mementos. Rationale: Photos and mementos provide visual stimulation to reduce sensory deprivation. 98. Answer: (B) The client lifts the walker, moves it forward 10 inches, and then takes several small steps forward. Rationale: A walker needs to be picked up, placed down on all legs. 99. Answer: (C) Isolation from their families and familiar surroundings. Rationale: Gradual loss of sight, hearing, and taste interferes with normal functioning. 100. Answer: (A) Encourage the client to perform pursed lip breathing. Rationale: Purse lip breathing prevents the collapse of lung unit and helps client control rate and depth of breathing. NP 4 1. Answer: (C) Hypertension Rationale: Hypertension, along with fever, and tenderness over the grafted kidney, reflects acute rejection. 2. Answer: (A) Pain Rationale: Sharp, severe pain (renal colic) radiating toward the genitalia and thigh is caused by uretheral distention and smooth muscle spasm; relief form pain is the priority. 3. Answer: (D) Decrease the size and vascularity of the thyroid gland. Rationale: Lugols solution provides iodine, which aids in decreasing the vascularity of the thyroid gland, which limits the risk of hemorrhage when surgery is performed. 4. Answer: (A) Liver Disease Rationale: The client with liver disease has a decreased ability to metabolize carbohydrates because of a decreased ability to form glycogen (glycogenesis) and to form glucose from glycogen. 5. Answer: (C) Leukopenia Rationale: Leukopenia, a reduction in WBCs, is a systemic effect of chemotherapy as a result of myelosuppression. 6. Answer: (C) Avoid foods that in the past caused flatus. Rationale: Foods that bothered a person preoperatively will continue to do so after a colostomy. 7. Answer: (B) Keep the irrigating container less than 18 inches above the stoma. Rationale: This height permits the solution to flow slowly with little force so that excessive peristalsis is not immediately precipitated. 8. Answer: (A) Administer Kayexalate Rationale: Kayexalate,a potassium exchange resin, permits sodium to be exchanged for potassium in the intestine, reducing the serum potassium level.
9. Answer:(B) 28 gtt/min Rationale: This is the correct flow rate; multiply the amount to be infused (2000 ml) by the drop factor (10) and divide the result by the amount of time in minutes (12 hours x 60 minutes) 10. Answer: (D) Upper trunk Rationale: The percentage designated for each burned part of the body using the rule of nines: Head and neck 9%; Right upper extremity 9%; Left upper extremity 9%; Anterior trunk 18%; Posterior trunk 18%; Right lower extremity 18%; Left lower extremity 18%; Perineum 1%. 11. Answer: (C) Bleeding from ears Rationale: The nurse needs to perform a thorough assessment that could indicate alterations in cerebral function, increased intracranial pressures, fractures and bleeding. Bleeding from the ears occurs only with basal skull fractures that can easily contribute to increased intracranial pressure and brain herniation. 12. Answer: (D) may engage in contact sports Rationale: The client should be advised by the nurse to avoid contact sports. This will prevent trauma to the area of the pacemaker generator. 13. Answer: (A) Oxygen at 1-2L/min is given to maintain the hypoxic stimulus for breathing. Rationale: COPD causes a chronic CO2 retention that renders the medulla insensitive to the CO2 stimulation for breathing. The hypoxic state of the client then becomes the stimulus for breathing. Giving the client oxygen in low concentrations will maintain the clients hypoxic drive. 14. Answer: (B) Facilitate ventilation of the left lung. Rationale: Since only a partial pneumonectomy is done, there is a need to promote expansion of this remaining Left lung by positioning the client on the opposite unoperated side. 15. Answer: (A) Food and fluids will be withheld for at least 2 hours. Rationale: Prior to bronchoscopy, the doctors sprays the back of the throat with anesthetic to minimize the gag reflex and thus facilitate the insertion of the bronchoscope. Giving the client food and drink after the procedure without checking on the return of the gag reflex can cause the client to aspirate. The gag reflex usually returns after two hours. 16. Answer: (C) hyperkalemia. Rationale: Hyperkalemia is a common complication of acute renal failure. Its life-threatening if immediate action isnt taken to reverse it. The administration of glucose and regular insulin, with sodium bicarbonate if necessary, can temporarily prevent cardiac arrest by moving potassium into the cells and temporarily reducing serum potassium levels. Hypernatremia, hypokalemia, and hypercalcemia dont usually occur with acute renal failure and arent treated with glucose, insulin, or sodium bicarbonate. 17. Answer: (A) This condition puts her at a higher risk for cervical cancer; therefore, she should have a Papanicolaou (Pap) smear annually. Rationale: Women with condylomata acuminata are at risk for cancer of the cervix and vulva. Yearly Pap smears are very important for early detection. Because condylomata acuminata is a virus, there is no permanent cure. Because condylomata acuminata can occur on the vulva, a condom wont protect sexual partners. HPV can be transmitted to other parts of the body, such as the mouth, oropharynx, and larynx. 18. Answer: (A) The left kidney usually is slightly higher than the right one. Rationale: The left kidney usually is slightly higher than the right one. An adrenal gland lies atop each
kidney. The average kidney measures approximately 11 cm (4-3/8) long, 5 to 5.8 cm (2 to 2) wide, and 2.5 cm (1) thick. The kidneys are located retroperitoneally, in the posterior aspect of the abdomen, on either side of the vertebral column. They lie between the 12th thoracic and 3rd lumbar vertebrae. 19. Answer: (C) Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 100 mg/dl and serum creatinine 6.5 mg/dl. Rationale: The normal BUN level ranges 8 to 23 mg/dl; the normal serum creatinine level ranges from 0.7 to 1.5 mg/dl. The test results in option C are abnormally elevated, reflecting CRF and the kidneys decreased ability to remove nonprotein nitrogen waste from the blood. CRF causes decreased pH and increased hydrogen ions not vice versa. CRF also increases serum levels of potassium, magnesium, and phosphorous, and decreases serum levels of calcium. A uric acid analysis of 3.5 mg/dl falls within the normal range of 2.7 to 7.7 mg/dl; PSP excretion of 75% also falls with the normal range of 60% to 75%. 20. Answer: (D) Alteration in the size, shape, and organization of differentiated cells Rationale: Dysplasia refers to an alteration in the size, shape, and organization of differentiated cells. The presence of completely undifferentiated tumor cells that dont resemble cells of the tissues of their origin is called anaplasia. An increase in the number of normal cells in a normal arrangement in a tissue or an organ is called hyperplasia. Replacement of one type of fully differentiated cell by another in tissues where the second type normally isnt found is called metaplasia. 21. Answer: (D) Kaposis sarcoma Rationale: Kaposis sarcoma is the most common cancer associated with AIDS. Squamous cell carcinoma, multiple myeloma, and leukemia may occur in anyone and arent associated specifically with AIDS. 22. Answer: (C) To prevent cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage Rationale: The client receiving a subarachnoid block requires special positioning to prevent CSF leakage and headache and to ensure proper anesthetic distribution. Proper positioning doesnt help prevent confusion, seizures, or cardiac arrhythmias. 23. Answer: (A) Auscultate bowel sounds. Rationale: If abdominal distention is accompanied by nausea, the nurse must first auscultate bowel sounds. If bowel sounds are absent, the nurse should suspect gastric or small intestine dilation and these findings must be reported to the physician. Palpation should be avoided postoperatively with abdominal distention. If peristalsis is absent, changing positions and inserting a rectal tube wont relieve the clients discomfort. 24. Answer: (B) Lying on the left side with knees bent Rationale: For a colonoscopy, the nurse initially should position the client on the left side with knees bent. Placing the client on the right side with legs straight, prone with the torso elevated, or bent over with hands touching the floor wouldnt allow proper visualization of the large intestine. 25. Answer: (A) Blood supply to the stoma has been interrupted Rationale: An ileostomy stoma forms as the ileum is brought through the abdominal wall to the surface skin, creating an artificial opening for waste elimination. The stoma should appear cherry red, indicating adequate arterial perfusion. A dusky stoma suggests decreased perfusion, which may result from interruption of the stomas blood supply and may lead to tissue damage or necrosis. A dusky
stoma isnt a normal finding. Adjusting the ostomy bag wouldnt affect stoma color, which depends on blood supply to the area. An intestinal obstruction also wouldnt change stoma color. 26. Answer: (A) Applying knee splints Rationale: Applying knee splints prevents leg contractures by holding the joints in a position of function. Elevating the foot of the bed cant prevent contractures because this action doesnt hold the joints in a position of function. Hyperextending a body part for an extended time is inappropriate because it can cause contractures. Performing shoulder range-of-motion exercises can prevent contractures in the shoulders, but not in the legs. 27. Answer: (B) Urine output of 20 ml/hour. Rationale: A urine output of less than 40 ml/hour in a client with burns indicates a fluid volume deficit. This clients PaO2 value falls within the normal range (80 to 100 mm Hg). White pulmonary secretions also are normal. The clients rectal temperature isnt significantly elevated and probably results from the fluid volume deficit. 28. Answer: (A) Turn him frequently. Rationale: The most important intervention to prevent pressure ulcers is frequent position changes, which relieve pressure on the skin and underlying tissues. If pressure isnt relieved, capillaries become occluded, reducing circulation and oxygenation of the tissues and resulting in cell death and ulcer formation. During passive ROM exercises, the nurse moves each joint through its range of movement, which improves joint mobility and circulation to the affected area but doesnt prevent pressure ulcers. Adequate hydration is necessary to maintain healthy skin and ensure tissue repair. A footboard prevents plantar flexion and footdrop by maintaining the foot in a dorsiflexed position. 29. Answer: (C) In long, even, outward, and downward strokes in the direction of hair growth Rationale: When applying a topical agent, the nurse should begin at the midline and use long, even, outward, and downward strokes in the direction of hair growth. This application pattern reduces the risk of follicle irritation and skin inflammation. 30. Answer: (A) Beta -adrenergic blockers Rationale: Beta-adrenergic blockers work by blocking beta receptors in the myocardium, reducing the response to catecholamines and sympathetic nerve stimulation. They protect the myocardium, helping to reduce the risk of another infraction by decreasing myocardial oxygen demand. Calcium channel blockers reduce the workload of the heart by decreasing the heart rate. Narcotics reduce myocardial oxygen demand, promote vasodilation, and decrease anxiety. Nitrates reduce myocardial oxygen consumption bt decreasing left ventricular end diastolic pressure (preload) and systemic vascular resistance (afterload). 31. Answer: (C) Raised 30 degrees Rationale: Jugular venous pressure is measured with a centimeter ruler to obtain the vertical distance between the sternal angle and the point of highest pulsation with the head of the bed inclined between 15 to 30 degrees. Increased pressure cant be seen when the client is supine or when the head of the bed is raised 10 degrees because the point that marks the pressure level is above the jaw (therefore, not visible). In high Fowlers position, the veins would be barely discernible above the clavicle. 32. Answer: (D) Inotropic agents Rationale: Inotropic agents are administered to increase the force of the hearts contractions, thereby increasing ventricular contractility and ultimately increasing cardiac output. Beta-
adrenergic blockers and calcium channel blockers decrease the heart rate and ultimately decreased the workload of the heart. Diuretics are administered to decrease the overall vascular volume, also decreasing the workload of the heart. 33. Answer: (B) Less than 30% of calories form fat Rationale: A client with low serum HDL and high serum LDL levels should get less than 30% of daily calories from fat. The other modifications are appropriate for this client. 34. Answer: (C) The emergency department nurse calls up the latest electrocardiogram results to check the clients progress Rationale: The emergency department nurse is no longer directly involved with the clients care and thus has no legal right to information about his present condition. Anyone directly involved in his care (such as the telemetry nurse and the on-call physician) has the right to information about his condition. Because the client requested that the nurse update his wife on his condition, doing so doesnt breach confidentiality. 35. Answer: (B) Check endotracheal tube placement. Rationale: ET tube placement should be confirmed as soon as the client arrives in the emergency department. Once the airways is secured, oxygenation and ventilation should be confirmed using an end-tidal carbon dioxide monitor and pulse oximetry. Next, the nurse should make sure L.V. access is established. If the client experiences symptomatic bradycardia, atropine is administered as ordered 0.5 to 1 mg every 3 to 5 minutes to a total of 3 mg. Then the nurse should try to find the cause of the clients arrest by obtaining an ABG sample. Amiodarone is indicated for ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation and atrial flutter not symptomatic bradycardia. 36. Answer: (C) 95 mm Hg Rationale: Use the following formula to calculate MAP MAP = systolic + 2 (diastolic) 3 MAP=126 mm Hg + 2 (80 mm Hg) 3 MAP=286 mm HG 3 MAP=95 mm Hg 37. Answer: (C) Electrocardiogram, complete blood count, testing for occult blood, comprehensive serum metabolic panel. Rationale: An electrocardiogram evaluates the complaints of chest pain, laboratory tests determines anemia, and the stool test for occult blood determines blood in the stool. Cardiac monitoring, oxygen, and creatine kinase and lactate dehydrogenase levels are appropriate for a cardiac primary problem. A basic metabolic panel and alkaline phosphatase and aspartate aminotransferase levels assess liver function. Prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time, fibrinogen and fibrin split products are measured to verify bleeding dyscrasias, An electroencephalogram evaluates brain electrical activity. 38. Answer: (D) Heparin-associated thrombosis and thrombocytopenia (HATT) Rationale: HATT may occur after CABG surgery due to heparin use during surgery. Although DIC and ITP cause platelet aggregation and bleeding, neither is common in a client after revascularization surgery. Pancytopenia is a reduction in all blood cells. 39. Answer: (B) Corticosteroids Rationale: Corticosteroid therapy can decrease antibody production and phagocytosis of the
antibody-coated platelets, retaining more functioning platelets. Methotrexate can cause thrombocytopenia. Vitamin K is used to treat an excessive anticoagulate state from warfarin overload, and ASA decreases platelet aggregation. 40. Answer: (D) Xenogeneic Rationale: An xenogeneic transplant is between is between human and another species. A syngeneic transplant is between identical twins, allogeneic transplant is between two humans, and autologous is a transplant from the same individual. 41. Answer: (B) Rationale: Tissue thromboplastin is released when damaged tissue comes in contact with clotting factors. Calcium is released to assist the conversion of factors X to Xa. Conversion of factors XII to XIIa and VIII to VIII a are part of the intrinsic pathway. 42. Answer: (C) Essential thrombocytopenia Rationale: Essential thrombocytopenia is linked to immunologic disorders, such as SLE and human immunodeficiency vitus. The disorder known as von Willebrands disease is a type of hemophilia and isnt linked to SLE. Moderate to severe anemia is associated with SLE, not polycythermia. Dresslers syndrome is pericarditis that occurs after a myocardial infarction and isnt linked to SLE. 43. Answer: (B) Night sweat Rationale: In stage 1, symptoms include a single enlarged lymph node (usually), unexplained fever, night sweats, malaise, and generalized pruritis. Although splenomegaly may be present in some clients, night sweats are generally more prevalent. Pericarditis isnt associated with Hodgkins disease, nor is hypothermia. Moreover, splenomegaly and pericarditis arent symptoms. Persistent hypothermia is associated with Hodgkins but isnt an early sign of the disease. 44. Answer: (D) Breath sounds Rationale: Pneumonia, both viral and fungal, is a common cause of death in clients with neutropenia, so frequent assessment of respiratory rate and breath sounds is required. Although assessing blood pressure, bowel sounds, and heart sounds is important, it wont help detect pneumonia. 45. Answer: (B) Muscle spasm Rationale: Back pain or paresthesia in the lower extremities may indicate impending spinal cord compression from a spinal tumor. This should be recognized and treated promptly as progression of the tumor may result in paraplegia. The other options, which reflect parts of the nervous system, arent usually affected by MM. 46. Answer: (C)10 years Rationale: Epidermiologic studies show the average time from initial contact with HIV to the development of AIDS is 10 years. 47. Answer: (A) Low platelet count Rationale: In DIC, platelets and clotting factors are consumed, resulting in microthrombi and excessive bleeding. As clots form, fibrinogen levels decrease and the prothrombin time increases. Fibrin degeneration products increase as fibrinolysis takes places. 48. Answer: (D) Hodgkins disease Rationale: Hodgkins disease typically causes fever night sweats, weight loss, and lymph mode enlargement. Influenza doesnt last for months. Clients with sickle cell anemia manifest signs and symptoms of chronic anemia with pallor of the mucous membrane, fatigue, and decreased tolerance for exercise; they dont show fever, night sweats, weight loss or lymph node enlargement. Leukemia doesnt cause lymph node enlargement.
49. Answer: (C) A Rh-negative Rationale: Human blood can sometimes contain an inherited D antigen. Persons with the D antigen have Rh-positive blood type; those lacking the antigen have Rh-negative blood. Its important that a person with Rhnegative blood receives Rhnegative blood. If Rh-positive blood is administered to an Rh-negative person, the recipient develops anti-Rh agglutinins, and sub sequent transfusions with Rh-positive blood may cause serious reactions with clumping and hemolysis of red blood cells. 50. Answer: (B) I will call my doctor if Stacy has persistent vomiting and diarrhea. Rationale: Persistent (more than 24 hours) vomiting, anorexia, and diarrhea are signs of toxicity and the patient should stop the medication and notify the health care provider. The other manifestations are expected side effects of chemotherapy. 51. Answer: (D) This is only temporary; Stacy will re-grow new hair in 3-6 months, but may be different in texture. Rationale: This is the appropriate response. The nurse should help the mother how to cope with her own feelings regarding the childs disease so as not to affect the child negatively. When the hair grows back, it is still of the same color and texture. 52. Answer: (B) Apply viscous Lidocaine to oral ulcers as needed. Rationale: Stomatitis can cause pain and this can be relieved by applying topical anesthetics such as lidocaine before mouth care. When the patient is already comfortable, the nurse can proceed with providing the patient with oral rinses of saline solution mixed with equal part of water or hydrogen peroxide mixed water in 1:3 concentrations to promote oral hygiene. Every 2-4 hours. 53. Answer: (C) Immediately discontinue the infusion Rationale: Edema or swelling at the IV site is a sign that the needle has been dislodged and the IV solution is leaking into the tissues causing the edema. The patient feels pain as the nerves are irritated by pressure and the IV solution. The first action of the nurse would be to discontinue the infusion right away to prevent further edema and other complication. 54. Answer: (C) Chronic obstructive bronchitis Rationale: Clients with chronic obstructive bronchitis appear bloated; they have large barrel chest and peripheral edema, cyanotic nail beds, and at times, circumoral cyanosis. Clients with ARDS are acutely short of breath and frequently need intubation for mechanical ventilation and large amount of oxygen. Clients with asthma dont exhibit characteristics of chronic disease, and clients with emphysema appear pink and cachectic. 55. Answer: (D) Emphysema Rationale: Because of the large amount of energy it takes to breathe, clients with emphysema are usually cachectic. Theyre pink and usually breathe through pursed lips, hence the term puffer. Clients with ARDS are usually acutely short of breath. Clients with asthma dont have any particular characteristics, and clients with chronic obstructive bronchitis are bloated and cyanotic in appearance. 56. Answer: D 80 mm Hg Rationale: A client about to go into respiratory arrest will have inefficient ventilation and will be retaining carbon dioxide. The value expected would be around 80 mm Hg. All other values are lower than expected. 57. Answer: (C) Respiratory acidosis Rationale: Because Paco2 is high at 80 mm Hg and the metabolic measure, HCO3- is normal, the client has respiratory acidosis. The pH is less than 7.35,
academic, which eliminates metabolic and respiratory alkalosis as possibilities. If the HCO3was below 22 mEq/L the client would have metabolic acidosis. 58. Answer: (C) Respiratory failure Rationale: The client was reacting to the drug with respiratory signs of impending anaphylaxis, which could lead to eventually respiratory failure. Although the signs are also related to an asthma attack or a pulmonary embolism, consider the new drug first. Rheumatoid arthritis doesnt manifest these signs. 59. Answer: (D) Elevated serum aminotransferase Rationale: Hepatic cell death causes release of liver enzymes alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) into the circulation. Liver cirrhosis is a chronic and irreversible disease of the liver characterized by generalized inflammation and fibrosis of the liver tissues. 60. Answer: (A) Impaired clotting mechanism Rationale: Cirrhosis of the liver results in decreased Vitamin K absorption and formation of clotting factors resulting in impaired clotting mechanism. 61. Answer: (B) Altered level of consciousness Rationale: Changes in behavior and level of consciousness are the first sins of hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatic encephalopathy is caused by liver failure and develops when the liver is unable to convert protein metabolic product ammonia to urea. This results in accumulation of ammonia and other toxic in the blood that damages the cells. 62. Answer: (C) Ill lower the dosage as ordered so the drug causes only 2 to 4 stools a day. Rationale: Lactulose is given to a patients with hepatic encephalopathy to reduce absorption of ammonia in the intestines by binding with ammonia and promoting more frequent bowel movements. If the patient experience diarrhea, it indicates over dosage and the nurse must reduce the amount of medication given to the patient. The stool will be mashy or soft. Lactulose is also very sweet and may cause cramping and bloating. 63. Answer: (B) Severe lower back pain, decreased blood pressure, decreased RBC count, increased WBC count. Rationale: Severe lower back pain indicates an aneurysm rupture, secondary to pressure being applied within the abdominal cavity. When ruptured occurs, the pain is constant because it cant be alleviated until the aneurysm is repaired. Blood pressure decreases due to the loss of blood. After the aneurysm ruptures, the vasculature is interrupted and blood volume is lost, so blood pressure wouldnt increase. For the same reason, the RBC count is decreased not increased. The WBC count increases as cell migrate to the site of injury. 64. Answer: (D) Apply gloves and assess the groin site Rationale: Observing standard precautions is the first priority when dealing with any blood fluid. Assessment of the groin site is the second priority. This establishes where the blood is coming from and determineshow much blood has been lost. The goal in this situation is to stop the bleeding. The nurse would call for help if it were warranted after the assessment of the situation. After determining the extent of the bleeding, vital signs assessment is important. The nurse should never move the client, in case a clot has formed. Moving can disturb the clot and cause rebleeding. 65. Answer: (D) Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA)
Rationale: PTCA can alleviate the blockage and restore blood flow and oxygenation. An echocardiogram is a noninvasive diagnosis test. Nitroglycerin is an oral sublingual medication. Cardiac catheterization is a diagnostic tool not a treatment. 66. Answer: (B) Cardiogenic shock Rationale: Cardiogenic shock is shock related to ineffective pumping of the heart. Anaphylactic shock results from an allergic reaction. Distributive shock results from changes in the intravascular volume distribution and is usually associated with increased cardiac output. MI isnt a shock state, though a severe MI can lead to shock. 67. Answer: (C) Kidneys excretion of sodium and water Rationale: The kidneys respond to rise in blood pressure by excreting sodium and excess water. This response ultimately affects sysmolic blood pressure by regulating blood volume. Sodium or water retention would only further increase blood pressure. Sodium and water travel together across the membrane in the kidneys; one cant travel without the other. 68. Answer: (D) It inhibits reabsorption of sodium and water in the loop of Henle. Rationale: Furosemide is a loop diuretic that inhibits sodium and water reabsorption in the loop Henle, thereby causing a decrease in blood pressure. Vasodilators cause dilation of peripheral blood vessels, directly relaxing vascular smooth muscle and decreasing blood pressure. Adrenergic blockers decrease sympathetic cardioacceleration and decrease blood pressure. Angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors decrease blood pressure due to their action on angiotensin. 69. Answer: (C) Pancytopenia, elevated antinuclear antibody (ANA) titer Rationale: Laboratory findings for clients with SLE usually show pancytopenia, elevated ANA titer, and decreased serum complement levels. Clients may have elevated BUN and creatinine levels from nephritis, but the increase does not indicate SLE. 70. Answer: (C) Narcotics are avoided after a head injury because they may hide a worsening condition. Rationale: Narcotics may mask changes in the level of consciousness that indicate increased ICP and shouldnt acetaminophen is strong enough ignores the mothers question and therefore isnt appropriate. Aspirin is contraindicated in conditions that may have bleeding, such as trauma, and for children or young adults with viral illnesses due to the danger of Reyes syndrome. Stronger medications may not necessarily lead to vomiting but will sedate the client, thereby masking changes in his level of consciousness. 71. Answer: (A) Appropriate; lowering carbon dioxide (CO2) reduces intracranial pressure (ICP) Rationale: A normal Paco2 value is 35 to 45 mm Hg CO2 has vasodilating properties; therefore, lowering Paco2 through hyperventilation will lower ICP caused by dilated cerebral vessels. Oxygenation is evaluated through Pao2 and oxygen saturation. Alveolar hypoventilation would be reflected in an increased Paco2. 72. Answer: (B) A 33-year-old client with a recent diagnosis of Guillain-Barre syndrome Rationale: Guillain-Barre syndrome is characterized by ascending paralysis and potential respiratory failure. The order of client assessment should follow client priorities, with disorder of airways, breathing, and then circulation. Theres no information to suggest the postmyocardial infarction client has an arrhythmia or other complication. Theres no
evidence to suggest hemorrhage or perforation for the remaining clients as a priority of care. 73. Answer: (C) Decreases inflammation Rationale: Then action of colchicines is to decrease inflammation by reducing the migration of leukocytes to synovial fluid. Colchicine doesnt replace estrogen, decrease infection, or decrease bone demineralization. 74. Answer: (C) Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis Rationale: Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis and can be extremely debilitating. It can afflict people of any age, although most are elderly. 75. Answer: (C) Myxedema coma Rationale: Myxedema coma, severe hypothyroidism, is a life-threatening condition that may develop if thyroid replacement medication isnt taken. Exophthalmos, protrusion of the eyeballs, is seen with hyperthyroidism. Thyroid storm is lifethreatening but is caused by severe hyperthyroidism. Tibial myxedema, peripheral mucinous edema involving the lower leg, is associated with hypothyroidism but isnt lifethreatening. 76. Answer: (B) An irregular apical pulse Rationale: Because Cushings syndrome causes aldosterone overproduction, which increases urinary potassium loss, the disorder may lead to hypokalemia. Therefore, the nurse should immediately report signs and symptoms of hypokalemia, such as an irregular apical pulse, to the physician. Edema is an expected finding because aldosterone overproduction causes sodium and fluid retention. Dry mucous membranes and frequent urination signal dehydration, which isnt associated with Cushings syndrome. 77. Answer: (D) Below-normal urine osmolality level, above-normal serum osmolality level Rationale: In diabetes insipidus, excessive polyuria causes dilute urine, resulting in a below-normal urine osmolality level. At the same time, polyuria depletes the body of water, causing dehydration that leads to an above-normal serum osmolality level. For the same reasons, diabetes insipidus doesnt cause above-normal urine osmolality or below-normal serum osmolality levels. 78. Answer: (A) I can avoid getting sick by not becoming dehydrated and by paying attention to my need to urinate, drink, or eat more than usual. Rationale: Inadequate fluid intake during hyperglycemic episodes often leads to HHNS. By recognizing the signs of hyperglycemia (polyuria, polydipsia, and polyphagia) and increasing fluid intake, the client may prevent HHNS. Drinking a glass of nondiet soda would be appropriate for hypoglycemia. A client whose diabetes is controlled with oral antidiabetic agents usually doesnt need to monitor blood glucose levels. A highcarbohydrate diet would exacerbate the clients condition, particularly if fluid intake is low. 79. Answer: (D) Hyperparathyroidism Rationale: Hyperparathyroidism is most common in older women and is characterized by bone pain and weakness from excess parathyroid hormone (PTH). Clients also exhibit hypercaliuria-causing polyuria. While clients with diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus also have polyuria, they dont have bone pain and increased sleeping. Hypoparathyroidism is characterized by urinary frequency rather than polyuria. 80. Answer: (C) Ill take two-thirds of the dose when I wake up and one-third in the late afternoon. Rationale: Hydrocortisone, a glucocorticoid, should be administered according to a schedule that closely reflects the bodys own secretion of this
hormone; therefore, two-thirds of the dose of hydrocortisone should be taken in the morning and one-third in the late afternoon. This dosage schedule reduces adverse effects. 81. Answer: (C) High corticotropin and high cortisol levels Rationale: A corticotropin-secreting pituitary tumor would cause high corticotropin and high cortisol levels. A high corticotropin level with a low cortisol level and a low corticotropin level with a low cortisol level would be associated with hypocortisolism. Low corticotropin and high cortisol levels would be seen if there was a primary defect in the adrenal glands. 82. Answer: (D) Performing capillary glucose testing every 4 hours Rationale: The nurse should perform capillary glucose testing every 4 hours because excess cortisol may cause insulin resistance, placing the client at risk for hyperglycemia. Urine ketone testing isnt indicated because the client does secrete insulin and, therefore, isnt at risk for ketosis. Urine specific gravity isnt indicated because although fluid balance can be compromised, it usually isnt dangerously imbalanced. Temperature regulation may be affected by excess cortisol and isnt an accurate indicator of infection. 83. Answer: (C) onset to be at 2:30 p.m. and its peak to be at 4 p.m. Rationale: Regular insulin, which is a short-acting insulin, has an onset of 15 to 30 minutes and a peak of 2 to 4 hours. Because the nurse gave the insulin at 2 p.m., the expected onset would be from 2:15 p.m. to 2:30 p.m. and the peak from 4 p.m. to 6 p.m. 84. Answer: (A) No increase in the thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH) level after 30 minutes during the TSH stimulation test Rationale: In the TSH test, failure of the TSH level to rise after 30 minutes confirms hyperthyroidism. A decreased TSH level indicates a pituitary deficiency of this hormone. Below-normal levels of T3 and T4, as detected by radioimmunoassay, signal hypothyroidism. A below-normal T4 level also occurs in malnutrition and liver disease and may result from administration of phenytoin and certain other drugs. 85. Answer: (B) Rotate injection sites within the same anatomic region, not among different regions. Rationale: The nurse should instruct the client to rotate injection sites within the same anatomic region. Rotating sites among different regions may cause excessive day-to-day variations in the blood glucose level; also, insulin absorption differs from one region to the next. Insulin should be injected only into healthy tissue lacking large blood vessels, nerves, or scar tissue or other deviations. Injecting insulin into areas of hypertrophy may delay absorption. The client shouldnt inject insulin into areas of lipodystrophy (such as hypertrophy or atrophy); to prevent lipodystrophy, the client should rotate injection sites systematically. Exercise speeds drug absorption, so the client shouldnt inject insulin into sites above muscles that will be exercised heavily. 86. Answer: (D) Below-normal serum potassium level Rationale: A client with HHNS has an overall body deficit of potassium resulting from diuresis, which occurs secondary to the hyperosmolar, hyperglycemic state caused by the relative insulin deficiency. An elevated serum acetone level and serum ketone bodies are characteristic of diabetic ketoacidosis. Metabolic acidosis, not serum alkalosis, may occur in HHNS.
87. Answer: (D) Maintaining room temperature in the low-normal range Rationale: Graves disease causes signs and symptoms of hypermetabolism, such as heat intolerance, diaphoresis, excessive thirst and appetite, and weight loss. To reduce heat intolerance and diaphoresis, the nurse should keep the clients room temperature in the low-normal range. To replace fluids lost via diaphoresis, the nurse should encourage, not restrict, intake of oral fluids. Placing extra blankets on the bed of a client with heat intolerance would cause discomfort. To provide needed energy and calories, the nurse should encourage the client to eat highcarbohydrate foods. 88. Answer: (A) Fracture of the distal radius Rationale: Colles fracture is a fracture of the distal radius, such as from a fall on an outstretched hand. Its most common in women. Colles fracture doesnt refer to a fracture of the olecranon, humerus, or carpal scaphoid. 89. Answer: (B) Calcium and phosphorous Rationale: In osteoporosis, bones lose calcium and phosphate salts, becoming porous, brittle, and abnormally vulnerable to fracture. Sodium and potassium arent involved in the development of osteoporosis. 90. Answer: (A) Adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) Rationale: Severe hypoxia after smoke inhalation is typically related to ARDS. The other conditions listed arent typically associated with smoke inhalation and severe hypoxia. 91. Answer: (D) Fat embolism Rationale: Long bone fractures are correlated with fat emboli, whichcause shortness of breath and hypoxia. Its unlikely the client has developed asthma or bronchitis without a previous history. He could develop atelectasis but it typically doesnt produce progressive hypoxia. 92. Answer: (D) Spontaneous pneumothorax Rationale: A spontaneous pneumothorax occurs when the clients lung collapses, causing an acute decreased in the amount of functional lung used in oxygenation. The sudden collapse was the cause of his chest pain and shortness of breath. An asthma attack would show wheezing breath sounds, and bronchitis would have rhonchi. Pneumonia would have bronchial breath sounds over the area of consolidation. 93. Answer: (C) Pneumothorax Rationale: From the trauma the client experienced, its unlikely he has bronchitis, pneumonia, or TB; rhonchi with bronchitis, bronchial breath sounds with TB would be heard. 94. Answer: (C) Serous fluids fills the space and consolidates the region Rationale: Serous fluid fills the space and eventually consolidates, preventing extensive mediastinal shift of the heart and remaining lung. Air cant be left in the space. Theres no gel that can be placed in the pleural space. The tissue from the other lung cant cross the mediastinum, although a temporary mediastinal shift exits until the space is filled. 95. Answer: (A) Alveolar damage in the infracted area Rationale: The infracted area produces alveolar damage that can lead to the production of bloody sputum, sometimes in massive amounts. Clot formation usually occurs in the legs. Theres a loss of lung parenchyma and subsequent scar tissue formation. 96. Answer: (D) Respiratory alkalosis Rationale: A client with massive pulmonary embolism will have a large region and blow off large
amount of carbon dioxide, which crosses the unaffected alveolar-capillary membrane more readily than does oxygen and results in respiratory alkalosis. 97. Answer: (A) Air leak Rationale: Bubbling in the water seal chamber of a chest drainage system stems from an air leak. In pneumothorax an air leak can occur as air is pulled from the pleural space. Bubbling doesnt normally occur with either adequate or inadequate suction or any preexisting bubbling in the water seal chamber. 98. Answer: (B) 21 Rationale: 3000 x 10 divided by 24 x 60. 99. Answer: (B) 2.4 ml Rationale: .05 mg/ 1 ml = .12mg/ x ml, .05x = .12, x = 2.4 ml. 100. Answer: (D) I should put on the stockings before getting out of bed in the morning. Rationale: Promote venous return by applying external pressure on veins. NP 5 1. Answer: (D) Focusing Rationale: The nurse is using focusing by suggesting that the client discuss a specific issue. The nurse didnt restate the question, make observation, or ask further question (exploring). 2. Answer: (D) Remove all other clients from the dayroom. Rationale: The nurses first priority is to consider the safety of the clients in the therapeutic setting. The other actions are appropriate responses after ensuring the safety of other clients. 3. Answer: (A) The client is disruptive. Rationale: Group activity provides too much stimulation, which the client will not be able to handle (harmful to self) and as a result will be disruptive to others. 4. Answer: (C) Agree to talk with the mother and the father together. Rationale: By agreeing to talk with both parents, the nurse can provide emotional support and further assess and validate the familys needs. 5. Answer: (A) Perceptual disorders. Rationale: Frightening visual hallucinations are especially common in clients experiencing alcohol withdrawal. 6. Answer: (D) Suggest that it takes awhile before seeing the results. Rationale: The client needs a specific response; that it takes 2 to 3 weeks (a delayed effect) until the therapeutic blood level is reached. 7. Answer: (C) Superego Rationale: This behavior shows a weak sense of moral consciousness. According to Freudian theory, personality disorders stem from a weak superego. 8. Answer: (C) Skeletal muscle paralysis. Rationale: Anectine is a depolarizing muscle relaxant causing paralysis. It is used to reduce the intensity of muscle contractions during the convulsive stage, thereby reducing the risk of bone fractures or dislocation. 9. Answer: (D) Increase calories, carbohydrates, and protein. Rationale: This client increased protein for tissue building and increased calories to replace what is burned up (usually via carbohydrates).
10. Answer: (C) Acting overly solicitous toward the child. Rationale: This behavior is an example of reaction formation, a coping mechanism. 11. Answer: (A) By designating times during which the client can focus on the behavior. Rationale: The nurse should designate times during which the client can focus on the compulsive behavior or obsessive thoughts. The nurse should urge the client to reduce the frequency of the compulsive behavior gradually, not rapidly. She shouldnt call attention to or try to prevent the behavior. Trying to prevent the behavior may cause pain and terror in the client. The nurse should encourage the client to verbalize anxieties to help distract attention from the compulsive behavior. 12. Answer: (D) Exploring the meaning of the traumatic event with the client. Rationale: The client with PTSD needs encouragement to examine and understand the meaning of the traumatic event and consequent losses. Otherwise, symptoms may worsen and the client may become depressed or engage in selfdestructive behavior such as substance abuse. The client must explore the meaning of the event and wont heal without this, no matter how much time passes. Behavioral techniques, such as relaxation therapy, may help decrease the clients anxiety and induce sleep. The physician may prescribe antianxiety agents or antidepressants cautiously to avoid dependence; sleep medication is rarely appropriate. A special diet isnt indicated unless the client also has an eating disorder or a nutritional problem. 13. Answer: (C) Your problem is real but there is no physical basis for it. Well work on what is going on in your life to find out why its happened. Rationale: The nurse must be honest with the client by telling her that the paralysis has no physiologic cause while also conveying empathy and acknowledging that her symptoms are real. The client will benefit from psychiatric treatment, which will help her understand the underlying cause of her symptoms. After the psychological conflict is resolved, her symptoms will disappear. Saying that it must be awful not to be able to move her legs wouldnt answer the clients question; knowing that the cause is psychological wouldnt necessarily make her feel better. Telling her that she has developed paralysis to avoid leaving her parents or that her personality caused her disorder wouldnt help her understand and resolve the underlying conflict. 14. Answer: (C) fluvoxamine (Luvox) and clomipramine (Anafranil) Rationale: The antidepressants fluvoxamine and clomipramine have been effective in the treatment of OCD. Librium and Valium may be helpful in treating anxiety related to OCD but arent drugs of choice to treat the illness. The other medications mentioned arent effective in the treatment of OCD. 15. Answer: (A) A warning about the drugs delayed therapeutic effect, which is from 14 to 30 days. Rationale: The client should be informed that the drugs therapeutic effect might not be reached for 14 to 30 days. The client must be instructed to continue taking the drug as directed. Blood level checks arent necessary. NMS hasnt been reported with this drug, but tachycardia is frequently reported. 16. Answer: (B) Severe anxiety and fear. Rationale: Phobias cause severe anxiety (such as a panic attack) that is out of proportion to the threat of the feared object or situation. Physical signs and symptoms of phobias include profuse sweating, poor motor control, tachycardia, and elevated blood
pressure. Insomnia, an inability to concentrate, and weight loss are common in depression. Withdrawal and failure to distinguish reality from fantasy occur in schizophrenia. 17. Answer: (A) Antidepressants Rationale: Tricyclic and monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor antidepressants have been found to be effective in treating clients with panic attacks. Why these drugs help control panic attacks isnt clearly understood. Anticholinergic agents, which are smooth-muscle relaxants, relieve physical symptoms of anxiety but dont relieve the anxiety itself. Antipsychotic drugs are inappropriate because clients who experience panic attacks arent psychotic. Mood stabilizers arent indicated because panic attacks are rarely associated with mood changes. 18. Answer: (B) 3 to 5 days Rationale: Monoamine oxidase inhibitors, such as tranylcypromine, have an onset of action of approximately 3 to 5 days. A full clinical response may be delayed for 3 to 4 weeks. The therapeutic effects may continue for 1 to 2 weeks after discontinuation. 19. Answer: (B) Providing emotional support and individual counseling. Rationale: Clients in the first stage of Alzheimers disease are aware that something is happening to them and may become overwhelmed and frightened. Therefore, nursing care typically focuses on providing emotional support and individual counseling. The other options are appropriate during the second stage of Alzheimers disease, when the client needs continuous monitoring to prevent minor illnesses from progressing into major problems and when maintaining adequate nutrition may become a challenge. During this stage, offering nourishing finger foods helps clients to feed themselves and maintain adequate nutrition. 20. Answer: (C) Emotional lability, euphoria, and impaired memory Rationale: Signs of antianxiety agent overdose include emotional lability, euphoria, and impaired memory. Phencyclidine overdose can cause combativeness, sweating, and confusion. Amphetamine overdose can result in agitation, hyperactivity, and grandiose ideation. Hallucinogen overdose can produce suspiciousness, dilated pupils, and increased blood pressure. 21. Answer: (D) A low tolerance for frustration Rationale: Clients with an antisocial personality disorder exhibit a low tolerance for frustration, emotional immaturity, and a lack of impulse control. They commonly have a history of unemployment, miss work repeatedly, and quit work without other plans for employment. They dont feel guilt about their behavior and commonly perceive themselves as victims. They also display a lack of responsibility for the outcome of their actions. Because of a lack of trust in others, clients with antisocial personality disorder commonly have difficulty developing stable, close relationships. 22. Answer: (C) Methadone Rationale: Methadone is used to detoxify opiate users because it binds with opioid receptors at many sites in the central nervous system but doesnt have the same deterious effects as other opiates, such as cocaine, heroin, and morphine. Barbiturates, amphetamines, and benzodiazepines are highly addictive and would require detoxification treatment. 23. Answer: (B) Hallucinations Rationale: Hallucinations are visual, auditory, gustatory, tactile, or olfactory perceptions that have no basis in reality. Delusions are false beliefs, rather than perceptions, that the client accepts as real.
Loose associations are rapid shifts among unrelated ideas. Neologisms are bizarre words that have meaning only to the client. 24. Answer: (C) Set up a strict eating plan for the client. Rationale: Establishing a consistent eating plan and monitoring the clients weight are very important in this disorder. The family and friends should be included in the clients care. The client should be monitored during meals-not given privacy. Exercise must be limited and supervised. 25. Answer: (A) Highly important or famous. Rationale: A delusion of grandeur is a false belief that one is highly important or famous. A delusion of persecution is a false belief that one is being persecuted. A delusion of reference is a false belief that one is connected to events unrelated to oneself or a belief that one is responsible for the evil in the world. 26. Answer: (D) Listening attentively with a neutral attitude and avoiding power struggles. Rationale: The nurse should listen to the clients requests, express willingness to seriously consider the request, and respond later. The nurse should encourage the client to take short daytime naps because he expends so much energy. The nurse shouldnt try to restrain the client when he feels the need to move around as long as his activity isnt harmful. High calorie finger foods should be offered to supplement the clients diet, if he cant remain seated long enough to eat a complete meal. The nurse shouldnt be forced to stay seated at the table to finish a meal. The nurse should set limits in a calm, clear, and self-confident tone of voice. 27. Answer: (D) Denial Rationale: Denial is unconscious defense mechanism in which emotional conflict and anxiety is avoided by refusing to acknowledge feelings, desires, impulses, or external facts that are consciously intolerable. Withdrawal is a common response to stress, characterized by apathy. Logical thinking is the ability to think rationally and make responsible decisions, which would lead the client admitting the problem and seeking help. Repression is suppressing past events from the consciousness because of guilty association. 28. Answer: (B) Paranoid thoughts Rationale: Clients with schizotypal personality disorder experience excessive social anxiety that can lead to paranoid thoughts. Aggressive behavior is uncommon, although these clients may experience agitation with anxiety. Their behavior is emotionally cold with a flattened affect, regardless of the situation. These clients demonstrate a reduced capacity for close or dependent relationships. 29. Answer: (C) Identify anxiety-causing situations Rationale: Bulimic behavior is generally a maladaptive coping response to stress and underlying issues. The client must identify anxietycausing situations that stimulate the bulimic behavior and then learn new ways of coping with the anxiety. 30. Answer: (A) Tension and irritability Rationale: An amphetamine is a nervous system stimulant that is subject to abuse because of its ability to produce wakefulness and euphoria. An overdose increases tension and irritability. Options B and C are incorrect because amphetamines stimulate norepinephrine, which increase the heart rate and blood flow. Diarrhea is a common adverse effect so option D in is incorrect. 31. Answer: (B) No, I do not hear your voices, but I believe you can hear them.
Rationale: The nurse, demonstrating knowledge and understanding, accepts the clients perceptions even though they are hallucinatory. 32. Answer: (C) Confusion for a time after treatment Rationale: The electrical energy passing through the cerebral cortex during ECT results in a temporary state of confusion after treatment. 33. Answer: (D) Acceptance stage Rationale: Communication and intervention during this stage are mainly nonverbal, as when the client gestures to hold the nurses hand. 34. Answer: (D) A higher level of anxiety continuing for more than 3 months. Rationale: This is not an expected outcome of a crisis because by definition a crisis would be resolved in 6 weeks. 35. Answer: (B) Staying in the sun Rationale: Haldol causes photosensitivity. Severe sunburn can occur on exposure to the sun. 36. Answer: (D) Moderate-level anxiety Rationale: A moderately anxious person can ignore peripheral events and focuses on central concerns. 37. Answer: (C) Diverse interest Rationale: Before onset of depression, these clients usually have very narrow, limited interest. 38. Answer: (A) As their depression begins to improve Rationale: At this point the client may have enough energy to plan and execute an attempt. 39. Answer: (D) Disturbance in recalling recent events related to cerebral hypoxia. Rationale: Cell damage seems to interfere with registering input stimuli, which affects the ability to register and recall recent events; vascular dementia is related to multiple vascular lesions of the cerebral cortex and subcortical structure. 40. Answer: (D) Encouraging the client to have blood levels checked as ordered. Rationale: Blood levels must be checked monthly or bimonthly when the client is on maintenance therapy because there is only a small range between therapeutic and toxic levels. 41. Answer: (B) Fine hand tremors or slurred speech Rationale: These are common side effects of lithium carbonate. 42. Answer: (D) Presence Rationale: The constant presence of a nurse provides emotional support because the client knows that someone is attentive and available in case of an emergency. 43. Answer: (A) Clients perception of the presenting problem. Rationale: The nurse can be most therapeutic by starting where the client is, because it is the clients concept of the problem that serves as the starting point of the relationship. 44. Answer: (B) Chocolate milk, aged cheese, and yogurt Rationale: These high-tyramine foods, when ingested in the presence of an MAO inhibitor, cause a severe hypertensive response. 45. Answer: (B) 4 to 6 weeks Rationale: Crisis is self-limiting and lasts from 4 to 6 weeks. 46. Answer: (D) Males are more likely to use lethal methods than are females Rationale: This finding is supported by research; females account for 90% of suicide attempts but
males are three times more successful because of methods used. 47. Answer: (C) Your cursing is interrupting the activity. Take time out in your room for 10 minutes. Rationale: The nurse should set limits on client behavior to ensure a comfortable environment for all clients. The nurse should accept hostile or quarrelsome client outbursts within limits without becoming personally offended, as in option A. Option B is incorrect because it implies that the clients actions reflect feelings toward the staff instead of the clients own misery. Judgmental remarks, such as option D, may decrease the clients self-esteem. 48. Answer: (C) lithium carbonate (Lithane) Rationale: Lithium carbonate, an antimania drug, is used to treat clients with cyclical schizoaffective disorder, a psychotic disorder once classified under schizophrenia that causes affective symptoms, including maniclike activity. Lithium helps control the affective component of this disorder. Phenelzine is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor prescribed for clients who dont respond to other antidepressant drugs such as imipramine. Chlordiazepoxide, an antianxiety agent, generally is contraindicated in psychotic clients. Imipramine, primarily considered an antidepressant agent, is also used to treat clients with agoraphobia and that undergoing cocaine detoxification. 49. Answer: (B) Report a sore throat or fever to the physician immediately. Rationale: A sore throat and fever are indications of an infection caused by agranulocytosis, a potentially life-threatening complication of clozapine. Because of the risk of agranulocytosis, white blood cell (WBC) counts are necessary weekly, not monthly. If the WBC count drops below 3,000/l, the medication must be stopped. Hypotension may occur in clients taking this medication. Warn the client to stand up slowly to avoid dizziness from orthostatic hypotension. The medication should be continued, even when symptoms have been controlled. If the medication must be stopped, it should be slowly tapered over 1 to 2 weeks and only under the supervision of a physician. 50. Answer: (C) Neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Rationale: The clients signs and symptoms suggest neuroleptic malignant syndrome, a life-threatening reaction to neuroleptic medication that requires immediate treatment. Tardive dyskinesia causes involuntary movements of the tongue, mouth, facial muscles, and arm and leg muscles. Dystonia is characterized by cramps and rigidity of the tongue, face, neck, and back muscles. Akathisia causes restlessness, anxiety, and jitteriness. 51. Answer: (B) Advising the client to sit up for 1 minute before getting out of bed. Rationale: To minimize the effects of amitriptylineinduced orthostatic hypotension, the nurse should advise the client to sit up for 1 minute before getting out of bed. Orthostatic hypotension commonly occurs with tricyclic antidepressant therapy. In these cases, the dosage may be reduced or the physician may prescribe nortriptyline, another tricyclic antidepressant. Orthostatic hypotension disappears only when the drug is discontinued. 52. Answer: (D) Dysthymic disorder. Rationale: Dysthymic disorder is marked by feelings of depression lasting at least 2 years, accompanied by at least two of the following symptoms: sleep disturbance, appetite disturbance, low energy or fatigue, low selfesteem, poor concentration, difficulty making decisions, and hopelessness. These symptoms may be relatively continuous or
separated by intervening periods of normal mood that last a few days to a few weeks. Cyclothymic disorder is a chronic mood disturbance of at least 2 years duration marked by numerous periods of depression and hypomania. Atypical affective disorder is characterized by manic signs and symptoms. Major depression is a recurring, persistent sadness or loss of interest or pleasure in almost all activities, with signs and symptoms recurring for at least 2 weeks. 53. Answer: (C) 30 g mixed in 250 ml of water Rationale: The usual adult dosage of activated charcoal is 5 to 10 times the estimated weight of the drug or chemical ingested, or a minimum dose of 30 g, mixed in 250 ml of water. Doses less than this will be ineffective; doses greater than this can increase the risk of adverse reactions, although toxicity doesnt occur with activated charcoal, even at the maximum dose. 54. Answer: (C) St. Johns wort Rationale: St. Johns wort has been found to have serotonin-elevating properties, similar to prescription antidepressants. Ginkgo biloba is prescribed to enhance mental acuity. Echinacea has immune-stimulating properties. Ephedra is a naturally occurring stimulant that is similar to ephedrine. 55. Answer: (B) Sodium Rationale: Lithium is chemically similar to sodium. If sodium levels are reduced, such as from sweating or diuresis, lithium will be reabsorbed by the kidneys, increasing the risk of toxicity. Clients taking lithium shouldnt restrict their intake of sodium and should drink adequate amounts of fluid each day. The other electrolytes are important for normal body functions but sodium is most important to the absorption of lithium. 56. Answer: (D) Its characterized by an acute onset and lasts hours to a number of days Rationale: Delirium has an acute onset and typically can last from several hours to several days. 57. Answer: (B) Impaired communication. Rationale: Initially, memory impairment may be the only cognitive deficit in a client with Alzheimers disease. During the early stage of this disease, subtle personality changes may also be present. However, other than occasional irritable outbursts and lack of spontaneity, the client is usually cooperative and exhibits socially appropriate behavior. Signs of advancement to the middle stage of Alzheimers disease include exacerbated cognitive impairment with obvious personality changes and impaired communication, such as inappropriate conversation, actions, and responses. During the late stage, the client cant perform self-care activities and may become mute. 58. Answer: (D) This medication may initially cause tiredness, which should become less bothersome over time. Rationale: Sedation is a common early adverse effect of imipramine, a tricyclic antidepressant, and usually decreases as tolerance develops. Antidepressants arent habit forming and dont cause physical or psychological dependence. However, after a long course of high-dose therapy, the dosage should be decreased gradually to avoid mild withdrawal symptoms. Serious adverse effects, although rare, include myocardial infarction, heart failure, and tachycardia. Dietary restrictions, such as avoiding aged cheeses, yogurt, and chicken livers, are necessary for a client taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor, not a tricyclic antidepressant. 59. Answer: (C) Monitor vital signs, serum electrolyte levels, and acid-base balance.
Rationale: An anorexic client who requires hospitalization is in poor physical condition from starvation and may die as a result of arrhythmias, hypothermia, malnutrition, infection, or cardiac abnormalities secondary to electrolyte imbalances. Therefore, monitoring the clients vital signs, serum electrolyte level, and acid base balance is crucial. Option A may worsen anxiety. Option B is incorrect because a weight obtained after breakfast is more accurate than one obtained after the evening meal. Option D would reward the client with attention for not eating and reinforce the control issues that are central to the underlying psychological problem; also, the client may record food and fluid intake inaccurately. 60. Answer: (D) Opioid withdrawal Rationale: The symptoms listed are specific to opioid withdrawal. Alcohol withdrawal would show elevated vital signs. There is no real withdrawal from cannibis. Symptoms of cocaine withdrawal include depression, anxiety, and agitation. 61. Answer: (A) Regression Rationale: An adult who throws temper tantrums, such as this one, is displaying regressive behavior, or behavior that is appropriate at a younger age. In projection, the client blames someone or something other than the source. In reaction formation, the client acts in opposition to his feelings. In intellectualization, the client overuses rational explanations or abstract thinking to decrease the significance of a feeling or event. 62. Answer: (A) Abnormal movements and involuntary movements of the mouth, tongue, and face. Rationale: Tardive dyskinesia is a severe reaction associated with long term use of antipsychotic medication. The clinical manifestations include abnormal movements (dyskinesia) and involuntary movements of the mouth, tongue (fly catcher tongue), and face. 63. Answer: (C) Blurred vision Rationale: At lithium levels of 2 to 2.5 mEq/L the client will experienced blurred vision, muscle twitching, severe hypotension, and persistent nausea and vomiting. With levels between 1.5 and 2 mEq/L the client experiencing vomiting, diarrhea, muscle weakness, ataxia, dizziness, slurred speech, and confusion. At lithium levels of 2.5 to 3 mEq/L or higher, urinary and fecal incontinence occurs, as well as seizures, cardiac dysrythmias, peripheral vascular collapse, and death. 64. Answer: (C) No acts of aggression have been observed within 1 hour after the release of two of the extremity restraints. Rationale: The best indicator that the behavior is controlled, if the client exhibits no signs of aggression after partial release of restraints. Options A, B, and D do not ensure that the client has controlled the behavior. 65. Answer: (A) increased attention span and concentration Rationale: The medication has a paradoxic effect that decrease hyperactivity and impulsivity among children with ADHD. B, C, D. Side effects of Ritalin include anorexia, insomnia, diarrhea and irritability. 66. Answer: (C) Moderate Rationale: The child with moderate mental retardation has an I.Q. of 35- 50 Profound Mental retardation has an I.Q. of below 20; Mild mental retardation 50-70 and Severe mental retardation has an I.Q. of 20-35. 67. Answer: (D) Rearrange the environment to activate the child
Rationale: The child with autistic disorder does not want change. Maintaining a consistent environment is therapeutic. A. Angry outburst can be rechanneling through safe activities. B. Acceptance enhances a trusting relationship. C. Ensure safety from self-destructive behaviors like head banging and hair pulling. 68. Answer: (B) cocaine Rationale: The manifestations indicate intoxication with cocaine, a CNS stimulant. A. Intoxication with heroine is manifested by euphoria then impairment in judgment, attention and the presence of papillary constriction. C. Intoxication with hallucinogen like LSD is manifested by grandiosity, hallucinations, synesthesia and increase in vital signs D. Intoxication with Marijuana, a cannabinoid is manifested by sensation of slowed time, conjunctival redness, social withdrawal, impaired judgment and hallucinations. 69. Answer: (B) insidious onset Rationale: Dementia has a gradual onset and progressive deterioration. It causes pronounced memory and cognitive disturbances. A,C and D are all characteristics of delirium. 70. Answer: (C) Claustrophobia Rationale: Claustrophobia is fear of closed space. A. Agoraphobia is fear of open space or being a situation where escape is difficult. B. Social phobia is fear of performing in the presence of others in a way that will be humiliating or embarrassing. D. Xenophobia is fear of strangers. 71. Answer: (A) Revealing personal information to the client Rationale: Counter-transference is an emotional reaction of the nurse on the client based on her unconscious needs and conflicts. B and C. These are therapeutic approaches. D. This is transference reaction where a client has an emotional reaction towards the nurse based on her past. 72. Answer: (D) Hold the next dose and obtain an order for a stat serum lithium level Rationale: Diarrhea and vomiting are manifestations of Lithium toxicity. The next dose of lithium should be withheld and test is done to validate the observation. A. The manifestations are not due to drug interaction. B. Cogentin is used to manage the extra pyramidal symptom side effects of antipsychotics. C. The common side effects of Lithium are fine hand tremors, nausea, polyuria and polydipsia. 73. Answer: (C) A living, learning or working environment. Rationale: A therapeutic milieu refers to a broad conceptual approach in which all aspects of the environment are channeled to provide a therapeutic environment for the client. The six environmental elements include structure, safety, norms; limit setting, balance and unit modification. A. Behavioral approach in psychiatric care is based on the premise that behavior can be learned or unlearned through the use of reward and punishment. B. Cognitive approach to change behavior is done by correcting distorted perceptions and irrational beliefs to correct maladaptive behaviors. D. This is not congruent with therapeutic milieu. 74. Answer: (B) Transference Rationale: Transference is a positive or negative feeling associated with a significant person in the clients past that are unconsciously assigned to another A. Splitting is a defense mechanism commonly seen in a client with personality disorder in which the world is perceived as all good or all bad C. Countert-transference is a phenomenon where the nurse shifts feelings assigned to someone in her past to the patient D. Resistance is the clients refusal to submit himself to the care of the nurse
75. Answer: (B) Adventitious Rationale: Adventitious crisis is a crisis involving a traumatic event. It is not part of everyday life. A. Situational crisis is from an external source that upset ones psychological equilibrium C and D. Are the same. They are transitional or developmental periods in life 76. Answer: (C) Major depression Rationale: The DSM-IV-TR classifies major depression as an Axis I disorder. Borderline personality disorder as an Axis II; obesity and hypertension, Axis III. 77. Answer: (B) Transference Rationale: Transference is the unconscious assignment of negative or positive feelings evoked by a significant person in the clients past to another person. Intellectualization is a defense mechanism in which the client avoids dealing with emotions by focusing on facts. Triangulation refers to conflicts involving three family members. Splitting is a defense mechanism commonly seen in clients with personality disorder in which the world is perceived as all good or all bad. 78. Answer: (B) Hypochondriasis Rationale: Complains of vague physical symptoms that have no apparent medical causes are characteristic of clients with hypochondriasis. In many cases, the GI system is affected. Conversion disorders are characterized by one or more neurologic symptoms. The clients symptoms dont suggest severe anxiety. A client experiencing sublimation channels maladaptive feelings or impulses into socially acceptable behavior 79. Answer: (C) Hypochondriasis Rationale: Hypochodriasis in this case is shown by the clients belief that she has a serious illness, although pathologic causes have been eliminated. The disturbance usually lasts at lease 6 with identifiable life stressor such as, in this case, course examinations. Conversion disorders are characterized by one or more neurologic symptoms. Depersonalization refers to persistent recurrent episodes of feeling detached from ones self or body. Somatoform disorders generally have a chronic course with few remissions. 80. Answer: (A) Triazolam (Halcion) Rationale: Triazolam is one of a group of sedative hypnotic medication that can be used for a limited time because of the risk of dependence. Paroxetine is a scrotonin-specific reutake inhibitor used for treatment of depression panic disorder, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Fluoxetine is a scrotonin-specific reuptake inhibitor used for depressive disorders and obsessive-compulsive disorders. Risperidome is indicated for psychotic disorders. 81. Answer: (D) It promotes emotional support or attention for the client Rationale: Secondary gain refers to the benefits of the illness that allow the client to receive emotional support or attention. Primary gain enables the client to avoid some unpleasant activity. A dysfunctional family may disregard the real issue, although some conflict is relieved. Somatoform pain disorder is a preoccupation with pain in the absence of physical disease. 82. Answer: (A) I went to the mall with my friends last Saturday Rationale: Clients with panic disorder tent to be socially withdrawn. Going to the mall is a sign of working on avoidance behaviors. Hyperventilating is a key symptom of panic disorder. Teaching breathing control is a major intervention for clients with panic disorder. The client taking
medications for panic disorder; such as tricylic antidepressants and benzodiazepines, must be weaned off these drugs. Most clients with panic disorder with agoraphobia dont have nutritional problems. 83. Answer: (A) Im sleeping better and dont have nightmares Rationale:MAO inhibitors are used to treat sleep problems, nightmares, and intrusive daytime thoughts in individual with posttraumatic stress disorder. MAO inhibitors arent used to help control flashbacks or phobias or to decrease the craving for alcohol. 84. Answer: (D) Stopping the drug can cause withdrawal symptoms Rationale: Stopping antianxiety drugs such as benzodiazepines can cause the client to have withdrawal symptoms. Stopping a benzodiazepine doesnt tend to cause depression, increase cognitive abilities, or decrease sleeping difficulties. 85. Answer: (B) Behavioral difficulties Rationale: Adolescents tend to demonstrate severe irritability and behavioral problems rather than simply a depressed mood. Anxiety disorder is more commonly associated with small children rather than with adolescents. Cognitive impairment is typically associated with delirium or dementia. Labile mood is more characteristic of a client with cognitive impairment or bipolar disorder. 86. Answer: (D) Its a mood disorder similar to major depression but of mild to moderate severity Rationale: Dysthymic disorder is a mood disorder similar to major depression but it remains mild to moderate in severity. Cyclothymic disorder is a mood disorder characterized by a mood range from moderate depression to hypomania. Bipolar I disorder is characterized by a single manic episode with no past major depressive episodes. Seasonalaffective disorder is a form of depression occurring in the fall and winter. 87. Answer: (A) Vascular dementia has more abrupt onset Rationale: Vascular dementia differs from Alzheimers disease in that it has a more abrupt onset and runs a highly variable course. Personally change is common in Alzheimers disease. The duration of delirium is usually brief. The inability to carry out motor activities is common in Alzheimers disease. 88. Answer: (C) Drug intoxication Rationale: This client was taking several medications that have a propensity for producing delirium; digoxin (a digitalis glycoxide), furosemide (a thiazide diuretic), and diazepam (a benzodiazepine). Sufficient supporting data dont exist to suspect the other options as causes. 89. Answer: (D) The client is experiencing visual hallucination Rationale: The presence of a sensory stimulus correlates with the definition of a hallucination, which is a false sensory perception. Aphasia refers to a communication problem. Dysarthria is difficulty in speech production. Flight of ideas is rapid shifting from one topic to another. 90. Answer: (D) The client looks at the shadow on a wall and tells the nurse she sees frightening faces on the wall. Rationale: Minor memory problems are distinguished from dementia by their minor severity and their lack of significant interference with the clients social or occupational lifestyle. Other options would be included in the history data but dont directly correlate with the clients lifestyle. 91. Answer: (D) Loose association
Rationale: Loose associations are conversations that constantly shift in topic. Concrete thinking implies highly definitive thought processes. Flight of ideas is characterized by conversation thats disorganized from the onset. Loose associations dont necessarily start in a cogently, then becomes loose. 92. Answer: (C) Paranoid Rationale: Because of their suspiciousness, paranoid personalities ascribe malevolent activities to others and tent to be defensive, becoming quarrelsome and argumentative. Clients with antisocial personality disorder can also be antagonistic and argumentative but are less suspicious than paranoid personalities. Clients with histrionic personality disorder are dramatic, not suspicious and argumentative. Clients with schizoid personality disorder are usually detached from other and tend to have eccentric behavior. 93. Answer: (C) Explain that the drug is less affective if the client smokes Rationale: Olanzapine (Zyprexa) is less effective for clients who smoke cigarettes. Serotonin syndrome occurs with clients who take a combination of antidepressant medications. Olanzapine doesnt cause euphoria, and extrapyramidal adverse reactions arent a problem. However, the client should be aware of adverse effects such as tardive dyskinesia. 94. Answer: (A) Lack of honesty Rationale: Clients with antisocial personality disorder tent to engage in acts of dishonesty, shown by lying. Clients with schizotypal personality disorder tend to be superstitious. Clients with histrionic personality disorders tend to overreact to frustrations and disappointments, have temper tantrums, and seek attention. 95. Answer: (A) Im not going to look just at the negative things about myself Rationale: As the clients makes progress on improving self-esteem, selfblame and negative self evaluation will decrease. Clients with dependent personality disorder tend to feel fragile and inadequate and would be extremely unlikely to discuss their level of competence and progress. These clients focus on self and arent envious or jealous. Individuals with dependent personality disorders dont take over situations because they see themselves as inept and inadequate. 96. Answer: (C) Assess for possible physical problems such as rash Rationale: Clients with schizophrenia generally have poor visceral recognition because they live so fully in their fantasy world. They need to have as indepth assessment of physical complaints that may spill over into their delusional symptoms. Talking with the client wont provide as assessment of his itching, and itching isnt as adverse reaction of antipsychotic drugs, calling the physician to get the clients medication increased doesnt address his physical complaints. 97. Answer: (B) Echopraxia Rationale: Echopraxia is the copying of anothers behaviors and is the result of the loss of ego boundaries. Modeling is the conscious copying of someones behaviors. Ego-syntonicity refers to behaviors that correspond with the individuals sense of self. Ritualism behaviors are repetitive and compulsive. 98. Answer: (C) Hallucination Rationale: Hallucinations are sensory experiences that are misrepresentations of reality or have no basis in reality. Delusions are beliefs not based in reality. Disorganized speech is characterized by jumping from one topic to the next or using unrelated words. An idea of reference is a belief that
an unrelated situation holds special meaning for the client. 99. Answer: (C) Regression Rationale: Regression, a return to earlier behavior to reduce anxiety, is the basic defense mechanism in schizophrenia. Projection is a defense mechanism in which one blames others and attempts to justify actions; its used primarily by people with paranoid schizophrenia and delusional disorder. Rationalization is a defense mechanism used to justify ones action. Repression is the basic defense mechanism in the neuroses; its an involuntary exclusion of painful thoughts, feelings, or experiences from awareness. 100.Answer: (A) Should report feelings of restlessness or agitation at once Rationale: Agitation and restlessness are adverse effect of haloperidol and can be treated with antocholinergic drugs. Haloperidol isnt likely to cause photosensitivity or control essential hypertension. Although the client may experience increased concentration and activity, these effects are due to a decreased in symptoms, not the drug itself
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- PNLE III Nursing PracticeDocumento11 paginePNLE III Nursing PracticeASDF ASDFNessuna valutazione finora
- NLE PreBoard QuestionsDocumento73 pagineNLE PreBoard QuestionsAaron Johnson Fantastico JarrellNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer NLEDocumento197 pagineReviewer NLECon GallanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing CribDocumento137 pagineNursing Cribmaicynthiachrisell67% (3)
- PNLE NursingDocumento631 paginePNLE NursingLenaj Ebron50% (2)
- Funda 1Documento8 pagineFunda 1Aijem RyanNessuna valutazione finora
- PNLE PreDocumento147 paginePNLE PreRS Buenavista100% (8)
- Refresher 2Documento8 pagineRefresher 2Michael Gustilo100% (1)
- Preboard NP VDocumento11 paginePreboard NP VAiNessuna valutazione finora
- MS1Documento60 pagineMS1Jayson Britania MayugaNessuna valutazione finora
- Preboard Exams W Answers RationaleDocumento91 paginePreboard Exams W Answers RationaleEve Marie FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Nle 2015 QuestionsDocumento4 pagineNle 2015 QuestionsJona Suarez100% (1)
- Med Surg PNLE Exam QuestionsDocumento9 pagineMed Surg PNLE Exam Questionsdanielle ordoñezNessuna valutazione finora
- Powerful Answer Key of Board QuestionsDocumento59 paginePowerful Answer Key of Board QuestionsKaren khaye AlvaradoNessuna valutazione finora
- Medsurg 1Documento59 pagineMedsurg 1Angel YN Patricio FlorentinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing. Midwifery. Pharmacy. Medtech. CriminologyDocumento5 pagineNursing. Midwifery. Pharmacy. Medtech. CriminologyJake CopradeNessuna valutazione finora
- PNLE III For Medical Surgical NursingDocumento13 paginePNLE III For Medical Surgical NursingZymer Lee Abasolo100% (1)
- Set 1Documento40 pagineSet 1Dick Morgan FerrerNessuna valutazione finora
- PNLE IV Nursing PracticeDocumento8 paginePNLE IV Nursing PracticeDanielle KayeNessuna valutazione finora
- 2008 NP4Documento11 pagine2008 NP4Jeremiash Noblesala Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- NP4Documento31 pagineNP4Kenny NadelaNessuna valutazione finora
- D - 10answer KeyDocumento16 pagineD - 10answer KeyJune DumdumayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Exam Questions 2023 Part 1Documento4 pagineNursing Exam Questions 2023 Part 1Lejo Sunny100% (1)
- Rationale: A Leader Doesn't Have Formal Power and Authority But Influences The SuccessDocumento32 pagineRationale: A Leader Doesn't Have Formal Power and Authority But Influences The SuccessJohn kananamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Diagnostic ExamDocumento28 pagineFinal Diagnostic ExamAlfred Benjamin CajitaNessuna valutazione finora
- MS ExamDocumento7 pagineMS Examjosephine100% (2)
- NP3 4Documento65 pagineNP3 4Edward Nicko Garcia100% (1)
- Post Test - Ob - Prof. Arzadon (SC)Documento2 paginePost Test - Ob - Prof. Arzadon (SC)Kristen FajilanNessuna valutazione finora
- NLE Practice Exam With AnswersDocumento43 pagineNLE Practice Exam With AnswersSuzette Rae TateNessuna valutazione finora
- MOCKBOARD PART 3 Ready To PrintDocumento7 pagineMOCKBOARD PART 3 Ready To PrintJayrald CruzadaNessuna valutazione finora
- NP2Documento12 pagineNP2mhamaenphapa27100% (2)
- Medical Surgical Nursing Exam 2Documento11 pagineMedical Surgical Nursing Exam 2Zymer Lee AbasoloNessuna valutazione finora
- MSDocumento17 pagineMSJonas Marvin AnaqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Comprehensive Exam 1Documento19 pagineComprehensive Exam 1karenkaren09100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Nursing Part 3Documento19 pagineFundamentals of Nursing Part 3Honeylie Patricio100% (1)
- FRENLE REVIE NP3 and NP4-1Documento49 pagineFRENLE REVIE NP3 and NP4-1eric100% (1)
- Review Practice QuestionsDocumento12 pagineReview Practice QuestionsJhannNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Practice 2-5Documento47 pagineNursing Practice 2-5Emir Mukhtar Malcampo KamidNessuna valutazione finora
- Testmanship - Medical Surgical Nursing Test Taking Strategy-Based June 2009 Nursing Licensure ExaminationDocumento16 pagineTestmanship - Medical Surgical Nursing Test Taking Strategy-Based June 2009 Nursing Licensure ExaminationJennine Reyes100% (1)
- Set A: NP1 Nursing Board Exam December 2006 Answer Key 'Foundation of Professional Nursing PracticeDocumento16 pagineSet A: NP1 Nursing Board Exam December 2006 Answer Key 'Foundation of Professional Nursing PracticeElizabella Henrietta TanaquilNessuna valutazione finora
- NP2 RationaleDocumento19 pagineNP2 RationaleElizabella Henrietta TanaquilNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Coaching NP4 Set 1Documento13 pagineFinal Coaching NP4 Set 1STEFFI GABRIELLE GOLEZNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Test 2 (NP Ii)Documento7 pagineNursing Test 2 (NP Ii)Yuxin LiuNessuna valutazione finora
- November 2008 PNLEDocumento78 pagineNovember 2008 PNLEDon MarcusNessuna valutazione finora
- OncologyDocumento19 pagineOncologyLiezel Cauilan0% (1)
- NP4 Nursing Board ExamDocumento5 pagineNP4 Nursing Board ExamNewb TobikkoNessuna valutazione finora
- ERDNDocumento128 pagineERDNJohiarra TabigneNessuna valutazione finora
- Nle NP1Documento8 pagineNle NP1dammenoelNessuna valutazione finora
- NCLEXDocumento13 pagineNCLEXJheanAlphonsineT.MeansNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Surgical Nursing Practice TestDocumento9 pagineMedical Surgical Nursing Practice TestjeshemaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2021 JULY COMPILATION W AnswersDocumento115 pagine2021 JULY COMPILATION W AnswersZanie CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer and Rationale MaternityDocumento21 pagineAnswer and Rationale MaternityMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- NLEDocumento18 pagineNLEKeij AranetaNessuna valutazione finora
- NP1Documento32 pagineNP1Louie Anne Cardines Angulo100% (1)
- Nursing Practice I.Documento32 pagineNursing Practice I.beautifulme031690Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Practice IDocumento11 pagineNursing Practice IPrecious Nidua100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Nursing PNLEDocumento69 pagineFundamentals of Nursing PNLEkarloeguiareyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Burns: TEST I - Foundation of Professional Nursing PracticeDocumento9 pagineBurns: TEST I - Foundation of Professional Nursing PracticeMc SuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ziane Angela: Please Join Us As We Celebrate The Christening of Our DaughterDocumento1 paginaZiane Angela: Please Join Us As We Celebrate The Christening of Our DaughterroldanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cancer - QDocumento7 pagineCancer - QroldanNessuna valutazione finora
- Normal Vital SignsDocumento2 pagineNormal Vital SignsroldanNessuna valutazione finora
- IV CalculationDocumento6 pagineIV CalculationroldanNessuna valutazione finora
- NLE Compilation 1Documento67 pagineNLE Compilation 1blazegomez91% (34)
- Clinical Focus - CHNDocumento3 pagineClinical Focus - CHNroldan100% (3)
- Balance Sheet AccountsDocumento7 pagineBalance Sheet AccountsroldanNessuna valutazione finora
- Vani FinalDocumento2 pagineVani FinalroldanNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary SystemDocumento48 pagineUrinary SystemroldanNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro Notes 1Documento3 pagineMicro Notes 1roldanNessuna valutazione finora
- Operating Manual CSDPR-V2-200-NDocumento19 pagineOperating Manual CSDPR-V2-200-NJohnTPNessuna valutazione finora
- PT4115EDocumento18 paginePT4115Edragom2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics 7 LAS Quarter 3Documento97 pagineMathematics 7 LAS Quarter 3Villamor Baculi82% (17)
- Instructor: DR - Ashok Kaushal: Orthogonal ViewsDocumento49 pagineInstructor: DR - Ashok Kaushal: Orthogonal ViewsKristi GjokaNessuna valutazione finora
- DSR Codes - 1Documento108 pagineDSR Codes - 1lakkireddy seshireddyNessuna valutazione finora
- TXN Alarms 18022014Documento12 pagineTXN Alarms 18022014Sid GrgNessuna valutazione finora
- ZW250-7 BROCHURE LowresDocumento12 pagineZW250-7 BROCHURE Lowresbjrock123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Manual de Electronica HardbookDocumento970 pagineManual de Electronica HardbookninoferNessuna valutazione finora
- Ae 2 PerformanceDocumento4 pagineAe 2 PerformanceankitNessuna valutazione finora
- The Royal Commonwealth Society of Malaysia: Function MenuDocumento3 pagineThe Royal Commonwealth Society of Malaysia: Function MenuMynak KrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.003 Homework #12 Solutions: ProblemsDocumento9 pagine6.003 Homework #12 Solutions: ProblemsSamu PacurucuNessuna valutazione finora
- Accessories 162-USDocumento20 pagineAccessories 162-USعايد التعزيNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson PlanDocumento18 pagineLesson PlanYasmin Abigail AseriosNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Introduction To KennametalDocumento40 pagine1.1 Introduction To KennametalVig PankajNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study On Customer Satisfaction With After Sales Services at BLUE STAR Air ConditionerDocumento99 pagineA Study On Customer Satisfaction With After Sales Services at BLUE STAR Air ConditionerVinay KashyapNessuna valutazione finora
- CSEC Chemistry June 2018 P2 AnswersDocumento7 pagineCSEC Chemistry June 2018 P2 AnswerscxcchemistryNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiation Formula SheetDocumento5 pagineRadiation Formula SheetJakeJosephNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Process DebottleneckingDocumento46 pagineChemical Process DebottleneckingAhmed Ansari100% (2)
- Third Quarter Pre-Test Mathematics 7 Directions: RDocumento4 pagineThird Quarter Pre-Test Mathematics 7 Directions: RAhron RivasNessuna valutazione finora
- Barium SulphateDocumento11 pagineBarium SulphateGovindanayagi PattabiramanNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd Stage ComplicationsDocumento84 pagine3rd Stage ComplicationsDream100% (1)
- 11 - Morphology AlgorithmsDocumento60 pagine11 - Morphology AlgorithmsFahad MattooNessuna valutazione finora
- Kulkarni Shilpa A.Documento148 pagineKulkarni Shilpa A.MSKCNessuna valutazione finora
- 3TRIGODocumento5 pagine3TRIGOCielo Pabilan ObemioNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Design of The Bukwimba Open Pit Final 12042017Documento31 pagineTechnical Design of The Bukwimba Open Pit Final 12042017Rozalia PengoNessuna valutazione finora
- Product Specifications: MB3F-PSA4-19DEDocumento2 pagineProduct Specifications: MB3F-PSA4-19DEВадим ЧеховскийNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Eye 5Documento7 pagineHuman Eye 5NanditaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science7 q2 Mod6of8 Asexual Sexualrep v2Documento26 pagineScience7 q2 Mod6of8 Asexual Sexualrep v2Ishi OcheaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aci 522R-06 PDFDocumento25 pagineAci 522R-06 PDFaldi raimon100% (2)