Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Oxygen Delivery
Caricato da
yourdirtysocksDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Oxygen Delivery
Caricato da
yourdirtysocksCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Oxygen Delivery Devices RsCr 220
OXYGEN DELIVERY DEVICES Indications for use: Correction of hypoxemia Decreases the workload which hypoxemia has on the heart Acute myocardial infarction Severe trauma Post anesthesia recovery Precautions & or possible complications (Support SaO2 with least FiO2) May depress ventilation in some patients with chronic hypercapnia (CO 2 retainers) May cause atelectasis (60% O2) in partially obstructed patient Oxygen toxicity (> 50% O2 in < 24-48 hours Can cause Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP) in premature infants A. LOW FLOW DEVICES Defined as a device that does NOT meet all the inspiratory flow demands of the patient. Do NOT confuse low flow with low oxygen concentrations (FiO2). (Some low flow will supply high O2 percentage & some high flow will provide low O2 percentage.) FiO2 can vary with: Patients respiratory rate & pattern Flow of gas from the equipment Equipment reservoir 1. NASAL CANNULA delivers O2 percentage of 24 44% with flow rates of 1 - 6 liters per minute. A humidifier is used with flow rates > 4 LPM or for patient comfort. Higher flow can cause nosebleeds and headaches. Recently, improved humidifiers has allowed for higher flows and higher FiO2 s to be delivered via nasal O2 Increasing the oxygen flow by 1L/min will increase the inspired O2 concentration by approximately 4%. 1L/min: 24% 2L/min: 28% 3L/min: 32% 4L/min: 36% 5L/min: 40% 6L/min: 44%
Oxygen Delivery Devices RsCr 220
2. SIMPLE MASK delivers O2 percentage of 40 - 50% with flow rates of 5 - 12 LPM. Flow rates must be at least 5 LPM to ensure that CO2 is being flushed out of the mask. Good for patients with blocked nasal passages and mouth breathers. Masks are difficult to tolerate with skin irritation and at meal times. Guard against aspiration. A humidifier is optional. 3. NON-REBREATHER MASK delivers O2 percentage of 50 - 70%. Utilizes 3 one-way valves and a bag reservoir to supply the highest possible oxygen concentration of any of the masks. Flow can be set to meet the patients maximum inspiratory needs. Bag should not completely deflate on inspiration. A tight fit mask is necessary to deliver a high FiO2. 4. PARTIAL REBREATHER MASKS (O2 percentage of 40 60%) can be achieved by removing valves from the mask. PALS recommends that you remove the valves on infants and children to prevent possible suffocation.
partial rebreather
non-rebreather
5. TRACHEOSTOMY MASK Similar to a simple mask, but designed to fit over neck area. Usually is supplied by the large blue tubing from a heated aerosol setup. 6. TRANSPORT TEE (or trach Tee) is the method used to oxygenate an intubated patient or patient with tracheostomy during transport. It fits onto the ET tube or can be adapted for use with a trach mask. It supplies oxygen through oxygen tubing while attached to a portable oxygen tank (flow 6-10 LPM).
Oxygen Delivery Devices RsCr 220
B. HIGH FLOW DEVICES Will give a guaranteed FiO2 no matter what the patients venilatory pattern is. It is consistent and predictable. They meet or exceed the peak inspiratory flow of the patient. (Flow is at least 4X the patients minute ventilation, or > 60 L/min) Do NOT confuse high flow with high oxygen concentrations (FiO2). 1. VENTURI MASK delivers O2 percentage of 24 - 50%. It is important that the appropriate flow rate is used for each setting to guarantee accuracy. External ports must remain open to entrain room air.
2. AEROSOL (MIST MASK) SYSTEM delivers O2 percentage of 28 - 100%. When FiO2 is greater than 0,5 they must be set up in tandem. This device delivers humidified oxygen. If the upper airway is bypassed, i.e. intubated or tracheostomy in situ, then the aerosol needs to be heated with an electric heater to provide adequate humidity. This prevents drying of mucosa, mucus plugs, altered cilia function and humidity deficit. Aerosols may be used in conjunction with aerosol facemasks, face tents, trach collars, or T-Pieces.
C. MORE ON HIGH FLOW SYSTEMS An oxygen delivery device that meets or exceeds the inspiratory flow demands of the patient. I.E.> 30 Lpm total flow delivered Examples:
Oxygen Delivery Devices RsCr 220
-Venti-mask or air entrainment mask -Large volume jet nebulizers (Aerosol Mist) Characteristics -Provide stable and reliable O2 percentage. Usually low concentrations 24 to 50% -Only precise if total flow from the unit is > 30 Lpm (Need to meet pt demand) Advantages -Precise and stable -Patients resp rate and tidal vol have no effect on FIO2 Disadvantages -May be difficult to achieve FIO2s > 0,5 -Uncomfortable. The size of the entrainment port determines the delivered FIO2. -The larger the port the lower the FIO2 -The smaller the port the greater the FIO2 The size of the jet determines the FIO2 delivered -The smaller the jet the lower the FIO2. NOTE: A heater must be added to the aerosol mist when the patients normal breathing system is bypassed (ET Tube or trach mask) A double nebulizer setup is one way to increase flow with high FIO2s. D. MONITORING THE EFFECTIVENESS OF OXYGEN THERAPY Pulse Oximetry Arterial Blood gas Work of Breathing Tidal Volume & Respiratory Rate Pulse & Blood Pressure E. LIMITATIONS OF A HIGH FLOW SYSTEM: The size of the jet may inhibit the ability to increase source gas flow. Many systems cannot deliver more than 12 liters of source flow. Downstream back pressure may inhibit the amount of room air entrainment. Water in the tubing causes backpressure resistance. This can cause the FIO2 to be inaccurate. (increased)
Oxygen Delivery Devices RsCr 220
F. OTHER LESS COMMONLY USED O2 DELIVERY DEVICES Infant head hood and incubators used with a nebulizer (large jet) used with heated humidifier Pendant or reservoir nasal cannula used primarily in home care conserves oxygen so that less is needed to achieve prescribed FIO2 Nasal Biflow a small resevoir cup instead of prongs Patient demand systems and transtracheal catheters Croup tents used to deliver O2 and cool mist Blenders (O2 blenders) allows for mixing of air & O2 for a desired O2% Newer devices: Vapotherm: http://vapotherm.inquisiq.com/default.asp http://www.oxyarm.com/ourProducts_oxyarm.shtml http://www.oxyarm.com/ourProducts_oxymask.shtml
G. HYPERBARIC OXYGEN THERAPY Monoplace chambers Clear plexiglass tube that patient is placed in Multiplace chambers RT and nurses accompany patient in chamber Indications: 1. Carbon monoxide poisoning 2. Decompression sickness (the bends) 3. Air embolism 4. Cyanide poisoning 5. Gas gangrene 6. Improve wound healing (decubitus ulcers) 7. Refractory osteomyelitis 8. Thermal burns 9. Improves skin grafting success 10. Severe anaerobic infections H. OTHER GASES OF NOTE:
Oxygen Delivery Devices RsCr 220
Carbogen: o Usually 95% oxygen and 5% carbon dioxide o Treats singultus (hiccups) o Provides a challenge to stimulate breathing in some patients Heliox o Useful with ventilators and in ER o Upper airway narrowing o Croup o Asthma o Stridor o Tracheal tumors Nitric Oxide o Treatment of neonates with hypoxic respiratory failure associated with pulmonary hypertension
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Respiratory System MedicationsDocumento2 pagineRespiratory System Medicationsmlbrown8Nessuna valutazione finora
- ABGs Respiratory/MetabolicDocumento3 pagineABGs Respiratory/MetabolicJoe B100% (1)
- Overview of Acute Pulmonary Embolism in AdultsDocumento9 pagineOverview of Acute Pulmonary Embolism in AdultsnathanaelandryNessuna valutazione finora
- STUDENT Sepsis Rapid ReasoningDocumento6 pagineSTUDENT Sepsis Rapid Reasoningghodghod123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Non Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)Documento16 pagineNon Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)Dilan GalaryNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 Fun Facts About Your Heart: Educational VersionDa Everand14 Fun Facts About Your Heart: Educational VersionNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept Map 360Documento6 pagineConcept Map 360api-273469220Nessuna valutazione finora
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideDa EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines for Measuring Household and Individual Dietary DiversityDa EverandGuidelines for Measuring Household and Individual Dietary DiversityNessuna valutazione finora
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDa EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Revised Asthma Action Plan 2010 (English)Documento3 pagineRevised Asthma Action Plan 2010 (English)DC Asthma PartnershipNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory Therapy Cave - Ventilator Graphics Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineRespiratory Therapy Cave - Ventilator Graphics Cheat SheetMarwa El-DegwiNessuna valutazione finora
- NRSG 115 CCL CDL Spring 2020 Lab Information SheetDocumento7 pagineNRSG 115 CCL CDL Spring 2020 Lab Information SheetSethNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Mix InsulinDocumento2 pagineHow To Mix InsulinchareneadamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Ventilation and Intracranial PressureDocumento30 pagineMechanical Ventilation and Intracranial PressureFlavius AnghelNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationLeirza OnibarNessuna valutazione finora
- ICU Scoring Systems A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandICU Scoring Systems A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- SBAR WorksheetDocumento3 pagineSBAR Worksheet6bigstar9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Noninvasive VentilationDocumento6 pagineNoninvasive VentilationEma MagfirahNessuna valutazione finora
- DKA Concept MapDocumento2 pagineDKA Concept MapJanetNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Nursing OutlineDocumento4 pagineFundamentals of Nursing OutlineNina Anne ParacadNessuna valutazione finora
- Fall Risk Assessment FormDocumento3 pagineFall Risk Assessment FormMichael Silva100% (1)
- 2017 05 GC Pocket CardDocumento2 pagine2017 05 GC Pocket Cardapi-312241089Nessuna valutazione finora
- Registered Respiratory TherapistDocumento3 pagineRegistered Respiratory Therapistapi-76909521Nessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocumento4 pagineImpaired Gas ExchangeNuraini Hamzah100% (1)
- Chronic BronchitisDocumento2 pagineChronic BronchitisEimhie Lee CasiNessuna valutazione finora
- Normal Pediatric RR and HRDocumento1 paginaNormal Pediatric RR and HRRick FreaNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Burns Based On Depth CharacteristicsDocumento2 pagineClassification of Burns Based On Depth CharacteristicsmexelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Head To Toe Physical Assessment: College of NursingDocumento4 pagineHead To Toe Physical Assessment: College of NursingMaicah ShaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Med-Surg Final Jeopardy Review.Documento3 pagineMed-Surg Final Jeopardy Review.jenn1722Nessuna valutazione finora
- Acid-Base Balance + Arterial Blood GasesDocumento30 pagineAcid-Base Balance + Arterial Blood GasesQusai IbraheemNessuna valutazione finora
- Discussion QuestionsDocumento2 pagineDiscussion QuestionsMary RiasNessuna valutazione finora
- 406 - Respiratory Therapy Consult Service HandbookDocumento28 pagine406 - Respiratory Therapy Consult Service HandbookIkhsan JohnsonNessuna valutazione finora
- 3112 MultisystemcasestudyDocumento9 pagine3112 Multisystemcasestudyapi-306118308Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shock Study GuideDocumento8 pagineShock Study GuideMadameb1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sleep Apnoea - Prof - DR K.K.PDocumento44 pagineSleep Apnoea - Prof - DR K.K.PjialeongNessuna valutazione finora
- Grady EMS Drug List 2017 FINALDocumento20 pagineGrady EMS Drug List 2017 FINALThomas LeachNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care of PlanDocumento16 pagineNursing Care of PlanDbyNessuna valutazione finora
- HW InotropesDocumento3 pagineHW InotropesNatalie YeohNessuna valutazione finora
- Extubation CriteriaDocumento17 pagineExtubation CriteriaOliver TabagNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Cases Assignment Nursing Student PathologyDocumento4 pagineStudy Cases Assignment Nursing Student PathologyRoody AdthinyNessuna valutazione finora
- Sbar 4Documento2 pagineSbar 4Nurse Betty100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Sample For BeginnersDocumento15 pagineNursing Care Plan Sample For BeginnersMoe KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- StrokeDocumento1 paginaStrokeMariel Febreo MerlanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ventilator Management ProtocolDocumento9 pagineVentilator Management ProtocolcrisdinasusenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Ventilation TherapyDocumento17 pagineMechanical Ventilation TherapyFaizal FlNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical VentilationDocumento9 pagineMechanical VentilationMario MagtakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Stages of ShockDocumento7 pagineStages of ShockNicholas TagleNessuna valutazione finora
- C 13Documento11 pagineC 13Jo100% (1)
- AA GradientDocumento2 pagineAA GradientzaminazzNessuna valutazione finora
- Cheat Sheet Acidosis and AlkalosisDocumento1 paginaCheat Sheet Acidosis and AlkalosisAkasha FrostmourneNessuna valutazione finora
- NursingCare PlanDocumento8 pagineNursingCare PlanSunSearra Kennedy RuffinNessuna valutazione finora
- Life and DeathDocumento23 pagineLife and DeathJea Joel MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Emergency DrugsDocumento9 pagineEmergency DrugsaldwinngNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Medication WorksheetDocumento1 paginaClinical Medication WorksheetSrkocher100% (1)
- Ekg Cheat SheetDocumento5 pagineEkg Cheat SheetAnonymous QBa0UurPNessuna valutazione finora
- Symptom Flow Chart (Difficulty Breathing)Documento2 pagineSymptom Flow Chart (Difficulty Breathing)Jeff ZhouNessuna valutazione finora
- Chest TubesDocumento12 pagineChest TubesMark Hammerschmidt100% (4)
- Shock Types 141009102815 Conversion Gate01Documento41 pagineShock Types 141009102815 Conversion Gate01Samjaisheel SamsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Agc332 Lecture 10-Wheat DiseasesDocumento33 pagineAgc332 Lecture 10-Wheat DiseasesSolomon MbeweNessuna valutazione finora
- Trauma Team UMDocumento13 pagineTrauma Team UMMohamad Hasnol HayatNessuna valutazione finora
- Contact Lens Complications and ManagementDocumento10 pagineContact Lens Complications and Managementstrawberry8832850% (2)
- FULL Download Ebook PDF Fundamentals of Human Neuropsychology 7th Edition PDF EbookDocumento41 pagineFULL Download Ebook PDF Fundamentals of Human Neuropsychology 7th Edition PDF Ebookjennifer.lawver532100% (44)
- Liver Pathology EMQDocumento1 paginaLiver Pathology EMQhazirmm100% (2)
- UnificationDocumento24 pagineUnificationFlyingWalrusNessuna valutazione finora
- Mental Disorder Due To AlcoholDocumento18 pagineMental Disorder Due To AlcoholAnonymous Oj5JCpO5xNessuna valutazione finora
- Inventarisasi Dan Identifikasi Hama Dan Penyakit Utama Tanaman Jagung (Zea Mays L.), Yustina M. S. W. Pu'u, Sri WahyuniDocumento11 pagineInventarisasi Dan Identifikasi Hama Dan Penyakit Utama Tanaman Jagung (Zea Mays L.), Yustina M. S. W. Pu'u, Sri WahyuniJefri DwiNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Teaching PlanDocumento4 pagineHealth Teaching Plani & vNessuna valutazione finora
- Kakawate Dog Soap ThesisDocumento55 pagineKakawate Dog Soap ThesisArturo Roman100% (4)
- EssayDocumento8 pagineEssayapi-308498731Nessuna valutazione finora
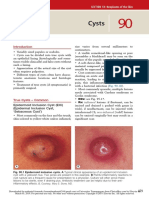
- CystsDocumento5 pagineCystsranindita maulyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Cardiac EKG Interpretation - Basics Part 1 - ScriptDocumento2 pagineAcute Cardiac EKG Interpretation - Basics Part 1 - ScriptDarby GravinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Master The Perfec Tnight of SleepDocumento10 pagineMaster The Perfec Tnight of SleepPaulo André Prada de CamargoNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Microbiology and Infection: Original ArticleDocumento6 pagineClinical Microbiology and Infection: Original ArticleAkira Masumi100% (1)
- The Validity of Acupuncture in Veterinary MedicineDocumento10 pagineThe Validity of Acupuncture in Veterinary MedicinePaolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Global Manual On Surveillance of AEFIDocumento128 pagineGlobal Manual On Surveillance of AEFIHarold JeffersonNessuna valutazione finora
- Bril (2002) - Validation of The Toronto Clinical Scoring System For Diabetic PolyneuropathyDocumento5 pagineBril (2002) - Validation of The Toronto Clinical Scoring System For Diabetic PolyneuropathyRicky WatariNessuna valutazione finora
- Hallie Berger Resume 11-2Documento2 pagineHallie Berger Resume 11-2api-281008760Nessuna valutazione finora
- Theory ApplicationDocumento38 pagineTheory ApplicationAnusha VergheseNessuna valutazione finora
- Illich 1982Documento5 pagineIllich 1982CsscamposNessuna valutazione finora
- Causes of Metabolic AcidosisDocumento10 pagineCauses of Metabolic AcidosisKimberly Anne SP PadillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Caffein Intox PDFDocumento3 pagineCaffein Intox PDFSejahtera SurbaktiNessuna valutazione finora
- Yvonne Farrell Psycho Emotional NotesDocumento10 pagineYvonne Farrell Psycho Emotional Notesபாலஹரிப்ரீதா முத்து100% (2)
- Par QDocumento1 paginaPar Qapi-39512869100% (1)
- VBAC MCQsDocumento3 pagineVBAC MCQsHanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kjadjk BkjbasjdDocumento23 pagineKjadjk BkjbasjdzaenalNessuna valutazione finora
- Intra-Arterial Catheterization For Invasive Monitoring: Indications, Insertion Techniques, and Interpretation - UpToDateDocumento40 pagineIntra-Arterial Catheterization For Invasive Monitoring: Indications, Insertion Techniques, and Interpretation - UpToDatejuanpbagurNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Function TestsDocumento23 pagineRenal Function TestsKer YehunNessuna valutazione finora
- Kode Penjelasan Keterangan: ObgynDocumento14 pagineKode Penjelasan Keterangan: Obgynanon_507132438Nessuna valutazione finora