Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Nephrolithiasis - Patho
Caricato da
Aia Javier0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
249 visualizzazioni1 paginaA 61-year-old male with a history of inadequate fluid intake, high purine diet, and holding off urination developed uric acid stones in his kidneys due to increased uric acid in his bloodstream and urine stasis. This partially obstructed his right kidney and caused hydronephrosis of his left kidney, resulting in flank pain, hematuria, and tissue damage due to unrelieved pressure buildup.
Descrizione originale:
CCCDD
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoA 61-year-old male with a history of inadequate fluid intake, high purine diet, and holding off urination developed uric acid stones in his kidneys due to increased uric acid in his bloodstream and urine stasis. This partially obstructed his right kidney and caused hydronephrosis of his left kidney, resulting in flank pain, hematuria, and tissue damage due to unrelieved pressure buildup.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
249 visualizzazioni1 paginaNephrolithiasis - Patho
Caricato da
Aia JavierA 61-year-old male with a history of inadequate fluid intake, high purine diet, and holding off urination developed uric acid stones in his kidneys due to increased uric acid in his bloodstream and urine stasis. This partially obstructed his right kidney and caused hydronephrosis of his left kidney, resulting in flank pain, hematuria, and tissue damage due to unrelieved pressure buildup.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
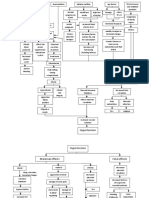
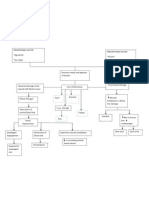
Chapter VII Pathophysiology of Nephrolithiasis
Male 61 y/o
Increased protein and purine intake Habits of inadequate fluid intake and holding off of urination
Increased uric acid in the blood stream due to increased purine intake
Body compensates by letting kidney eliminate the excess uric acid
Concentration of uric acid due to inadequate fluid intake
Accumulation of uric acid in the kidney
Urinary stasis due to holding off of urination
Formation of uric acid stones
Partial obstruction of the kidney
Trauma to kidney tissues
Flank pain
Hematuria
Probable reflux of urine (unidentified cause)
Reflux of urine to the kidneys, however, only mostly to the left due to the partial obstruction to the right
Hydronephrosis of the left
Acute colicky flank pain that radiates to the groin
Distention of the renal pelvis and calyces
Hematuria
Damage to the tissues due to unrelieved pressure
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Pathophysiology of NephrolithiasisDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of Nephrolithiasismissmakai100% (2)
- Case Study On Bilateral NephrolithiasisDocumento84 pagineCase Study On Bilateral NephrolithiasisSteph BulanNessuna valutazione finora
- NEPHROLITHIASIS - PathophysiologyDocumento2 pagineNEPHROLITHIASIS - PathophysiologyJon Corpuz Aggasid100% (5)
- NephrolithiasisDocumento2 pagineNephrolithiasisDeepthiNessuna valutazione finora
- IV. The PATIENTS ILLNESS (Nephrolithiasis) Pathophysiology (Book-Based)Documento3 pagineIV. The PATIENTS ILLNESS (Nephrolithiasis) Pathophysiology (Book-Based)wapakalypseNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperthyroidism Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramDocumento1 paginaHyperthyroidism Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramMarielle CabanbanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of AGEDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of AGEtinatin9890% (1)
- PathophysiologyDocumento4 paginePathophysiologyDante SalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of The GallbladderDocumento1 paginaAnatomy and Physiology of The GallbladderRojanisa Baculi RomathoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Gouty ArthritisDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of Gouty ArthritiskyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Hernandez NCP Drug StudyDocumento7 pagineHernandez NCP Drug StudyEliza Joyce HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrolithiasis Case StudyDocumento41 pagineNephrolithiasis Case StudyRachel Semilla50% (2)
- Right Sided Congestive Heart FailureDocumento1 paginaRight Sided Congestive Heart FailureEzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ov Ov OvDocumento15 pagineOv Ov OvHayyana Mae Taguba LadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Patho Pleural EffusionDocumento2 paginePatho Pleural EffusionJess Prodigo50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of UrolithiasisDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of UrolithiasisNavjot Brar100% (2)
- Pathophysiology Sickle Cell Anemia PDFDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology Sickle Cell Anemia PDFTine GuibaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Schematic Diagram of Alcoholic CirrhosisDocumento2 pagineSchematic Diagram of Alcoholic CirrhosisCyrus De Asis0% (1)
- Etiology, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Manifestations of CholecystitisDocumento3 pagineEtiology, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Manifestations of CholecystitisGerriNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary Tract Infectio Case StudyDocumento17 pagineUrinary Tract Infectio Case Studyjunex123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophsyiology of AGEDocumento1 paginaPathophsyiology of AGEmariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of NephrolithiasisDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of Nephrolithiasisanreilegarde80% (5)
- Pa Tho Irritable Bowel SyndromeDocumento1 paginaPa Tho Irritable Bowel Syndromekaye0403Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ijser: A Case Study On CholelithiasisDocumento2 pagineIjser: A Case Study On CholelithiasisRuby Cubionalanting100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Gastroenteritis, Dehydration, and NecatoriasisDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of Gastroenteritis, Dehydration, and NecatoriasisRalph Delos Santos100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionDocumento50 paginePathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionPryo UtamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of HemorrhoidsDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of HemorrhoidsTrixie FayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Anemia PathophysiologyDocumento2 pagineAnemia PathophysiologyHoney Lorie D. Simbajon67% (6)
- Nephrolithiasis Case StudyDocumento31 pagineNephrolithiasis Case StudyL.a.Zumárraga67% (3)
- Patho UGIBDocumento3 paginePatho UGIBKristineBungcagNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryDocumento4 paginePathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryJane Arian Berzabal0% (1)
- Etiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocumento5 pagineEtiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsJanelle NarcisoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Acute AppendicitisDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of Acute AppendicitissiarahNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute PyelonephritisDocumento59 pagineAcute PyelonephritisKylie Golindang100% (1)
- Pre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesDocumento3 paginePre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesPrincess Diane S. VillegasNessuna valutazione finora
- Pa Tho Physiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocumento2 paginePa Tho Physiology of Acute Gastroenteritisromeo rivera100% (16)
- AGE With Pa Tho PhysiologyDocumento3 pagineAGE With Pa Tho PhysiologyChichi Licuben OresacamNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Nephrolithiasis, Struvites Stone (Staghorn Calculi)Documento2 paginePathophysiology of Nephrolithiasis, Struvites Stone (Staghorn Calculi)Floyd100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureMel Izhra N. MargateNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology - AppendicitisDocumento5 paginePathophysiology - AppendicitisAzielle Joyce RosquetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocumento5 paginePathophysiology of Acute Gastroenteritisheron_bayanin_15Nessuna valutazione finora
- AGE PathophysiologyDocumento1 paginaAGE PathophysiologyZhenmeiNessuna valutazione finora
- CholelithiasisDocumento3 pagineCholelithiasisMIlanSagittarius0% (1)
- Copd PathoDocumento1 paginaCopd PathoRey AngeloNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of ESRDDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of ESRDjake90210100% (1)
- Prioritization of ProblemsDocumento3 paginePrioritization of ProblemsBLABLEBLIBLOBLUUUNessuna valutazione finora
- Cholecystectomy - James Conrad SalengaDocumento14 pagineCholecystectomy - James Conrad SalengaJames Conrad SalengaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gordons Pattern of Functioning (518 - Sanvitores Victoria)Documento7 pagineGordons Pattern of Functioning (518 - Sanvitores Victoria)Anthony Jay Luz Foronda100% (1)
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension PathophysiologyDocumento2 paginePregnancy Induced Hypertension PathophysiologyCamille Grace100% (1)
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Documento10 pagineSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocumento3 paginePathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsMizchelle Angeles VilladorNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Renal Failure DiagramDocumento3 pagineAcute Renal Failure DiagramMichelle BarojaNessuna valutazione finora
- Liver CirrohosisDocumento157 pagineLiver CirrohosisSeema SachdevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Patho of Liver Cirrhosis 22222 (Repaired)Documento2 paginePatho of Liver Cirrhosis 22222 (Repaired)Maxie PacadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Calculi in HomoeopathyDocumento37 pagineRenal Calculi in HomoeopathyTarique ImamNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology Acute PyelonephritisDocumento2 paginePathophysiology Acute PyelonephritisAnonymous 75TDy2y100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephriti1Documento2 paginePathophysiology Acute Pyelonephriti1Stephanie Joy EscalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Kidney Disease in Homoeopathy Part-1Documento31 pagineChronic Kidney Disease in Homoeopathy Part-1Tarique ImamNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology FinalDocumento2 paginePathophysiology FinallarissedeleonNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Renal FailureDocumento101 pagineAcute Renal FailureRowshon AraNessuna valutazione finora
- Barangay 2: Community Health NursingDocumento1 paginaBarangay 2: Community Health NursingAia JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and SssDocumento9 pagineAnatomy and SssAia JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Male 755: I. Vital StatisticsDocumento4 pagineMale 755: I. Vital StatisticsAia JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrolithiasis - NCPDocumento9 pagineNephrolithiasis - NCPAia Javier83% (6)
- Nephrolithiasis - Drug StudyDocumento5 pagineNephrolithiasis - Drug StudyAia JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Psych So DDDocumento2 paginePsych So DDAia JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study - Psyche (2) DDDDocumento3 pagineDrug Study - Psyche (2) DDDAia JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- List of AntibioticsDocumento10 pagineList of AntibioticsAia JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Musculoskeletal Care ModalitiesDocumento45 pagineMusculoskeletal Care ModalitiesAia JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Balance Skeletal Traction ApplicationDocumento6 pagineBalance Skeletal Traction ApplicationAia JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- CaseDocumento7 pagineCaseAia JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Communicable Disease Prevention and ControlDocumento4 pagineCommunicable Disease Prevention and ControlAia JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- AppendectomyDocumento15 pagineAppendectomyAia JavierNessuna valutazione finora