Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Diabetes
Caricato da
Jadie PrenioCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Diabetes
Caricato da
Jadie PrenioCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Diabetes
Study online at quizlet.com/_bxzg
1.
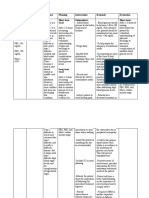
characteristic of IDDM classic signs and symptoms of Diabetes:
decrease in size and number of islet cells resulting inadequate prodution of insulin 1.Elevated blood sugar (hyperglicemia), 2.Elevated sugar in urine (glycosuria), 3.Excessive excretion of urine (polyuria), 4.Excessive thirst (polidipsia), 5.Excessive hunger (polyphaisa)6. Weight gain, 7.Fatigue libile, irritable, headache, blurred vision, slured speech, difficulty concentrating, confusion, incoordination a complex disorder of carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism caused by deficiency or absence of insulin secretion by the beta cells of pancreas or by defects of the insulin receptors abrupt oneset iof symptoms in the age of puberty, juwenile failure to eat after taking insulin, excessive insulin, precipitated by exerciseing wash feet daily in warm water, apply petroleum jely or lotion, clean white socks should be worn, with minimal wrinkles and wide. thurst, flushed ( signs of dehydration), nausa, vomiting, abdomianl pain, deep, rapid respiration,pulse is rapid and weak, fruity odor to the breath, weakness, insulin dependent dulled sense, confused, diminished reflexes, parasthesias, kidney failure, atherosclerosis, neropathies, infections, retinopathy, cardiac complications, diaphoresis, pallor, pillow erection, tachycardia, heart palpitation, nervousness, irritability, weakness, shekiness, trembling, hunger fasting plasma glucose test, urine analisis high blood sugar ,>250 mg/dL a diabetic coma caused by hyperosmolarity of extracellular fluid and dehydration, can lead to death,
16.
what is a hypoglycemia? what is a hypoglycemic coma? what is the age of diagnosis with NIDDM what is the best time to exercise Pt with DM? what is the etiology of DM? what is the Gestational DM? what is the hollmark of DM What is the Impaired Glucose Tolerance? what is the onset of hyperglycemia? what is the onset of NIDDM? what is the patient that had IDDM prone to? What is type II DM? what to do if glucose between 70- 100 mg/dL? what to do if glucose level is < 70 mg/dL? what to do if glucose level. 250 mg/dL? what to do when patient has signs of hypoglycemia? when not to exercise patient after insulin injection?
low blood sugar, <60 mg/dL a loss of conciousness taht results from an abnormal low sugar in the blood maturity, adolescent, over the age of 40
17.
2.
18.
3.
CNS changes with Hypoglycemia?
19.
1 hour after meal
20.
4.
definition of Diabetes mellitus DM?
acuired, familial, idiopathic, neurogenic, nephrogenic, possible viral, and genetic glucose intolerance associated with pregnancy, in III trimester frequent urination and increased thirst assymptomatic or borderline diabetes with abnormal response to oral glucose test. many peole will convert to type II DM within 10 years gradual ( days)
21.
22.
5.
onset of Type I Diabetes possible causes of HYPOGLYCEMIA: proper foot care in DM?
23.
6.
7.
24.
25.
gradual
8.
sympathetic signs of hyperglycemia?
26.
ketoacidosis
9. 10.
Type I Diabetes what are the CNS signs in hyperglycemia? what are the secundary effects of DM? what are the sympathetic changes with hypoglycemia? what are the tests for DM? what is a hyperglycemia what is a hyperglycemic coma?
27.
noninsulin-dependent food should be given if symptoms for hypoglycemia are present a carbohydrate snack or juice should be give to PT, and the level checked again in 15 min. pt should not exercise
28.
11.
29.
12.
30.
13.
31.
give sugar, candy, orange juice
14.
15.
32.
between 2-4 hours after insulin injection
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Cardiovascular Physical TherapDocumento7 pagineCardiovascular Physical TherapJadie Prenio100% (4)
- Catholic Prayers: Novena To The Holy SpiritDocumento7 pagineCatholic Prayers: Novena To The Holy SpiritJessamine TorrefrancaNessuna valutazione finora
- The BibleDocumento1.415 pagineThe BibleBooks100% (2)
- 1 - PassTheNPTEGuide by Gigi Lampa-AlcantaraDocumento28 pagine1 - PassTheNPTEGuide by Gigi Lampa-AlcantaraMichael Clark0% (1)
- Nutrition Exam Multiple ChoiceDocumento8 pagineNutrition Exam Multiple ChoiceSofia Spears Elma100% (6)
- General Practitioner - Endocrinology MCQsDocumento17 pagineGeneral Practitioner - Endocrinology MCQsAsif Newaz100% (3)
- Testmanship Tips-Test Wiseness by AnonymousDocumento6 pagineTestmanship Tips-Test Wiseness by AnonymousJadie PrenioNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (5 Edition) 2015Documento13 pagineClinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (5 Edition) 2015Azim Abd Razak100% (1)
- Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose (DM)Documento4 pagineRisk For Unstable Blood Glucose (DM)Ace Khiel Peralta50% (2)
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramDocumento1 paginaDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramJhe Lyn82% (11)
- Seminar 5 - Thyroid Disease in PregnancyDocumento25 pagineSeminar 5 - Thyroid Disease in PregnancyHakimah K. SuhaimiNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuromuscular DisordersDocumento1 paginaNeuromuscular DisordersJadie PrenioNessuna valutazione finora
- Complications of PregnancyDocumento1 paginaComplications of PregnancyJadie PrenioNessuna valutazione finora
- Nodules BrochureDocumento2 pagineNodules BrochurebigbollexNessuna valutazione finora
- 05.adult BMI WallChart Letter SizeDocumento2 pagine05.adult BMI WallChart Letter SizeJadie PrenioNessuna valutazione finora
- Questionnaire On Awareness of Diabetes Mellitus Dr. Kanak ChoudhuryDocumento3 pagineQuestionnaire On Awareness of Diabetes Mellitus Dr. Kanak ChoudhuryBichayan Debbarma100% (1)
- Switching Between InsulinDocumento2 pagineSwitching Between InsulinThoufiNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 - Endocrine Disorders 1Documento59 pagine7 - Endocrine Disorders 1boboNessuna valutazione finora
- Children Presentation Nutrition and DiabetesDocumento19 pagineChildren Presentation Nutrition and Diabetesapi-516120803Nessuna valutazione finora
- Acog Practice Bulletin: Pregestational Diabetes MellitusDocumento21 pagineAcog Practice Bulletin: Pregestational Diabetes MellitusGia DuyNessuna valutazione finora
- St. Paul College of Ilocos Sur: ABG AnalysisDocumento7 pagineSt. Paul College of Ilocos Sur: ABG AnalysisCharina AubreyNessuna valutazione finora
- Medycyna Metaboliczna - 2016, Tom XX, NR 4Documento100 pagineMedycyna Metaboliczna - 2016, Tom XX, NR 4Towarzystwo Edukacji TerapeutycznejNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiometabolic RiskDocumento1 paginaCardiometabolic RiskVaidya Priyanka SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Labreportnew - 2023-08-15T114659.034Documento1 paginaLabreportnew - 2023-08-15T114659.034Yashi GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Diabetes Mellitus Epidemiology of Diabetes MellitusDocumento4 pagineIntroduction To Diabetes Mellitus Epidemiology of Diabetes MellitusMARK 365Nessuna valutazione finora
- Insulin NewDocumento41 pagineInsulin NewSheikNessuna valutazione finora
- Karakteristik Ulkus Diabetikum Pada Penderita Diabetes Mellitus Di RSUD Dr. Zainal Abidin Dan RSUD Meuraxa Banda AcehDocumento8 pagineKarakteristik Ulkus Diabetikum Pada Penderita Diabetes Mellitus Di RSUD Dr. Zainal Abidin Dan RSUD Meuraxa Banda AcehDwi IstutikNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketogenic Diet IF-Philippine Lipid Society Consensus-Statement-20191108v4Documento21 pagineKetogenic Diet IF-Philippine Lipid Society Consensus-Statement-20191108v4donmd98Nessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes Care in MauritiusDocumento52 pagineDiabetes Care in MauritiusAmritKaliasethiNessuna valutazione finora
- Hba1 Conversion Table: DefinitionsDocumento1 paginaHba1 Conversion Table: DefinitionsWidya Astri LinteraNessuna valutazione finora
- ADA Management Adults DKA - UpToDateDocumento2 pagineADA Management Adults DKA - UpToDateHiKa SaGoNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Excerpt From 96Documento5 pagineQuestion Excerpt From 96Lorainne FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study On: Lyceum of The Philippines UniversityDocumento4 pagineCase Study On: Lyceum of The Philippines UniversityarturogarcesjrNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes: What Are The Different Types of Diabetes?Documento2 pagineDiabetes: What Are The Different Types of Diabetes?ZH. omg sarNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care of The Patient With Diabetes Mellitus-2Documento56 pagineNursing Care of The Patient With Diabetes Mellitus-2hevyNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes Mellitus Complications: Ssenabulya F Ronny MBCHB V Moderator Dr. Mutebi 4B Endocrinology UnitDocumento55 pagineDiabetes Mellitus Complications: Ssenabulya F Ronny MBCHB V Moderator Dr. Mutebi 4B Endocrinology UnitNinaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1644 4544 1 PB PDFDocumento4 pagine1644 4544 1 PB PDFsitti nur vanesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid Base 2013Documento60 pagineAcid Base 2013Belial ZaheuerNessuna valutazione finora
- Insulin Therapy: by Dr. Adithya PolavarapuDocumento18 pagineInsulin Therapy: by Dr. Adithya Polavarapuadithya polavarapuNessuna valutazione finora