Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Concrete Report
Caricato da
choppersureCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Concrete Report
Caricato da
choppersureCopyright:
Formati disponibili
On designing any structure ,wind effect is calculated for the following elements.
1- The structure as a whole 2- Structural members as ceilings, walls etc... 3- Coverings, windows and interfaces. The calculated wind load is The algebraic sum of compression or tension on the first side and compression or tension on the second side Wind loads: the forces the wind affects in a perpendicular direction to the surface of structures .it is positive in case of compression(Pe) and negative in case of tension(Pi) . Compression or tension of wind(q): wind loads per unit area measured in kN/m2 . Total wind force (F): the total wind force on structure measured in KN . Coefficient of external wind compression (Ce): it is the coefficient determining distribution of wind compression on external surfaces of the structure. Coefficient of internal wind compression(Ci): it is the coefficient determining distribution of wind compression on internal surfaces of the structure Coefficient of exposure (k) : it is the coefficient determining the distribution of wind loads with respect to height from ground level. Area of structure interface facing the direction of wind (A). Wind loads calculation: Pe= Ce k q Pi=Ci k q In case of structures that does not require calculating the distribution of wind loads on its surface specially those with relatively large heights in comparison to its other dimensions,its preferred to calculate the total wind force on the structure as a whole. F=Cf k q A Q=0.5 * 10^-3F=Cf k q A Q=0.5 * 10^-35yey ku rbku6 V: main wind speed wind velocity equivalent to wind blast lasts for 3 seconds at high of 10 m above ground surface P: air density Ct: coefficient of earth topography
Cs: coefficient of structure it takes into consideration the effect of wind loads in case of unsuccessive wind load compression on the structure in addition to the effect of structure vibration during turbulence Exposure coefficient k: There are three regions where k is calculated according to the ground roughness length (Zo) A- Open exposure: B- Suburban exposure C- City center exposure Table 1 On calculating the external wind compression ,The height Z (upon which the coefficient k is calculated) is the height at which external wind compression is required, where Z is measured from ground surface On calculating internal wind compression at any place inside the structure the height Z (upon which the coefficient k is calculated) is: A- For buildings with separate floors, the height(at which internal wind compression is required ) is measured from ground surface to mean level of the floor. B- For other buildings the height, (at which the internal wind compression is required) is measured from ground surface to mean level of openings in external structure walls. Jhfjhgdhfshgshgfhjgdh page 89 Rectangular structures Picture 2 Structures with rectangular interfaces and inclined ceilings Picture 3 Ceilings of single floor structures with multiple spans Picture 4
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Children of AlcoholicsDocumento7 pagineChildren of AlcoholicschoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- Unclos DraftDocumento19 pagineUnclos DraftchoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Generation PakistanDocumento16 paginePower Generation PakistanchoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- Final ReportDocumento87 pagineFinal ReportchoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost Process DefinationsDocumento8 pagineCost Process DefinationschoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- Multi Purpose Ic QT113Documento12 pagineMulti Purpose Ic QT113choppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- ApendixDocumento1 paginaApendixchoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutritional Needs of AdolescentsDocumento6 pagineNutritional Needs of AdolescentschoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- Callanta Notes (Criminal Law1)Documento166 pagineCallanta Notes (Criminal Law1)aer0211100% (2)
- SupplementsDocumento1 paginaSupplementschoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Hiding in Motion Vectors of Compressed Video PDFDocumento46 pagineData Hiding in Motion Vectors of Compressed Video PDFchoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- VirtualDJ 7 - Audio Setup GuideDocumento29 pagineVirtualDJ 7 - Audio Setup GuideLek ChongNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Profibus Operation Chapter1Documento20 pagineBasics of Profibus Operation Chapter1kerusacba_2011Nessuna valutazione finora
- How To Make A Simplest Inverter CircuitDocumento4 pagineHow To Make A Simplest Inverter CircuitchoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- EogDocumento16 pagineEogchoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 - Lipids 2Documento4 pagine5 - Lipids 2choppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- Power ControlDocumento49 paginePower ControlchoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics motion descriptionDocumento1 paginaKinematics motion descriptionchoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- Concrete ReportDocumento2 pagineConcrete ReportchoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- Third Party LicensesDocumento14 pagineThird Party LicenseschoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- Box Sync ReadMeDocumento1 paginaBox Sync ReadMechoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- Adaptive ThesisDocumento28 pagineAdaptive ThesischoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- 4-20 Ma. Cálculo de Distancia MáximaDocumento3 pagine4-20 Ma. Cálculo de Distancia MáximaMarco Antonio Arroyo RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 - Lipids 4Documento3 pagine5 - Lipids 4choppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- ConcreteDocumento5 pagineConcretechoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 - Lipids 3Documento4 pagine5 - Lipids 3choppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- Concrete ReportDocumento2 pagineConcrete ReportchoppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 - Lipids 1Documento3 pagine5 - Lipids 1choppersureNessuna valutazione finora
- Ventilated FacadesDocumento31 pagineVentilated Facadeschoppersure100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
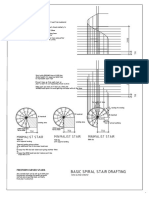
- The Front Edges (Below) : Minimalist Stair Minimalist Stair Minimalist StairDocumento3 pagineThe Front Edges (Below) : Minimalist Stair Minimalist Stair Minimalist StairCIVILNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of Interior DesignDocumento20 pagineTheory of Interior DesignRidhima Sharma100% (5)
- Boy Scouts of America Merit Badge For Foundry Practice 1930Documento34 pagineBoy Scouts of America Merit Badge For Foundry Practice 1930foundryjoe100% (2)
- Lightning Protection SystemDocumento4 pagineLightning Protection SystemBimadraj Sharan SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Control Cables SpecDocumento15 pagineControl Cables SpecnatbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Pitched Roof PergolaDocumento4 paginePitched Roof PergolaNdahiro Gordon JamesNessuna valutazione finora
- Blower Door Manual InglesDocumento100 pagineBlower Door Manual InglesDeco DluxeNessuna valutazione finora
- Malice in WonderlandDocumento16 pagineMalice in WonderlandkatsinclaireNessuna valutazione finora
- Kh711 Kiln Compact User Manual: Do Not Use Before Reading These InstructionsDocumento4 pagineKh711 Kiln Compact User Manual: Do Not Use Before Reading These InstructionsDave WalkerNessuna valutazione finora
- DeflectionDocumento31 pagineDeflectionAnonymous nQ9RqmNessuna valutazione finora
- En 1991Documento95 pagineEn 1991basilscript100% (2)
- PC8900 InstallationDocumento4 paginePC8900 InstallationDavid BiscegliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Points To Trac Fujico.Documento2 pagineCommon Points To Trac Fujico.venka07Nessuna valutazione finora
- ALHuxtable-Le Corbusier PessacDocumento8 pagineALHuxtable-Le Corbusier PessacAnonymous Psi9GaNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel Frame InnovationDocumento6 pagineSteel Frame InnovationKeanu Joseph VelascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Carpentry ShopDocumento26 pagineCarpentry ShoplogwolvyNessuna valutazione finora
- English Architecture VocabularyDocumento2 pagineEnglish Architecture VocabularyAbah GeotNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Lowry Close, Sandhurst - Steelwork DesignDocumento8 pagine12 Lowry Close, Sandhurst - Steelwork DesignInoshan Madushika JayawickramaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mountain Park Brochure FinalDocumento77 pagineMountain Park Brochure FinalMostafa ElghifaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Lightning Protection For Offshore Oil RigsDocumento0 pagineLightning Protection For Offshore Oil RigsNoli OtebaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Disappointments Room PDFDocumento129 pagineThe Disappointments Room PDFMufti Akhmad Shadiq Afnas0% (1)
- Eleanor Mckenna-Honors ThesisDocumento6 pagineEleanor Mckenna-Honors ThesisBafreen BnavyNessuna valutazione finora
- Konnerup (2012) Design of Steel-Concrete Composite Structures For A High-Rise BuildingDocumento185 pagineKonnerup (2012) Design of Steel-Concrete Composite Structures For A High-Rise Buildingint8Nessuna valutazione finora
- How To Tie Rebar - 15 Steps (With Pictures) - Wikihow PDFDocumento4 pagineHow To Tie Rebar - 15 Steps (With Pictures) - Wikihow PDFa769Nessuna valutazione finora
- Despiece DPX ExpertDocumento49 pagineDespiece DPX ExpertSucesores de Ortiz de Zárate S.L.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Existing Building Dock Area PlanDocumento1 paginaExisting Building Dock Area PlanSudeshna Mahapdi - PawarNessuna valutazione finora
- Timber Design - ConnectionsDocumento10 pagineTimber Design - ConnectionsEmmanuel LazoNessuna valutazione finora
- Preliminary Size of RCC MembersDocumento24 paginePreliminary Size of RCC MembersV.m. Rajan75% (4)
- Home-immediately access 800+ free online publications. Download CD3WD (680 Megabytes) and distribute it to the 3rd WorldDocumento9 pagineHome-immediately access 800+ free online publications. Download CD3WD (680 Megabytes) and distribute it to the 3rd WorldLungmuaNa RanteNessuna valutazione finora