Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
B - PreHistoric - Egypt 01 - 13 Revised
Caricato da
Paolo OcampoCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
B - PreHistoric - Egypt 01 - 13 Revised
Caricato da
Paolo OcampoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
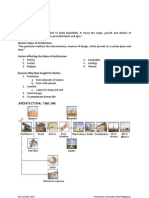
TABLE
OF CONTENTS
1. Collage of Pictures from Pre-Historic Structures to Modern 2004 skyscrapers 2. Pre-Historic Structures . 1 3. Egyptian Architecture.. 5 4. Mesopotamian Architecture..13 a. Persian Architecture b. Assyrian Architecture c. Babylonian Architecture 5. Greek Architecture... 17 6. Roman Architecture.. 31 7. Early Christian Architecture.. 38 8. Byzantine Architecture..... 41 9. Saracenic or Muslim Architecture .... 44 10. Romanesque Architecture.. 47 11. English Medieval Architecture... 52 12. Gothic Architecture55 13. Renaissance Architecture61 Italian Renaissance French Renaissance German Renaissance Belgium , Dutch Renaissance English Renaissance Russian Renaissance ..67 14. Australian Architecture 66 15. American Architecture .68 16. Age of the Revivals ( Continental Europe ) .69 17. Famous works of Architects of the 18th and 19th Century ..71 18. 200 Worlds Tallest Bldgs. With Respective Archts. ( As of 2005)79 19. South East Asian Architecture ( Buddhist and Hindu Countries ) ..86 a. Chinese Architecture b. Japanese Architecture c. Indian Architecture d. Korean Architecture e. Cambodian Architecture f. Thailand Architecture g. Indonesian Architecture 20. Philippine Architecture ... 94 a. b. c. 21. Filipino Pre - Spanish Period Spanish Period American Period Architects of the 60s to 80s100 a. b. c. d. e.
22. Philippine Tallest Bldgs. with respective Archts . ( As of 2005 )104 23. Theory of Architecture106 24. Theory ll ( Famous Filipino Archts. Philosophies and Dictums ).108
PRE HISTORIC ARCHITECTURE 2
PRE HISTORIC ARCHITECTURE
20th Century REVIVAL 19th Century)
RENAISSANCE
(15th18th Cent)
GOTHIC (13th 15th Century)
BYZANTINE (4th Century)
SARACENIC (7th Century)
ROMAN( 2nd C.B.C. 4TH C. A.D. ) GREEK ( 8nd C.B.C. 2ND CA.D.
EGYPTIAN (5000 B.C. 1ST Cent. A.D.) MEXICAN PERUVIAN
ASSYRIAN (4000 B.C. 4 TH Cent. A.D.) INDIAN CHINESE JAPANESE
( Theory of Development of Architecture )
INFLUENCES OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF ARCITECTURE
A. Geographical b. Geological c. Climatic d. Religious e. Socialpolitical f. Historical
PRE HISTORIC STRUCTURES
CULTURAL STAGES I STONE AGE a.) Paleolithic ( Old Stone Age ) b.) Mesolithic ( Middle S Age) c.) Neolithic ( New S Age ) II BRONZE AGE Covered the Minoan Period of the Crete & Greek Pd. III IRON AGE 25 to 50 yrs. Before Julius Ceasar
4 CONSTRUCTIVE PRINCIPLES
A. POST & LINTEL (Trabeated) C. CORBEL OR CANTILLEVERED 1. Dwellings 2. Religious Monuments B. ARCH & VAULT D. TRUSSED 3. Burial Grounds
3 CLASSIFICATIONS OF EARLY KNOWN TYPES OF ARCHITECTURE FROM THE DWELLINGS STRUCTURES
A. ROCK CAVE Earliest form of dwellings 3 STAGES OF THE EVOLUTION OF CAVE 1. NATURAL CAVE 2. ARTIFICIAL CAVE 3. CAVE Above the Ground B. TENTS AND HUTS Made from tree barks, Animal skins & Plant leaves. HUTS usually made up of reeds, brushes and wattles.
RELIGIOUS MONUMENTS
2 CLASSIFICATIONS OF RELIGIOUS STRUCTURES
A. MONOLITH isolated single upright stone also known as menhir
Menhir - memorial of victory over one tribe. Prototypes of Egyptian pyramid.
B. MEGALITHIC Several number of stones 1. Dolmen - 2 or more upright stones supporting a horizontal slab. 2. Cromlech 3 or more upright stones capped by an unchain flat stone,
Indicates place of religious rites , e.g. Found at LANYON Cornwall
3. Stone Circle or Stone Row - made up of 3,000 stones spaced upright
e.g. Stonehenge, located @ Wiltshire & on Salisbury Plain
PRE HISTORIC ARCHITECTURE 4
STONEHENGE are made up of Concentric rings with the ff.
A. B. C. D. Outer ring 106 in diameter Isolated blue stone Innermost cirle Smaller blue stone
BURIAL MOUNDS TUMULI or Barrows earthen mounds use for burials of several to couple hundred
of ordinary persons. Prototypes of pyramids in Egypt also of the beehive huts.
ELEMENTS OF CLASSICAL SUPPORTS
1.) BASIC FORMS a.) PIER b.) COLUMN c.) PILASTER d.) PEDESTAL e.) ENGAGED COLUMN f.) BALUSTER 2.) SPECIAL FORMS a.) CARYATIDS drapped female figure without hands & carrying nothing. b.) CANEPHORAE same as caryatids but this time w/ basket on her head.
c.) ATLAS OR ATLANTES male figure in kneeling position supporting the world at his
shoulders. d.) TELAMON or TELAMONES male figure in standing position in place of a column. e.) ANTA COLUMN -- pier or pilaster formed by a thickening at the end of the wall.
PIER
PILASTERS
COLUMN CLASSICAL ORDERS
Engaged Columns
Baluster
Pedestal
ORDERS it includes the column ( capital , shaft , base ) with an entablature, which is following
a certain rule with regards to systems of designing.
FROM GREECE
1. DORIC ORDER the simplest , earliest and the most perfect among the orders , made up
of wood. 2. IONIC ORDER -- the most sophisticated, less heavy than the Doric order. 3. CORINTHIAN ORDER -- the slenderest, elegant, and the most elaborated order.
FROM ROME
4. COMPOSITE ORDER -- roman elaboration of the Corinthian order. 5. TUSCAN ORDER -- the simplified version of the Roman Doric order and has no shaft flutes. SUPERIMPOSITION or SUPERCOLUMNATION -- the placing of one order after another or above another. INTERCOLUMNATION -- the clear space between two adjacent columns usually measured at the lower parts of the shafts. ARCADE
a line of counterthrusting arches raised on columns of piers.
ENTASIS a swelling or curving along the outline of a column shaft . It was designed to counter-act the Optical illusion which gives a shaft bounded by straight line appearance of curving inwards
PRE HISTORIC ARCHITECTURE 5 TWO KINDS OF ENTASIS 1. Single 2. Double
EGYPTIAN ARCHITECTURE 6
AVENUE OF SPHINX
TEMPLE OF KHONS
CRIOSPHINX
ANDRO SPHINX
SETHMET
TEMPLE OF HATHOR
TEMPLE OF QUEEN HATSHEPSUT
PYLON AT EDFU
TEMPLE OF HATHOR
TEMPLE OF AMON
PHARAOH MUMMIFICATION
TEMPLE OF LUXOR
AVE. OF SPHINX
OBELISK
HYPOSTYLE HALL
M A S T A B A
EGYPTIAN ARCHITECTURE 7
FROM
5000 B. C. 1st CENTURY A. D.
A. GEOGRAPHICAL INFLUENCE Egypt known as The Land of Pharaoh , & desert Land . The Nile River is their means of communication , highway , & lifeline . Egypts greatest wealth was its fertile soil. B. GEOLOGICAL INFLUENCE STONE abundant building material except on temples & pyramids Soft stone limestone , sandstone , alabaster . Hard stone granite , quartzite , basalt , porphyry SAND DRIED BRICKS made up of clay & chopped stone for pyramids & temples. DATE PALM for roofings & PALM LEAVES for roofing materials . ACACIA for their boat SYCAMORE mummy cases C. CLIMATIC INFLUENCE Structure have no downspout , drainage , gutters due to absence of rain . No windows to cut heat penetration and sandstorm. D. RELIGIOUS INFLUENCE Pyramids were built bec. they believe in Life after Death & for the preservation of the dead body. Pharaoh is not only king but also god both political & religious ruler, when he dies he becomes osiris, god of dead. Theyre monotheistic in theory & polytheistic in practice.
DIFFERENT EGYPTIAN GODS: a.) AMUNRA : chief god b.) RAH : symbol of the sun , hope for eternal life , sun god fr. Heliopolis c.) ATUM : world creator d.) OSIRIS : god of the dead
wife of osiris sky god, son of osiris, also reincarnation of Ra himself dread god of evil, brother of pleasure ibis headed god of wisdom jackal headed god of death god of craftsmen : bull god E. HISTORICAL INFLUENCE 30 DYNASTIES started from 3rd Millennium B.C. to Roman Period. Egypt was part of Persian Empire for 2 Centuries, before the invasion of ALEXANDER the Great . 1. ANCIENT KINGDOM ( 1ST 10TH DYNASTY ) Development of two types of tombs a.) Mastaba b.) Pyramid 2. MIDDLE KINGDOM ( 11TH 17TH DYNASTY ) Important Personalities a.) MENTUHETEP II developed the 3rd type of tomb Rockcut Tomb. b.) SENUSRETS erected the earliest known Obelisk @ Heliopolis. c.) AMENEMHAT I founded Great Temple of Ammon Kharnak Grandest of all temples 3. NEW EMPIRE ( 18TH 30TH DYNASTY ) Important Personalities a.) THOTMES 1- began the additions to the Temple of AMMON, Kharnak. b.) HATSHEPSUT queen of Egypt, famous for her funerary temple @ Mt.Der-El-Bahari. c.) THOTMES 1V the one responsible for the cleaning away of sand fr. the Sphinx d.) AMENOPHIS III erected the Colossi of Memnon,one of the wonders of the world . e.) RAMESES I began the construction of the Great Hypostyle Hall, @ Kharnak f.) RAMESES II finished the construction of the Hypostyle Hall, & erection of the Rock Temple @ ABU- SIMBEL , and the Remission,Thebes. 4. THE PTOLEMAIC PERIOD Important Personalities a.) PTOLEMY II built the Pharaohs or the Light House . b.) PTOLEMY III founded the Greatest Serapeum at Alexandria. F. SOCIAL AND POLITICAL INFLUENCE MONARCHY form of government PHARAOH King of Egypt, ruler , highest priest in Egypt SON OF PHARAOH normal successor to the throne VIZIER Kings most powerful official CHANCELORhe controls the royal treasuries, granaries ,& supervises the census CHIEF STEWARD- in charge of the Kings personal estate & household. SOCIAL RANKS: 1. NOBLE FAMILIESroyal throne with his family 2. SOLDIERS, VIZIERS, CHANCELLORS, CHIEF STEWARDS next to leaders 3. FISHERMEN, FARMERS, CRAFTMENS, MERCHANTS - ordinary Egyptians 4. SLAVES- lowest form
e.) ISIS f.) HORUS g.) SET i.) THOT j.) ANUBIS k.) PTAH l.) SERAPIS
: : : : : :
EGYPTIAN ARCHITECTURE 8
G. ARCHITECTURAL CHARACTER
1.) SIMPLICITY 2.) MONUMENTALITY 3.) SOLIDITY OR MASSIVENESS
SYSTEMS OF CONSTRUCTION:
POST & LINTEL; COLUMNAR OR TRABEATED.
FEATURES
OF EGYPTIAN ARCHITECTURE:
1. BATTERWALL- inclination from base to top of the faade. 2. HIEROGLYPHICS- use as ornaments, pictures & writings from the walls .
EXAMPLE OF STRUCTURES:
1. TOMBS ( 3 TYPES) A. MASTABA- flat top or tapered solid temple 3 IMPORTANT PARTS OF MASTABA 1. OUTER CHAMBER- where offerings were placed 2. SERDAB inner chamber containing the statues of the deceased member of the family 3. SARCOPHAGUS chamber containing the coffin reached by an under ground shaft. e.g. MASTABA OF THI ( THI - is a royal architect, superindentent of pyramids in Egypt ) Mastaba are Tomb-houses that were made to take the body at full length . STELE is the upright stone slab containing the name of the dead found in the mastaba B. PYRAMIDS evolved from MASTABA ; w/ four sides facing the Cardinal points , they were made by 100,000 men for 100 years. 1.) STEP PYRAMID evolved from Mastaba e.g. PYRAMID OF KING ZOSER or ISER built by IMHOTEP, oldest surviving masonry bldg. structure in the world.
2.)
BENT OR BLUNT PYRAMID 2 degrees of inclination of slope e.g. PYRAMID OF SENEFERU
EGYPTIAN
ARCHITECTURE 9
3.) SLOPE PYRAMID parts ( kings chamber , Queens chamber , subterranean chamber, grand gallery, airshafts. e.g. 3 Famous Pyramid @ GIZEH Great Pyramids of the Cheops was equated to the size of St. Peter Rome
a) PYRAMID OF THE CHEOPS OR KHUFU (146.4 mts. High & ( 750 sq. ft. )
in plan two times the area of the famous St. Peter Basilica in Rome. b) PYRAMID OF CHEOPS or Khafra ( 143.0 mts. high ) & (705 sq. ft. ) in plan. c) PYRAMID OF MYKERINOS or Menkaura (109.0 mts. high) & (218ft. high). PARTS OF PYRAMID COMPLEX: 1. elevated causeway 2. Offering chapel 3. Mortuary 4. Valley bldg.
2.
C. ROCK CUT TOMB OR ROCK HEWN TOMB cut deep into the mountain rock e. g. Tombs of the kings, Thebes TEMPLES ( 2 TYPES) they were sanctuaries that only Kings and Priests can penetrate . a.) Montuary built in honor of the Pharaohs b.) Cult built for the worship of the gods, only high priest can enter in both types of temple.
Egyptian architecture was designed principally for internal effect PARTS OF AN EGYPTIAN TEMPLE 1) Entrance Pylon massive sloping towers fronted by an obelisks known as gateways in Egypt . 2) Hypaethral Court large outer court open to the sky 3) Hypostyle Hall - a pillared hall in which the roofs rest on column. 4) Sanctuary usually surrounded by passages & chambers used in connection w/ the temple service. 5) Avenue of Sphinx where mystical monster were placed. EXAMPLE OF TEMPLES 1) Great Temple of Abu Simbel entrance forecourt leads to an imposing faade formed by a pylon carved w/ 4 Colossal seated statues.( RAMESSES 1-1V) 2) Great Temple of Ammon, Khanak most grandest temple in Egyptian planning & was commenced by Amenemhat 1 ; occupying an area of 1,200 ft. x 360 ft PARTS OF AN EGYPTIAN TEMPLE 3) Temple of Ammon, Der El Bahari 4) Temple of Queen Hatshepsut 5) Temple of Elephantine 6) Temple of Hathor, Dendera 7) Temple of Horus, Edfu 8) Temple of Isis, Philae 9) Temple of Khons, kharnak, by Ramesses III 10) Temple of Luxor 11) Temple of Mamimisi 12) Temple of Mentuhetep, Thebes 13) Temple of Seti I, Abydos 14) Temple of Ramesseum, Thebes
EGYPTIAN ARCHITECTURE 10
The Great Temple of Abu- Simbel
It is one of the rock- hewn temples at this place commanded by the indefatigable Rameses II. An entrance forecourt leads to the imposing faade, 36 m ( 119 ft. ) wide and 32 m ( 105 ft. ) high formed as pylon, immediately in front of which are four rock-cut seated colossal statues of Rameses, over 20 m ( 65 ft. ) high.
10
The Great Temple of Ammon, Karnak, Thebes The grandest of all Egyptian temples, was not built upon one complete plan but owes its size, disposition and magnificence to the work of many Kings. built from the XIIth Dynasty to the ptolemaic period .
Temple of Queen HATSHEPSUT , Mt. Der El - Bahari
Queen of Egypt, famous for her funerary temple @ Mt.Der-El-Bahari.
11
EGYPTIAN ARCHITECTURE 11
Temple of Hathor , Dendera
Temple of Amon Ra
3. OBELISKS are monumental pillars usually in pairs at the temple entrances considered the symbol of Heliopolis the sun god. They are square in plan & stands at the ht. of 9 to 10 times the diameter of the base. The four sides tapers to the top on the form of a small pyramid. e.g. Cleopatras Needle, Embankment, London Piazza of St. John Laterano, Rome. 4. SPHINX a mystical monster with a body of a lion and head of a man or androsphinx, body of a lion & head of a hawk or heiraosphinx , & body lion & head of a ram or criosphinx. e.g. Great Sphinx at Gizeh near the Pyramid of the Cheops. 5. CAPITALS & COLUMNS a.) Bud & Bell Capital b.) Polygonal Columns c.) Papyrus Capital d.) Volute Capital e.) Palm type Capital f. ) Square Pillars g.) Hathor Headed Capital h.) Osiris Pillars
6. MOULDINGS Gorge and Hollow Moulding used to cover the angles .
The torus mould in Egyptian temples were
ORNAMENTS a) Lotus Papyrus & Palm for fertility b) Solar Discs & Vutures w/ wings for protection c) Spiral & feather ornament for eternity d) Scarab or sacred beetle for ressurection
12
EGYPTIAN ARCHITECTURE 12
13
EGYPTIAN ARCHITECTURE 13
14
HIEROGLYPHICS WITH HATHOR COLUMNS
15
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Lara CroftDocumento58 pagineLara CroftMarinko Tikvicki67% (3)
- Prehistoric to Modern Architecture TimelineDocumento107 paginePrehistoric to Modern Architecture TimelineFlorisel Joy Antoni100% (2)
- Obelisks: Towers of Power: The Mysterious Purpose of ObelisksDa EverandObelisks: Towers of Power: The Mysterious Purpose of ObelisksValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- BERMAN, Joshua A. - Inconsistency in The TorahDocumento321 pagineBERMAN, Joshua A. - Inconsistency in The TorahWilian Cardoso100% (5)
- 3,200-Year-Old Pictures of Israelites Found in EgyptDocumento29 pagine3,200-Year-Old Pictures of Israelites Found in Egypt한사무엘100% (2)
- Meskerem 'The Ancient Future' PDFDocumento13 pagineMeskerem 'The Ancient Future' PDFTom GruberNessuna valutazione finora
- Food Analysis Lab #1Documento11 pagineFood Analysis Lab #1VLNessuna valutazione finora
- #Zodiax 1622 #AcademicZodiac 1008Documento16 pagine#Zodiax 1622 #AcademicZodiac 1008Antonio SolisNessuna valutazione finora
- Oil and Gas Commission Judgment Enforcement CaseDocumento7 pagineOil and Gas Commission Judgment Enforcement CaseLeyton MisterNessuna valutazione finora
- A Russian Mathematician Rewrote World History - and It Is BonkersDocumento3 pagineA Russian Mathematician Rewrote World History - and It Is BonkersdpolsekNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Historical Truths and Lies: An Exhibit CatalogueDocumento11 pagine1 Historical Truths and Lies: An Exhibit CatalogueRaymoon Twopass DaysNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Mannual Pharmacedutical ChemDocumento11 pagineLab Mannual Pharmacedutical Chemsumit kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Planetary conjunctions 2015-2020Documento20 paginePlanetary conjunctions 2015-2020Jagmohan Chandra Pathak0% (1)
- The Ark, The Shroud and MaryDocumento4 pagineThe Ark, The Shroud and MaryReal2Can.com67% (3)
- The Expected OnesDocumento61 pagineThe Expected OnesRose-Marie Mukarutabana100% (1)
- The Christian Swastika Verbal VandalDocumento4 pagineThe Christian Swastika Verbal VandalAaron SwartzNessuna valutazione finora
- B - PreHistoric - Egyptian 01-13 RevisedDocumento13 pagineB - PreHistoric - Egyptian 01-13 RevisedYbette Anorico VillamarinNessuna valutazione finora
- HISTORY OF ARCHI CompleteDocumento110 pagineHISTORY OF ARCHI CompleteCharelle DomoNessuna valutazione finora
- History of ArchitectureDocumento107 pagineHistory of ArchitectureMichael Francis MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Egyptian Arch're - EDITEDDocumento120 pagine2 Egyptian Arch're - EDITEDrazelrufino8Nessuna valutazione finora
- B - PreHistoric - Egyptian 01-12Documento12 pagineB - PreHistoric - Egyptian 01-12NiigataNessuna valutazione finora
- History of ArchitectureDocumento107 pagineHistory of ArchitectureDreidell RayelNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Egyptian ArchitectureDocumento8 pagine03 Egyptian ArchitecturePaolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Sculpture - Sculptor and Its WorksDocumento76 pagineHistory of Sculpture - Sculptor and Its WorksMichael Jay MostolesNessuna valutazione finora
- History of World Art, Architecture & Interior DesignDocumento196 pagineHistory of World Art, Architecture & Interior DesignRamcy AddulamNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson1 PREHISTORIC AND EGYPTIAN ARCHITECTUREDocumento14 pagineLesson1 PREHISTORIC AND EGYPTIAN ARCHITECTUREjamsnssNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-historic Architecture Styles Through the AgesDocumento24 paginePre-historic Architecture Styles Through the AgesTitser JoNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Architecture Lecture NotesDocumento7 pagineHistory of Architecture Lecture NotesgardecristianabNessuna valutazione finora
- GE 6 Art MovementsDocumento99 pagineGE 6 Art MovementsAlexis Becendario Quintayo BanicioNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Quarter Arts SummaryDocumento3 pagine1st Quarter Arts SummaryJosa Gracia PanganibanNessuna valutazione finora
- Time To Float: Art Through The Ages ResearchDocumento33 pagineTime To Float: Art Through The Ages ResearchChie SierraNessuna valutazione finora
- Egyptian Architecture 1 LastDocumento5 pagineEgyptian Architecture 1 LastzekimamaruNessuna valutazione finora
- Mohamad Darwish Hussein EissaDocumento26 pagineMohamad Darwish Hussein EissaZed ZizoNessuna valutazione finora
- Art AppDocumento20 pagineArt Appenriquezalexandre17Nessuna valutazione finora
- HistoryDocumento40 pagineHistoryChristel Jean RegisNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Architecture 1 BS Architecture 1 Term AY 2012-2013Documento50 pagineHistory of Architecture 1 BS Architecture 1 Term AY 2012-2013J VNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 2 - Summary - EgyptianArchitectureDocumento12 pagineMODULE 2 - Summary - EgyptianArchitectureLois BenedictosNessuna valutazione finora
- A Beautiful Thing Is Never Perfect.Documento12 pagineA Beautiful Thing Is Never Perfect.Lloyd UyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mapeh - Arts: Department of EducationDocumento7 pagineMapeh - Arts: Department of Educationcheri elaineNessuna valutazione finora
- Egypt SummaryDocumento12 pagineEgypt SummaryJeffrey CarduceNessuna valutazione finora
- Proporited Hellenic Prehistory ... Pyramides: Is Probably The Most Subversive Modern Archaeological Discovery!Documento26 pagineProporited Hellenic Prehistory ... Pyramides: Is Probably The Most Subversive Modern Archaeological Discovery!LoxaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Seven Wonders of The Ancient WorldDocumento26 pagineThe Seven Wonders of The Ancient Worlddejeh ocbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5 - Art MovementDocumento100 pagineModule 5 - Art MovementGabo AlfonsoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3:lesson 1: Art History and DevelopmentDocumento87 pagineChapter 3:lesson 1: Art History and DevelopmentBSABEN 1BNessuna valutazione finora
- RomanPantheonDocumento12 pagineRomanPantheonEmily WithfordNessuna valutazione finora
- Artapp030 Chapter 2Documento19 pagineArtapp030 Chapter 2SJO1 G6- Escaro,Shaira JoyNessuna valutazione finora
- PRE-HISTORIC ART LESSON I: CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRESENTATIVE WORKSDocumento25 paginePRE-HISTORIC ART LESSON I: CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRESENTATIVE WORKSVi LorelieNessuna valutazione finora
- Mapeh Sculpture2sDocumento2 pagineMapeh Sculpture2sjisa52053Nessuna valutazione finora
- HISTORY OF ARCHITECTURE: EGYPTIAN AND GREEK ARCHITECTUREDocumento105 pagineHISTORY OF ARCHITECTURE: EGYPTIAN AND GREEK ARCHITECTUREadyjoy antonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Artapp030 Chapter 2 (Visual Art)Documento19 pagineArtapp030 Chapter 2 (Visual Art)Reinrose Sophia LimaNessuna valutazione finora
- World History & Civ 1 Handout Part 1Documento21 pagineWorld History & Civ 1 Handout Part 1Ron StyxNessuna valutazione finora
- Egyptian ArtDocumento27 pagineEgyptian ArtJobert John BatallonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1Documento88 pagineModule 1karthikaNessuna valutazione finora
- A History of Art for Beginners and Students: Painting—Sculpture —Architecture with Complete “Quoted Indexes” and “Numerous Illustrations”Da EverandA History of Art for Beginners and Students: Painting—Sculpture —Architecture with Complete “Quoted Indexes” and “Numerous Illustrations”Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Greco-Roman Art HistoryDocumento4 pagineGreco-Roman Art HistoryJePongNessuna valutazione finora
- Arts 1stqrtr ReviewerDocumento4 pagineArts 1stqrtr ReviewerLhilyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ancient Architecture TrendsDocumento73 pagineAncient Architecture TrendsRajendra KunwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Greek Civilization: Group 3 - Amanda Jacela & Kathleen AyqueDocumento47 pagineGreek Civilization: Group 3 - Amanda Jacela & Kathleen AyqueAmanda JacelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Tourism2-2Documento35 paginePrinciples of Tourism2-2Paul Jasper BaronaNessuna valutazione finora
- Art History (The Beginning)Documento66 pagineArt History (The Beginning)Himari MardayNessuna valutazione finora
- Art LastDocumento20 pagineArt LastIrika SapanzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Egyptian Art and Greek Art Group 5 PresentationDocumento32 pagineEgyptian Art and Greek Art Group 5 Presentation3pl JaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Yaba ElevatorDocumento67 pagineYaba ElevatorPaolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Citadel Chapter 10Documento2 pagineCitadel Chapter 10Paolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- ClusterDocumento12 pagineClusterPaolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 4 Data Presentation and AnalysisDocumento8 pagineChap 4 Data Presentation and AnalysisPaolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Food Processing Equipment DesignDocumento6 pagineFood Processing Equipment DesignPaolo Ocampo67% (3)
- H - Continental 68 - 85 RevisedDocumento19 pagineH - Continental 68 - 85 RevisedPaolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- InteriorsDocumento5 pagineInteriorsPaolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- EquipmentDocumento2 pagineEquipmentPaolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Roman ArchitectureDocumento9 pagineRoman Architecturewhojackie88Nessuna valutazione finora
- Types of RocksDocumento6 pagineTypes of RocksPaolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire CodeDocumento7 pagineFire CodePaolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- RA 9266 Architecture Act of 2004Documento10 pagineRA 9266 Architecture Act of 2004Botenes Mallorca RhonNessuna valutazione finora
- Ancient Mesopotamian and Greek Architectural StylesDocumento20 pagineAncient Mesopotamian and Greek Architectural StylesPaolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-Historic Architecture PUPDocumento7 paginePre-Historic Architecture PUPPaolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 Greek ArchitectureDocumento7 pagine04 Greek ArchitecturePaolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Plumbing 2Documento215 pagineFinal Plumbing 2Paolo Ocampo88% (8)
- Color CombinationDocumento20 pagineColor CombinationPaolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Egyptian ArchitectureDocumento8 pagine03 Egyptian ArchitecturePaolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- PANTONE Color ReferenceDocumento19 paginePANTONE Color ReferencePaolo Ocampo100% (3)
- B - PreHistoric - Egypt 01 - 13 RevisedDocumento15 pagineB - PreHistoric - Egypt 01 - 13 RevisedPaolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Near East ArchitectureDocumento10 pagine02 Near East ArchitecturePaolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- PANTONE Color ReferenceDocumento19 paginePANTONE Color ReferencePaolo Ocampo100% (3)
- Color CombinationDocumento20 pagineColor CombinationPaolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Color CombinationDocumento20 pagineColor CombinationPaolo OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- PANTONE Color ReferenceDocumento19 paginePANTONE Color ReferencePaolo Ocampo100% (3)
- Access LeafletDocumento64 pagineAccess Leafletindreraluca67% (3)
- Depictional Study of Chariot Use in New Kingdom Egypt: January 2012Documento19 pagineDepictional Study of Chariot Use in New Kingdom Egypt: January 2012ٍSaiid MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Primitive and Egyptian ArtDocumento68 paginePrimitive and Egyptian ArtArmenie Ruth Tecne DueNessuna valutazione finora
- The Tragic End of The Bronze Age (The Screenplay)Documento69 pagineThe Tragic End of The Bronze Age (The Screenplay)Tom Slattery60% (5)
- 202003261536151812anil Kumar Ancient Egypt1Documento23 pagine202003261536151812anil Kumar Ancient Egypt1ShreyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hornung Erik Ancient Egyptian ChronologyDocumento22 pagineHornung Erik Ancient Egyptian Chronology马超Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ramses II - Builder of Monuments - Part 1: BiographyDocumento3 pagineRamses II - Builder of Monuments - Part 1: BiographygumelarNessuna valutazione finora
- Egyptian Domination: 6 The Late Bronze Age (1550-1200)Documento19 pagineEgyptian Domination: 6 The Late Bronze Age (1550-1200)nilecruisedNessuna valutazione finora
- Occupation: Pharaoh of Egypt Born: 1303 BC Died: 1213 BC Reign: 1279 BC To 1213 BC (66 Years) Best Known For: The Greatest Pharaoh of Ancient Egypt Biography: Early LifeDocumento3 pagineOccupation: Pharaoh of Egypt Born: 1303 BC Died: 1213 BC Reign: 1279 BC To 1213 BC (66 Years) Best Known For: The Greatest Pharaoh of Ancient Egypt Biography: Early LifeDindin FlojoNessuna valutazione finora
- Exodus EventsDocumento8 pagineExodus EventsHUSAIN, HAIZIAH-YASMINNessuna valutazione finora
- Timeline of Human History IDocumento225 pagineTimeline of Human History IZorana Dimković100% (1)
- 3bulletin de L Institut D EgypteDocumento54 pagine3bulletin de L Institut D Egyptefadyrodanlo0% (1)
- A Workbook On EgyptDocumento9 pagineA Workbook On EgyptGa Tap Bayy100% (1)
- Art History: Iconography Is A Major Part of Art History. It Consists in Analyzing The Symbolism ofDocumento5 pagineArt History: Iconography Is A Major Part of Art History. It Consists in Analyzing The Symbolism ofQueen ValleNessuna valutazione finora
- The Quest For The Red Sea Crossing, GM MethanyDocumento64 pagineThe Quest For The Red Sea Crossing, GM MethanyNuno NevesNessuna valutazione finora
- OzymandiasDocumento6 pagineOzymandiasAyah Paasa100% (1)
- Abu Simbel 1Documento5 pagineAbu Simbel 1mahmad92Nessuna valutazione finora
- "Ramses II BYU Exhibit: Supplementary Comments On The Artifacts," FARMS Preliminary Report, SMI-86 (Provo: FARMS, 1986) .Documento24 pagine"Ramses II BYU Exhibit: Supplementary Comments On The Artifacts," FARMS Preliminary Report, SMI-86 (Provo: FARMS, 1986) .Robert F. Smith100% (1)
- A Short History of The Egyptian People PDFDocumento316 pagineA Short History of The Egyptian People PDFGarvey LivesNessuna valutazione finora
- The Temple of Abydos-G3Documento69 pagineThe Temple of Abydos-G3Omar MattarNessuna valutazione finora
- BYRAM CAMPBELL - New Mythology of Racial Equality (1963)Documento75 pagineBYRAM CAMPBELL - New Mythology of Racial Equality (1963)Géza HegedűsNessuna valutazione finora
- Ramses II and His Time - Ages of Chaos II - Immanuel VelikovskyDocumento206 pagineRamses II and His Time - Ages of Chaos II - Immanuel Velikovskymika2k01100% (10)
- Lutz, Cora E. - The Oldest Library MottoDocumento5 pagineLutz, Cora E. - The Oldest Library MottoSan TurNessuna valutazione finora
- The Peace Treaty Between Ramses II and Hattusili IIIDocumento8 pagineThe Peace Treaty Between Ramses II and Hattusili IIILakshmi NarayananNessuna valutazione finora
- Mummies of The Pharaohs (Maurice Bucaille) (Bookmarked)Documento294 pagineMummies of The Pharaohs (Maurice Bucaille) (Bookmarked)Tariq IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Social+Studies Study+Guide 2021Documento17 pagineSocial+Studies Study+Guide 2021Ahmad ElnabawyNessuna valutazione finora
- The RamesseumDocumento83 pagineThe RamesseumDyehuty-ThotNessuna valutazione finora