Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Form 5 Chapter 4 Physics
Caricato da
Angie Kong Su MeiTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Form 5 Chapter 4 Physics
Caricato da
Angie Kong Su MeiCopyright:
Formati disponibili
4. ELECTRONICS SECTION A Structured Items Instruction: Answer all questions in this section.
[/25 x 100 = % ]
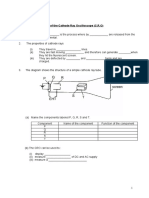
4.1 Understanding the uses of the Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (C.R.O) A student is able to : explain thermionic emission. Describe the properties of cathode rays. Describe the uses of a cathode ray oscilloscope. -- Measure potential difference using the C.R.O. -- Measure short time intervals using the C.R.O. -- Display wave forms using the C.R.O. Solve problems based on the C.R.O. display
1. 2.
______________________ is the process where by ____________ are released from the surface of a heated metal. The properties of cathode rays (i) (ii) (iii) They travel in ________________ lines. They are fast moving ____________ and therefore can generate ________when they hit the fluorescent screen. They are deflected by _________ and ____________ fields and are _________ charged.
3.
The diagram shows the structure of a simple cathode ray tube.
(a) Name the components labeled P, Q, R, S and T. Component P Q R S T (b) The CRO can be used to : Name of the component Function of the component
i. display _________________ ii. measure ________________ of DC and AC supply iii. measure a _________________________ 4. The figure below shows a trace formed on the screen of a CRO.
If the Y-gain control on the CRO is set at 0.5 V cm-1 and the time-base is set at 5 ms cm-1. Find the peak voltage VP , Period, T and Frequency, f. peak voltage VP Peak voltage, VP = = 5. Period, T Period, T = = Frequency, f. frequency, f = 1/T = =
If the same signal is applied to the CRO but the time base is readjusted to 10 ms/cm, draw a sketch to show the trace that will now be formed on the screen?
4.2 Understanding semiconductor diodes.
[ ../31 x 100 = % ]
1.
(a) A semiconductor is a material whose resistance is between the resistance of a _______________ and an ____________________. (b) ___________ is a process when small amounts of ________________ are added to pure semiconductors causing an increase in the _________________ of the material. (c) A p-type semiconductor is produced when a semiconductor material such _________________ is doped with a ____________ element like _________________
(d) A n-type semiconductor is produced when a semiconductor material such as germanium/silicon is doped with a ____________________ element like _____________________. . (e) A ______________________ is a p-n junction diode where the p-type material is called the __________ and the n-type material is called the ______________ In ___________-biased a current ________ through the diode but in _________-biased current ________________ through the diode.
(f)
(g)
_____________-biased,
Bulb lights / does not light up
_______ _______ Symbol of diode
2.
Diagram 1 shows an electric circuit with one diode and the trace produced is shown on a CRO connected across the resistor R. Diagram 2 shows an electric circuit with four diodes and the trace produced is shown on a CRO connected across the resistor R.
(a)
________________ is a process to convert an alternating current into a _______________________ by using a _____________. Comparision between : Diagram 1 Diagram 2 The diode is connected in _________ to The diodes are connected in a the resistor R. ____________ with two junctions connected to the power supply and the other two junction across the resistor R. Diode is used as a ____________ Diode are used as a __________ rectifier rectifier. Both input are ______________ voltages and the outputs are _______________.
(b)
(c)
Trace the path taken by the current in Diagram.2 if the terminal X is positive. Current flows from _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
(d)
A _______________ is an electric component that needs to be connected to the output of both the circuits to produce a more constant output.
4.3 Understanding transistors
[ ../18 x 100 = .. % ]
A student is able to: Describe a transistor in terms of its terminals. Describe how a transistor can be used as a current amplifier.
Describe how a transistor can be used as an automatic switch.
1. Name the two types of transistors as shown in Figure 4.31(a) and 4.31(b) and label the three terminals X _______ Z Y Figure 4.31 (a) __________ ___________
Type of transistor : _______ transistor X
Y Figure 4.31 (b) Type of transistor : ________ transistor
2. Transistor as a Current Amplfier
mA
R2 R1 IB IE
IC
A transistor can function as a ______________________ by allowing a small current to control a larger current. Rheostat R changes the _______ current. A _________ change in the base current, IB will cause a _______ change in the collector current, IC. The current amplification can be calculated as follows: Current Amplification =
I C I B
3.
The diagram below shows a circuit which acts as an automatic switch to turn on the motor M when the surroundings is dark.
(a) Name the component labeled P,Q and S. Component P Q S (b) What is the function of the component labeled R? To control the ________current. (c) The figure below shows how the collector current, Ic and the base current, Ib flow. Name of the components
(d) What happens to the magnitude of the potential difference VS when the surroundings become bright? Tick ( ) the correct answer in the box provided Increase Decrease (e) Explain how the change in the potential difference, VS, will cause the motor M to be turned on? As VS ____________, the base current ______________ causing the collector current to _______________ by a large magnitude. This will cause the relay to ___________ the circuit and switch on the motor.
4.4 Analysing logic gates
[ / 21 x 100 = % ]
A student is able to: Draw symbols for the following logic gates . i. ii. iii. iv. v. AND OR N0T NAND NOR
Build truth tables for logic gates in combination for a maximum of 2 inputs. State that logic gates are switching circuits in computers and other electronic systems. Describe applications of logic gates control systems.
1. Draw symbols for the following logic gates and state their action in a truth table i. AND ii. OR
iii.
N0T
iv.
NAND
v.
NOR
2.
The figure below shows a circuit consisting of three different logic gates.
(a) Name the logic gates Logic gate P Q Name of the logic gate
(b) Complete the truth table for the system shown above. Input A 0 0 1 1 B 0 1 0 1 Output
(c) (i)
The combination of the logic gates above can be replaced by a single logic gate. What is this equivalent logic gate?
(ii)
Give the Boolean equation for the logic gate in your answer in ( c)(i) above.
2.
The circuit below shows a logic circuit used in a cold room where frozen meat is stored. The alarm will be turned on if the temperature of the cold room is too high. The buzzer will be turned OFF if the output logic is 0 and be turned ON if the output logic is 1.
(a) Name the logic gate used in the circuit above.
(b) Based on the information above, complete the truth table for the logic gate above. Input 1 0 Output 0 1 Alarm
(c) Name the component labeled E.
(d) If the temperature of the cold room increases, what happens to the quantity in the table below? Complete the table with the appropriate answers. Resistance of E Current flowing through the logic gate Condition of the alarm
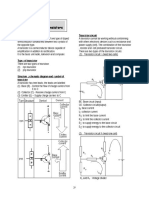
9.2.3 Transistor as an Automatic Switch. 1. Complete the statement below.
The switching action is produced by using a potential divider. In a working circuit shown in figure, a resistor, RX and a . are being used to form a potential divider. If the variable resistor is set to zero, the base voltage is . And the transistor switches . However, if the resistance of the variable resistor is increased, the base voltage will. When the base voltage reached a certain minimum value, the base 9
current, IB switches on the transistor. A large collector current, IC flows to light up the bulb. 2. What type of transistor is used in an automatic switch circuit? 3. (a) Light Controlled Switch (i) Complete the statement below.
Figure shows a transistor-based circuit that functions as a light controlled switch. The .. (LDR) has a very high resistance in the . and a low resistor in ... R is a fixed . The LDR and R form a potential divider in the circuit. In bright light, the LDR has a very . resistance compared to R. Therefore, the base voltage of the transistor is too .. to switch on the transistor. In darkness, the resistance of the LDR is very and the voltage across the LDR is enough to switch on the transistor and thus lights up the bulb. This circuit can be used to automatically switch the bulb at night. (ii) Complete the table below.
(iii) How can the circuit in figure be modified to switch on the light at daytime? .. (b) A Heat-Controlled Switch
10
(i) Complete the statement below. Figure shows a transistor-based circuit that function as a heat controlled switch. A ..is a special type of resistor. Its resistance becomes very when it is cold. When the thermistor is heated, its resistance rapidly. At room temperature, the thermistor has a . resistance compared to R. Therefore, the base voltage of the transistor is too low to switch on the transistor. When the thermistor is heated, its . drops considerablely compared to R. Therefore, the ., VB is high enough to switch . the transistor. When the transistor is switch on, the relay switch is activated and the relay is switched . The circuit can also be used in a fire alarm system. (ii) What is the function of a diode is used in the heat-controlled circuit? .. .. (iii) Complete the table below.
9.2 . 4 Transistor as a Current Amplfier 1. Complete the statement below.
A transistor functions as a current amplifier by allowing a small current to control a larger current. The magnitude of the ., IC is primarily determined by the .., IB. A .. change in the base current, IB will cause a .. change in the collector current, IC. The current amplification can be calculated as follows: 2. Name the type of the transistor used. 3. What will happened to the readings of the miliammeter, mA and microammeter, A when the resistance of R is reduced? 4. A transistor is said to have two states, the ON state and OFF state. 11
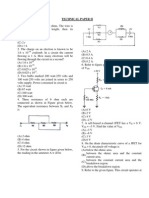
(a) Explain the meaning of the ON state of a transistor. (b) Explain the meaning of the OFF state of a transistor. (c) What is the function of the rheostat, R? (d) What is the function of the resistor, S? Reinforcement Chapter 9 Part A: Objective questions 1. Which of the following is not a property of cathode rays? A. It is positively charged. B. It travels in a straight line. C. It can be deflected by magnetic field. D. It can be deflected by electric field. 2. Cathode rays consists of A. Fluorescent particles B. Light rays from a screen C. Beams of fast moving particles D. Light rays from hot filament 3. A beam of electrons is being deflected due to a potential difference between plates P and Q. Which of the following statements is not true? A. The potential at plate P is positive. B. The deflection would be greater if the potential difference is greater. C. The deflection would be greater if the electrons are moving faster. D. The electron beam will return to straight line if a suitable magnetic field is applied between the plates.
4. The figure 9.34 shows the trace displayed on a CRO with the Ygain control is turned to 3.75 V/div. What is the maximum value of the potential difference being measured? A. 2.5 V B. 5.5 V C. 7.5 V D. 12.5 V E. 15.0 V 5. In p-type semiconductor A. The number of holes are equal to the number of electrons. B. The number of the holes are more than the number of electrons. C. The number of the holes are less than the number of electrons. 6. Which of the following is not true about diode? A. It can be used to rectify alternating current. B. It can only conduct electricity when 12
it is connected in forward in forward bias in a circuit. C. It is formed by joining an ntype and a p-type semiconductor. D. The majority charge carriers in the diode are electrons.
9. The figure 9.37 shows a circuit consisting of two diodes and a bulb. When the switch is on, the bulb does not light up. What needs to be done to light up the bulb?
7. The figure 9. 35 shows the arrangement of silicon atoms after an atom P is doped to form an extrinsic semiconductor.
A. Replace the diode with a new one. B. Reverse the connection of the diode. C. Increase the number of bulbs. D. Connect a resistor in series with the bulb. 10. Figure 9.38 shows four identical bulbs, P, Q, R and S, and four electronic components connected in a circuit. Which of the following bulbs will light up continuously when the switch is on?
Which of the following is not true? A. The conductivity of the semiconductor increases. B. The semiconductor becomes an ntype. C. The majority charge carrier is electron. D. Atom P is a trivalent atom. 8. The figure 9.36 shows a rectifier circuit. Which of the following statements is true?
A. P and Q only B. P, Q and R only C. R and S only D. P, Q and S only A. A rectifier changes d.c to a.c. B. Device P allows current to flow in any directions. C. Device Q acts as a rectifier. D. The rectifier circuit would still work if device P is reversed. 11. Which of the following circuits shows the connect directions of the base current IB, emitter current, IE and collector current, IC?
13
12. Which of the following statements about a transistor is not true? A. A transistor can act as an amplifier B. A transistor can act as a relay switch. C. The function of a transistor is the same as that of two diodes. D. A transistor is a combination of two types of semiconductors. 13. What is the function of the transistor circuit shown in figure 9.39? A. As an amplifier B. As a rectifier C. As a switch device D. As a modulator 14. The figure 9.40 shows a transistor being used as a current amplifier. Which of the following is correct? A. IB > IC B. IB = IC C. IB < IC 15. Figure 9.41 shows a circuit consisting of a transistor which acts as an automatic switch. When the potential difference across the thermistor is 3 V and the resistance of the thermistor is 1000 , the resistance value of resistor, R is .. A. 3 k B. 4 k C. 5 k D. 6 k E. 7 k
16. The figure 9. 42 shows a transistor circuit being used to amplify sound. Which of the following is not correct about the circuit?
A. T is an npn transistor B. The capasitor prevents d.c current but allows a.c current to pass through it. C. Speaker amplifies the sound. D. R1 and R2 act as potential divider. Part B: Structured Questions. 1. Figure 9.46 shows a trace obtained on an oscilloscope screen when an a.c voltage is connected to the Y-plates of an oscilloscope.
(a) Explain what is meant by thermionic emission. (b) Determine the peak voltage of a.c voltage. (c) Determine the time for one complete oscillation on the screen. 14
(d) What is the frequency of the a.c voltage? (e) With the same a.c voltage applied to the oscilloscope, the time-base setting is altered to 2.5 ms/cm and the Y-gain setting is altered to 2 V/cm. On the space below, sketch the new trace would appear on the oscilloscope.
(c) Using the axes in figure 9.48, sketch the voltage-time graph across the resistor, R.
(d) On the figure 9.49, sketch the voltage-time graph across the resistor if a capacitor is connected across the resistor if a capacitor is connected across the resistor R parallel with the resistor.
2. Figure 9. 47 shows a full wave bridge rectifier. The a.c supply has a frequency of 50 Hz.
(e) Explain how the capacitor causes the voltage across the resistor to vary with time in the way that you have drawn.
(a) When the polarity of the a.c supply voltage is positive at A, state the two diodes which are forward biased. . . (b) When the polarity of the a.c supply voltage is negative at A, state the two diodes which are forward biased.
15
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Power Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignDa EverandPower Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignBruno AllardNessuna valutazione finora
- F5 CH 4 StudentDocumento11 pagineF5 CH 4 StudentMadAm JaJaNessuna valutazione finora
- T ElectronicsDocumento6 pagineT ElectronicsGan Hock KiamNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Electronics ConceptsDocumento10 pagineUnderstanding Electronics ConceptsYusfalina Mohd YusoffNessuna valutazione finora
- Uses of the Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRODocumento21 pagineUses of the Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CROKalai SelviNessuna valutazione finora
- 12th Electronics Most Likely Questions SetDocumento19 pagine12th Electronics Most Likely Questions SetomdombareNessuna valutazione finora
- Da2 271222Documento4 pagineDa2 271222rh457707Nessuna valutazione finora
- Digi Anal5Documento4 pagineDigi Anal5NGOUNENessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento15 pagineUntitledAnthony McPhersonNessuna valutazione finora
- University of Edinburgh College of Science and Engineering School of Engineering and ElectronicsDocumento15 pagineUniversity of Edinburgh College of Science and Engineering School of Engineering and ElectronicsSyed Fasih Ur RehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution of Guessing Paper 2018 PDFDocumento17 pagineSolution of Guessing Paper 2018 PDFVidyasagar AcademyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3 - Understanding Transistors: Transistor CircuitDocumento9 pagineLesson 3 - Understanding Transistors: Transistor CircuitSiti Arbaiyah AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- New Assignment Electrical MachinesDocumento17 pagineNew Assignment Electrical MachinesAli BalochNessuna valutazione finora
- DDDC87ECAA084E5DA4D2D77F7DC80391Documento5 pagineDDDC87ECAA084E5DA4D2D77F7DC80391Sameer NandagaveNessuna valutazione finora
- CMOS Translinear CellsDocumento4 pagineCMOS Translinear CellsSumitChoudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Semester-1 - Chemistry Stream - Mid+end PaperDocumento15 pagineSemester-1 - Chemistry Stream - Mid+end PaperGopiNessuna valutazione finora
- Prework Questions For KI-1Documento5 paginePrework Questions For KI-1Danial SadiqNessuna valutazione finora
- TECHNICAL QUIZ EceDocumento7 pagineTECHNICAL QUIZ EceAnonymous eWMnRr70qNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformer-Alternator-Power System-Dc MachinesDocumento7 pagineTransformer-Alternator-Power System-Dc MachinesSumit KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Capacitive Reactance Experiment - LAB 7Documento6 pagineCapacitive Reactance Experiment - LAB 7Mr_asad_20Nessuna valutazione finora
- High Performance CMOS Four Quadrant Analog Multiplier in 45 NM TechnologyDocumento6 pagineHigh Performance CMOS Four Quadrant Analog Multiplier in 45 NM TechnologyInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNessuna valutazione finora
- Viva QuestionsDocumento4 pagineViva QuestionsgbksnNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 2005 Physics 4Documento4 pagine12 2005 Physics 4ShubhamBhardwajNessuna valutazione finora
- Ansoft Designer Harmonic BalanceDocumento9 pagineAnsoft Designer Harmonic BalanceAbdul Kadir Ramos FaisalNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit Components and Their ApplicationsDocumento10 pagineCircuit Components and Their ApplicationsJavaid IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Elec2091st Semester Exam Papr20221 - 1705355554568Documento7 pagineElec2091st Semester Exam Papr20221 - 1705355554568family7482pleaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Latihan Diode and TransistorDocumento7 pagineLatihan Diode and TransistorayydenNessuna valutazione finora
- PART-A (30 Marks) Time: 60 Minutes Solve The Following QuestionsDocumento3 paginePART-A (30 Marks) Time: 60 Minutes Solve The Following QuestionsGaneshan MalhotraNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical, Digital and Industrial Circuits: Second Sequence ExamDocumento4 pagineElectrical, Digital and Industrial Circuits: Second Sequence ExamNGOUNENessuna valutazione finora
- Exam SolutionsDocumento7 pagineExam SolutionsfaisalphyNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics MQP Ii Puc 2023-24Documento4 pagineElectronics MQP Ii Puc 2023-24sanjaykashiNessuna valutazione finora
- TestDocumento2 pagineTestNaveen ChaubeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 3B Impedance of RC Circuits: Parallel RC Circuits 3B.1 Program Outcomes (Pos) Addressed by The ActivityDocumento8 pagineActivity 3B Impedance of RC Circuits: Parallel RC Circuits 3B.1 Program Outcomes (Pos) Addressed by The ActivityNicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure Questions: 1. SPM 2013: QUESTION 3Documento22 pagineStructure Questions: 1. SPM 2013: QUESTION 3Cart KartikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Last Assignment Seu2012 Space KL 29/4/2012Documento13 pagineLast Assignment Seu2012 Space KL 29/4/2012DanielNessuna valutazione finora
- S D S D D D S S D D S: P N N PDocumento5 pagineS D S D D D S S D D S: P N N PPankajSinghBhatiNessuna valutazione finora
- IV Characteristic TransistorDocumento7 pagineIV Characteristic TransistorNida RidzuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Eletronic and RadioactiveDocumento16 pagineEletronic and RadioactiveShiu Ping WongNessuna valutazione finora
- Mesh Solution With 2 SourcesDocumento4 pagineMesh Solution With 2 SourcesNATHANIEL OLSEN PARRENASNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6: Electricity and Magnetism 6.1 Generation of ElectricityDocumento12 pagineChapter 6: Electricity and Magnetism 6.1 Generation of ElectricityNorita JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- Model Question Paper: Basic ElectronicsDocumento3 pagineModel Question Paper: Basic Electronicsravishpy100% (2)
- Technical Paper 2Documento5 pagineTechnical Paper 2Pradeepa Natarajan100% (1)
- Lab#11 EEDocumento16 pagineLab#11 EEJunaid KhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Parity Bit Generator Using 3 Input XOR GDocumento6 pagineParity Bit Generator Using 3 Input XOR Gvirat sharma100% (1)
- Civil Service Common Examination (Csce) 2008 Examination Category: TechnicalDocumento10 pagineCivil Service Common Examination (Csce) 2008 Examination Category: Technicalrohith87nairNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.2 V BiCMOS Sinh-Domain FiltersDocumento21 pagine1.2 V BiCMOS Sinh-Domain Filterschr kasimNessuna valutazione finora
- Logic Gates and Circuits Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento13 pagineLogic Gates and Circuits Multiple Choice QuestionsnguyentrongtinNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits: Final ExaminationDocumento13 pagine6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits: Final ExaminationhelpsatyaNessuna valutazione finora
- NTNU Project Report Designs Integrated Circuits CameraDocumento41 pagineNTNU Project Report Designs Integrated Circuits CameraFilip SavicNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit Tracker PaperDocumento5 pagineCircuit Tracker PaperAmit DhandNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee270 HW2Documento7 pagineEe270 HW2saiedali2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- DC/DC Boost Converter Report: Do Nguyen NghiaDocumento34 pagineDC/DC Boost Converter Report: Do Nguyen NghiaNguyên NghĩaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultra-Low: Power Silicon-on-Sapphire Energy-ScavengingDocumento4 pagineUltra-Low: Power Silicon-on-Sapphire Energy-ScavengingGurkaranjot SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- A) Closed, Open: A) Identical Magnetic AxisDocumento16 pagineA) Closed, Open: A) Identical Magnetic AxisArmy Joel MarianoNessuna valutazione finora
- A Low-Voltage Current Conveyor Using Inverter-Based Error Amplifier and Its Oscillator ApplicationDocumento7 pagineA Low-Voltage Current Conveyor Using Inverter-Based Error Amplifier and Its Oscillator ApplicationAshin AntonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cape PhysicsDocumento15 pagineCape PhysicsFabian Sealey83% (6)
- Qs & As Class I+IIDocumento9 pagineQs & As Class I+IIphyoNessuna valutazione finora
- QA - Copy - Copy2Documento12 pagineQA - Copy - Copy2Physical DesignNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Robolution Induction Test Paper 1Documento24 pagineFinal Robolution Induction Test Paper 1aryanNessuna valutazione finora
- ReproductionDocumento3 pagineReproductionRos Mawar MelatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Verbs and Past Tense Form 4 EnglishDocumento6 pagineVerbs and Past Tense Form 4 EnglishAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Essay 2) Identify: To Prepare Soap From Palm Oil and Sodium Hydroxide. Labelled Diagram: 1)Documento2 pagineEssay 2) Identify: To Prepare Soap From Palm Oil and Sodium Hydroxide. Labelled Diagram: 1)Angie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Countable NounsDocumento5 pagineCountable NounsAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Verbs and Past Tense Form 4 EnglishDocumento6 pagineVerbs and Past Tense Form 4 EnglishAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- CZ Grandmother 1. Loving 3. Attentive 2. Caring 4. Understanding 5. Wonderful / Best Grandmother in The WorldDocumento5 pagineCZ Grandmother 1. Loving 3. Attentive 2. Caring 4. Understanding 5. Wonderful / Best Grandmother in The WorldAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Present and Present Continuous Tenses GuideDocumento9 pagineSimple Present and Present Continuous Tenses GuideAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Secondary Growth of PlantsDocumento13 pagineSecondary Growth of PlantsAngie Kong Su Mei50% (2)
- Functions Pure MathsDocumento20 pagineFunctions Pure MathsAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Electromagnet Teacher's Guide 2009Documento48 pagineChapter 8 Electromagnet Teacher's Guide 2009Mohd Khairul Anuar100% (18)
- Stem and Leaf DiagramsDocumento1 paginaStem and Leaf DiagramsAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Countable NounsDocumento5 pagineCountable NounsAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
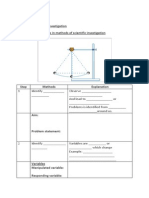
- Scientific investigation stepsDocumento4 pagineScientific investigation stepsAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 15 I Trigonometry II StudentDocumento41 pagineChapter 15 I Trigonometry II StudentAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Form 5 NutritionDocumento5 pagineScience Form 5 NutritionAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Verbs and Past Tense Form 4 EnglishDocumento6 pagineVerbs and Past Tense Form 4 EnglishAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Fertilisation Reproduction Systems Pregnancy Birth ControlDocumento2 pagineFertilisation Reproduction Systems Pregnancy Birth ControlAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon Compounds ChapterDocumento2 pagineCarbon Compounds ChapterAngie Kong Su Mei67% (3)
- Adverbs StudentsDocumento4 pagineAdverbs StudentsAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon Compounds and Their PropertiesDocumento23 pagineCarbon Compounds and Their PropertiesAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- f3 Science c6 Land and Resources StudentDocumento36 paginef3 Science c6 Land and Resources StudentAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Physics Concepts Through Diagrams and ExamplesDocumento46 pagineUnderstanding Physics Concepts Through Diagrams and ExamplesAngie Kong Su Mei0% (1)
- Physics Heat F4Ch4studentDocumento9 paginePhysics Heat F4Ch4studentAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Stem and Leaf DiagramsDocumento1 paginaStem and Leaf DiagramsAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 5 Carbon Carboxilic Acid and Ester StudentDocumento10 pagineChemistry 5 Carbon Carboxilic Acid and Ester StudentAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2.9Documento15 paginePhysics Form 4 Chapter 2.9Farain RashdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Form 5 Chapter 3 Preservation Conservation StudentDocumento8 pagineScience Form 5 Chapter 3 Preservation Conservation StudentAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Verbs and Past Tense Form 4 EnglishDocumento6 pagineVerbs and Past Tense Form 4 EnglishAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 4 Understanding LensesDocumento4 paginePhysics 4 Understanding LensesAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Contoh Modul LKS IPADocumento12 pagineContoh Modul LKS IPAasep_mulyana_4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Puranmal Lahoti Government Polytechnic College, Latur: Micro-Project ProposalDocumento14 paginePuranmal Lahoti Government Polytechnic College, Latur: Micro-Project ProposalAadil • ShaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- A PhototransistorDocumento9 pagineA PhototransistorGur PreetNessuna valutazione finora
- B tech-CSE PDFDocumento183 pagineB tech-CSE PDFkunal yadavNessuna valutazione finora
- MOSFET vs BJT vs FET ComparisonDocumento6 pagineMOSFET vs BJT vs FET ComparisonJade JoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Peak Atlas DCA Pro: User GuideDocumento49 paginePeak Atlas DCA Pro: User GuideLaurentEuniceNessuna valutazione finora
- Tesla Switch GuideDocumento32 pagineTesla Switch GuideRagnarLothbrokNessuna valutazione finora
- Shure t4 ReceiverDocumento31 pagineShure t4 Receiverantenorrochafilho1Nessuna valutazione finora
- FET-Circuits by Rufus-TurnerDocumento83 pagineFET-Circuits by Rufus-TurnerJoserGesalzen100% (1)
- Low Cost 150 Watt Amplifier CircuitDocumento3 pagineLow Cost 150 Watt Amplifier CircuitjnaguNessuna valutazione finora
- Transistor As A Switch: Transistor at Cut-OffDocumento3 pagineTransistor As A Switch: Transistor at Cut-Offvenkatraao784Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sesi Perkongsian Ilmu:Pelaksanaan Obe Di Dalam Memenuhi Keperluan EtacDocumento55 pagineSesi Perkongsian Ilmu:Pelaksanaan Obe Di Dalam Memenuhi Keperluan EtackijangNessuna valutazione finora
- BD436G, BD438G, BD440G, BD442G Plastic Medium Power Silicon PNP TransistorDocumento5 pagineBD436G, BD438G, BD440G, BD442G Plastic Medium Power Silicon PNP TransistorJaPan LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- GaAs HEMTDocumento13 pagineGaAs HEMTvchatlanNessuna valutazione finora
- Microwave PresentationDocumento49 pagineMicrowave PresentationPawan YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Bachelor of Technology (Civil Engineering) : Study &Documento104 pagineBachelor of Technology (Civil Engineering) : Study &neeraj dasNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Fundamentals: B) The Active ElementDocumento45 pagineElectronic Fundamentals: B) The Active ElementZbor ZborNessuna valutazione finora
- I R D S: Nternational Oadmap FOR Evices and YstemsDocumento23 pagineI R D S: Nternational Oadmap FOR Evices and YstemsSnehaNessuna valutazione finora
- John Mark Lubong Bsce 1D Module 1 Activities Computer Fundamental & ProgrammingDocumento5 pagineJohn Mark Lubong Bsce 1D Module 1 Activities Computer Fundamental & ProgrammingJhon Mark Nelmida LubongNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Semiconductor Devices: Betty Lise Anderson - Richard L. AndersonDocumento52 pagineFundamentals of Semiconductor Devices: Betty Lise Anderson - Richard L. Andersonfourier76Nessuna valutazione finora
- TIP42 On SemiconductorDocumento1 paginaTIP42 On SemiconductorMario Raziel BerztructionNessuna valutazione finora
- JLTsDocumento67 pagineJLTsJawar SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Transistor Configuration PDFDocumento42 pagineTransistor Configuration PDFfozle rahad100% (2)
- Transistor Switching GuideDocumento26 pagineTransistor Switching GuidePaolo EscoberNessuna valutazione finora
- 106 Sample ChapterDocumento30 pagine106 Sample ChapterMARYAM ACHIKNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Electrodynamic Vibration Testing HandbookDocumento26 pagineFundamentals of Electrodynamic Vibration Testing Handbookramonh11Nessuna valutazione finora
- VLSI Design Interview QuestionsDocumento11 pagineVLSI Design Interview QuestionsRohit SomkuwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Engineering Design & ManufacturingDocumento10 pagineFundamentals of Engineering Design & ManufacturingPushpinder Singh Khalsa0% (1)
- UiTM FKE Student Handbook Electrical Engineering DiplomaDocumento27 pagineUiTM FKE Student Handbook Electrical Engineering DiplomaFardiana EdrinaNessuna valutazione finora
- High-power transistor for audio & motor controlDocumento2 pagineHigh-power transistor for audio & motor controlDJORJENessuna valutazione finora
- Logarithmic AmplifierDocumento11 pagineLogarithmic AmplifierDan GoleaNessuna valutazione finora