Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Candle Lab
Caricato da
Harrison LeeDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Candle Lab
Caricato da
Harrison LeeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lee 1
Harrison Lee 9/11/12 Period 11 Malisa Ray Candle Lab
Objective: To observe a candle flame as conditions are changed Test the behavior of the candle under a variety of conditions To determine the products formed by a burning candle.
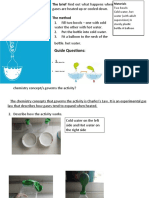
Data: Procedure Number Part A 1 and 2 Hypotheses The candle will lose mass as it burns. Observations and Data Beginning mass: 22.04g Final mass: 21.55g Beaker #1 time: 14 sec Beaker #2 time: 2 sec Analysis The candle lost mass as the matter was converted into energy. The larger beaker contained more oxygen, allowing the flame to continue burning for a longer period of time. The match fire split because the area where it was being blown by CO2 from the candle flame was being suffocated. The flame was extinguished because the copper wire crippled the incoming supply of oxygen to the flame. The water droplets
Part B 1 and 2
The flame will burn for a longer period of time in the larger beaker than the smaller one. The fire on the match will go out because the candle fire will only feed it with CO2.
The match fire split.
The flame will be extinguished by the copper coil.
The candle flame got extinguished.
I think the flame will
The fire weakened
Lee 2
get extinguished.
then went out.
probably cut off the supply of wax (the fuel) to the flame.
Part C 1
I think one of the products of the flame would be water, and the test paper will turn pink.
The cobalt chloride test paper turned pink on contact with the drop of water. There was moisture in One of the products the beaker. Paper of combustion must turned pink. be water.
3 4
There are charred deposits. The limewater became cloudy.
The carbon dioxide gas in the flask made the limewater turn cloudy.
Initial temperature: 86.2 30 seconds: 93 60 seconds: 107 90 seconds: 128 120 seconds: 135
Lee 3
Conclusions: Interpretations 1. On the basis of this experiment, describe the difference between an observation and an interpretation. What are some of the limitations of this experiment? Based on the experiment, an observation is what a person sees as the result of an experiment. An interpretation is how the person perceives the observation as. One of the limitations of this experiment was the inability to test the candle flame in an environment with lots of oxygen and no oxygen. 2. Find out the difference between qualitative and quantitative measurements. Which of the investigations of the burning candle involved quantitative measurement? What other quantitative measurements might be made? The weighing of the candle from before to after required quantitative measurement. Other quantitative investigations included recording the time it took for the candle fire to extinguish, and the temperature changes as the test tube half-full of water was heated over a period of 2 minutes. 3. Based on your analysis of part C, steps 2, 3 and 5, identify the 3 products formed as the candle burned. According to my analysis, the 3 products produced by the candle flame were H2O, CO2, and carbon. 4. Where does the heat energy coming from the burning candle originate? The heat coming from the burning candle originates from the candle wax. 5. In Step 1 of Part B, why was the candle ame extinguished when covered with a ask? It was suggested that one of the products of the candles combustion was carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is used in some re extinguishers. How do you think gases in the air and carbon dioxide affect the behavior of the ame? The candle flame was extinguished when it was covered with a flask because gradually, the oxygen required for combustion was depleted in the flask. Instead, the oxygen was replaced with CO2. Gases in the air and CO2 can affect the behavior of a flame by either weakening the combustion rate or strengthening it. 6. . What do you think caused the ame to be extinguished in Step 4 of Part B when the copper coil was placed in the ame? I think the flame was extinguished when a copper coil was placed over it because the coil crippled the source of oxygen that was feeding the flame.
Lee 4
7. If it is assumed that a candle reacts with oxygen, O2, in the air and the only products are energy, carbon dioxide, CO2, and water, H2O, what two elements must be present in the composition of a candle? If a candle reacts with oxygen and the products are CO2, and H2O, hydrogen and carbon must be present in the composition of the candle. 8. Write a short paragraph describing what you think is occurring during the combustion of a candle. List starting materials and end products. (This is your theory.) During the combustion of a candle, energy(heat) melts some of the candle wax, to a certain point in which the wax and the surrounding oxygen combust. Molten wax flows up the wick in a continual flow, feeding the flame that is consuming both the wax and the oxygen. Carbon dioxide (CO2), water(H2O), and carbon are produced. Further Investigations 9. Do you think a candle with a larger diameter would produce a larger flame? How could you find out? I think a candle with a larger diameter would not produce a larger flame. I can find out by burning a candle with a large diameter and another with a small diameter under the same conditions. Then I would record my data. 10. What do you think is the purpose of the candle wick? Do you think size makes a difference? How can you find out? I think the purpose of the candle wick is to have molten wax travel up continuously up to feed the flame. The size of the wick makes a difference. I can try testing my hypothesis by burning a candle with a thick wick and another candle with a thinner wick.
Lee 5
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Candletestsheet PDFDocumento1 paginaCandletestsheet PDFStephanieNessuna valutazione finora
- Example Balloon Write UpDocumento8 pagineExample Balloon Write UpAnonymous L77eD5uoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report Template 1Documento4 pagineLab Report Template 1names LNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat of Combustion of Candle WaxDocumento14 pagineHeat of Combustion of Candle Waxmarzinus0% (1)
- Combustion and Flame Subjective Ass-2 (Answers)Documento4 pagineCombustion and Flame Subjective Ass-2 (Answers)Saiyam GargNessuna valutazione finora
- WK 14 Myp 5 Chem HW ExemplarDocumento3 pagineWK 14 Myp 5 Chem HW ExemplarJustteenNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercises:: Combustion & FlameDocumento6 pagineExercises:: Combustion & FlameSubhasish RoyNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Burners and FlamesDocumento12 pagine1 Burners and Flameskhan.pakiNessuna valutazione finora
- MODEL ANSWER - Combustion - Flame - Class - VIIIDocumento12 pagineMODEL ANSWER - Combustion - Flame - Class - VIIIRajarshi100% (1)
- 8th Combustion and Flame Living Science SolutionDocumento4 pagine8th Combustion and Flame Living Science SolutionJanardan Sunil100% (9)
- Sencie 1Documento3 pagineSencie 1Paula Tolosa KouryNessuna valutazione finora
- 875542-QA-Combustion and FlameDocumento7 pagine875542-QA-Combustion and FlameNikita RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Combustion WorkshetDocumento6 pagineCombustion WorkshetMadhu geraNessuna valutazione finora
- Asgn 1229143031812Documento7 pagineAsgn 1229143031812rappycatNessuna valutazione finora
- Combustion and Flame Class 8Documento24 pagineCombustion and Flame Class 8Noori ShaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Lab Report Observing A CandleDocumento3 pagineSample Lab Report Observing A CandleJoe JwbejdkdndNessuna valutazione finora
- Combustion and Flame Glossary and NCERT QandADocumento6 pagineCombustion and Flame Glossary and NCERT QandANiyatiNessuna valutazione finora
- NAME: - CLASS: VIII SEC: - DATE:: Delhi Public School Bangalore-East Topic: Combustion and FlameDocumento3 pagineNAME: - CLASS: VIII SEC: - DATE:: Delhi Public School Bangalore-East Topic: Combustion and FlameSujayNessuna valutazione finora
- Combustion and FlameDocumento9 pagineCombustion and Flamesirswal kingNessuna valutazione finora
- Combustion and FlameDocumento24 pagineCombustion and FlameVikranth PonnalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sencie 1Documento7 pagineSencie 1Paula Tolosa KouryNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 8 Chapter 6-Combustion and Flame Notes - HakimDocumento19 pagineClass 8 Chapter 6-Combustion and Flame Notes - HakimHakim AbbasNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Lab ReportDocumento4 pagine2 Lab ReportSasquatchCornNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Chemviiich Combustion and Flame S.kaushikDocumento12 pagineNotes Chemviiich Combustion and Flame S.kaushikjeetjyoti787Nessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER-6 CombustionDocumento6 pagineCHAPTER-6 CombustionAkshara ChawlaNessuna valutazione finora
- NOTESDocumento16 pagineNOTESAadi SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE 8 Science CBSE - Combustion and Flame, Free Test Papers, Sample Questions, HOTS Questions and Notes, CBSE - Combustion and FlameDocumento9 pagineCBSE 8 Science CBSE - Combustion and Flame, Free Test Papers, Sample Questions, HOTS Questions and Notes, CBSE - Combustion and FlameR.Shruti 1040-12Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4 - Oxygen Is Needed For CombustionDocumento14 pagine4 - Oxygen Is Needed For CombustionmizwhiteNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM II-MatterDocumento10 pagineCHEM II-MatterAlyssa Jana Meneses TonogbanuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Combustion Flame - Worksheet-1Documento1 paginaCombustion Flame - Worksheet-1neev choithramaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 8 - Science - Combustion and FlameDocumento4 pagineClass 8 - Science - Combustion and FlameAyaan KhuranaNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 0 CandleDocumento2 pagineExp 0 CandleR-lau R-pizNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer in Fire Technology.........Documento4 pagineAnswer in Fire Technology.........Yevrah ZeuqirneNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem Pt..Documento10 pagineChem Pt..Anne Paulene SobretodoNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment in Chem7a LectureDocumento1 paginaAssignment in Chem7a LecturemkcerbollesNessuna valutazione finora
- Candle Experiment UnmaskedDocumento13 pagineCandle Experiment UnmaskedVijay TrivediNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry BC Investigate A Candle Burning Inside An Inverted Beaker Sealed With PlasticineDocumento9 pagineChemistry BC Investigate A Candle Burning Inside An Inverted Beaker Sealed With Plasticineangle5858zhaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sabarigiri English School, Anchal: Class - Viii Chemistry: Chapter - 6Documento2 pagineSabarigiri English School, Anchal: Class - Viii Chemistry: Chapter - 6Aman AnsalNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 8 Physics Chapter 6 NotesDocumento5 pagineClass 8 Physics Chapter 6 NotesUzma MajeedNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 6 Combustion and Flames Qs AnsDocumento4 pagineCH 6 Combustion and Flames Qs AnsAditya Kumar MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- GeneralChemistry 1 W7 Gaga AMaryCarmelDocumento5 pagineGeneralChemistry 1 W7 Gaga AMaryCarmelEloisa MadrilenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Combustion and Flame: AnswerDocumento5 pagineCombustion and Flame: Answerniranjan bhagatNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Science NCERT Chapter 6Documento13 pagine8 Science NCERT Chapter 6Priyanshu Priyadarshi MeherNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT G8 BOC Chemistry Combustion-And-FlameDocumento4 pagineNCERT G8 BOC Chemistry Combustion-And-FlameAgnes AgnesNessuna valutazione finora
- Combustion and Flame'Documento10 pagineCombustion and Flame'N-Cog-NitoNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEMISTRY - COMBUSTION AND FLAME NOTES - Indumathi VenugopalDocumento13 pagineCHEMISTRY - COMBUSTION AND FLAME NOTES - Indumathi VenugopalSanthosh 456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Combustion Worksheet (MLL)Documento4 pagineCombustion Worksheet (MLL)divyanshNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt6 HeatofcombustionDocumento4 pagineExpt6 HeatofcombustionBo Marayag100% (1)
- Experiment 4Documento2 pagineExperiment 4Nour FaizahNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.4 Science Form 1Documento20 pagine5.4 Science Form 1norsalimahNessuna valutazione finora
- SABRINACAMPBELL DraftIPLabReport DueFeb11Documento4 pagineSABRINACAMPBELL DraftIPLabReport DueFeb11sabrinacampbell1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Combustion and Flame 2022Documento11 pagineCombustion and Flame 2022Debomoy PatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Equipment Materials: TH THDocumento6 pagineEquipment Materials: TH THjarissa bannerNessuna valutazione finora
- Combustion ReactionsDocumento48 pagineCombustion Reactionstai057482Nessuna valutazione finora
- Learning1120231801232349196011 PDFDocumento4 pagineLearning1120231801232349196011 PDFHG MaNessuna valutazione finora
- Burning Town TG Oct2021Documento11 pagineBurning Town TG Oct2021Rafael Galleguillos CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Bunsen BurnerDocumento28 pagineBunsen BurnerMac SensNessuna valutazione finora
- The Bunsen BurnerDocumento17 pagineThe Bunsen BurnerDara Ellaine RicafortNessuna valutazione finora
- f1 Chapter 7 AirDocumento12 paginef1 Chapter 7 AirshshshchinNessuna valutazione finora
- Combustion and Flame - 2Documento12 pagineCombustion and Flame - 2Ayan BordoloiNessuna valutazione finora
- Probability 20170520112434Documento3 pagineProbability 20170520112434Harrison LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Changes and Equations LabDocumento3 pagineChemical Changes and Equations LabHarrison Lee33% (3)
- Scarlett Letter FormatDocumento1 paginaScarlett Letter FormatHarrison LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurements LabDocumento5 pagineMeasurements LabHarrison LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic Law LabDocumento2 paginePeriodic Law LabHarrison Lee80% (5)
- Mole Relationship in A Chemical ReactionDocumento2 pagineMole Relationship in A Chemical ReactionHarrison LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9 Review AnswersDocumento4 pagineChapter 9 Review AnswersHarrison LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 8 Maths IgcseDocumento132 pagineGrade 8 Maths IgcsePRATHAP CHITRA100% (3)
- GSK N7 Controller Instruction Manual 6thDocumento131 pagineGSK N7 Controller Instruction Manual 6thgdprabaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2000 High Speed CMOS Data DL129-D c20000324Documento408 pagine2000 High Speed CMOS Data DL129-D c20000324Dara Nyara Ricardo SocorroNessuna valutazione finora
- 2018 Owner'S Manual and Maintenance Information: For Your Safety, Read Carefully and Keep in This VehicleDocumento458 pagine2018 Owner'S Manual and Maintenance Information: For Your Safety, Read Carefully and Keep in This VehicleAlejandro GonzalezNessuna valutazione finora
- 8810A Operations ManualDocumento34 pagine8810A Operations ManualJoão LopesNessuna valutazione finora
- Karet Susu Hino 500Documento3 pagineKaret Susu Hino 500JokoNessuna valutazione finora
- U3 WORKSHEET # 2.3.C EXTEND Impact - 2 - Unit - 3 - V - and - G - Extend - Worksheet - 2.3.cDocumento4 pagineU3 WORKSHEET # 2.3.C EXTEND Impact - 2 - Unit - 3 - V - and - G - Extend - Worksheet - 2.3.cMayte FrancoNessuna valutazione finora
- Local Balloon Professional Earns Recognition As Certified Balloon ArtistDocumento2 pagineLocal Balloon Professional Earns Recognition As Certified Balloon ArtistPR.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Computing in Distributed System IJERTV1IS10199Documento8 pagineCloud Computing in Distributed System IJERTV1IS10199Nebula OriomNessuna valutazione finora
- Schneider Indonesia April 13, 2005: Ge MultilinDocumento40 pagineSchneider Indonesia April 13, 2005: Ge MultilinMarioNessuna valutazione finora
- CRM S1 MergedDocumento352 pagineCRM S1 Mergedspam ashishNessuna valutazione finora
- Framework of CRMDocumento10 pagineFramework of CRMsachin vermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ot - Smart Surgeon Control PanelDocumento1 paginaOt - Smart Surgeon Control PanelSachin GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tis Aut TMRDocumento2 pagineTis Aut TMRLas PalmasNessuna valutazione finora
- 2014-008-R-Annex To ED Decision 2014-008-R-CS-FCDDocumento38 pagine2014-008-R-Annex To ED Decision 2014-008-R-CS-FCDMyo Myint AungNessuna valutazione finora
- ARO Pump ManualDocumento8 pagineARO Pump Manualrazaq athabNessuna valutazione finora
- Slug Tracking Simulation of Severe Slugging Experiments: Tor Kindsbekken Kjeldby, Ruud Henkes and Ole Jørgen NydalDocumento6 pagineSlug Tracking Simulation of Severe Slugging Experiments: Tor Kindsbekken Kjeldby, Ruud Henkes and Ole Jørgen NydalAyauwu LovedayNessuna valutazione finora
- 1118mm - Thickness Calculator For MS or DI PipesDocumento8 pagine1118mm - Thickness Calculator For MS or DI Pipesanirbanpwd76Nessuna valutazione finora
- Product CatalogueDocumento44 pagineProduct CatalogueTo Van TinhNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Gcse Coursework ExamplesDocumento4 pagineElectronics Gcse Coursework Examplesqrsirljbf100% (2)
- CIVL 4750 Numerical Solutions To Geotechnical Problems: I: TA: T V: Tuesday/ C ODocumento3 pagineCIVL 4750 Numerical Solutions To Geotechnical Problems: I: TA: T V: Tuesday/ C OChoffo YannickNessuna valutazione finora
- ComNet CNGE2FE8MSPOEPLUS Instruction ManualDocumento107 pagineComNet CNGE2FE8MSPOEPLUS Instruction ManualJMAC SupplyNessuna valutazione finora
- Radovan Damjanović Srbsko Srbski Rečnik: Download NowDocumento9 pagineRadovan Damjanović Srbsko Srbski Rečnik: Download NowTinamou0001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Enterprise Management Framework BrochureDocumento4 pagineEnterprise Management Framework BrochureHarish PillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Caterpillar Forklift Trucks Fault Codes DTCDocumento2 pagineCaterpillar Forklift Trucks Fault Codes DTCMahmoud MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Databricks Data Processing Addendum 25 Sept 2021 FINALDocumento12 pagineDatabricks Data Processing Addendum 25 Sept 2021 FINALVaibhav AntilNessuna valutazione finora
- TeM-9007 enDocumento238 pagineTeM-9007 eneugeniuciobanu100% (3)
- Problem StatementDocumento4 pagineProblem Statementjanardhan gortiNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Architecture, Test RetrofitDocumento22 pagineTest Architecture, Test RetrofitReza MobashsherniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Xray2Go Manual Portable X-Ray SystemDocumento36 pagineXray2Go Manual Portable X-Ray SystemEbb Bay100% (1)