Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Pdfa4 2
Caricato da
aizat0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
528 visualizzazioni1 paginaHot metal rods of the same temperature penetrate a block of wax to different depths. The heat content of a substance depends on its Material mass temperature. Specific Heat Capacity is the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one kilogram of the substance through a temperature of one degree Celsius.
Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
pdfa4_2
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoHot metal rods of the same temperature penetrate a block of wax to different depths. The heat content of a substance depends on its Material mass temperature. Specific Heat Capacity is the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one kilogram of the substance through a temperature of one degree Celsius.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
528 visualizzazioni1 paginaPdfa4 2
Caricato da
aizatHot metal rods of the same temperature penetrate a block of wax to different depths. The heat content of a substance depends on its Material mass temperature. Specific Heat Capacity is the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one kilogram of the substance through a temperature of one degree Celsius.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
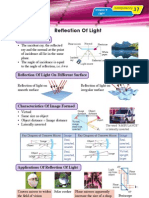
Chapter 4
Transparency
30
Heat
Specific Heat Capacity (I)
Hot metal rods of the same temperature penetrate a block of wax to different depths.
A 5 cm iron rod penetrates deeper than a 5 cm aluminium Aluminium rod
rod due to its lower heat capacity. 5 cm Aluminium
Iron rod
5 cm rod
A 5 cm aluminium rod penetrates deeper than a 3 cm 3 cm
aluminium rod due to its bigger mass.
If two 5 cm aluminium rods of different temperatures are
placed on the block of wax, the hotter aluminium rod will
penetrate deeper.
Hence, the heat content of a substance depends on its
• Material • Mass • Temperature Block of wax
Specific Heat Capacity, c, of a substance is the quantity of heat required to raise the
temperature of one kilogram of the substance through a temperature of one degree
Celsius. Unit for c is J kg–1 oC–1 (or J kg–1 K–1).
Heat energy = Mass × specific heat capacity × temperature change
Q = mcθ
Solid Specific heat capacity, Liquid Specific heat capacity,
(J kg–1 ºC–1) (J kg–1 ºC–1)
Lead 130 Mercury 140
Silver 235 Benzene 1 740
Copper 400 Oil 1 890
Aluminium 890 Ethanol 2 450
Ice 2 100 Water 4 200
Determination Of Specific Heat Capacity Of A Solid
If there is no heat loss to the surroundings, Transformer
Heat gain by aluminium block = Electric energy supplied Switch
mcθ = VIt
c = VIt Rheostat
mθ A
V Switch
m: mass of aluminium block
c: specific heat capacity of aluminium Thermometer
θ : temperature change Electric Aluminium
V: voltage supplied heater
block
I: current supplied Insulation
t: time taken
© Marshall Cavendish ( Malaysia ) Sdn. Bhd.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Pdfa5 3Documento1 paginaPdfa5 3aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Pdfa4 8Documento1 paginaPdfa4 8aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Pdfa5 2Documento1 paginaPdfa5 2aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Pdfa5 3Documento1 paginaPdfa5 3aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Pdfa5 1Documento1 paginaPdfa5 1aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Pdfa4 7Documento1 paginaPdfa4 7aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Specific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form VapourDocumento1 paginaSpecific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form VapouraizatNessuna valutazione finora
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Pdfa4 1Documento1 paginaPdfa4 1aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa4 6Documento1 paginaPdfa4 6aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Pdfa4 3Documento1 paginaPdfa4 3aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa4 5Documento1 paginaPdfa4 5aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Pdfa3 6Documento1 paginaPdfa3 6aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Pdfa2 16Documento1 paginaPdfa2 16aizat100% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Pdfa3 7Documento1 paginaPdfa3 7aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa3 4Documento1 paginaPdfa3 4aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Pdfa3 3Documento1 paginaPdfa3 3aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa2 13Documento1 paginaPdfa2 13aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa3 5Documento1 paginaPdfa3 5aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Pdfa3 2Documento1 paginaPdfa3 2aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Pdfa2 15Documento1 paginaPdfa2 15aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa3 1Documento1 paginaPdfa3 1aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa2 14Documento1 paginaPdfa2 14aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa2 10Documento1 paginaPdfa2 10aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa2 9Documento1 paginaPdfa2 9aizat100% (1)
- Pdfa2 11Documento1 paginaPdfa2 11aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Pdfa2 12Documento1 paginaPdfa2 12aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa2 8Documento1 paginaPdfa2 8aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Crafer. The Apocriticus of Macarius Magnes (S.P.C.K. Edition) - 1919.Documento188 pagineCrafer. The Apocriticus of Macarius Magnes (S.P.C.K. Edition) - 1919.Patrologia Latina, Graeca et OrientalisNessuna valutazione finora
- Pelayo PathopyhsiologyDocumento13 paginePelayo PathopyhsiologyE.J. PelayoNessuna valutazione finora
- SavannahHarbor5R Restoration Plan 11 10 2015Documento119 pagineSavannahHarbor5R Restoration Plan 11 10 2015siamak dadashzadeNessuna valutazione finora
- IOT Questions and Answers - SolutionDocumento8 pagineIOT Questions and Answers - SolutionOmar CheikhrouhouNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Trends and Issues in Nursing ManagementDocumento8 pagineCurrent Trends and Issues in Nursing ManagementMadhu Bala81% (21)
- Generalized Class of Sakaguchi Functions in Conic Region: Saritha. G. P, Fuad. S. Al Sarari, S. LathaDocumento5 pagineGeneralized Class of Sakaguchi Functions in Conic Region: Saritha. G. P, Fuad. S. Al Sarari, S. LathaerpublicationNessuna valutazione finora
- Priest, Graham - The Logic of The Catuskoti (2010)Documento31 paginePriest, Graham - The Logic of The Catuskoti (2010)Alan Ruiz100% (1)
- Reflection in Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDocumento1 paginaReflection in Sexually Transmitted Diseasewenna janeNessuna valutazione finora
- Alphabetic KnowledgeDocumento8 pagineAlphabetic KnowledgejsdgjdNessuna valutazione finora
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- KMKT Pra PSPM ANS SCHEMEDocumento16 pagineKMKT Pra PSPM ANS SCHEMEElda AldaNessuna valutazione finora
- Procter and Gamble - MarketingDocumento10 pagineProcter and Gamble - MarketingIvana Panovska100% (5)
- SICHEM Brochure 2023Documento8 pagineSICHEM Brochure 2023krishnarao badisaNessuna valutazione finora
- CAREDocumento11 pagineCARELuis SementeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics - Mathematics of Magic - A Study in Probability, Statistics, Strategy and Game Theory XDocumento32 pagineMathematics - Mathematics of Magic - A Study in Probability, Statistics, Strategy and Game Theory XHarish HandNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymes IntroDocumento33 pagineEnzymes IntropragyasimsNessuna valutazione finora
- Guncha Arora: Professional Profile Career HistoryDocumento1 paginaGuncha Arora: Professional Profile Career HistoryNitin MahawarNessuna valutazione finora
- Benedict Anderson, Imagined CommunitiesDocumento2 pagineBenedict Anderson, Imagined CommunitiesMonir Amine0% (1)
- Ahmad Syihabudin: BiodataDocumento2 pagineAhmad Syihabudin: BiodatabhjjqrgrwmNessuna valutazione finora
- Caradol sc48 08Documento2 pagineCaradol sc48 08GİZEM DEMİRNessuna valutazione finora
- DN102-R0-GPJ-Design of Substructure & Foundation 28m+28m Span, 19.6m Width, 22m Height PDFDocumento64 pagineDN102-R0-GPJ-Design of Substructure & Foundation 28m+28m Span, 19.6m Width, 22m Height PDFravichandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study - Montana Mountain BikingDocumento6 pagineCase Study - Montana Mountain Bikingbonny MishNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition 2022 PIRDocumento22 pagineNutrition 2022 PIRAlmira LacasaNessuna valutazione finora
- LLM Letter Short LogoDocumento1 paginaLLM Letter Short LogoKidMonkey2299Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1: Composition: Parts of An EggDocumento22 pagineLesson 1: Composition: Parts of An Eggjohn michael pagalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cultural Sensitivity BPIDocumento25 pagineCultural Sensitivity BPIEmmel Solaiman AkmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Final MS Access Project Class-10Documento17 pagineFinal MS Access Project Class-10aaas44% (9)
- Unit 2 - Industrial Engineering & Ergonomics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocumento15 pagineUnit 2 - Industrial Engineering & Ergonomics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inSACHIN HANAGALNessuna valutazione finora
- Nfpa 1126 PDFDocumento24 pagineNfpa 1126 PDFL LNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.161000 702010 New Perspectives 2ndedDocumento43 pagine1.161000 702010 New Perspectives 2ndedbimobimoprabowoNessuna valutazione finora
- ABI TM 13 16 SL - EngDocumento1 paginaABI TM 13 16 SL - EngJuan Carlos Benitez MartinezNessuna valutazione finora