Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Pdfa2 4
Caricato da
aizat0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
679 visualizzazioni1 paginaTitolo originale
pdfa2_4
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
679 visualizzazioni1 paginaPdfa2 4
Caricato da
aizatCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
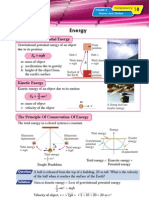
Chapter 2
Transparency
9
Forces And Motion
Motion Graphs (II)
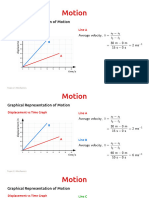
Velocity-Time Graph Interpretation
Velocity Direction of motion
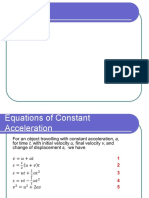
Acceleration
= Gradient
y
=—x
y The rate of change of velocity is uniform.
Uniform acceleration is represented by the
x gradient of the graph.
Time
Velocity The rate of change of velocity is increasing
since the gradient of the graph is increasing.
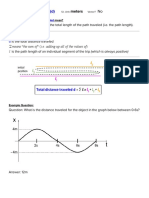
Area under graph This means that the acceleration of the
= Displacement object is increasing.
Note: The area under the graph represents
Time the displacement travelled.
Velocity Velocity Graph A: Positive lower uniform
acceleration
Graph B: Positive higher uniform
acceleration
A Time B Time (Objects are moving towards the right.)
Velocity Velocity Graph C: Negative lower uniform
acceleration
Graph D: Negative higher uniform
acceleration
C Time D Time (Objects are moving towards the left.)
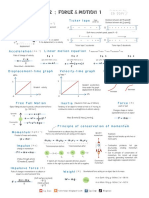
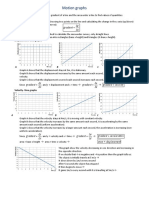
Example
From the velocity-time graph, acceleration
= gradient of graph Velocity (m s−1 )
= 100 – 50 m s−1
4–0 100
= 12.5 m s−2
The displacement travelled 50
= Area under the graph (area of trapezium)
1 0 2 4
= 2 (50 + 100)(4) m Time (s)
= 300 m
© Marshall Cavendish ( Malaysia ) Sdn. Bhd.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Pdfa2 3Documento1 paginaPdfa2 3aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2 Motion GraphsDocumento20 pagine2.2 Motion GraphsfizikkopuNessuna valutazione finora
- Interpret Speed-Time GraphsDocumento11 pagineInterpret Speed-Time GraphsUSHA DEVI A/P LINGAPPAN MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Graphs Representing Motion: Distance-Time GraphDocumento26 pagineGraphs Representing Motion: Distance-Time GraphRandom GuyNessuna valutazione finora
- E-Book Chapter 2 and Experiment 2 Dp014Documento35 pagineE-Book Chapter 2 and Experiment 2 Dp014nurfarahanii06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics SL - Topic 2.1c - MotionDocumento16 paginePhysics SL - Topic 2.1c - MotionAhmad SyahroniNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Kinematic in 1D (Part 1) (PHY130)Documento26 pagineChapter 2 Kinematic in 1D (Part 1) (PHY130)FiqajasmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2-KinematicsDocumento1 paginaChapter 2-KinematicsantonstefanbiehlerNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 2 Kinematics in 1 DDocumento12 pagineWeek 2 Kinematics in 1 DKA R LANessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2 Motion GraphDocumento12 pagine2.2 Motion GraphNURUL FAEZAH BINTI MUSTAPA Moe100% (1)
- SHORT NOTES Force and Motion 1Documento1 paginaSHORT NOTES Force and Motion 1YARSHANA A/P SIVAM MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics (Chapter 2)Documento39 pagineKinematics (Chapter 2)Ali JawwadNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3 Velocity - Time GraphDocumento4 pagineLesson 3 Velocity - Time GraphSomrik LangapNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2. Motion Along A Straight Line: Lecture 3. Displacement, Time, VelocityDocumento6 pagineChapter 2. Motion Along A Straight Line: Lecture 3. Displacement, Time, VelocityBianca Chellyne AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Motion NotesDocumento6 pagineMotion NotesUnkown HumanNessuna valutazione finora
- Motion in One Dimension 2Documento3 pagineMotion in One Dimension 2Naveen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- KinematicsDocumento8 pagineKinematicsMuhammad QadirNessuna valutazione finora
- Position-Time - and - Velocity-Time - Graphs 2Documento21 paginePosition-Time - and - Velocity-Time - Graphs 24.2 (2023) AMELIA CHAN ZI ENNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2 Motion Graphs: Part 1: Displacement vs. Time Graph Part 2: Velocity vs. Time GraphDocumento20 pagine2.2 Motion Graphs: Part 1: Displacement vs. Time Graph Part 2: Velocity vs. Time GraphSyaza IzzatyNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics Lesson 3 and 4Documento36 pagineKinematics Lesson 3 and 4ClareNessuna valutazione finora
- D-Time and Velocity-Time GraphsDocumento20 pagineD-Time and Velocity-Time Graphsmistymint.crewneticNessuna valutazione finora
- Significant Figures: Scalar and Vector QuantitiesDocumento6 pagineSignificant Figures: Scalar and Vector QuantitiesMr ModsNessuna valutazione finora
- Position-Time and Velocity-Time GraphsDocumento29 paginePosition-Time and Velocity-Time GraphsKrislyn Con-Ek DumulagNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics For PDFDocumento20 pagineKinematics For PDFjalanhello71Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH.3Motion in A Straight Line NOTESDocumento22 pagineCH.3Motion in A Straight Line NOTESzoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Accelerated Motion: 2 Motion With Constant AccelerationDocumento8 pagineAccelerated Motion: 2 Motion With Constant AccelerationMohamed AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- The Branch of Mechanics That Studies The Motion of A Body Without Caring About What Caused The MotionDocumento56 pagineThe Branch of Mechanics That Studies The Motion of A Body Without Caring About What Caused The MotionNasir IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Kiematics II AnswersDocumento14 pagineKiematics II Answersethancrestfallen111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module 10Documento14 pagineModule 10Alona DelacruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Motion in A Straight LineDocumento26 pagineMotion in A Straight LineLord Siva100% (3)
- CE Board April 2023 - Engineering Mechanics - Set 5Documento4 pagineCE Board April 2023 - Engineering Mechanics - Set 5Daryl ArizoNessuna valutazione finora
- 1D Motion AP 1 Concept Sheets PDFDocumento10 pagine1D Motion AP 1 Concept Sheets PDFjoseperozo45Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Notes 2012Documento23 pagineChapter 2 Notes 2012Aref DahabrahNessuna valutazione finora
- Graphing Motion PDFDocumento14 pagineGraphing Motion PDFsfgdfgsdfgdfggNessuna valutazione finora
- GraphicalAnalysis2 0Documento15 pagineGraphicalAnalysis2 0shayanhussain764Nessuna valutazione finora
- Motion GraphDocumento6 pagineMotion GraphCt HajarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Kinematic in 1D (Part 1) (PHY 130)Documento26 pagineChapter 2 Kinematic in 1D (Part 1) (PHY 130)FiqajasmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Distance Time Graph J and Velocity TimeDocumento29 pagineUnderstanding Distance Time Graph J and Velocity Timeimran siddiquiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Motions in One and Two Dimensions: Section 3.1 Motion Along A LineDocumento8 pagineChapter 3 Motions in One and Two Dimensions: Section 3.1 Motion Along A LineKF YipNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 2 As Kinematics NotesDocumento8 pagineTopic 2 As Kinematics NotesIffahNessuna valutazione finora
- Motion in A Straight Line PDFDocumento32 pagineMotion in A Straight Line PDFRohit SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mackenzie Rodriguez - Physics Everything SheetDocumento6 pagineMackenzie Rodriguez - Physics Everything Sheetapi-529582727100% (1)
- Complete Guide PDFDocumento42 pagineComplete Guide PDFLeslie UyNessuna valutazione finora
- HP 02 Motion in One DimensionDocumento63 pagineHP 02 Motion in One DimensionEng-Mahamed Dayib NourNessuna valutazione finora
- PPT1Documento5 paginePPT1Jianna Francesca GayodNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.2 MotionDocumento5 pagine1.2 MotionDhanBahadurNessuna valutazione finora
- C3. Motion in 2D or 3DDocumento7 pagineC3. Motion in 2D or 3DBianca Chellyne AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 KinematicsDocumento17 pagine2 KinematicsAmad AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Nehakumari BEdrollno 43Documento29 pagineNehakumari BEdrollno 43Anubhav KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- M1 Mei PDFDocumento10 pagineM1 Mei PDFOmar HashemNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes - Motion & Force and Laws of MotionDocumento47 pagineNotes - Motion & Force and Laws of MotionRajveer KaushalNessuna valutazione finora
- PTM Phy F.4.Ch.2.4Documento13 paginePTM Phy F.4.Ch.2.4Bazil BoliaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Kinematics-Vertical MotionDocumento5 pagine1 - Kinematics-Vertical Motionraynhan06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ch2 Motion in Straight LineDocumento56 pagineCh2 Motion in Straight Linecvxg5hk5xxNessuna valutazione finora
- Hsslive - Plus One Chapter 2 - 2024Documento9 pagineHsslive - Plus One Chapter 2 - 2024ritheshparas39Nessuna valutazione finora
- Motion PDFDocumento5 pagineMotion PDFWhite DevilNessuna valutazione finora
- Motion GraphsDocumento1 paginaMotion GraphsAidan Gabriele DrewNessuna valutazione finora
- A Complete Course in Physics ( Graphs ) - First EditionDa EverandA Complete Course in Physics ( Graphs ) - First EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa5 1Documento1 paginaPdfa5 1aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Pdfa5 3Documento1 paginaPdfa5 3aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa5 3Documento1 paginaPdfa5 3aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa5 2Documento1 paginaPdfa5 2aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Pdfa4 2Documento1 paginaPdfa4 2aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa4 6Documento1 paginaPdfa4 6aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa4 8Documento1 paginaPdfa4 8aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Specific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form VapourDocumento1 paginaSpecific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form VapouraizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa4 5Documento1 paginaPdfa4 5aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa2 13Documento1 paginaPdfa2 13aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa4 7Documento1 paginaPdfa4 7aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa4 3Documento1 paginaPdfa4 3aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa3 1Documento1 paginaPdfa3 1aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa3 7Documento1 paginaPdfa3 7aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa4 1Documento1 paginaPdfa4 1aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa3 3Documento1 paginaPdfa3 3aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa3 4Documento1 paginaPdfa3 4aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa3 5Documento1 paginaPdfa3 5aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa2 16Documento1 paginaPdfa2 16aizat100% (1)
- Pdfa2 15Documento1 paginaPdfa2 15aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa2 14Documento1 paginaPdfa2 14aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa3 6Documento1 paginaPdfa3 6aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa3 2Documento1 paginaPdfa3 2aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa2 11Documento1 paginaPdfa2 11aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa2 12Documento1 paginaPdfa2 12aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa2 8Documento1 paginaPdfa2 8aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa2 10Documento1 paginaPdfa2 10aizatNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfa2 9Documento1 paginaPdfa2 9aizat100% (1)
- Barbara H. Watters - Horary Astrology and The Judgement of Events PDFDocumento226 pagineBarbara H. Watters - Horary Astrology and The Judgement of Events PDFyuorme88% (8)
- HJHJBBBBDocumento6 pagineHJHJBBBBSupri GunNessuna valutazione finora
- Competitive Bidding in The 21st CenturyDocumento256 pagineCompetitive Bidding in The 21st CenturyOvidiu Manolescu100% (9)
- Introduction To Cosmology Matt Roots - IndexDocumento9 pagineIntroduction To Cosmology Matt Roots - IndexTiago MarquesNessuna valutazione finora
- Strrategic Planning For ResultsDocumento311 pagineStrrategic Planning For ResultsabhisentyNessuna valutazione finora
- Customer Relationship ManagementDocumento4 pagineCustomer Relationship ManagementPrity MahatoNessuna valutazione finora
- MSC Social Development Practice at The Bartlett Development Planning Unit. University College LondonDocumento2 pagineMSC Social Development Practice at The Bartlett Development Planning Unit. University College LondonThe Bartlett Development Planning Unit - UCLNessuna valutazione finora
- CLEMENT GREENBERG - Detached ObservationsDocumento8 pagineCLEMENT GREENBERG - Detached ObservationsDaniel BaiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Skimming & Scanning VerbosDocumento2 pagineSkimming & Scanning VerbosMonica FosterNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines For Investigation CommitteesDocumento2 pagineGuidelines For Investigation CommitteesRob Bonner100% (1)
- 1008 Names of Shiva Version 2Documento17 pagine1008 Names of Shiva Version 2Gaurav SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis by AfkDocumento25 pagineThesis by AfkAyushi KohliNessuna valutazione finora
- Apropiacion - Marcel Duchamp - Isaac PDFDocumento39 pagineApropiacion - Marcel Duchamp - Isaac PDFIsaac OlveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Emi QuestDocumento8 pagineEmi Questhanshi123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Corporate Social Responsibility and StrategyDocumento10 pagineCorporate Social Responsibility and StrategygagansrikankaNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnets Lesson Plan Ap PhysicsDocumento3 pagineMagnets Lesson Plan Ap Physicsapi-257588494Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biographical Tribute-Fr Honeybunch-ByDocumento6 pagineBiographical Tribute-Fr Honeybunch-Byapi-292433277Nessuna valutazione finora
- WEB SUPPORT: The Pearson Guide To Bank Clerical Recruitment ExaminationDocumento35 pagineWEB SUPPORT: The Pearson Guide To Bank Clerical Recruitment ExaminationIshaBarapatreNessuna valutazione finora
- Five Year MA Integrated Regulations & Syllabus-030714Documento100 pagineFive Year MA Integrated Regulations & Syllabus-030714anoopNessuna valutazione finora
- Cognitive Functions - The How ToDocumento8 pagineCognitive Functions - The How ToRomaximus BarrikkadNessuna valutazione finora
- Discussion Guide TED Talks For Aspiring Student LeadersDocumento4 pagineDiscussion Guide TED Talks For Aspiring Student LeadersZachNessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook For WritersDocumento433 pagineHandbook For Writersgelunn100% (1)
- REPORT CARD (New Format G1 & 2) SY 2018-2019Documento2 pagineREPORT CARD (New Format G1 & 2) SY 2018-2019Goldine Barcelona EteNessuna valutazione finora
- Thirty Alawāt For Easing That Which Has Been Decreed: Inspired To Shaykh Abd Al-Ghanī B.Shaykh Al-Ja FarīDocumento6 pagineThirty Alawāt For Easing That Which Has Been Decreed: Inspired To Shaykh Abd Al-Ghanī B.Shaykh Al-Ja FarīSouvenir Tas Blacu Solo100% (1)
- The Love Affairs of Great Musicians, Volume 2 by Hughes, Rupert, 1872-1956Documento123 pagineThe Love Affairs of Great Musicians, Volume 2 by Hughes, Rupert, 1872-1956Gutenberg.org100% (7)
- Book of Proceedings EsdParis2018 OnlineDocumento535 pagineBook of Proceedings EsdParis2018 Onlineca taNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 The Filipino Value System and Its Effects On BusinessDocumento7 pagineChapter 7 The Filipino Value System and Its Effects On BusinessMara Gianina Quejada100% (1)
- B.A. (Hons.) Pol. Science 5th Semester-2017Documento12 pagineB.A. (Hons.) Pol. Science 5th Semester-2017Subham RajputNessuna valutazione finora
- The History of Matengo HighlandsDocumento34 pagineThe History of Matengo HighlandsOsmund KapingaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rise of The DEO PDFDocumento22 pagineRise of The DEO PDFMarcia Matos0% (1)