Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Nursing Care Plan for Respiratory Conditions
Caricato da
Jonathan Delos ReyesTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Nursing Care Plan for Respiratory Conditions
Caricato da
Jonathan Delos ReyesCopyright:
Formati disponibili
VIII.
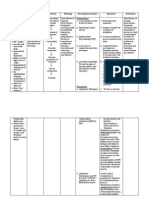
NCP Assessment Subjective: hindi ako masyado makagalaw Nursing Diagnosis Risk for Activity Intolerance r/t decrease oxyge nation Planning After 4 hours of nursing intervention the patient will participate willingly in necessary/ desired activities such as deep breathing exercises. Interventions 1. Monitor VS. 2. Assess motor function. 3. Note contributing factors to fatigue. 4. Evaluate degree of deficit. 5. Ascertain ability to stand and move about. 6. Assess emotional or psychological factors 7. Plan care with rest periods between activities 8. Increase activity/exercise gradually such as assisting the patient in doing PROM to active or full range of motions. 9. Provide adequate rest periods. 10. Assist client in doing self care needs 11. Place knees and hips in extended position Rationale 1. For baseline data. 2. To identify causative factors. 3. To identify precipitating factors. 4. To identify severity. 5. To identify necessity of assistive devices. 6. Stress and/or depression may increase the effects of illness. 7. To reduce fatigue 8. Minimizes muscle atrophy, promotes circulation, helps to prevent contractures 9. To replenish energy. 10. To promote independence and increase activity tolerance 11. Maintains functional position Evaluation Patientparticipat ed willingly in necessary/ desired activities such as deep breathing exercises.
Objective: Weak Easy Fatigability Pallor RR-26bpm P-106bpm Capillary refill 3-4seconds With thoracostomy tube
Nursing Diagnosis Subjective: Ineffective Nahihirapanakong breathing huminga as pattern r/t verbalized by the presence of patient secretions AEB productive Objective: cough and wheezing upon dyspnea inspiration and expiration dyspnea tachycardia chest tightness
Assessment
Planning After 4-5 hours of nursing intervention Patient will manifest signs of decreased respiratory effort AEB absence of dyspnea
Interventions 1. Establish rapport. 2. assess pt.s condition 3. VS monitor and record 4. Auscultate breath sounds and assess airway pattern 5. Elevate head of the bed and change position of the pt. every 2 hours. 6. Encourage deep breathing and coughing exercises. 7. Demonstrate diaphragmatic and pursed-lip breathing. 8. Encourage increase in fluid intake 9. Encourage
Rationale 1. To gain pt.s trust. 2. To obtain baseline data 3. Serve to track important changes 4. to check for the presence of adventitious breath sounds 5. To minimize difficulty in breathing 6. To maximize effort for expectoration. 7. To decrease air trapping and for efficient breathing. 8. To prevent fatigue. 9. To prevent situations that will aggravate the condition
Evaluation
Patient demonstrated pursed-lip breathing and diaphragmatic breathing.
opportunities for rest and limit physical activities. 10. Reinforce low salt, low fat diet as ordered.
10. To mobilize secretions.
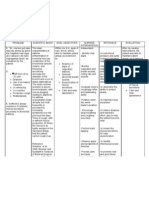
Nursing Diagnosis Subjective: Ineffective Nahihirapanakong airway huminga as clearance RT verbalized by the bronchoconstri patient ction, increased Objective: mucus wheezing upon production, and inspiration and respiratory infection AEB expiration wheezing, dyspnea dyspnea, and tachycardia chest tightness cough productive cough yellowish color of phlegm
Assessment
Planning After 5-6 hours of nursing intervention the Patient will maintain/impro ve airway clearance AEB absence of signs of respiratory distress
Interventions 1. Adequately hydrate the pt. 2. Teach and encourage the use of diaphragmatic breathing and coughing exercises. 3. Instruct pt to avoid bronchial irritants such as cigarette smoke, aerosols, extremes of temperature, and fumes. 4. Teach early signs of infection that are to be reported to the clinician immediately.
Rationale 1. Systemic hydration keeps secretion moist and easier to expectorate. 2. These techniques help to improve ventilation and mobilize secretions without causing breathlessness and fatigue. 3. Bronchial irritants cause bronchoconstrictio n and increased mucus production, which then interfere with
Evaluation Patient state Ok napoangakingp aghinga, hindinaakonahih irapan
Increases sputum production Change in color of sputum Increased thickness of sputum Increased SOB, tightness of chest, or fatigue Increased coughing Fever or chills
airway clearance. 4. Minor respiratory infections that are of no consequence to the person with normal lungs can produce fatal disturbances in the lungs of an asthmatic person. Early recognition is crucial.
5. If indicated, perform postural drainage with percussion and vibration in the morning and at night as prescribed.
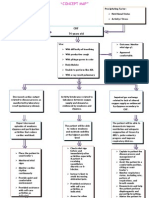
Assessment SUBJECTIVE: Medyo inuubo pa po ako As verbalized by the patient OBJECTIVE: wheezing upon expirationV/S: BP100/70mmH
Nursing Diagnosis Ineffective airway clearance related to bronchospasm and increase production of mucus secretions
Planning After 4hrs of nursing intervention, the patient will improve airway clearance and can demonstrate behaviors to improve her condition.
Interventions 1. Auscultate breath sounds. Note adventitious breath sounds.
Rationale 1. Some degree of bronchospasms presents with obstructions in airway and may/may not be manifested in adventitious breath sounds. 2. To serve as baseline data.
Evaluation After nursing intervention ,the patient can improve airway clearance and can demonstrate coughing effectively and Expectorating secretions.
2. Assess /Monitor respiratory rate. Note respiratory/expiratory ratio.
3. Elevation of the head of the bed
g T- 36 c PR- 71bpm RR- 18 bpm
3. Advised high or semifowlers position
facilitates respiratory function by use of gravity and for optimum lung expansion. 4. Precipitators of allergic type of respiratory reactions that can trigger/ exacerbate onset of acute episodes. 5. Provide patient with some means 6. These techniques help to improve ventilation and mobilize secretions without causing breathlessness and fatigue Rationale
4. Keep environmental pollution to a minimum.
5. Encourage/assist with pursed-lip 6. Teach and encourage the use of diaphragmatic breathing and coughing exercise
Assessment
Nursing Diagnosis Fatigue r/t physical exertion to maintain adequate ventilation AEB use of accessory
Planning
Interventions
Evaluation Patients will perform ADLs within clients ability and participates in desired activities
Objective:
wheezing upon inspiration and expiration
After the nursing intervention patient will be able to identify basis of fatigue and be able to cope up with
1. Establish rapport 2. Monitor and record vital signs. 3. Provide environment conducive to relief of fatigue.
1. To gain patients trust 2. For baseline data 3. Temperature and level of humidity are known to affect
dyspnea coughing, sputum is yellow and sticky tachypnea, prolonged expiration tachycardia chest tightness
muscles to breathe
the problem. 4. 4. Assist client to identify appropriate coping behaviors. 5. 5. Encourage patient to restrict activity and rest in bed as much as possible. 6. 6. Avoid topics that irritate or upset patient. Discuss ways to respond to these feelings. 7. Discuss with the patient the need for activity 8. Alternate activity with the rest periods 8.
cyanosis
7.
exhaustion Promotes sense of control and improves selfesteem Helps counteract effect of increased metabolism Increased irritability of the CNS may cause to the patient to be easily excited, agitated and prone to emotional outburst Education may provide motivation to increase activity Prevents excessive fatigue
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Revised NCP (Baiae)Documento9 pagineRevised NCP (Baiae)Jennifer BactatNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 NCP's FinalDocumento9 pagine4 NCP's FinalZenel Yap100% (1)
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Documento6 pagineWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasNessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumonia Nursing Care Plans in 40 CharactersDocumento1 paginaPneumonia Nursing Care Plans in 40 Charactersjustin_saneNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento9 pagineNCPEjie Boy Isaga67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan - 1 AlyanaDocumento1 paginaNursing Care Plan - 1 AlyanaKen100% (1)
- NCP #2Documento4 pagineNCP #2Nutz TolentinoNessuna valutazione finora
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 pagineANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- Nursing ManagementDocumento16 pagineNursing ManagementNica Marie LumbaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento2 pagineNCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDivine Jane PurciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Patho PneumoniaDocumento2 paginePatho Pneumoniaailyne_galicia100% (2)
- Oxygenation - NCPDocumento5 pagineOxygenation - NCPCazze SunioNessuna valutazione finora
- Pleural EffusionDocumento5 paginePleural EffusionTerizla MobileNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento3 pagineNCP For Ineffective Airway ClearanceJennelyn BayleNessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumonia Nursing Care Plans: Assessment, Interventions & OutcomesDocumento1 paginaPneumonia Nursing Care Plans: Assessment, Interventions & Outcomesjustin_saneNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento2 pagineNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKhat100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento6 pagineIneffective Airway ClearanceBenly Grace Rebuyon MosquedaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento4 pagineNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceMary Joyce Limoico100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 pagineNursing Care Planapi-309251523Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cap NCPDocumento6 pagineCap NCPMarlo Parayno100% (2)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento2 pagineNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearancelarapatricia1215Nessuna valutazione finora
- (Patho) PTB COPDDocumento1 pagina(Patho) PTB COPDKyle HannahNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPDocumento1 paginaImpaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPKaycee BinanNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP PTBDocumento2 pagineNCP PTBKath TalubanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocumento1 paginaHyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_saneNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDocumento3 pagineNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tarasoff CaseDocumento2 pagineTarasoff Casealyssa marie salcedo100% (1)
- NCP PneumoniaDocumento47 pagineNCP Pneumoniabhevpat251100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocumento1 paginaIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee BaluyotNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Breathing PatternDocumento1 paginaImpaired Breathing PatternHanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan for Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento9 pagineNursing Care Plan for Ineffective Airway ClearanceAngelokeizer GavinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDocumento3 pagineAssessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDyanne BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Documento1 paginaNursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Caroline ChaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento1 paginaIneffective Airway ClearancejomerdalonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocumento7 pagineIneffective Breathing PatternJanmae JivNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance (Mary Ann Solomon)Documento6 pagineNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance (Mary Ann Solomon)Karissa GuerreroNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Documento1 paginaChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Bheru LalNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP CopdDocumento4 pagineNCP CopdJoshua ValdrizNessuna valutazione finora
- Adhf NCPDocumento3 pagineAdhf NCPkristine keen buanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento1 paginaNursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceLei OrtegaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Copd4Documento15 pagineNCP Copd4Alessa Marie Crisostomo Salazar100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPDocumento2 pagineNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPpa3kmedina100% (1)
- CopdDocumento6 pagineCopdapi-3717941100% (2)
- NCP Acitivity IntoleranceDocumento3 pagineNCP Acitivity IntolerancegizelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept Map - Abby !Documento2 pagineConcept Map - Abby !Abegail Abaygar100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPLP Benoza100% (2)
- Idoc - Pub Ncp-SinusitisDocumento2 pagineIdoc - Pub Ncp-SinusitisEdson John Demayo100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Impaired Gas ExchangeDocumento6 pagineNursing Care Plan for Impaired Gas ExchangePrincess Andrea Bulatao100% (1)
- Chest Tube Reflective EssayDocumento2 pagineChest Tube Reflective EssayAnjae GariandoNessuna valutazione finora
- NURSING CARE PLAN of CoughDocumento1 paginaNURSING CARE PLAN of Coughrhizalyn1383% (6)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento2 pagineIneffective Airway Clearancejancel_bollaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento3 pagineNCPWendy EscalanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Far Eastern University Nursing Care Plan Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento1 paginaFar Eastern University Nursing Care Plan Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationSarah CarreteroNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP BMDocumento1 paginaNCP BMSourabh MehraNessuna valutazione finora
- Causes and Nursing Care of Pleural EffusionDocumento4 pagineCauses and Nursing Care of Pleural EffusionHania Polangi100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento1 paginaNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceImation DataNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale Expected OutcomeDocumento3 pagineAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale Expected OutcomeIsabel Barredo Del MundoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan Problem: Difficulty of BreathingDocumento5 pagineNursing Care Plan Problem: Difficulty of BreathingIvan Louise Fajardo ManiquizNessuna valutazione finora
- Improve Activity Tolerance Through Rest and RelaxationDocumento7 pagineImprove Activity Tolerance Through Rest and RelaxationKrisJane Ratilla Abiva100% (2)
- Pleural Effusion NCPsDocumento7 paginePleural Effusion NCPsJaja Nagallo100% (2)
- TL ExamDocumento3 pagineTL ExamJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Pure or Basic ResearchDocumento2 paginePure or Basic ResearchJonathan Delos Reyes0% (1)
- A History of The Philippines by David P. BarrowsDocumento932 pagineA History of The Philippines by David P. BarrowsCarl Taawan100% (1)
- Bahay KuboDocumento4 pagineBahay KuboJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Affixes: NAME: Delcon Anthony D. Bañares COURSE: Bachelor of Art in Communications DATE: July 27, 2014Documento1 paginaAffixes: NAME: Delcon Anthony D. Bañares COURSE: Bachelor of Art in Communications DATE: July 27, 2014Jonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Interpretation of Data FormulasDocumento5 pagineInterpretation of Data FormulasEliana GerzonNessuna valutazione finora
- Tuesdays With Morrie PDFDocumento1.931 pagineTuesdays With Morrie PDFJonathan Delos Reyes18% (33)
- Nle Notes PediaDocumento53 pagineNle Notes PediaJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- TL ExamDocumento3 pagineTL ExamJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Disease ProfileDocumento5 pagineDisease ProfileJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Interpretation of Data FormulasDocumento5 pagineInterpretation of Data FormulasEliana GerzonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento10 pagineChapter 1Jonathan Delos Reyes100% (1)
- Disease ProfileDocumento5 pagineDisease ProfileJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- At The I Was Informed That We Are Going To CaviteDocumento1 paginaAt The I Was Informed That We Are Going To CaviteJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Disease ProfileDocumento5 pagineDisease ProfileJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- LaboratoryDocumento9 pagineLaboratoryJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Disease ProfileDocumento5 pagineDisease ProfileJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Fracture IntroductionDocumento21 pagineFracture IntroductionJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Jade DapolDocumento10 pagineJade DapolJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer FundamentalsDocumento13 pagineComputer FundamentalsJonathan Delos Reyes100% (1)
- System ProgramDocumento1 paginaSystem ProgramJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- TL ExamDocumento3 pagineTL ExamJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Fracture IntroductionDocumento21 pagineFracture IntroductionJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study ToinkDocumento5 pagineDrug Study ToinkJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BrainDocumento22 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of The BrainJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Fracture IntroductionDocumento21 pagineFracture IntroductionJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Traumatic Brain InjuryDocumento21 pagineTraumatic Brain InjuryJonathan Delos Reyes67% (3)
- Eric OsteomyelitisDocumento22 pagineEric OsteomyelitisJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Case StudyDocumento18 pagineCase StudyJonathan Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathogenesis of AtherosclerosisDocumento21 paginePathogenesis of Atherosclerosishakky gamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdominal Compartment SyndromeDocumento15 pagineAbdominal Compartment SyndromePierinaNessuna valutazione finora
- M 371Documento14 pagineM 371Anonymous h0DxuJTNessuna valutazione finora
- Pe Lecture NotesDocumento7 paginePe Lecture NotesAnonymous LJrX4dzNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology-REVIEWER-Practical ExamDocumento12 pagineAnatomy and Physiology-REVIEWER-Practical ExamDeity Ann ReuterezNessuna valutazione finora
- The Integumentary SystemDocumento11 pagineThe Integumentary SystemHamdy Pagilit DimaporoNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Clients With Disturbances in OxygenationDocumento13 pagineManagement of Clients With Disturbances in OxygenationClyde CapadnganNessuna valutazione finora
- Identification of BacteriaDocumento4 pagineIdentification of BacteriaVasugiNessuna valutazione finora
- Zoology: Zoology Previous Eamcet QuestionsDocumento8 pagineZoology: Zoology Previous Eamcet QuestionsGaganpreetSingh100% (1)
- Exam 3 NotesDocumento3 pagineExam 3 NotesStanley ChuNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are The Types of EndosDocumento3 pagineWhat Are The Types of EndosSailu KatragaddaNessuna valutazione finora
- Artificial Lung Design & Gas ExchangeDocumento25 pagineArtificial Lung Design & Gas Exchangealoove66Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biochem QbankDocumento16 pagineBiochem Qbank786waqar786Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3.03 Understand Structures, Functions and Disorders of The Nervous SystemDocumento38 pagine3.03 Understand Structures, Functions and Disorders of The Nervous SystemLoriwinchesterNessuna valutazione finora
- Foot and Ankle ArthrokinematicsDocumento6 pagineFoot and Ankle ArthrokinematicsCraig StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- GIT Physio D&R AgamDocumento67 pagineGIT Physio D&R Agamvisweswar030406Nessuna valutazione finora
- SPM Bio Perlis 2009 Serta SkemaDocumento96 pagineSPM Bio Perlis 2009 Serta Skemahilmi72100% (1)
- 16th Week of Pregnancy: Tips for Safe Travel While ExpectingDocumento4 pagine16th Week of Pregnancy: Tips for Safe Travel While ExpectingNaveenbabu SoundararajanNessuna valutazione finora
- H2S Training Slides ENGLISHDocumento46 pagineH2S Training Slides ENGLISHf.B100% (1)
- Fuel Metabolism in StarvationDocumento27 pagineFuel Metabolism in Starvationilluminel100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocumento11 pagineDrug StudyKimberly Ann MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronobiology and Anesthesia: Review ArticleDocumento15 pagineChronobiology and Anesthesia: Review ArticleGabriela Lizbeth ArmentaNessuna valutazione finora
- CP Angle SOLDocumento8 pagineCP Angle SOLVinay GNessuna valutazione finora
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1Documento10 pagineScience: Quarter 1 - Module 1RUTH PIANGNessuna valutazione finora
- Fta Dna ExtractionDocumento20 pagineFta Dna Extractionnorma eunice gonzalezNessuna valutazione finora
- Long-Term Memory Encoding and RetrievalDocumento24 pagineLong-Term Memory Encoding and RetrievalThavasi mari selvam NNessuna valutazione finora
- HerniaDocumento36 pagineHerniashankarrao3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Parasites Immunity and PathologyDocumento389 pagineParasites Immunity and Pathologyrild278111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vacuole FunctionDocumento8 pagineVacuole Functionkbansal981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hematology Analyzers, Coagulation Systems Product GuideDocumento4 pagineHematology Analyzers, Coagulation Systems Product GuideElvan Dwi WidyadiNessuna valutazione finora