Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Receivables Management
Caricato da
Puneet JindalDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Receivables Management
Caricato da
Puneet JindalCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Receivables management
Debt owed to the firm by customers arising from sale of goods or services in the ordinary course of business. It means making decision relating to the investment in these current assets and the objective being maximization of return on investment in receivables.
Introduction of receivable management:
Accounts receivable (A/R) is one of a series of accounting transactions dealing with the billing of a customer for goods and serviceshe/she has ordered. In most business entities this is typically done by generating an invoice and mailing or electronically delivering it to the customer, who in turn must pay it within an established timeframe called "creditor payment terms." An example of a common payment term is Net 30, which means payment is due in the amount of the invoice 30 days from the date of invoice. Other common payment terms include Net 45 and Net 60 but could in reality be for any time period agreed upon by the vendor and the customer. While booking a receivable is accomplished by a simple accounting transaction, the process of maintaining and collecting payments on the accounts receivable subsidiary account balances can be a full-time proposition. Depending on the industry in practice, accounts receivable payments can be received up to 10 - 15 days after the due date has been reached. These types of payment practices are sometimes developed by industry standards, corporate policy, or because of the financial condition of the client. On a company's balance sheet, accounts receivable is the money owed to that company by entities outside of the company. The receivables owed by the company's customers are called trade receivables. Account receivables are classified as current assets assuming that they are due within one year. To record a journal entry for a sale on account, one must debit a receivable
and credit a revenue account. When the customer pays off their accounts, one debits cash and credits the receivable in the journal entry. The ending balance on the trial balance sheet for accounts receivable is always debit. Business organizations which have become too large to perform such tasks by hand (or small ones that could but prefer not to do them by hand) will generally use accounting software on a computer to perform this task. Associated accounting issues include recognizing accounts receivable, valuing accounts receivable, and disposing of accounts receivable. Accounts receivable departments use the sales ledger. Accounts receivable is more commonly known as Credit Control in the UK, where most companies have a credit control department. Other types of accounting transactions include accounts payable, payroll, and trial balance. Since not all customer debts will be collected, businesses typically record an allowance for bad debts which is subtracted from total accounts receivable. When accounts receivable are not paid, some companies turn them over to third party collection agencies or collection attorneys who will attempt to recover the debt via negotiating payment plans, settlement offers or legal action. Outstanding advances are part of accounts receivables if a company gets an order from its customers with payment terms agreed in advance. Since no billing is being done to claim the advances several times this area of collectible is not reflected in accounts receivables. Ideally, since advance payment is mutually agreed term, it is the responsibility of the accounts department to take out periodically the statement showing advance collectible and should be provided to sales & marketing for collection of advances. The payment of accounts receivable can be protected either by a letter of credit or by Trade Credit Insurance. Companies can use their accounts receivable as collateral when obtaining a loan (asset-based lending) or sell them through factoring. Pools or portfolios of accounts receivable can be sold in the capital markets through a securitization
Objective of receivables management:
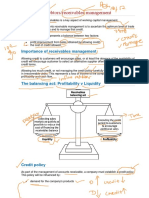
From creation of receivables the firm gets a few advantages & it has to bear bad debts, administrative expenses, financing costs etc. In the management of receivables financial manager should follow such policy through which cash resources of the firm can be fully utilised. Management of receivables is a process under which decisions to maximise returns on the investment blocked in them are taken. Thus, the main objectives of management receivable is to maximise the returns on investment in receivables & to minimise risk of bad debts etc. Because investment in receivables affects liquidity and profitability, it is, therefore, significant to maintain proper level of receivables. In other words, the basic objectives of receivables management is to maximise the profits. Efficient credit management helps to increase the sales of the firm. Thus, following are the main objectives of receivables management:-
(1) To optimise the amount of sales. (2) To minimise cost of credit. (3) To optimise investment in receivables.
Therefore, the main objective of receivable management is to establish a balance between profitability and risk (cost). A business can afford to invest in its receivables unless the marginal costs and marginal profits are the same. Although the level of receivables is affected by various external factors like standards of industry, economic conditions, seasonal factors, rate of competition etc, management can control its receivables. Though credit policies, credit terms, credit standards and collection procedures.
Benefits of receivables management:
Help improve customer satisfaction. Enhance service levels and increase retention with customized information, history, and notes that are easily accessible when working with customers.
Take control of sales processes. Manage your sales process more effectively by measuring trends and analyzing performance with comprehensive customer tracking combined with sales tracking by person or territory.
Enhance your productivity. Help reduce administrative costs and enhance office productivity with automated receipt processing and posting and personalized statement cycles that fit your customers and business.
Streamline revenue allocation. Simplify the task of deferring revenues over multiple periods with automatically managed calculations and journal entries customized to fit your business needs.
Provide access to vital information. Find the information you need to make more effective business decisions with comprehensive reporting capabilities and straightforward customer account and sales performance tracking.
Features of receivable management:
View un-posted, posted, and historical transactions, plus complete customer, period sales, yearly sales, payment history, and receivables summary information. Utilize user-defined fields to track the customer information you need to improve sales and customer service. Automate customer installment payments by creating schedules, calculating interest, amortizing amounts, and forecasting the impact of variable interest rates, payment amounts, and installment changes. Maintain full control over the receivables process with automated lockbox processing, customer billing defaults, insufficient funds (NSF) tracking, multicurrency support, and the ability to fully define customer statement cycles. Analyze your sales performance with receivables tracking for each salesperson or sales territory, including commissions, commissioned sales, noncommissioned sales, and cost of sales for the year to date. Create a comprehensive suite of reports or combine with Microsoft Dynamics GP modules such as Report Writer or Crystal Reports for greater reporting flexibility and power. Automate processes for writing off and adjusting overpayments and underpayments, and create and apply debit and credit documents for open balances.
Why should businesses consider outsourcing Receivables Management?
When an outsourcing partner is well-chosen to complement existing in-house credit procedures, the benefits are innumerable: > Real cash flow improvement > Reduced bad debt losses > Decreased average of days sales outstanding (DSO) > Reduced costs > More time & resources to focus on core business issues > Better customer care through specialist knowledge & expertise
> Improved payment habits on the part of your customers
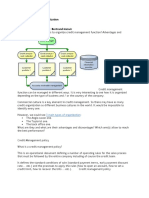
Receivables management involves the three decision areas:
Credit standards. Credit period Cash discount Collection period
Credit standard Minimum criteria of extension of credit to a customer.Credit rating, credit references, and average payment period. Credit period The period of time, for which credit is allowed to a customer to economic value of purchases.It is generally expressed in terms of net data(i.e.., if a firms credit term are net 60),that is payment will be made with in 60 days from the date to credit sales. Cash discount A percent reduction in sales or purchases price allowed for early payment of invoices.It encourages the customers to pay credit obligations within a specified period of time, which will be less than the normal credit period. For example, 2/20 net 60, which means that credit grants 2 percent discount, if debtor pays his a/c with in 20 days after beginning of the credit period. Collection period The collection policy of a firm is the procedure passed to collect amount receivables, when they become due.It is needed because all customer do not pay the bills receivables in time
Evaluation of individual account
Obtaining credit information Internal sources. External sources. Financial statements or annual reports. Bank references.
STEPS IN CREDIT ANALYSIS Customer Evaluation- The 5 Cs Character- Reputation, Track Record Capacity- Ability to repay( earning capacity) Capital- Financial Position of the co. Collateral- The type and kind of assets pledged Conditions- Economic conditions & competitive factors that may affect the profitability of the customer.
Techniques of account receivables:
Receivables turnover Average collection period Aging schedule
Collection matrix
Receivables turnover It provides relationship between credit sales and debtors of a firm. It indicates how quickly receivables or debtors are converted in to cash.Receivables turnover rate: credit sales/average debtor or receivables. Average collection period It is a significant measure of the collection activities of debtors.365/debtors or receivables turnover. Aging schedule It shows age wise grouping of debtors.It break down debtors according to the length of time for which they have been outstanding.
Collection matrix: It is a method of showing percentage of receivables collection during the month of sales. Factors influencing the receivables of management Volume of credit sales Trade credit Trade terms Seasonality of business Collection policy Bill discounting
Account receivable process:
The process of accounts receivable starts when products or services are provided to a customer on credit. The company that details the transaction including the total amount and duration of credit creates an invoice. The invoice is then recorded. If payment is on time the accounts receivable process ends there. However, often this is not the case. That's when the collection department takes over. First, the customer is afforded the opportunity to explain the delay. If there's a complaint regarding products or services, the matter is forwarded to the respective departments. Once the issue is resolved and payment is received the process is ended. Sometimes the process will end if the product is shown to be faulty or not up to the customer's expectations, at which point the debt may be expunged or reduced. This may or not be the case with your company or the company your represent. Some companies prefer to hire an accounts receivable outsourcing firm. These firms take over the process of collecting overdue payments in a professional manner. A certain amount of fee or commission is charged for successfully completing the process of collection. In some extreme instances, a customer goes bankrupt and simply can't pay in which case the debt is transferred to the bad debts account from accounts receivable. The bad debts account will stay on record, but the comany may or may not ever be able to collect on the debt. Some debts are lost causes, and those losses must be cut so that the system does not get bogged down.
5 STEPS OF RECEIVABLE MANAGEMENT RECOVERY:
As a small business owner, one of the most challenging tasks of owning a small business is COLLECTING on past due accounts.
STEP ONE The first step in the collection process is to send the debtor a past due INVOICE stating their account is 30 days past due and payment must be received within 14 days or their account maybe subject to further collection efforts. It is important to DOCUMENT each contact you make with the debtor, this will make your job easier down the line for more aggressive collection approaches.
STEP TWO After 14 days, contact the debtor by PHONE and kindly REMIND them of their outstanding debt, because in some cases they may have simply forgot about the bill and sometimes will pay in full or make partial payment. After making your phone call to the debtor, allow an additional 14 days for payment to be received before sending a letter of demand for payment.
STEP THREE A DEMAND for payment maybe needed after the debt is 60 days past due, include all documentation supporting the debt. Mail a letter, along with a copy of the past due invoice, and any other supporting documentation to the debtor. State in the letter that payment must be received within 10 days or the account will be turned over to a collection AGENCY.
STEP FOUR Collection agency services may be needed to collect debts beyond 60 days past due. It is important to start the collection process early. Do not wait until the account is 1-2 years past due, because as time passes the debt becomes increasingly DIFFICULT to collect and collection agencies typically charge higher fees for older accounts. The collection agency will then mail the client a validation, which is a letter that states the balance due and who the original creditor the debt is owed.
The debtor then has 30 days to dispute the debt, if after 30 days no dispute is received, the debt is assumed VALID and the collection process continues. If you decide to send an account to a collection agency, it is very important that you cease all communications with the debtor. Be sure to give the collection agency all the documentation available about the debtor as it will make the collection process easier with the more information you can provide.
STEP FIVE The final step in the collection process is utilized when all other collection attempts have failed and involves taking LEGAL action against the debtor to force payment of the debt. Typically, collection agencies use lawsuits as a last resort to collect past due balances. Most of the time collection agencies will work together with the debtor to arrange payment plans, however if the debtor does not contact the agency or does not maintain their payment plan, the end result is usually taking them to COURT and obtaining a judgment. A judgment allows the agency to utilize many remedies available to them to finally collect the debt and pay their clients.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Receivable & Payable Management PDFDocumento7 pagineReceivable & Payable Management PDFa0mittal7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Credit ManagementDocumento14 pagineCredit ManagementThe Cultural CommitteeNessuna valutazione finora
- Credit Risk Management in BanksDocumento34 pagineCredit Risk Management in BanksDhiraj K DalalNessuna valutazione finora
- Approach For Safety of Loans Follow Up and Monitoring Process Q3Documento6 pagineApproach For Safety of Loans Follow Up and Monitoring Process Q3maunilshahNessuna valutazione finora
- Approval, Disburshment and RecoveryDocumento6 pagineApproval, Disburshment and Recoveryakash_0000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Credit Management - IntroductionDocumento14 pagineStrategic Credit Management - IntroductionDr VIRUPAKSHA GOUD G50% (2)
- Factors For Rise in NpasDocumento10 pagineFactors For Rise in NpasRakesh KushwahNessuna valutazione finora
- Credit Risk Management - Reading Material For E Learning-FinalDocumento19 pagineCredit Risk Management - Reading Material For E Learning-FinalMatthew ButlerNessuna valutazione finora
- Audit of InsuranceDocumento26 pagineAudit of Insuranceashokkeeli100% (1)
- Credit Appraisal in MuthootDocumento30 pagineCredit Appraisal in MuthootNISHI1994100% (1)
- Deposit Policy: 3.1.1 Savings AccountDocumento15 pagineDeposit Policy: 3.1.1 Savings AccountKumar RockyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mse Lending PolicyDocumento10 pagineMse Lending PolicytanweerwarsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Factors, Impact, Symptoms of NPADocumento7 pagineFactors, Impact, Symptoms of NPAMahesh ChandankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Credit Management PartsDocumento5 pagineCredit Management Partsdarma bonarNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Control and Compliance Risk and To Compare The Existing Credit Policy of Dhaka Bank LimitedDocumento22 pagineInternal Control and Compliance Risk and To Compare The Existing Credit Policy of Dhaka Bank LimitedHafiz IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- BRPD Circular No 14 PDFDocumento16 pagineBRPD Circular No 14 PDFMuhammad Ali Jinnah100% (1)
- Loan Portfolio Managment JournalDocumento1 paginaLoan Portfolio Managment Journalwain synergyNessuna valutazione finora
- Credit PolicyDocumento4 pagineCredit PolicyArslan AshfaqNessuna valutazione finora
- GST Compliance in Statutory Bank Branch Audit: Ca. Vineet RathiDocumento46 pagineGST Compliance in Statutory Bank Branch Audit: Ca. Vineet Rathianon_127497276Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Management ProcessesDocumento9 pagineQuality Management Processesselinasimpson0701Nessuna valutazione finora
- Interest Rate Risk AuditDocumento4 pagineInterest Rate Risk AuditpascaruionNessuna valutazione finora
- Audit of BankDocumento23 pagineAudit of BankSai Naveen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Updated Loan Policy To Board 31.03.2012 Sent To Ro & ZoDocumento187 pagineUpdated Loan Policy To Board 31.03.2012 Sent To Ro & ZoAbhishek BoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Credit Appraisal of Term Loans by Financial Institutions Like BanksDocumento4 pagineCredit Appraisal of Term Loans by Financial Institutions Like BanksKunal GoldmedalistNessuna valutazione finora
- ML and TF in The Securities SectorDocumento86 pagineML and TF in The Securities SectorYan YanNessuna valutazione finora
- Importance of Post Sanction Follow Up NafcubDocumento48 pagineImportance of Post Sanction Follow Up NafcubKETANNessuna valutazione finora
- Maximize Efficiency How Automation Can Improve Your Loan Origination ProcessDocumento7 pagineMaximize Efficiency How Automation Can Improve Your Loan Origination ProcessShakil ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study On Credit Appraisal For Working Capital Finance To Smes at Ing Vysya BankDocumento22 pagineA Study On Credit Appraisal For Working Capital Finance To Smes at Ing Vysya Bankprincejac4u2478894Nessuna valutazione finora
- Presented By: 1. Pravin Gavali 2. Vickram Singh MIT-MBA (Finance)Documento24 paginePresented By: 1. Pravin Gavali 2. Vickram Singh MIT-MBA (Finance)shrikant_gaikwad100Nessuna valutazione finora
- Project Report of Lok Nath BhusalDocumento69 pagineProject Report of Lok Nath BhusalManoj Yadav100% (1)
- ICRRS Guidelines - BB - Version 2.0Documento25 pagineICRRS Guidelines - BB - Version 2.0Optimistic EyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Credit Managers. Lesson 3Documento40 pagineCredit Managers. Lesson 3Joseph PoNessuna valutazione finora
- General Principles of LendingDocumento3 pagineGeneral Principles of LendingSNessuna valutazione finora
- Credit Analysis: DR C SitharamayyaDocumento21 pagineCredit Analysis: DR C SitharamayyaVvs Ramaraju0% (1)
- TOPIC 3d - Audit PlanningDocumento29 pagineTOPIC 3d - Audit PlanningLANGITBIRUNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategies of Recovering Default LoansDocumento7 pagineStrategies of Recovering Default LoansMariam Adams100% (1)
- Comprehensive Deposit PolicyDocumento13 pagineComprehensive Deposit PolicyShakirkapraNessuna valutazione finora
- On Bank AuditDocumento101 pagineOn Bank Auditrinky123123100% (4)
- Research PaperDocumento14 pagineResearch PaperSoumya SaranjiNessuna valutazione finora
- Credit ManagementDocumento46 pagineCredit ManagementMohammed ShaffanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Audit Process - Final ReviewDocumento5 pagineThe Audit Process - Final ReviewFazlan Muallif ResnuliusNessuna valutazione finora
- Credit Procedures and ControlsDocumento5 pagineCredit Procedures and ControlsJR DevienteNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 1.11 Credit Policy Sample 02022016Documento13 pagine4 1.11 Credit Policy Sample 02022016o'brianNessuna valutazione finora
- WIP IA Manual - Audit Program - PayablesDocumento6 pagineWIP IA Manual - Audit Program - PayablesMuhammad Faris Ammar Bin ZainuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Credit Risk Grading-Apex TanneryDocumento21 pagineCredit Risk Grading-Apex TanneryAbdullahAlNomunNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Control On SalesDocumento3 pagineInternal Control On SalesGhuellene Velarde MagalonaNessuna valutazione finora
- PWC Publications Due DiligenceDocumento8 paginePWC Publications Due DiligencegranantoNessuna valutazione finora
- PgcIA - Scope, Process and Tools - ICAI Sep 05, 2014Documento56 paginePgcIA - Scope, Process and Tools - ICAI Sep 05, 2014Aayushi AroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Annual Internal Audit PlanDocumento8 pagineAnnual Internal Audit PlanMuri EmJayNessuna valutazione finora
- Credit Risk Management Using MLDocumento4 pagineCredit Risk Management Using MLZoran EreizNessuna valutazione finora
- Credit PolicyDocumento13 pagineCredit PolicyUDAYNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Audit C Hecklist ofDocumento27 pagineInternal Audit C Hecklist ofRUBELNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Policy and Procedures ManualDocumento18 pagineFinancial Policy and Procedures ManualAahna Mittal100% (1)
- Manual - Fixed AssetsDocumento48 pagineManual - Fixed AssetsIliIllilI IliIllilIIliIllilINessuna valutazione finora
- Credit Report On MCBDocumento16 pagineCredit Report On MCBuzmabhatti34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Taxguru - In-Checklist For Statutory Audit of Bank Branch Audit An OverviewDocumento8 pagineTaxguru - In-Checklist For Statutory Audit of Bank Branch Audit An OverviewBhavani GirineniNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 33 Credit+Analysis+-+Corporate+Credit+Analysis+ (Ratios)Documento33 pagineLecture 33 Credit+Analysis+-+Corporate+Credit+Analysis+ (Ratios)Taan100% (1)
- Revenue Assurance A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionDa EverandRevenue Assurance A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Risk Management A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa EverandDigital Risk Management A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Control Final o LevelDocumento18 pagineControl Final o Levelparwez_0505Nessuna valutazione finora
- O2C Cycle With Accounting EntriesDocumento3 pagineO2C Cycle With Accounting Entriessudharsan49100% (1)
- Oracle-Fusion-Financials Sample Resumes-3Documento6 pagineOracle-Fusion-Financials Sample Resumes-3pradeep191988Nessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Manual: (Updated Through November 11, 2013)Documento55 pagineSolution Manual: (Updated Through November 11, 2013)Jay BrockNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Receivables Oracle Cloud - 3 - FIMDocumento68 pagineTest Receivables Oracle Cloud - 3 - FIMMariana SalgadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz No. 2Documento5 pagineQuiz No. 2VernnNessuna valutazione finora
- ACCO 20063 Homework 4 Review of Accounting CycleDocumento3 pagineACCO 20063 Homework 4 Review of Accounting CycleVincent Luigil Alcera100% (1)
- Oracle Utilities Customer Care and Billing: Administration Guide 3 Release 2.3.1Documento352 pagineOracle Utilities Customer Care and Billing: Administration Guide 3 Release 2.3.1LakshmiNarayana PuttamchettyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12 Events After The Reporting Period PDFDocumento4 pagineChapter 12 Events After The Reporting Period PDFAthena LansangNessuna valutazione finora
- Resume DetailsDocumento40 pagineResume DetailsParvati BNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Statement Analysis: RatiosDocumento23 pagineFinancial Statement Analysis: RatiosHerraNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ 1Documento6 pagineMCQ 1Ankush NohriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11: Error Correction Cash/Accrual and Single EntryDocumento27 pagineChapter 11: Error Correction Cash/Accrual and Single EntryYoshidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Galatians 6: 9 "Let Us Not Become Weary in Doing Good, For at The Proper Time We Will Reap A Harvest If We Do Not Give Up."Documento5 pagineGalatians 6: 9 "Let Us Not Become Weary in Doing Good, For at The Proper Time We Will Reap A Harvest If We Do Not Give Up."Kei Tsukishima100% (2)
- Afm - Mod IiiDocumento21 pagineAfm - Mod IiiVaibhav BadgiNessuna valutazione finora
- Tax and Revenue ManagementDocumento24 pagineTax and Revenue ManagementDonald Chiwakira100% (1)
- Accounting What The Numbers Mean Marshall 10th Edition Solutions ManualDocumento30 pagineAccounting What The Numbers Mean Marshall 10th Edition Solutions ManualDrMartinSmithbxnd100% (34)
- Completing The Tests in The Sales and Collection Cycle: Accounts ReceivableDocumento35 pagineCompleting The Tests in The Sales and Collection Cycle: Accounts ReceivableTeddy HaryadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ratio Analysis. A) Liquidity Ratio - 1) Current Ratio Current Asset Current LiabilityDocumento6 pagineRatio Analysis. A) Liquidity Ratio - 1) Current Ratio Current Asset Current LiabilitysolomonNessuna valutazione finora
- Working Capital ManagementDocumento45 pagineWorking Capital ManagementssanjitkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.1 - AUDIT ON RECEIVABLES (Problems)Documento10 pagine5.1 - AUDIT ON RECEIVABLES (Problems)LorraineMartinNessuna valutazione finora
- Oracle EBSR12 Inventory Version 01Documento256 pagineOracle EBSR12 Inventory Version 01MosunmolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Analysis of Solvency, Liquidity, and Financial FlexibilityDocumento19 pagineChapter 2 Analysis of Solvency, Liquidity, and Financial FlexibilityYusuf Abdurrachman100% (1)
- Nuqui - Quiz On Special JournalsDocumento25 pagineNuqui - Quiz On Special JournalsJesther NuquiNessuna valutazione finora
- Source: CPA Review Schools: Cash, Receivables, Inventory, Biological Assets, PPEDocumento7 pagineSource: CPA Review Schools: Cash, Receivables, Inventory, Biological Assets, PPEasdfNessuna valutazione finora
- Kiem 2Documento86 pagineKiem 218071369 Nguyễn ThànhNessuna valutazione finora
- Tle NotesDocumento49 pagineTle NotesFerlynNessuna valutazione finora
- Auditing Problems v1 2018 CompressDocumento36 pagineAuditing Problems v1 2018 CompressMr. CopernicusNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 5 Audit Evidence 2015Documento101 pagineCH 5 Audit Evidence 2015simaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial PerakaunanDocumento5 pagineTutorial PerakaunanNureenKamalNessuna valutazione finora