Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Strategic Management (MGMT 2301) : The Cost Leadership Strategy
Caricato da
DusmahomedTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Strategic Management (MGMT 2301) : The Cost Leadership Strategy
Caricato da
DusmahomedCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Strategic Management (MGMT 2301) 2012
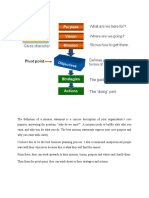
Generic strategies The Cost Leadership Strategy Porter's generic strategies are ways of gaining competitive advantage that gets you the sale and takes it away from your competitors. There are two main ways of achieving this within a Cost Leadership strategy: Increasing profits by reducing costs, while charging industry-average prices. Increasing market share through charging lower prices, while still making a reasonable profit on each sale because you've reduced costs. Cost Leadership is about minimizing the cost to the organization of delivering products and services. The Cost Leadership strategy is exactly that it involves being the leader in terms of cost in your industry or market. Simply being amongst the lowest-cost producers is not good enough, as you leave yourself wide open to attack by other low cost producers who may undercut your prices and therefore block your attempts to increase market share. You therefore need to be confident that you can achieve and maintain the number one position before choosing the Cost Leadership route. Companies that are successful in achieving Cost Leadership usually have: Access to the capital needed to invest in technology that will bring costs down. Very efficient logistics. A low cost base (labor, materials, facilities), and a way of sustainably cutting costs below those of other competitors. The greatest risk in pursuing a Cost Leadership strategy is that these sources of cost reduction are not unique to you, and that other competitors copy your cost reduction strategies. This is why it's important to continuously find ways of reducing every cost. One successful way of doing this is by adopting the Japanese Kaizenphilosophy of "continuous improvement".
1|Page
DUSMAHOMED Goolamally (DTM/11A/PT/110520)
Strategic Management (MGMT 2301) 2012
The Differentiation Strategy Differentiation involves making your products or services different from and more attractive those of your competitors. How you do this depends on the exact nature of your industry and of the products and services themselves, but will typically involve features, functionality, durability, support and also brand image that your customers value. To make a success of a Differentiation strategy, organizations need: Good research, development and innovation. The ability to deliver high-quality products or services. Effective sales and marketing, so that the market understands the benefits offered by the differentiated offerings. Large organizations pursuing a differentiation strategy need to stay agile with their new product development processes. Otherwise, they risk attack on several fronts by competitors pursuing Focus Differentiation strategies in different market segments. The Focus Strategy Companies that use Focus strategies concentrate on particular niche markets and, by understanding the dynamics of that market and the unique needs of customers within it, develop uniquely low cost or well-specified products for the market. Be cause they serve customers in their market uniquely well, they tend to build strong brand loyalty amongst their customers. This makes their particular market segment less attractive to competitors. As with broad market strategies, it is still essential to decide whether you will pursue Cost Leadership or Differentiation once you have selected a Focus strategy as your main approach: Focus is not normally enough on its own.
2|Page
DUSMAHOMED Goolamally (DTM/11A/PT/110520)
Strategic Management (MGMT 2301) 2012
But whether you use Cost Focus or Differentiation Focus, the key to making a success of a generic Focus strategy is to ensure that you are adding something extra as a result of serving only that market niche. It's simply not enough to focus on only one market segment because your organization is too small to serve a broader market (if you do, you risk competing against better-resourced broad market companies' offerings.) The "something extra" that you add can contribute to reducing costs (perhaps through your knowledge of specialist suppliers) or to increasing differentiation (though your deep understanding of customers' needs). Generic strategies apply to not-for-profit organizations too. A not-for-profit can use a Cost Leadership strategy to minimize the cost of getting donations and achieving more for their income, while one with pursing a Differentiation strategy will be committed to the very best outcomes, even if the volume of work they do as a result is lower. Local charities are great examples of organizations using Focus strategies to get donations and contribute to their communities. Boston consulting group matrix Boston Consulting Group Matrix is a four celled matrix developed by BCG, USA. It is the most renowned corporate portfolio analysis tool. It provides a graphic representation for an organization to examine different businesses in its portfolio on the basis of their related market share and industry growth rates. It is a comparative analysis of business potential and the evaluation of environment. BCG matrix has four cells, with the horizontal axis representing relative market share and the vertical axis denoting market growth rate. The four cells of this matrix have been called as stars, cash cows, question marks and dogs. Each of these cells represents a particular type of business.
3|Page
DUSMAHOMED Goolamally (DTM/11A/PT/110520)
Strategic Management (MGMT 2301) 2012
Stars represent business units having large market share in a fast growing industry. They may generate cash but because of fast growing market, stars require huge investments to maintain their lead. Net cash flow is usually modest. SBUs located in this cell are attractive as they are located in a robust industry and these business units are highly competitive in the industry. If successful, a star will become a cash cow when the industry matures.
4|Page
DUSMAHOMED Goolamally (DTM/11A/PT/110520)
Strategic Management (MGMT 2301) 2012
Cash Cows represent business units having a large market share in a mature, slow growing industry. Cash cows require little investment and generate cash that can be utilized for investment in other business units. These SBUs are the corporations key source of cash, and are specifically the core business. They are the base of an organization. These businesses usually follow stability strategies. When cash cows lose their appeal and move towards deterioration, then a retrenchment policy may be pursued. Question marks represent business units having low relative market share and located in a high growth industry. They require huge amount of cash to maintain or gain market share. They require attention to determine if the venture can be viable. Question marks are generally new goods and services which have a good commercial prospective. There is no specific strategy which can be adopted. If the firm thinks it has dominant market share, then it can adopt expansion strategy, else retrenchment strategy can be adopted. Most businesses start as question marks as the company tries to enter a high growth market in which there is already a market-share. If ignored, then question marks may become dogs, while if huge investment is made, and then they have potential of becoming stars. Dogs represent businesses having weak market shares in low-growth markets. They neither generate cash nor require huge amount of cash. Due to low market share, these business units face cost disadvantages. Generally retrenchment strategies are adopted because these firms can gain market share only at the expense of competitors/rival firms. These business firms have weak market share because of high costs, poor quality, ineffective marketing, etc. Unless a dog has some other strategic aim, it should be liquidated if there is fewer prospects for it to gain market share. Number of dogs should be avoided and minimized in an organization.
5|Page
DUSMAHOMED Goolamally (DTM/11A/PT/110520)
Strategic Management (MGMT 2301) 2012
When should I use the BCG matrix model? Each product has its product life cycle, and each stage in product's life-cycle represents a different profile of risk and return. In general, a company should maintain a balanced portfolio of products. Having a balanced product portfolio includes both high-growth products as well as low-growth products. A high-growth product is for example a new one that we are trying to get to some market. It takes some effort and resources to market it, to build distribution channels, and to build sales infrastructure, but it is a product that is expected to bring the gold in the future. An example of this product would be an iPod. A low-growth product is for example an established product known by the market. Characteristics of this product do not change much, customers know what they are getting, and the price does not change much either. This product has only limited budget for marketing. The is the milking cow that brings in the constant flow of cash. An example of this product would be regular Colgate toothpaste. But the question is, how do we exactly find out what phase our product is in, and how do we classify what we sell? Furthermore, we also ask, where does each of our products fit into our product mix? Should we promote one product more than the other one? The BCG matrix can help with this. The BCG matrix reaches further behind product mix. Knowing what we are selling helps managers to make decisions about what priorities to assign to not only products but also company departments and business units.
6|Page
DUSMAHOMED Goolamally (DTM/11A/PT/110520)
Strategic Management (MGMT 2301) 2012
Limitations of BCG Matrix The BCG Matrix produces a framework for allocating resources among different business units and makes it possible to compare many business units at a glance. But BCG Matrix is not free from limitations, such as BCG matrix classifies businesses as low and high, but generally businesses can be medium also. Thus, the true nature of business may not be reflected. Market is not clearly defined in this model. High market share does not always leads to high profits. There are high costs also involved with high market share. Growth rate and relative market share are not the only indicators of profitability. This model ignores and overlooks other indicators of profitability. At times, dogs may help other businesses in gaining competitive advantage. They can earn even more than cash cows sometimes. This four-celled approach is considered as to be too simplistic. Are there any problems with the BCG matrix model? Some limitations of the BCG matrix model include: The first problem can be how we define market and how we get data about market share A high market share does not necessarily lead to profitability at all times The model employs only two dimensions market share and product or service growth rate Low share or niche businesses can be profitable too (some Dogs can be more profitable than cash Cows) The model does not reflect growth rates of the overall market The model neglects the effects of synergy between business units Market growth is not the only indicator for attractiveness of a market There are probably even more aspects that need to be considered in a particular use of the BCG model.
7|Page DUSMAHOMED Goolamally (DTM/11A/PT/110520)
Strategic Management (MGMT 2301) 2012
8|Page
DUSMAHOMED Goolamally (DTM/11A/PT/110520)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- PDF Document PDFDocumento6 paginePDF Document PDFIrine Afroza AurpaNessuna valutazione finora
- Porter's Generic Strategies ExplainedDocumento11 paginePorter's Generic Strategies ExplainedmeghaNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Management FinalDocumento9 pagineStrategic Management FinalGovind SuroliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Porters Generic StrategiesDocumento6 paginePorters Generic Strategiessaransh maheshwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Home Sample Plans Guidelines Web Resources Software Tools ConsultantsDocumento24 pagineHome Sample Plans Guidelines Web Resources Software Tools ConsultantsPrateek KhandelwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Market Plan Guidelines for BusinessDocumento9 pagineMarket Plan Guidelines for BusinessWawa YusofNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing PlanDocumento10 pagineMarketing PlanDibya MahakudNessuna valutazione finora
- Bahria University Islamabad - Generic Strategies ExplainedDocumento8 pagineBahria University Islamabad - Generic Strategies ExplainedjaveriaNessuna valutazione finora
- SM AssignmentDocumento10 pagineSM AssignmentvaibhavNessuna valutazione finora
- GE NINE-CELL PLANNING GRID AS A GRAND STRATEGY TOOLDocumento3 pagineGE NINE-CELL PLANNING GRID AS A GRAND STRATEGY TOOLRenge Geevarghese100% (1)
- Strategic Management December 2021 ExaminationDocumento10 pagineStrategic Management December 2021 ExaminationSaquib ShaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- MDI GDPI Prep - StrategyDocumento10 pagineMDI GDPI Prep - StrategyDevavrat SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT-4-Choice of Business Strategies: Understanding The ToolDocumento12 pagineUNIT-4-Choice of Business Strategies: Understanding The ToolNishath NawazNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Management STDocumento11 pagineStrategic Management STGovind SuroliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment No. 01 Autumn, 2016: Marketing Management (8511) MBA / M. ComDocumento13 pagineAssignment No. 01 Autumn, 2016: Marketing Management (8511) MBA / M. ComDanyal ChaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Master of Business Administration MBA Semester-4: Clearanc Certificate Number: 0013Documento45 pagineMaster of Business Administration MBA Semester-4: Clearanc Certificate Number: 0013Apu MajumdarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 BCG MatrixDocumento5 pagineChapter 7 BCG Matriximranpathan30Nessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Plan: PranamDocumento9 pagineMarketing Plan: PranamSonia RainaNessuna valutazione finora
- Porter's 3 Generic StrategiesDocumento4 paginePorter's 3 Generic StrategiesDave DeNessuna valutazione finora
- Corporate Growth StrategiesDocumento13 pagineCorporate Growth StrategiesClarisse jane ojo0% (1)
- Assignment - Strategic Management: Answer No. 1)Documento8 pagineAssignment - Strategic Management: Answer No. 1)harshit singhalNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Management CH 8Documento26 pagineStrategic Management CH 8karim kobeissiNessuna valutazione finora
- SBL SwotDocumento7 pagineSBL SwotDr Kennedy Amadi.PhD100% (1)
- Porter's Generic StrategiesDocumento3 paginePorter's Generic StrategiesAhmed ElGeoshyNessuna valutazione finora
- SMU MBA 4th Sem Information Systems Management AssignmentsDocumento3 pagineSMU MBA 4th Sem Information Systems Management AssignmentsPooja Upreti PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- SM Ques Module 2Documento7 pagineSM Ques Module 2Akash ReghuNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: Saptarshi Das Mba - 4 Semester Reg. No. 511010222Documento16 pagineName: Saptarshi Das Mba - 4 Semester Reg. No. 511010222Nayan DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Bahria University IslamabadDocumento12 pagineBahria University IslamabadjaveriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategy ManagementDocumento6 pagineStrategy ManagementSadhan PadhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Business StrategyDocumento13 pagineBusiness StrategyMAx100% (1)
- Porter's Generic Strategies and How Firms Position Themselves for Competitive AdvantageDocumento4 paginePorter's Generic Strategies and How Firms Position Themselves for Competitive AdvantageromirathiNessuna valutazione finora
- MB0052Documento34 pagineMB0052Prateek TutejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tugas Mgt. Stratejik EnglishDocumento3 pagineTugas Mgt. Stratejik EnglishGilang PerdanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Types SM StategyDocumento6 pagineTypes SM StategykhazhafazzNessuna valutazione finora
- Diversification & Porters Generic StategiesDocumento11 pagineDiversification & Porters Generic StategiesvaryushNessuna valutazione finora
- AnsoffDocumento18 pagineAnsoffVinay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Figure 1 - Porter's Five ForcesDocumento12 pagineFigure 1 - Porter's Five ForcesHarshad AroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Porter's Generic StrategiesDocumento4 paginePorter's Generic StrategiesAshish PereNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Analysis Tools and TechniquesDocumento10 pagineStrategic Analysis Tools and TechniquesANKUR CHOUDHARYNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3Documento20 pagineChapter 3Varun BNessuna valutazione finora
- Group Assigement 1Documento4 pagineGroup Assigement 1Ibrahim MagemesoNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 6 Business StrategyDocumento5 pagineCH 6 Business StrategyfirasNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam SMDocumento19 pagineExam SMhtet sanNessuna valutazione finora
- Porter's Generic Strategies ExplainedDocumento27 paginePorter's Generic Strategies ExplainedSAURABH DWIVEDI 22DM242Nessuna valutazione finora
- Porter's Generic Strategies and PESTLE Analysis for Entering Indian MarketDocumento9 paginePorter's Generic Strategies and PESTLE Analysis for Entering Indian MarketSadhan PadhiNessuna valutazione finora
- How Businesses Can Develop a Competitive StrategyDocumento7 pagineHow Businesses Can Develop a Competitive StrategyFevilynNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Level StrategiesDocumento2 pagineBusiness Level StrategiesAyushi SajwanNessuna valutazione finora
- What is Corporate Strategy and How is it ManagedDocumento34 pagineWhat is Corporate Strategy and How is it ManagedDecalcomani EnthusiastNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Midterm NoteDocumento48 pagineMarketing Midterm NoteChanikarnNessuna valutazione finora
- BUSINESS Level StrategiesDocumento5 pagineBUSINESS Level StrategiesOrkhan KhalafovNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic DecisionDocumento3 pagineStrategic Decisionshin maNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Management Matrix ComparisonDocumento26 pagineStrategic Management Matrix ComparisonMariappan RamaiahNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Apply The PorterDocumento4 pagineHow To Apply The Portertanuias2009Nessuna valutazione finora
- Porter - Generic StrategiesDocumento3 paginePorter - Generic StrategiesAnushka JagtapNessuna valutazione finora
- Jani SirDocumento21 pagineJani SirRishi MurarkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Master of Business Administration-MBA Semester IV MB0052 - Strategic Management and Business Policy Assignment Set-1Documento25 pagineMaster of Business Administration-MBA Semester IV MB0052 - Strategic Management and Business Policy Assignment Set-1Darshit ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Role of Strategic Management in Marketing 1Documento4 pagineRole of Strategic Management in Marketing 1arnica_id80% (5)
- Porter's Generic Strategies ExplainedDocumento5 paginePorter's Generic Strategies ExplainedbiswasjoyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Profit Zone (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Morrison's Book)Da EverandThe Profit Zone (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Morrison's Book)Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Ultimate Business Competition Guide : Reverse Engineer The Competition And Make 'em Eat Your Dust!Da EverandThe Ultimate Business Competition Guide : Reverse Engineer The Competition And Make 'em Eat Your Dust!Nessuna valutazione finora
- The 100 Most Influential World Leaders of All TimeDocumento383 pagineThe 100 Most Influential World Leaders of All TimeLiviu Orlescu100% (1)
- Quality ManualDocumento105 pagineQuality ManualSambit NayakNessuna valutazione finora
- Case StudyDocumento1 paginaCase StudyDusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment: This Section Constitutes The Main Body of The ReportDocumento2 pagineAssignment: This Section Constitutes The Main Body of The ReportDusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- Japanese InnovationDocumento2 pagineJapanese InnovationDusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- InnovationDocumento62 pagineInnovationDusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning and CreativityDocumento62 pagineLearning and CreativityDusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- Japanese InnovationDocumento2 pagineJapanese InnovationDusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- Empowerment of Service QualityDocumento2 pagineEmpowerment of Service QualityDusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- Main Obstacle To Service Quality ImprovementDocumento4 pagineMain Obstacle To Service Quality ImprovementDusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- Dissertation TemplateDocumento7 pagineDissertation TemplateDusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- Factors Required For Attainment of Service Quality.Documento2 pagineFactors Required For Attainment of Service Quality.DusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- Code of Corporate Governance-April 2004Documento144 pagineCode of Corporate Governance-April 2004DusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- Dissertation TemplateDocumento7 pagineDissertation TemplateDusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 C's of TQM.Documento2 pagine06 C's of TQM.DusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Key Elements in Implementing TQM. (No Description)Documento3 pagine5 Key Elements in Implementing TQM. (No Description)DusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- Getting Chatty: Conversation at The Virtual Reference DeskDocumento5 pagineGetting Chatty: Conversation at The Virtual Reference DeskDusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- Free Punch LessonDocumento16 pagineFree Punch LessonDusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic ManagementDocumento2 pagineStrategic ManagementDusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- Lean Six SigmaDocumento2 pagineLean Six SigmaCasey McFarlaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Teamwork and Team LeadershipDocumento5 pagineTeamwork and Team LeadershipDusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Sigma DiagramDocumento1 pagina6 Sigma Diagrammohamed ezz eldeen100% (1)
- 6 Sigma DiagramDocumento1 pagina6 Sigma Diagrammohamed ezz eldeen100% (1)
- Determinance of Service QualityDocumento3 pagineDeterminance of Service QualityDusmahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- Seduciones de AmorDocumento32 pagineSeduciones de AmorsalmoprNessuna valutazione finora
- 1b Evolution MGT TheoryDocumento22 pagine1b Evolution MGT TheoryDheeraj100% (1)
- WK03 - UT01 - Post Assignment PDFDocumento3 pagineWK03 - UT01 - Post Assignment PDFAkshay GiteNessuna valutazione finora
- COMELEC Ruling on Jalosjos ResidencyDocumento9 pagineCOMELEC Ruling on Jalosjos ResidencyHannah MedNessuna valutazione finora
- Ipc2022-86892 Pig Sweep Nanoparticles Transform PipelineDocumento5 pagineIpc2022-86892 Pig Sweep Nanoparticles Transform PipelineOswaldo MontenegroNessuna valutazione finora
- BSBSTR601 Project PortfolioDocumento20 pagineBSBSTR601 Project PortfolioJojoNessuna valutazione finora
- 10bioavailability AbsorptionDocumento67 pagine10bioavailability AbsorptionNikki ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Notes For NISM Series V - A: Mutual Fund Distributors Exam (Earlier - AMFI Exam)Documento38 pagineStudy Notes For NISM Series V - A: Mutual Fund Distributors Exam (Earlier - AMFI Exam)Dixith GandheNessuna valutazione finora
- Viscosity - CatalogDocumento5 pagineViscosity - Catalogdéborah_rosalesNessuna valutazione finora
- America and The Federal ReserveDocumento32 pagineAmerica and The Federal ReserveTony Sanchez100% (1)
- Silo Manufacturing CorporationDocumento22 pagineSilo Manufacturing CorporationCee Phanthira100% (1)
- Three Dimensions of ChangeDocumento6 pagineThree Dimensions of ChangeMarcelo ManucciNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 7 Quiz AnswersDocumento6 pagineSection 7 Quiz Answersdaemon29Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ilac G24Documento17 pagineIlac G24waqarNessuna valutazione finora
- OB2301W On BrightElectronicsDocumento11 pagineOB2301W On BrightElectronicsIlago BenignoNessuna valutazione finora
- Protection of Fashion Design A Comparative Case Study Between Intellectual Property Code (Code de La Propriété IntDocumento12 pagineProtection of Fashion Design A Comparative Case Study Between Intellectual Property Code (Code de La Propriété IntGlobal Research and Development ServicesNessuna valutazione finora
- Environment Education Year PlanDocumento4 pagineEnvironment Education Year PlanJai GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ontario Standard Lease 2021Documento1 paginaOntario Standard Lease 2021exohguilianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ipcrf 3-4Documento12 pagineIpcrf 3-4adrienn earl NarzabalNessuna valutazione finora
- RSM Tax Card 2022Documento18 pagineRSM Tax Card 2022Bilal BashirNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Make Money Off CrackingDocumento13 pagineHow To Make Money Off CrackingFlávio Santos100% (2)
- IT1802 Word AutoCorrect, Comments, Track Changes & CollaborationDocumento1 paginaIT1802 Word AutoCorrect, Comments, Track Changes & CollaborationRonibeMalinginNessuna valutazione finora
- Asme Ii Sfa 5. 20Documento32 pagineAsme Ii Sfa 5. 20yogliolivaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Operator'S Manual: NidekDocumento114 pagineOperator'S Manual: NidekdvfaNessuna valutazione finora
- People vs. Romualdez G.R. NO. 166510 - April 29, 2004Documento2 paginePeople vs. Romualdez G.R. NO. 166510 - April 29, 2004MC100% (2)
- Importance of Statistics in Different FieldsDocumento2 pagineImportance of Statistics in Different FieldsAshley Causy100% (2)
- DI CFS FSI Outlook-BankingDocumento70 pagineDI CFS FSI Outlook-Bankinghuizhi guoNessuna valutazione finora
- Dicks Sporting GoodsDocumento6 pagineDicks Sporting GoodsAnonymous 57oCRhtNessuna valutazione finora
- TM 9 759 Tank Medium M4a3 9 15 1944Documento477 pagineTM 9 759 Tank Medium M4a3 9 15 1944Wiesshund100% (1)
- Surge Protection of Distribution EquipmentDocumento3 pagineSurge Protection of Distribution EquipmentjdeloyolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification and Composition of Fruits and VegetablesDocumento27 pagineClassification and Composition of Fruits and VegetablesLau Yu BinNessuna valutazione finora
- ISCEA Flyer 2023 - (NEW)Documento17 pagineISCEA Flyer 2023 - (NEW)arubinaldoNessuna valutazione finora