Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Reference STG Fu 2007
Caricato da
Shee YingTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Reference STG Fu 2007
Caricato da
Shee YingCopyright:
Formati disponibili
201 references referring to the Games teaching approaches inspired by the TGfU idea
List compiled by Tim Hopper and Richard Light. 8/14/2007 Alexander, K., & Penney, D. (2005). Teaching under the influence: Feeding games for understanding into the sport education development-refinement cycle. Physical Education & Sport Pedagogy, 10(3), 287 - 301. Alexander-Hall, J. (1986). Please start the lesson with a game. Hockey Field, 74(2), 7273. Alison, S., & Thorpe, R. (1997). A comparison of the effectiveness of two approaches to teaching games within physical education. A skills approach versus a games for understanding approach. The British Journal of Physical Education, 28(3), 9-13. Almond, L. (1986a). Asking teachers to research. In R. Thorpe, D. Bunker & L. Almond (Eds.), Rethinking games teaching (pp. 35-44). Loughborough: University of Loughborough, Nene Litho. Almond, L. (1986b). Games making. In R. Thorpe, D. Bunker & L. Almond (Eds.), Rethinking games teaching (pp. 67-70). Loughborough: University of Technology, Loughborough. Almond, L. (1986c). Primary and secondary rules. In R. Thorpe, D. Bunker & L. Almond (Eds.), Rethinking games teaching (pp. 73-74). Loughborough: University of Technology, Loughborough. Almond, L. (1986d). Reflecting on themes: A games classification. In R. Thorpe, D. Bunker & L. Almond (Eds.), Rethinking games teaching (pp. 71-73). Loughborough: University of Loughborough. Armstrong, S. (1988). Games for understanding -- breaking new ground. Bulletin of Physical Education, 24(3), 28-32. Asquith, A. (1989). Teaching games for understanding. In A. Williams (Ed.), Issues in physical education for the primary years (pp. 76-90). London: The Falmer Press. Atack, M. (1985). There has to be a better way. Bulletin of Physical Education, 21(2), 4144. Australia and the USA. R. Light (Ed) An international perspective on Teaching Barrett, K., & Turner, A. (2000). Sandy's challenge: New game, new paradigm <a correspondence>. Journal of teaching in physical education, 19, 162-181. Bean, D. (1990). A fresh look at games teaching: Making games more appropriate for the learner. RUNNER, 28(1), 20-23. Bean, D. (1991). A fresh look at games teaching. RUNNER, 29(4), 19-23. Bean, D. (1992a). Improve your outdoor games teaching by using a grid. RUNNER, 30(3), 25-27. Bean, D. (1992b). Without the game, what's the point? RUNNER, 30(2), 25-26. Belka, D. (1994). Teaching children games. Oxford, Ohio: Human Kinetics. Bell, R., & Hopper, T. (1999a). A 't.A.C.T.I.C' approach to teaching territory games. Wolfville, Nova Scotia: CAHPER '99 national conference.
Bell, R., & Hopper, T. (2003). Space the first frontier: Tactical awareness in teaching games for understanding. Physical and Health Education Journal, 69(1), 4-7. Bell, R., & Hopper, T. F. (1999b). Let's get the play back into the game. Wolfville, Nova Scotia: CAHPER '99 national conference. Berkowitz, R. (1996). A practitioner's journey: From skill to tactics. JOPERD, 67(4), 4145. Blomqvist, M., Luhtanen, P., Laakso, L., & Keskinen, E. (2000). Validation of a videobased game-understanding test procedure in badminton. Journal of Teaching Elementary Physical Education, 19(3), 325-337. Booth, K. (1986). An introduction to netball - an alternative approach. In R. Thorpe, D. Bunker & L. Almond (Eds.), Rethinking games teaching (pp. 27-31). Loughborough: University of Technology, Loughborough. Brooker, R., Kirk, D., Braiuka, S., & Bransgrove, A. (2000). Implementing a game sense approach to teaching junior high school basketball in a naturalistic setting. European Physical Education Review, 6(1), 7-26. Brown, S., & Hopper, T. (2006). Should all students in pe get an 'a'? Game performance assessment by peers as a critical component of student learning. The PHE, 72(1), 1421. Brunton, J. A. (2003). Changing hierarchies of power in physical education using sport education. European Physical Education Review, 9(3), 267-284. Buck, M., & Harrison, J. (1990a). An analysis of game play in volleyball. Journal of Teaching in Physical Education, 10, 38-48. Buck, M., & Harrison, J. (1990b). Improving student achievement in physical education. JOPERD, 62(7), 40-44. Bunker, B., & Thorpe, R. (1986a). The curriculum model. In R. Thorpe, Bunker, D., & Almond, L (Ed.), Rethinking games teaching (pp. 7-10). Loughborough: University of Technology, Loughborough. Bunker, D. (1983). Taking an understanding approach to the teaching of cricket: An example of a fielding game. Bulletin of PE, 19(1), 20-26. Bunker, D., & Thorpe, R. (1986b). From theory to practice. In R. Thorpe, D. Bunker & L. Almond (Eds.), Rethinking games teaching (pp. 11-14). Loughborough: University of Technology, Loughborough. Bunker, D., & Thorpe, R. (1986c). Is there a need to reflect? In R. Thorpe, D. Bunker & L. Almond (Eds.), Rethinking games teaching (pp. 25-34). Loughborough: University of Technology, Loughborough. Burrows, L., & Abbey, W. (1986). A teacher's reactions. In R. Thorpe, D. Bunker & L. Almond (Eds.), Rethinking games teaching (pp. 45-51). Loughborough: University of Technology, Loughborough. Butler, J. (1996a). Teacher responses to teaching games for understanding. JOPERD, 67(9), 17-20. Butler, J. (1997). How would socrates teach games? A constructivist approach. JOPERD, 68(9), 42-47. Butler, J. (2003). Starting a majors' club. JOPERD: The Journal of Physical Education, Recreation & Dance, 74(3), 33. Butler, J. I. (1996b). Teacher responses to teaching games for understanding. JOPERD: The Journal of Physical Education, Recreation & Dance, 67(9), 17.
Butler, J., & McCahan, J. (2005). Teaching games for understanding as a curriculum model. In L. Griffin & J. Butler (Eds.), Teaching games for understanding: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 33-54). Windsor: Human Kinetics. Butler, J., Griffin, L., Lombardo, B., & Nastasi, R. (Eds.). (2003). Teaching games for understanding in physical education and sport. Reston: NASPE an Assocuation of AAHPERD. Capel, S. (1991). Teaching games as interactive activities. International Journal of Physical Education, 27(2), 6-9. Casbon, C. (1991). The place of games in the physical education of children. British Journal of Physical Education, 22(1), 7-10. Chandler, T. (1996a). Reflections and further questions. JOPERD, 67(4), 49-51. Chandler, T. (1996b). Teaching games for understanding: Reflections and further questions. JOPERD, 67(4), 49-51. Chandler, T., & Mitchell, S. (1990). Reflections on "models of games education". JOPERD, 61(6), 19-21. Coakley, J. (1986). What coaches can learn from children. RUNNER, 24(4), 16-19. Collier, C. (2005). Integrating tactical games and sport education models. In L. Griffin & J. Butler (Eds.), Teaching games for understanding: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 137-148). Windsor: Human Kinetics. Collier, C., & LaVine, M. (2003). Potential of net/wall games in elementary physical education. Journal of Teaching Elementary Physical Education, 14(2), 28-30. CSC. (2005). Canadian sport for life: Through long-term athlete development. Curtner-Smith, M. (1996). Using games invention with elementary children. JOPERD, 67(3), 33-37. Dollman, J., Boshoff, K., & Dodd, G. (2006). The relationship between curriculum time for physical education and literacy and numeracy standards in south australian primary schools. European Physical Education Review, 12(2), 151-163. Doolittle, S. (1986). Reflecting on an innovation. In R. Thorpe, D. Bunker & L. Almond (Eds.), Rethinking games teaching (pp. 53-55). Loughborough: University of Technology, Loughborough. Doolittle, S. (1995). Teaching net games to low skilled students: A teaching for understanding approach. JOPERD, 66(3), 18-23. Doolittle, S., & Girard, K. (1991). A dynamic approach to teaching games in elementary pe. JOPERD, 62(4), 57-62. Dyson, B. (2005). Integrating cooperative learning and tactical games models: Focusing on social interactions and decision making. In L. Griffin & J. Butler (Eds.), Teaching games for understanding: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 1-18). Windsor: Human Kinetics. Dyson, B., Griffin, L., & Hastie, P. (2004). Sport education, tactical games and cooperative learning: Theoretical and pedagogical considerations. QUEST, 56, 226240. Earl, L. (2003). Assessment as learning. Californa: Corwin Press. Ellis, M. (1983). Similarities and differences in games: A system for classification: Paper presented at the AIESEP conference, Rome, Italy. Ellis, M. (1985). Decision-making: The key to success in games. RUNNER, XXIII(3), 24-28.
Ellis, M. (1986). Making and shaping games. In Rethinking games teaching (pp. 61-65). Loughborough: University of Technology, Loughborough. Evans, J. (2004). Making a difference? Education and abilityi in physical education. European Physical Education Review, 10(1), 95-108. French, K., & Thomas, J. (1987). The relation of knowledge development to children's basketball performance. Journal of sport psychology, 9, 15-32. Gallahue, D. L. (1996). Developmental physical education for today's children (3rd ed.). Madison: Brown & Benchmark. Games for Understanding. Physical Education and Sport Pedagogy, 10(3), 241Gee, J. (2003). What video games have to teach us about learning and literacy. New York: Palgrave. Grehaigne, J., Godbout, P., & Bouthier, D. (1999). The foundations of tactics and strategy in team sports. Journal of Teaching in Physical Education, 18, 159-174. Grehaigne, J., Richard, J.-F., & Griffin, L. (2005a). Research and development: Working toward evidence-based practice. In J. Grehaigne, J.-F. Richard & L. Griffin (Eds.), (pp. 155-164). New York: RoutledgeFalmer. Grehaigne, J., Richard, J.-F., & Griffin, L. (2005b). Teaching and learning team sports and games. New York: RoutledgeFalmer. Grehaigne, J., Richard, J.-F., & Griffin, L. (2005c). Underlying theories in the teachinglearning process of games and sports. In J. Grehaigne, J.-F. Richard & L. Griffin (Eds.), (pp. 103-122). New York: RoutledgeFalmer. Griffin, L. (1996). Improving net/wall game performance. JOPERD, 67(2), 34-38. Griffin, L. L., & Placek, J. H. (2001). The understanding and development of learners' domain-specific knowledge. Journal of Teaching in Physical Education, 20(4), 1. Griffin, L. L., Brooker, R., & Patton, K. (2005). Working towards legitimacy: Two decades of teaching games for understanding. Physical Education & Sport Pedagogy, 10(3), 213 - 223. Griffin, L., & Butler, J. (Eds.). (2005). Teaching games for understanding: Theory, research, and practice. Windsor: Human Kinetics. Griffin, L., & Patton, K. (2005). Two decades of teaching games for understanding: Looking at the past, present, and future. In L. Griffin & J. Butler (Eds.), Teaching games for understanding: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 1-18). Windsor: Human Kinetics. Griffin, L., & Richard, J. (2003). Using authentic assessment to improve students' net/wall game play. Journal of Teaching Elementary Physical Education, 14(2), 2327. Griffin, L., Dodds, P., & Rovengo, I. (1996). Peagogical content knowledge for teachers: Integrate everything you know to help students learn. JOPERD, 67(9), 58-61. Griffin, L., Mitchell, S. A., & Oslin, J. L. (1997). Teaching sport concepts and skills: A tactical games approach. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics. Griffin, L., Oslin, J., & Mitchell, S. (1995). An analysis of two instructional approaches to teaching net games. Paper presented at the AAHPERD National Convention, Portland, Oregon. Gubacs-Collins, K. (2007). Implementing a tactical approach through action research. Physical Education & Sport Pedagogy, 12(2), 105 - 126.
Haslam, I. (1989). A movement approach to the variability of practice hypothesis. International Journal of Physical Eduation, 25(1), 13-16. Hastie, P. A., & Curtner-Smith, M. D. (2006). Influence of a hybrid sport education—teaching games for understanding unit on one teacher and his students. Physical Education & Sport Pedagogy, 11(1), 1 - 27. Holt, J. E., Ward, P., & Wallhead, T. L. (2006). The transfer of learning from play practices to game play in young adult soccer players. Physical Education & Sport Pedagogy, 11(2), 101 - 118. Holt, N., Strean, B., & Garcia Bengoechea, E. (2002). Expanding the teaching games for understanding model: New avenues for future research and practice. Journal of Teaching in Physical Education, 21(2), 162-167. Hopper, T. (1990). Practical assessment in physical education. The Bulletin of Physical Education, 26(1), 23-34. Hopper, T. (1994). Can we play the game? RUNNER, 32(2), 21-22. Hopper, T. (1998). Teaching games for understanding using progressive principles of play. CAHPERD, 27(1), 1-5. Hopper, T. (2002). Teaching games for understanding: The importance of student emphasis over content emphasis. JOPERD, 73(7), 44-48. Hopper, T. (2003). Four r's for tactical awareness: Applying game performance assessment in net/wall games. Journal of Teaching Elementary Physical Education, 4(2), 16-21. Hopper, T. (2005, December 14-17). Learning to read - learning to play: An assessment process to teach the interdependance of skill performance and tactical understanding (abstract). Paper presented at the The III teaching games for understanding international conference, Hong Kong. Hopper, T. (2007). Teaching tennis with assessment for/as learning: A net/wall example in tgfu. The PHE, (In Press). Hopper, T., & Bell, F. (2001a). Can we play the game again? STRATEGIES, 15(1). Hopper, T., & Bell, R. (1999). A 't.A.C.T.I.C' approach to teaching net/wall games. Wolfville, Nova Scotia: CAHPER '99 national conference. Hopper, T., & Bell, R. (2000). Lets put the play back into the game: Net/wall games. Geneva Park, Ontario: CAHPERD/OPHEA national conference. Hopper, T., & Bell, R. (2001b). A tactical framework for teaching games: Teaching strategic understanding and tactical awareness. Physical and Health Education Journal, 29(4), 14-19. Hopper, T., Wiley, B., K, W., Myles, J., & Marinucci, C. (2006, February 14, 2006). Learning to read, learning to play: Insights on tgfu from games units taught in local schools. Paper presented at the 3rd annual Greater Victoria Physical Education association conference, Spectrum High School, Victoria, BC. Howarth, K. (2005). Introducing the teaching games for understanding model in teacher education programs. In L. Griffin & J. Butler (Eds.), Teaching games for understanding: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 91-106). Windsor: Human Kinetics. Jackson, S. (1982). Teaching for understanding in invasion games. BAALPE, 18(1), 2728.
Jackson, S. (1986). Teaching for understanding in games - a working curriculum 11-16. Bulletin of Physical Education, 22(2), 27-30. Jones, C., & Farrow, D. (1999). The transfer of strategic knowledge: A test of the games classifcation curriculum model. Bulletin of Physical Education(9), 41-45. Jones, D. (1982). Teaching for understanding in tennis. Bulletin of Physical Education, 18, 29-31. Kidman, L. (2001). Developing decision makers: An empowerment approach to coaching. Christchurch, NZ: Innovative Print Communications. Kirk, D. (1982). Theoretical guidelines for 'teaching for understanding'. BAALPE, 18(1), 41-45. Kirk, D. (2005a). Future prospects for teaching games for understanding. In L. Griffin & J. Butler (Eds.), Teaching games for understanding: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 213-227). Windsor: Human Kinetics. Kirk, D. (2005b). Physical education, youth sport and lifelong participation: The importance of early learning experiences. European Physical Education Review, 11(3), 239-255. Kirk, D., & Gorely, T. (2000). Challenging thinking about the relationship between school physical education and sport performance. European Physical Education Review, 6(2), 119-134. Kirk, D., & Macdonald, D. (1998). Situating learning in physical education. Journal of Teaching in Physical Education(17), 376-387. Kirk, D., & MacPhail, A. (2002). Teaching games for understanding and situated learning: Rethinking the bunker-thorpe model. Journal of Teaching Physical Education, 21(2), 177-193. Kirk, D., Brooker, R., & Braiuka, S. (2000, April 24-28). Teaching games for understanding: A situated perspective on student learning. Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New Orleans, LA. knowledge, and game play. Research Quarterly Exercise Science, 70(3), 286-296. Kraft, R. (1987). Learning through games discovery. The Physical Educator, 44(4), 420421. Kretchmar, S. (2005). Teaching games for understanding and the delights of human activity. In L. Griffin & J. Butler (Eds.), Teaching games for understanding: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 199-212). Windsor: Human Kinetics. Lathrop, A., & Drake, V. (2000). Teaching elementry and secondary school games: A common framework. CAHPERD, 66(2), 16-21. Laws, C. (1990). Individualism and teaching games - a contradiction of terms. BJPE, PEA, 8, 1-6. Laws, C. (1994). Rhetorical justification for new approaches to teaching games - are physical education teachers deluding themselves? Paper presented at the Proceedings for the 10th Commonwealth & International Scientific Congress, Victoria, British Columbia. Lawton, J. (1989). Comparison of two teaching methods in games. Bulletin of Physical Education, 25(1), 35-38. Lawton, J., & Werner, P. (1989). A program of badminton/net games which emphasize tactical awareness. The Physical Educator, 46, 99-106.
Light, R. & Butler, J. (2005). A personal journey: TGfU teacher development in Light, R. & Fawns, R. (2001). The thinking body: Constructivist approaches to games teaching in Physical Education. Melbourne Studies in Education, 42(2): 69-87. Light, R. & Fawns, R. (2003). Knowing the game: Integrating speech and action through TGfU, Quest, 55: 161-177. Light, R. (2002). Engaging the body in learning: Promoting cognition in games through TGfU, ACHPER Healthy Lifestyles Journal, 49(2): 23-26, Light, R. (2002). The social nature of games: Australian preservice primary teachersí first experiences of teaching games for understanding. European Physical Education Review, 8(3), 286-304. Light, R. (2002). The social nature of games: Pre-service primary teachers first experiences of TGfU, European Physical Education Review. 8(3): 291-310. Light, R. (2003). No room for heroes: Australian, pre-service teachers responses to TGfU. In L. Griffin, J. Butler, R. Nastasi & B. Lombardo (Eds), Teaching Games for Understanding in Physical Education and Sport: An International Perspective (pp.67-78). Oxon Hill, MD, USA: National Association for Sport and Physical Education. Light, R. (2003). Light up the sport with Game Sense. Sports Coach, 26 (2); 33-35. Light, R. (2003). The joy of learning: Emotion, cognition and learning in games through TGfU, New Zealand Journal of Physical Education, 36(1): 94-108. Light, R. (2004) Australian coaches experiences of Game Sense: Opportunities and challenges, Physical Education and Sport Pedagogy, 9(2), 115-132. Light, R. (2004). Coaches' experiences of game sense: Opportunities and challenges. Physical Education & Sport Pedagogy, 9(2), 115 - 131. Light, R. (2004). Implementing a Game Sense approach in youth sport. Waikato Journal of Education, 10, 169-180. Light, R. (2005). Making sense of chaos: Australian coaches talk about game sense. In L. Griffin & J. Butler (Eds.), Teaching games for understanding: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 169-182). Windsor: Human Kinetics. Light, R. (2005). Making sense of the chaos: Games Sense coaching in Australia. In L. Griffin and J. Butler (Eds), Examining a Teaching Games for Understanding Model. Champaigne Il: Human Kinetics. Light, R. (2006) Implementing Understanding Approaches to Teaching Games and Sport in Asia. to Asian Journal of Exercise and Sport Science, 2(1). 39-48. Light, R., & Fawns, R. (2002). The embodied mind: Blending speech and action in games Teaching through TGfU. 2002 Australian Council for Health, Physical Education and Recreation National Conference Proceedings Full, peer reviewed paper published [on line] Australian Council for Health, Physical Education and Recreation (pp.1-12) (not numbered sequentially in proceedings). Light, R., & Fawns, R. (2003). Knowing the game: Integrating speech and action in games teaching through tgfu. QUEST, 55, 161-176. Light, R., & Tan, S. (2006). Culture, embodied experience and teachers' development of tgfu in australia and singapore. European Physical Education Review, 12(1), 99-117. Liu, R., Li, C., & Cruz, A. (Eds.). (2006). Teaching games for understanding in the asiapacific region. Hong Kong: The Hong Kong Institute for Education.
Mandigo, J. L., & Anderson, A. T. (2003). Net/wall games: Part i. Using pedagogical principles in net/wall games to enhance teaching effectiveness. Teaching Elementary Physical Education, 14(1), 8-11. Mandigo, J., Butler, J., & Hopper, T. (2007). What is teaching games for understanding? A canadian perspective. The PHE, In press. Mauldon, E., & Redfern, H. (1981). Games teaching. London: Macdonald and Evans. Maxwell, T. (1984). Teach games concepts. RUNNER, 22(1). Maxwell, T. (2003). Progressions for net/wall game development: A volleyball example. Journal of Teaching Elementary Physical Education, 14(2), 10-14. Maynard, I. (1991). An understanding approach to the teaching of rugby union. British journal of Physical Education, 22(1), 11-17. McMorris, T. (1998). Teaching games for understanding: Its contribution to the knowledge of skill acquisition from a motor learning perspective. European Journal of Physical Education, 3, 65-74. McNeill, M., & Fry, J. (2003). Teaching net/wall games in elementary schools. Journal of Teaching Elementary Physical Education, 14(1), 22-26. McPherson, S. (1994). The development of sport expertise: Mapping the tactical domain. QUEST, 46, 223-240. McPherson, S., & French, K. (1991). Changes in cognitive strategy and motor skill in tennis. Journal of Sport and Exercise Psychology, 13, 26-41. McPherson, S., & Thomas, J. (1989). Relation of knowledge and performance in boys tennis: Age and expertise. Journal of experimental child psychology, 48, 190-211. Metzler, M. (2005). Implications of models-based instruction for research on teaching: A focus on teaching games for understanding. In L. Griffin & J. Butler (Eds.), Teaching games for understanding: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 183-198). Windsor: Human Kinetics. Mitchell, S. (1996). Improving invasion game performance. JOPERD, 67(2), 30-34. Mitchell, S. (2005a). Different paths up the same mountain: Global perspectives on tgfu (pp. Keynote presentation). Hong Kong: III Teacher Games for Understanding (TGFU) International Conference. Mitchell, S. (2005b). Teaching and learning games at the elementary level. In L. Griffin & J. Butler (Eds.), Teaching games for understanding: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 55-70). Windsor: Human Kinetics. Mitchell, S., & Clemens, L. (2003). Introducing game play in elementary physical education: A net/wall games example. Journal of Teaching Elementary Physical Education, 14(1), 12-15. Mitchell, S., & Griffin, L. (1994). Tactical awareness as a developmentally appropriate focus for the teaching of games in elementary. Physical Educator, 51(1), p. 8-29. Mitchell, S., & Oslin, J. (1999). An investigation of tactical transfer in net games. European Journal of Physical Education, 4, 162-172. Mitchell, S., Griffin, L., & Olsen, J. (2006). Teaching sport concepts and skills: A tactical games approach. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics. Mitchell, S., Griffin, L., & Oslin, J. (1995). A comparison of two instructional approaches to teaching invasion games. Paper presented at the AAHPERD National Convention, Portland, OR.
Morris, D. (1980). How to change the games children play (2nd ed.). Minneapolis: Burgess Publishing Company. Olsen, J., Mitchell, S., & Griffin, L. (1998). The game performance assessment instrument (gpai): Development and preliminary validation. Journal of Teaching in Physical Education, 2, 213-243. Oslin, J. (1996). Tactical approaches to teaching games. JOPERD, 67(1), 27. Oslin, J. (2005). The role of assessment in teaching games for understanding. In L. Griffin & J. Butler (Eds.), Teaching games for understanding: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 125-136). Windsor: Human Kinetics. Oslin, J., Mitchell, S., & Griffin, L. (1995). The game performance assessment instrument (gpai): Develpment and preliminary validation. Paper presented at the AAHPERD National Convention, Portland, Oregon. Pigott, B. (1982). A psychological basis for trends in games teaching. BAALPE, 18(1), 17-22. Randall, L., & Radford, K. (2003). Introducing basic tactics in wall and net games. Journal of Teaching Elementary Physical Education, 14(1), 16-20. Reid, P. (2003). More than a game? The role of sports governing bodies in the development of sport education programmes. European Physical Education Review, 9(3), 309-317. Richard, J.-F., & Nathalie, W. (2005). Emphasizing student engagement in the construction of game performance. In L. Griffin & J. Butler (Eds.), Teaching games for understanding: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 19-32). Windsor: Human Kinetics. Richard, J.-F., Godbout, P., Tousignant, M., & Grehaigne, J. (1999). The try-out of a team sport performance assessment procedure in elementary and junior high school physical education classes. Journal of Teaching Elementary Physical Education, 18(3), 336-356. Rink, J. (1996). Tactical and skill approaches to teaching sport and games: Introduction. Journal of teaching in physical education, 15, 397-398. Rink, J., French, K., & Graham, K. (1996). Implications for practice and research. Journal of Teaching in Physical Education, 15, 490-502. Rovegno, I. (1993). The development of curricular knowledge: A case of problematic pedagogical content knowlledge during advaned knowledge acquisition. Research quarterly for exercise and sport, 56-68. Rovegno, I., & Bandhauer, D. (1994). Child designed games--experience teachers' concerns. The Journal of Physical Education, Recreation and Dance, 65(6), 60-64. Schwager, S., & Labate, C. (1993). Teaching for critical thinking in physical education. JOPERD, May-June 1993, 24-26. Silverman, S. (1997). Is the tactical approach to teaching games better than a skills approach? JOPERD, 68(7), 5. Smith, M. (1991). Utilizing the games for understanding model at the elementary school level. The Physical Educator, 48(3), 184-187. Spackman, L. (1983). Invasion games: An instructional strategy. British Journal of Physical Education, 14(4), 98-99. Spackman, L., Booth, K., & Doolittle, S. (1982). Towards guidelines for thinking about games. Bulletin of Physical Education, 18(1), 39-40.
Stoddart, P. (1985). Teaching games for understanding: The practicalities of developing new courses in schools. Bulletin of Physical Education, 21(2), 29-34. Strean, B. (2003). Strategic control factors: A tool for teaching net/wall games. Journal of Teaching Elementary Physical Education, 14(2), 7-9. Tan, S. (2005). Implementing teaching games for understanding: Stories of change. In L. Griffin & J. Butler (Eds.), Teaching games for understanding: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 107-124). Windsor: Human Kinetics. Thorpe, R. (1983). An "understanding approach" to the teaching of tennis. BAALPE, 19(1), 12-19. Thorpe, R. (1986). A demonstration of a different focus. In R. Thorpe, D. Bunker & L. Almond (Eds.), Rethinking games teaching (pp. 17-24). Loughborough: University of Technology. Thorpe, R. (1990). New directions in games teaching. In N. Armstrong (Ed.), New directions in physical education (pp. 79-100). London: Human Kinetics Books. Thorpe, R. (1992). The psychological factors underpinning the "teaching for understanding" movement. In Sport and physical activity: Moving toward excellence (proceedings of the aiesep world convention, loughborough, uk). London: E & FN Spon. Thorpe, R., & Bunker, D. (1989). A changing focus in games teaching. In L. Almond (Ed.), The place of physical education in schools (pp. 42-71). London: Kogan/Page. Thorpe, R., Bunker, D., & Almond, L. (1984). Four fundamentals for planning a games curriculum. Bulletin of Physical Education, 20(1)(Spring 1984), 24-28. Thorpe, R., Bunker, D., & Almond, L. (Eds.). (1986). Rethinking games teaching. Loughborough: University of Technology, Loughborough. Thorpe, R., Bunker, DJ. (1997). A changing focus in games teaching. In L. Almond (Ed.), Physical education in schools. London: Kogan Page. Turner, A. (1996). Teaching for understanding: Myth or reality? JOPERD, 67(4), 46-47, 55. Turner, A. (2005). Teaching and learning games at the secondary level. In L. Griffin & J. Butler (Eds.), Teaching games for understanding: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 71-90). Windsor: Human Kinetics. Turner, A., & Martinek, J. (1995). Teaching for understanding: A model for improving decision making during game play. QUEST, 47, 44-63. Turner, A., & Martinek, J. (1999). An investigation into teaching games for understanding: Effects on skill, Turner, A., & Martinek, T. (1992). A comparative analysis of two models for teaching games (technique approach and game centered (tactical focus) approach). International Journal of Physical Education, XXIX, 131-152. Underwood, G. (1988). Teaching and learning in physical education: A social psychological perspective. London.: The Falmer Press. Wade, A. (1982). What's the game then? BAALPE, 18(2), 45-46. Wall, J., & Murray, N. (1994). Children and movement. Dubuque, IA: Wm. C. Brow Publishers. Waring, M. (2004). Book review: The future of physical education. European Physical Education Review, 10(3), 325-328.
Waring, M., & Almond, L. (1995). Game-centred games - a revolutionary or evolutionary alternative for games teaching. European Physical Education Review, 1(1), 55-66. Werner, P. (1989). Teaching games: A tactical perspective. JOPERD, 60(3), 97-101. Werner, P., & Almond, L. (1990). Models of games education. JOPERD, 61(4), 23-27. Werner, P., Thorpe, R., & Bunker, D. (1996). Teaching games for understanding: Evolution of model. JOPERD, 67(1), 28-33. Williamson, T. (1982). A critical look at the games curriculum. Bulletin of Physical Education, 18(1), 23-26. Wilson, G. (2002). A framework for teaching tactical game knowledge. JOPERD, 73(1), 21-26. Wright, S., McNeil, M., & Butler, J. I. (2004a). The role that socialization can play in promoting teaching games for understanding. JOPERD: The Journal of Physical Education, Recreation & Dance, 75(3), 46. Wright, S., McNeill, M., & Butler, J. I. (2004b). The role that socialization can play in promoting teaching games for understanding. Journal of Physical Education Recreation and Dance JOPERD, 75(3), 46.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 50 Ways To Balance MagicDocumento11 pagine50 Ways To Balance MagicRodolfo AlencarNessuna valutazione finora
- Oxy AcetyleneDocumento43 pagineOxy Acetyleneregupathi100% (1)
- Book of Lost Spells (Necromancer Games)Documento137 pagineBook of Lost Spells (Necromancer Games)Rodrigo Hky91% (22)
- Download 12,000 Shed PlansDocumento27 pagineDownload 12,000 Shed PlansRadu_IS100% (2)
- 2019 IL and Federal Pharmacy Law Review PDFDocumento176 pagine2019 IL and Federal Pharmacy Law Review PDFAnonymous 3YNJfYNQ100% (5)
- Graphic Organizers for Organizing IdeasDocumento11 pagineGraphic Organizers for Organizing IdeasMargie Tirado JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- The Transformation of Metaphysical ScienceDocumento7 pagineThe Transformation of Metaphysical ScienceblavskaNessuna valutazione finora
- Asus X553MA Repair Guide Rev2.0Documento7 pagineAsus X553MA Repair Guide Rev2.0UMA AKANDU UCHENessuna valutazione finora
- Cefoxitin and Ketorolac Edited!!Documento3 pagineCefoxitin and Ketorolac Edited!!Bryan Cruz VisarraNessuna valutazione finora
- OM - Rieter - UNIMix A76Documento321 pagineOM - Rieter - UNIMix A76Phineas FerbNessuna valutazione finora
- Changing the Game: Title IX, Gender, and College AthleticsDa EverandChanging the Game: Title IX, Gender, and College AthleticsNessuna valutazione finora
- Writing Simple Sentences to Describe ScenariosDocumento5 pagineWriting Simple Sentences to Describe Scenariosepol67% (3)
- Of Psychopathology: Ill Social Competence in Children. Hanover, NH: University Press of New EnglandDocumento2 pagineOf Psychopathology: Ill Social Competence in Children. Hanover, NH: University Press of New EnglandDamien KhooNessuna valutazione finora
- Sport Education PublicationsDocumento9 pagineSport Education Publicationsapi-443327549Nessuna valutazione finora
- ReferencesDocumento10 pagineReferenceshenryekeNessuna valutazione finora
- Rujukan VivaDocumento13 pagineRujukan VivaRos Shamizawati ShaharudinNessuna valutazione finora
- RUJUKANDocumento2 pagineRUJUKANmar_hisham8900Nessuna valutazione finora
- REFERENCESDocumento12 pagineREFERENCESRichelle IldefonsoNessuna valutazione finora
- Motivaciones e Intereses de Los Universitarios ReferenciasDocumento26 pagineMotivaciones e Intereses de Los Universitarios ReferenciasJhojan Cardona PatiñoNessuna valutazione finora
- ReferencesDocumento10 pagineReferencesMuhammad MujtabaNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Games For Understanding - 1Documento36 pagineTeaching Games For Understanding - 1louis.vandenbulcke49Nessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar PustakaDocumento9 pagineDaftar PustakaAmipaNadapdapNessuna valutazione finora
- References 2Documento1 paginaReferences 2api-376809503Nessuna valutazione finora
- European Physical Education Review 2014 Stolz 36 71Documento36 pagineEuropean Physical Education Review 2014 Stolz 36 71Lourdes100% (1)
- T KIM 1502671 BibliographyDocumento14 pagineT KIM 1502671 BibliographyAruf Rofi ZainiNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 BackDocumento68 pagine06 Backaderina9032Nessuna valutazione finora
- ReferencesDocumento4 pagineReferencesARLYN ABOGATALNessuna valutazione finora
- ReferencesDocumento2 pagineReferencesMarknel O. PeñedaNessuna valutazione finora
- RujukanDocumento8 pagineRujukanAlvin AngNessuna valutazione finora
- RujukanDocumento2 pagineRujukanace7eoNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar PustakaDocumento4 pagineDaftar PustakardtrpanselatimgundulNessuna valutazione finora
- ReferencesDocumento39 pagineReferencesAndi SyahputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Rujukan: Sebagai Pemimpin. Kuala Lumpur: PTS ProfessionalDocumento18 pagineRujukan: Sebagai Pemimpin. Kuala Lumpur: PTS ProfessionalNurlailie Md JamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Spe 503 ReferencesDocumento14 pagineSpe 503 ReferencesjmstetekluhNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods Results: Title Statement of The ProblemDocumento21 pagineMethods Results: Title Statement of The ProblemMaya Angelika SalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Vocabulary. USA: Cambridge University PressDocumento4 pagineVocabulary. USA: Cambridge University PressRou Ma IssaNessuna valutazione finora
- Jay ResearchDocumento8 pagineJay ResearchAngel Delos SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Sport Coaching Pedagogy BibliographyDocumento3 pagineSport Coaching Pedagogy BibliographySASI KUMAR SUNDARA RAJANNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Assessment & Classroom Management ArticlesDocumento4 pagineStudent Assessment & Classroom Management ArticlesGari Vi LaoNessuna valutazione finora
- ReferencesDocumento4 pagineReferencespolianNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 ReferencesDocumento32 pagine12 ReferencesPiyali Ghosh ChatterjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Bibliografi Dokumen Mengenai Konsep Pembelajaran PelajarDocumento7 pagineBibliografi Dokumen Mengenai Konsep Pembelajaran PelajarAtikah ErmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar PustakaDocumento6 pagineDaftar PustakavvirginummenggaNessuna valutazione finora
- References from Eastern and Western Philosophy of EducationDocumento2 pagineReferences from Eastern and Western Philosophy of EducationLizweNessuna valutazione finora
- Reference ListDocumento2 pagineReference Listapi-318327111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bibliography v1Documento7 pagineBibliography v1api-310932620Nessuna valutazione finora
- RujukanDocumento5 pagineRujukanChe Airell MiqailNessuna valutazione finora
- D Ipa 0706669 BibliographyDocumento9 pagineD Ipa 0706669 Bibliographywindi oktavianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cohort BibDocumento8 pagineCohort Bibkingsley4Nessuna valutazione finora
- SHAKTIMANNNDocumento6 pagineSHAKTIMANNNgopanovNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar ReferensiDocumento9 pagineDaftar ReferensiAfifah Yumna NovintaNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Pustaka PDFDocumento18 pagineDaftar Pustaka PDFZeinor RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading ListDocumento6 pagineReading ListAlice ReidNessuna valutazione finora
- Benefits of Class ParticipationDocumento16 pagineBenefits of Class Participationustad73Nessuna valutazione finora
- References: Intel Teach Elements Inquiry in The Science ClassroomDocumento5 pagineReferences: Intel Teach Elements Inquiry in The Science ClassroomjacafyNessuna valutazione finora
- Works CitedDocumento3 pagineWorks Citedapi-271017391Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bibliography A. Books: Educational Psychology, 25, 54-67Documento11 pagineBibliography A. Books: Educational Psychology, 25, 54-67Bambie de JesusNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdullah, R., (2005), Pembangunan Dan Keberkesanan Pakej MultimediaDocumento5 pagineAbdullah, R., (2005), Pembangunan Dan Keberkesanan Pakej MultimediaROHAZMY RIZKINessuna valutazione finora
- Formation in Canada West. Toronto, Canada: University of Toronto PressDocumento4 pagineFormation in Canada West. Toronto, Canada: University of Toronto Pressapi-112643368Nessuna valutazione finora
- Draft References: Laman Matlamat&bhs MyDocumento4 pagineDraft References: Laman Matlamat&bhs MyNor'Azman Bin SallehNessuna valutazione finora
- ReferencesDocumento3 pagineReferencesapi-285093538Nessuna valutazione finora
- Livro Catálogo Sobre Concepções Alternativas - DuitDocumento579 pagineLivro Catálogo Sobre Concepções Alternativas - DuitRaquel MartinsNessuna valutazione finora
- References CitedDocumento3 pagineReferences CitedKimberly Sheen Medina YamsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Bibliography 2005 (Dianne Allen)Documento38 pagineTotal Bibliography 2005 (Dianne Allen)Dianne AllenNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Pustaka: Geographic Space (Hal. 117-136) - Dordrecht: KluwerDocumento5 pagineDaftar Pustaka: Geographic Space (Hal. 117-136) - Dordrecht: KluwerdeaNessuna valutazione finora
- References 1Documento2 pagineReferences 1api-238904329Nessuna valutazione finora
- Childrens Ideas Science0Documento7 pagineChildrens Ideas Science0Kurtis HarperNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching To The Test or Testing To Teach - Exams Requiring Higher Order Thinking Skills Encourage Greater Conceptual Understanding - SpringerDocumento12 pagineTeaching To The Test or Testing To Teach - Exams Requiring Higher Order Thinking Skills Encourage Greater Conceptual Understanding - SpringerKaran MannNessuna valutazione finora
- BIBLODocumento3 pagineBIBLOkamilicious27Nessuna valutazione finora
- Submitted By: Aqsa Batool Student No: S/2019-1621 Submitted To: Dr. Ummara SeharDocumento7 pagineSubmitted By: Aqsa Batool Student No: S/2019-1621 Submitted To: Dr. Ummara SeharAhsan IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Behavioral Sport Psychology: Evidence-Based Approaches to Performance EnhancementDa EverandBehavioral Sport Psychology: Evidence-Based Approaches to Performance EnhancementNessuna valutazione finora
- Cursive Writing BookletDocumento25 pagineCursive Writing BookletShee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- 625382b92d654 PBD Transit Form With Descriptors Year 2Documento17 pagine625382b92d654 PBD Transit Form With Descriptors Year 2Shee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Jwi Jan2013 S3pismp V17disDocumento3 pagineJwi Jan2013 S3pismp V17disShee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- JOH Part 3 Chapter1Documento1 paginaJOH Part 3 Chapter1Shee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Senior Hasil DapatanDocumento4 pagineSenior Hasil DapatanShee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- BC1Documento1 paginaBC1Shee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetically Modified Food2Documento7 pagineGenetically Modified Food2Shee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Sce Pearso NDocumento1 paginaSce Pearso NShee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Report (Without Conclusion)Documento1 paginaReport (Without Conclusion)Shee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer QuizDocumento1 paginaAnswer QuizShee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Father Mother O O A ODocumento1 paginaFather Mother O O A OShee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetically Modified Food1techDocumento4 pagineGenetically Modified Food1techShee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Jadual UK1Documento1 paginaJadual UK1Shee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- BCDocumento1 paginaBCShee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- English Presentation-Mobile PhonesDocumento3 pagineEnglish Presentation-Mobile PhonesShee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- English Presentation-Mobile PhoneDocumento1 paginaEnglish Presentation-Mobile PhoneShee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Sce 3014 Set 2Documento16 pagineSce 3014 Set 2Shee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Work Addmath Form 5Documento5 pagineProject Work Addmath Form 5Shee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Rules RegulationsDocumento3 pagineRules RegulationsShee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Done AcknowledgementDocumento1 paginaDone AcknowledgementShee YingNessuna valutazione finora
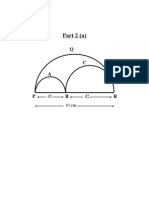
- Done Part 2 (A)Documento3 pagineDone Part 2 (A)Shee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Circles in Daily Life 2009 Math ProjectDocumento1 paginaCircles in Daily Life 2009 Math ProjectShee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- JuneDocumento1 paginaJuneShee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Done Part 2 (B) Ii) C)Documento1 paginaDone Part 2 (B) Ii) C)Shee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- JuneDocumento1 paginaJuneShee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Done IntroductionDocumento1 paginaDone IntroductionShee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Done Part 2 (B) I)Documento2 pagineDone Part 2 (B) I)Shee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Done ContentDocumento1 paginaDone ContentShee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- WebsitesDocumento1 paginaWebsitesShee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Definition Of Pi, π: cos (x) = 0Documento1 paginaDefinition Of Pi, π: cos (x) = 0Shee YingNessuna valutazione finora
- New Company Profile.Documento8 pagineNew Company Profile.Allen AsirNessuna valutazione finora
- Bahasa InggrisDocumento8 pagineBahasa InggrisArintaChairaniBanurea33% (3)
- Theory Is An Explanation Given To Explain Certain RealitiesDocumento7 pagineTheory Is An Explanation Given To Explain Certain Realitiestaizya cNessuna valutazione finora
- Powers of Central Govt under Environment Protection ActDocumento13 paginePowers of Central Govt under Environment Protection Actsirajudeen INessuna valutazione finora
- Activities/Assessments 2:: Determine The Type of Sampling. (Ex. Simple Random Sampling, Purposive Sampling)Documento2 pagineActivities/Assessments 2:: Determine The Type of Sampling. (Ex. Simple Random Sampling, Purposive Sampling)John Philip Echevarria0% (2)
- L P 10Documento13 pagineL P 10Bình Minh HoàngNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer BehaviourDocumento48 pagineConsumer BehaviourdooncollegeNessuna valutazione finora
- SCM PPT (Supply Chain Management)Documento19 pagineSCM PPT (Supply Chain Management)Mairaj NaseemNessuna valutazione finora
- Preparatory Lights and Perfections: Joseph Smith's Training with the Urim and ThummimDocumento9 paginePreparatory Lights and Perfections: Joseph Smith's Training with the Urim and ThummimslightlyguiltyNessuna valutazione finora
- HUMAN RIGHTS, RATIONALITY, AND SENTIMENTALITYDocumento13 pagineHUMAN RIGHTS, RATIONALITY, AND SENTIMENTALITYJohn HunterNessuna valutazione finora
- E.bs 3rd-Unit 22Documento46 pagineE.bs 3rd-Unit 22DUONG LE THI THUYNessuna valutazione finora
- Frequently Asked Questions: Wiring RulesDocumento21 pagineFrequently Asked Questions: Wiring RulesRashdan HarunNessuna valutazione finora
- FED - Summer Term 2021Documento18 pagineFED - Summer Term 2021nani chowdaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Turabian Sample PaperDocumento9 pagineTurabian Sample Paperemme_lopez908133% (3)
- Teaching TrigonometryDocumento20 pagineTeaching Trigonometryapi-21940065Nessuna valutazione finora
- Remembrance 23 Names PDFDocumento1 paginaRemembrance 23 Names PDFJennifer ThuncherNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy 090819Documento30 pagineAnatomy 090819Vaishnavi GourabathiniNessuna valutazione finora
- GBM Auction Versus English Auction A Large-Scale Empirical Study - E. Bessire, K. Elhadji Tchiambou (October 2021)Documento18 pagineGBM Auction Versus English Auction A Large-Scale Empirical Study - E. Bessire, K. Elhadji Tchiambou (October 2021)Guillaume GonnaudNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt 1 Yarn Formation (Sherley Trash Analyser)Documento7 pagineExpt 1 Yarn Formation (Sherley Trash Analyser)Yashdeep Sharma0% (1)