Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
The Working Cell Sp'12 Reduced Size
Caricato da
Brian BradyCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
The Working Cell Sp'12 Reduced Size
Caricato da
Brian BradyCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1he Worklng Cell
Learnlng CuLcomes
Lnergy 1ransformauon ln blologlcal reacuons
Adenoslne 1rlphosphaLe (A1) ls used Lo power
blologlcal reacuons
Pow enzymes work
1he sLrucLure and funcuon of Lhe plasma
membrane
1ransporL of molecules across Lhe plasma
membrane
Csmosls
WhaL ls Lnergy, exacLly?
Energy (n.) is the capacity to perform work.
1wo Laws Culde Lnergy 1ransformauons
llrsL Law of 1hermodynamlcs- ?ou cannoL
creaLe or desLroy energy.
! Second Law- SOME of the energy used to
power reactions is lost as HEAT.
1wo Lhlngs can happen Lo energy ln a
blologlcal reacuon:
1. Lnergy can be S1C8Lu or...
2. Lnergy can be 8LLLASLu.
Endergonic Reaction Exergonic Reaction
WhaL ls A1, and why ls lL called Lhe
cells unlL of currency?
Breaking off the last phosphate from ATP releases a LOT of energy!!!
What kind of reactions are NON-SPONTANEOUS, or REQUIRE ENERGY?
ENDERGONIC
A1 ls used Lo couple non-favorable reacuons
wlLh favorable ones.
The ATP cycle
Pow does A1 power Cellular Work?
Lnzymes!!!: 8uL rsL, an enzyme analogy
Lnzymes are Lhe cells caLalysLs.
8lochemlcal reacuons are sped up (caLalzyed)
by Lnzymes!
The Krebs Cycle AKA Citric Acid Cycle
Lnzymes caLalyze speclc reacuons
WhaL facLors aecL enzyme acuvlLy?
1emperaLure (Lhlnk: Lhermal sprlngs bacLerla
vs. your guL bacLerla)
pP (Lhlnk: sLomach acld)
CofacLors- cerLaln molecules, lnorganlc or
organlc (coenzymes) LhaL an enzyme canL
work wlLhouL
Lnzyme lnhlbluon
Lnzyme lnhlblLors: deLrlmenLal and
Lherapeuuc
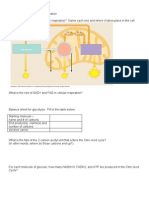
Membrane sLrucLure and funcuon
1he membrane ls acLually a uld mosalc
What are the various components of a plasma membrane???
WhaL do membrane proLelns do?
Enzyme
activity
Signal
Transduction
Transport
across
membrane
Pow do cells allow passage of
maLerlals lnLo and ouL of Lhe cell?
asslve LransporL
laclllLaLed dluslon
Acuve LransporL
Lndo- and exocyLosls.
asslve 1ransporL uoes nC1 8equlre
Lnergy Lo Move SoluLes Across a
Membrane
asslve 1ransporL
http://www.youtube.com/v/s0p1ztrbXPY
laclllLaLed uluslon requlres proLelns for
LransporL across Lhe membrane
Membranes are selectively permeable. They dont let just any solute in!
Csmosls: Lhe dluslon of P2C across a
selecuvely permeable membrane
http://
www.youtube.com/
v/sdiJtDRJQEc
WhaL eecL does LonlclLy have on a cell?
Acuve LransporL across Lhe membrane requlres
energy
1. The solute binds
to the transport
protein.
2. ATP
phosphorylates the
transport protein.
3. The solute is
transported across
the membrane.
4. The protein is
dephosphorylated
and the transport
protein returns to
its open
conformation.
LxocyLosls and LndocyLosls LransporL Lhe
LA8CL MCLLCuLLS lnLo a cell.
http://www.youtube.com/v/U9pvm_4-bHg
Pow does a cell geL A1? An lnLro
Lo cellular resplrauon.
Cellular respiration is how the cell obtains ATP from glucose and O
2
.
Respiration is comprised of: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle,
and oxidative phosphorylation.
Understanding the flow of electrons from glucose to power
ATP synthesis.
Understanding chemiosmosis as a gradient of electrons.
8esplrauon
DONT BE MISLED by this picture!! All cells perform
respiration- they MUST in order to obtain energy.
8esplrauon: CvL8slmplled!
C
6
P
12
C
6
+ 6C
2
" 6CC
2
+ 6P
2
C
INPUT OUTPUT
WhaL klnds of enzymes perform
8LuCx reacuons?
BIG QUESTION: WHAT HAPPENS
TO THE ELECTRONS???!!!!
Cvervlew of 8esplrauon
roLelns ln Lhe mlLochondrlal lnner
membrane funcuon ln A1 synLhesls.
Energy of
ATP: 7.3
kcal/mol
WhaL oLher membrane-bound organelle
conLrlbuLes Lo cellular energy?
hoLosynLhesls reacuons
(overslmplled)
6CC
2
+ 6P
2
C " C
6
P
12
C
6
+ 6C
2
INPUT OUTPUT
hoLosynLhesls: A Summary
roLelns ln Lhe Lhylakold membranes funcuon ln
A1 synLhesls ln Lhe chloroplasL.
WhaL ls Lhe
relauonshlp
beLween
phoLosynLhesls and
resplrauon?
1he molecule A1 possesses whlch
klnd of energy?
A. klneuc energy
8. 1hermal energy
C. oLenual energy
u. Cellular energy
Whlch of Lhe followlng sLaLemenLs besL
descrlbes how enzymes funcuon?
A. Lnzymes creaLe energy ln Lhe cell.
8. Lnzymes caLalyze blochemlcal reacuons.
C. Lnzymes creaLe A1.
u. Lnzymes lnhlblL blochemlcal reacuons.
Whlch of Lhe followlng modes of
LransporL of soluLe across
membranes doe nC1 requlre a
LransporL proLeln?
A. asslve dluslon
8. laclllLaLed dluslon
C. Acuve LransporL
8educuon speclcally refers Lo
A. 1he loss of hydrogen.
8. 1he loss of a proLon.
C. 1he loss of an elecLron.
u. 1he galn of an elecLron.
L. 1he galn of a charge.
uurlng cellular resplrauon,
A. Cxygen ls consumed and sugar ls produced.
8. Cxygen and waLer are consumed.
C. Carbon dloxlde ls consumed and sugar ls
produced.
u. Cxygen ls consumed and carbon dloxlde ls
produced.
A cell wlll lose waLer when lL ls
lmmersed lnLo a ________
envlronmenL.
A. PyperLonlc
8. PypoLonlc
C. lsoLonlc
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- ALM Transcription TranslationDocumento3 pagineALM Transcription TranslationBrian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- ALM Evolutionary ForcesDocumento2 pagineALM Evolutionary ForcesBrian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution Lecture F'12Documento56 pagineEvolution Lecture F'12Brian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- ALM Evolutionary ForcesDocumento2 pagineALM Evolutionary ForcesBrian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- ALM DNA Structure Sp'13 NameDocumento4 pagineALM DNA Structure Sp'13 NameBrian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Biology LectureDocumento43 pagineMolecular Biology LectureBrian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide For RCC Bio1 Lab MidtermDocumento1 paginaStudy Guide For RCC Bio1 Lab MidtermBrian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics Bio101 LectureDocumento41 pagineGenetics Bio101 LectureBrian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- ALM GeneticsDocumento2 pagineALM GeneticsBrian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Replication Mitosis Meiosis Sp'13Documento39 pagineDNA Replication Mitosis Meiosis Sp'13Brian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics Bio101 LectureDocumento41 pagineGenetics Bio101 LectureBrian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- Macromolecules LectureDocumento51 pagineMacromolecules LectureBrian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis: - I. Bottom Line of PhotosynthesisDocumento21 paginePhotosynthesis: - I. Bottom Line of PhotosynthesisBrian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- ALM Photosynthesis and RespirationDocumento4 pagineALM Photosynthesis and RespirationBrian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 100:101 Introduction Lecture Sp'13Documento22 pagineBio 100:101 Introduction Lecture Sp'13Brian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiration Lecture F'12Documento36 pagineRespiration Lecture F'12Brian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- ALM The Working Cell F'12Documento3 pagineALM The Working Cell F'12Brian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- ALM BiochemistryDocumento4 pagineALM BiochemistryBrian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- ALM Introduction Atoms Molecules Water PHDocumento5 pagineALM Introduction Atoms Molecules Water PHBrian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- ALM Origin of Life and Tour of Cell F'12Documento3 pagineALM Origin of Life and Tour of Cell F'12Brian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Atoms Molecules Water PH Sp'13Documento24 pagineLecture Atoms Molecules Water PH Sp'13Brian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Theory and Tour of Cell Sp'13Documento44 pagineCell Theory and Tour of Cell Sp'13Brian BradyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Anatomy & Plant PhysiologyDocumento27 pagineAnatomy & Plant Physiologyshree devNessuna valutazione finora
- GENBIO 1 Q2 Periodic TestDocumento5 pagineGENBIO 1 Q2 Periodic TestCelsa ChicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sugar For The Brain: The Role of Glucose in Physiological and Pathological Brain FunctionDocumento11 pagineSugar For The Brain: The Role of Glucose in Physiological and Pathological Brain FunctionNashaly PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- HND Sector 2 Vol3-1Documento530 pagineHND Sector 2 Vol3-1mbabit leslieNessuna valutazione finora
- Valorization of CTC Tea Waste Through Kombucha Production and Insight Into GC-MS Based MetabolomicsDocumento20 pagineValorization of CTC Tea Waste Through Kombucha Production and Insight Into GC-MS Based MetabolomicsRiyadh arefinNessuna valutazione finora
- Pys 212 (Energy Transfer Questions)Documento20 paginePys 212 (Energy Transfer Questions)Odigo OfujeNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 1 - BSC 2010 - T2 Practice Set 1 Spr08 Bsc2010Documento6 pagineBiology 1 - BSC 2010 - T2 Practice Set 1 Spr08 Bsc2010alphacetaNessuna valutazione finora
- AP M10 Ch9 Respiration Worksheet2Documento5 pagineAP M10 Ch9 Respiration Worksheet2Jakie Ubina0% (1)
- Syllabi For Ph.D. Entrance TestDocumento144 pagineSyllabi For Ph.D. Entrance TestSonia AroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy: Osasenaga Macdonald Ighodaro TDocumento7 pagineBiomedicine & Pharmacotherapy: Osasenaga Macdonald Ighodaro TMohammed RickyNessuna valutazione finora
- Bioenergetics of Exercise and TrainingDocumento62 pagineBioenergetics of Exercise and Trainingswordplay716Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practicetests2019 Demo EngeeconDocumento11 paginePracticetests2019 Demo EngeeconAyesha100% (1)
- UrineDocumento41 pagineUrineWahab KhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- On Sugar Sensing in Saccharomyces Cerevisiase - PHD Thesis - Daniel Bosch IbáñezDocumento157 pagineOn Sugar Sensing in Saccharomyces Cerevisiase - PHD Thesis - Daniel Bosch IbáñezDanielNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological Chemistry (Concept To Remember)Documento8 pagineBiological Chemistry (Concept To Remember)Kecilyn AmbrocioNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Biology SupplementDocumento86 pagineAP Biology SupplementLama DiriyehNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Cell Respiration LaboratoryDocumento15 pagineIntroduction To Cell Respiration LaboratoryNor safikahNessuna valutazione finora
- BiochemistryDocumento10 pagineBiochemistryArjayle Airobail LlevadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 21 LipidsDocumento43 pagineChapter 21 Lipidsdaoud sarrawyNessuna valutazione finora
- Q1M8Documento30 pagineQ1M8Jesus GombaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Classroom Script and HandoutDocumento8 pagineCellular Classroom Script and Handoutapi-262224129Nessuna valutazione finora
- Precision Nutrition and Metabolic Syndrome ManagementDocumento224 paginePrecision Nutrition and Metabolic Syndrome ManagementNguyễn Trung NguyênNessuna valutazione finora
- Med Board Biochem MCQ-Answer KeyDocumento14 pagineMed Board Biochem MCQ-Answer KeyVince CabahugNessuna valutazione finora
- Mountain Dog Diet - Injectable Carnitine For Fat LossDocumento10 pagineMountain Dog Diet - Injectable Carnitine For Fat LossZacharyJones100% (2)
- RespirationDocumento11 pagineRespirationthushyanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry Answer Key BLUE PACOPDocumento26 pagineBiochemistry Answer Key BLUE PACOPRizzel Angeles100% (1)
- Crop ScienceDocumento87 pagineCrop ScienceArjay Mendoza100% (1)
- General Biology 1 Module FINALSDocumento12 pagineGeneral Biology 1 Module FINALSKenneth Vince AlonzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen Physiology 2015Documento423 pagineGen Physiology 2015cathlynjoy.marsamoloNessuna valutazione finora
- 11th Bio - Botany One Mark Question Bank With Answer Key English Medium 2022-23Documento8 pagine11th Bio - Botany One Mark Question Bank With Answer Key English Medium 2022-23Cute Sweet100% (1)