Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
CT-2 Test
Caricato da
muru0105Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CT-2 Test
Caricato da
muru0105Copyright:
Formati disponibili
VELAMMAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Department of Mechanical Engineering / CT 2/ STRENGTH OF MATERIALS / ME2254 / IV SEM /04-03-13/100MIN/60MAKS/SET A Part-A(6 X2 = 12)
1. Write down the simple torsion formula with the meaning of each symbol for circular cross section. APRIL/MAY 2011 2. Define the term stiffness of a spring. APRIL/MAY 2010
3. A cantilever beam of spring 2 m is carrying a point load of 20 kN at its free end. Calculate the slope at the free end. Assume EI = 12 103 kN-m2. NOV/DEC2010 4. Differentiate open coiled helical spring from the close coiled helical spring and state the type of stress induced in each spring due to an axial load. NOV/DEC2010 5. Calculate the effective length of a long column, whose actual is 4 m when: (a) both ends are fixed (b) One end fixed while the other is free. NOV/DEC2010 6. What are the assumptions made in Eulers column theory? APRIL/MAY 2010
Part-B(3 X16 = 48)
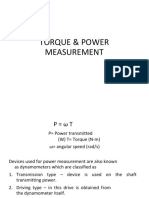
(a) (i) Obtain a relation for the torque and power, a solid shaft can transmit. (8) (ii) A solid steel shaft has to transmit 100 kW at 160 r.p.m. taking allowable shear stress as 70 MPa, find the suitable diameter of the shaft. The maximum torque transmitted in each revolution exceeds the mean by 20%. (8) Or (b) (i) Derive an equation for deflection of an open coiled helical spring. (8) (ii) A closely coiled helical spring is made up of 10 mm diameter steel wire having 10 coils with 80 mm mean diameter. If the spring is subjected to an axial twist of 10 kN-mm, determine the bending stress and increase in the number of turns. Take E as 200 GPa. (8) 14. (a) A cantilever AB, 2 m long, is carrying a load of 20 kN at free end and 30 kN at a distance 1 m from the free end. Find the slope and deflection at the free end. Take E = 200 GPa and I = 150X106mm4 Or (b) A simply supported beam AB of span 4 m, carrying a load of 100 kN at its mid span C has cross sectional moment of inertia 24 x 106 mm4. Find the slope at two supports and the deflection under the load. Take E = 200 GPa. (a) A steel shaft is required to transmit 75 kW power at 100 r.p.m. and the maximum twisting moment is 30% greater than the mean. Find the diameter of the steel shaft if the maximum stress is 70 N/mm2. Also determine the angle of twist in a length of 3 m of the shaft. Assume the modulus of rigidity for steel as 90 kN/mm2 Or (b) A helical spring, in which the mean diameter of the coils is 12 times the wire diameter, is to be designed to absorb 300 J energy with an extension of 150 mm. The maximum shear stress is not to exceed 140 N/mm2. Determine the mean diameter of the spring, diameter of the wire which forms the spring and the number of turns. Assume the modulus of rigidity of the material of the spring as 80 kN/mm2. 3 11410 14. (a) A beam of length 6 m is simply supported at the ends and carries two point loads of 48 kN and 40 kN at a distance of 1 m and 3 m respectively from the left support. Compute the slope and deflection under each load. Assume EI = 17000 kNm2. Or (b) A hollow cast iron strut 150 mm outer and 100 mm in diameter and 8 m long, one end pin jointed and other end is fixed, is subjected to an axial compressive load. Taking factor of safety as 5 and Rankines constants 550 N/mm2 and 1/1600, calculate the safe load.
VELAMMAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Department of Mechanical Engineering / CT 2/ STRENGTH OF MATERIALS / ME2254 / IV SEM /04-03-13/100MIN/60MAKS/SET A Part-A
1. List any four methods of determining slope and deflection of loaded beam. APRIL/MAY 2011 2. The actual length of a column is 10 m. Determine its effective length if both the ends of the column are rigidity fixed. APRIL/MAY 2011 3. Write the assumption for finding out the shear stress of a circular shaft, subjected to torsion. APRIL/MAY 2010
4. Find the torque which a shaft of 50 mm diameter can transmit safely, if the allowable shear stress is 75 N/mm2. APRIL/MAY 2011
5. Define stiffness of spring and mention its unit in SI system. APRIL/MAY 2011
6. Differentiate open coiled helical spring from the close coiled helical spring and state the type of stress induced in each spring due to an axial load. NOV/DEC2010 13 (a) Calculate the power that can be transmitted at a 300 rpm by a hollow steel shaft of 75 mm external diameter and 50 mm internal diameter when the permissible shear stress for the steel is 70N/mm2 and the maximum torque is 1.3 times the mean. Compare the strength of this hollow shaft with that of an solid shaft. The same material, weight and the length of both the shafts are the same. (16) (b) A helical spring of circular cross-section wire 18 mm in diameter is loaded by a force of 500 N. The mean coil diameter of the spring is 125 mm. The modulus of rigidity is 80 kN/mm 2. Determine the maximum shear stress in the material of the spring. What number of coils must the spring have for its deflection to be 6mm? (16) 14 (a) beam is simply supported at its ends over a span of 10 m and carries two concentrated loads of 100 kN and 60 kN at a distance of 2 m and 5 m respectively from the left support. Calculate (i) slope at the left support (ii) slope and deflection under the 100 kN load. Assume EI = 36 104 kN-m2. (16) Or (b) Find the Euler critical load for a hollow cylindrical cast iron column 150mm external diameter, 20 mm wall thickness if it is 6 m long with hinged at both ends. Assume Youngs modulus of cast iron as 80 kN/mm2. Compare this load with that given by Rankine formula. Using Rankine constants = 1/1600 and 567 N/mm2. (16)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Pricelist 1Documento8 paginePricelist 1ChinangNessuna valutazione finora
- Reclaimer PDFDocumento8 pagineReclaimer PDFSiti NurhidayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- ParagraphDocumento1 paginaParagraphmuru0105Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cent Pump DesignDocumento37 pagineCent Pump Designmuru0105Nessuna valutazione finora
- Steps For Design of Heat ExchangerDocumento11 pagineSteps For Design of Heat Exchangermuru0105Nessuna valutazione finora
- Instrumentation and Measurements - AssignmentDocumento1 paginaInstrumentation and Measurements - Assignmentmuru0105Nessuna valutazione finora
- Composite Floors PDFDocumento17 pagineComposite Floors PDFmuru0105Nessuna valutazione finora
- Infrared IR LED 940nm 5 MM 60degree - : 2. Blood Pressure Sensor With Serial OutputDocumento2 pagineInfrared IR LED 940nm 5 MM 60degree - : 2. Blood Pressure Sensor With Serial Outputmuru0105Nessuna valutazione finora
- Instrumentation CH3Documento84 pagineInstrumentation CH3muru0105Nessuna valutazione finora
- Embassy of India, Abu Dhabi, U.A.EDocumento3 pagineEmbassy of India, Abu Dhabi, U.A.Emuru0105Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bannari Amman Institute of Technology: Application For The Post of - in The Department ofDocumento3 pagineBannari Amman Institute of Technology: Application For The Post of - in The Department ofmuru0105Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fill in The Blanks With Correct Tense Form of Verbs Given in The BracketDocumento1 paginaFill in The Blanks With Correct Tense Form of Verbs Given in The Bracketmuru0105Nessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Word - Recruitment FormDocumento1 paginaMicrosoft Word - Recruitment Formmuru0105Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Renewable Energy: Frank SpencerDocumento77 pagineIntroduction To Renewable Energy: Frank Spencermuru0105Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cource Outline MeasuremntDocumento3 pagineCource Outline Measuremntmuru0105Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dts PDFDocumento531 pagineDts PDFmuru0105Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chap - 1 - Process Design ParametersDocumento14 pagineChap - 1 - Process Design Parametersmuru0105Nessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Health Benefits of AvocadosDocumento2 pagine10 Health Benefits of Avocadosmuru0105Nessuna valutazione finora
- Naik 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 338 012039Documento7 pagineNaik 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 338 012039muru0105Nessuna valutazione finora
- Torque & Power MeasurementDocumento10 pagineTorque & Power Measurementmuru0105Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3D Tetris Cake Evening 2Documento13 pagine3D Tetris Cake Evening 2Subham KarmakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1: Power and Responsibility: 1. Important Leadership QualitiesDocumento6 pagineUnit 1: Power and Responsibility: 1. Important Leadership QualitiesTrần Thanh MinhNessuna valutazione finora
- Leadership Nursing and Patient SafetyDocumento172 pagineLeadership Nursing and Patient SafetyRolena Johnette B. PiñeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Tripura 04092012Documento48 pagineTripura 04092012ARTHARSHI GARGNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagrama Hilux 1KD-2KD PDFDocumento11 pagineDiagrama Hilux 1KD-2KD PDFJeni100% (1)
- Arte PoveraDocumento13 pagineArte PoveraSohini MaitiNessuna valutazione finora
- Prof Ed 3 Module 1Documento9 pagineProf Ed 3 Module 1alexa dawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Blackstone The Dash Model #1610 Owner's ManualDocumento53 pagineBlackstone The Dash Model #1610 Owner's ManualSydney Adam SteeleNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1 - Vertical Alignment - SolutionsDocumento6 pagineAssignment 1 - Vertical Alignment - SolutionsArmando Ramirez100% (1)
- Oss Kpi SummaryDocumento7 pagineOss Kpi SummaryMohd FaizNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 6 q2 Mathematics LasDocumento151 pagineGrade 6 q2 Mathematics LasERIC VALLE80% (5)
- Volvo HU 803Documento8 pagineVolvo HU 803GiegloNessuna valutazione finora
- (2016) A Review of The Evaluation, Control and Application Technologies For Drillstring S&V in O&G WellDocumento35 pagine(2016) A Review of The Evaluation, Control and Application Technologies For Drillstring S&V in O&G WellRoger GuevaraNessuna valutazione finora
- GeminiDocumento397 pagineGeminiJohnnyJC86Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final Project Synopsis 1Documento90 pagineFinal Project Synopsis 1Shyam YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- L Rexx PDFDocumento9 pagineL Rexx PDFborisg3Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1207 - RTC-8065 II InglesDocumento224 pagine1207 - RTC-8065 II InglesGUILHERME SANTOSNessuna valutazione finora
- Ccie R&s Expanded-BlueprintDocumento12 pagineCcie R&s Expanded-BlueprintAftab AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- Hospital Furniture: Project Profile-UpdatedDocumento7 pagineHospital Furniture: Project Profile-UpdatedGaurav GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Principal Examiner Feedback Summer 2016: Pearson Edexcel GCSE in Statistics (2ST01) Higher Paper 1HDocumento14 paginePrincipal Examiner Feedback Summer 2016: Pearson Edexcel GCSE in Statistics (2ST01) Higher Paper 1HHeavenly SinNessuna valutazione finora
- IOM - Rampa Hidráulica - Blue GiantDocumento32 pagineIOM - Rampa Hidráulica - Blue GiantPATRICIA HERNANDEZNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Institutions With Ladderized Program Under Eo 358 JULY 2006 - DECEMBER 31, 2007Documento216 pagineList of Institutions With Ladderized Program Under Eo 358 JULY 2006 - DECEMBER 31, 2007Jen CalaquiNessuna valutazione finora
- DocsDocumento4 pagineDocsSwastika SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- IJISRT23JUL645Documento11 pagineIJISRT23JUL645International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- JOB Performer: Q .1: What Is Permit?Documento5 pagineJOB Performer: Q .1: What Is Permit?Shahid BhattiNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus of Finite Differences: Andreas KlappeneckerDocumento30 pagineCalculus of Finite Differences: Andreas KlappeneckerSouvik RoyNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 - SHM, Springs, DampingDocumento4 pagine10 - SHM, Springs, DampingBradley NartowtNessuna valutazione finora
- Neural Computing and ApplicationsDocumento49 pagineNeural Computing and ApplicationsLine PhamNessuna valutazione finora