Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Glyco Sides
Caricato da
vishwanathz47Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Glyco Sides
Caricato da
vishwanathz47Copyright:
Formati disponibili
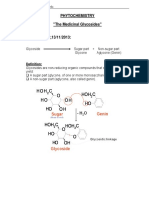
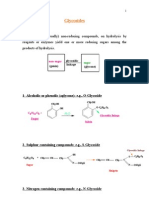
Glycosides : There are compounds that yield on hydrolysis , one or more sugar among the other products of hydrolysis,
the sugar part is known as glycone and the non sugar part is the aglycone. Glycoside may be considered as sugar ether. Tow forms of glycosides are present , the a form and the b form , the b form is the one that occur in plants, even the hydrolytic enzymes act on this type. Inside the body the glycoside will be cleaved to glycone and aglycone parts. The glycone part confers on the molecule solubility properties , thus is important in the absorption and distribution in the body , while the aglycone part is responsible for the pharmacological activity. All glycoside are hydrolyzed by boiling with mineral acid , on the other hand the presence of specific enzyme in the plant tissue , but in deferent cells from those that contain the glycosides , are able to hydrolyzed the glycosides. Generally in the extraction of the glycosides we need the following points: 1 . A polar solvent , which is mostly alcohol , but not water , since water may induce fermentation , in addition water needs high temperature due to its high boiling point. 2. Neutralization of the extract with base, since the presence of acid lead to hydrolysis of the glycoside.
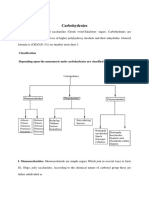
3. Use of heat is to inhibit the activity of the hydrolytic enzymes that is present in the plant cell. The glycosides are classified according to the chemical nature of the aglycone to: 1. Cardio active glycosides. 2. Anthraquinone glycosides.. 3. Saponin glycosides. 4. Cyanophore glycosides. 5. Isothiocyanate glycosides. 6. Flavonol glycosides. 7. Alcohol glycosides. 8. Aldehyde glycosides. 9. Lactone glycosides. 10. Phenol glycosides.
They named so , due to their action on the heart muscle. The aglycone part here is steroid, which is chemically cyclopenta phenanthrene. The steroidal aglycones are of two types , cardenolide and bufadienolide. The more prevalent in nature is the cardenolide type. Digitalis is plant containing cardio active glycosides , but the plant used in our laboratory is Nerium oleander of the family Apocyanaceae. Here the aglycone part is oleandrin. The isolation and extraction of the cardio active glycosides:
Cardio active glycosides :
Procedure : an alcoholic extract of the plant is prepared by maceration 10gm of the powdered leaf in 100ml of 70% ethanol for 24hr. The macerate then filtered through a sintered glass to yield a clear filtrate. Place 60ml of the alcoholic extract in a conical flask , and then add 25 ml of lead sub acetate. Mix thoroughly and allow standing for two min. placing the mixture in the centrifuge tubes and centrifuging for several min. decant and take the supernatant into a flasks and add 35ml of 10% sodium phosphate solution. Mix thoroughly and centrifuge. Now divide the mixture you had into two divisions. Fraction A: Take one of the two divisions you made above , and put in a separatory funnel , then shake it with three quantities each of 50ml of Chloroform ethanol ( 3:1 v/v ). Combine the organic extract , then dry by the addition of small quantity of anhydrous sodium sulphate and allow standing for a few minutes. Decants the Chloroform ethanol extract and reduce the volume to about 1ml on a rotatory evaporator or water bath. Fraction B: Place the other division of the extract in a conical flask, and then add 6ml of 4N HCl and place in a boiling water bath for 20 minutes. Cool the hydrolysate and transfer to a
separatory funnel , then partition with three quantities each of 25ml of Chloroform. Combine the Chloroform extracts and dry with a small quantity of anhydrous sodium sulphate. Decant the Chloroform and reduce the volume to about 1ml on a rotatory evaporator. The chemical test: 1. Baljet's test : the aim of it to identify the cardio active glycosides in general. Procedure : take one ml of fraction A, and add two drops of picric acid. Make it alkaline with sodium hydroxide solution. 2. Keller - Killians test : the identification of cardio active glycosides in general. Procedure: take two mls of fraction A , and add 3 ml of glacial acetic acid , add two drops of 0.1% of ferric chloride solution. Take 1 ml of concentrated H2SO4 and add to the above mixture in drops so as to make two layers.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Practical Pharmacognosy - Third YearDocumento43 paginePractical Pharmacognosy - Third YearraviomjNessuna valutazione finora
- PharmacognosyDocumento101 paginePharmacognosyimam mahdi tv officialNessuna valutazione finora
- GlycosidesDocumento52 pagineGlycosidesAhmed Kamran Abbasi50% (4)
- Glyc o SidesDocumento151 pagineGlyc o Sidesbakhtawar shaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- GlycosidesintroductionDocumento41 pagineGlycosidesintroductionvershaparchaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec.1 Glycosides Hala 2014 Pharos PDFDocumento9 pagineLec.1 Glycosides Hala 2014 Pharos PDFRamling PatrakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycosides: Next SlideDocumento4 pagineGlycosides: Next SlideJonafe JuntillaNessuna valutazione finora
- GlycosidesDocumento67 pagineGlycosidesdiptishona143100% (1)
- Experiment On TABADocumento15 pagineExperiment On TABAHanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Isolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesDocumento4 pagineIsolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesEvans DionNessuna valutazione finora
- Extraction and Hydrolysis of Glycogen and Characterization Tests For CarbohydratesDocumento7 pagineExtraction and Hydrolysis of Glycogen and Characterization Tests For CarbohydratesangelsiopaoNessuna valutazione finora
- BiochemistryDocumento6 pagineBiochemistrySofia AbainciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Isolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesDocumento4 pagineIsolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesNadz Gonzalez100% (3)
- Chem 600L Experiment 7 Oral ReportDocumento64 pagineChem 600L Experiment 7 Oral ReportAudrey100% (2)
- Histology: Introduction To Special Stains Techniques: Carbohydrates & AmyloidsDocumento22 pagineHistology: Introduction To Special Stains Techniques: Carbohydrates & Amyloidsapi-15026641100% (2)
- Lecture 6 - Glycosides ShortenedDocumento114 pagineLecture 6 - Glycosides ShortenedToukir AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycosides - Part 1Documento27 pagineGlycosides - Part 1Fuad RimawiNessuna valutazione finora
- Secondary Plant Metabolites (Active Constituents)Documento28 pagineSecondary Plant Metabolites (Active Constituents)fhruztrated_0095843Nessuna valutazione finora
- Glycosides May Be Defined As The Organic Compounds From PlantsDocumento16 pagineGlycosides May Be Defined As The Organic Compounds From Plantsratheeshkumar100% (2)
- UNIT4 Expt1Documento6 pagineUNIT4 Expt1Christian Franco RuizNessuna valutazione finora
- GLYCOSIDESDocumento31 pagineGLYCOSIDESasma nizamNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment On Phytochemical Study of Phospholipids % SteroidsDocumento27 pagineAssignment On Phytochemical Study of Phospholipids % Steroidsjaydeep raiyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycosides: Adila IbrahimDocumento11 pagineGlycosides: Adila IbrahimSamah AbboNessuna valutazione finora
- Formal Report FamsDocumento4 pagineFormal Report FamsAlexander David FamadulanNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycosides and TanninsDocumento73 pagineGlycosides and Tanninshermella tegegneNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar On Phytochemical Study of GlycosideDocumento39 pagineSeminar On Phytochemical Study of GlycosideINDER MAKHIJA100% (1)
- Cardiac GlycosidesDocumento11 pagineCardiac Glycosidesتقوى سميع مجيدNessuna valutazione finora
- Isolation, General Tests, and Hydrolysis of Polysaccharides Formal ReportDocumento4 pagineIsolation, General Tests, and Hydrolysis of Polysaccharides Formal ReportJuliefer May Fanilag Pleños100% (1)
- Experiment 2 Polysaccharides: Biochemistry Laboratory Manual Experiment 2Documento4 pagineExperiment 2 Polysaccharides: Biochemistry Laboratory Manual Experiment 2Pol Marasigan BanzonNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal GlycogenDocumento4 pagineJournal GlycogenJuvinch R. Vicente100% (2)
- Biochem. Lab. ReportDocumento18 pagineBiochem. Lab. ReportBernardo Milleniu De Vera100% (2)
- Chap 7 ALKALOIDSDocumento73 pagineChap 7 ALKALOIDSUkash sukarmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotech FR Exp 2Documento14 pagineBiotech FR Exp 2Nico YowNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Natural Products IntroductionDocumento21 pagineChapter 1 Natural Products IntroductionBakhita MaryamNessuna valutazione finora
- Life Process (Introduction)Documento13 pagineLife Process (Introduction)Dhruvi PanchalNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4secondary Metabolites FinalDocumento29 pagineChapter 4secondary Metabolites FinalDhruv KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- CHO Chemistry: Functions of CarbohydratesDocumento3 pagineCHO Chemistry: Functions of CarbohydratesSaadia AnjumNessuna valutazione finora
- Starch Hydrolysis by AmylaseDocumento13 pagineStarch Hydrolysis by AmylaseNahusenay TewodrosNessuna valutazione finora
- Starch Hydrolysis by AmylaseDocumento9 pagineStarch Hydrolysis by Amylasegaurav saxenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 6 Glycogen Intro and MethodsDocumento6 pagineExperiment 6 Glycogen Intro and Methodsvanessa olgaNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 8. Analysis of CarbohydratesDocumento3 pagineExercise 8. Analysis of CarbohydratesAte MerlsNessuna valutazione finora
- Isolation and Characterization of Saponifiable and NonDocumento18 pagineIsolation and Characterization of Saponifiable and NonJhoanna Rein Duzon100% (2)
- Glycogen Isolation 1 0Documento19 pagineGlycogen Isolation 1 0Sebastian SmytheNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry of Lipids PDFDocumento51 pagineBiochemistry of Lipids PDFZayan HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- AlkaloidsDocumento110 pagineAlkaloidsSarika Khosla100% (3)
- Glycogen Isolation and Determination ofDocumento14 pagineGlycogen Isolation and Determination ofChristian De LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Pharmacognosy Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Documento16 pagineChapter 4 Pharmacognosy Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Hannan MariyamNessuna valutazione finora
- PHR 113 GlycosidesDocumento20 paginePHR 113 GlycosidesRahul Banik888Nessuna valutazione finora
- AlkaloidsDocumento110 pagineAlkaloidsGrenadeforce100% (2)
- حل كتاب القسم كامل bio 102Documento46 pagineحل كتاب القسم كامل bio 102Naba KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- CarbohydratesDocumento12 pagineCarbohydratesDynamic & CannyNessuna valutazione finora
- Music Acid TestDocumento3 pagineMusic Acid TestainakmliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycosides Note - 2020 (JB)Documento11 pagineGlycosides Note - 2020 (JB)Jaytirmoy BarmonNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterDa EverandPlant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterNessuna valutazione finora
- The Greatest Classics of Russian Literature in One VolumeDa EverandThe Greatest Classics of Russian Literature in One VolumeNessuna valutazione finora
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDa EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Biochemistry Applied to Beer Brewing - General Chemistry of the Raw Materials of Malting and BrewingDa EverandBiochemistry Applied to Beer Brewing - General Chemistry of the Raw Materials of Malting and BrewingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Biochemistry Applied to the Brewing Processes - Fermentation and the Finished BeerDa EverandBiochemistry Applied to the Brewing Processes - Fermentation and the Finished BeerValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- 2 Benzoic AcidDocumento3 pagine2 Benzoic Acidvishwanathz47Nessuna valutazione finora
- 5 To Study The Presence of Insecticides and Pesticides in Fruits and VegetablesDocumento1 pagina5 To Study The Presence of Insecticides and Pesticides in Fruits and Vegetablesvishwanathz47Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Analysis of Fluoride in Ground Water and Potable WaterDocumento2 pagine1 Analysis of Fluoride in Ground Water and Potable Watervishwanathz47Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Determination of Complex Ion by Jobs MethodDocumento2 pagine3 Determination of Complex Ion by Jobs Methodvishwanathz47Nessuna valutazione finora
- Qualitative Tests For PhytochemicalsDocumento9 pagineQualitative Tests For Phytochemicalsvishwanathz47Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ephedra FoliataDocumento16 pagineEphedra Foliatavishwanathz47Nessuna valutazione finora
- MahabharataDocumento20 pagineMahabharataKetan Bhatt100% (3)
- Pilot'S Operating Handbook: Robinson Helicopter CoDocumento200 paginePilot'S Operating Handbook: Robinson Helicopter CoJoseph BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Interactions PDFDocumento1 paginaProcess Interactions PDFXionNessuna valutazione finora
- Vodafone M2M Integrated M2M Terminals Overview BrochureDocumento4 pagineVodafone M2M Integrated M2M Terminals Overview BrochureJamie JordanNessuna valutazione finora
- Writing Task The Strategy of Regional Economic DevelopementDocumento4 pagineWriting Task The Strategy of Regional Economic DevelopementyosiNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank For Vlsi LabDocumento4 pagineQuestion Bank For Vlsi LabSav ThaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fletcher Theophilus Ato CVDocumento7 pagineFletcher Theophilus Ato CVTHEOPHILUS ATO FLETCHERNessuna valutazione finora
- Overcurrent CoordinationDocumento93 pagineOvercurrent CoordinationKumar100% (1)
- Your Electronic Ticket ReceiptDocumento2 pagineYour Electronic Ticket Receiptjoana12Nessuna valutazione finora
- CBC Building Wiring Installation NC IIDocumento72 pagineCBC Building Wiring Installation NC IIFaysbuk KotoNessuna valutazione finora
- Income Tax Calculator 2023Documento50 pagineIncome Tax Calculator 2023TARUN PRASADNessuna valutazione finora
- Defeating An Old Adversary Cement Kiln BallsDocumento5 pagineDefeating An Old Adversary Cement Kiln BallsManish KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Hierarchy of The Inchoate Crimes: Conspiracy Substantive CrimeDocumento18 pagineHierarchy of The Inchoate Crimes: Conspiracy Substantive CrimeEmely AlmonteNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.admin Rosal Vs ComelecDocumento4 pagine9.admin Rosal Vs Comelecmichelle zatarainNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuitos Digitales III: #IncludeDocumento2 pagineCircuitos Digitales III: #IncludeCristiamNessuna valutazione finora
- Power For All - Myth or RealityDocumento11 paginePower For All - Myth or RealityAshutosh BhaktaNessuna valutazione finora
- Exoskeleton ArmDocumento5 pagineExoskeleton Armc214ocNessuna valutazione finora
- We Move You. With Passion.: YachtDocumento27 pagineWe Move You. With Passion.: YachthatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Terms and Conditions 27 06 PDFDocumento4 pagineTerms and Conditions 27 06 PDFShreyash NaikwadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lexington School District Two Return To School GuideDocumento20 pagineLexington School District Two Return To School GuideWLTXNessuna valutazione finora
- Sony SL HF-900 Owners ManualDocumento53 pagineSony SL HF-900 Owners ManualThomas Christoph100% (1)
- Rs 422Documento1 paginaRs 422rezakaihaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Purchases + Carriage Inwards + Other Expenses Incurred On Purchase of Materials - Closing Inventory of MaterialsDocumento4 paginePurchases + Carriage Inwards + Other Expenses Incurred On Purchase of Materials - Closing Inventory of MaterialsSiva SankariNessuna valutazione finora
- MWG Installation 7.6.2 IG INSTALLATION 0516 en - PDDocumento64 pagineMWG Installation 7.6.2 IG INSTALLATION 0516 en - PDjbondsrNessuna valutazione finora
- SMK Techno ProjectDocumento36 pagineSMK Techno Projectpraburaj619Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sangeetahealingtemples Com Tarot Card Reading Course in UsaDocumento3 pagineSangeetahealingtemples Com Tarot Card Reading Course in UsaSangeetahealing templesNessuna valutazione finora
- Toa Valix Vol 1Documento451 pagineToa Valix Vol 1Joseph Andrei BunadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Capsule Research ProposalDocumento4 pagineCapsule Research ProposalAilyn Ursal80% (5)
- Communication On The Telephone InfoDocumento30 pagineCommunication On The Telephone Infomelese100% (1)
- PHP IntroductionDocumento113 paginePHP Introductionds0909@gmailNessuna valutazione finora