Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Transverse Frame Analysis
Caricato da
Florin PanianopolDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Transverse Frame Analysis
Caricato da
Florin PanianopolCopyright:
Formati disponibili
TRANSVERSE FRAME AI\ALISYS
l. STRUCTURAL LAYOUT
See the transverse section (cross-section of the building).
2.
STRUCTURAL CONFIGURATION AND LOADING
Single storey sway frame
l0 ?
l,
latEral support, =,vBrtj,cd bfacing
between tws Dolur.TflS' of the longitr.roiRal: fram,E
. :
wlnd pressure
wlnd sucti0n
3. LOADS" LOAD
FACTORS, LOAD COMBINATIONS
Loads
Nominal Load
Factor
of
Safety
1.35
Factored Load
IrN/m2]
0.45...0.50
tKN/m1
+
Dead Loads
Roofweight:.....
-hy dro-insulation (tar roofi ng)
(P)
Permanent Loads
-thermal insulation (mineral wool) -corrugated sheet
4 *
Purlin weight: Truss weisht:. Industrial dust:....
Technological Ioad :CeXCtX|lX
0.10...0.15
0.15 0.25 0.20
1.35 1.35 1.35 1.35
(c)
+ +
Snow:
where:
grourrd snow load (as is shown in ground snow load map)
Ss1
exposure factor (to account for wind effects); c": 1.00 fornormal conditions of exposure. ct: therml factor; ct: 1.00
ce:
1.s0
Variable Loads
(V)
(environmental ioads)
Wind
pr=C"xCnxEref
- Pressure
cn: *
c
0'8 o: - 0.3
cofficients
wind Pressure wind suction
1.50
- Velocity pressure exposure cofficienl c-: iosk m ljI_Q_E2-04;
- .4*:
the basic wind veiocity pressure (to 10m above the ground), see the
project data.
Earthquake (|Jormativ
Sersmrc Force
:
P 1 00-92)
G is the total weight of building as follows
. . o
dead loads
pefinanenl ioads snow (y
I |
y
(nomrnalloads)
"*pr);
":0.40 )
F, *a,
q
Cr=d
(global seismic factor)
a =7.0O
a
is the Importance factor.for normal buildings; ts tl;re grormd acceleration according to seismic risk zones (on the map);
.i...rr:,
rr:o2\ ':'' :o
A trno: 1
. .t
dno ts
UN
JEI
,,11,
' I
.$e
'.
: rrr
{ClTl l
"-.
-l- . : lr. / .
li l
'l
4i-?
: rnl$ ./$)
,l/
d;
="
dns
F,=2.75 if T" <7"; F,=2.75-(E-7,)>7 tf T,>7" (4 is the Site Structure Resonance Factor);
I f
q
is the fundamental elastic period of vibration of the building;
is the Seismic Zone Dumping Period (Dumping Period Map);
3 for transverse frame;
q:
4 for longitudinal braced bay.
(the Ductility Factor);
e,: 1.00 is the Equivalency
structure to the first degree.
Factor befween effeetive structure and statically indeterminate
b)IPi* T"xSnow+Seism
LOAD COMBINATIONS a) ) 1.35 x Pi + 1.5 x Vi+ 0.7 xl1.5
V.;
(V:
y,:0.40.
varable loads)
DETERMINATION OF THE LOADS AND MOMENT DISTRIBUTION
i.
Permanent
(P):
''. ",
:: ,,
A;n(,fcr Blmlum:?)
:
Q(rl = P" x Aou. tKNl
t:: 1.. :.:::::
',1,,',,,,,, :::-: ,1,,,
Q(rl=
t4of
r" xAor tKNl
t: l:
r
',,1"
'l.,.,'l ", "
: txL/2
2.
Cvasipermanent (C)
Of^,=C'xA,*\L ) Oi-r=Cn xA.UJJ
tKN] tKN]
gtg/4x
Snow (Z)
Z" = Tp x pzxAq, tKN] Z" =T,x P,xAor. tKN]
4.
O ro ct
I
Wind (W)
n
L,
pressure
I:
P,
= 1.60 x 0.80 x
p;
r(z)x g, =1.60x0.40 xcr(z)x g*
c
I [KNlmz ]
IIQ\Imz
suction
-+ 4 = p* xt + p", = p, *y, xt p: p;
=
IKN/ml;
W=
pr,ou"rog,
x1.35x t -+W" =W
xTp
tKN]
P.
P,xTp IKN/ml;
W'= p'r,*"*snxl.35x t -+W"
-W'xTp IKN]
H H
H H
This frame is indeterminate to the first degree; it is a sidesway frame (oint translation is possible).
H H H
F;
Mr (<M r)
Calculation of bending moment distribution
arlificial joint restraint
step
sep 2
Moment induced due to joint
trenslation
Moment induced if sidesway is
prevented
a_a_
R=W" +W'" +r-x
p:" x& +
i,
p''. *h
M'r=
rt"+
Pt"'"i
D
M''=
h2
M'= Lx h
2
->
WWMlffi^
= M'n+.
5.
Seismic Force (S)
=!^h 2
lKNml
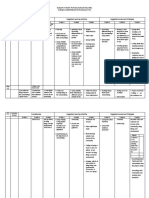
Results of calculation: After finishing all the calculations, the results will be centraltzedin the follor,ving table for both sections 1 -1 and 2 - 2 of the column.
Column sketch
0
Section
I
Efforts
2
Permanent Loads (Pr) Factored
J
Quasipermanent
Snow
Loads
5
(Cr)
6 7
(z)
Factored
Nominal
4
Factored
Nominal
Nominal
8
M &Nm)
l-1
ftN)
T (kN)
M
aa
(kNm) N
ftN)
T &N)
(The nominal load for snow is considered for the earthquake combination
- 0.30 x p,)
Wind
Eartquake
Relevant Load Combinations
(w)
Factored
9
(s)
n.lx Pi+
nix C;* nex
nix Vi
7+9
M-"* N-io l3
P1+
I Ci+ y"xZ + S 46810
N-o
M"^"
15
S=crxG
i0
M-u* N"^, l1
N-u* M"^.
M-u"
N"o.
M*ur.
N-;.
76
I2
l4
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Python BookDocumento669 paginePython BookK Kunal Raj100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- A Practical Guide To IFRS - Revenue Rec. - Engenering and Construction Industry SupplementDocumento11 pagineA Practical Guide To IFRS - Revenue Rec. - Engenering and Construction Industry SupplementFlorin PanianopolNessuna valutazione finora
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Finishing Works Project: Student: Panianopol Florin Fils An Iv Grupa 2Documento13 pagineFinishing Works Project: Student: Panianopol Florin Fils An Iv Grupa 2Florin PanianopolNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- LemnDocumento6 pagineLemnFlorin PanianopolNessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- CHAPTER 8-Lecture 9Documento5 pagineCHAPTER 8-Lecture 9Florin PanianopolNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Politici Monetare InternationaleDocumento1 paginaPolitici Monetare InternationaleFlorin PanianopolNessuna valutazione finora
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- CHAPTER 8-Lecture 7Documento6 pagineCHAPTER 8-Lecture 7Florin PanianopolNessuna valutazione finora
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Lemn CursuriDocumento5 pagineLemn CursuriFlorin PanianopolNessuna valutazione finora
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Journey To The Centre of The Earth by Jules Verne Retold by Elizabeth Gray Book PDFDocumento35 pagineJourney To The Centre of The Earth by Jules Verne Retold by Elizabeth Gray Book PDFElian LimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- Case Study #1: Public-Private PartnershipsDocumento4 pagineCase Study #1: Public-Private PartnershipsJulan CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Raz ls35 Penguins CLR PDFDocumento11 pagineRaz ls35 Penguins CLR PDFAnonymous 8LSJvbNessuna valutazione finora
- Science GR 345 4th Quarter MG Bow 1Documento8 pagineScience GR 345 4th Quarter MG Bow 1api-359551623Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Munters Seminar: Controlling Humidity for Preservation ApplicationsDocumento35 pagineMunters Seminar: Controlling Humidity for Preservation ApplicationsMoe LattNessuna valutazione finora
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- ClimateDocumento26 pagineClimateJenny ManagoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Air Pollution: Effects and Control MeasuresDocumento11 pagineAir Pollution: Effects and Control MeasuresPark Soo HaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- From the Hollow World Set, Dungeon Master's Sourcebook, Atlas, pp. 80-85Documento23 pagineFrom the Hollow World Set, Dungeon Master's Sourcebook, Atlas, pp. 80-85Arghya RaihanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nimbus, Cumulus, Stratus, Cirrus cloud typesDocumento2 pagineNimbus, Cumulus, Stratus, Cirrus cloud typesMarianne FelixNessuna valutazione finora
- Geo Engineering April 23, 2020Documento17 pagineGeo Engineering April 23, 2020Captain HendoNessuna valutazione finora
- Equest Training Work BookDocumento602 pagineEquest Training Work BookMason LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Flight Behaiour Assignment FinalDocumento6 pagineFlight Behaiour Assignment FinalUnmesh BiswasNessuna valutazione finora
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Society and Cultures of DisasterDocumento251 pagineSociety and Cultures of DisasterJohn Cedrick JagapeNessuna valutazione finora
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- Literary Analysis and in Another Country by ErnestDocumento9 pagineLiterary Analysis and in Another Country by Ernestapi-237740013Nessuna valutazione finora
- Causes of Climate ChangeDocumento24 pagineCauses of Climate ChangeToby Zayontz100% (1)
- Detail - Juli 2019Documento140 pagineDetail - Juli 2019Pepo Girones Masanet100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Bison Epoxy 5 MinDocumento1 paginaBison Epoxy 5 MinRadu ConstantinNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrology: Hydrology (Agriculture) Hydrology (Album) Outline of HydrologyDocumento6 pagineHydrology: Hydrology (Agriculture) Hydrology (Album) Outline of HydrologyBernard PalmerNessuna valutazione finora
- Water ResourceDocumento6 pagineWater ResourceElmaeen Bitang BagiohanonNessuna valutazione finora
- ProportionAndRates WEBDocumento36 pagineProportionAndRates WEByonesNessuna valutazione finora
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Vega Atlantic CrossingDocumento6 pagineVega Atlantic Crossingjoswas100% (2)
- ARAB 102 Review This & Ism Wa SifaDocumento1 paginaARAB 102 Review This & Ism Wa Sifaresilient34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Week6 Module 6Documento15 pagineWeek6 Module 6BENNY CALLONessuna valutazione finora
- Why Does Trend Following WorkDocumento3 pagineWhy Does Trend Following Workapi-3701488Nessuna valutazione finora
- Centralbusstationvadodara 150209122028 Conversion Gate02Documento11 pagineCentralbusstationvadodara 150209122028 Conversion Gate02Pranshu Natekar100% (12)
- Polillo Conservation DataDocumento20 paginePolillo Conservation DatamgllacunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Official SSC CHSL Question Paper 19th Jan 2017 Tier I With Answer KeyDocumento24 pagineOfficial SSC CHSL Question Paper 19th Jan 2017 Tier I With Answer Keynidhi tripathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Charlie and LolaDocumento22 pagineCharlie and LolaPeterHanley100% (1)
- C208 Technical LecturesDocumento73 pagineC208 Technical Lecturesschabur412389% (9)
- Periodic Test in Science 4 1st - 4thDocumento17 paginePeriodic Test in Science 4 1st - 4th엘라엘라Nessuna valutazione finora
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)