Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
NURSING CARE PLAN for 8yo Male with CHD
Caricato da
Donna Co IgDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
NURSING CARE PLAN for 8yo Male with CHD
Caricato da
Donna Co IgCopyright:
Formati disponibili
NURSING CARE PLAN
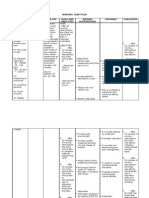
Baseline data of client: Name: A. J. Mondejar Age: 8y.o. Sex: Male Cues Nursing Diagnosis A. Actual or Abnormal Cues Subjective: Patient verbalizes complaints of frontal splitting headache: Sakit akun ulo; dw mabuka. Patient verbalizes complaints of cramplike pain of lower extremitie s (intermitte nt claudicatio n): Daw ga binhod akun tiil; felt either together Ineffective Cerebral, Cardiopulmonary & Peripheral Tissue Perfusion R/T impaired transport of oxygen secondary to Congenital Heart Defect: Tetralogy of Fallot AEB dyspnea upon exertion, frontal splitting headache, intermittent claudication, restlessness, generalized weakness of extremities, clubbing of fingers and toes, mild cyanosis of fingernails and toenails, delayed physical growth and development, and mild bradycardia. Chief Complaint: headaches & chills Medical Diagnosis: CHD (Congenital Heart Defect: ToF) in Failure Attending Physician: Dr. Castronuevo Pathophysiology of Tetralogy of Fallot Desired Nursing Outcome Intervention Predisposing factors: After 8 hours of A. Independent Advanced maternal age nursing Genetic predisposition intervention, the client will be able Congenital Heart Defect: Tetralogy of Fallot to: Structural malformation of the heart Large Sub-aortic ventricular septal defect Pulmonic Stenosis 1. Folks will be 1. a. Educate able to verbalize parents as needed understanding of regarding condition, congenital heart therapy regimen, disease. purpose of medications, and when to contact healthcare provider. 1.b. Provide information on normal tissue perfusion and possible causes for impairment. c. Instruct folks to inform the nurse immediately if symptoms of decreased perfusion persist, increase, or
Justification
Evaluation After 8 hours of nursing intervention:
Overriding of Aorta
Decreased Pulmonary blood flow
Increased effort to force blood through the pulmonary artery
Decreased amount of oxygenated blood returning to the heart
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Parents need an understanding of patients condition to respect and comply with the need for rest and medications. Knowledge of causative factors provides understanding for treatments. Early assessment facilitates prompt treatment.
1.Goal met Folks were able to recognize the severity of the disease including the Importance of therapy regimen to improve patients condition AEB active participation during discussions, compliance to medications and verbalizations of the need to contact health provider when patient complains of difficulty of breathing and presence of cyanosis.
Increased pressure at the right side of the heart
20
with splitting headache or independe ntly. Patient verbalizes feeling of dyspnea upon exertion: Kabudlay magginhawa kng daw makapuya n or mamwersa ko. Objective: Clubbing of fingers and toes Mild cyanosis of fingernails and toenails noted Generalized weakness of extremities noted Restlessness noted Delayed physical growth and development:
Definition: Decrease in oxygen resulting in the failure to nourish the tissues at the capillary level. [Tissue perfusion problems can exist without decreased cardiac output; however there may be a relationship between cardiac output and tissue perfusion.] Source: NANDA 11th Edition
Venous blood from right ventricle shunted to left ventricle via ventricular septal defect Mixing of oxygenaed and unoxygenated blood Preferential flow of the mixed blood from both ventricles through the dextropositioned aorta
return (e.g. cyanosis and difficulty of breathing). c. 2.a. Discuss the These importance of positions exert prevention of pressure on 2. Demonstrate venous stasis (e.g. vessels in the behaviors/ not crossing legs, lower lifestyle changes and elevating feet extremities, to improve without bending which circulation such knees.) compromises as the blood flow. performance of 2.b. Provide for a Rest is a major ROM exercises quiet atmosphere aspect of care and prevention of and limit since it venous stasis. procedures to reduces the those that are metabolic rate necessary to and tissue provide for rest oxygen periods. demand. 2.c If the client is To enhance on bed rest, instruct venous return. and assist with range of motion exercises at least 3 times/day and active foot and leg exercises every 1-2 hours. 2.d.Implement measures to prevent vasoconstriction: Vasoconstricti on narrows vessel lumens, which results 2. Goal met Patient and SO were able to implement behavioral changes to improve blood flow AEB able to rest with minimal disruption, performance of assistive exercises under the supervision of the nurse and avoidance of activities that may cause venous stasis.
Low blood oxygen saturation in systemic circulation Ineffective Cerebral, Cardiopulmonary & Peripheral Tissue Perfusion
Sources: Textbook of Pediatrics; 15th Edition by Behrman, Klegman & Arvin Pediatrics; January 1991 Edition Maternal & Child Health Nursing; 5th Edition by Pillitteri Understanding Pathophysiology 3rd Edition by Sue E. Huether and Kathryn L. McCane
21
Wt.: 19.3kg; Ht.: 123 cm (Normal: Wt: 39kg; Ht: 142cm) Weak but palpable pulse of 66bpm as of 8pm of 10-08-08 Presence of systolic murmur upon auscultation of left sternal border 2-D Echo findings 10-0608: ToF with severe infundibular pulmonic stenosis; Mild aortic insufficiency; Right atrial enlargement; Right ventricular enlargement; Right ventricular hypertrophy; Good cardiac contractility; McGoons index: 1.4-1.5 CT Scan findings as of
2.
e.perform actions to reduce stress
in diminished blood flow through the affected vessels. Stress stimulates the sympathetic nervous system, which results in vasoconstricti on. When the body is cold, peripheral constriction occurs in an attempt to contain body heat.
2.f. Perform actions to keep client from getting cold (e.g. maintain a comfortable room temperature, provide adequate clothing and blankets)
3. Demonstrate increased perfusion as individually
3.a. Elevate head of bed by 10 and maintain head/neck in midline or neutral position.
To promote circulation/ven ous drainage and increase gravitational blood flow.
3.Goal met patient was able to exhibit signs of increased tissue perfusion AEB degree of cyanosis at the fingernails and toenails lessened, able to transfer form
22
10-07-08 show presence of multiple brain abscess (Left tempoparietal; Left parietosagittal) B. Risk Related Factors Condition may call for multiple hospitalizations Monetary constraints C. Strengths Strong belief in God Good emotional support from family Positive outlook regarding condition
appropriate as characterized by decreased cyanosis & episodes or extent of pain and observable increase in activity tolerance.
3.b.If hypoxic Squatting spells occur, gives relief to instruct patient to an assume a squatting overstressed position if dyspneic heart by or knee-chest trapping blood position. in lower extremities; knee-chest position increases intraabdomina l pressure; decreases systemic venous return; decreases right-to-left shunting. B. Collaborative Assist with To improve tissue treatment of underlying perfusion/orga n function. conditions such as administration of medications for infections, as indicated. Monitor laboratory Polycythemia findings (CBC) for causes blood polycythemia, to become thick, so clots decreased blood glucose levels and in blood vessels may reduced oxygen
bed to chair, reduced frequency of complains of pain and splitting headache, and able to perform ADLs with minimal support such as feeding oneself.
23
saturation; refer.
occur; children with cyanotic heart disease are likely to develop hypoglycemia; thus proper intervention will be undertaken. Dyspneic attacks may be precipitated by iron deficiency; iron therapy improves exercise tolerance & general well being.
Monitor for relative iron deficiency; refer.
Review medical To maintain regimen and physical safety appropriate safety of patient. measures in assisting with administration of Diazepam prn for frank seizures.
24
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Bleeding NCPDocumento13 pagineBleeding NCPBiway Regala100% (1)
- NCP Nausea and VomitingDocumento4 pagineNCP Nausea and VomitingKingJayson Pacman06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care for Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocumento4 pagineNursing Care for Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusionalliahjoyce ignacioNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessing Nursing Diagnoses and Expected OutcomesDocumento20 pagineAssessing Nursing Diagnoses and Expected OutcomesZamranosNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 pagineTissue PerfusionMichael John LeandichoNessuna valutazione finora
- Disturbed Sleep PatternDocumento2 pagineDisturbed Sleep PatternROxanne S. RendonNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology Sickle Cell AnemiaDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology Sickle Cell AnemiaTine GuibaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan for Acute Pain ManagementDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan for Acute Pain ManagementSheene Lysethea Sioteco AguilosNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan for Billy Admitted with Ear and Throat InfectionsDocumento6 pagineNursing Care Plan for Billy Admitted with Ear and Throat InfectionsNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- Problem PrioritizationDocumento2 pagineProblem PrioritizationRegie GonzagaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP LymphomaDocumento4 pagineNCP LymphomaRene John Francisco100% (2)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento3 pagineIneffective Tissue PerfusionMitsika AnadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Precipitous Labor/Delivery or Unplanned/Out-of-Hospital DeliveryDocumento7 paginePrecipitous Labor/Delivery or Unplanned/Out-of-Hospital DeliveryLei Ortega100% (1)
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocumento1 paginaNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNessuna valutazione finora
- Hirschsprung Disease: A Congenital Birth Defect of the IntestinesDocumento3 pagineHirschsprung Disease: A Congenital Birth Defect of the IntestinesJan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Coronary Artery Disease Care PlanDocumento2 pagineCoronary Artery Disease Care PlanDanelle Harrison, RN100% (2)
- Erceflora Antidiarrheal ClassDocumento1 paginaErceflora Antidiarrheal ClassfLOR_ZIANE_MAENessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan for 1-Year-Old Male Admitted for Dehydration and SeizuresDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan for 1-Year-Old Male Admitted for Dehydration and SeizuresKwini Jeyn50% (2)
- Aspirin Uses, Side Effects, Interactions and Nursing ConsiderationsDocumento4 pagineAspirin Uses, Side Effects, Interactions and Nursing ConsiderationsAubrey Unique EvangelistaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocumento12 pagineNCP - Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisAya BolinasNessuna valutazione finora
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCYDocumento2 paginePATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCYrye100% (1)
- Discharge PlanningDocumento3 pagineDischarge PlanningAlex Marie100% (2)
- POST NATAL FNCP - DotdotDocumento1 paginaPOST NATAL FNCP - DotdotGiselle EstoquiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Interventions for Ineffective Breathing PatternDocumento1 paginaNursing Interventions for Ineffective Breathing PatternnikkilyceeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ov Ov OvDocumento15 pagineOv Ov OvHayyana Mae Taguba LadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- TAT and TIG Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineTAT and TIG Drug StudyMaria NorilynNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Raynauds Disease-Acute PainDocumento3 pagineNCP Raynauds Disease-Acute PainEerie EraNessuna valutazione finora
- FHP SampleDocumento8 pagineFHP SampleJade GordoncilloNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP PrioritizationDocumento7 pagineNCP PrioritizationLouwella RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Interventions for Fever Management: Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, and EvaluationDocumento1 paginaNursing Interventions for Fever Management: Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, and EvaluationChristine Esguerra OrozcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Neonatal SepsisDocumento2 pagineStudent Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Neonatal SepsisChristian Remetio100% (1)
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFDocumento2 pagineNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFswapnilazarusNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDocumento1 paginaAcute GlomerulonephritisTaz Bagul MutiNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Patient For Electrocardiogram (ECG)Documento1 paginaNCP - Patient For Electrocardiogram (ECG)SelwynVillamorPatenteNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study: Acetaminophen Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento1 paginaDrug Study: Acetaminophen Nursing ResponsibilitiesAyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study NCP ActualDocumento3 pagineCase Study NCP Actualdhamy florNessuna valutazione finora
- Individual Case Study Acute GlomerulonephritisDocumento26 pagineIndividual Case Study Acute GlomerulonephritisBatrisyia HalimsNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocumento1 paginaNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationlaehaaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan for a Child with IntussusceptionDocumento1 paginaNursing Care Plan for a Child with IntussusceptionCharina Aubrey100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento6 pagineNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceCaroline ChaNessuna valutazione finora
- Subjective: Short Term Goal: Independent: Short Term EvaluationDocumento2 pagineSubjective: Short Term Goal: Independent: Short Term EvaluationKyla Castro100% (1)
- Nifedepine Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineNifedepine Drug StudyCheezy BreadNessuna valutazione finora
- D 5 IMBDocumento2 pagineD 5 IMBAloyan Rose JoyNessuna valutazione finora
- CELINDocumento9 pagineCELINaikoestrellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento3 pagineIneffective Tissue PerfusionAngel Hernandez100% (1)
- Assessing Seizure Risk and InterventionsDocumento2 pagineAssessing Seizure Risk and Interventionshanyaklein100% (3)
- Client Initials: Medical Diagnosis: Cephalopelvic Disproportion Eu DEFINITION: The RelationshipDocumento2 pagineClient Initials: Medical Diagnosis: Cephalopelvic Disproportion Eu DEFINITION: The RelationshipLyssa Monique67% (3)
- Drug Study LosartanDocumento3 pagineDrug Study LosartanChris Denver BancaleNessuna valutazione finora
- CHRONIC HEART FAILURE CASE STUDYDocumento12 pagineCHRONIC HEART FAILURE CASE STUDYMary Cris CanonNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulmonary Hypertension, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesDa EverandPulmonary Hypertension, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Peripheral Tissue PerfusionDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan Ineffective Peripheral Tissue PerfusionRosalie Delfin90% (10)
- Nursing Care for Critically Ill MI Patient in CCUDocumento14 pagineNursing Care for Critically Ill MI Patient in CCUTukiminNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM 106 Acute Biologic CrisisDocumento142 pagineNCM 106 Acute Biologic CrisisEllamae Chua88% (8)
- SCI Case Study Key QuestionsDocumento4 pagineSCI Case Study Key QuestionsDeez NutsNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseDocumento16 pagineHypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseTintin Ponciano100% (1)
- Truncus ArteriosusDocumento20 pagineTruncus ArteriosusjustinahorroNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnosing Isolated Systolic HypertensionDocumento4 pagineDiagnosing Isolated Systolic HypertensionVien Marie Palaubsanon SilawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Angina Pectoris Pathophysiology, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocumento8 pagineAngina Pectoris Pathophysiology, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentPrince DuNessuna valutazione finora
- Case 5: Tutor GuideDocumento18 pagineCase 5: Tutor GuidelubnaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM 118 L 3rd ExamDocumento3 pagineNCM 118 L 3rd Examj UNessuna valutazione finora
- Abbreviations & SymbolsDocumento2 pagineAbbreviations & SymbolsDonna Co IgNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical ExaminationDocumento2 paginePhysical ExaminationDonna Co IgNessuna valutazione finora
- HodgkinDocumento6 pagineHodgkinDonna Co IgNessuna valutazione finora
- ANATOMY and Physiology Case PreDocumento4 pagineANATOMY and Physiology Case PreDonna Co IgNessuna valutazione finora
- A.Maternal and Birth History: TreatmentDocumento5 pagineA.Maternal and Birth History: TreatmentDonna Co IgNessuna valutazione finora
- AsepsissDocumento3 pagineAsepsissDonna Co IgNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Surgical InstrumentsDocumento37 pagineBasic Surgical Instrumentsapi-2658787991% (33)
- TractionDocumento2 pagineTractionDonna Co IgNessuna valutazione finora
- AneurismDocumento3 pagineAneurismDonna Co IgNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Objective Content Teaching Strategy Time Alloted EvaluationDocumento3 pagineLearning Objective Content Teaching Strategy Time Alloted EvaluationAmera DimatingcalNessuna valutazione finora
- Case ProgressionDocumento2 pagineCase Progressionczeremar chanNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF 4 Admission of Neonates in The Neonatal Intensive Care UnitsDocumento7 paginePDF 4 Admission of Neonates in The Neonatal Intensive Care UnitsSanjay Kumar SanjuNessuna valutazione finora
- 2010 Guideline AFDocumento61 pagine2010 Guideline AFyamtotlNessuna valutazione finora
- Spindle Cell TumorsDocumento138 pagineSpindle Cell TumorsMadhura ShekatkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Cervicovaginitis.Documento23 pagineAcute Cervicovaginitis.Kevin VillagranNessuna valutazione finora
- فندمنتل وظيفة رقم 2Documento2 pagineفندمنتل وظيفة رقم 2Dental LecturesMMQNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood TransfusionDocumento30 pagineBlood TransfusionnoorgianilestariNessuna valutazione finora
- Herpes Zoster OticusDocumento12 pagineHerpes Zoster Oticusraghad.bassalNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood and Tissue Flagellates para LecDocumento8 pagineBlood and Tissue Flagellates para LecLian MallareNessuna valutazione finora
- Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia - UpToDateDocumento22 pagineHereditary Spastic Paraplegia - UpToDateMatheus AraújoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 20 - Keith Conners PioneersDocumento4 pagineChapter 20 - Keith Conners PioneersMaro KaNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 5 Research Paper 22the Causes of The Increasing Anxiety Amongst The Grade 10 Student of Maligaya Highschool22 1Documento3 pagineGroup 5 Research Paper 22the Causes of The Increasing Anxiety Amongst The Grade 10 Student of Maligaya Highschool22 1Lean De MesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Status of PPR in Nepal 2007Documento14 pagineStatus of PPR in Nepal 2007anon-921861100% (2)
- Multi Lab Id ReportDocumento12 pagineMulti Lab Id ReportMayuresh NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- CV SAMEEP - PathologistDocumento7 pagineCV SAMEEP - PathologistMumtaj AnsariNessuna valutazione finora
- ClonidineDocumento4 pagineClonidineJoshua GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Prostate Cancer PDFDocumento2 pagineProstate Cancer PDFkapczukNessuna valutazione finora
- 1903 Pediatric Acute Icu: Anthony - Lee@Utsouthwestern - EduDocumento4 pagine1903 Pediatric Acute Icu: Anthony - Lee@Utsouthwestern - EdurupaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Travel and PneumothorakDocumento7 pagineAir Travel and PneumothorakRojullun TaufikNessuna valutazione finora
- Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)Documento70 pagineIschemic Heart Disease (IHD)Deborah AnnNessuna valutazione finora
- Insert - Elecsys CEA.07027079500.V5.EnDocumento4 pagineInsert - Elecsys CEA.07027079500.V5.EnVegha NedyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Salmonella in The CaribbeanDocumento3 pagineSalmonella in The CaribbeanAlvin KiruiNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic Disorders Screening and PreventionDocumento36 pagineGenetic Disorders Screening and PreventionManovaPrasannaKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamicsofdiseasetransmission 160905060144Documento33 pagineDynamicsofdiseasetransmission 160905060144Samjaisheel SamsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Nicu Observation SummaryDocumento2 pagineNicu Observation Summaryapi-663517905Nessuna valutazione finora
- Health Assessment 9Documento16 pagineHealth Assessment 9shannon c. lewisNessuna valutazione finora
- ROLE OF A MICROBIOLOGIST IN PREVENTION OF HEALTHCARE-ASSOCIATED INFECTIONS - v3Documento12 pagineROLE OF A MICROBIOLOGIST IN PREVENTION OF HEALTHCARE-ASSOCIATED INFECTIONS - v3vijayasree bavireddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Poliomyelitis: Dr. Eiman Sumayyah DPT (Kmu), Ms Neuro (Kmu)Documento14 paginePoliomyelitis: Dr. Eiman Sumayyah DPT (Kmu), Ms Neuro (Kmu)Haniya KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study FluvoxamineDocumento2 pagineDrug Study FluvoxamineAngeline de Gala0% (1)