Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Coombs Test
Caricato da
ANIS MURNIATIDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Coombs Test
Caricato da
ANIS MURNIATICopyright:
Formati disponibili
Coombs test (also known as Coombs' test, antiglobulin test or AGT) refers to two clinical blood tests used
in immunohematology and immunology. The two Coombs tests are the direct Coombs test (DCT, also known as direct antiglobulin test or DAT), and the indirect Coombs test (also known as indirect antiglobulin test or IAT). The Direct Coombs test is used to test for autoimmune hemolytic anemia; ie, a condition of a low count of red blood cells (aka RBCs) caused by immune system lysis or breaking of RBC membranes causing RBC destruction. In certain diseases or conditions an individual's blood may contain IgG antibodies that can specifically bind to antigens on the RBC surface membrane, and their circulating RBCs can become coated with IgG alloantibodies and/or IgG autoantibodies. Complement proteins may subsequently bind to the bound antibodies and cause RBC destruction. [1] The direct Coombs test is used to detect these antibodies or complement proteins that are bound to the surface of red blood cells; a blood sample is taken and the RBCs are washed (removing the patient's own plasma) and then incubated with antihuman globulin (also known as "Coombs reagent"). If this produces agglutination of RBCs, the direct Coombs test is positive, a visual indication that antibodies (and/or complement proteins) are bound to the surface of red blood cells. The indirect Coombs test is used in prenatal testing of pregnant women, and in testing blood prior to a blood transfusion. It detects antibodies against RBCs that are present unbound in the patient's serum. In this case, serum is extracted from the blood sample taken from the patient. Then, the serum is incubated with RBCs of known antigenicity; that is, RBCs with known reference values from other patient blood samples. If agglutination occurs, the indirect Coombs test is positive. [2] Mechanism
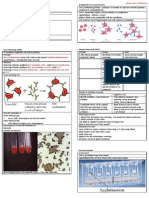
Schematic showing the direct and indirect Coombs tests. The two Coombs tests are based on the fact that anti-human antibodies, which are produced by immunizing non-human species with human serum, will bind to human antibodies, commonly IgG or IgM. Animal anti-human antibodies will also bind to human antibodies that may be fixed onto antigens on the surface of red blood cells (also referred to as RBCs), and in the appropriate test tube conditions this can lead to agglutination of RBCs. The phenomenon of agglutination of RBCs is important here, because the resulting clumping of RBCs can be visualised; when clumping is seen the test is positive and when clumping is not seen the test is negative. Common clinical uses of the Coombs test include the preparation of blood for transfusion in cross-matching, screening for atypical antibodies in the blood plasma of pregnant women as part of antenatal care, and detection of antibodies for the diagnosis of immune-mediated haemolytic anemias. Coombs tests are done on serum from venous blood samples which are taken from patients by venepuncture. The venous blood is taken to a laboratory (or blood bank), where trained scientific technical staff do the Coombs tests. The clinical significance of the result is assessed by the physician who requested the Coombs test, perhaps with assistance from a laboratory-based hematologist. [edit] Direct Coombs test The direct Coombs test (also known as the direct antiglobulin test or DAT) is used to detect if antibodies or complement system factors have bound to RBC surface antigens in vivo. The DAT is not currently required for pre-transfusion testing but may be included by some laboratories. [edit] Examples of diseases that give a positive direct Coombs test The direct Coombs test is used clinically when immune-mediated hemolytic anemia (antibody-mediated destruction of RBCs) is suspected. A positive Coombs test indicates that an immune mechanism is attacking the patient's own RBC's. This mechanism could be autoimmunity, alloimmunity or a drug-induced immune-mediated mechanism. [edit] Examples of alloimmune hemolysis Hemolytic disease of the newborn (also known as HDN or erythroblastosis fetalis) o Rh D hemolytic disease of the newborn (also known as Rh disease)
o ABO hemolytic disease of the newborn (the indirect Coombs test may only be weakly positive) o Anti-Kell hemolytic disease of the newborn o Rh c hemolytic disease of the newborn o Rh E hemolytic disease of the newborn o Other blood group incompatibility (RhC, Rhe, Kidd, Duffy, MN, P and others) Alloimmune hemolytic transfusion reactions
[edit] Examples of autoimmune hemolysis/immunohemolytic hemolysis Warm antibody autoimmune hemolytic anemia o Idiopathic o Systemic lupus erythematosus o Evans' syndrome (antiplatelet antibodies and hemolytic antibodies) Cold antibody immunohemolytic anemia o Idiopathic cold hemagglutinin syndrome o Infectious mononucleosis o Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria (rare)
[edit] Drug-induced immune-mediated hemolysis Methyldopa (IgG mediated type II hypersensitivity) Penicillin (high dose) Quinidine (IgM mediated activation of classical complement pathway and Membrane attack complex, MAC)
(A memory device to remember that the DAT tests the RBCs and is used to test infants for haemolytic disease of the newborn is: Rh Disease; R = RBCs, D = DAT.) [edit] Laboratory method The patient's red blood cells (RBCs) are washed (removing the patient's own serum) and then incubated with antihuman globulin (also known as Coombs reagent). If immunoglobulin or complement factors have been fixed on to the RBC surface in-vivo, the antihuman globulin will agglutinate the RBCs and the direct Coombs test will be positive. (A visual representation of a positive direct Coombs test is shown in the upper half of the schematic). [edit] Indirect Coombs test The indirect Coombs test (also known as the indirect antiglobulin test or IAT) is used to detect in-vitro antibody-antigen reactions. It is used to detect very low concentrations of antibodies present in a patient's plasma/serum prior to a blood transfusion. In antenatal care, the IAT is used to screen pregnant women for antibodies that may cause hemolytic disease of the newborn. The IAT can also be used for compatibility testing, antibody identification, RBC phenotyping, and titration studies. [edit] Examples of clinical uses of the indirect Coombs test [edit] Blood transfusion preparation Main articles: blood transfusion and cross-matching The indirect Coombs test is used to screen for antibodies in the preparation of blood for blood transfusion. The donor's and recipient's blood must be ABO and Rh D compatible. Donor blood for transfusion is also screened for infections in separate processes. Antibody screening
A blood sample from the recipient and a blood sample from every unit of donor blood are screened for antibodies with the indirect Coombs test. Each sample is incubated against a wide range of RBCs that together exhibit a full range of surface antigens (i.e. blood types).
Cross matching
The indirect Coombs test is used to test a sample of the recipient's serum against a sample of the blood donor's RBCs. This is sometimes called cross-matching blood. [edit] Antenatal antibody screening The indirect Coombs test is used to screen pregnant women for IgG antibodies that are likely to pass through the placenta into the fetal blood and cause haemolytic disease of the newborn. [edit] Laboratory method The IAT is a two-stage test. (A cross match is shown visually in the lower half of the schematic as an example of an indirect Coombs test). [edit] First stage Washed test red blood cells (RBCs) are incubated with a test serum. If the serum contains antibodies to antigens on the RBC surface, the antibodies will bind onto the surface of the RBCs. [edit] Second stage The RBCs are washed three or four times with isotonic saline and then incubated with antihuman globulin. If antibodies have bound to RBC surface antigens in the first stage, RBCs will agglutinate when incubated with the antihuman globulin (also known Coombs reagent) in this stage, and the indirect Coombs test will be positive. [edit] Titrations By diluting a serum containing antibodies the quantity of the antibody in the serum can be gauged. This is done by using doubling dilutions of the serum and finding the maximum dilution of test serum that is able to produce agglutination of relevant RBCs. [edit] Coombs reagent Coombs reagent (also known as Coombs antiglobulin or antihuman globulin) is used in both the direct Coombs test and the indirect Coombs test. Coombs reagent is antihuman globulin. It is made by injecting human globulin into animals, which produce polyclonal antibodies specific for human immunoglobulins and human complement system factors. More specific Coombs reagents or monoclonal antibodies can be used. [edit] Enhancement media Both IgM and IgG antibodies bind strongly with their antigens. IgG antibodies are most reactive at 37C. IgM antibodies are easily detected in saline at room temperature as IgM antibodies are able to bridge between RBCs owing to their large size, efficiently creating what is seen as agglutination. IgG antibodies are smaller and require assistance to bridge well enough to form a visual agglutination reaction. Reagents used to enhance IgG detection are referred to as potentiators. RBCs have a net negative charge called zeta potential which causes them to have a natural repulsion for one another. Potentiators reduce the zeta potential of RBC membranes. Common potentiators include low ionic strength solution (LISS), albumin, polyethylene glycol (PEG), and proteolytic enzymes. [edit] History of the Coombs test The Coombs test was first described in 1945 by Cambridge immunologists Robin Coombs (after whom it is named), Arthur Mourant and Rob Race.[3] Historically, it was done in test tubes. Today, it is commonly done using microarray and gel technology.
Coombs test (juga dikenal sebagai, uji antiglobulin Coombs 'test atau AGT) mengacu pada dua klinis blood tests used in immunohematology and immunology . tes darah yang digunakan dalam immunohematology dan imunologi . The two Coombs tests are the direct Coombs test ( DCT , also known as direct antiglobulin test or DAT ), and the indirect Coombs test (also known as indirect antiglobulin test or IAT ). Kedua tes Coombs adalah tes Coombs langsung (DCT, juga dikenal sebagai tes antiglobulin langsung atau DAT), dan tes Coombs tidak langsung (juga dikenal sebagai tes antiglobulin langsung atau IAT). The Direct Coombs test is used to test for autoimmune hemolytic anemia ; ie, a condition of a low count of red blood cells (aka RBCs) caused by immune system lysis or breaking of RBC membranes causing RBC destruction. Tes Coombs langsung digunakan untuk menguji autoimun anemia hemolitik , yaitu, suatu kondisi jumlah rendah sel darah merah (sel darah merah alias) yang disebabkan oleh lisis sistem kekebalan tubuh atau melanggar membran RBC menyebabkan kerusakan RBC. In certain diseases or conditions an individual's blood may contain IgG antibodies that can specifically bind to antigens on the RBC surface membrane, and their circulating RBCs can become coated with IgG alloantibodies and/or IgG autoantibodies. Dalam penyakit tertentu atau kondisi darah individu mungkin berisi antibodi IgG yang secara khusus dapat mengikat antigen pada permukaan membran RBC, dan sel darah merah yang bersirkulasi dapat menjadi dilapisi dengan alloantibodies IgG dan / atau autoantibodi IgG. Complement proteins may subsequently bind to the bound antibodies and cause RBC destruction. [1] The direct Coombs test is used to detect these antibodies or complement proteins that are bound to the surface of red blood cells; a blood sample is taken and the RBCs are washed (removing the patient's own plasma) and then incubated with antihuman globulin (also known as "Coombs reagent"). Protein komplemen selanjutnya dapat berikatan dengan antibodi terikat dan menyebabkan kerusakan sel darah merah. [1] Tes Coombs langsung digunakan untuk mendeteksi antibodi atau protein komplemen yang terikat pada permukaan sel darah merah, sampel darah diambil dan sel darah merah yang dicuci (menghapus plasma pasien sendiri) dan kemudian diinkubasi dengan globulin antihuman (juga dikenal sebagai "reagen Coombs"). If this produces agglutination of RBCs, the direct Coombs test is positive, a visual indication that antibodies (and/or complement proteins) are bound to the surface of red blood cells . Jika ini menghasilkan aglutinasi sel darah merah, tes Coombs langsung positif, indikasi visual yang antibodi (dan / atau protein komplemen) terikat pada permukaan sel darah merah . The indirect Coombs test is used in prenatal testing of pregnant women, and in testing blood prior to a blood transfusion . Tes Coombs tidak langsung digunakan dalam pengujian pralahir wanita hamil, dan dalam pengujian darah sebelum ke transfusi darah . It detects antibodies against RBCs that are present unbound in the patient's serum . Mendeteksi antibodi terhadap sel darah merah yang terikat hadir dalam pasien serum . In this case, serum is extracted from the blood sample taken from the patient. Dalam hal ini, serum diekstraksi dari sampel darah yang diambil dari pasien. Then, the serum is incubated with RBCs of known antigenicity ; that is, RBCs with known reference values from other patient blood samples. Kemudian, serum diinkubasi dengan sel darah merah yang diketahui antigenisitas , yaitu sel darah merah dengan nilai acuan diketahui dari sampel darah pasien lain. If agglutination occurs, the indirect Coombs test is positive. [2] Jika terjadi aglutinasi, tes Coombs langsung positif. [2] Mechanism Mekanisme
Schematic showing the direct and indirect Coombs tests . Skema menunjukkan Coombs langsung dan tidak langsung tes. The two Coombs tests are based on the fact that anti-human antibodies , which are produced by immunizing non-human species with human serum , will bind to human antibodies, commonly IgG or IgM . Kedua Coombs tes didasarkan pada kenyataan bahwa anti-manusia antibodi , yang diproduksi oleh imunisasi spesies non-manusia dengan manusia serum , akan mengikat antibodi manusia, umumnya IgG atau IgM . Animal anti-human antibodies will also bind to human antibodies that may be fixed onto antigens on the surface of red blood cells (also referred to as RBCs), and in the appropriate test tube conditions this can lead to agglutination of RBCs . Hewan anti-antibodi manusia juga akan mengikat antibodi manusia yang dapat tetap ke antigen pada permukaan sel darah merah (juga disebut sebagai sel darah merah), dan dalam kondisi tabung uji yang tepat ini dapat menyebabkan aglutinasi dari sel darah merah . The phenomenon of agglutination of RBCs is important here, because the resulting clumping of RBCs can be visualised; when clumping is seen the test is positive and when clumping is not seen the test is negative. Fenomena aglutinasi sel darah merah yang penting di sini, karena penggumpalan sel darah merah yang dihasilkan dapat divisualisasikan, ketika menggumpal terlihat tes positif dan ketika menggumpal tidak terlihat tes negatif. Common clinical uses of the Coombs test include the preparation of blood for transfusion in cross-matching , screening for atypical antibodies in the blood plasma of pregnant women as part of antenatal care , and detection of antibodies for the
diagnosis of immune-mediated haemolytic anemias . Menggunakan klinis yang umum dari tes Coombs termasuk persiapan darah untuk transfusi di cross-matching , skrining untuk antibodi atipikal dalam plasma darah dari hamil perempuan sebagai bagian dari perawatan antenatal , dan deteksi antibodi untuk diagnosis kekebalan-dimediasi hemolitik anemia . Coombs tests are done on serum from venous blood samples which are taken from patients by venepuncture . Tes Coombs dilakukan pada serum dari sampel darah vena yang diambil dari pasien dengan venepuncture . The venous blood is taken to a laboratory (or blood bank), where trained scientific technical staff do the Coombs tests. Darah vena diambil ke laboratorium (atau bank darah), di mana staf teknis terlatih ilmiah melakukan tes Coombs. The clinical significance of the result is assessed by the physician who requested the Coombs test, perhaps with assistance from a laboratory-based hematologist . Signifikansi klinis hasilnya dinilai oleh dokter yang meminta tes Coombs, mungkin dengan bantuan dari laboratorium berbasis hematologi . [ edit ] Direct Coombs test [ sunting ] Direct Coombs tes The direct Coombs test (also known as the direct antiglobulin test or DAT) is used to detect if antibodies or complement system factors have bound to RBC surface antigens in vivo . Tes Coombs langsung (juga dikenal sebagai tes antiglobulin langsung atau DAT) yang digunakan untuk mendeteksi jika antibodi atau melengkapi sistem faktor telah terikat ke antigen permukaan RBC in vivo . The DAT is not currently required for pre-transfusion testing but may be included by some laboratories. DAT tersebut saat ini tidak diperlukan untuk pra-transfusi pengujian tetapi dapat dimasukkan oleh beberapa laboratorium. [ edit ] Examples of diseases that give a positive direct Coombs test [ sunting ] Contoh penyakit yang memberikan langsung positif Coombs tes The direct Coombs test is used clinically when immune-mediated hemolytic anemia (antibody-mediated destruction of RBCs) is suspected. Tes Coombs langsung digunakan secara klinis ketika sistem imun anemia hemolitik (antibodidimediasi penghancuran sel darah merah) diduga. A positive Coombs test indicates that an immune mechanism is attacking the patient's own RBC's. Sebuah tes Coombs positif menunjukkan bahwa mekanisme kekebalan tubuh menyerang pasien sendiri RBC. This mechanism could be autoimmunity , alloimmunity or a drug-induced immune-mediated mechanism. Mekanisme ini bisa menjadi autoimunitas , alloimmunity atau obat-induced kekebalan-dimediasi mekanisme. [ edit ] Examples of alloimmune hemolysis [ sunting ] Contoh hemolisis aloimun Hemolytic disease of the newborn (also known as HDN or erythroblastosis Hemolytic penyakit pada bayi baru lahir (juga dikenal sebagai HDN atau eritroblastosis fetalis ) fetalis) Rh D hemolytic disease of the newborn (also known as Rh disease) Rh D penyakit hemolitik pada bayi baru lahir (juga dikenal sebagai penyakit Rh) ABO hemolytic disease of the newborn (the indirect Coombs test may only be weakly positive) ABO hemolitik penyakit pada bayi baru lahir (tes Coombs tidak langsung mungkin hanya lemah positif) Anti- Kell hemolytic disease of the newborn Anti-Kell hemolytic penyakit pada bayi baru lahir Rh c hemolytic disease of the newborn Rh c penyakit hemolitik pada bayi baru lahir Rh E hemolytic disease of the newborn Rh E penyakit hemolitik pada bayi baru lahir Other blood group incompatibility ( RhC , Rhe , Kidd, Duffy, MN, P and others) Darah lainnya kelompok ketidakcocokan (RHC, Rhe, Kidd, Duffy, MN, P dan lain-lain)
Alloimmune hemolytic transfusion reactions Aloimun hemolitik reaksi transfusi
[ edit ] Examples of autoimmune hemolysis/immunohemolytic hemolysis [ sunting ] Contoh hemolisis autoimun / hemolisis immunohemolytic Warm antibody autoimmune hemolytic anemia Antibodi anemia hemolitik autoimun hangat Idiopathic Idiopatik Systemic lupus erythematosus Sistemik lupus erythematosus Evans' syndrome ( antiplatelet antibodies and hemolytic antibodies) Evans syndrome (antibodi antiplatelet dan antibodi hemolitik) Idiopathic cold hemagglutinin syndrome Idiopathic dingin hemagglutinin sindrom Infectious mononucleosis Infeksi mononucleosis
Cold antibody immunohemolytic anemia Antibodi anemia dingin immunohemolytic
Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria (rare) Paroksismal dingin hemoglobinuria (jarang)
[ edit ] Drug-induced immune-mediated hemolysis [ sunting ] Obat-diinduksi kekebalan-mediated hemolisis Methyldopa ( IgG mediated type II hypersensitivity) Metildopa (IgG dimediasi hipersensitivitas tipe II) Penicillin (high dose) Penisilin (dosis tinggi) Quinidine ( IgM mediated activation of classical complement pathway and Membrane attack complex, MAC) Quinidine (IgM dimediasi aktivasi komplemen jalur klasik dan kompleks Membran serangan, MAC)
(A memory device to remember that the DAT tests the RBCs and is used to test infants for haemolytic disease of the newborn is: R h D isease ; R = RBCs, D = DAT.) (Sebuah perangkat memori untuk mengingat bahwa DAT yang menguji sel darah merah dan digunakan untuk menguji bayi untuk penyakit hemolitik pada bayi baru lahir adalah: R h D isease, R = RBCs, D = DAT.) [ edit ] Laboratory method [ sunting ] Laboratorium metode The patient's red blood cells (RBCs) are washed (removing the patient's own serum ) and then incubated with antihuman globulin (also known as Coombs reagent). Para pasien sel darah merah (sel darah merah) yang dicuci (menghapus pasien sendiri serum ) dan kemudian diinkubasi dengan globulin antihuman (juga dikenal sebagai reagen Coombs). If immunoglobulin or complement factors have been fixed on to the RBC surface in-vivo , the antihuman globulin will agglutinate the RBCs and the direct Coombs test will be positive. Jika imunoglobulin atau komplemen faktor telah diperbaiki pada permukaan RBC in-vivo , globulin antihuman akan mengaglutinasi sel darah merah dan tes Coombs langsung akan positif. (A visual representation of a positive direct Coombs test is shown in the upper half of the schematic). (Sebuah representasi visual dari tes Coombs positif langsung ditampilkan di bagian atas skema). [ edit ] Indirect Coombs test [ sunting ] Indirect Coombs tes The indirect Coombs test (also known as the indirect antiglobulin test or IAT) is used to detect in-vitro antibody-antigen reactions. Tes Coombs tidak langsung (juga dikenal sebagai tes antiglobulin langsung atau IAT) yang digunakan untuk mendeteksi in-vitro reaksi antigen-antibodi. It is used to detect very low concentrations of antibodies present in a patient's plasma/serum prior to a blood transfusion. Hal ini digunakan untuk mendeteksi konsentrasi yang sangat rendah dari antibodi hadir dalam plasma pasien / serum sebelum transfusi darah. In antenatal care, the IAT is used to screen pregnant women for antibodies that may cause hemolytic disease of the newborn . Dalam perawatan antenatal, IAT digunakan untuk layar wanita hamil untuk antibodi yang dapat menyebabkan penyakit hemolitik pada bayi baru lahir . The IAT can also be used for compatibility testing , antibody identification, RBC phenotyping, and titration studies. IAT juga dapat digunakan untuk pengujian kompatibilitas , identifikasi antibodi, fenotip RBC, dan studi titrasi. [ edit ] Examples of clinical uses of the indirect Coombs test [ sunting ] Contoh penggunaan klinis tes Coombs tidak langsung [ edit ] Blood transfusion preparation [ sunting ] Blood persiapan transfusi Main articles: blood transfusion and cross-matching Artikel utama: transfusi darah dan cross-matching The indirect Coombs test is used to screen for antibodies in the preparation of blood for blood transfusion . Tes Coombs tidak langsung digunakan untuk layar untuk antibodi dalam penyusunan darah untuk transfusi darah . The donor's and recipient's blood must be ABO and Rh D compatible. Para donor dan penerima darah yang harus ABO dan Rh D kompatibel. Donor blood for transfusion is also screened for infections in separate processes. Donor darah untuk transfusi juga diperiksa untuk infeksi dalam proses terpisah. Antibody screening Antibodi skrining A blood sample from the recipient and a blood sample from every unit of donor blood are screened for antibodies with the indirect Coombs test. Sebuah sampel darah dari penerima dan sampel darah dari setiap unit donor darah disaring untuk antibodi dengan tes Coombs tidak langsung. Each sample is incubated against a wide range of RBCs that together exhibit a full range of surface antigens (ie blood types ). Setiap sampel diinkubasi terhadap berbagai sel darah merah yang bersamasama menunjukkan berbagai macam antigen permukaan (yaitu tipe darah ). Cross matching Silang pencocokan The indirect Coombs test is used to test a sample of the recipient's serum against a sample of the blood donor's RBCs. Tes Coombs tidak langsung digunakan untuk menguji sampel serum penerima terhadap sampel dari donor darah sel darah merah. This is sometimes called cross-matching blood. Hal ini kadang-kadang disebut cross-matching darah. [ edit ] Antenatal antibody screening [ sunting ] skrining antibodi Antenatal
The indirect Coombs test is used to screen pregnant women for IgG Tes Coombs tidak langsung digunakan untuk layar wanita hamil untuk IgG antibodies that are likely to pass through the placenta into the fetal blood and cause haemolytic disease of the newborn . antibodi yang mungkin melewati plasenta ke dalam darah janin dan menyebabkan penyakit hemolitik pada bayi baru lahir . [ edit ] Laboratory method [ sunting ] Laboratorium metode The IAT is a two-stage test. IAT adalah tes dua tahap. (A cross match is shown visually in the lower half of the schematic as an example of an indirect Coombs test). (Sebuah pertandingan silang ditampilkan secara visual di bagian bawah skema sebagai contoh tes Coombs tidak langsung). [ edit ] First stage [ sunting ] Tahap Pertama Washed test red blood cells (RBCs) are incubated with a test serum. Dicuci tes sel darah merah (sel darah merah) yang diinkubasi dengan serum tes. If the serum contains antibodies to antigens on the RBC surface, the antibodies will bind onto the surface of the RBCs. Jika serum mengandung antibodi untuk antigen pada permukaan RBC, antibodi akan mengikat ke permukaan sel darah merah. [ edit ] Second stage [ sunting ] Kedua tahap The RBCs are washed three or four times with isotonic saline and then incubated with antihuman globulin. Sel darah merah dicuci tiga atau empat kali dengan saline isotonik dan kemudian diinkubasi dengan globulin antihuman. If antibodies have bound to RBC surface antigens in the first stage, RBCs will agglutinate when incubated with the antihuman globulin (also known Coombs reagent) in this stage, and the indirect Coombs test will be positive. Jika antibodi telah terikat ke antigen permukaan RBC di tahap pertama, sel darah merah akan mengaglutinasi ketika diinkubasi dengan globulin antihuman (juga dikenal Coombs reagen) di tahap ini, dan tes Coombs tidak langsung akan positif. [ edit ] Titrations [ sunting ] Titrasi By diluting a serum containing antibodies the quantity of the antibody in the serum can be gauged. Dengan menipiskan suatu antibodi serum yang mengandung jumlah antibodi dalam serum dapat diukur. This is done by using doubling dilutions of the serum and finding the maximum dilution of test serum that is able to produce agglutination of relevant RBCs. Hal ini dilakukan dengan menggunakan pengenceran dua kali lipat dari serum dan menemukan dilusi maksimal serum tes yang mampu menghasilkan aglutinasi sel darah merah yang relevan. [ edit ] Coombs reagent [ sunting ] Coombs reagen Coombs reagent (also known as Coombs antiglobulin or antihuman globulin ) is used in both the direct Coombs test and the indirect Coombs test. Coombs reagen (juga dikenal sebagai antiglobulin Coombs atau globulin antihuman) digunakan dalam kedua tes Coombs langsung dan tes Coombs tidak langsung. Coombs reagent is antihuman globulin . Reagen Coombs antihuman globulin . It is made by injecting human globulin into animals, which produce polyclonal Hal ini dilakukan dengan menyuntikkan globulin manusia ke hewan, yang menghasilkan poliklonal antibodies specific for human immunoglobulins and human complement system factors. antibodi spesifik untuk manusia imunoglobulin manusia dan melengkapi sistem faktor. More specific Coombs reagents or monoclonal antibodies can be used. Lebih spesifik Coombs reagen atau antibodi monoklonal dapat digunakan. [ edit ] Enhancement media [ sunting ] Peningkatan Media Both IgM and IgG Kedua IgM dan IgG antibodies bind strongly with their antigens . IgG antibodies are most reactive at 37C. antibodi mengikat kuat dengan mereka antigen . IgG antibodi yang paling reaktif pada suhu 37 C. IgM antibodies are easily detected in saline at room temperature as IgM antibodies are able to bridge between RBCs owing to their large size, efficiently creating what is seen as agglutination . IgM antibodi mudah terdeteksi dalam garam pada suhu kamar sebagai antibodi IgM dapat menjembatani antara RBC s karena ukurannya yang besar, efisien menciptakan apa yang dilihat sebagai aglutinasi . IgG antibodies are smaller and require assistance to bridge well enough to form a visual agglutination reaction. Antibodi IgG lebih kecil dan membutuhkan bantuan untuk menjembatani cukup baik untuk membentuk visual aglutinasi reaksi. Reagents used to enhance IgG detection are referred to as potentiators. Reagen yang digunakan untuk meningkatkan deteksi IgG disebut sebagai potensiator. RBCs have a net negative charge called zeta potential which causes them to have a natural repulsion for one another. Sel darah merah memiliki muatan negatif bersih disebut potensial zeta yang menyebabkan mereka memiliki tolakan alami untuk satu sama lain. Potentiators reduce the zeta potential of RBC membranes. Potensiator mengurangi potensi zeta dari membran RBC. Common potentiators include low ionic strength solution (LISS), albumin , polyethylene glycol (PEG), and proteolytic enzymes . Potensiator umum termasuk solusi kekuatan rendah ion (LISS), albumin , polietilen glikol (PEG), dan proteolitik enzim . [ edit ] History of the Coombs test [ sunting ] Sejarah tes Coombs
The Coombs test was first described in 1945 by Cambridge Tes Coombs pertama kali dijelaskan pada 1945 oleh Cambridge immunologists immunologists Robin Coombs (after whom it is named), Arthur Mourant and Rob Race. [3] Historically, it was done in test tubes . Robin Coombs (setelah yang dinamai), Arthur Mourant dan Rob Ras. [3] Secara historis, hal itu dilakukan dalam tabung reaksi . Today, it is commonly done using microarray and gel technology. Hari ini, itu biasanya dilakukan dengan menggunakan microarray dan teknologi gel.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Essentials of ABO -Rh Grouping and Compatibility Testing: Theoretical Aspects and Practical ApplicationDa EverandEssentials of ABO -Rh Grouping and Compatibility Testing: Theoretical Aspects and Practical ApplicationValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Coombs TestDocumento6 pagineCoombs TestjnsenguptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Wikipedia - Coombs Test (For CHECK)Documento6 pagineWikipedia - Coombs Test (For CHECK)vitruvianxyzNessuna valutazione finora
- Coombs Test - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento6 pagineCoombs Test - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAniket MittalNessuna valutazione finora
- 9BBK Lec9 - Coombs Test MQA 2019-09-26 08 - 15 - 27Documento18 pagine9BBK Lec9 - Coombs Test MQA 2019-09-26 08 - 15 - 27gothai sivapragasamNessuna valutazione finora
- Coombs TestDocumento1 paginaCoombs TestSherly CokrosaputroNessuna valutazione finora
- Coombs TestDocumento13 pagineCoombs TestPatNoppadolNessuna valutazione finora
- CrossmatchingDocumento4 pagineCrossmatchingEl Marie SalungaNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment #10: Direct Antihuman Globulin Test: ReferenceDocumento8 pagineExperiment #10: Direct Antihuman Globulin Test: ReferenceKriziaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 22 PDFDocumento5 pagineLesson 22 PDFfaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Coombs TestDocumento1 paginaCoombs Testapurva shewaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunohematology 2Documento2 pagineImmunohematology 2Mark JacobsNessuna valutazione finora
- Serological TestsDocumento6 pagineSerological TestsShuhada HamidNessuna valutazione finora
- Serological Tests (Antigen Antibody Interactions) : Prepared By: Mahmoud Alhabib Supervised By:dr - Hissham RdduanDocumento27 pagineSerological Tests (Antigen Antibody Interactions) : Prepared By: Mahmoud Alhabib Supervised By:dr - Hissham RdduanDevika RaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Serology 1Documento28 pagineSerology 1yousernameNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunohematology 3Documento3 pagineImmunohematology 3Mark JacobsNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Uses: Blood DonationDocumento4 pagineMedical Uses: Blood DonationHerryanto SimanjuntakNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemolytic Disease of The NewbornDocumento16 pagineHemolytic Disease of The NewbornStanculescu MarianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Compatibilty of Antigen AwaisDocumento7 pagineCompatibilty of Antigen AwaisAwais AkramNessuna valutazione finora
- BVMLT-304 Blood BankingDocumento23 pagineBVMLT-304 Blood BankingManisha khanNessuna valutazione finora
- SerologyDocumento442 pagineSerologyPura Javier100% (2)
- بنك الدم ٥Documento30 pagineبنك الدم ٥hussien shelbayeNessuna valutazione finora
- TransfusiDocumento142 pagineTransfusiJenadi BinartoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Direct Antiglobulin Test: Indications, Interpretation, and PitfallsDocumento6 pagineThe Direct Antiglobulin Test: Indications, Interpretation, and Pitfallsabbhyasa5206Nessuna valutazione finora
- SerologyDocumento3 pagineSerologyنوف الحربي.Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Brief Overview of Clinical Significance of Blood Group AntibodiesDocumento3 pagineA Brief Overview of Clinical Significance of Blood Group AntibodiesSantiago López JosueNessuna valutazione finora
- Compilation of BB Lec ReviewerDocumento19 pagineCompilation of BB Lec ReviewerKenj Yolleth IbañezNessuna valutazione finora
- Cross Matching WikipediaDocumento8 pagineCross Matching WikipediaZain AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Coombs Test - Principle, Types, Procedure and Result InterpretationDocumento34 pagineCoombs Test - Principle, Types, Procedure and Result InterpretationABHINABA GUPTANessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Bank Coombs ReportDocumento5 pagineBlood Bank Coombs Reportleen.dimashkiehNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibody Detection and IdentificationDocumento19 pagineAntibody Detection and IdentificationErika Leah ManaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 14: Compatibility TestDocumento2 pagineExperiment 14: Compatibility TestKriziaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Procedures PDFDocumento76 pagineLab Procedures PDFWenz MacuteNessuna valutazione finora
- Agglutination TestsDocumento6 pagineAgglutination TestsmaniiiiiiiiNessuna valutazione finora
- المحاضرة 4Documento5 pagineالمحاضرة 4Shi no MeNessuna valutazione finora
- Typing, Screening and Crossmatching of BloodDocumento55 pagineTyping, Screening and Crossmatching of BloodAsad MirzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Troubleshooting in CXMDocumento3 pagineTroubleshooting in CXMquerokeropi100% (1)
- Case 1Documento11 pagineCase 1Kent MaravillosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Is BB Final Coaching NotesDocumento8 pagineIs BB Final Coaching NotesLeomill MendiolaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 - Serological TechniquesDocumento13 pagine6 - Serological Techniquesجير يكو (جيريكو)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Cells, Molecules and Diseases: George B. Segel, Marshall A. LichtmanDocumento9 pagineBlood Cells, Molecules and Diseases: George B. Segel, Marshall A. LichtmanIqra ButtNessuna valutazione finora
- Coombs FinalDocumento32 pagineCoombs FinalMedicine 0786Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hematology Block Immunology Wrap 2021Documento4 pagineHematology Block Immunology Wrap 2021Liv GrahamNessuna valutazione finora
- B Blab 6 Crossmatch SP 05Documento14 pagineB Blab 6 Crossmatch SP 05Rutchelle Joyce PugoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Immuno HematologyDocumento24 pagineImmuno HematologyHoraa H AL-marhoonNessuna valutazione finora
- ABO Grouping - Overview, Clinical Indications - Applications, Test PerformanceDocumento7 pagineABO Grouping - Overview, Clinical Indications - Applications, Test PerformanceleandroNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Banking MT1ADocumento10 pagineBlood Banking MT1ALeoPaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Infusion Warmer DeviceDocumento16 pagineBlood Infusion Warmer DeviceSRL MECHNessuna valutazione finora
- Crossmatch: What Is Crossmatching?Documento3 pagineCrossmatch: What Is Crossmatching?mommy928Nessuna valutazione finora
- SerologyDocumento84 pagineSerologyngsusannasuisum100% (2)
- Identification of Antibodies To Red Cell Antigens - FinalDocumento51 pagineIdentification of Antibodies To Red Cell Antigens - FinalMohamed EltonsyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cross Matching-Wps OfficeDocumento22 pagineCross Matching-Wps Officeashwini priyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Blood TransfusionDocumento13 pagineClinical Blood TransfusionAdeniran CharlesNessuna valutazione finora
- SIMPAO BB Lab - Activity #5Documento4 pagineSIMPAO BB Lab - Activity #5simpao2121700Nessuna valutazione finora
- Antihuman GlobulinDocumento18 pagineAntihuman GlobulinChariss Pacaldo ParungaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 6 Crossmatch: Exercise 6 Laboratory Procedure ManualDocumento14 pagineExercise 6 Crossmatch: Exercise 6 Laboratory Procedure ManualEmad ManniNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Blood Banking & Transfusion Practices Ed6 Harmening-235-257Documento23 pagineModern Blood Banking & Transfusion Practices Ed6 Harmening-235-257ivanlchNessuna valutazione finora
- CoombsDocumento112 pagineCoombsratnadilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunological Techniques FallDocumento45 pagineImmunological Techniques Fallali.menem15Nessuna valutazione finora
- In Vitro Engineering of Human Autogenous Cartilage: Ursula Anderer and Jeanette LiberaDocumento10 pagineIn Vitro Engineering of Human Autogenous Cartilage: Ursula Anderer and Jeanette LiberaANIS MURNIATINessuna valutazione finora
- Ujian SMP 2 My VersionDocumento13 pagineUjian SMP 2 My VersionANIS MURNIATINessuna valutazione finora
- Hum. Reprod.-2006-García-Pérez-880-7Documento8 pagineHum. Reprod.-2006-García-Pérez-880-7ANIS MURNIATINessuna valutazione finora
- Long Live Th2Documento18 pagineLong Live Th2ANIS MURNIATINessuna valutazione finora
- Jadwal Kuliah Sem 2Documento6 pagineJadwal Kuliah Sem 2ANIS MURNIATINessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation NandaDocumento32 paginePresentation NandaANIS MURNIATINessuna valutazione finora
- GXM GSHDocumento1 paginaGXM GSHGerardLum100% (1)
- RH Incompatibility: DR - Minal M. Patil Dr. Jyotsna P. PatilDocumento27 pagineRH Incompatibility: DR - Minal M. Patil Dr. Jyotsna P. Patilchitushri100% (1)
- Transfusion Medicine - 2019Documento126 pagineTransfusion Medicine - 2019Aria Jean MostajoNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Bank QuizDocumento13 pagineBlood Bank Quizdimalawang.af100% (1)
- Blood Grouping 12thDocumento17 pagineBlood Grouping 12thPranjal SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Types WorksheetDocumento3 pagineBlood Types WorksheetRoana Marie TapiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rhesus Type and Abo Incompatibility in Jaundiced NeonatesDocumento7 pagineRhesus Type and Abo Incompatibility in Jaundiced Neonatesdaniel_iosif_glNessuna valutazione finora
- 5th Handbook of Transfusion Medicine PDFDocumento186 pagine5th Handbook of Transfusion Medicine PDFreywae100% (3)
- ABO Blood Grouping Cbsebiology4uDocumento14 pagineABO Blood Grouping Cbsebiology4uRahit BiswasNessuna valutazione finora
- Meny, G. (N.D.) - Recognizing and Resolving ABO DiscrepanciesDocumento3 pagineMeny, G. (N.D.) - Recognizing and Resolving ABO DiscrepanciesValdez Francis ZaccheauNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunohematology 3Documento3 pagineImmunohematology 3Mark JacobsNessuna valutazione finora
- Rational Use of BloodDocumento21 pagineRational Use of BloodAllan MacacapagalNessuna valutazione finora
- Is RPRDocumento1 paginaIs RPRMary Criscebel Kyla LoquireNessuna valutazione finora
- Clsi Ila06 ADocumento39 pagineClsi Ila06 ACristian Gutiérrez VeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Transfusion Error and Near MissesDocumento35 pagineTransfusion Error and Near Missesanaeshkl100% (1)
- Blood Groups: DR - Agus Alim Abdullah, SPPK (K)Documento60 pagineBlood Groups: DR - Agus Alim Abdullah, SPPK (K)Salim JufriNessuna valutazione finora
- Price List Finecare April 2020Documento1 paginaPrice List Finecare April 2020Ibrahim BoNessuna valutazione finora
- Imulfex WB-SP For Leukocyte ReductionDocumento2 pagineImulfex WB-SP For Leukocyte ReductiondatitoxNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood TransfusionDocumento17 pagineBlood TransfusionRayne BonifacioNessuna valutazione finora
- IFU 1110001731 Fastep D-SYP-42 CE英文说明书 041619Documento1 paginaIFU 1110001731 Fastep D-SYP-42 CE英文说明书 041619BPG ServiceNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Typing Activity For Lab Practical 2Documento11 pagineBlood Typing Activity For Lab Practical 2Liliana PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- MLSP IsbbDocumento3 pagineMLSP IsbbmariakrishajewelfranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Fungal Infections of The LungsDocumento163 pagineFungal Infections of The Lungsmeaza rorisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood TransfusionDocumento37 pagineBlood TransfusionSumathi Akshaya100% (1)
- Immunology and Serology Part 4Documento108 pagineImmunology and Serology Part 4UnixoftNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Transfusion Guideline (MSF) 2019Documento169 pagineBlood Transfusion Guideline (MSF) 2019hiba.khellow100% (1)
- CMVDocumento24 pagineCMVecko Roman100% (1)
- Blood Groups, Blood Typing and Blood TransfusionsDocumento4 pagineBlood Groups, Blood Typing and Blood TransfusionsShahnawaz KhanNessuna valutazione finora
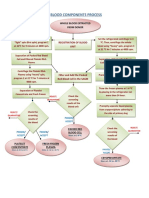
- Blood Components Process FlowchartDocumento1 paginaBlood Components Process FlowchartCatherine Constantino BaintoNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Significance of Maternal Anti-Cw Antibodies - A Review ofDocumento3 pagineClinical Significance of Maternal Anti-Cw Antibodies - A Review ofKirandragonNessuna valutazione finora