Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Electrical Energy Electric Loads: The Computer Power Supply
Caricato da
Resy ApolinarioDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Electrical Energy Electric Loads: The Computer Power Supply
Caricato da
Resy ApolinarioCopyright:
Formati disponibili
THE COMPUTER POWER SUPPLY
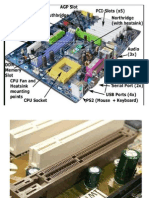
A power supply is a device that supplies electrical energy to one or more electric loads. What Does A Power Supply Do? A power supply is one of the most important pieces of your computer system. For a desktop PC, it converts the electricity coming from your wall outlet (in the U.S., that is 110-120 volts Alternating Current, 60 Hz) into four different flavors that your computer commonly uses, all Direct Current (DC) power: - 5 volts, +5 volts, +12 volts and -12 volts. There are two major types of computer power supplies: AT and ATX. 1. AT Power Supply An AT power supply is what was used for most older computers. This type of power supply powered the first personal computers made by IBM, and the standard was adopted for other manufacturers as well. Specifically, it powered all AT and AT-compatible motherboards. The AT-compatible motherboard obtained its power from a special two-part power connector from the AT power supply. This power connector contained four +5 volt DC wires, four ground (0 volt) wires, one - 5 volt wire, one +12 volt wire and one -12 volt wire. The remaining wire was a signal wire that allowed the power supply to tell the motherboard that "Power is good." With an AT power supply, you were required to manually turn off your computer by pressing the power switch (which generally was a dedicated On/Off switch). 2. ATX Power Supply With advances in software and operating systems, computers could do more, such as enter "Power-Save" or "Sleep" mode. Software could now be used to turn off the computer, rather than having to turn off a computer with a power switch. This has all been made possible by use of ATX power supplies and ATX-compatible motherboards. The ATX power supply, therefore, is more complex. An ATX power supply has more outputs that connect to an ATXcompatible motherboard. Whereas the AT power supply only had 8 outputs, the ATX power supply uses either 20 or 24 outputs. Most ATX power supplies take into account that an ATX motherboard can contain either 20 or 24 outputs, so the extra 4 outputs are often split out as a separate plug that will only fit one way into a 24 output motherboard connector. The ATX power supply also supports more voltage settings, and is capable of accepting signals from the ATXcompatible motherboard other than simply "Power Good." The 24-pin ATX power supply has the following number of outputs, all voltages DC: three +3.3 volt, eight ground (0 volt), five +5 volt, one -5 volt, two +12 volt, one -12 volt and four "signal" wires ("Power Good," "+5 volt standby," "+3.3 volt sense" and "Power on"). Which Type Does My Computer Use? If you have a computer that was manufactured after 1997, chances are that you have an ATX power supply. Most modern operating systems (post-Windows 98) support the advanced power functions that an ATX power supply / motherboard combination can offer, such as Power Save/Sleep mode. If your computer was manufactured previous to 1997, it's much more likely that you have an AT power supply.
Types of Power Supply Connector 1. Original PC main power cables: AT connector The original PC debuted in 1981 and used two cables to connect the PSU (power supply) to the motherboard. The two cables plug side by side into the motherboard connectors. Sometimes they are keyed so they only plug in one way and sometimes they aren't. Even if they're keyed you can insert them the wrong way if you put a little effort into it. You always have to remember to plug them in so the black wires are next to each other. It's either "black to black" or smoke and a shower of sparks.
Pinout Pin number Wire color Description 1 orange power good 2 red +5 volts or connector key 3 yellow +12 volts 4 blue -12 volts 5 black ground 6 black ground 1 black ground 2 black ground 3 white -5 volts 4 red +5 volts 5 red +5 volts 6 red +5 volts
2. 4 pin peripheral power cable The four pin peripheral power cable dates back to the original PC. It was used for floppy drives and hard disks. It's still around and is now also used for all kinds of things including add-on fans, extra video card power, supplemental motherboard power, and case lighting. It's as old as the hills but is still very widely used. The connector is shaped so that it only fits in one way. You don't have to worry about inserting it the wrong way. People often use the term "4 pin Molex power cable" or "4 pin Molex" to refer to a four pin peripheral power cable. It's not a technically useful term because the 4 pin 12 volt cable is also a 4 pin Molex cable (Molex makes lots of connectors) but "4 pin Molex" is commonly used to refer to peripheral cables anyway.
Pinout Pin number 1 2 3 4 Wire color yellow black black red Description +12 volts ground ground +5 volts
3. Floppy drive power cable The four pin floppy drive cable showed up when PCs started including 3.5 inch floppy drives. This kind of cable is also sometimes used as an auxiliary power cable for AGP video cards which use more power than can be drawn from the motherboard slot. The connector is shaped so that it only fits in one way so you don't have to worry about inserting it the wrong way. Floppy cables are built with small connectors and 20 awg wire so they are limited to relatively low current uses.
Pinout Pin number 1 2 3 4 Wire color red black black yellow Description +5 volts ground ground +12 volts
4. 6 pin auxiliary power cable The aux power cable was added to provide extra wattage to motherboards for 3.3 and 5 volts. This connector is rarely used anymore. It's most commonly found on older dual CPU AMD motherboards. You're more likely to sight Bigfoot than a motherboard which uses this connector. It plugs into the 6 pin version of the motherboard connector used by the original PC main power cables.
Pinout Pin number 1 2 3 4 5 6 Wire color black black black orange orange red Description ground ground ground +3.3 volts +3.3 volts +5 volts
5. SATA power cable SATA was introduced to upgrade the ATA interface (also called IDE) to a more advanced design. SATA includes both a data cable and a power cable. The power cable replaces the old 4 pin peripheral cable and adds support for 3.3 volts (if fully implemented). The connector is shaped so it can only be plugged in the correct way.
Pinout Pin number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Wire number 5 5 5 4 4 4 3 3 3 2 2 2 1 1 1 Wire color orange orange orange black black black red red red black black black yellow yellow yellow Description +3.3 volts +3.3 volts +3.3 volts ground ground ground +5 volts +5 volts +5 volts ground ground ground +12 volts +12 volts +12 volts
6. ATX 20 pin main power cable In 1996 PC makers started switching to the ATX standard which defined a new 20 pin motherboard power connector. It includes a 3.3 volt rail which is used to power newer chips which require a lower voltage than 5 volts. It also has a standby 5 volt rail which is always on even when the power supply is turned off to provide standby power to the motherboard when the machine is sleeping. The new connector also allows the motherboard to turn the power supply on and off rather than depend on the user to flip a power switch. This connector is polarized so it can only be plugged in pointing in the correct direction.
Pinout Pins 1 through 10 Description +3.3 volts +3.3 volts ground +5 volts ground +5 volts ground PWR_OK VSB +5 volts +12 volts Wire color orange orange black red black red black gray purple yellow Pin number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Pin number 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Pins 11 through 20 Wire color orange blue black green black black black white red red Description +3.3 volts -12 volts ground PS_ON# ground ground ground -5 volts (optional) +5 volts +5 volts
7. ATX 24 pin main power cable The 24 pin main power connector was added in ATX12V 2.0 to provide extra power needed by PCI Express slots. The older 20 pin main power cable only has one 12 volt line. The new 24 pin connector added one line apiece for ground, 3.3, 5, and 12 volts. The extra pins made the auxiliary power cable unnecessary so most ATX12V 2.x power supplies don't have them. The 24 pin connector is polarized so it can only be plugged in pointing in the correct direction.
Pinout Pins 1 through 12 Description +3.3 volts +3.3 volts ground +5 volts ground +5 volts ground PWR_OK VSB +5 volts +12 volts +12 volts +3.3 volts Wire color orange orange black red black red black gray purple yellow yellow orange Pin number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Pin number 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Pins 13 through 24 Wire color orange blue black green black black black white red red red black Description +3.3 volts -12 volts ground PS_ON# ground ground ground -5 volts (optional) +5 volts +5 volts +5 volts ground
8. ATX 20+4 pin main power cable Motherboards can come with either a 20 pin main power connector or a 24 pin main power connector. Many power supplies come with a 20+4 cable which is compatible with both 20 and 24 pin motherboards. A 20+4 power cable has two pieces: a 20 pin piece, and a 4 pin piece. If you leave the two pieces separate then you can plug the 20 pin piece into a 20 pin motherboard and leave the 4 pin piece unplugged. Be sure to leave the 4 pin piece unplugged even if it fits into another connector. The 4 pin piece is not compatible with any other connectors. If you plug the two pieces of a 20+4 power cable together then you have a 24 pin power cable which can be plugged into a 24 pin motherboard.
9. 4 pin ATX +12 volt power cable The power cable which plugs into the 4 pin connector has two black wires and two yellow wires. This cable is sometimes called an "ATX12V" cable or "P4" cable although neither of those are technically accurate descriptions.
10. 8 pin EPS +12 volt power cable This cable was originally created for workstations to provide 12 volts to power multiple CPUs. But as time has passed many CPUs require more 12 volt power and the 8 pin 12 volt cable is often used instead of a 4 pin 12 volt cable. Depending on the power supply, the connector may contain one 12 volt rail in all 8 pins or two 12 volt rails taking up 4 pins apiece. It is often refered to as an "EPS12V" cable.
11. 4+4 pin +12 volt power cable Motherboards can come with either a 4 pin 12 volt connector or an 8 pin 12 volt connector. Many power supplies come with a 4+4 pin 12 volt cable which is compatible with both 4 and 8 pin motherboards. A 4+4 power cable has two separate 4 pin pieces. If you plug the two pieces of a 4+4 power cable together then you have a 8 pin power cable which can be plugged into an 8 pin 12 volt connector. If you leave the two pieces separate then you can plug one of the 4 pin pieces into a 4 pin 12 volt connector and leave the other 4 pin piece unplugged.
12. 6 pin PCI Express power cable This cable is used to provide extra 12 volt power to PCI Express expansion cards. PCI Express motherboard slots can provide a maximum of 75 watts. Many video cards draw significantly more than 75 watts so the 6 pin PCI Express power cable was created. These high-power cards draw most of their power from the 12 volt rail so this cable provides only 12 volts. These are sometimes called "PCI Express cables". They are also occasionally called "PEG cables" where "PEG" stands for PCI Express Graphics. If your power supply doesn't have a 6 pin PCI Express cable then you can use the adapter shown above on the right to convert two 4 pin peripheral cables into a PCI Express cable.
13. 8 pin PCI Express power cable The PCI Express 2.0 specification released in January 2007 added an 8 pin PCI Express power cable. It's just an 8 pin version of the 6 Pin PCI Express power cable. Both are primarily used to provide supplemental power to video cards. The older 6 pin version officially provides a maximum of 75 watts (although unofficially it can usually provide much more) whereas the new 8 pin version provides a maximum of 150 watts. It is very easy to confuse the 8 pin version with the very similar-looking EPS 8 pin 12 volt cable.
14. 6+2 pin PCI Express power cable Some video cards have 6 Pin PCI Express power connectors and others have 8 Pin PCI Express power connectors. Many power supplies come with a 6+2 PCI Express power cable which is compatible with both kinds of video cards. The 6+2 PCI Express power cable is made up of two pieces: a 6 pin piece, and a 2 pin piece. If you put the two pieces together then you have a full 8 pin PCI Express power cable. But if you split the connector into two parts then you can plug the 6 pin part into the older 6 pin PCI Express connector and leave the 2 pin part unplugged. That way, your power supply only needs to have one 6+2 cable to be compatible with both 6 pin and 8 pin PCI Express connectors.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Practice Quiz Reflection Project Initiation and Key ComponentsDocumento3 paginePractice Quiz Reflection Project Initiation and Key ComponentsFalastin Tanani67% (3)
- Troubleshooting Flow ChartDocumento3 pagineTroubleshooting Flow ChartNullumCrimen NullumPoena SineLegeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Mine Ventialtion ProblemDocumento3 pagineChapter 3 Mine Ventialtion ProblemfahimNessuna valutazione finora
- The Impact of Social Networking Sites To The Academic Performance of The College Students of Lyceum of The Philippines - LagunaDocumento15 pagineThe Impact of Social Networking Sites To The Academic Performance of The College Students of Lyceum of The Philippines - LagunaAasvogel Felodese Carnivora64% (14)
- Loi 33-2012e-Library - PNP Document Management SystemDocumento6 pagineLoi 33-2012e-Library - PNP Document Management SystemResy Apolinario100% (3)
- All About The Various PC Power Supply Cables and ConnectorsDocumento27 pagineAll About The Various PC Power Supply Cables and Connectorsquestiones11Nessuna valutazione finora
- All About The Various PC Power Supply Cables and ConnectorsDocumento24 pagineAll About The Various PC Power Supply Cables and Connectorssirsa11100% (2)
- LESSON 5 - Parts and Function (Power Supply Unit)Documento25 pagineLESSON 5 - Parts and Function (Power Supply Unit)Gerry Jr. GohilNessuna valutazione finora
- Atx and p4 Power SuppliesDocumento6 pagineAtx and p4 Power SuppliesSantosh DevadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cases and Power SuppliesDocumento18 pagineCases and Power SuppliesnitinNessuna valutazione finora
- Power ConnectorsDocumento15 paginePower ConnectorsKYLE ROGER CENIZANessuna valutazione finora
- Power SupplyDocumento18 paginePower SupplyFazrul RosliNessuna valutazione finora
- I. Power SupplyDocumento18 pagineI. Power SupplyBernadeth GuiasilonNessuna valutazione finora
- ATX and P4 Power Supplies PDFDocumento6 pagineATX and P4 Power Supplies PDFvladareanucatalindanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 6 - Power Supply - Berja, Cykee Anne A.Documento20 pagineLesson 6 - Power Supply - Berja, Cykee Anne A.CYKEE ANNE BERJANessuna valutazione finora
- Power SupplyDocumento17 paginePower Supplyrheza oropaNessuna valutazione finora
- Convert Computer ATX Power Supply To Lab Power Supply PDFDocumento9 pagineConvert Computer ATX Power Supply To Lab Power Supply PDFGabriel GabiNessuna valutazione finora
- SmpsDocumento7 pagineSmpsmanoj22490Nessuna valutazione finora
- Identify The Connectors of The Power SupplyDocumento7 pagineIdentify The Connectors of The Power Supplyagoyal514Nessuna valutazione finora
- Information Sheet 1.3-A The Power Supply Learning ObjectivesDocumento83 pagineInformation Sheet 1.3-A The Power Supply Learning Objectivessuper novaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7-1 Power SupplyDocumento7 pagineChapter 7-1 Power Supplyapi-3750451Nessuna valutazione finora
- Power SuppliesDocumento55 paginePower SuppliesEric Vincent MagnoNessuna valutazione finora
- 15 SMPSDocumento16 pagine15 SMPSperweeng31Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2-Lesson 2 (Computer Power Supply) )Documento9 pagineUnit 2-Lesson 2 (Computer Power Supply) )Aldrei BobierNessuna valutazione finora
- ATX - NapajanjeDocumento5 pagineATX - NapajanjeBranislav TomašNessuna valutazione finora
- Power SuppliesDocumento2 paginePower SuppliesJaveed AhamedNessuna valutazione finora
- BTX Connector PinoutDocumento10 pagineBTX Connector PinoutJEETENDRANessuna valutazione finora
- Convert ATX PSU To Bench Supply To Power CircuitsDocumento7 pagineConvert ATX PSU To Bench Supply To Power CircuitsHotel WijayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ingl 3 SDocumento3 pagineIngl 3 SCarlos Nina QuisbertNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer MotherboardDocumento54 pagineComputer Motherboardrandex3r100% (2)
- Power Supply: Computer Systems ServicingDocumento31 paginePower Supply: Computer Systems ServicingCHRISTIAN MABALONessuna valutazione finora
- ATX PC Power Supply Diagnostic FlowchartDocumento31 pagineATX PC Power Supply Diagnostic FlowchartWali SauyunanNessuna valutazione finora
- CMTS Handout 5 and 6Documento17 pagineCMTS Handout 5 and 6Tolosa TafeseNessuna valutazione finora
- A+ Study Guide: Domain 1.0: Personal Computer Components: Power SuppliesDocumento3 pagineA+ Study Guide: Domain 1.0: Personal Computer Components: Power SuppliesAmarRajChandraNessuna valutazione finora
- PC Wiring Stuff 12v DCDocumento9 paginePC Wiring Stuff 12v DCDharmendra PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- T-568A Straight-Through Ethernet CableDocumento9 pagineT-568A Straight-Through Ethernet CableesshorNessuna valutazione finora
- Parallel ATADocumento6 pagineParallel ATAhusainibaharinNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.1 Computer Hardware ComponentDocumento70 pagine3.1 Computer Hardware ComponentBiha RoseliNessuna valutazione finora
- ATX Supply DifferentiateDocumento5 pagineATX Supply DifferentiatedbmasterNessuna valutazione finora
- ATX Power Supply Connector Pinout and Wiring at PinoutsDocumento2 pagineATX Power Supply Connector Pinout and Wiring at PinoutsNightMystNessuna valutazione finora
- Powersupply Form FactorsDocumento5 paginePowersupply Form FactorsFredrick MugoNessuna valutazione finora
- Inductor : Diode The Most Common Function of Diode Is To Allow The Current ToDocumento3 pagineInductor : Diode The Most Common Function of Diode Is To Allow The Current ToUmair SoomroNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Supply Pinouts - ATX, Dell, Power MacDocumento3 paginePower Supply Pinouts - ATX, Dell, Power Macder comptNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 02Documento3 pagineLab 02Umair SoomroNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Power SupplyDocumento1 pagina2 Power SupplyStephen MccarthyNessuna valutazione finora
- A Hobby Power Over Ethernet Solution (Homebrew Poe) : AbstractDocumento3 pagineA Hobby Power Over Ethernet Solution (Homebrew Poe) : AbstractfdgNessuna valutazione finora
- Atx Power Conector WiresDocumento8 pagineAtx Power Conector WiresparatosayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Atx Power Conector WiresDocumento8 pagineAtx Power Conector WiresparatosayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Atx Power Conector WiresDocumento8 pagineAtx Power Conector WiresparatosayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Molex ConnectorDocumento5 pagineMolex Connectorcarlosxxx1234Nessuna valutazione finora
- The ST Louis SwitcherDocumento4 pagineThe ST Louis SwitcherKiril Van Abid AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- MOBO Basic PartsDocumento17 pagineMOBO Basic PartsJohara Mundas DiocolanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Convert ATX PSU To Bench SupplyDocumento11 pagineConvert ATX PSU To Bench SupplyOlanrewaju OjediranNessuna valutazione finora
- ATX Power Supply Pinout TablesDocumento4 pagineATX Power Supply Pinout TablesElectrical EEENessuna valutazione finora
- ATX Power Supply Connector Pinout and Wiring @Documento3 pagineATX Power Supply Connector Pinout and Wiring @costelchelariuNessuna valutazione finora
- About SMPS & TypesDocumento14 pagineAbout SMPS & TypesBABU ENessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Hardware Servicing: Grade 11A - ICTDocumento15 pagineComputer Hardware Servicing: Grade 11A - ICTMayen Duallo RagotNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Convert A Computer ATX Power Supply To A Lab Power SupplyDocumento6 pagineHow To Convert A Computer ATX Power Supply To A Lab Power SupplyJenny YongNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 2 Power SupplyDocumento7 pagineCHAPTER 2 Power Supplykevinkingili450Nessuna valutazione finora
- Convert ATX To DC Power SupplyDocumento15 pagineConvert ATX To DC Power SupplyRendy Alfiq0% (1)
- Dell Atxpower PinoutDocumento1 paginaDell Atxpower PinoutVulpea RosieNessuna valutazione finora
- SMPSDocumento8 pagineSMPSnishant thakreNessuna valutazione finora
- Radio Shack TRS-80 Expansion Interface: Operator's Manual: Catalog Numbers: 26-1140, 26-1141, 26-1142Da EverandRadio Shack TRS-80 Expansion Interface: Operator's Manual: Catalog Numbers: 26-1140, 26-1141, 26-1142Nessuna valutazione finora
- Audio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsDa EverandAudio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsNessuna valutazione finora
- Job VacancyDocumento1 paginaJob VacancyResy ApolinarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Comex Advisory 2014 05Documento3 pagineComex Advisory 2014 05Eli Benjamin Nava TaclinoNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Band Graphic EqualiserDocumento2 pagine5 Band Graphic EqualiserDhivya SureshKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Om0076 2014Documento4 pagineOm0076 2014Resy ApolinarioNessuna valutazione finora
- (Ymya) 5-Band Graphic EqualizerDocumento1 pagina(Ymya) 5-Band Graphic EqualizerDivyanshu YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- IP Address ClassesDocumento2 pagineIP Address ClassesDouglas MoodyNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction Power Supply Rev7 22Documento19 pagineIntroduction Power Supply Rev7 22Resy ApolinarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Health and SafetyDocumento6 pagineComputer Health and SafetyResy ApolinarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 07Documento35 pagineChapter 07api-26103409Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pag-IBIG Branch Areas of CoverageDocumento3 paginePag-IBIG Branch Areas of CoverageResy ApolinarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Kirchoffs Law With Cramers RuleDocumento14 pagineKirchoffs Law With Cramers RuleRoy BernardNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction Power Supply Rev7 22Documento19 pagineIntroduction Power Supply Rev7 22Resy ApolinarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Switching TheoryDocumento245 pagineFundamentals of Switching TheoryMichelle Arellano100% (1)
- Latches and Flip-Flops: Experiment E10Documento9 pagineLatches and Flip-Flops: Experiment E10Resy ApolinarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Trig 1Documento32 pagineTrig 1Resy ApolinarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Trigonometric Functions: Peggy Adamson and Jackie NicholasDocumento39 pagineIntroduction To Trigonometric Functions: Peggy Adamson and Jackie NicholasResy ApolinarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebra 1 End-of-Course and Geometry End-of-Course Assessments Reference SheetDocumento2 pagineAlgebra 1 End-of-Course and Geometry End-of-Course Assessments Reference SheetResy Apolinario100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Logic Design 6th Edition Chapter 11Documento3 pagineFundamentals of Logic Design 6th Edition Chapter 11Jessica Garner50% (2)
- Basics of TrigonometryDocumento11 pagineBasics of TrigonometryMuralikrishna SingamaneniNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Trigonometric Functions: Peggy Adamson and Jackie NicholasDocumento39 pagineIntroduction To Trigonometric Functions: Peggy Adamson and Jackie NicholasResy ApolinarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of RAM and ROMDocumento6 pagineTypes of RAM and ROMTinu Elza Vinu100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Logic Design 6th Edition Chapters 16-18Documento20 pagineFundamentals of Logic Design 6th Edition Chapters 16-18Resy ApolinarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Ip Addressing TutorDocumento69 pagineIp Addressing Tutorb_y4uNessuna valutazione finora
- MemoryDocumento62 pagineMemoryLKNessuna valutazione finora
- Photoelectric EXP84Documento5 paginePhotoelectric EXP84Resy ApolinarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Do's & Dont's N Assemblng PCDocumento1 paginaDo's & Dont's N Assemblng PCResy ApolinarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of RAM and ROMDocumento6 pagineTypes of RAM and ROMTinu Elza Vinu100% (1)
- 2 Fundamentals of Electronic DevicesDocumento77 pagine2 Fundamentals of Electronic DevicesResy ApolinarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Wa200-8 Venss06304 1904 PDFDocumento24 pagineWa200-8 Venss06304 1904 PDFOktiano BudiNessuna valutazione finora
- Rotc Reviewer FinalsDocumento11 pagineRotc Reviewer FinalsAngel Atienza100% (1)
- Sample Spec For AWWA HDPE Pipe Fittings 6.02revDocumento6 pagineSample Spec For AWWA HDPE Pipe Fittings 6.02revmg4myNessuna valutazione finora
- Norma Geral Astm Bronze Alumínio - b150b150m.19198Documento7 pagineNorma Geral Astm Bronze Alumínio - b150b150m.19198EduardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pesud Abadi Mahakam Company Profile Abdul Basith-DikonversiDocumento48 paginePesud Abadi Mahakam Company Profile Abdul Basith-DikonversiAndi HafizNessuna valutazione finora
- Celestino vs. CIRDocumento6 pagineCelestino vs. CIRchristopher d. balubayanNessuna valutazione finora
- THE Ketofeed Diet Book v2Documento43 pagineTHE Ketofeed Diet Book v2jacosta12100% (1)
- STS Reviewer FinalsDocumento33 pagineSTS Reviewer FinalsLeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Shaft DeflectionDocumento15 pagineShaft Deflectionfreek_jamesNessuna valutazione finora
- (Essential Skills For Nurses Series) Philippa Sully - Joan Dallas-Essential Communication Skills For Nursing and Midwifery-Mosby - Elsevier (2010) PDFDocumento250 pagine(Essential Skills For Nurses Series) Philippa Sully - Joan Dallas-Essential Communication Skills For Nursing and Midwifery-Mosby - Elsevier (2010) PDFRetno SumaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Modal Verbs of Ability and PossibilityDocumento12 pagineModal Verbs of Ability and PossibilitymslolinrNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Love Spells That WorkDocumento14 pagineSimple Love Spells That Workagg24ankitNessuna valutazione finora
- G2A Glitch DONT LEAK 2Documento7 pagineG2A Glitch DONT LEAK 2qDeficiencyNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019q123.ev3-Descon Engro Level Gauges-QDocumento7 pagine2019q123.ev3-Descon Engro Level Gauges-Qengr_umer_01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Job Sheet 1Documento5 pagineJob Sheet 1Sue AzizNessuna valutazione finora
- Towards A Brighter Ecological Future: Group 2Documento24 pagineTowards A Brighter Ecological Future: Group 2As YangNessuna valutazione finora
- RCD ManagementDocumento6 pagineRCD ManagementPindoterONessuna valutazione finora
- Digital ThermometerDocumento12 pagineDigital Thermometershahpatel19Nessuna valutazione finora
- 30xa 100t PDFDocumento162 pagine30xa 100t PDFleung ka kitNessuna valutazione finora
- 1evolution of O and M TheoryDocumento27 pagine1evolution of O and M TheoryTracy AdraNessuna valutazione finora
- Stitch2421 1 Kit PDFDocumento8 pagineStitch2421 1 Kit PDFJoshua Robertson100% (1)
- Lecture 5: Triangulation Adjustment Triangulation: in This Lecture We Focus On The Second MethodDocumento5 pagineLecture 5: Triangulation Adjustment Triangulation: in This Lecture We Focus On The Second MethodXogr BargarayNessuna valutazione finora
- Al Multaqaa Presentation v2Documento22 pagineAl Multaqaa Presentation v2Hasaan WaheedNessuna valutazione finora
- About TableauDocumento22 pagineAbout TableauTarun Sharma67% (3)
- Thom22e ch03 FinalDocumento44 pagineThom22e ch03 FinalDionisius AlvianNessuna valutazione finora
- Panel Hospital List IGIDocumento6 paginePanel Hospital List IGIAbdul RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- College Invitation Letter - Managedia 2023Documento2 pagineCollege Invitation Letter - Managedia 2023Sandeep DeyNessuna valutazione finora