Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
1-CCNA - Internetworking - Introduction PDF
Caricato da
chana107Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1-CCNA - Internetworking - Introduction PDF
Caricato da
chana107Copyright:
Formati disponibili
CCNA - Internetworking - Introduction
http://ciscotests.org/ccna.php?part=1&page=1
Home
Courses
Tests
Useful
Articles
About
CiscoTests.ORG Want to Learn?
Sponsored Links Navigation
Part 1 - Internetworking Part 2 - IP Addressing and Subnetting. NAT Part 3 - LAN Switching. Spanning Tree Protocol Part 4 - Cisco IOS Part 5 - Virtual LANs (VLANs) Part 6 - RIP, IGRP and Static Routes Part 7 - EIGRP and OSPF Part 8 - Internet Protocol Version 6 Part 9 - Poit-to-Point Lines Part 10 - ISDN and Dial-on-Demand Routing Part 11 - Frame Relay Part 12 - IP Access Lists (ACLs) Part 13 - Wireless Networks
CCNA :: Part 1 - Internetworking
Pages: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
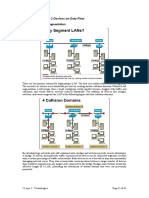
Networks and networking have grown exponentially over the last 15 years. Theyve had to evolve at light speed just to keep up with huge increases in basic missioncritical user needs such as sharing data and printers, as well as more advanced demands such as voice and video conferencing. Unless everyone who needs to share network resources is located in the same office area (an increasingly uncommon situation), the challenge is to connect the sometimes many relevant networks together so all users can share the network resources. Its also likely that at some point, youll have to break up one large network into a number of smaller ones because user response has decresed to a trickle as the network grew and grew and LAN traffic congestion reached overwhelming proportions. Breaking up a larger network into a number of smaller ones is called network segmentation, and its accomplished using routers, switches, and bridges. Possible causes of LAN traffic congestion are: Too many hosts in a broadcast domain Broadcast storms Multicasting Low bandwidth Adding hubs for connectivity to the network A large amount of ARP or IPX traffic (IPX is a Novell routing protocol) Routers are used to connect networks together and route packets of data from one network to another. Cisco became the de facto standard of routers because of their high-quality router products, great selection, and fantastic service. Routers, by default, break up a broadcast domain, which is the set of all devices on a network segment that hear all broadcasts sent on that segment. Breaking up a broadcast domain is important because when a host or server sends a network broadcast, every device on the network must read and process that broadcast unless youve got a router. When the routers interface receives this broadcast, it can respond by basically saying Thanks, but no thanks, and discard the broadcast without forwarding it on to other networks. Even though routers are known for breaking up broadcast domains by default, its important to remember that they break up collision domains as well. Two advantages of using routers in your network are: They dont forward broadcasts by default. They can filter the network based on layer 3 (Network layer) information (i.e., IP address).
Search
Search
Four router functions in your network can be listed as: Packet switching Packet filtering Internetwork communication Path selection Switches arent used to create internetworks, theyre employed to add functionality to an internetwork LAN. The main purpose of a switch is to make a LAN work betterto optimize its performanceproviding more bandwidth for the LANs users. And switches dont forward packets to other networks as routers do. Instead, they only switch frames from one port to another within the switched network. Unlike layer 2 switches that forward or filter frames, routers (layer 3 switches) use logical addressing and provide what is called packet switching. Routers can also provide packet filtering by using access-lists (discussed later), and when routers connect two or more networks together and use logical addressing (IP), this is called an internetwork. Lastly, routers use a routing table (map of the internetwork) to make path selections and to forward packets to remote networks.
Support us
If you are interested in supporting our work and would like to contribute, you are welcome to make a small donation. Please contact us for more details! If you have a private blog or you are participating in some community, feel free to post a link to this site or any part of it! It will be a great help and will surely be appreciated. Thank you!
Switches create separate collision domains, but a single broadcast domain. Routers provide a separate broadcast domain for each interface.
1 of 2
11/21/2011 9:00 PM
CCNA - Internetworking - Introduction
http://ciscotests.org/ccna.php?part=1&page=1
Fig. 1 Notice that the router is found at center stage, and that it connects each physical network together! The best network connected to the router is the LAN switch network on the left, because each port on that switch breaks up collision domains. But its not all goodall devices are still in the same broadcast domain. If your broadcast domains are too large, the users have less bandwidth and are required to process more broadcasts, and network response time will slow to a level that could cause office riots. Obviously, the best network is one thats correctly configured to meet the business requirements of the company it serves. LAN switches with routers, correctly placed in the network, are the best network design. This book will help you understand the basics of routers and switches so you can make tight, informed decisions on a case-by-case basis. Pages: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
2007 CiscoTests.ORG | Valid: XHTML | Valid: CSS
Web Hosting
Home | RSS Feed
All pages within this Internet site ("Site") are the property of CiscoTests.ORG. Cisco, Cisco Systems, CCDA, CCENT, CCNA, CCDP, CCIP, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, CCIE and the Cisco Systems logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. in the United States and certain other countries. All other trademarks are trademarks of their respective owners.
2 of 2
11/21/2011 9:00 PM
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- vLAN SwitchingDocumento30 paginevLAN Switchingapi-3728377100% (1)
- Nhap NETDocumento46 pagineNhap NEThoangdo11122002Nessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA 1 - Chapter 10: Planning and Cabling NetworksDocumento62 pagineCCNA 1 - Chapter 10: Planning and Cabling NetworksFrank ChenNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.5 Effects of Layer 2 Devices On Data Flow: 7.5.1 Ethernet LAN SegmentationDocumento9 pagine7.5 Effects of Layer 2 Devices On Data Flow: 7.5.1 Ethernet LAN SegmentationgkshishirNessuna valutazione finora
- Netapp Best PractiseDocumento25 pagineNetapp Best PractiseJohn MathewNessuna valutazione finora
- VLANS and Broadcast DomainsDocumento5 pagineVLANS and Broadcast Domainsartsan3Nessuna valutazione finora
- SW 3/22/2010 CCNA3 Chap 1 Study Answers 1Documento7 pagineSW 3/22/2010 CCNA3 Chap 1 Study Answers 1Hien TauNessuna valutazione finora
- Project ReportDocumento26 pagineProject ReportRashmi GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch07 - Wired and Wireless LAN - Q&ADocumento21 pagineCh07 - Wired and Wireless LAN - Q&ATuan Doan100% (1)
- Network Engineer Interview Questions-2Documento14 pagineNetwork Engineer Interview Questions-2mushahidNessuna valutazione finora
- Configuring A RouterDocumento6 pagineConfiguring A Routerartsan3Nessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Planning and Cabling NetworksDocumento35 pagine10 Planning and Cabling NetworksErangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rail NetDocumento24 pagineRail NetAugust mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment ACNDocumento7 pagineAssignment ACNMukeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Router Vs SwitchDocumento2 pagineRouter Vs SwitchKaustubh ParkerNessuna valutazione finora
- VlanDocumento46 pagineVlanchitrang_11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Network Essentials Fundamentals of NetworkingDocumento6 pagineNetwork Essentials Fundamentals of NetworkingNaveen JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking AssignmentDocumento80 pagineNetworking AssignmentSimon NdongaNessuna valutazione finora
- IT7 - Networking 2 Module 1Documento47 pagineIT7 - Networking 2 Module 1Christian Jay CusayNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA3 Study GuideDocumento42 pagineCCNA3 Study Guidesoma45100% (1)
- Ccna3 Mod5 SwitchesDocumento22 pagineCcna3 Mod5 SwitchesPrahallad RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Reprot ON: Cover PageDocumento43 pagineProject Reprot ON: Cover PageArun KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch08 Backbone Network Q&ADocumento11 pagineCh08 Backbone Network Q&ATuan Doan0% (1)
- Routers 2 Gateway 3: Table of ContentDocumento10 pagineRouters 2 Gateway 3: Table of ContentmaxpainNessuna valutazione finora
- VLAN DOC'mDocumento7 pagineVLAN DOC'mvinod kapateNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNADocumento195 pagineCCNAirfan_yousaf4231Nessuna valutazione finora
- Recommended Resilient Campus Network Design: Best Practice DocumentDocumento28 pagineRecommended Resilient Campus Network Design: Best Practice DocumentAnonymous BjaA0IiYNessuna valutazione finora
- Reports On VlanDocumento25 pagineReports On Vlanshiva200100% (2)
- Richard Brown Unit5Documento1 paginaRichard Brown Unit5Rick BrownNessuna valutazione finora
- Materi Sesi 2 SDLRDocumento12 pagineMateri Sesi 2 SDLRfitriNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 07Documento44 pagineCH 07Varun SrinivasNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA-2::: Module-1:::: OverviewDocumento36 pagineCCNA-2::: Module-1:::: OverviewbuwenekabaNessuna valutazione finora
- Moxa White Paper: Optimizing Subnet Interconnections With Industrial Layer 3 SwitchesDocumento7 pagineMoxa White Paper: Optimizing Subnet Interconnections With Industrial Layer 3 Switchesgob7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Network Essentials Fundamentals of NetworkingDocumento11 pagineNetwork Essentials Fundamentals of Networkingneeraj kumar singhNessuna valutazione finora
- High Performance Networking UnleashedDocumento428 pagineHigh Performance Networking UnleashedCoco LinoNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A LANDocumento4 pagineWhat Is A LANLakshmana Rao SNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Part 2 Network DesignDocumento34 pagineChapter 1 Part 2 Network DesignEncik BurnNessuna valutazione finora
- Net+2009CP p04Documento77 pagineNet+2009CP p04Nigel RamasawmyNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 1 LAN DesignDocumento5 pagineExercise 1 LAN Designmysticman0628Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ccna Interview Questions AnswersDocumento30 pagineCcna Interview Questions AnswersMistah RoflcopterNessuna valutazione finora
- NN - LAN Troubleshooting and Base LiningDocumento20 pagineNN - LAN Troubleshooting and Base LiningJae Phoenix JohnsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Ccna NotesDocumento13 pagineCcna NotesfudgeboyNessuna valutazione finora
- 5implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH) Foundation Learning Guide - Fundamentals Review - Switching Introduction PDFDocumento5 pagine5implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH) Foundation Learning Guide - Fundamentals Review - Switching Introduction PDFAbdulkerim SeidNessuna valutazione finora
- Network ProcDocumento12 pagineNetwork Procmilan20Nessuna valutazione finora
- IT7 - Networking 2 Module 3Documento143 pagineIT7 - Networking 2 Module 3Christian Jay CusayNessuna valutazione finora
- Internetworking Devices Used On A NetworkDocumento25 pagineInternetworking Devices Used On A NetworkmanjitNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Implement OSPF: PC Network AdvisorDocumento5 pagineHow To Implement OSPF: PC Network AdvisorKabir HindustaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking and Internetworking DevicesDocumento21 pagineNetworking and Internetworking DevicesDip DasNessuna valutazione finora
- IP-Router Design - Part 1Documento29 pagineIP-Router Design - Part 1doodoo33Nessuna valutazione finora
- Local Area Networks Part IDocumento33 pagineLocal Area Networks Part Ianon_493194912Nessuna valutazione finora
- Planning and Cabling NetworksDocumento35 paginePlanning and Cabling NetworksJohn Carmelo SaulonNessuna valutazione finora
- Bridging and Switching BasicsDocumento6 pagineBridging and Switching BasicsRicardo Herrera PradoNessuna valutazione finora
- Opnet ResearchDocumento7 pagineOpnet Researchhossam80Nessuna valutazione finora
- Software-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachDa EverandSoftware-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Switch and RouterDocumento7 pagineSwitch and RouterIsmail Hossain RanaNessuna valutazione finora
- DCCN Project FNL 5Documento8 pagineDCCN Project FNL 5Pratik SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Data Link Layer SwitchesDocumento12 pagineUnderstanding Data Link Layer SwitchesReymond D. SeNessuna valutazione finora
- Distributed DatabasesDocumento165 pagineDistributed DatabasesAvanakshSinghNessuna valutazione finora
- TCP/IP: Network+ Protocols And Campus LAN Switching FundamentalsDa EverandTCP/IP: Network+ Protocols And Campus LAN Switching FundamentalsNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewDa EverandCisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- Asp inDocumento103 pagineAsp inAndrew Loniak0% (1)
- Week 1 - Webinar Slides - 1 PDFDocumento13 pagineWeek 1 - Webinar Slides - 1 PDFBilal MehmoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 7.5.2: Challenge Wireless Configuration: Topology DiagramDocumento35 pagineLab 7.5.2: Challenge Wireless Configuration: Topology DiagramAlberto BaldaNessuna valutazione finora
- Layer 2 Switching and Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) :: Revision No.: PPT/2K804/04Documento64 pagineLayer 2 Switching and Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) :: Revision No.: PPT/2K804/04subhashkNessuna valutazione finora
- Gs33l01a10 40eDocumento12 pagineGs33l01a10 40esina20795100% (1)
- Cisco 3Documento396 pagineCisco 3Vihaga JayalathNessuna valutazione finora
- ITN InstructorPPT Chapter 5 CiscoDocumento67 pagineITN InstructorPPT Chapter 5 Ciscohendrian15Nessuna valutazione finora
- Layer 3 Switches PPT 3464Documento17 pagineLayer 3 Switches PPT 3464skskumarkadwa24Nessuna valutazione finora
- Huawei Quidway Ar 2921 GuideDocumento59 pagineHuawei Quidway Ar 2921 Guideanoop.ashu9376Nessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA 1 v5.0 R&S ITN Final Exam Answers 2014Documento22 pagineCCNA 1 v5.0 R&S ITN Final Exam Answers 2014jonmicNessuna valutazione finora
- ESwitching Lab 1 3 3Documento6 pagineESwitching Lab 1 3 3Ninja NuggetNessuna valutazione finora
- High Speed Lan'sDocumento35 pagineHigh Speed Lan'sbrr_ranj100% (1)
- SW Ch01Documento33 pagineSW Ch01Fabio QuintanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Show Vlan CommandsDocumento101 pagineShow Vlan CommandsJesús Solís de OvandoNessuna valutazione finora
- HP2 Z12 Study GuideDocumento1.086 pagineHP2 Z12 Study GuideBadBrew0% (1)
- Alteon Application Switch 25.1.0 RNDocumento13 pagineAlteon Application Switch 25.1.0 RNMoreno GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks (BCMSN)Documento9 pagineBuilding Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks (BCMSN)Hebert MolinaNessuna valutazione finora
- 98-366 MTA Networking Fundamental - SlidesDocumento232 pagine98-366 MTA Networking Fundamental - Slidesharyanto100% (3)
- En ESwitching SLM v4030Documento192 pagineEn ESwitching SLM v4030Coliseo De Gallos Fina EstampaNessuna valutazione finora
- F05 Work PDFDocumento114 pagineF05 Work PDFzaabullaNessuna valutazione finora
- 640 822Documento233 pagine640 822Rana TariqNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA 3 Final Exam Answers (2012)Documento27 pagineCCNA 3 Final Exam Answers (2012)Juan Diego Arellano VitelaNessuna valutazione finora
- NetEngine 80E, 40E Core Router Product Brochure (Eng) PDFDocumento16 pagineNetEngine 80E, 40E Core Router Product Brochure (Eng) PDFCole HeikNessuna valutazione finora
- ESwitching Lab 2 5 1-Answer PDFDocumento16 pagineESwitching Lab 2 5 1-Answer PDFgakin2Nessuna valutazione finora
- ESwitching PTAct 2 5 1-Answer 3Documento10 pagineESwitching PTAct 2 5 1-Answer 3Hari HermanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.3.1.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Layer 3 Switching and Inter-VLAN RoutingDocumento4 pagine2.3.1.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Layer 3 Switching and Inter-VLAN RoutingJessica GregoryNessuna valutazione finora
- Top CCNA QuestionsDocumento31 pagineTop CCNA QuestionsDinesh LambatNessuna valutazione finora
- L2, L3, L4 Protocols Chapter 2Documento24 pagineL2, L3, L4 Protocols Chapter 2sathish77s100% (1)
- Lab 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration: (Instructor Version)Documento14 pagineLab 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration: (Instructor Version)Phạm Tùng DươngNessuna valutazione finora