Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Cerebrovascular Accident Pathophysiology
Caricato da
Berde KangleonDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Cerebrovascular Accident Pathophysiology
Caricato da
Berde KangleonCopyright:
Formati disponibili
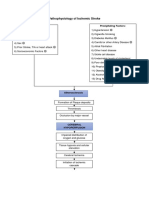
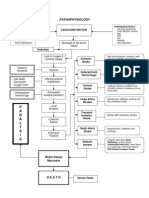
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Precipitating factors: Hypertension
Atrial fibrillation Atherosclerosis Stenosis of the artery Blood swirls around the irregular surface of the plaques, causing platelets to adhere to the plaque. [thrombus formation] Obstruction of vessel lumen [emboli formation] High cholesterol Diabetes Atherosclerosis Smoking Alcohol Obesity Carotid Artery Predisposing factors: Disease Age Gender Race Heredity Pregnancy Sudden onset of manifestations Hemorrhagic stroke Bleeding into brain tissue Rupture of cerebral vessel
Emboli detachment Travels through the cerebral circulation until it lodges & occludes a cerebral artery Ischemic stroke
Slow onset of manifestations
Sx: occipital or nuchal headache, vertigo or syncope, paresthesias, transient paralysis, epistaxis, and retinal hemorrhages
Cells in the center of the stroke area, or the core, die almost immediately after the stroke onset [primary neuronal injury] A cascade of biochemical processes occurs within minutes of cerebral ischemia. Local acidosis occurs.
Sx: apahsia, dysarthia, dysphagia, apraxia, visual changes, homonymous hemianopia, Horners Syndrome, agnosia, unilateral neglect, sensory deficits, behavioral changes, incontinence
Membrane depolarization occurs.
Results in influx of calcium and sodium.
May lead to temporary neurologic deficits
Cytotoxic edema & cell death [secondary neuronal injury]
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocumento3 pagineStroke PathophysiologyMaureen Balagtas89% (9)
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocumento3 pagineStroke PathophysiologyMaureen EricaNessuna valutazione finora
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocumento2 pagineStroke PathophysiologyJaessa Feliciano100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of CVADocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of CVAChristine Joy Ilao PasnoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsDocumento4 paginePathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsLilot Antonio Rodriguez Vinarao100% (5)
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocumento2 paginePathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsJames John Galac88% (8)
- Pathophysiology CVADocumento1 paginaPathophysiology CVANenette Aquino100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke FinalDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke FinalAcohCChao75% (4)
- 3 PathophysiologyDocumento4 pagine3 PathophysiologySherlyn KirisakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology Diagram - StrokeDocumento3 paginePathophysiology Diagram - Strokemisstheatricality130100% (1)
- Schematic Pathophysiology CVADocumento10 pagineSchematic Pathophysiology CVAheiyu100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentByron Paz Te100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentJohn Michael FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of CVADocumento7 paginePathophysiology of CVAsarzlasco0967% (3)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of StrokeJoy Rachelle Fermin100% (2)
- Pathophysiology CVADocumento2 paginePathophysiology CVASewyel Garburi100% (6)
- CVA PathophysiologyDocumento3 pagineCVA Pathophysiologyshmily_0810Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of CVADocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of CVAYoussry JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology CVADocumento2 paginePathophysiology CVATerence Valdehueza67% (3)
- Pathophysiology CVA (Final2)Documento10 paginePathophysiology CVA (Final2)Jayselle Costes FelipeNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology Hemor CVADocumento4 paginePathophysiology Hemor CVAMatthew Emmanuel M. Martinez100% (2)
- General Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocumento2 pagineGeneral Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsIrish Nicole DCNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 4 - Hemorrhagic StrokeDocumento60 pagineGroup 4 - Hemorrhagic StrokeKitz T AnasarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Cva-Hpnii-Hemorrhagic StrokeDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of Cva-Hpnii-Hemorrhagic StrokeLarisse de Leon82% (11)
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocumento5 pagineStroke Pathophysiologycinnabon_heart9100% (3)
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocumento2 pagineSubarachnoid HemorrhageJethro Bacayo Zamora100% (1)
- Schematic Diagram of StrokeDocumento1 paginaSchematic Diagram of StrokeCyrus De Asis100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentPaulo de Jesus86% (7)
- Bachelor of Nursing Science With HonoursDocumento17 pagineBachelor of Nursing Science With HonoursMaryam HasanahNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of StrokeACe JAy100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocumento4 paginePathophysiology of StrokeACe JAyNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology HypertensionDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology HypertensionAlinor Abubacar100% (3)
- Concept Map TBIDocumento2 pagineConcept Map TBIraquel maniego67% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology of CVADocumento4 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of CVAKimsha ConcepcionNessuna valutazione finora
- INTRODUCTION A Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA), An Ischemic Stroke or "BrainDocumento30 pagineINTRODUCTION A Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA), An Ischemic Stroke or "BrainCherie May100% (5)
- Acute Ischemic Stroke Concept MapDocumento6 pagineAcute Ischemic Stroke Concept MapMoonyeen Jann Casera Balic100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of StrokeAqeel Al-Mahdaly0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Acute Ischemic StrokeDocumento12 paginePathophysiology of Acute Ischemic Strokeidno1008100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocumento7 paginePathophysiology of StrokeCHANDAN RAINessuna valutazione finora
- Path o Client BasedDocumento3 paginePath o Client BasedJane TuazonNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology CKDDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology CKDReymon Mary Janine100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of CHFDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of CHFImae Mayo60% (5)
- Subarachnoid Haemorrhage:Pathology, Clinical Features and ManagementDocumento48 pagineSubarachnoid Haemorrhage:Pathology, Clinical Features and Managementesene1100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CVADocumento11 paginePathophysiology CVAallyana kim figueroa lavarias100% (1)
- CVA Case StudyDocumento20 pagineCVA Case Studybetchai18100% (5)
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureDocumento3 paginePathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart Failurea_samiane64% (11)
- Presenter: DR Edalia Facilitator: Prof AdamDocumento35 paginePresenter: DR Edalia Facilitator: Prof AdamUzma KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Casebased PathoDocumento2 pagineCasebased PathoJm MapulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Stroke Pa Tho PhysiologyDocumento2 pagineStroke Pa Tho PhysiologyBrandoSantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Stroke: Pathophysiology, Types, Management Categories, and Vascular SyndromesDocumento49 pagineStroke: Pathophysiology, Types, Management Categories, and Vascular Syndromesrabia khalidNessuna valutazione finora
- REPORTDocumento34 pagineREPORTClaire GidoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocumento79 pagineCerebrovascular AccidentKathy B. AbuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Original StrokeDocumento130 pagineOriginal StrokeGafencu SergiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Stroke MsDocumento57 pagineStroke MsAishwarya ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Cva Swiss Bell HotelDocumento80 pagineCva Swiss Bell HotelKumbendy Sada0% (1)
- Cerebrovascular DseDocumento303 pagineCerebrovascular DsejjamadriagaNessuna valutazione finora
- StrokeDocumento66 pagineStrokeJoshua Smith100% (1)
- CvaDocumento79 pagineCvaAnn Heerah100% (1)
- Cerebrovascular Accident or StrokeDocumento3 pagineCerebrovascular Accident or StrokeJohn DNessuna valutazione finora
- BAU PTR-Neurology-Lecture 11-StrokeDocumento133 pagineBAU PTR-Neurology-Lecture 11-Strokeerfan mohammadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Tachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Assess Appropriateness For Clinical ConditionDocumento1 paginaTachycardia With A Pulse Algorithm: Assess Appropriateness For Clinical ConditionDendy Frannuzul RamadhanNessuna valutazione finora
- ACLS Exam - A&B VersionsDocumento36 pagineACLS Exam - A&B VersionsMohamed El-sayed100% (1)
- Assignment CVSDocumento6 pagineAssignment CVSBSN 2-2 Espiritu Melody Mae DNessuna valutazione finora
- Vital Sign #1: Body TemperatureDocumento5 pagineVital Sign #1: Body TemperaturePrimelift Safety Resources LimitedNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepare For The Critically Complex Patient.: Swan-Ganz Advanced Technology Pulmonary Artery CatheterDocumento4 paginePrepare For The Critically Complex Patient.: Swan-Ganz Advanced Technology Pulmonary Artery Cathetermaria claudia angaritaNessuna valutazione finora
- OmerDocumento33 pagineOmerNoor Hasan WaheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart Dissection, Lab Report GuideDocumento5 pagineHeart Dissection, Lab Report GuideJohn OsborneNessuna valutazione finora
- Vital Signs TakingDocumento1 paginaVital Signs TakingReu MarquezNessuna valutazione finora
- CACVS2016 AbstractBookDocumento100 pagineCACVS2016 AbstractBookChuk IfeanyiNessuna valutazione finora
- Model 1Documento4 pagineModel 1Arini NingrumNessuna valutazione finora
- Plante PacemakersDocumento57 paginePlante Pacemakersdragon66100% (1)
- Current State of Noninvasive, Continuous.12 PDFDocumento7 pagineCurrent State of Noninvasive, Continuous.12 PDFFIA SlotNessuna valutazione finora
- ACUTE INFLAMMATION (Vascular Changes)Documento22 pagineACUTE INFLAMMATION (Vascular Changes)Ramesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- ACLS Study GuideDocumento305 pagineACLS Study GuideRahma Rafina100% (2)
- CertainlyDocumento8 pagineCertainlyroseneels9Nessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 1.1 and 1.2 SOFTDocumento5 pagineMODULE 1.1 and 1.2 SOFTJason SebastianNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular System Test PDFDocumento10 pagineCardiovascular System Test PDFMonique Mavronicolas75% (4)
- Physioex Activity 2Documento4 paginePhysioex Activity 2Shania Milky ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Efficacy of Varmam On Varicose Veins: December 2015Documento8 pagineEfficacy of Varmam On Varicose Veins: December 2015Murali SmatNessuna valutazione finora
- Percutaneous InterventionsDocumento55 paginePercutaneous InterventionsShannon Bellamy-FoggNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecg TestDocumento67 pagineEcg TestEm KayNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemo Dynamic Disorders Thrombo Embolism and ShockDocumento29 pagineHemo Dynamic Disorders Thrombo Embolism and ShockMai ÜüNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardio QuizDocumento100 pagineCardio QuizEvidence ChaibvaNessuna valutazione finora
- STRIDE BP Office-Clinic BP Monitors 26 Jun 2020Documento1 paginaSTRIDE BP Office-Clinic BP Monitors 26 Jun 2020rizkitrismimandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tadano Hydraulic Crane Ar 1000m 1 p2 1ej Parts Catalog EnjpDocumento22 pagineTadano Hydraulic Crane Ar 1000m 1 p2 1ej Parts Catalog Enjprachelharrison091289kdj100% (103)
- Congestive Heart Failure (PH 2 Bemdiji)Documento1 paginaCongestive Heart Failure (PH 2 Bemdiji)api-285694335Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wiggers Diagram SlidesDocumento15 pagineWiggers Diagram SlidesKuro ShiroNessuna valutazione finora
- Herbal Medicine For The Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease: Clinical ConsiderationsDocumento10 pagineHerbal Medicine For The Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease: Clinical ConsiderationsTasneem AnwaraliNessuna valutazione finora
- Say No To Code Blue, Say YesDocumento36 pagineSay No To Code Blue, Say YesTheodorus PY PranotoNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocumento13 pagineAcute Myocardial InfarctionSajjad KabirNessuna valutazione finora