Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Tissue
Caricato da
Mark PangilinanCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Tissue
Caricato da
Mark PangilinanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
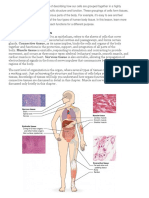
Animal tissues Based on morphology, animal tissues can be grouped into four basic types.
Multiple tissue types comprise organs and body structures. While all animals can generally be considered to contain the four tissue types, the manifestation of these tissues can differ depending on the type of organism. For example, the origin of the cells comprising a particular tissue type may differ developmentally for different classifications of animals. The epithelium in all animals is derived from the ectoderm and endoderm with a small contribution from the mesoderm which forms the endothelium. By contrast, a true connective tissue is present only in triploblastic animals; diploblastic animals such as sponges, jellyfish and coral in effect do not have connective tissue but rather an acellular gel known as the mesoglea separates different tissues types in these animals. The mesoglea serves the function of a connective tissue but is derived from ectoderm.
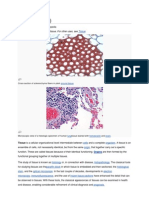
Epithelium
Epithelium is single layer of cells held together via occluding junctions called tight junctions, to create a selectively permeable barrier. This tissue covers all organismal surfaces that come in contact with the external environment such as the skin, the airways, and the digestive tract. It serves functions of protection, secretion, and absorption, and is separated from other tissues below by a basal lamina. Endothelium, which comprises the vasculature, is a specialized type of epithelium.
Connective tissue
Connective tissue is comprised of cells separated by non-living material, which is called extracellular matrix. Connective tissue holds other tissues together such as in the formation of organs, and has the ability to stretch and contract passively. Bone, often referred to as osseous tissue, and blood are examples of specialized connective tissues.
Muscle tissue
Muscle cells form the active contractile tissue of the body known as muscle tissue. Muscle tissue functions to produce force and cause motion, either locomotion or movement within internal organs. Muscle tissue is separated into three distinct categories: visceral or smooth muscle, which is found in the inner linings of organs; skeletal muscle, which is found attached to bone providing for gross movement; and cardiac muscle which is found in the heart, allowing it to contract and pump blood throughout an organism.
Neural tissue
Cells comprising the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system are classified as neural tissue. In the central nervous system, neural tissue forms the brain, cranial nerves and spinal cord and, in the peripheral nervous system, peripheral nerves inclusive of the motor neurons. Source: wikipedia_ bioligical tissue
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Animal TissueDocumento3 pagineAnimal TissueAkmal MusyaffaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Report of Animal Tissue Observation ResultDocumento4 pagineThe Report of Animal Tissue Observation Resulthilmisifa0% (1)
- Nselec TissueDocumento6 pagineNselec TissueClaire funtilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Información de TissueDocumento2 pagineInformación de TissueEduardo Boixo MartínezNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreDocumento9 pagineExercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreMaria MarmitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ministry of Education Academia Latina Level: 11"A ScienceDocumento18 pagineMinistry of Education Academia Latina Level: 11"A ScienceleoNessuna valutazione finora
- Class Discussion On TissueDocumento2 pagineClass Discussion On TissueKristhine Abegail Manangan-GamiaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Tissues and Animal Tissues 1Documento6 paginePlant Tissues and Animal Tissues 1PawanNessuna valutazione finora
- This Article Is About Biological Tissue. For Other Uses, SeeDocumento5 pagineThis Article Is About Biological Tissue. For Other Uses, Seerjohn 7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Body Tissues: Tissue Matrix MuscleDocumento8 pagineBody Tissues: Tissue Matrix Muscle9. Hoàng Mai ChiNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Tissue Hand-Out Bio 101Documento3 pagineAnimal Tissue Hand-Out Bio 101Amor Panopio MagtibayNessuna valutazione finora
- Specificatio N: Tissues: Epithelial: Simple (CuboidalDocumento22 pagineSpecificatio N: Tissues: Epithelial: Simple (CuboidalFatma AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Audio 1 Types of TissuesDocumento9 pagineAudio 1 Types of TissuesTricia De TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- The Four Types of Tissues: Epithelial Tissue, Also Referred To As Epithelium, Refers To The Sheets of Cells That CoverDocumento9 pagineThe Four Types of Tissues: Epithelial Tissue, Also Referred To As Epithelium, Refers To The Sheets of Cells That CoveraudreyNessuna valutazione finora
- Histology Notes: Epithelial TissueDocumento4 pagineHistology Notes: Epithelial TissueSteph AsideNessuna valutazione finora
- Human TissuesDocumento7 pagineHuman Tissuesapi-269312030Nessuna valutazione finora
- Animal TissueDocumento1 paginaAnimal TissueDicelleєїзShell OreoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues and Cells Part 1 - Grade 7 - BiologyDocumento4 pagineTissues and Cells Part 1 - Grade 7 - BiologyYasmina Jamal GholoumNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue - WikipediaDocumento42 pagineTissue - WikipediaLumina More100% (1)
- Speech SciebnceDocumento2 pagineSpeech SciebnceluisNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal TissuesDocumento13 pagineAnimal TissuesYudatami TiaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology LabDocumento12 pagineAnatomy and Physiology Labشهد إياد0% (1)
- TissueDocumento36 pagineTissueMinan Fahnanza100% (1)
- Human Body Tissues Power PointDocumento60 pagineHuman Body Tissues Power PointMaxwell C Jay KafwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- TISSUESDocumento12 pagineTISSUESMaria Stephanie LabutapNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal TissuesDocumento1 paginaAnimal TissuesIan BergadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaphy ReportingDocumento8 pagineAnaphy ReportingRushyl Angela FaeldanNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Tissue and Animal TissueDocumento2 paginePlant Tissue and Animal TissueJibril Halim SilaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue Form & FunctionDocumento14 pagineTissue Form & FunctionLi KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresDocumento58 pagineLesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresPhoenixNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell: Vertebrate Body OrganizationDocumento11 pagineCell: Vertebrate Body OrganizationSyuri MustikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Is Cell Important For HumansDocumento2 pagineIs Cell Important For HumansniallevetriscaNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Animal TissueDocumento8 pagine01 Animal TissueRohit SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Lect1. Type of Tissue DR - Aida AlobaidiDocumento22 pagineBiology Lect1. Type of Tissue DR - Aida AlobaidiYaqeen AlaidyNessuna valutazione finora
- Abella, Franz Karl - Zoology Reviewer Pt. 1Documento4 pagineAbella, Franz Karl - Zoology Reviewer Pt. 1Franz AbellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento23 pagineAnatomy and Physiologyapi-464344582100% (1)
- CHAPTER V: Tissues: Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Muscular Tissue Nervous TissueDocumento10 pagineCHAPTER V: Tissues: Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Muscular Tissue Nervous TissueAem TalNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal CellDocumento5 pagineAnimal CellNan Fen Jin Sabolarce100% (1)
- Fundamental Types of Animal TissuesDocumento12 pagineFundamental Types of Animal TissuesBriana Franshay Aguilar SiotingNessuna valutazione finora
- ZOO 112 - Module 1Documento26 pagineZOO 112 - Module 1Hakeem LawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Tissues 1. EpithelialDocumento3 pagineAnimal Tissues 1. EpithelialRogeimar Claire MangomayaoNessuna valutazione finora
- General Biology 2 Quarter 4 (Week 1-4) : Animals Specialized StructuresDocumento18 pagineGeneral Biology 2 Quarter 4 (Week 1-4) : Animals Specialized StructuresHannah CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Tissue: Epidermis (Outermost Covering) Simple Tissues: Epidermis TissueDocumento6 paginePlant Tissue: Epidermis (Outermost Covering) Simple Tissues: Epidermis TissueBhoomika GoyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Word - TISSUES OF THE BODY - MEDICS 20102011Documento5 pagineMicrosoft Word - TISSUES OF THE BODY - MEDICS 20102011AJAY KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue (Biology) - Wikipedia PDFDocumento37 pagineTissue (Biology) - Wikipedia PDFKissa FrecNessuna valutazione finora
- GEN BIO Q1M1subtopic WK 4 LectureDocumento4 pagineGEN BIO Q1M1subtopic WK 4 LectureDonnalyn Mae EscrupoloNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen Bio Module 4Documento8 pagineGen Bio Module 4rodriguezelmind20Nessuna valutazione finora
- TissueDocumento31 pagineTissuealiyyah aswinanda100% (1)
- ScienceDocumento4 pagineScienceMark timothy LumanlanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Theory and Types of CellsDocumento6 pagineCell Theory and Types of CellsLance Afraim MortelNessuna valutazione finora
- Why Human Beings Are Considered Complex Organisms Group 5Documento37 pagineWhy Human Beings Are Considered Complex Organisms Group 5Nuraini Zul100% (3)
- Topic Types of Connective Tissues in Human BodyDocumento13 pagineTopic Types of Connective Tissues in Human Bodysaeed qurashiNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Tissues1Documento4 pagine3 Tissues1api-159564163Nessuna valutazione finora
- That Means That Underlying The Cells That Are The Cellular Component of The Epithelial TissueDocumento3 pagineThat Means That Underlying The Cells That Are The Cellular Component of The Epithelial TissueDivine HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues (Notes)Documento11 pagineTissues (Notes)Rezeil CaNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Tissues: Epithelial Tissue Is Made Up of Layers of Tightly Packed Cells That Line The SurfacesDocumento3 pagineAnimal Tissues: Epithelial Tissue Is Made Up of Layers of Tightly Packed Cells That Line The SurfacesJamesNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal TissuesDocumento17 pagineAnimal TissuesMuskan Shree100% (1)
- Sri Arliza Febriani TGS 2 No.1Documento22 pagineSri Arliza Febriani TGS 2 No.1Sriarliza FebrianiNessuna valutazione finora