Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
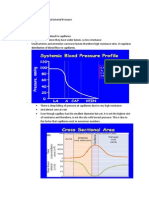
The Coronary Circulation
Caricato da
Amalina ZolkefleeCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
The Coronary Circulation
Caricato da
Amalina ZolkefleeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lecture 3- The Coronary Circulation 1.
Exit valves from ventricles - Pulmonary and aortic valve - Comprised of three semilunar cusps
Aortic sinus : a dilatation [orifice being dilated] between the aortic wall and each of the semilunar cusps of the aortic valve; from two of these sinuses the coronary arteries take origin.
Aortic valve Superior to each valve is the aortic sinus There are generally three aortic sinuses : the left posterior ( which gives rise to left coronary artery), the anterior( give rise to right coronary artery), and the right posterior ( no vessels arise from the right posterior aortic sinus- also known as non-coronary sinus)
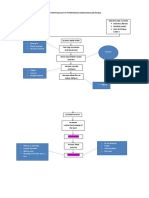
Right coronary artery From the right aortic sinus Sinuatrial node branch Site of the fastest depolarisation All hearts cells have the ability to generate the electrical impulses that trigger cardiac contraction, the SAN normally initiates it simply because it generates impulses slightly faster than other areas with pacemaker potential. Depolarisation becomes slower when it reaches AV and ventricle Right auricle and infundibulum Infundibulum- the conus arteriosus[ conical pouch formed from the upper and left angle of right ventricle in the chordate heart, from which the pulmonary trunk arises] is the outflow portion of the right ventricle, known as infundibulum of the heart[ is a funnel-shaped cavity or organ]
A-V groove Right coronary artery travel between right atrium and right ventricle Right marginal branch Right marginal branch of right coronary artery ( or also known as right marginal artery)is a large marginal branch which follows the acute margin of the heart and supplies branches to both surfaces of the right ventricle
AV nodal branch It electrically connects atrial and ventricular chambers Is an area of specialised tissue between the atria and the ventricles of the heart, in the posteroinferior region of interatrial septum near the opening of coronary sinus
## coronary sinus- opens into the right atrium between the inferior vena cava and the atrio-ventricular orifice Posterior interventricular artery (PIVA) Is an artery running in the posterior interventricular sulcus[groove that separate ventricles of the heart] to the apex of the heart where it meets with the anterior interventricular artery (AIVA) Septal branch Supply blood to posterior atrioventricular septum, Arteriolar anastomoses [ alternate pathways for blood]
Refers to connection between blood vessels or between other tubular structures such as loops of intestine. SUMMARY Right coronary artery supplies RA and most RV Diaphragmatic surface of LV Posterior 1/3 septum SAN[60%] ; AVN[80%] Left coronary artery Is an artery that arise from the aorta above the left cusp of the aortic valve and feeds blood to the left side of the heart. Left auricle and infundibulum It typically runs for 1 to 25 mm and then bifurcates into the anterior interventricular artery (AIVA) also called left anterior descending(LAD) artery and left circumflex artery(LCX) Left marginal artery is a branch of the circumflex artery Summary Left coronary artery supplies to : LA, most LV
Anterior surface of RV Anterior 2/3 of IV septum SAN [40%]; AVN[20%]
2. Anastomoses Anteriolar anastomoses In septum In posterior wall of LV Occlusion [blockage]: Angina, AMI[Myocardial Infarction] Gives time for healthy arterioles to open - Surface ( Capillary) Anastomoses Apex AV groove With pericardial arteries
3. DOMINANCE: Depends on PIVA - 60%+ of patients the right coronary artery(RCA) is said to be dominant because it supplies circulation to the inferior portion of interventricular septum via the right posterior descending coronary artery - 15% of patients the RCA is said to be non-codominat because it does not supply circulation to the inferior portion of interventricular septum via the right posterior descending coronary artery - In 8% of patients- the left coronary artery(LCA) is dominant because it travels to the cross section of AV groove and the posterior interventricular http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=endscreen&NR=1&v=eefHDKGWSR4 4. Myocardial Infarction: Complications - Possible within 20 minutes onset - Arrhythmias [disturbance or loss of regular rhythm]/ heart block - Cardiogenic shock/ CCF - Valve problems : acute mitral regurgitation[ a disorder of the heart in which the mitral valve does not close properly when the heart pumps out blood- abnormal leaking of blood from the left ventricle, through mitral valve, and the into left atrium, when left ventricle contracts- ie regurgitation of blood back into the left atrium] Papillary muscles may die off due to blockage in coronary artery
Can predict which coronary artery is blocked by injury pattern on the ECG 5. Veins of the Heart - The coronary sinus o Receives 60% venous blood opens at the lower end of the AV groove into the posterior wall of the right atrium
o o
Receives : Great cardiac vein(LAD/LCx) Middle cardiac vein(PIVA) Posterior vein of the LV Small cardiac vein(MA) Anterior cardiac veins Comprise three or four small vessels which collect blood from the front of the right ventricle and open into the right atrium Right marginal vein frequently opens into the right atrium and is therefore sometimes regarded as belonging to this group Cross anterior Surface RV Drain directly into RA ( unlike most cardiac veins which usually end in the coronary sinus Drain remaining 40% Venae cordis minimae Smallest cardiac vein: numerous small veins arising in the muscular walls and draining independently into the cavities of the heart, particularly the right atrium and ventricle Drains directly into all 4 chambers Valveless- forms AV shunts/ Collateral[ secondary or accessory] Circulation for parts of myocardium
6. Blood supply: Pericardium o Pericardiacophrenic arteries(internal thoracic)is a long slender branch of the internal thoracic artery. It accompanies the phrenic nerve, between pleura and pericardium, to the diaphragm, to which it is distributed.
o o o
Coronary arteries Supply from nearby structures/ extra-cardiac anastomosis [ it anastomoses with musculophrenic and inferior phrenic arteries]
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Arterial PressureDocumento7 pagineArterial PressureAmalina ZolkefleeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Conducting System in Health and DiseaseDocumento5 pagineCardiac Conducting System in Health and DiseaseAmalina ZolkefleeNessuna valutazione finora
- Microscopic Structures of Cardiac CellDocumento9 pagineMicroscopic Structures of Cardiac CellAmalina ZolkefleeNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of Urinary Bladder and UrethraDocumento16 pagineAnatomy of Urinary Bladder and UrethraAmalina ZolkefleeNessuna valutazione finora
- Embryology of Kidneys and UreterDocumento10 pagineEmbryology of Kidneys and UreterAmalina Zolkeflee100% (1)
- Vessels ResistanceDocumento10 pagineVessels ResistanceAmalina ZolkefleeNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood CapillariesDocumento7 pagineBlood CapillariesAmalina ZolkefleeNessuna valutazione finora
- Water, Fluid, Spaces and CompartmentsDocumento15 pagineWater, Fluid, Spaces and CompartmentsAmalina ZolkefleeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mouth, Larynx and TracheaDocumento23 pagineMouth, Larynx and TracheaAmalina ZolkefleeNessuna valutazione finora
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Acute Care Handbook For Physical Therapists - 2nd Edition PDFDocumento977 pagineAcute Care Handbook For Physical Therapists - 2nd Edition PDFShahid Ahmed Heera90% (10)
- Hemodynamic Monitoring ExplainedDocumento19 pagineHemodynamic Monitoring ExplainedAlma SusanNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL Science-6 Q2 W3Documento6 pagineDLL Science-6 Q2 W3Grea Dela Cruz EdnilaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathology - Lab: Pathology of The Blood VesselsDocumento5 paginePathology - Lab: Pathology of The Blood VesselsRazel PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Planeador Semanal Junio 2010 Biologia MYPDocumento7 paginePlaneador Semanal Junio 2010 Biologia MYPPaula MartyNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure QuestionsDocumento7 pagineStructure QuestionsChee Jin TangNessuna valutazione finora
- JV Electrophysiology of HeartDocumento19 pagineJV Electrophysiology of HeartRiya GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute HF-IAIDocumento49 pagineAcute HF-IAIAndita ListyannisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiology Mcq's Part - 1Documento31 pagineCardiology Mcq's Part - 1aymenNessuna valutazione finora
- Fisio1 Exc6 Act1Documento5 pagineFisio1 Exc6 Act1Fadli Nurul HanifNessuna valutazione finora
- Programbook IsicamDocumento36 pagineProgrambook Isicamadi bestaraNessuna valutazione finora
- UWORLD Notes by Systems (Usmle Grassroots)Documento79 pagineUWORLD Notes by Systems (Usmle Grassroots)Had Moe100% (3)
- 0572 Biology Assessment SyllabusDocumento41 pagine0572 Biology Assessment SyllabusHope MaboteNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease: Chest Pain Muscle Weakness Shortness of BreathDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease: Chest Pain Muscle Weakness Shortness of BreathCyril Jane Caanyagan AcutNessuna valutazione finora
- Echocardiography ExaminationDocumento10 pagineEchocardiography ExaminationYanira NoemíNessuna valutazione finora
- Coronary Artery Disease Guide: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & TreatmentDocumento4 pagineCoronary Artery Disease Guide: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & TreatmentViktoria Leeahna LehNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs for Heart FailureDocumento39 pagineDrugs for Heart FailureOngKahYeeNessuna valutazione finora
- BSC Nursing - Cardiac OutputDocumento10 pagineBSC Nursing - Cardiac OutputDIKSHA RANI DEKANessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Arrhythmias Guide - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment OptionsDocumento5 pagineCardiac Arrhythmias Guide - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment OptionsaksinuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ehad 488Documento3 pagineEhad 488Jorge ZúnigaNessuna valutazione finora
- ECG InterpretationDocumento268 pagineECG InterpretationEba'a GamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Kuliah 1 OVERVIEW Titipan Dari (DR Pipiet)Documento465 pagineKuliah 1 OVERVIEW Titipan Dari (DR Pipiet)Gangsar DamaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart Disease in Pregnancy: Understanding RisksDocumento2 pagineHeart Disease in Pregnancy: Understanding RisksChandra KusumaningtiasNessuna valutazione finora
- Candon City, Ilocos Sur Grade 9 Reviewer School Year 2021 - 2022Documento7 pagineCandon City, Ilocos Sur Grade 9 Reviewer School Year 2021 - 2022Aleah TungbabanNessuna valutazione finora
- Arterial HyperemyDocumento10 pagineArterial HyperemyRohit NaiduNessuna valutazione finora
- What is BiologyDocumento33 pagineWhat is BiologySA - 10WB 933839 The Woodlands SSNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Lymphatic SystemDocumento153 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of The Lymphatic SystemNellie Grace Montes Aba-aNessuna valutazione finora
- ECG Essentials Quick ReviewDocumento45 pagineECG Essentials Quick Reviewjaikishan marathe 69Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cara Hitung MPAP, CO, dan Penilaian Regurgitasi dan Stenosis Valve JantungDocumento6 pagineCara Hitung MPAP, CO, dan Penilaian Regurgitasi dan Stenosis Valve JantungwinNessuna valutazione finora
- Dwnload Full Ekg Plain and Simple 3rd Edition Ellis Test Bank PDFDocumento7 pagineDwnload Full Ekg Plain and Simple 3rd Edition Ellis Test Bank PDFpeterrodriguezcwbqomdksi100% (10)