Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Tuberculosis Treatment Guide & Patient Information
Caricato da
Shila LupiyatamaDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Tuberculosis Treatment Guide & Patient Information
Caricato da
Shila LupiyatamaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Tuberculosis Treatment Guide & Patient Information
1 s t a n d 2 n d P h a s e Tr e a t m e n t s
A prescribing and treatment guide for the primary treatment of Tuberculosis in adults.
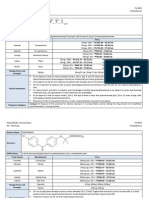
TB MEDICATION - Dosage Reference Guide Phase 1
Body weight (Kg) 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 Ethambutol
Hydrochloride
Ethambutol
Hydrochloride
Ethambutol
Hydrochloride 400mg (Grey) 100mg (Yellow)
Rifater
1 pink tablet tablet contains
15mg/Kg (actual) 600mg 615mg 630mg 645mg 660mg 675mg 690mg 705mg 720mg 735mg 750mg 765mg 780mg 795mg 810mg 825mg 840mg 855mg 870mg 885mg 900mg 915mg 930mg 945mg 960mg 975mg 990mg 1005mg 1020mg 1035mg 1050mg 1065mg 1080mg 1095mg 1110mg 1125mg 1140mg 1155mg 1170mg 1185mg
Dosage 600mg 600mg 600mg 600mg 700mg 700mg 700mg 700mg 700mg 700mg 800mg 800mg 800mg 800mg 800mg 800mg 800mg 900mg 900mg 900mg 900mg 900mg 900mg 900mg 1g 1g 1g 1g 1g 1g 1.1g 1.1g 1.1g 1.1g 1.1g 1.1g 1.1g 1.2g 1.2g 1.2g
Isoniazid 50 mg Pyrazinamide 300 mg Rifampicin 120 mg
80+ 1200mg 1.2g If body weight exceeds 80 (Kg) Dosage must remain the same as that of 80 (Kg)
1+2 1+2 1+2 1+3 1+3 1+3 1+3 1+3 1+3 2 x Grey 2 x Grey 2 x Grey 2 x Grey 2 x Grey 2 x Grey 2 x Grey 2+1 2+1 2+1 2+1 2+1 2+1 2+1 2+2 2+2 2+2 2+2 2+2 2+2 2+3 2+3 2+3 2+3 2+3 2+3 2+3 3 x Grey 3 x Grey 3 x Grey 3 x Grey 3 x Grey
1+2
and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and
4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6
4 4
TB MEDICATION - Dosage Reference Guide Phase 2
Body weight (Kg) Rifinah 150 mg
(1 pink tablet tablet contains Rifampicin 150 mg Isoniazid 100 mg)
Rifinah 300 mg
(1 orange tablet tablet contains Rifampicin 300 mg Isoniazid 150 mg)
40
Phase 2 TB treatment to be implemented AFTER 2 months of Phase 1 TB treatment. (ref: page opposite)
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56
3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
3 3
Rifinah 150 mg
Rifampicin 150 mg Isoniazid 100 mg
57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80+ If body weight exceeds 80 (Kg) Dosage must remain the same as that of 80 (Kg)
Rifinah 300 mg
Rifampicin 300 mg Isoniazid 150 mg
* Colour coding refers to TB Patient Medication Leaflets Information contained in this leaflet was prepared and produced by Genus Pharmaceuticals in partnership with TB Alert
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
2 2 2
ABBREVIATED PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
ABBREVIATED PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
ABBREVIATED PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
RIFINAH 150 & RIFINAH 300
Presentations: Tablets containing 150mg of rifampicin and 100mg of isoniazid (Rifinah 150) or 300mg of rifampicin and 150mg of isoniazid (Rifinah 300). Indications: Tuberculosis. Dosage & Administration: Preferably take 30 mins before or 2 hours after food as a single dose. Adults: Rifinah 150: patients 50kg or less - 3 tablets; Rifinah 300: for patients 50kg or more - 2 tablets. Elderly patients: Use with caution. Contra-indications: Hypersensitivity to rifamycins or isoniazid; presence of jaundice. Precautions: Give under the supervision of a respiratory or other suitably qualified physician. All patients should have pre-treatment LFT. If impaired liver function, only give in cases of necessity with dose reduction and careful monitoring of LFT. Rifinah should be withdrawn if clinically significant changes in hepatic function occur. If impaired liver function, elderly, malnourished patients, and possibly children under 2yrs, caution is recommended if isoniazid is used concurrently. In some patients hyperbilirubinemia can occur in the early days of treatment. Possibility of an immunological reaction with intermittent therapy. Patients should be cautioned that interruption of the dosage regimen should be avoided. If serious complications occur, rifampicin should be stopped and never restarted. Interactions: Rifampicin has enzyme-inducing properties. Reduced activity of anticoagulants, corticosteroids, cyclosporin, digitalis preparations, oral contraceptives (non-hormonal birth control methods are recommended during Rifinah therapy), oral hypoglycaemic agents, dapsone, phenytoin, quinidine, narcotics and analgesics. Diabetes may become difficult to control. Give p-aminosalicylic acid at least 8hrs apart from Rifinah. Isoniazid may decrease excretion of phenytoin or enhance its effects. Pregnancy & Lactation: Only use if potential benefit outweighs potential risk. Side effects: Rifampicin - Mild cutaneous reactions and general hypersensitivity reactions involving skin, exfoliative dermatitis, Lyells syndrome, pemphigoid reactions. Anorexia, nausea, vomiting abdominal discomfort, diarrhoea, pseudomembranous colitis, hepatitis. Thrombocytopenia with or without purpura, eosiniphilia, leucopenia, oedema, muscle weakness and myopathy. Discolouration of urine, sputum and tears. Occasional disturbances of the menstrual cycle. Reactions occurring after intermittent dosage regimens include: Flu syndrome; shortness of breath and wheezing; blood pressure reduction and shock; acute haemolytic anaemia; acute renal failure. Isoniazid - Hepatitis, eosinophilia, agranulycytosis, anaemia, convulsions. Legal Category: POM Marketing Authorisation Number: Rifinah 150: PL 04425/0041, Rifinah 300: PL 04425/0042 NHS Price: Rifinah 150 Tablets x 84 17.80; Rifinah 300 Tablets x 56 23.52 Full prescribing information available on request from: Aventis Pharma Ltd., 50 Kings Hill Avenue, West Malling, Kent, ME19 4AH. Date of Preparation: August 2003.
RIFATER
Presentations: Tablets containing 120mg of rifampicin, 50mg of isoniazid and 300mg of pyrazinamide. Indications: Pulmonary tuberculosis. Dosage & Administration: Rifater is recommended for daily administration during the initial 2-month intensive phase of short course treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis (concomitant administration of ethambutol or intramuscular streptomycin is advised). Preferably take 30 mins before or 2 hours after food as single dose. Adults: Patients less than 40kg 3 tablets o.d., patients 40-49kg 4 tablets o.d., patients 50-64kg 5 tablets o.d., patients 65kg or more 6 tablets o.d.. Children: Use only in special cases. Elderly patients: Use with caution. Contra-indications: Hypersensitivity to rifamycins, isoniazid or pyrazinamide; presence of jaundice. Precautions: Give under the supervision of a respiratory or other suitably qualified physician. All patients should have pre-treatment LFT. If impaired liver function, only give in cases of necessity with dose reduction and careful monitoring of LFT. Rifampicin should be withdrawn if clinically significant changes in hepatic function occur. In some patients hyperbilirubinemia can occur in the early days of treatment. Use with caution in patients with a history of gout or haemoptysis. Possibility of an immunological reaction with intermittent therapy. Patients should be cautioned that interruption of the dosage regimen should be avoided. If serious complications occur, rifampicin should be stopped and never restarted. Interactions: Rifater has enzyme-inducing properties. Reduced activity of antiarrhythmics, anticoagulants, anticonvulsants, antifungals, antivirals, benzodiazepines, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, chloramphenicol, clarithromycin, corticosteroids, cyclosporin, digitalis preparations, tricyclic antidepressants, oral contraceptives (non-hormonal birth control methods are recommended during Rifater therapy), oral hypoglycaemic agents, dapsone, haloperidol, levothyroxine, quinidine, analgesics, tacrolimus and theophylline. Rifater may reduce plasma concentration of atovaquone. Give p-aminosalicylic at least 8hrs apart from Rifampicin. Concomitant antacid may reduce absorption of rifampicin. Hepatoxicity potential increased in combination with an anaesthetic. Diabetes may become difficult to control. Isoniazid may decrease excretion of phenytoin and carbamazepine or enhance its effects. Pyrazinamide antagonises effects of probenecid and sulphinpyrazone. Pregnancy & Lactation: Only use if potential benefit outweighs potential risk. Side effects: Rifampicin - Mild cutaneous reactions and general hypersensitivity reactions involving skin, exfoliative dermatitis, Lyells syndrome, pemphigoid reactions. Anorexia, nausea, vomiting abdominal discomfort, diarrhoea, pseudomembranous colitis, hepatitis. Thrombocytopenia with or without purpura, eosiniphilia, leucopenia, oedema, muscle weakness and myopathy. Discolouration of urine, sputum and tears. Occasional disturbances of the menstrual cycle. Reactions occurring after intermittent dosage regimens include: Flu syndrome; shortness of breath and wheezing; blood pressure reduction and shock; acute haemolytic anaemia; acute renal failure. Isoniazid Hepatitis, hypersensitivity reactions, eosinophilia, agranulocytosis, anaemia. Convulsions, systemic lupus erythromatosus-like syndrome, pellagra. Pyrazinamide active gout, sideroblastic anaemia, arthralgia, anorexia, nausea and vomiting, dysuria, malaise, fever, urticaria, aggravation of peptic ulcer, a range of hepatic reactions. Legal Category: POM Marketing Authorisation Number: PL 4425/0060 NHS Price: Rifater Tablets x 100 23.60 Full prescribing information available on request from: Aventis Pharma Ltd., 50 Kings Hill Avenue, West Malling, Kent, ME19 4AH. Date of Preparation: August 2003.
ETHAMBUTOL
Presentations: Tablets containing 100mg and 400mg of Ethambutol Hydrochloride (BP). Indications: Primary treatment and re-treatment of tuberculosis, and for prophylaxis in cases of inactive tuberculosis or large-tuberculin-positive reaction. Ethambutol should only be used in conjunction with other anti-tuberculosis drugs to which the patients organisms are susceptible. Dosage & Administration: The dosage of ethambutol must be adjusted according to the body weight of the patient. Adults: For primary treatment and prophylaxis: Ethambutol should be administered in a single daily oral dose of 15mg/kg, concomitant drugs being maintained at their recommended dosage levels. For re-treatment: For the first 60 days of treatment, ethambutol should be administered in a single daily oral dose of 25mg/kg. Thereafter the dosage should be reduced to 15mg/kg, concomitant drugs being maintained at their recommended dosage levels. Children: For primary treatment and re-treatment: For the first 60 days of treatment, a single daily oral dose of 25mg/kg. Thereafter the dosage should be reduced to 15mg/kg, concomitant drugs being maintained at their recommended dosage levels. For prophylaxis: A single daily oral dose of 15mg/kg, concomitant drugs being used at their recommended dosage levels. Elderly: As for adults. However, patients with decreased renal function may need to have the dosage adjusted as determined by blood levels of ethambutol. In order to obtain maximum effect due to high serum levels, drug administration should be once daily. Contra-indications: Hypersensitivity to ethambutol; patients with known optic neuritis unless clinical judgement determines that ethambutol may be used. Precautions: Patients with decreased renal function may need to have the dosage adjusted as determined by blood levels of ethambutol. As this drug has a unique effect on the eye, it is recommended that patients undergo a full ophthalmic examination before starting treatment. This should include visual acuity, colour vision, perimetry and ophthalmoscopy. Many physicians consider that routine ophthalmological examinations for adults are unnecessary but patients should be informed of the importance of reporting any change in vision. However, routine ophthalmological examinations may be considered desirable when treating young children. Interactions: None. Pregnancy & Lactation: Should not be use unless the potential benefit is considered to outweigh any possible risk. Side effects: Hypersensitivity reactions are rare, although rash, pruritus and urticaria have been reported. There are isolated reports of photosensitive lichenoid eruptions, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, epidermal necrolysis, and bullous dermatitis. Interstitial nephritis and anaphylactoid reactions are extremely rare. Hyperuricaemia has been reported although clinical effects are unlikely. Gastro-intestinal disturbances such as anorexia, nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea have been noted in patients on multiple anti-tuberculosis drug therapy including ethambutol, although not in test patients receiving ethambutol as sole therapy. Reports of thrombocytopenia are rare. Hepatic reactions have been reported in patients treated with multiple drug therapy including ethambutol, and liver function tests should be performed in patients who develop symptoms suggestive of hepatitis or who become generally unwell during treatment. Numbness and paraesthesia of the extremities have been reported. Ethambutol may produce a unique type of visual impairment that is generally reversible and which appears to be due to optic neuritis and to be related to dose and duration of treatment. Less than 1% of patients undergoing treatment with the higher dose regimen of 25mg/kg/day for two months, and 15mg/kg/day thereafter, have exhibited decrease in visual acuity. The change may be unilateral or bilateral and hence both eyes must be tested individually. The effects are generally reversible when administration of the drug is discontinued promptly. In rare cases, recovery may be delayed for up to one year or more and the effect may possibly be irreversible in these cases. Recovery of visual acuity has usually occurred over a period of weeks to months after the drug was discontinued, and patients have then received ethambutol at lower dosages without toxicity. Legal Category: POM Marketing Authorisation Number: Ethambutol Tablets 100mg: PL 17225/0004; Ethambutol Tablets 400mg: PL 17225/0005 NHS Price: Ethambutol Tablets 100mg x 56 11.50; Ethambutol Tablets 400mg x 56 42.73 Full prescribing information available on request fromFurther information is available from the Marketing Authorisation Holder: Genus Pharmaceuticals, Benham Valence, Newbury, Berkshire RG20 8LU. Date of Preparation: August 2003.
Date of preparation: September 2003 1. - Ref. Product SmPC
Information contained in this leaflet was prepared by Genus Pharmaceuticals with help from Sandwell Hospital in partnership with TB Alert
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Drug StuDyDocumento11 pagineDrug StuDyMel SevillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Buffered Aspirin ProductsDocumento7 pagineBuffered Aspirin ProductsKimsha ConcepcionNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Product CharacteristicsDocumento9 pagineSummary of Product Characteristicsddandan_2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Obat ObgynDocumento8 pagineObat ObgynMuhammad Naqiuddin JalaluddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento3 pagineDrug Studyanon_11638632Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fixcom 4® (Tab) : Natrapharm Natrapharm Anti-TB AgentsDocumento13 pagineFixcom 4® (Tab) : Natrapharm Natrapharm Anti-TB AgentsApril_Jane_Nat_8299Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pregnancy Category C (First Trimester), D (Second and Third Trimesters)Documento3 paginePregnancy Category C (First Trimester), D (Second and Third Trimesters)anggunNessuna valutazione finora
- Pyra TBDocumento6 paginePyra TBRaya Ibarra LumogdangNessuna valutazione finora
- Annex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsDocumento65 pagineAnnex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsMikro BatomouroNessuna valutazione finora
- Pustaka AHFS - ESODocumento8 paginePustaka AHFS - ESORindang RizkyNessuna valutazione finora
- Antiretroviral Therapy (ART)Documento41 pagineAntiretroviral Therapy (ART)Ashik Jithu JohnNessuna valutazione finora
- CyclosporineDocumento25 pagineCyclosporineraki9999Nessuna valutazione finora
- Atacor SPCDocumento9 pagineAtacor SPCRannia1Nessuna valutazione finora
- AzithromycinDocumento4 pagineAzithromycinBrittany ClontzNessuna valutazione finora
- Risperdal PiDocumento16 pagineRisperdal PiNadhila ByantNessuna valutazione finora
- Emergency Drugs Drug StudyDocumento15 pagineEmergency Drugs Drug StudyCathrine Sandile Tangwara100% (1)
- Pedia Drug StudyDocumento11 paginePedia Drug StudyPeetah PanNessuna valutazione finora
- Care Plan:, Wrong, Wrong, Wrong, WrongDocumento8 pagineCare Plan:, Wrong, Wrong, Wrong, Wronglovelylife theNessuna valutazione finora
- Atorvastatin CalciumDocumento2 pagineAtorvastatin Calciumshiraz.aNessuna valutazione finora
- LalalalaaaaDocumento6 pagineLalalalaaaaRobert LeblancNessuna valutazione finora
- Aspirin Drug StudyDocumento8 pagineAspirin Drug StudyAngie Mandeoya0% (1)
- Therapeutic:: Brand Name: PLASIL ClassificationsDocumento5 pagineTherapeutic:: Brand Name: PLASIL ClassificationsAbby MontealegreNessuna valutazione finora
- Common TreatmentsDocumento5 pagineCommon TreatmentsRaj MandumulaNessuna valutazione finora
- 7-Lipid DisorderDocumento6 pagine7-Lipid DisorderApple MaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Aspirin: Age (Yr) Dosage (MG Q 4 HR) 2-3 162 4-5 243 6-8 324 9-10 405 11 486 12 648Documento3 pagineAspirin: Age (Yr) Dosage (MG Q 4 HR) 2-3 162 4-5 243 6-8 324 9-10 405 11 486 12 648Angel CatalanNessuna valutazione finora
- New Hope Hospital Drug Formulary: First EditionDocumento17 pagineNew Hope Hospital Drug Formulary: First EditionBrunette CesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tuberculosos MeningititsDocumento14 pagineTuberculosos MeningititsFerina UNessuna valutazione finora
- Tishk International University: ApixabanDocumento4 pagineTishk International University: ApixabanDyar MzafarNessuna valutazione finora
- Parkinson's Disease Review of Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Current TherapyDocumento38 pagineParkinson's Disease Review of Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Current TherapyYurissa KarimahNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento15 pagineDrug StudyLene Derlene Gerona100% (2)
- All Veterinary DrugsDocumento37 pagineAll Veterinary DrugsRai Sajid94% (17)
- Drug StudyDocumento8 pagineDrug Studymaryhiromi10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study Ko ToDocumento4 pagineDrug Study Ko ToGian Carlo FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Propranolol HydrochlorideDocumento8 paginePropranolol HydrochlorideKrima PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 AntihyperlipidemicsDocumento6 pagine1 AntihyperlipidemicsChristian VillacruzesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lisinopril PDFDocumento3 pagineLisinopril PDFHannaNessuna valutazione finora
- VIGOCIDDocumento2 pagineVIGOCIDKaren DamoNessuna valutazione finora
- FebuxostatDocumento2 pagineFebuxostatJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocumento9 pagineDrug StudyChristine PunsalanNessuna valutazione finora
- DR/ Mohammad Abdul Baset Badr: Prepared byDocumento75 pagineDR/ Mohammad Abdul Baset Badr: Prepared byamrharidi446Nessuna valutazione finora
- File1 146 1714383Documento366 pagineFile1 146 1714383Mutiara SazkiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Digitekâ® (Digoxin Tablets, Usp) Recalled (Actavis Totowa LLC) - April 28, 2008Documento18 pagineDigitekâ® (Digoxin Tablets, Usp) Recalled (Actavis Totowa LLC) - April 28, 2008LenyNessuna valutazione finora
- WWW - Fda.gov: High Alert Medication: The Institute For Safe Medication Practices (ISMP) Includes ThisDocumento13 pagineWWW - Fda.gov: High Alert Medication: The Institute For Safe Medication Practices (ISMP) Includes ThisAnonymous KNQjkBmNessuna valutazione finora
- Nifras, Marielle: Name: Garnizo, AlmieDocumento6 pagineNifras, Marielle: Name: Garnizo, AlmieAnthony PamolinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti-Anginal DrugsDocumento39 pagineAnti-Anginal Drugspoonam rana100% (1)
- Duplicate Therapy Issues: This Product Contains Acetaminophen, Which May Be A ComponentDocumento15 pagineDuplicate Therapy Issues: This Product Contains Acetaminophen, Which May Be A ComponentDevi KusumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gastrointestinal and Gastrointestinal and Antiemetic Drugs Antiemetic DrugsDocumento34 pagineGastrointestinal and Gastrointestinal and Antiemetic Drugs Antiemetic DrugsZakir UllahNessuna valutazione finora
- (C) Propranolol: Adult: PO HTN As Conventional Tab or Oral Soln: Initial: 40-80 MGDocumento6 pagine(C) Propranolol: Adult: PO HTN As Conventional Tab or Oral Soln: Initial: 40-80 MGaprilaratNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharma Cards CHF DVTDocumento14 paginePharma Cards CHF DVTRiza Angela BarazanNessuna valutazione finora
- AcetaminophenDocumento3 pagineAcetaminophenapi-3797941Nessuna valutazione finora
- Albenza, (Albendazole) Dosing, Indications, Interactions, Adverse Effects, and MoreDocumento4 pagineAlbenza, (Albendazole) Dosing, Indications, Interactions, Adverse Effects, and MoreSourav GhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- General: Genetic Implications: Pronunciation: Maz Trade Name(s)Documento7 pagineGeneral: Genetic Implications: Pronunciation: Maz Trade Name(s)jenm1228Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pravastatin SodiumDocumento3 paginePravastatin Sodiumapi-3797941Nessuna valutazione finora
- MALARIA DR - PAULDocumento67 pagineMALARIA DR - PAULNodi Rahma DiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Generic Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: ActionDocumento22 pagineGeneric Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: Actionp_dawg100% (14)
- Drug Study Case PresentationDocumento5 pagineDrug Study Case PresentationRobert MedinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Immune SystemDocumento3 pagineImmune SystemShila LupiyatamaNessuna valutazione finora
- 18 Aggression in EpilepsyDocumento21 pagine18 Aggression in EpilepsyShila LupiyatamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Laryngeal CarcinomaDocumento11 pagineLaryngeal CarcinomaEmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 18 Aggression in EpilepsyDocumento21 pagine18 Aggression in EpilepsyShila LupiyatamaNessuna valutazione finora
- H and N Cases MPH CRDocumento5 pagineH and N Cases MPH CRShila LupiyatamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Frozen ShoulderDocumento14 pagineFrozen ShoulderShila LupiyatamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Harrison's 17th EdDocumento3 pagineHarrison's 17th EdShila Lupiyatama50% (2)
- Urinary Tract Infection: DR Badriya Al-Mahrouqi 12/11/2017Documento51 pagineUrinary Tract Infection: DR Badriya Al-Mahrouqi 12/11/2017NinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiology Procedure ManualDocumento29 pagineRadiology Procedure ManualAnonymous ic2CDkF100% (1)
- PBL 1 - Post Streptococcal Rheumatic Fever PolicyDocumento8 paginePBL 1 - Post Streptococcal Rheumatic Fever PolicyAinur AbdrakhmanovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Immediate Care of The NewbornDocumento4 pagineImmediate Care of The NewbornMichelle GambolNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Deaths in Jefferson County 2015Documento16 pagineDrug Deaths in Jefferson County 2015Jeremy W. Gray100% (1)
- Biggs Medicine, SurgeryDocumento19 pagineBiggs Medicine, Surgerymary20149Nessuna valutazione finora
- International Journal of PharmaceuticsDocumento6 pagineInternational Journal of PharmaceuticsSjis11362Nessuna valutazione finora
- IOL Masuk Keluar BM SDA NO Nama Obat Awal: Laporan BHP + Iol Ok Smec MojokertoDocumento6 pagineIOL Masuk Keluar BM SDA NO Nama Obat Awal: Laporan BHP + Iol Ok Smec MojokertoNaira Calya basagitaNessuna valutazione finora
- CAPNOGRAPHYDocumento10 pagineCAPNOGRAPHYJessica GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Social Stratification in The PhilippinesDocumento11 pagineSocial Stratification in The PhilippinesMichael VillavertNessuna valutazione finora
- Mix It Up and SqueezeDocumento3 pagineMix It Up and Squeezeapi-233757247100% (1)
- 200 Terms & Definition From Pharmacology. WatermarkedDocumento17 pagine200 Terms & Definition From Pharmacology. Watermarkedsuresh adgaonkar100% (1)
- Complex Partial SeizuresDocumento5 pagineComplex Partial SeizuresNouf MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- NantesDiagnosticCriteria For Pudendal NeuralgiaDocumento5 pagineNantesDiagnosticCriteria For Pudendal NeuralgiaTeresa BeckNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation Checklist Case 7 Bronchial AsthmaDocumento7 pagineEvaluation Checklist Case 7 Bronchial AsthmaChristian MendiolaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Paediatric X-Ray Exposure ChartDocumento11 pagineA Paediatric X-Ray Exposure Chartdddemourita9249Nessuna valutazione finora
- HFS PHILIPPINES, INC., G.R. No. 168716 Ruben T. Del Rosario and Ium Shipmanagement As, Petitioners, Ronaldo R. Pilar, Respondent. PromulgatedDocumento8 pagineHFS PHILIPPINES, INC., G.R. No. 168716 Ruben T. Del Rosario and Ium Shipmanagement As, Petitioners, Ronaldo R. Pilar, Respondent. PromulgateddanexrainierNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Neo 900Documento76 pagineManual Neo 900Bismarck Pablo Ibañez Piotti67% (3)
- Top 5 Lavender Home RemediesDocumento16 pagineTop 5 Lavender Home RemediesjeslynNessuna valutazione finora
- Poster Role of Clinical Exome SequencingDocumento1 paginaPoster Role of Clinical Exome SequencingLudy ArfanNessuna valutazione finora
- Interpretation of Histograms and Its Correlation WDocumento5 pagineInterpretation of Histograms and Its Correlation WrezqiNessuna valutazione finora
- Bishara, R. - Qualification Versus ValidationDocumento4 pagineBishara, R. - Qualification Versus ValidationLuis Gustavo PachecoNessuna valutazione finora
- Addiction, Treatment, and Evidence-Based Medicine - Wilcox, SeanDocumento150 pagineAddiction, Treatment, and Evidence-Based Medicine - Wilcox, Seanadu66650% (2)
- The Letter of Intent To Enter PracticeDocumento4 pagineThe Letter of Intent To Enter Practicekazniels100% (1)
- CD4 Count CutDocumento51 pagineCD4 Count Cutibrahim 12Nessuna valutazione finora
- SDS - Balloxy HB Light - Comp. B - Marine - Protective - English (Uk) - AustraliaDocumento7 pagineSDS - Balloxy HB Light - Comp. B - Marine - Protective - English (Uk) - AustraliaDonNessuna valutazione finora
- GEHC Site Planning Specifications Safety and Specifications PDFDocumento57 pagineGEHC Site Planning Specifications Safety and Specifications PDFD&KNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Data Sheet: Virbac New Zealand LimitedDocumento5 pagineSafety Data Sheet: Virbac New Zealand LimitedХорен МакоянNessuna valutazione finora
- Are Errors in Otorhinolaryngology Always A Sign of Medical MalpracticeDocumento7 pagineAre Errors in Otorhinolaryngology Always A Sign of Medical MalpracticeMyrellaAlexandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparing Risk Factors of HIV Among Hijra SexDocumento9 pagineComparing Risk Factors of HIV Among Hijra SexmariaelismecaNessuna valutazione finora