Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Drug Study For Bronchiectasis
Caricato da
Edith AlegreDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Drug Study For Bronchiectasis
Caricato da
Edith AlegreCopyright:
Formati disponibili
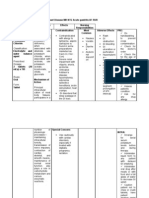
DRUG STUDY Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Unknown.
Appears toinhibit cellwallbiosynthesis byinterferingwit h lipidand DNAsynthesis Nursing Responsibilities >Activelygrowingt Contraindicated in >Peripheralneuro > Use cautiously ubercle bacilli patientswith pathy,fluiddiscol inelderlypatients > Prevention acutehepatic diseaseor oration,optic of tubercle bacilliin isoniazid-related neuritis,hepatitis > Peripheral thoseexposed liver damage neuropathy is more totuberculosisor common inpatients those withpositive who are slow skintest acetylators or who are resultswhose malnourished, chestx-rays alcoholic or diabetic andbacteriologicst udies >Monitor hepaticfunct areconsistentwith ionclosely for changes nonprogressivetuberc ulosis Indication Contraindication Side Effects
GENERIC NAME: Anti-infective HRZE (isoniazid+rifam picin+pyrazinami de+ethambutol) Brand name: Myrin
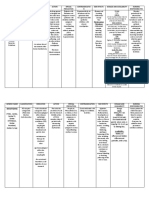
Generic: Fluimucil Brand Name: Acetylcysteine Classification : Antidotes Dose: 600mg/tab x5day more OD
Decrease viscosity of respiratory tract secretions and promote their removal by breaking disulfide bonds. In acetaminophen overdose, it protects the liver from injury by restoring glutathione levels or by acting as alternate substrate for acetaminophen metabolism.
Treatment of Hypersensitivity respiratory affections characterized by thick and viscous hypersecretions: acute and chronic bronchitis and its exacerbation, pulmonary emphysema, mucoviscidosis and bronchiectasis. Antidote in poisoning caused by paracetamol.
Nausea, vomiting and other G.I. symptoms, mild fever, hypotension, wheezing, dyspnea
Instruct the patient to follow directions exactly. Teach patient how to use and clean nebulizer. Inform patient that drug may have foul smell or taste. Tell patient to avoid driving or other hazardous activities
Generic Name: Levodropropizine Brand Name: Levopront
Anti-tussives
This medication is an antitussive, prescribed for cough.
Contraindicated in patients with severe liver impairment, excessive mucus discharge, and hypersensitivity.
Nausea, vomiting, heartburn, diarrhea, fatigue, weakness, drowsiness, dizziness, headache and palpitations.
* Caution should be exercised in patients with history of severe kidney insufficiency, any allergy, children, during pregnancy and breastfeeding. * It may cause dizziness or drowsiness, do not drive a car or operate machinery while taking this medication.
Generic Name: Ferrous Sulfate Tablets (FER-us SULL-fate) Brand Name: Examples include Feosol and Feratab
Vitamins & Minerals (Pre & Post Natal) / Anti-anemics
Ferrous sulfate facilitates O2 transport via hemoglobin. It is used as iron source as it replaces iron found in hemoglobin, myoglobin and other enzymes. Onset: Oral: 3-10 days. Absorption: Duodenum and upper jejunum: 10% absorption after oral admin in persons with normal serum iron stores; 20-30% absorption in those with inadequate iron stores. Excretion: Via urine, sweat, sloughing of the intestinal mucosa and menstruation.
Irondeficiency anemia
Patients receiving repeated blood transfusions; anemia not due to iron deficiency.
GI irritation, abdominal pain and cramps, nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, dark stool and discoloration of urine; heartburn.
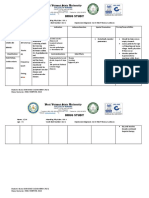
Nursing Care Plan
ASSESSMENT
Subjective: Medyonahihirapanpoakonghumingaat inuubopoako, as verbalized by the patient Objective: > RR= 26 cycles per minute > Dyspnea > Use of accessory muscles when breathing. > Pale in appearance > Nasal flaring
DIAGNOSIS
Ineffective airway clearance related to the presence of secretions on the lung fields
PLANNING
Short Term Goal: After 1 hour of nursing intervention, the pt. will be able to cough up secretions effectively Long Term Goal: The patient will be able to verbalize effective airway clearance as characterized by: a. absence of cough b. lessenedsecretions
INTERVENTION
Independent: > Assessed airway patency
RATIONALE
-To monitor airway is always the first priority -To consider possible causes for ineffective cough -To ascertain state and note patients progress -To assess breathing pattern
EVALUATION
Short Term Goal: The patient is able to cough up secretions effectively. Goal met. Long Term Goal: Patient was uncooperative as manifested by her fatalistic attitude towards her condition. Goal partially met.
> Assessed cough for effectiveness and productivity > Auscultate breath sounds
> Observed for signs of respiratory distress(increased rate, use of accessory muscles) >Position patient to Semi-fowlers or sitting position
-To promote better lung expansion and improve air exchange -To reduce viscosity of mucus and easier
> Encourage to increase oral fluid intake
Recommendation: Take prescribed medications regularly
mobilization of secretions > Encourage deep breathing exercise -To reduce viscosity of mucus and easier mobilization of secretions -Prevents/reduces fatigue
> Encourage opportunities for rest; limit activities to level of respiratory resistance Dependent: > Administer Salbutamol NEB
-Increases the size of the tracheobronchial tree thus opening the airway passages -To examine and report changes in color and amount
> Provide information about the necessity of raising expectorations versus swallowing them
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- DrugsDocumento7 pagineDrugsEloisa Abarintos RacalNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP CholeraDocumento2 pagineNCP CholeraMichael Angelo Garcia RafananNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento6 pagineDrug StudyBadeth BustamanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento11 pagineDrug StudyKimberly Ann MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento15 pagineDrug StudyDon Laurence P. CasauayNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study: Brokenshire CollegeDocumento2 pagineDrug Study: Brokenshire CollegeJai GoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: Histolytica, ADocumento4 pagineNursing Care Plan: Histolytica, AkristennemarieNessuna valutazione finora
- Acc Phu Case NCP HyperthermiaDocumento1 paginaAcc Phu Case NCP Hyperthermiamacy_bautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineDrug StudyemmanuelmyagokayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug 101Documento12 pagineDrug 101Alyzza DagoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Example of Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineExample of Drug Studydonna mae junioNessuna valutazione finora
- PrednisoloneDocumento2 paginePrednisoloneKatie McPeekNessuna valutazione finora
- DRUGSTUDY Tetanus ToxoidDocumento1 paginaDRUGSTUDY Tetanus ToxoidMicaela Andrea CieloNessuna valutazione finora
- Darbepoetin AlfaDocumento3 pagineDarbepoetin Alfaapi-3797941Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocumento5 pagineDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationWyeth Earl Padar EndrianoNessuna valutazione finora
- DP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Documento6 pagineDP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Maemae SumalinogNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypertension NCPDocumento4 pagineHypertension NCPssairej06Nessuna valutazione finora
- DS KetosterilDocumento1 paginaDS KetosteriljessicamaysNessuna valutazione finora
- Diarrhea Care PlanDocumento2 pagineDiarrhea Care Planzepoli_zepoly6232100% (1)
- Docu - Tips Drug StudyDocumento14 pagineDocu - Tips Drug StudyArdel LabadaNessuna valutazione finora
- DRUG RovuvastatinDocumento2 pagineDRUG RovuvastatinDharyl JoshuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineDrug StudyGrace CadawasNessuna valutazione finora
- ClonidineDocumento2 pagineClonidineFlora Angeli PastoresNessuna valutazione finora
- ClonidineDocumento1 paginaClonidineGabby Robles PajeNessuna valutazione finora
- AGE PathophysiologyDocumento2 pagineAGE Pathophysiologyjosephcanlas67% (3)
- Hydrocortisone Inj. (IV)Documento2 pagineHydrocortisone Inj. (IV)zepoli_zepoly6232Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento26 pagineDrug Studyrn msnNessuna valutazione finora
- Cetirizine 2Documento2 pagineCetirizine 2ianNessuna valutazione finora
- Ectrin. Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaEctrin. Drug StudyWeng Maesa Montemayor100% (1)
- NCP Autism101Documento5 pagineNCP Autism101Gio Padallan PisquizaNessuna valutazione finora
- AGE PathophysiologyDocumento1 paginaAGE PathophysiologyZhenmeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study AzathioprineDocumento3 pagineDrug Study AzathioprineBunnie AlphaNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocumento1 paginaClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsENessuna valutazione finora
- Tranexamic AcidDocumento2 pagineTranexamic AcidAlexis Coronado100% (2)
- Myonal, LevoprontDocumento1 paginaMyonal, LevoprontMarieCrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study HepatitisDocumento7 pagineDrug Study HepatitisKateLayaogNessuna valutazione finora
- Dexamethasone Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineDexamethasone Drug StudyVIDMENTON PHNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloxacillin: By: Edamarie B. CabasaDocumento11 pagineCloxacillin: By: Edamarie B. CabasaIrene Grace BalcuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study For SLEDocumento28 pagineDrug Study For SLERomwella May AlgoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lactulose: (Enuluse, Kristalose, Duphalac, Chronulac Syrup)Documento30 pagineLactulose: (Enuluse, Kristalose, Duphalac, Chronulac Syrup)Joanna Dela Torre100% (2)
- Ds in Delivery RoomDocumento11 pagineDs in Delivery RoomArian May MarcosNessuna valutazione finora
- ClarithromycinDocumento3 pagineClarithromycinapi-3797941Nessuna valutazione finora
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocumento2 pagineName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationNicole CalpoturaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aspirin Drug SummDocumento2 pagineAspirin Drug SummWarren0% (1)
- Name of Drug SoludexideDocumento2 pagineName of Drug SoludexideSian AsadaNessuna valutazione finora
- LevofloxacinDocumento3 pagineLevofloxacinapi-3797941100% (2)
- Duavent Drug Study - CunadoDocumento3 pagineDuavent Drug Study - CunadoLexa Moreene Cu�adoNessuna valutazione finora
- Omeprazole Drug StudyDocumento4 pagineOmeprazole Drug StudyFeliza Therese A. DeloriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento14 pagineDrug StudyJenniferValmocenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Atropine SulfateDocumento1 paginaAtropine SulfateTrishaaMayolNessuna valutazione finora
- LidocaineDocumento1 paginaLidocaineRich LewisNessuna valutazione finora
- Amlodipine CPDocumento2 pagineAmlodipine CPRose EchevarriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: Lipa City CollegesDocumento13 pagineNursing Care Plan: Lipa City CollegesVincent Maralit MaterialNessuna valutazione finora
- Aerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFADocumento3 pagineAerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFAGwyn RosalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineDrug Studypopoyoio100% (2)
- Drug Study (AFP)Documento10 pagineDrug Study (AFP)Summer SuarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 pagineTissue Perfusionnursezey100% (3)
- DrugsDocumento5 pagineDrugsJicel Camille EdeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study ProjectDocumento7 pagineDrug Study ProjectMaRic Gabutin Guerra100% (1)
- Discharged PlanDocumento6 pagineDischarged Planqueenieann100% (1)
- Capital BudgetingDocumento24 pagineCapital BudgetingHassaan NasirNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Spoken English in Half The TimeDocumento86 pagineLearning Spoken English in Half The TimeΔέσποινα ΤζουτNessuna valutazione finora
- TTC 1000Documento2 pagineTTC 1000svismaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Cpa Review School of The Philippines: Related Psas: Psa 700, 710, 720, 560, 570, 600 and 620Documento49 pagineCpa Review School of The Philippines: Related Psas: Psa 700, 710, 720, 560, 570, 600 and 620Jasmine LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Growth Performance of Papaya Plants As Influenced by Organic MulchesDocumento9 pagineGrowth Performance of Papaya Plants As Influenced by Organic MulchesMa. Christine Lyn AustriaNessuna valutazione finora
- A. in What Way Is Khatri A Surplus Unit?Documento5 pagineA. in What Way Is Khatri A Surplus Unit?Aakriti SanjelNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Minutes of MeetingDocumento3 pagineSample Minutes of MeetingMohamad AzmeerNessuna valutazione finora
- Focus GroupDocumento20 pagineFocus GroupItzel H. ArmentaNessuna valutazione finora
- SolutionsManual NewDocumento123 pagineSolutionsManual NewManoj SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Subject-Verb AgreementDocumento10 pagineSubject-Verb AgreementLouie Jay Cañada AbarquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Recycling of Textile PolymersDocumento8 pagineChemical Recycling of Textile PolymersVaishali RaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Authority To TravelDocumento39 pagineAuthority To TraveljoraldNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid Bases and Salts Previous Year Questiosn Class 10 ScienceDocumento5 pagineAcid Bases and Salts Previous Year Questiosn Class 10 Scienceclashhunting123123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Installation ManualDocumento16 pagineInstallation ManualJosé Manuel García MartínNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study-BPPVDocumento97 pagineCase Study-BPPVArbie Jacinto83% (6)
- CS 2400 - 2500 BrochureDocumento8 pagineCS 2400 - 2500 BrochureOo Kenx OoNessuna valutazione finora
- International Standard: Iso/Iec 7816-2Documento16 pagineInternational Standard: Iso/Iec 7816-2Anwar MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Semi Formal Asking To Borrow BooksDocumento75 pagineSemi Formal Asking To Borrow BooksPei Cheng WuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 5 Flight of Projectile, Air Resistance Neglected: OverviewDocumento7 pagineLesson 5 Flight of Projectile, Air Resistance Neglected: OverviewNadjer C. AdamNessuna valutazione finora
- Punctuation WorksheetsDocumento10 paginePunctuation WorksheetsRehan Sadiq100% (2)
- Guide: Daily ReferenceDocumento8 pagineGuide: Daily ReferenceGalina TodorovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sacramento County Compensation Survey Board of SupervisorsDocumento13 pagineSacramento County Compensation Survey Board of SupervisorsCBS13Nessuna valutazione finora
- Docker Tutorial: Anthony BaireDocumento99 pagineDocker Tutorial: Anthony BairesuderNessuna valutazione finora
- Banana Stem Patty Pre Finale 1Documento16 pagineBanana Stem Patty Pre Finale 1Armel Barayuga86% (7)
- Form ConstructionDocumento36 pagineForm ConstructionYhoga DheviantNessuna valutazione finora
- LGDocumento36 pagineLGNanchavisNessuna valutazione finora
- APA 6th Edition - Citation Styles APA, MLA, Chicago, Turabian, IEEE - LibGuDocumento2 pagineAPA 6th Edition - Citation Styles APA, MLA, Chicago, Turabian, IEEE - LibGuJan Louis SalazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Monorail Hoist SystemDocumento17 pagineMonorail Hoist SystemypatelsNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar ReportDocumento15 pagineSeminar ReportNipesh MAHARJANNessuna valutazione finora