Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Interference of Light
Caricato da
Sivakami RadhakrashnanTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Interference of Light
Caricato da
Sivakami RadhakrashnanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
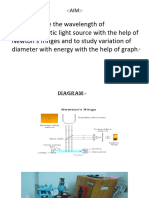
Interference of light Absolute refractive index =c/v where c is the speed of light in vacuum ,v is speed of light in the medium
m Optical path = refractive index X distance travelled by light in the medium
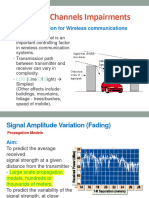
Ratio of intensities of light emitted by two sources
Where w1 and w2 are the widths of the two slits.a1 and a2 are the amplitude of two waves. In Young's double slit experiment ,
The distanceof the nth bright fringe The distance of the nth dark fringe Fringe width Angular fringe width
Where D distance between slits and screen in m d is the distance between two slits in m no of fringes observed if the wavelength is changed
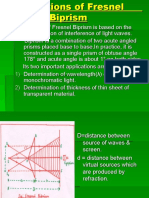
In Fresnel's biprism experiment, d is the distance between two coherent sources
d by displacement method. If is the refracting angle of the biprism
1
d= 2a(-1) ,
Where "a" is the distance between the slits and the prism and the refracting angle.
Fringe width
Electromagnetic waves Maxwell's equations are
Velocity of the electromagnetic wave
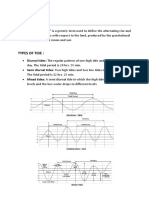
Diffracion In Fraunhofer diffraction The condition for the formation of secondary minimum
For the formation of secondary maximum
semi angular width of central maximum =
GRATING (e+d) =grating element
2
e-width of each slit d-the width of opaque space between the slits. Condition for maximum intensity (e+d )sin =n
N -number of rulings per cm on the grating polarization -transverse nature of the wave ip = angle of polarization Brewster's law
n -refractive index of glass Snell's law
=sinr
tanr =sinic r = tan-1(sinic)
Refraction of light
Reversibility of light
3
Refraction through multiple media
1 2
n2 X 2n3X 3n1 =1 n3 =1n3/ 1n2
where t is the real depth/thickness of the glass
In case of more than one liquid
Prism graph between i and
i+e =A+
4
Deviation for a thin prism m =(n-1)A Refraction of light at spherical surfaces For convex surface/concave surface
Len's maker's formula
Power P = Gaussian form of lens equation
if fa and fg are the focal length of the lens in air and in liquid respectively
When two lenses of focal length f1and f2are in contact ,then their combined focal length is given by f is givenby
power p =p1 +p2 If thin lenses are placed at a distance d
power P =P1 + P2 -d P1 P2 Dispersion angular dispersion =V -R= Y For thin prism m =(n-1)A angular dispersion =V -R =(nV-nR)A Dispersive power = Dispersive power =
F -sky green C red line of hydrogen spectrum D- yellow line of sodium spectrum To reduce chromatic aberrations using two plano convex lenses the distance between the two lenses d= f1 -f2 fR -fV = X fY Condition for achromatism of the lens combination
for 2 lenses separated by a distance d d=f1 -f2 Simple Microscope
Compound Microscope Total magnification produced by the compound microscope M M=Mo X Me
For objective
in case u0 =f0 and v0 =L(length of the microscope tube)
Astronomical telescope If the final image is formed at the distance of least distinct vision
If the image is at infinity
length=Distance between 2 lenses =fo+fe
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- No StoneDocumento15 pagineNo StoneRachel EscrupoloNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 Days Prayer For Total HealingDocumento137 pagine14 Days Prayer For Total Healingnkugwa6brian80% (5)
- DDI Au Recruiting For Culture FitDocumento20 pagineDDI Au Recruiting For Culture Fitjlg-jlgNessuna valutazione finora
- 21 Jusmag v. NLRCDocumento2 pagine21 Jusmag v. NLRCRem Serrano83% (6)
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsDa EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNessuna valutazione finora
- The Zero Point Energy of The Quantum-VacuumDocumento5 pagineThe Zero Point Energy of The Quantum-VacuumBob HwknsNessuna valutazione finora
- InterferenceDocumento38 pagineInterferenceSadek PiashNessuna valutazione finora
- InterferenceDocumento38 pagineInterferenceAbror md FayiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Declamation Pieces For High SchoolDocumento21 pagineDeclamation Pieces For High SchoolMelito Vinarao100% (3)
- Khechari Mudra - Advance Yoga PracticeDocumento18 pagineKhechari Mudra - Advance Yoga PracticeDeepak Samal100% (4)
- Wave OpticsDocumento39 pagineWave OpticsMadzombie100% (1)
- Scientific Revolution, Enlightenment, French RevolutionDocumento2 pagineScientific Revolution, Enlightenment, French RevolutionTamara Lewis0% (1)
- Diffraction ExperimentsDocumento5 pagineDiffraction ExperimentsArooj Mukarram100% (2)
- Chapter Three Light As Wave MotionDocumento11 pagineChapter Three Light As Wave MotionSabrina NevilleLongbottom RitterNessuna valutazione finora
- As 23b OpticsDocumento57 pagineAs 23b OpticsHany ElGezawyNessuna valutazione finora
- RefractionDocumento15 pagineRefractionSudharsan Gupta Sudhir100% (1)
- Refraction 1Documento8 pagineRefraction 1Sudharsan Gupta SudhirNessuna valutazione finora
- New Text DocumentDocumento10 pagineNew Text DocumentTanuja MagarNessuna valutazione finora
- 3) Diffraction - Final 23 Sep 2021Documento38 pagine3) Diffraction - Final 23 Sep 2021Game 1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Plane Surfaces and PrismsDocumento22 pagineChapter 2 Plane Surfaces and PrismsEric Doctore KrageNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT2 Interference DiffractionDocumento57 pagineUNIT2 Interference Diffractionfunkpatel123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Formula CHapter10 Wave Optics PDFDocumento10 paginePhysics Formula CHapter10 Wave Optics PDFRakeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Key Concept: Ansal Lasses Wave OpticsDocumento11 pagineKey Concept: Ansal Lasses Wave Opticssrihari bandarupalliNessuna valutazione finora
- MODERN PHYSICS: Unit 2Documento11 pagineMODERN PHYSICS: Unit 2Self Study Zone IndiaNessuna valutazione finora
- AP 2 Module 3Documento25 pagineAP 2 Module 3Anshuman NandanNessuna valutazione finora
- Wave Optics HandoutDocumento12 pagineWave Optics HandoutBEEMI REDDY VENKATA REDDYNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 DiffractdionDocumento124 pagine2 DiffractdionShrinivas PrabhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Double Slit Project 2Documento18 pagineDouble Slit Project 2mnaqash272000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wave Optics: Exercise - I Exercise - Ii Exercise - Iii Answer KeyDocumento12 pagineWave Optics: Exercise - I Exercise - Ii Exercise - Iii Answer KeyRoNNessuna valutazione finora
- Interference McqsDocumento15 pagineInterference McqsJerry Johnson88% (8)
- 6 3diffraction NotesDocumento5 pagine6 3diffraction NotesDraganDusperNessuna valutazione finora
- 11.3.1 Sketch The Variation With Angle of Diffraction of The Relative Intensity of Light Diffracted at A Single SlitDocumento4 pagine11.3.1 Sketch The Variation With Angle of Diffraction of The Relative Intensity of Light Diffracted at A Single SlitAliiAmiirNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Lab ManualDocumento62 paginePhysics Lab ManualKrishna MahajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Wave OpticsDocumento12 pagineWave OpticsRaju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- InterferenceDocumento13 pagineInterferenceYugandhar VeeramachaneniNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet Wave OpticsDocumento12 pagineSheet Wave OpticsNalin GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- 12th ch-10 PhyDocumento5 pagine12th ch-10 PhyNishaNessuna valutazione finora
- OPTICS 1. Light From Sodium Lamp PassesDocumento21 pagineOPTICS 1. Light From Sodium Lamp PassesNavneet100% (1)
- Ch-10 Wave OpticsDocumento34 pagineCh-10 Wave Opticstessa mariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Optics Interference 2h Class 2022Documento53 pagineOptics Interference 2h Class 2022Aman KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Interference-Newtons Ring ExperimentDocumento15 pagineInterference-Newtons Ring ExperimentManoj Manu86% (7)
- Physics Project File SampleDocumento12 paginePhysics Project File SampleRbcNessuna valutazione finora
- Newtonsring 1doc)Documento9 pagineNewtonsring 1doc)Ojas AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report 10 PDFDocumento7 pagineLab Report 10 PDFDM RafiunNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Physics Laboratory Course Code: PHY119Documento26 pagineEngineering Physics Laboratory Course Code: PHY119Dhruva is liveNessuna valutazione finora
- InterferenceDocumento6 pagineInterferenceavi taylorNessuna valutazione finora
- Newton RingDocumento9 pagineNewton RingOjas AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- EngPhy Module v&VIDocumento100 pagineEngPhy Module v&VISanjeevNessuna valutazione finora
- Investigatory Project by Divyam GiriDocumento23 pagineInvestigatory Project by Divyam GiriPriyanshu GiriNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Study Materials - Wave OpticsDocumento7 paginePhysics Study Materials - Wave OpticschashmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grating and Prism SpectrometerDocumento2 pagineGrating and Prism SpectrometersovinoriNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec RTEDocumento75 pagineLec RTEhossein soltanipourNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Propagation Effects - ModelsDocumento17 pagine1 - Propagation Effects - ModelsSaher ZayedNessuna valutazione finora
- Tut6 SolDocumento11 pagineTut6 Solanon_965498458Nessuna valutazione finora
- B.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsDocumento72 pagineB.Tech First Year: Course Name: Engineering PhysicsDhyey DESAIIINessuna valutazione finora
- Fresnel Biprism ExperimentDocumento11 pagineFresnel Biprism ExperimentanuragNessuna valutazione finora
- Interference: A. Double Slit InterferenceDocumento22 pagineInterference: A. Double Slit InterferenceMade TamaraNessuna valutazione finora
- 7-Diffraction at A Slit and Double Slit PDFDocumento9 pagine7-Diffraction at A Slit and Double Slit PDFWakkuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lloyd's MirrorDocumento8 pagineLloyd's Mirrorchiranjib214Nessuna valutazione finora
- BiprismDocumento35 pagineBiprismAviral99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fresnel BiprismDocumento18 pagineFresnel BiprismRohan RajagopalNessuna valutazione finora
- Wave Optics (MCQS)Documento21 pagineWave Optics (MCQS)Ronda StewartNessuna valutazione finora
- Optics Bhu Third Sem AllDocumento209 pagineOptics Bhu Third Sem AllSHREYA SONINessuna valutazione finora
- Useful Concepts Wave OpticsDocumento2 pagineUseful Concepts Wave OpticsAli AsgerovNessuna valutazione finora
- KCET 2022 Physics SolutionsDocumento25 pagineKCET 2022 Physics Solutionsdeekshitha2532005Nessuna valutazione finora
- Newton'S RingsDocumento13 pagineNewton'S RingsAppidi Sai Sushrith ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Optics BSC NM Semester 2Documento95 pagineOptics BSC NM Semester 2Dr. Neha KondalNessuna valutazione finora
- Waves Light Content Guide CompleteDocumento3 pagineWaves Light Content Guide Completeritchiesalvador4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Articulo JMC2015Documento9 pagineArticulo JMC2015A.s. BezmalinovićNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Wushu - IWUFDocumento5 pagineHistory of Wushu - IWUFStanislav Ozzy PetrovNessuna valutazione finora
- The Creator of This Universe Creates It For All of His Creatures AutosavedDocumento2 pagineThe Creator of This Universe Creates It For All of His Creatures Autosavedmunawar456Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Murid 1 Sukan - ESSEYDocumento4 pagine1 Murid 1 Sukan - ESSEYUmmuJamilahNessuna valutazione finora
- Tide ReportDocumento11 pagineTide ReportAhmad AbdelsattarNessuna valutazione finora
- 524 799 Coach - K - Coach - Knight - CaseDocumento15 pagine524 799 Coach - K - Coach - Knight - Casekaushalmighty100% (1)
- Ultrasound Quiz 1Documento9 pagineUltrasound Quiz 1saleemut3Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Rescue FindingsDocumento8 pagineThe Rescue FindingsBini Tugma Bini Tugma100% (1)
- Continuous Improvement Proposal Process and OperatDocumento9 pagineContinuous Improvement Proposal Process and OperatIzzul Asyraf ZulkifliNessuna valutazione finora
- Bca 1st Sem P.O.MDocumento52 pagineBca 1st Sem P.O.MsinghalitiNessuna valutazione finora
- q2 English Performance TaskDocumento1 paginaq2 English Performance TaskCHEIRYL DAVOCOLNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.steven Epstein - The Construction of Lay Expertise - AIDS ActivismDocumento31 pagine3.steven Epstein - The Construction of Lay Expertise - AIDS ActivismTatiana SoaresNessuna valutazione finora
- THE LEGAL PROFESSION: Lawyers in Society and A Society of LawyersDocumento13 pagineTHE LEGAL PROFESSION: Lawyers in Society and A Society of Lawyersdancingorange100% (1)
- An Intelligent Fuzzy Sliding Mode Controller For A BLDC MotorDocumento5 pagineAn Intelligent Fuzzy Sliding Mode Controller For A BLDC Motorvasu_koneti5124Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fianl Essay of OMDocumento4 pagineFianl Essay of OMApurbo Sarkar ShohagNessuna valutazione finora
- Prov Plagiarism Research PaperDocumento4 pagineProv Plagiarism Research Paperapi-356313086Nessuna valutazione finora
- Density and Lava LampsDocumento3 pagineDensity and Lava Lampsapi-337712799Nessuna valutazione finora
- Narrative ReportDocumento2 pagineNarrative ReportDIANNE SANCHEZNessuna valutazione finora
- 13 - The Diagnosis of Some Kidney Diseases in A Small Prolog Expert SystemDocumento6 pagine13 - The Diagnosis of Some Kidney Diseases in A Small Prolog Expert SystemArvinder KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Thought ReformDocumento112 pagineThought ReformDavid BriggsNessuna valutazione finora
- Man As Prince of Creation and His Potential: Ommunity As Ontologic NecessityDocumento5 pagineMan As Prince of Creation and His Potential: Ommunity As Ontologic NecessityElena ParisNessuna valutazione finora
- HRM - 5 - TrainingDocumento3 pagineHRM - 5 - TrainingSk. Wahed BariNessuna valutazione finora